Open source robot 3d print
🤖 Best 3D files for 3D printing of robots・Cults
🤖 Best 3D files for 3D printing of robots
Animated creatures, created by humans, robots fascinate as much as they frighten. But don't worry, with this collection of 3D printed robots you won't risk anything except learning and having fun! 3D printing has enabled many researchers to create robots that are more precise, more efficient and, above all, reduce manufacturing costs. These 3D robots are inanimate but coupled with electronic components, they could come to life!
Lucius Wardog Titan
Free
Massive Iron Giant and Hogarth
Free
Maker Faire Robot Action Figure (Single file)
Free
Wall-E Robot - Fully 3D Printed
Free
Jointed Robot
Free
R2D2 - This is the Droid You're Looking For
Free
BCN3D MOVEO - A fully OpenSource 3D printed Robot Arm
Free
Robot woman - Robotica
Free
SMARS modular Robot
Free
Mechwarrior Catapult Assembly Model warfare set
Free
Titan BT 7274
Free
BeWho, Jointed Robot
Free
Megaman X Posed Figurine
Free
Action Robot
Free
ARTICULATED G1 TRANSFORMERS OPTIMUS PRIME - NO SUPPORT
Free
Robot Family Simple No Support
Free
Poppy Humanoid
Free
Heavy Construction Walker (Action Figure)
Free
POWER RANGERS THUNDER MEGAZORD
Free
Wall-E Figure
Free
Gizmo - Robotic Dog
Free
Clank Figure - Ratchet & Clank
Free
Wip: Tiny articulated bot
Free
Bender Pen Holder
Free
Android
Free
3D Hubs Marvin - Key Chain
Free
Low Poly Optimus Prime
€3. 03
Laputa Q Robot
Free
SMARS V4 vertical Ultrasonic
Free
ARTICULATED G1 TRANSFORMERS BUMBLEBEE - NO SUPPORT
Free
Giant Impostor Among Us
Free
Goldorak
Free
The Iron Giant
Free
K-2SO 3D MODEL (SIMPLE VERSION)
Free
Heavy Gun Walker (Torso option part)
Free
TFA Marauder Megatron
Free
Guardian Robot Hackable – Bottom Remix
Free
Shovel DLC for SMARS
Free
Roberto [Futurama]
Free
Maker Faire Robot Action Figure PIP (with supports): 2015 3D Printer Shoot Out Test Models
Free
PLP ROBOT HEART
Free
Female Humanoid Robot
Free
Grippy Bot
Free
Robo Kitty v1.
 0
0Free
Robot HORIKAWA style
Free
Triple A connector + connector extender for SMARS
Free
G1 Transformers Hound - No Support
Free
Otto DIY build your own robot
Free
G1 TRANSFORMERS SOUNDWAVE
Rosie the Robot
PIT DROID 1:2
Lucius Wardog Titan
Discover our selection of the best robot 3D models, all these magnificent creations come from the 3D file library Cults and are perfectly 3D printable.
This collection includes free STL files from many robots. There are two main categories: articulated robots that can be 3D printed that actually work and 3D robots decoration files.
The functional robots 3D printed are obviously the most incredible, but they will require more work time. These are real projects including electronics (Raspberry pi or Arduino) and some programming skills.
Decoration robots are less complicated to print and assemble, but they are still excellent. It is really a subject that inspires the 3D designers, they create their own design or are inspired by already existing robots like Bender from Futurama, Optimus Prime, R2-D2, Well-E, etc..
Top 12 3D-Printed Robots — From Amphibians to Humanoids
Published on August 26, 2021 by Mikahila L.
Robotics brings together all the technologies that make it possible to design autonomous machines; combining knowledge in electronics, mechanics, and even biology. This is a field that has evolved quite a bit since C-3PO first hit the movie screens in Star Wars in1973. Roboticists have been in constant search of innovations that result in greater speed and productivity. Today, we have smarter robots because of advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and of course, additive manufacturing. Indeed, 3D printing is widely used to manufacture robots, whether in the prototyping or final production stage, to imagine structure, materials, and new functionality. This is why we wanted to present to you some of the fascinating 3D printed robots we’ve come across, everything from humanoids, research tools, or even DIY machines—a section that should be of interest to all makers!
Roboticists have been in constant search of innovations that result in greater speed and productivity. Today, we have smarter robots because of advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and of course, additive manufacturing. Indeed, 3D printing is widely used to manufacture robots, whether in the prototyping or final production stage, to imagine structure, materials, and new functionality. This is why we wanted to present to you some of the fascinating 3D printed robots we’ve come across, everything from humanoids, research tools, or even DIY machines—a section that should be of interest to all makers!
DIY Projects
Intel Openbot
Research organization Intel Labs used 3D printing to develop the Openbot, one of the robots that caught our team’s attention the most. The objective of the project was to create a small electric vehicle intended for smartphones, with the motto ‘Transforming smartphones into robots‘. The device is equipped with vast networks of sensors and has powerful computing capabilities allowing it to take advantage of the advanced functionalities of smartphones.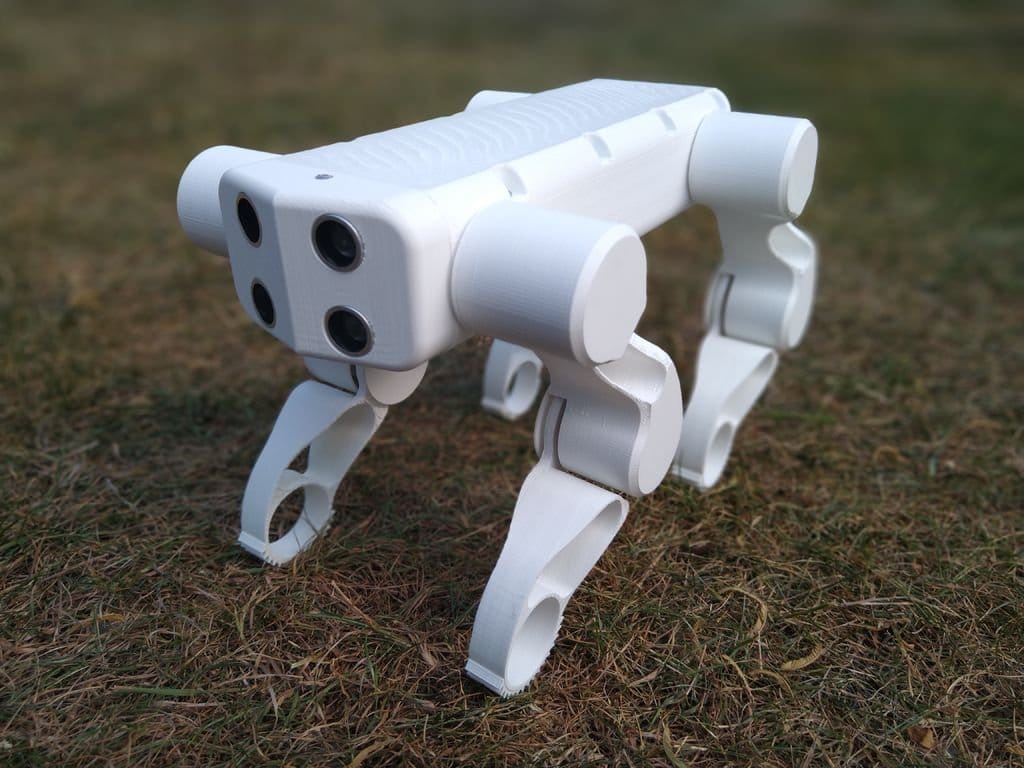 Intel experts say they have opted for 3D printing because of its great accessibility, and also thanks to free software that facilitates the development of this type of project.
Intel experts say they have opted for 3D printing because of its great accessibility, and also thanks to free software that facilitates the development of this type of project.
LittleBots is another project that you can do at home with your 3D printer. This robotics kit was created to serve as an introduction to robotics. It features all the necessary components of robotics: sensors, decision-making, and articulation, all in one simple, easy-to-assemble kit. What’s interesting is that LittleBot is fully 3D printed, so it can be made with just 3 screws. The device is open-source and controlled by an Arduino Nano, to take advantage of the global community around it. You can find the 3D print files of these robots through Thingiverse; The Arduino code can be found on the LittleBots download page.
