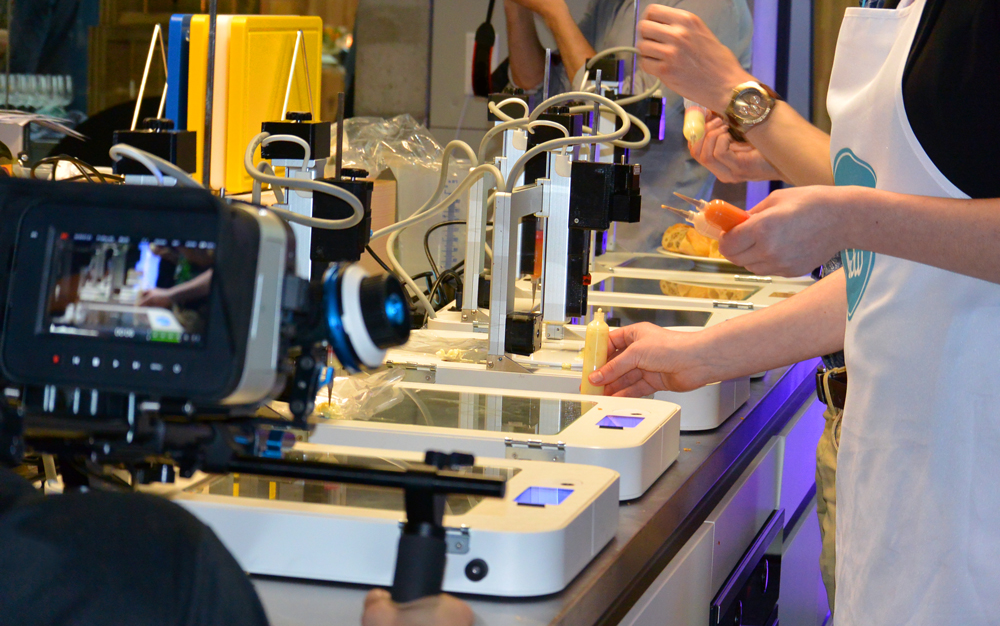
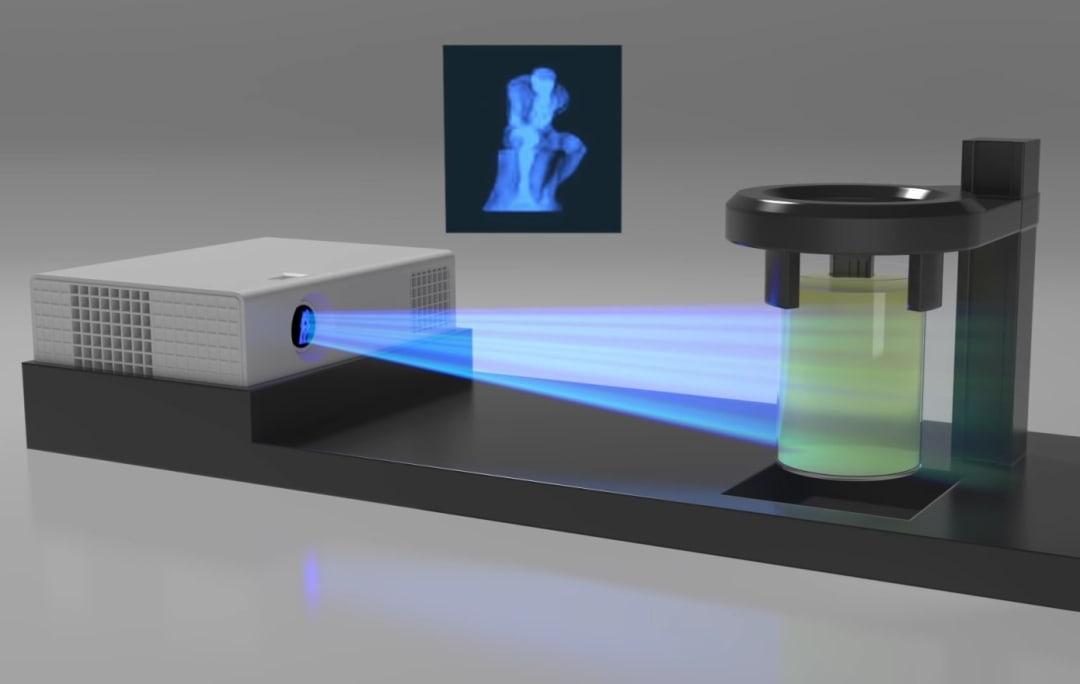
Future for 3d printing
What Does the Future of 3D Printing Look Like?
3D printing has come a long way from the early days of desktop figurines. As technology continues to evolve, the future is brighter than ever.
Once a novelty pipe dream but now an established technology, 3D printing (or additive manufacturing) is positioned for real, important growth. Remember the early days of 3D printing? We shared a collective excitement for model versions of the Brooklyn Bridge and iconic cartoon characters to adorn our desks. Now, 3D printing is tackling much larger issues and solving complex problems across industries of varying scales.
