Tpe 3d printing filament
TPE filament - learn everything about the TPE material for 3D printing
TPE filament - learn everything about the TPE material for 3D printingTPE material (Thermoplastic Elastomer) is a flexible material. In order to achieve the best possible outcome when 3D printing with TPE material you have to optimize the feed rate. It is recommended to print at a reduced layer height of around 0.1mm to 0.2mm range. As the height is lower, a reduced amount of plastic is required. This enables the extruder to use a reduced feed rate, easing the pressure on the filament.
The best results when printing with TPE will be seen when printing with a slow and consistent speed. As TPE has a high level of elasticity, it can mean that any sudden changes can cause a loss of control in the print speed. Fast print speeds can result in the filament compressing and will lead to a jam. Conluding: slow and steady is the best approach to take when printing TPE.
Specifications for TPE
| Features | |
| Durability | High |
| Strength | High |
| Flexibility | Very high |
| Resistance | |
| Abrasion resistance | High |
| Chemical resistance | Medium high |
| Fatigue resistance | Extremely high |
| Water resistance | Medium |
| Temperatures | |
| Nozzle temperature | 220 - 250 °C |
| Heated bed | up to 60 °C |
See all specs Hide specs
Download the full specsheet
Features of TPE material
Thermoplastic Elastomer has a wide range of features, making it a suitable choice for various applications when it comes to 3D printing.
Fatigue resistant
It is extremely fatigue resistant when it comes to flexing which makes it perfect for those applications where it will be required to flex. Due to its superb electrical properties, it is often found in applications where it is required to prevent electricity conduction such as wiring.
Tear resistant
Capable of heavy use, it is resistant to tear, abrasions and high impact. TPE material is also capable of withstanding temperatures as low as -30 degrees Celsius and as high as 140 degrees Celsius.
For businesses that are looking to enhance the way in which they work and improve the impact on the environment, Thermoplastic Elastomer is a specifically good material as it is recyclable.
Down points of TPE filament
TPE is more difficult to print compared to other filament materials, mainly due to its flexibility.
- ✓ Extremely fatigue resistant
- ✓ Very flexible
- ✓ Good resistances
5 Tips for 3D printing with TPE
Using TPE as a 3D printing material offers a wide range of benefits but there are some issues worth considering before printing with the material. Too much filament can cause a wide range of problems. For example it can result in an increase in pressure on the drive gear, which then causes more filament to feed through. Excessive friction before and after the drive gear can cause problems. So when printing with Thermoplastic Elastomer, it is important to remember that there are some requirements that have to be met in order to obtain a successful outcome.
Too much filament can cause a wide range of problems. For example it can result in an increase in pressure on the drive gear, which then causes more filament to feed through. Excessive friction before and after the drive gear can cause problems. So when printing with Thermoplastic Elastomer, it is important to remember that there are some requirements that have to be met in order to obtain a successful outcome.
-
1. Slow and consistent printing speed
As mentioned, the slower the print speed, the better the result. So, printing at 35 mm/sec or less will deliver better results. It is not required to use a heated build platform. When using a heated build plate, do not set the temperature higher than 60 degrees Celsius because this will negatively influence the adhesion.
-
2. Avoid using rafts and use a negative tolerance
When 3D printing with TPE material, it is important to avoid the use of rafts. Because the base layers of the raft often have an increased extrusion rate and that could lead to potential problems. With regard to 3D prints where the finished product will need to fit on top of another object, a negative tolerance should be used between the parts. This will ensure that the flexible part will have the ability to stretch over the other object in order to fit tightly.
With regard to 3D prints where the finished product will need to fit on top of another object, a negative tolerance should be used between the parts. This will ensure that the flexible part will have the ability to stretch over the other object in order to fit tightly.
-
3. Shorten the distance
If there is a gap between the extruder drive gear and the entry hole of the hot end, then the filament could buckle. If this occurs then the filament will seek another way out. If left unattended, it can cause a so-called bird’s nest or spaghetti, resulting in a jam. To experience the best results the distance between the drive gear and the melt zone of the hot end should not be too long. This ensures that the filament can be fed into the nozzle efficiently. Even more important is that there should also be tight tolerances along the pathway that the filament will travel, in order to prevent kinking and coiling.