Humanoids
Atlas by Boston Dynamics
Boston Dynamics’ Atlas humanoid robots have recently caused quite a stir online with their performance during an obstacle course.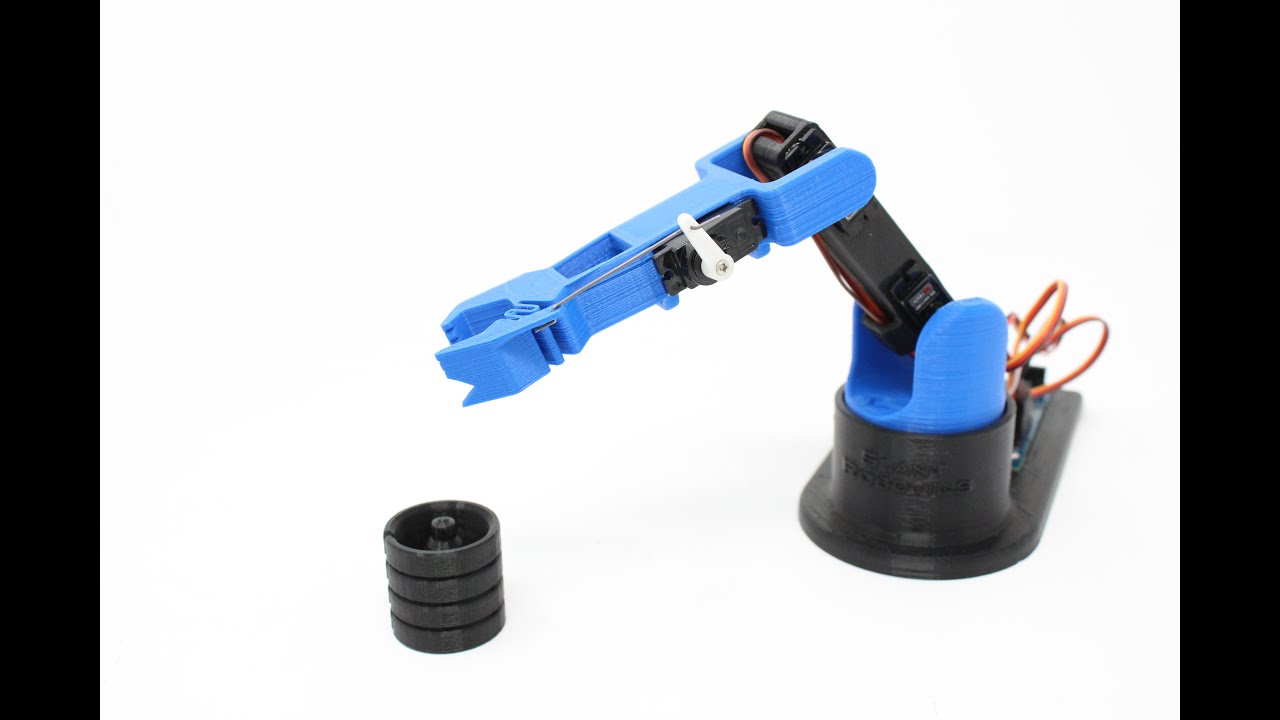 Although they have already had some success, Boston Dynamics aims to test the limits of what is possible and continue developing Atlas to make robots withstand extreme conditions. The company relied on 3D printed components for the development of Atlas robots. For example, the legs are 3D printed, which made it possible to integrate hydraulic lines into the structure. Additive manufacturing has also been used to produce custom servo valves.
Although they have already had some success, Boston Dynamics aims to test the limits of what is possible and continue developing Atlas to make robots withstand extreme conditions. The company relied on 3D printed components for the development of Atlas robots. For example, the legs are 3D printed, which made it possible to integrate hydraulic lines into the structure. Additive manufacturing has also been used to produce custom servo valves.
We could have classified the InMoov robot in the DIY category, as it is an open-source project. Indeed, it is the first human-sized open-source 3D printed robot in the world, created in 2012 by the French Gaël Langevin. Anyone with a 3D printer can therefore design their humanoid robot at home, all you need is a printing area of 120 x 120 x 120 mm. The different parts of the body are printed separately—arms, head, neck, back, shoulder, etc. Everything is meticulously detailed on the dedicated site, whether it is the printing, assembly, and commissioning of this 3D printed robot.
The different parts of the body are printed separately—arms, head, neck, back, shoulder, etc. Everything is meticulously detailed on the dedicated site, whether it is the printing, assembly, and commissioning of this 3D printed robot.
The humanoid robot ‘Poppy’ was developed by INRIA Flowers Laboratory in Bordeaux, France. Poppy is open-source and is used by a community of educators, scientists, and artists by sharing hardware, software, and web tools used for a wide variety of visual programming, simulation, and experiments. The robot relies on 3D-printed components made using polyamide material, giving the robot thermal and high-abrasion resistance. Standing at 83 cm tall (32.6 inches) and weighing 3.5 kg (7.7 lbs), Poppy includes a series of electronic components including a 4.2-inch screen and HD camera and costs about €9,039 ($10,610), with less expensive versions available including the Poppy Torso and Ergo Jr.
Jimmy the 21st Century RobotJimmy is a 3D printed robot that was developed by the 21st Century Robot company with the goal of getting as many people as possible to build and customize their own robot through 3D printing. Jimmy is made up of custom 3D printed shells that cover his humanoid endoskeleton. Completely open-source, it is powered by an Intel Edison microcomputer, and controlled via WiFi on a smartphone, tablet, or PC using a dedicated application.
Pollen Robotics Reachy
Another offering from the French company Pollen Robotics (also the creators of Pollen), Reachy is described by the company as an expressive open-source humanoid platform that is programmable with Python and made using 3D printing. Though really just a torso, head, and arms, the main drawing point of this particular robot is not just how expressive it is but also how good it is at interacting with people and manipulating objects. The robot’s maneuverability is to thank for these features. For example, its head is free-moving and it can use antennas to convey emotions. Its two arms have similar dimensions, proportions, and movement as an adult human arm, capable of lifting up to 500 grams. Best of all, the robot is completely customizable and learns thanks to machine learning and AI capabilities.
The robot’s maneuverability is to thank for these features. For example, its head is free-moving and it can use antennas to convey emotions. Its two arms have similar dimensions, proportions, and movement as an adult human arm, capable of lifting up to 500 grams. Best of all, the robot is completely customizable and learns thanks to machine learning and AI capabilities.