The basis of 3D printing — also called additive manufacturing — is adding layers of materials compounded to make an object. Where cutting and soldering were once required, additive manufacturing gracefully adds layers to build the same type of structures. However, these results are stronger, lighter, more temperature resistant, and require fewer parts.
Applications Showcasing What the Future Holds for 3D Printing
While there are endless examples of 3D printing being used for incredible things, here are a few examples of what the future holds:
- 3D printers have long been able to print rocket-shaped objects, but now companies in the aerospace industry are actually printing rockets.
Companies like Aerojet Rocketdyne are using additive manufacturing for rocket engine and defense system applications. These companies cite reduced lead times, affordability, and new approaches to design as factors in the decision to use additive manufacturing to deliver hypersonic flight.
- In healthcare, additive manufacturing is also making grand promises. 3D Systems, in partnership with CollPlant, is working on printing artificial tissues and scaffolds, advancing regenerative medicine through the use of rhCollagen as a 3D printing substrate.
- The electric vehicle industry is a similar story. Local Motors Industries, a company with only 130 employees, has already printed a 3D car that has since been discontinued. Now, they’re printing an urban electric shuttle, citing digital design advancements as a contributing factor.
At the Forefront of Evolving Technology
A generatively designed color part from the HP MJF 580 3d printer at the Autodesk Technology Center in Toronto.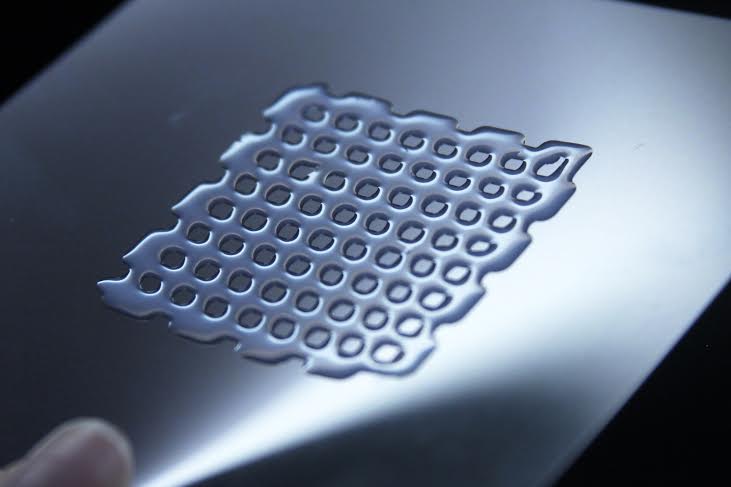
Experts predict the largest industry leaps will happen in the technology facilitating additive manufacturing. Printers will likely become even faster, meaning they’ll be able to work on larger, industrial types of projects. Forbes also reports that MELD Manufacturing has designed machines that allow additive manufacturing in uncontrolled environments, which means they can operate in the field. As a result, they’re more useful in remote areas and enable a greater variety of 3D printed structures.
3D printing seeks to address efficiency problems throughout supply chains as well. Nora Toure, Founder of Women in 3D Printing, writes, “I predict there will be a countless number of companies that have adopted additive manufacturing into their supply chain commercially with a vast majority of products to be produced on-demand and locally (not necessarily through additive manufacturing, but more as a combination of manufacturing tools, including additive manufacturing).”
3D printers will also add versatility in other ways — using different materials, including metal and even ceramics, even within the same machine.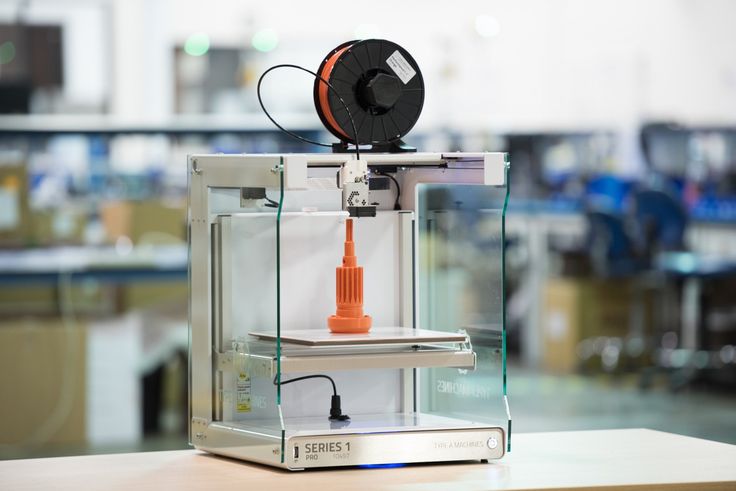 Printers will be able to print one object containing multiple materials, paving the way for a significantly widened field of use.
Printers will be able to print one object containing multiple materials, paving the way for a significantly widened field of use.