When using TPE it is possible to obtain good results by using both Bowden type extruders and direct drive extruders. When switching between materials, it is crucial to purge thoroughly before 3D printing.
When switching between materials, it is crucial to purge thoroughly before 3D printing.
-
4. Placement of the spool
Tweaking the material spool can make a huge difference. Naturally, the extruder will pull the filament into the nozzle, resulting in the filament spool that is mounted on your 3D printer to unwind a small amount of plastic. However, the elasticity of TPE filament will mean that the filament will be stretched out when it is pulled in by the extruder leading to under-extrusion. So, try mounting the spool above the printer so that the filament unwinds downwards which can lead to a reduced level of resistance.
Industries that use TPE material in 3D Printing
TPE filament is flexible. As a result it can be stretched to twice their length when they are at room temperature. Once the material has been stretched, it will return to its original size. For that reason it’s now being used more frequently in the 3D printing process. In fact, it is now a material that is beginning to replace traditional rubbers due to its wide range of benefits and uses. There are many different industries that use Thermoplastic Elastomer because its features offer them a number of advantages.
In fact, it is now a material that is beginning to replace traditional rubbers due to its wide range of benefits and uses. There are many different industries that use Thermoplastic Elastomer because its features offer them a number of advantages.
Food Contact TPE
The filament has been food-contact approved. Therefor it will often be found in baby spoons and toddler cup spouts. This is because it is free from concern-causing chemicals.
Medical and Healthcare
As a result of the high regulations regarding safety in this industry, TPE material is the perfect choice. Due to the fact it can be sterilized by using autoclaves and even gamma radiation. They can also be designed so that they can be biocompatible with high levels of purity and low levels of leachable substances. In some instances, they can be used in place of latex and even silicone.
Industries that use seals
There are many industries that use seals such as the marine and automotive industry. Traditionally, sealing rings have been developed using thermoset rubbers. Now TPE makes it possible to create two-component sealings that are colored and co-moulded . There is an increased level of efficiency when using TPE material, which means that seals can be produced quicker than thermoset rubbers.
Traditionally, sealing rings have been developed using thermoset rubbers. Now TPE makes it possible to create two-component sealings that are colored and co-moulded . There is an increased level of efficiency when using TPE material, which means that seals can be produced quicker than thermoset rubbers.
Wires and Cables
TPE material is used in industries that use wire and cable, fibre optic and electrical applications. TPE offers a wide range of functionalities, it can be customized and it is perfect for engineering and prototyping.
TPE 3D printers
Other 3D filaments
Copyright 2020 Terms of agreement Privacy statement
TPE Filament - Durable, Elastic, Versatile Material (Sept. 2022)
TPE filaments are a great 3D printing material because it is very flexible that’s why it’s sometimes called flexible filament. The 3D printing outputs you produce using TPE material will be flexible while remaining strong and durable.
3D printing is exciting especially when you are starting to use new materials for your prints. Have you tried using flexible filaments for 3D printing? One of these flexible and rubber-like materials is the TPE filament.
The TPE material is among the top varieties of elastic and durable 3D printing material in the market. It is versatile, thanks to its rubber-like properties, so you can use it for a wide range of applications. This material is more available in the market, and softer, too, compared to other flexible filament 3D printer materials.
If all these are new to you, don’t worry. You will learn more about TPE 3D printing filament as you read along. So, let’s get started with the basics.
Contents
- 1 What is TPE Filament?
- 2 Usual Challenges You’ll Encounter with TPE Filament
- 2.1 Buckling of the Material
- 2.2 Getting the Material to Stick
- 2.3 Messy Prints
- 3 Tips for 3D Printing TPE Filaments Successfully
- 3.
 1 Don’t Speed Up the Printing
1 Don’t Speed Up the Printing - 3.2 Try Using a Direct Drive Extruder
- 3.3 Keep the Extruder Temperature Hot Enough
- 3.4 Adjusting the Retraction Settings
- 3.5 Adjusting the Temperature of the Hot Bed
- 3.6 Pros & Cons
- 3.
- 4 Best TPE Filament Brands
- 4.1 1. NinjaFlex TPE Filament
- 4.2 2. Robotjoy Flex 3D TPE Filament
- 4.3 3. eSUN Elastic TPE Flexible Filament
- 5 Conclusion
TPE 3D printer filament is a popular flexible filament. It is made up of ThermoPlastic Elastomer. It is a favorite material when it comes to 3D printing flexible materials. It is a kind of plastic which has similar qualities to that of rubber. Once you start using TPE 3D printing filament for 3D printing, you will notice that your prints are elastic.