Research Projects
JSK Laboratory’s Kengoro
Researchers at the JSK laboratory in Tokyo have succeeded in developing a humanoid robot capable of doing push-ups. But playing sports is not Kengoro’s only special feature—its 3D printed metal coating also makes it unique. A well-known problem with humanoid robots is the overheating of motors. In order to better dissipate the heat generated by the 108 engines, the research team opted for an efficient cooling system that can be implemented using SLS 3D printing.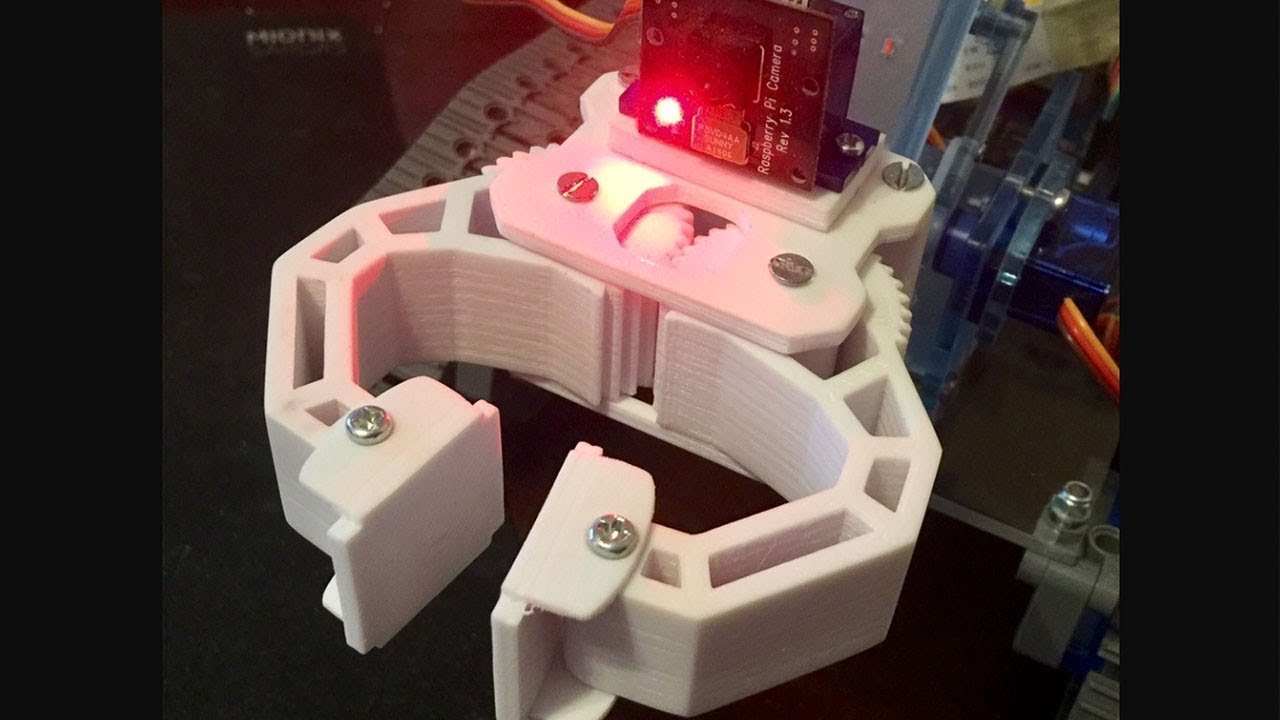 The process made it possible to integrate a cooling system into the Kengoro housing and to modify the energy density of the material at various points. This allows water to escape easily and increases Kengoro’s performance. You might even think that the robot sweats during its athletic efforts!
The process made it possible to integrate a cooling system into the Kengoro housing and to modify the energy density of the material at various points. This allows water to escape easily and increases Kengoro’s performance. You might even think that the robot sweats during its athletic efforts!
Pleurobot the Amphibious Robot
Pleurobot is a 3D-printed robot that mimics a salamander and was designed by the Ecole Polytechnique de Lausanne in Switzerland. This amphibious robot has practical application for neuroscientists, biomechanists, functional morphologists, and paleontologists as well as roboticists. For instance, Pleurobot will enable research that benefits quadriplegic patients as researchers gain better insights into anatomy and motor skills. Research may also focus on the evolution of the passage from a swimming animal to one that walks. Swiss engineers also replicated a nervous system using electronic components with a careful scan of a real salamander. Equipped with motors, Pleurobot can swim, crawl and walk like its amphibian counterparts.
‘Astro’, the Intelligent Robodog that Sees and Hears
Scientists at Florida Atlantic University’s Cognitive Robotics and Machine Perception Laboratory (MPCR) have developed Astro, one of the few quadrupedal robots in the world. Unlike many robots, Astro is specified to have a computerized brain inside his head. This one, which looks like that of a Doberman, has been 3D printed. But the commonalities with dogs don’t end with the physical. Astro also has artificial intelligence and machine learning that allows it to learn like a canine. Equipped with sensors, radars, and a microphone, the robotic dog responds to classic commands such as “sit”, “stand” and “lie down”. In some time, Astro will be able to help the police as a scout dog or as a service dog for the visually impaired.
“Micro-Bristle-Bots”
While most of the time human-designed robots are large, this is not always the case. At the Georgia Institute of Technology, researchers have developed microscopic 3D printed robots. Dubbed ‘micro-bristle-bots’, they are barely visible to the naked eye and can be controlled by tiny vibrations. Like ants, microscopic robots work in teams and are able to transport materials. To manufacture the ‘micro-bristle-bots’, the Georgia Tech team used Nanoscribe’s Photonic Professional GT 3D printer, based on the two-photon polymerization (TPP) process. According to the manufacturer, this technology achieves a high level of precision and detail and is ideally suited for micro-printing.
Soft Robots from UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering
At the University of California San Diego’s Jacobs School of Engineering, engineers have been working on soft robotics, or the construction of robots from compliant materials, often taking significant inspiration from the movements of living organisms.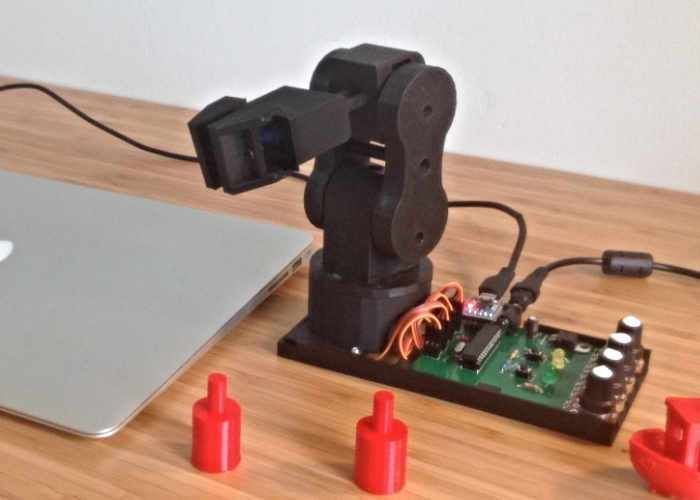 One such recent project was when researchers designed and tested 3D-printed insect-like robotics. Using FDM and filaments like ABS or PLA, the insects were made using a flexoskeleton process that added rigid features to key components, allowing them to keep their flexibility. This is not the only 3D-printed soft robotics project coming from the school with more expected in the future.
One such recent project was when researchers designed and tested 3D-printed insect-like robotics. Using FDM and filaments like ABS or PLA, the insects were made using a flexoskeleton process that added rigid features to key components, allowing them to keep their flexibility. This is not the only 3D-printed soft robotics project coming from the school with more expected in the future.
What do you think of our selection of 3D-printed robots? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages. Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly newsletter, with all the latest news in 3D printing delivered straight to your inbox!
Top 10 DIY 3D Printing Manipulators
3DPrintStory Reviews 10 Best DIY 3D Printing Manipulators
There are many different configurations of robotic arms, but most of them work on the same general principles of movement.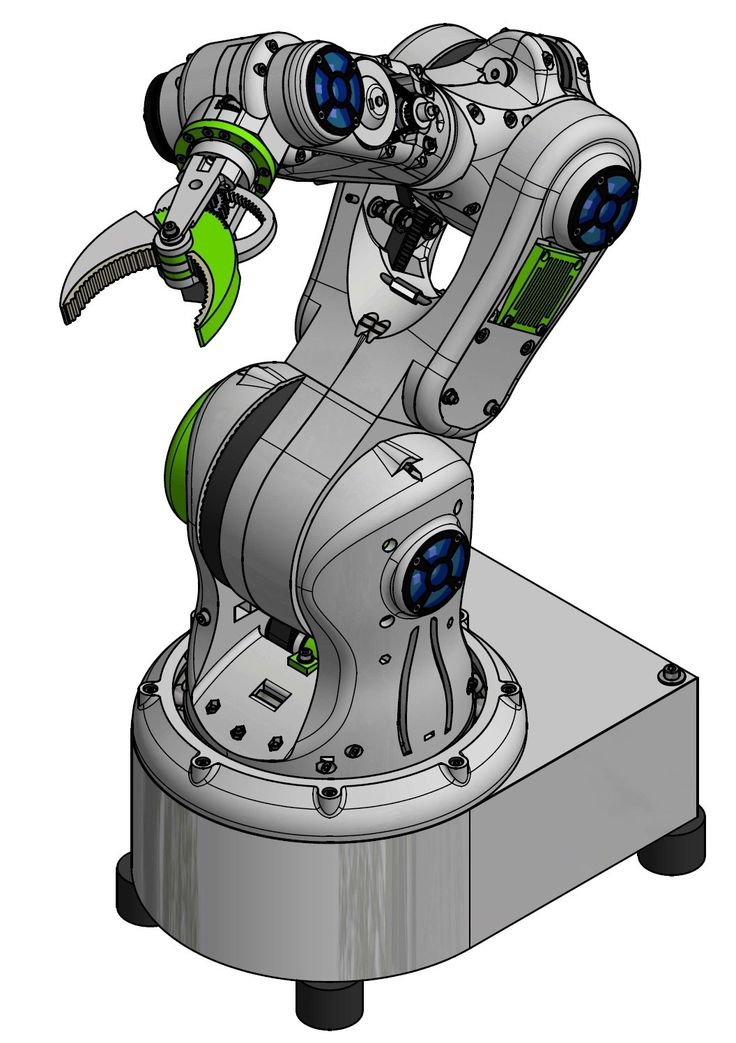 Unlike mechanisms that work in the Cartesian coordinate system, such as, for example, 3D printers, manipulators mostly use the polar coordinate system for movement and have an arc-shaped work area. Robotic arms are unique in that they are not limited by footprint and take up very little space compared to other machines with similar features.