Autodesk Fusion 360 and Additive Manufacturing
Integrated CAD + CAM software like Autodesk Fusion 360 will enable additive manufacturing to soar to entirely new levels. The Fusion 360 team is constantly thinking of ways to improve and enhance the additive manufacturing process. We recently announced a new method for generating additive manufacturing outcomes using generative design. This new method does a better job of meeting minimum thickness requirements, balancing design mass, and minimizing support material — without sacrificing shape quality to be fully self-supporting.
Many leading companies have explored the benefits of using generative design in tandem with additive manufacturing, including Hyundai, Panasonic, and more. Download Fusion 360 today to explore innovative additive manufacturing solutions.
What’s the Future of 3D Printing?
Welcome to Thomas Insights — every day, we publish the latest news and analysis to keep our readers up to date on what’s happening in industry.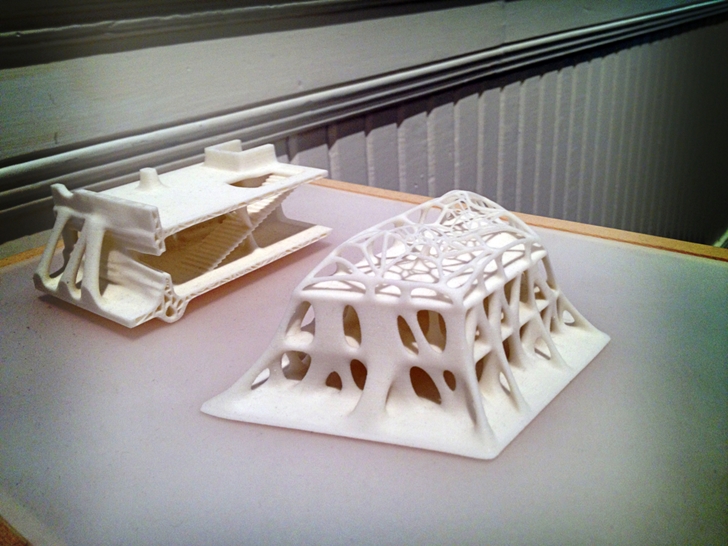 Sign up here to get the day’s top stories delivered straight to your inbox.
Sign up here to get the day’s top stories delivered straight to your inbox.
The global 3D printing market is projected to quadruple over the next decade to exceed $50 billion, according to a report issued by Lux Research, a tech consulting firm based in Boston. Prototyping, which is what 3D printing has been traditionally used for, is expected to grow from $4.4 billion to nearly $10 billion.
The largest overall value, however, will likely occur in 3D printing’s other primary use: molds and tooling. They will grow from 2020’s value of $5.2 billion to $21 billion by 2030. The greatest jump in value is for 3D-printed end-use parts, which will grow sevenfold to reach $19 billion in 2030.
Xometry, a global custom manufacturer network based in Gaithersburg, Maryland, is also seeing the manufacturing sector expand from using 3D printing mainly for prototyping to a more significant portion of end-use applications. Its AI-enabled marketplace for on-demand manufacturing matches buyers sourcing 3D printed parts with its network of more than 5,000 suppliers. The proprietary technology gives Xometry deep insight into additive manufacturing trends.
The proprietary technology gives Xometry deep insight into additive manufacturing trends.
Greg Paulsen, director of application engineering at Xometry, shared with us how 3D printing — a technology that was invented in the 1980s — has changed over the years and where he sees it headed.
“3D printing applications can be as simple as electronics housing covering or a customized medical device,” says Paulsen. “These days, the molds used for dental aligners are almost whole-heartedly 3D printed. All these applications have come out of this ability to do mass-customized, just-in-time direct digital manufacturing.”
Greg PaulsenThomas Insights (TI): How have applications for 3D printing changed?Greg Paulsen (GP): I've been in and out of additive manufacturing going on 15 years. We used to call it rapid prototyping (RP) because that's the way we thought of it. It was just prototyping.
Over the years, the percentage of parts that we make that are designed for either low-volume production — or production goods that we're making in batch sizes, and then when they need another batch, they reorder — and those where they're designed for end-use has kept on growing. It's really exciting for me to see the adoption of 3D printing for end-use parts over time.
It's really exciting for me to see the adoption of 3D printing for end-use parts over time.
[Get an instant quote and lead time estimates for any 3D project here.]
TI: How have the materials changed?GP: There has been an increase in materials. We don't just print in plastics — we print in metals as well. With the increase of different options for surface finishing, we now have things like chemical vapor smoothing, which can give you a semi-gloss part.
TI: How is Xometry advancing 3D printing standards?GP: 3D printing still has a little bit of Wild West to it when it comes to expectations of the parts and consistency from part to part, especially when you're looking at some of the more consumer-grade products. Can I order this part today in a quantity of one, and then 90 days from now order 40 more, and they'll still be identical?