Once you start using TPE 3D printing filament for 3D printing, you will notice that your prints are elastic.
With these elastic prints, you can even stretch them up to double their length and they will easily go back to their original form. And this you can do without damaging your prints. Apart from the elasticity, the prints are soft. The shore hardness of prints made from TPE material is 85A.
TPE rubber-based filaments are very helpful for anything that needs impact, or vibration resistance. Its non-slip properties are also great if you want to 3D print non slip rubber pad or anti-slip shower mats.
As you may already know by now, when it comes to working with flexible 3D filaments, it can be challenging. However, this depends greatly on the type of extruder which you are using in 3D printing your design.
Usual Challenges You’ll Encounter with TPE FilamentNo one can deny the fact that TPE filaments along with other flexible filaments like TPU are very useful. But as you would expect from any new technology, there can be a few hiccups. Let’s take a look at some of the challenges you will encounter with this material.
But as you would expect from any new technology, there can be a few hiccups. Let’s take a look at some of the challenges you will encounter with this material.
1. Feeding the TPE Filament to the Extruder
A TPE 3D printer filament is softer than regular 3D printing filaments. You may find it challenging to feed TPE filaments into the extruder because the risk of them getting stuck and deformed is quite high. As a consequence, you may experience jams.
To be able to feed the filament successfully from your drive gear towards the hot end, you will need to have a direct path for the filament. You may not have encountered this issue with other filaments before because they are stiff.
Buckling of the MaterialBecause of the nature of a flexible TPE filament, the nozzle’s pressure may, at times, cause the filament to buckle while it is being pushed through the extruder. The usual cause for this is when you print too fast. Also, it may be possible that the pathway may not be narrow and tight. This may cause jams in the process.
The usual cause for this is when you print too fast. Also, it may be possible that the pathway may not be narrow and tight. This may cause jams in the process.
When 3D printing with TPE filaments, you may discover that it is quite challenging for it to stick to the build plate. To be able to get good adhesion to the heated bed as well as to avoid any shrinkage, try adjusting the temperature of the print bed.
It could be that the cause of unsuccessful adhesion is incorrect leveling or print beds that are not at the right temperature. So, try to adjust the temperature and see if there are any improvements to the adhesion.
Messy PrintsWhen there is a build-up of pressure in your extruder, you can expect that some extra filaments will be oozing out. This will create a print that is stringy or messy. There are several factors that can cause this. It can be retraction settings, speed, or temperature.
It can be retraction settings, speed, or temperature.
Now that you are aware of the challenges of 3D printing with flexible filaments, let us share with you some useful tips on how you can get good prints with TPE filaments.
Don’t Speed Up the PrintingGenerally, it is recommended that you set the speed at 30mm to 40mm per second when printing with TPE and other flexible filaments. This is so that you can get the best timing as well as print quality. If in case you will be using Flexifil, the speed recommended is 10mm to 20mm per second.
You can set your print speed to 5mm per second to make sure that your prints are precise. Yes, it can be very slow but this will ensure you that you have better chances of getting the perfect print that you want to have.
Also, the benefit of slow print speed is that you can avoid creating too much pressure on your extruder. Remember, too much pressure on the extruder will make prints that are stringy and messy.
Remember, too much pressure on the extruder will make prints that are stringy and messy.
It can really be a hassle when your filament jams the extruder. To avoid this from happening, you can lessen the space between the nozzle and the cold end. You can do this by using a direct drive extruder.
Keep in mind though that it is not recommended to use Bowden extruders for printing with TPE materials or other flexible filaments. You may still use it but you will surely find it a bit more challenging.
Keep the Extruder Temperature Hot EnoughWhen your extruder is hot enough, the filament will be able to flow a lot easier through the nozzle. However, there is a downside to this. If the extruder is too hot, there can be a lot of oozing. The prints can turn out uneven or stringy.
To get the best print, you will have to make adjustments to your printer so that you will know which settings are the most appropriate for a flexible TPE filament. At this point, don’t be afraid to try out several settings until you find the right one.
At this point, don’t be afraid to try out several settings until you find the right one.