Unlike mechanisms that work in the Cartesian coordinate system, such as, for example, 3D printers, manipulators mostly use the polar coordinate system for movement and have an arc-shaped work area. Robotic arms are unique in that they are not limited by footprint and take up very little space compared to other machines with similar features.
In robotics there is such a definition as degrees of freedom (DOF). The term is used to refer to the number of rotating joints or axles on a particular arm, for example a 4DOF arm can be rotated by four separate joints.
Robotic arms are used in a variety of ways, but most are capable of picking up and moving, while some are designed to work in tandem with CNC machines, laser engraving, and even 3D printing.
Because there are hundreds of great designs and designs to consider when choosing a good arm to buy or 3D print, we've narrowed it down to 10 of the best and most popular arms that you can find and reproduce designs using your 3D printer as well.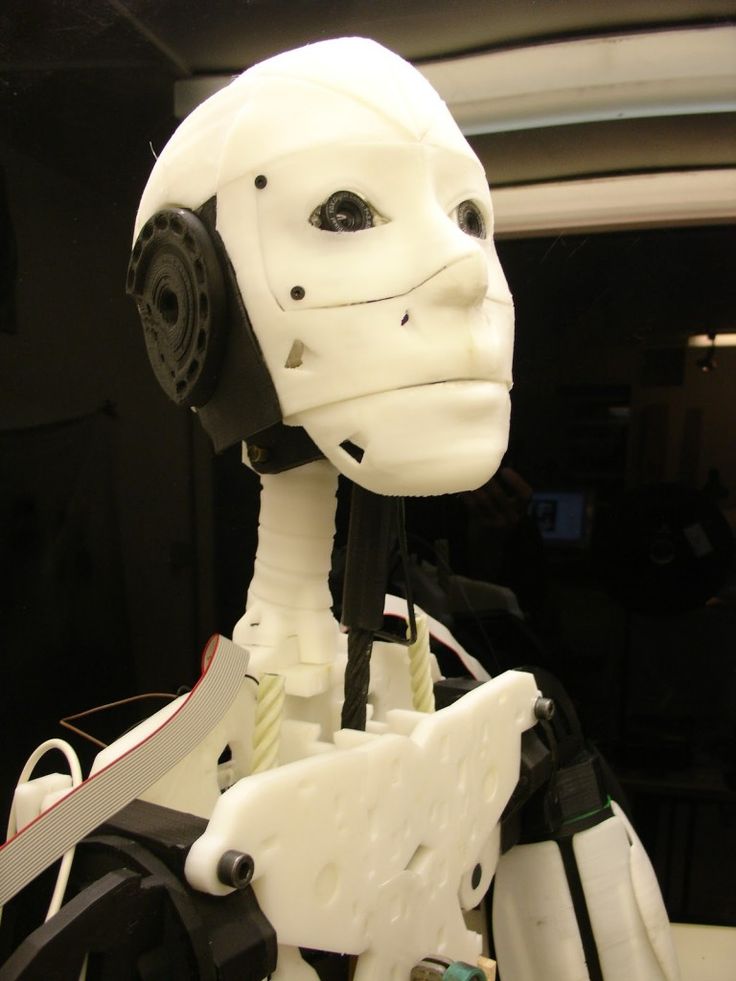 .
.
UFactory uArm
UArm is probably one of the most versatile of all the robot arms on this list. At the moment, this design already has the third release version - uArm Swift and more functional Swift Pro.
This open source robot arm is fully compatible with Arduino, Raspberry Pi and Seeed Studio Grove kits. It's unique in that the Swift Pro can do laser engraving and 3D printing - provided it's equipped with the right heads - and can "learn" the movements without the need for a computer.
This is a 4DOF manipulator with an accuracy of 0.2 millimeters.
You can find more information and where to buy it on the UFactory product page.
Thor
This arm, developed by Hackaday AngelLM, is completely open source and can be used for 3D printing. This is a 6DOF paddle with a maximum payload of 750 grams and a unique design for great flexibility.
You can find all the 3D printing files for this robot on the Thor project page.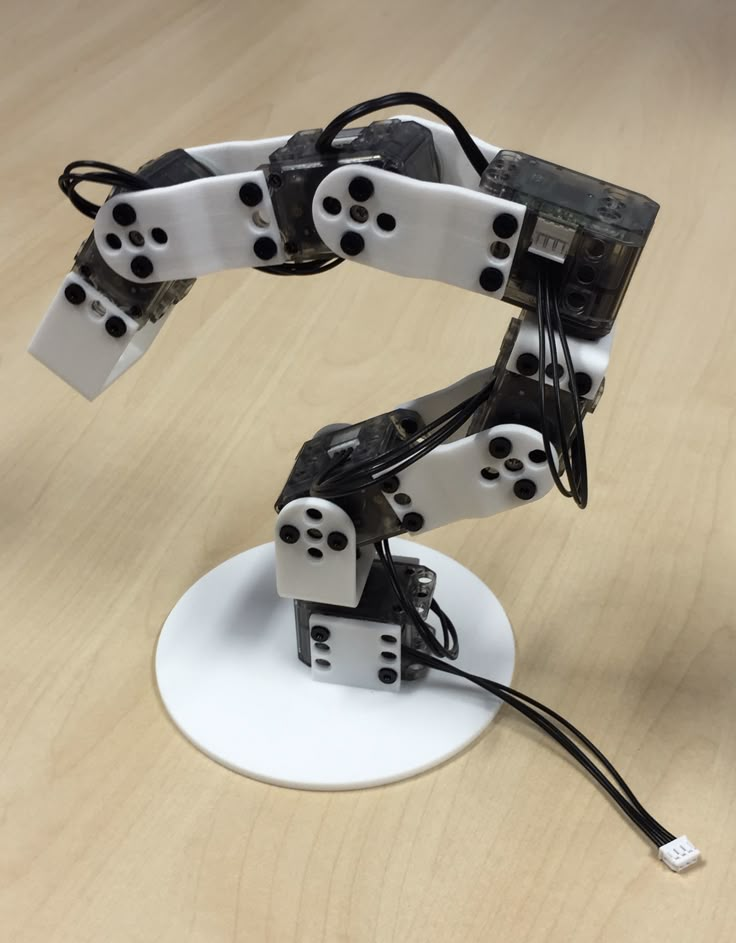
EEZYbotARM MK2
The EEZYbotARM MK2 is a 4DOF reference arm that is fully 3D printed with excellent building instructions. This robotic arm has won several competitions and is probably one of the easiest robotic arms to make. An MK3 version is also being developed.
You can find complete assembly instructions on the EEZYbotARM webpage.
Roboteurs RBX1
This is another great fully 3D printed robot arm that has amazing flexibility and aesthetics. In addition to purchasing the components yourself, Roboteurs offers a complete parts kit with a proprietary stepper motor driver to run the RBX1. All you need is a Raspberry Pi and a 3D printer. This manipulator is a 6DOF type design and has a beautiful appearance.
You can find the complete specification and parts kit on the Roboteurs product page.