Xometry is creating consistent expectations.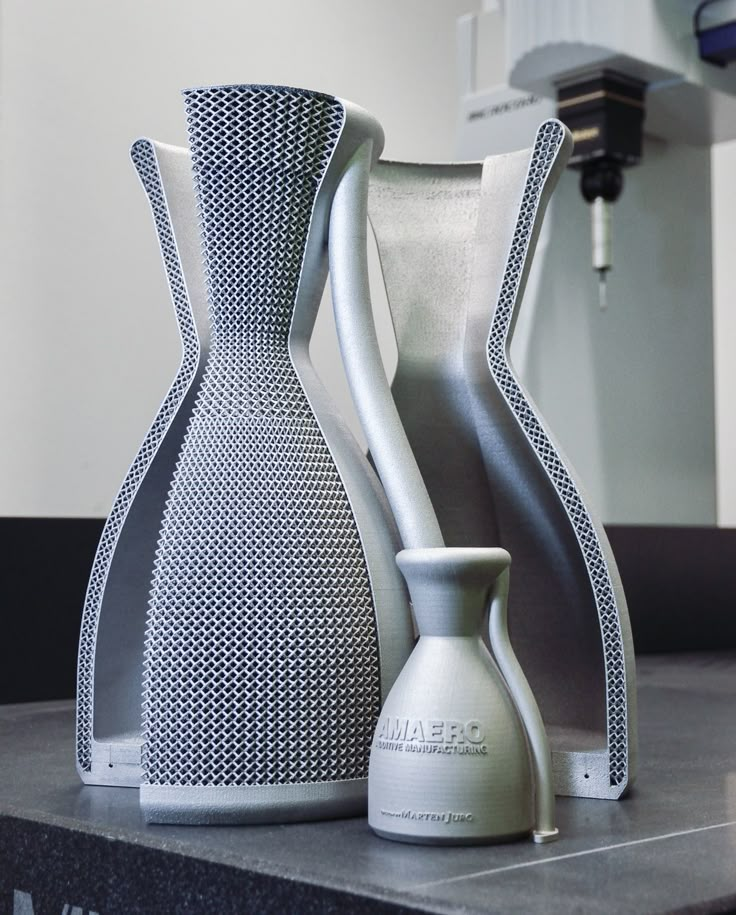 We actually build quality manufacturing standards around every single one of our processes. As well, we're using the latest and greatest industrial manufacturing platforms. So these are not your desktop 3D printers. These are industrial pieces of equipment that produce parts with repeatable tolerances, clean finishes, and consistent properties.
We actually build quality manufacturing standards around every single one of our processes. As well, we're using the latest and greatest industrial manufacturing platforms. So these are not your desktop 3D printers. These are industrial pieces of equipment that produce parts with repeatable tolerances, clean finishes, and consistent properties.
We also provide datasheets, which help engineers confidently design around a 3D printing process. And that includes not just the design or the shape itself, but also understanding the material properties, doing engineering simulation, and building generative design tools. That brings consistency and reliability within the industry.
TI: Where do you see 3D printing headed?GP: I do see 3D printing becoming boring. I just want it to be another process available to designers, sourcing, and other manufacturers without it being a specialized tool.
One of the more exciting things of the future of additive manufacturing is building a robust set of tools so when a customer presses “buy” on their site, they get the part that they expect. 10 years ago, that was a very different story. I would be getting my tools out to sand and drill and fix the part after I receive it. But today, it's more normal to just get your part, open the box from Xometry, install it into your product, and it just works. And that's where we're seeing additive as an industry going.
10 years ago, that was a very different story. I would be getting my tools out to sand and drill and fix the part after I receive it. But today, it's more normal to just get your part, open the box from Xometry, install it into your product, and it just works. And that's where we're seeing additive as an industry going.
Image Credit: Stock-Asso / Shutterstock.com
Auto Supplier Announces $8 Million Tennessee Plant Next Story »
More from Engineering & Design
what lies ahead for 3D printing
The prospects for 3D printing
Even now, the prospects for 3D printing are extremely promising. Scientists are actively developing existing 3D printing techniques, developing new technologies and types of materials, and finding new areas of application. Many call 3D printing the technology of the future, and for good reason. The technique is able to completely turn the usual way of life, changing the way most things are produced. In fact, a 3D printer is a real multifunctional factory, small and compact. Due to this, the future of 3D printing can definitely be called successful.
In fact, a 3D printer is a real multifunctional factory, small and compact. Due to this, the future of 3D printing can definitely be called successful.
3D printers can significantly reduce production costs, thereby reducing the cost of products. Judging by the growing trend towards the popularization of 3D technologies, raw materials for 3D printing will become the main commodity unit in the future. In general, the prospects for 3D printing are defined for many areas. And now we will try to reveal them as much as possible.
The Future of 3D Printing
If you try to imagine the future of 3D printing, your imagination paints a rather interesting picture. Given the great interest of scientists in the 3D bioprinting technique, which is one of the most promising 3D printing technologies, the production of artificial organs on a 3D printer is not far off. It is also safe to say that the future of 3D printing will bring us dramatic changes in areas such as:
- Construction.