LittleArm
LittleArm, designed by Slant Concepts on Hackaday.io, is the simplest robotic arm on this list. With only 3DOF, this arm can be a great introduction to Arduino programming for students and opens exciting doors of new technologies for newcomers to the world of 3D printing and robotics.
With only 3DOF, this arm can be a great introduction to Arduino programming for students and opens exciting doors of new technologies for newcomers to the world of 3D printing and robotics.
This fully 3D printed arm is very easy to assemble. The creators even developed an application with a simple interface for computers that can be used with this robot.
You can find full documentation on the LittleArm project page.
3D Printable Robot Arm
Created by Andreas Helldorfer on Hackaday.io. It's a large arm, fully 3D printed, with many uses. The creator developed it for 4 iterations before making a really worthy industrial design that is available to everyone. With a 6DOF design and a maximum payload of up to 2kg, this arm can really be used in many applications.
To find the 3D print files for this arm and the full specification, visit the project page.
MeArm
MeArm is one of the most popular manipulators and for good reason.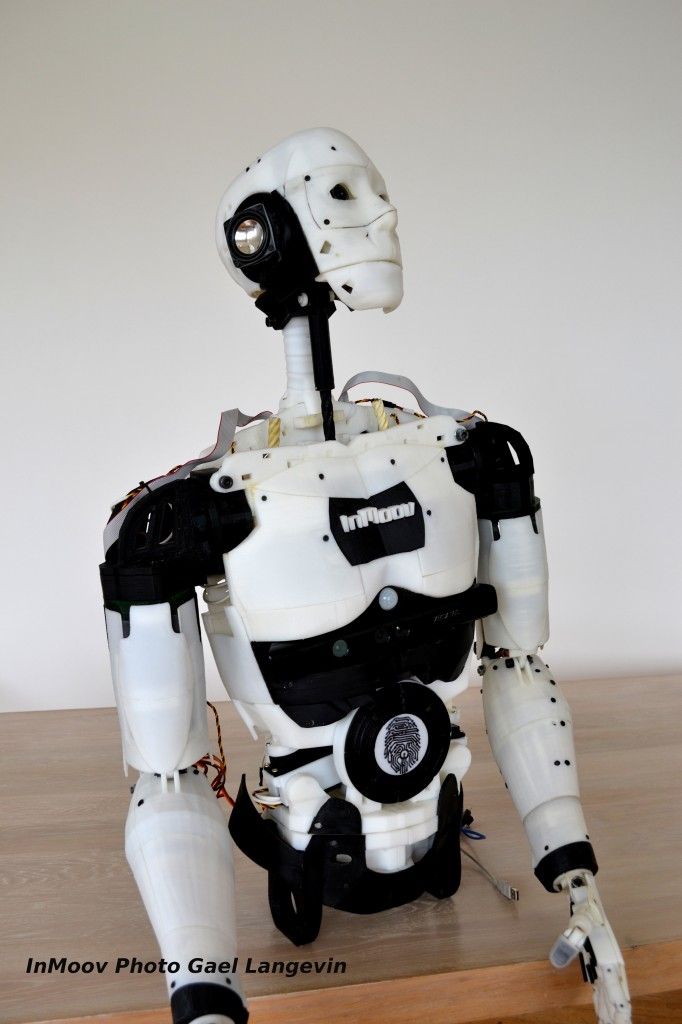 It consists of simple parts that can be laser cut or 3D printed and features a simple yet robust 4DOF construction.
It consists of simple parts that can be laser cut or 3D printed and features a simple yet robust 4DOF construction.
This design is so popular that two others on this list copy it. This is a manipulator equipped with four servos and either an Arduino or a Raspberry Pi. It is available in several different colors as a kit, or you can make all the parts yourself.
For pre-assembled kits, check out the MeArm product page.
For 3D printing files, take a look at MeArm on Thingiverse.
Zortrax Robotic Arm
The 5DOF Zortrax Robotic Arm is not the strongest for its size, with a maximum payload of only 100 grams, but it has a very impressive design. And it's a fully 3D printed arm, making it worthy of a mention on the current list. Its uniqueness lies in the fact that only three axles are driven, while the rest are set manually.
This manipulator is primarily used for supplying a set of interchangeable tool heads.
For a complete list of part files, including those for 3D printing, visit the project page.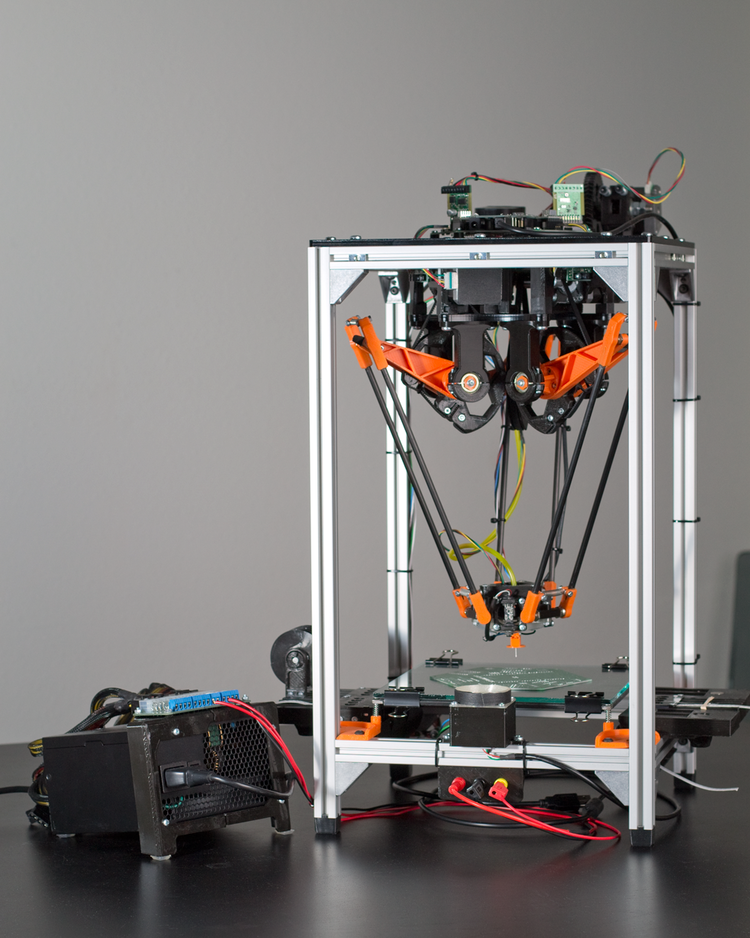
BCN3D Moveo
BCN3D Moveo is an impressive Arduino controlled 4DOF robot arm. It is fully 3D printed, open source, and has been well tested as a mockup for educational purposes and is already in active use in educational institutions.
Being open source, this manipulator is not limited to its intended use and, as such, can be modified to perform all kinds of tasks and can be used as a dedicated household apprentice or used on an industrial scale.
For more information, visit the BCN3D Moveo webpage.
OWI Robotic Arm Edge
Another 4DOF design, the OWI Robotic Arm Edge is a simple manipulator designed for educational purposes. It is only available as a kit.
When powered by DC motors without encoders, accuracy is limited, making this manipulator more suitable for use as a toy. We included it on this list because it's a fantastic kit for students interested in robotics and technology, and it can be a great "desk toy" during boring lunch breaks.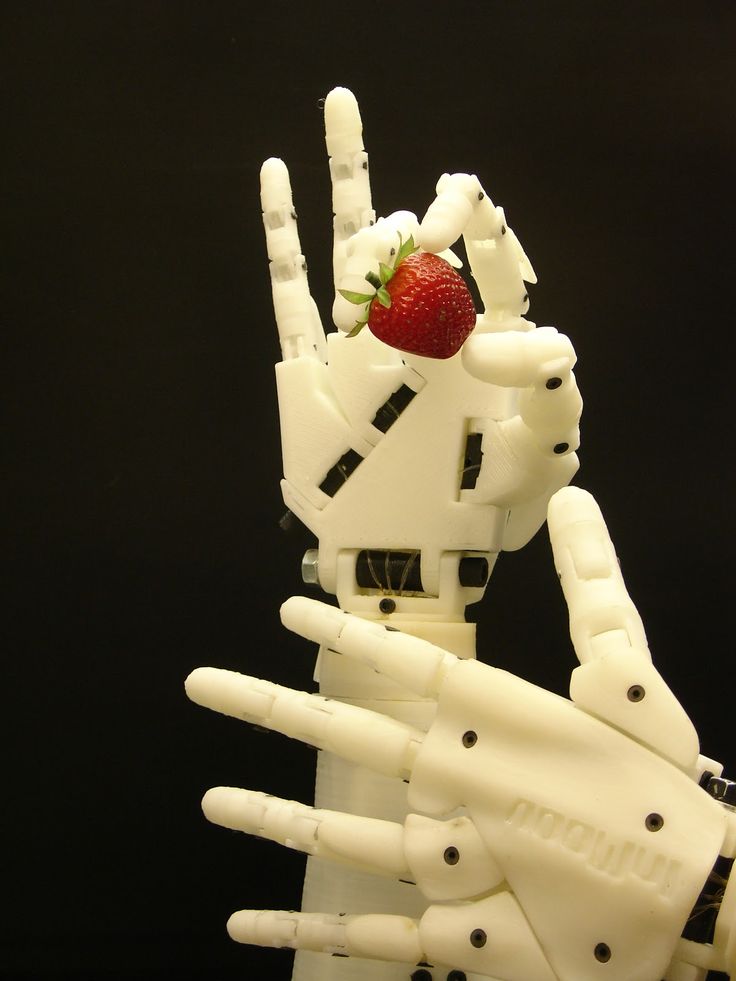 It can also be extensively modified to serve as a base platform for Arduino projects and other DIY developments.
It can also be extensively modified to serve as a base platform for Arduino projects and other DIY developments.
You can buy it on the OWI website, well, or Amazon, Aliexpress is also at your service.
Top 20 Free 3D Printing and 3D Printing Software
Looking for 3D printing software? We've rounded up the top 20 software tools for beginners and professionals alike. Most slicers are free.
What is a slicer? This is a program for preparing a digital model for printing. Models for 3D printing are usually distributed in STL files. To turn an STL file into G-code (a language that a 3D printer understands), a slicer program is required. It is called a slicer because it cuts (to slice - English) a 3D model into many flat two-dimensional layers, from which a 3D printer will add a physical object.
Which slicer should I choose? In this article, we will tell you which slicer is the best choice for 3D printing for each stage of your work.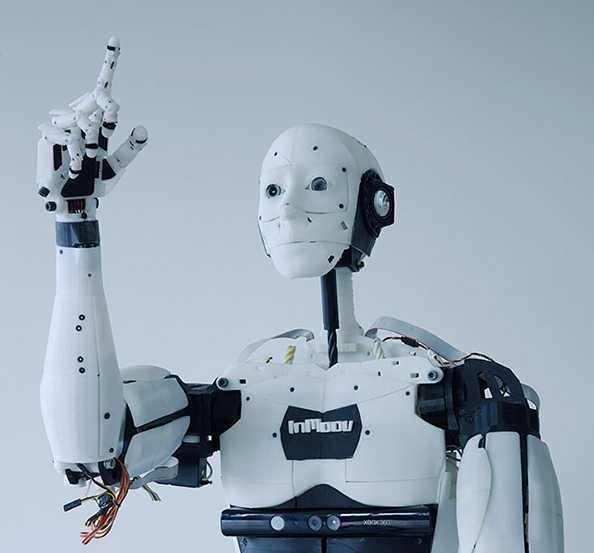 Which one is better for preparing a 3D model for printing? But what if you need to create a 3D model from scratch? And if you are only taking the first steps in 3D?
Which one is better for preparing a 3D model for printing? But what if you need to create a 3D model from scratch? And if you are only taking the first steps in 3D?
Don't be afraid: we've answered all of these questions, including the required skill level for each program and where you can download it. The great thing is that most of these programs are completely free and open source.
- Cura
- CraftWare
- 123D Catch
- 3D Slash
- TinkerCAD
- 3DTin
- Sculptris
- ViewSTL
- Netfabb Basic
- Repetier
- FreeCAD
- SketchUp
- 3D Tool
- Meshfix
- Simplify3D
- Slic3r
- Blender
- MeshLab
- Meshmixer
- OctoPrint
#1: Cura
For beginners who need a slicer to prepare STL files for 3D printing
Cura is the standard slicer software for all Ultimaker 3D printers, but can be used with most others , including RepRap, Makerbot, Printrbot, Lulzbot and Witbox.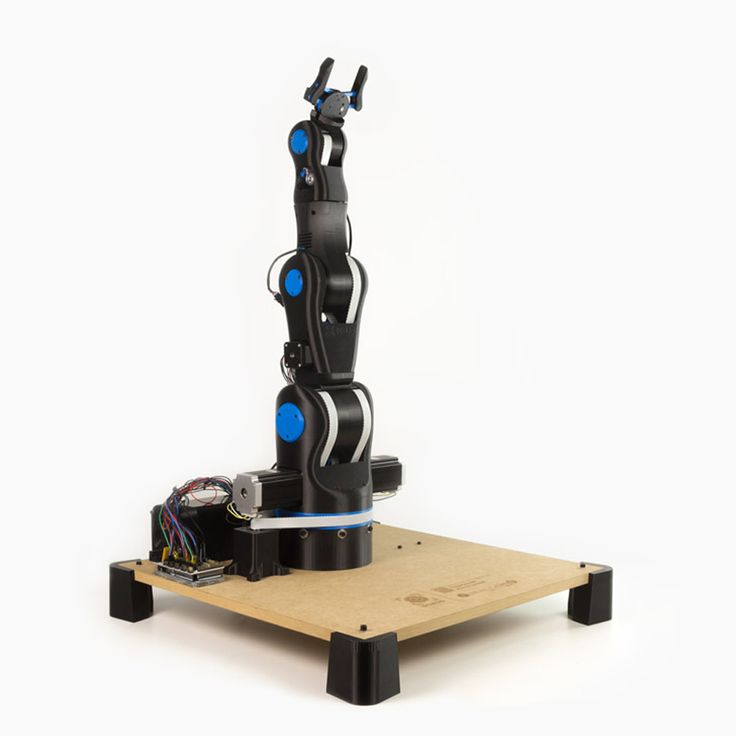 The program is completely open source, its capabilities can be extended using plugins.
The program is completely open source, its capabilities can be extended using plugins.
This program is very easy to use and allows you to manage the most important 3D printing settings through a clear interface. Start in Basic mode to quickly get up to speed and change print quality settings. If finer control is required, switch to Expert mode.
Cura can also be used to directly control the printer, but then the printer and computer must be connected to each other.
Download: Cura
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#2: CraftWare
For beginners to prepare STL files for 3D printing 3D printers by the Hungarian startup CraftUnique to support their CraftBot crowdfunding machine. However, the program works with other printers.
Like Cura, CraftWare allows you to switch from "Easy" to "Expert" mode, depending on how confident you feel. It's a colorful app that features a visual G-code visualization with each function represented by a different color.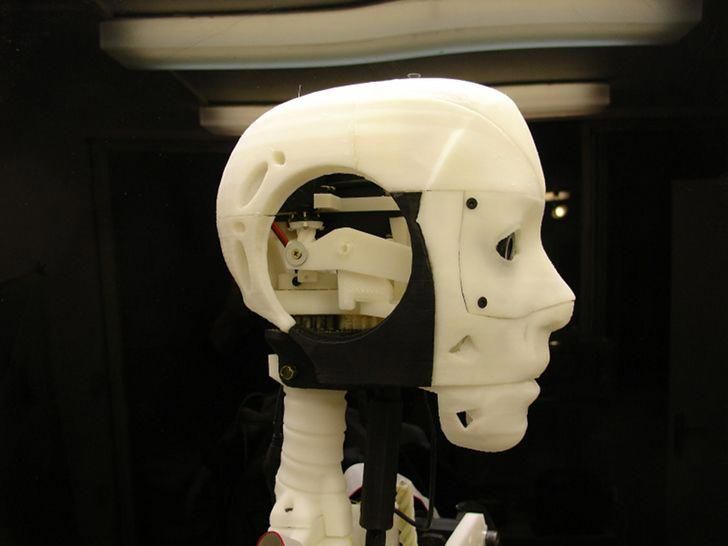 But the most outstanding feature is the individual support service. As far as we know, only the paid program Simplify3D has this.