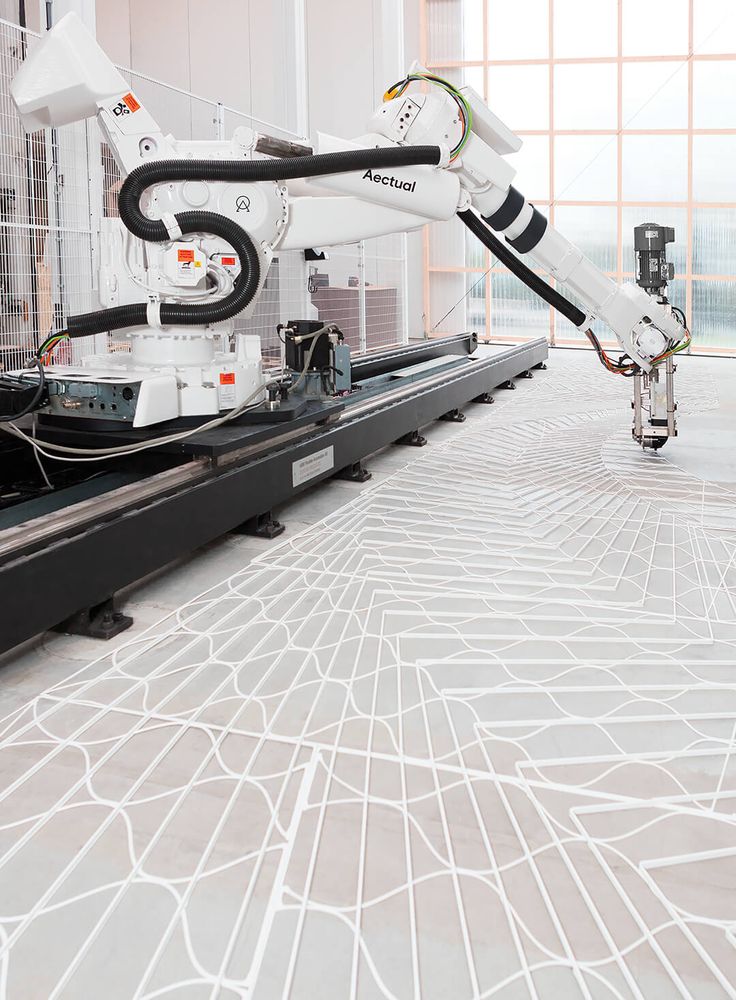 3D printing of houses, or contour construction, attracts many with its futurism and simplicity. The first steps in this direction have already been taken. The pioneers in 3D printing of houses were the Chinese, followed by the government of Dubai who discovered contour building. The first 3D printed office building has already been built in this city of the future, and an entire block is planned to be printed in the near future. And just recently, the first printed house in Europe was created on a 3D printer;
3D printing of houses, or contour construction, attracts many with its futurism and simplicity. The first steps in this direction have already been taken. The pioneers in 3D printing of houses were the Chinese, followed by the government of Dubai who discovered contour building. The first 3D printed office building has already been built in this city of the future, and an entire block is planned to be printed in the near future. And just recently, the first printed house in Europe was created on a 3D printer; - Electronics. When listing the prospects for 3D printing, this point should be given special attention. Scientists believe 3D printing of electronics is the future of digital device manufacturing, and with good reason. Graphene properties and its application in additive manufacturing are currently being actively researched. A huge breakthrough in this area is the creation of a graphene battery with an unlimited service life on a 3D printer;
- Automotive and aerospace industry.
 The future of 3D printing is largely based on its ability to reproduce almost any element of varying complexity. In this regard, 3D printing is already widely used in the development of aircraft, machines and satellites. The ISS even has its own 3D printer, not to mention a number of successful 3D printing of cars.
The future of 3D printing is largely based on its ability to reproduce almost any element of varying complexity. In this regard, 3D printing is already widely used in the development of aircraft, machines and satellites. The ISS even has its own 3D printer, not to mention a number of successful 3D printing of cars. - Pharmaceutical industry. Yes, yes, you can imagine. The future of 3D printing is in the manufacture of tablets and other medicines. This is confirmed by epilepsy pills legalized in the USA, made according to a special technique. The essence of this perspective of 3D printing is the gradual release of active substances, so that instead of many tablets, you can drink just one.
- Food industry. 3D food printers are gradually gaining space in cafes and restaurants. While this is probably one of the most raw 3D printing technologies out there, it has potential. Food 3D printers are especially interesting for the possibility of making food for astronauts, as well as the freedom to display culinary talent.
 This is confirmed by the amazing 3D-printed desserts of our compatriot.
This is confirmed by the amazing 3D-printed desserts of our compatriot.
Other questions and answers about 3D printers and 3D printing:
- Finance Which 3D printer manufacturers are best?
- Finance Which 3D printer is better to buy?