But the most outstanding feature is the individual support service. As far as we know, only the paid program Simplify3D has this.
Please note, however, that this program is still in beta, so bugs may occur.
Download: CraftWare
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#3: 123D Catch
-systems, smartphones and tablets, which allows you to convert images of objects into a 3D model. Pictures can be taken with a smartphone/tablet or digital camera.
You need many photos of an object from different angles - the more the better - after which they will be compiled into a 3D model.
123D Catch is more of a fun app than a professional 3D printing tool, but after some tambourine dancing, you can get good results, especially when paired with an STL editor like MeshLab or Meshmixer.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Android, iOS, Windows Phone
#4: 3D Slash
and surprisingly simple, and refreshingly new.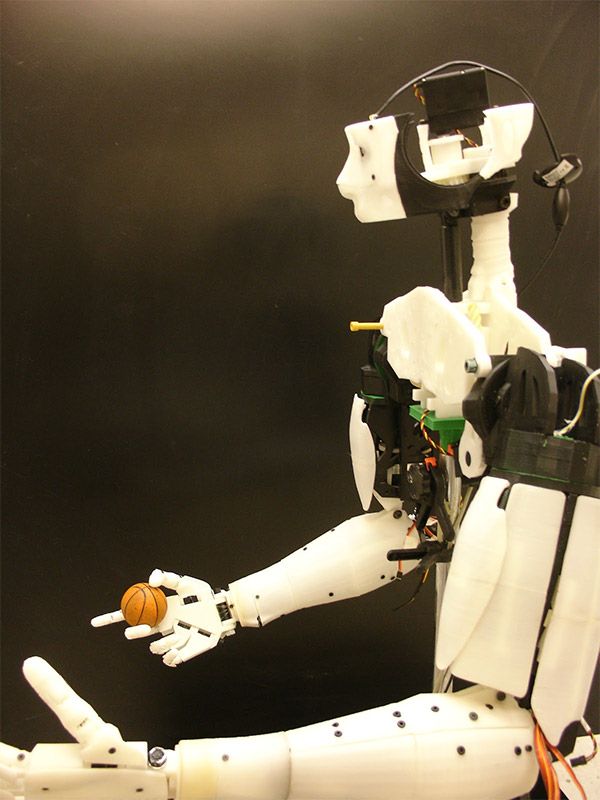 With 3D Slash, you can design 3D models using your dice skills.
With 3D Slash, you can design 3D models using your dice skills.
You can start with a large block and, like a virtual sculptor, remove small cups from it with tools such as a hammer or drill, or start from empty space and build a model from cubes and other shapes. You can paint with flowers or use template pictures.
Other features worth mentioning are tools for creating logos and 3D text. The Logo Wizard imports an image and creates a 3D model, while the Text Wizard allows you to enter and format text, and then turn it into 3D.
Recommended!
Download: 3dslash.net
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux, Browser
#5: TinkerCAD
- A computer-aided design (CAD) system for 3D printing, which is a good starting point for beginners. Since its capabilities are limited compared to Blender, FreeCAD and SketchUp, many users switch to more powerful tools after some time.
As in 3D Slash, here you can build models from basic shapes. At the same time, unlike 3D Slash, TinkerCAD allows you to create vector shapes in 2D and convert them into three-dimensional models.
At the same time, unlike 3D Slash, TinkerCAD allows you to create vector shapes in 2D and convert them into three-dimensional models.
Come in: Autodesk TinkerCAD
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#6: 3DTin
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
another easy and intuitive online tool choice for beginners in 3D modeling. All you need is a Chrome or Firefox browser with WebGL enabled.
Choose from a huge library of 3D shapes and add them to your sketch. All sketches are stored in the cloud, access to them is free if you honor the Creative Commons license. Everything can be exported to STL or OBJ formats.
Enter: 3DTin
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#7: Sculptris
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
clay. This is a fantastic 3D modeling program if figurines are your main task. For example, you can make a bust of your favorite video game or comic book character.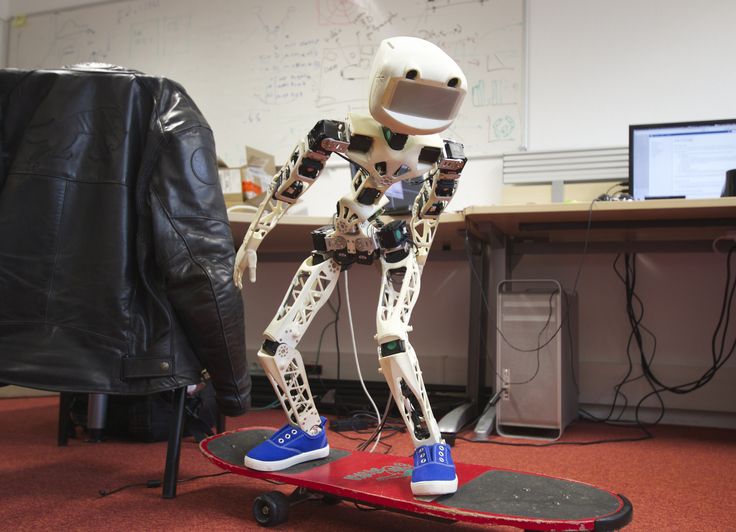 Sculptris is completely free and bills itself as a stepping stone to the more complex (and expensive) ZBrush tool.
Sculptris is completely free and bills itself as a stepping stone to the more complex (and expensive) ZBrush tool.
Download: Pixologic Sculptris
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#8: ViewSTL
For beginners who want to view STL files
ViewSTL is the easiest way to view STL files . Simply open a web page and drag the STL onto the dotted box.
The STL online viewer allows you to display the model in one of three views: flat shading (for a quick view), smooth shading (for a high-quality image), and wireframe.
Come in: ViewSTL
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#9: Netfabb Basic
some nice features that allow you to analyze, "repair" and edit STL files before moving on to the model cutting stage.
A good choice if you need more than just a slicer and want to be able to quickly fix STL files without having to learn programs like MeshLab or Meshmixer.
Don't let the 'Basic' in the title fool you, Netfabb Basic is actually a very powerful 3D printing tool. It's "basic" only in the sense that it doesn't cost €1,500 like Netfabb Professional!
It's "basic" only in the sense that it doesn't cost €1,500 like Netfabb Professional!
Download: netfabb.de
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
No. 10: Repetier
For advanced to prepare STL files for 3D printing
9002 If you are ready to upgrade to the next level of 3D printer slicer software, but if you want to stay open source, you should look into Repetier. It is the great grandfather of 3D printing software and a favorite of the RepRap community.To date, the program is moving by leaps and bounds from the level for beginners to advanced users. Packaged in an all-in-one configuration, it supports up to 16 extruders, multi-slicing via plug-ins, and virtually every fusing 3D printer on the market. Get ready to tinker!
What's more, Repetier Host works remotely via Repetier Server, so that the 3D printer can be controlled via a browser, tablet or smartphone.