The future of 3D printers
Now let's try to imagine the future of 3D printers. There are several important points to be noted here. Below we list the most likely scenarios for the future of 3D printers.
- Improving the reliability and quality of devices. Surely, many users are looking forward to this, because most of the existing models of 3D printers cannot boast of uninterrupted operation and the absence of printing errors;
- Large-scale distribution. It is certain that the future of 3D printers will please us with their popularization. Even now, one can observe a growing trend towards the use of 3D printing in almost all areas of industry. In parallel with the fact that more and more users learn about the possibilities of technology, the demand for desktop 3D printers is also growing;
- Availability.
 In continuation of the previous paragraph, it is worth noting that the growing demand for 3D printers will lead to lower prices for these devices. The use of 3D printing for domestic purposes is gaining momentum, which brings new equipment manufacturers to the market. Naturally, such a step will entail a reduction in the cost of devices;
In continuation of the previous paragraph, it is worth noting that the growing demand for 3D printers will lead to lower prices for these devices. The use of 3D printing for domestic purposes is gaining momentum, which brings new equipment manufacturers to the market. Naturally, such a step will entail a reduction in the cost of devices; - Enlargement of the construction area. 3D printing of large-sized objects has long occupied the minds of developers. Of course, this applies to industrial 3D printers, because the functionality of 3D printing at this scale will allow you to create full-fledged components, for example, cars and aircraft;
- Expanding the range of available materials. The future of 3D printers depends a lot on 3D printing materials, because more means more possibilities. The development of special equipment and related materials is being carried out by many companies, and news about the release of new polymers is constantly appearing.
3D technologies of the future
Summing up, it remains to consider only 3D technologies of the future. These include various futuristic scenarios that, to one degree or another, are already beginning to develop today. These include the technique of virtual reality, 3D scanning to create the perfect clothes and shoes, 3D printed makeup, and more. In a way, 3D technologies of the future also include bioprinting. By the way, scientists are talking about building the first 3D printed settlement on the Moon and Mars, so the prospects for 3D printing are also relevant outside the Earth.
These include various futuristic scenarios that, to one degree or another, are already beginning to develop today. These include the technique of virtual reality, 3D scanning to create the perfect clothes and shoes, 3D printed makeup, and more. In a way, 3D technologies of the future also include bioprinting. By the way, scientists are talking about building the first 3D printed settlement on the Moon and Mars, so the prospects for 3D printing are also relevant outside the Earth.
This was a list of the main scenarios for the future of 3D printing. Let's see how they are destined to come true. If you have additional questions that we have not covered, write to us by e-mail and we, if necessary, will add your questions! Best regards, 3DDevice team.
Our store offers a wide range of 3D printers, 3D scanners, 3D plastics and resins, as well as other accessories at the best prices on the Ukrainian market with delivery to all cities (Kharkiv, Nikolaev, Dnepropetrovsk, Lviv, Zaporozhye, Kherson, Donetsk, Odessa ). We also provide 3D printing, 3D scanning and 3D modeling services. For all questions, please contact us in any way convenient for you. Contacts are listed here. We look forward to collaborating!
We also provide 3D printing, 3D scanning and 3D modeling services. For all questions, please contact us in any way convenient for you. Contacts are listed here. We look forward to collaborating!
Back to Home
Perspectives, development and the future of 3d printers
3D printing is an extremely promising technology that has the potential to change how many things are made. In addition, the use of 3D printers will significantly reduce the production time of various products and reduce their final cost. Let's consider in which areas the use of 3D printing is most promising, what is the future of this technology and how quickly it will develop.
Relevance of 3D printing
3D printing technology is relevant due to its ease of use and saving time spent on the production of various types of products.
Printing of 3D objects also provides high-precision reproduction of the necessary shapes and details of a particular object. At the same time, manual labor is practically reduced to zero, which means that the cost of the operator and maintenance of the 3D printer will be minimal.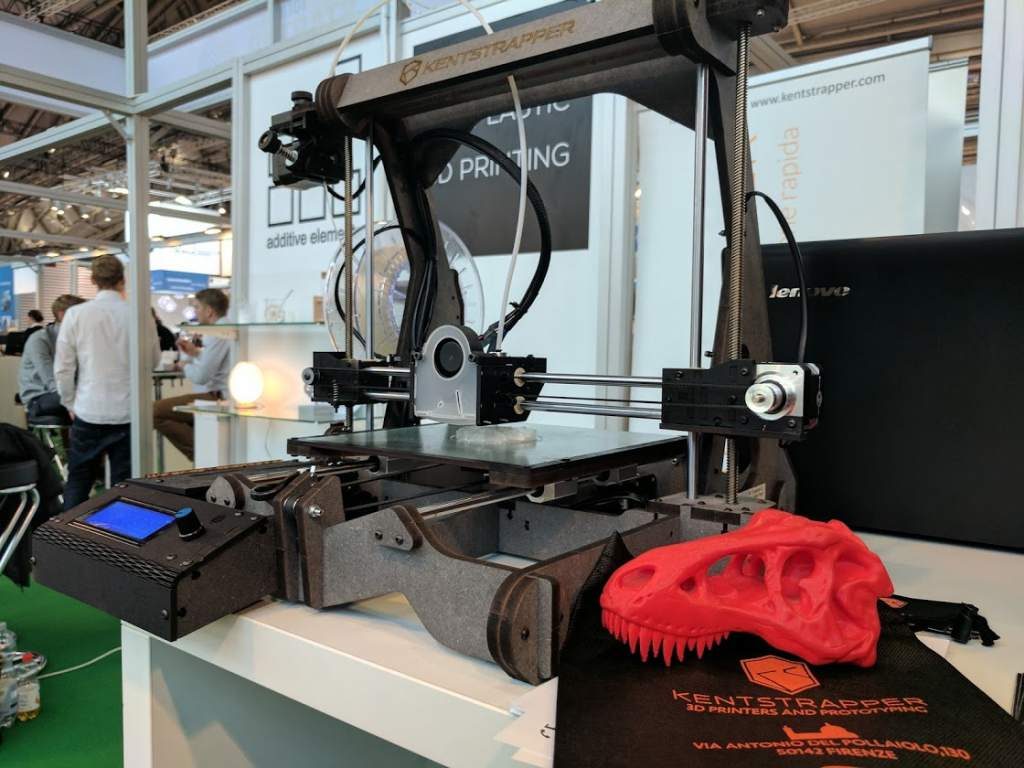 Subsequently, this will reduce the cost of the finished product.
Subsequently, this will reduce the cost of the finished product.
Thanks to these benefits, 3D printing is successfully used in many industries and everyday life.
The promise of 3D printers in various fields
3D printing technology has quite a lot of promise when applied correctly. The following areas of activity are most in need of 3D printing services:
- Construction. In the construction industry, 3D printing can be a powerful addition to traditional construction methods. Since this technology does not require the involvement of a large number of people to perform hard work. A few operators and craftsmen are enough to service the construction 3D printer. The first successful experiments in the manufacture of building parts and the construction of houses have already been carried out in China and the United Arab Emirates.
- Electronics. In the manufacture of digital devices, 3D printing will reduce the time for the manufacture of labor-intensive parts, microcircuits and hardware electronics.
 In particular, 3D printing is already developing the first samples of graphene batteries that have an unlimited service life.
In particular, 3D printing is already developing the first samples of graphene batteries that have an unlimited service life. - Mechanical engineering and automotive industry. In this area, with the help of three-dimensional printing, experimental models of future spare parts and parts are created, which later allow the production of products of perfect quality. This is possible due to the detailed study of a three-dimensional object during its creation and printing of a finished computer model, which has a high level of detail.
- Aerospace industry. The use of 3D printing in this industry is explained by the ability to create innovative designs of any complexity. Details of satellites, rockets and other space objects are printed from metal, polymers and other types of heavy-duty materials.
- Medicine and pharmaceuticals. In medicine, 3D printing technology is extremely important. Therefore, in this industry it is studied in great detail. With the help of a 3D printer, it is possible to print prototypes of human organs, prostheses, bone tissue implants.
 Even the first steps are being taken to develop and print real organs that will take root well in the human body. In the pharmaceutical industry, 3D printing is mainly used to create tablets that will gradually release active substances after ingestion.
Even the first steps are being taken to develop and print real organs that will take root well in the human body. In the pharmaceutical industry, 3D printing is mainly used to create tablets that will gradually release active substances after ingestion. - Advertising. For advertising purposes, 3D printers print prototypes of various products, demonstration and handouts.
- Food industry. 3D food printers are especially interesting because they allow you to create edible objects from familiar foods. 3D printing makes it possible to create unique decorations and complex multi-color objects with high detail.
The future of 3D printing
3D printing, if properly developed and explored, will be more accessible in the future. Since 3D printers will be common as a work unit in many areas. At the same time, prices for such equipment are likely to fall. Since they will be produced by various companies in large quantities to satisfy the demand of all buyers.
The growing demand for 3D printing will lead to the development of new types of 3D printers and materials for creating products.
Also for larger 3D printing, large-scale equipment will be created that will allow printing very large products for construction needs, engineering and other industries.
Unexpected possibilities of 3D printing
In addition to the standard creation of three-dimensional objects, the development and 3D printing of unique and customized products is also available on a 3D printer. Their shape, structure and design features are limited only by the user's imagination. It is possible to produce unusual products. For example, non-melting ice sculptures, curly perfectly fried pancakes or fine jewelry.
Who is the future of 3D printing?