Download: Repetier
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#11: FreeCAD
The program is a great option for developing your design skills.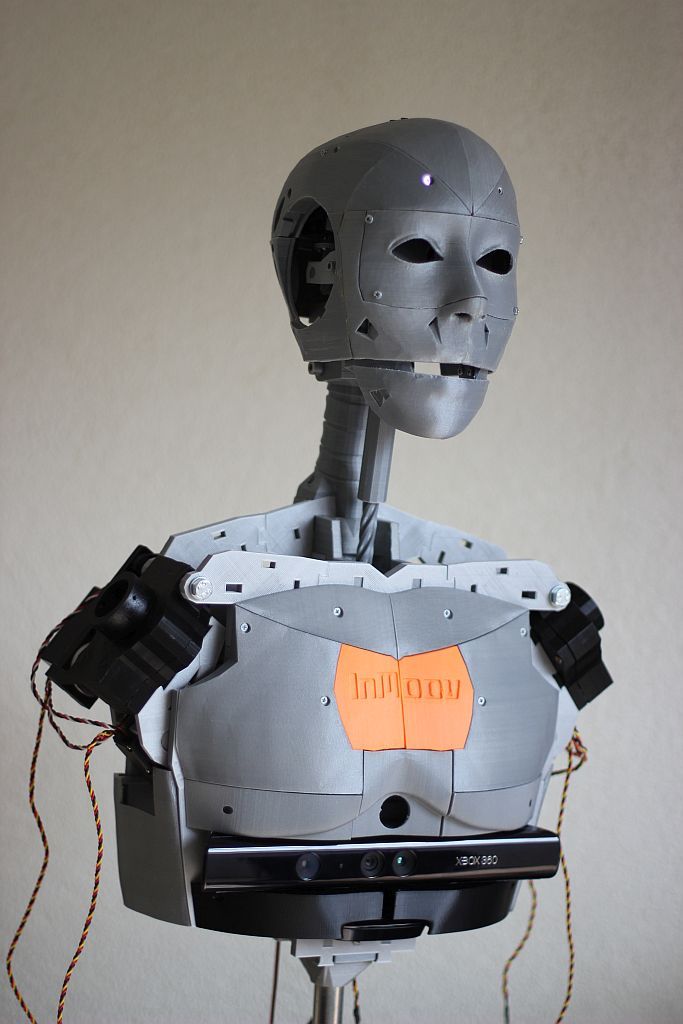 More technically, this parametric 3D modeling program allows you to easily change the project by rolling back through the history of the model and editing the parameters.
More technically, this parametric 3D modeling program allows you to easily change the project by rolling back through the history of the model and editing the parameters.
Download: freecadweb.org
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#12: SketchUp
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
SketchUp functionality, with a user-friendly interface and a relatively flat learning curve (i.e., as experience grows with the time spent), the ideal program for developing three-dimensional models.
The Make SketchUp version is free and will include everything you need for 3D modeling if you also download and install the free STL exporter. There is also a professional edition for architects, interior designers and engineers.
Download: sketchup.com
Price: Free (SketchUp Make), $695 (SketchUp Pro)
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#13: 3D-Tool Free Viewer
view and validate STL files
3D-Tool Free Viewer is a sophisticated tool that, among other things, allows you to check the structural integrity and printability of your file. With the Cross-Section function, for example, you can look at the model from the inside and check the wall thickness. Very useful if you want to check your STL file for killer errors before printing.
With the Cross-Section function, for example, you can look at the model from the inside and check the wall thickness. Very useful if you want to check your STL file for killer errors before printing.
Download: 3D-Tool
Price: Free
Systems: PC
#14: Meshfix
your model for errors.
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#15: Simplify3D
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing print. A flexible algorithm checks the model for problems, fixes them, shows a preview of the printing process (ideal for identifying potential problems), and then slices it.
This slicer offers the best infill pattern options in the competition. For models that require supports, Simplify3D will create the appropriate structures on its own and give you full control over their placement. For printers with a dual extruder, when printing with different materials, the Dual Extrusion wizard will help, as a result of which, for example, it will be easier to remove the dissolving filament.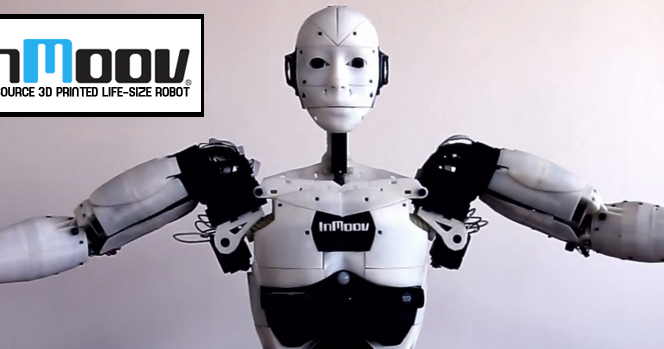
Simplify3D supports 90% of today's commercially available desktop 3D printers and is compatible with Marlin, Sprinter, Repetier, XYZprinting, FlashForge, Sailfish and MakerBot firmware. Simplify3D can also be used to directly control the printer, but then the printer and computer must be connected to each other.
Download: simplify3d.com
Price: $149
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#16: Slic3r
source code, which has a reputation as a carrier of super new functionality, which you will not find anywhere else. The current version of the program is able to show the model from multiple angles, so that the user gets a better preview experience.
There's also an incredible 3D honeycomb infill, the first of its kind that can extend over multiple layers rather than repeating itself like a stamp. This significantly increases the strength of the internal filling of the model and the final printout.
Another option is direct integration with Octoprint.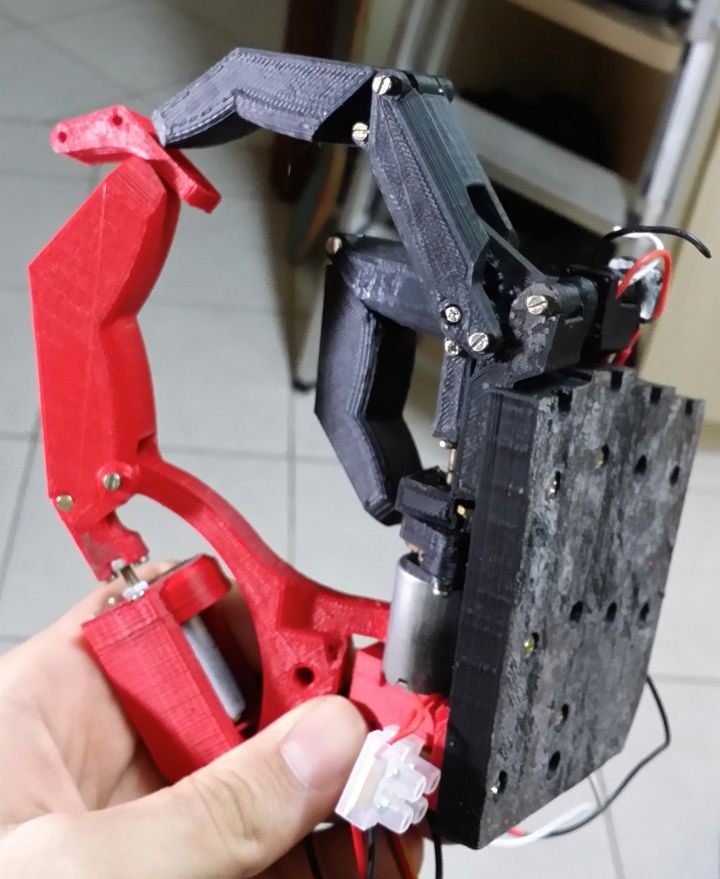 Once the files on the user's desktop are sliced, they can be directly uploaded to Octoprint with one click.
Once the files on the user's desktop are sliced, they can be directly uploaded to Octoprint with one click.
Download: Slic3r
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#17: Blender
For professionals who want to create 3D printable models
Blender is a popular computer-aided design (CAD) system with a steep learning curve. Not at all the best choice for beginners, but what you need if you are quite experienced and need something more complex for modeling and printing.
In short, Blender is one of the most powerful tools out there. Its community is always ready to help, there are a lot of educational materials. It's also open source, so enthusiasts often write extensions to make it even better and more powerful.
Download: blender.org
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#18: MeshLab
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing
MeshLab - advanced editor. It allows you to remove parts of a 3D model, merge two models into one, patch holes. If you need a program to modify models for 3D printing or some kind of "repair" work, MeshLab is the right choice.
It allows you to remove parts of a 3D model, merge two models into one, patch holes. If you need a program to modify models for 3D printing or some kind of "repair" work, MeshLab is the right choice.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#19: Meshmixer
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing files. It's especially good for identifying potential problems and fixing them automatically. For example, it will show paper-thin walls that can lead to problems with 3D printing. Meshmixer is part of the Autodesk family of 3D printer software, so it should work well with tools like TinkerCAD.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#20: OctoPrint
start, pause or interrupt 3D print jobs. Combined with Wi-Fi capable devices, it makes for a great monitor for remotely monitoring the 3D printing process.
Octoprint understands the G-codes of almost all 3D printers and slicers and includes a gCodeVisualizer to visualize this code before or during printing.