Primarily, the future of 3D printing depends on inventors who create new types of printers and develop new printing technologies depending on the type of material used. Most often, 3D printing novelties appear in research centers, industrial enterprises and technical departments of various universities. This is due to the fact that people working in such institutions are interested in the development of new technologies. Since innovation will help to improve and improve the processes of creating products in specific areas. In addition to researchers and students, a large number of developments are carried out by children and 3D printing enthusiasts. For example, the invention of the first 3D-printed prosthesis belongs to 17-year-old Easton LaChapelle.
This is due to the fact that people working in such institutions are interested in the development of new technologies. Since innovation will help to improve and improve the processes of creating products in specific areas. In addition to researchers and students, a large number of developments are carried out by children and 3D printing enthusiasts. For example, the invention of the first 3D-printed prosthesis belongs to 17-year-old Easton LaChapelle.
In addition to inventors, organizations that sponsor new developments are also responsible for the continued development and improvement of printing techniques.
Help. Three companies are considered the most famous in the field of 3D printing: Shapeways, Sculpteo and Materialize. They are engaged in the professional development and release of new models of 3D printers, materials, as well as the improvement of existing technologies and the creation of new ones.
What's in store for 3D printing in the next few years?
Experts in the field of 3D printing in 2021 make the following forecasts for its development:
- The spread of 3D printing will be massive.
 Studios for creating three-dimensional objects will be distributed in much the same way as studios for photocopying and printing materials. 3D printing will be carried out both on standard models and on individual projects.
Studios for creating three-dimensional objects will be distributed in much the same way as studios for photocopying and printing materials. 3D printing will be carried out both on standard models and on individual projects. - Small-scale production of various products will completely switch to 3D printing technology. This will help to significantly reduce the price of finished products.
- Medical scientists will master the creation of full-fledged and fully compatible organs on a 3D printer, which will be printed from dividing human cells.
- With due diligence confirming the safety of 3D printing for construction purposes, many companies in the industry will start using powerful industrial printers to create the required building elements. At the same time, the time to build houses will be reduced and the proportion of hired workers who perform hard work will decrease.
A revolution in materials
A standard 3D printer uses plastic materials as a filament.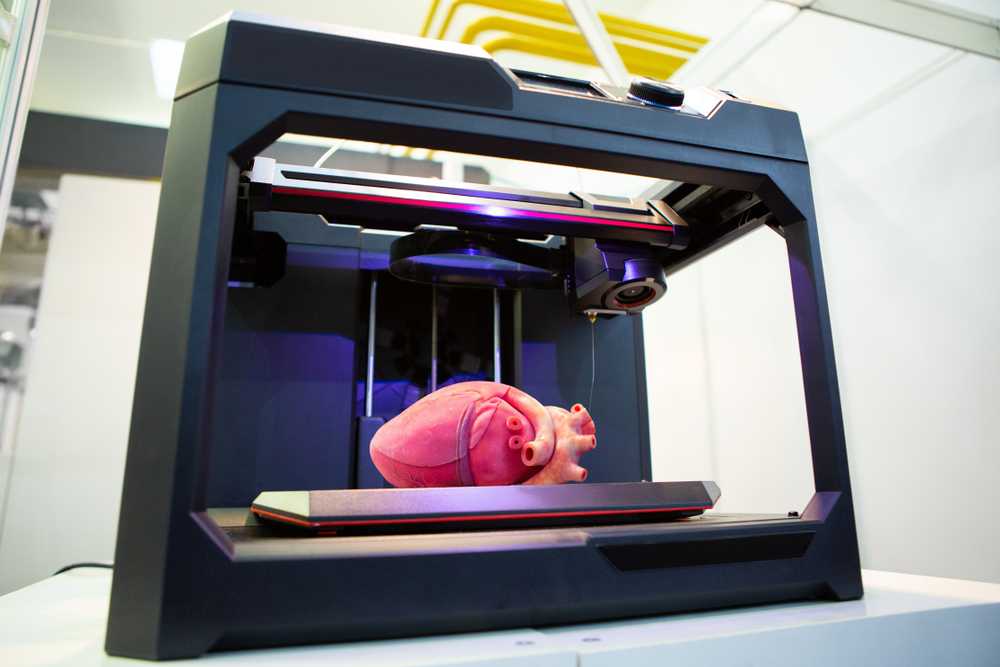 However, technology development continues at an accelerated pace. Thanks to this, innovative materials appear on the market, such as:
However, technology development continues at an accelerated pace. Thanks to this, innovative materials appear on the market, such as:
- Metal powder. This material is mixed with a polymer during printing and is used in the technology of laser sintering of metals. Products printed from a mixture of polymer and metal powder have increased strength comparable to real metal.
- Graphene. This carbon material is being used experimentally to develop a new composite. Ideally, a 3D-printed graphene sheet would be one molecule thick. By weight, the material will be lighter than air, but its strength properties will be very high - the sheet is ten times stronger than steel.
- Ceramic foam. Such material has flexible characteristics that can be changed depending on the purpose of use. From ceramic foam on a 3D printer, you can print both a very light figure and a heavy monument. In theory, development already exists. But it requires a series of tests and stabilization of functional properties.

Learn more