Retraction may be able to lessen the hot end’s pressure. Also, it will be able to stop the filament from being moved towards the nozzle when your extruder is not printing. Adjustments can be made to your retractions settings.
The adjustments may depend on the issues that you are having. For example, if the extruder clogs, you can lower the retraction. There are others who have successfully printed their designs at zero retraction.
What you can do is to find the least amount of retraction that is necessary so that there are fewer issues with your prints being stringy. If you observe that extra material comes out from the nozzle, you can try increasing the retraction speed or distance.
Adjusting the Temperature of the Hot BedThe temperature settings of your hotbed depend on the material you are using as well as the kind of printer that you have.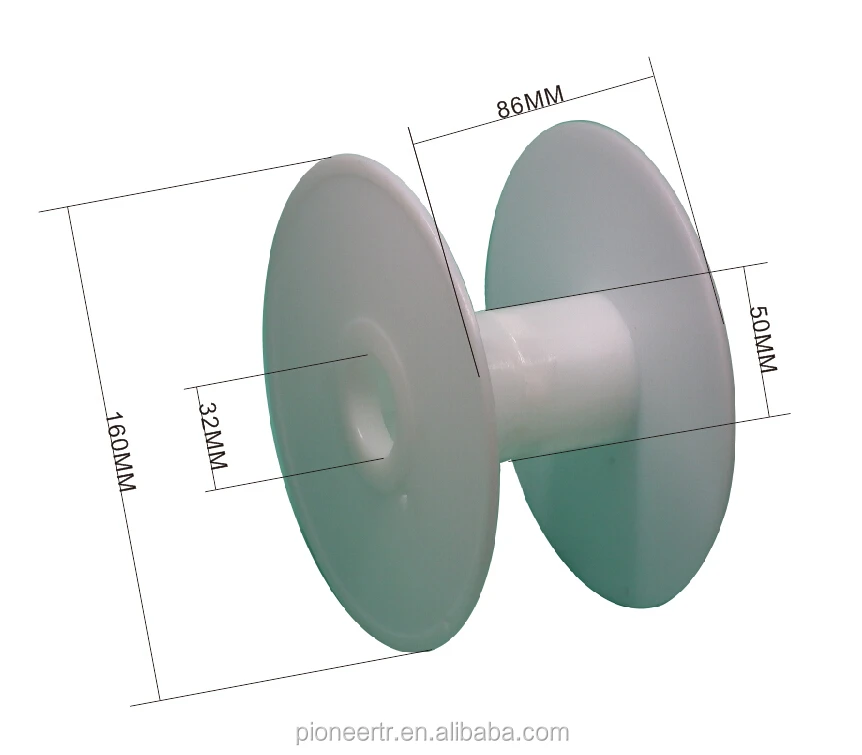 The usual recommendation for the temperature is 40°C to 50°C. But to get even better prints, do check the filament guide of the brand of TPE 3D printer filament you have selected before you start 3D printing.
The usual recommendation for the temperature is 40°C to 50°C. But to get even better prints, do check the filament guide of the brand of TPE 3D printer filament you have selected before you start 3D printing.
Pros & Cons
Pros
- Non-toxic and safe 3D printing material
- Produces durable prints
- TPE rubber base is a good choice for anti-slip objects.
- Great TPE 3D printer filament for phone cases, door stoppers, springs, belts, etc.
Cons
- Difficult to feed into the extruder
- Material may buckle when pushed to the extruder
- May ooze out while printing, creating messy prints
Go to top
Best TPE Filament BrandsIf you’re all excited to try 3D printing with TPE, here are some of the best brands in the market that you can try. They are widely available in many stores online. Let’s take a closer look at their features.
1. NinjaFlex TPE FilamentCheck Price at Amazon
NinjaFlex is among the top TPE 3D printer filament brands that produce flexible filaments like TPE. It is also one of the easiest to use. You will find that you won’t have a lot of issues when it comes to feeding the filament to the printer.
It is also one of the easiest to use. You will find that you won’t have a lot of issues when it comes to feeding the filament to the printer.
You can print many designs with NinjaFlex including watch bands, phone cases, as well as shoes. You can print designs that need to be flexible while remaining strong. This is one of the TPE filament brands that you should definitely try.
Check Price at Amazon
Go to top
2. Robotjoy Flex 3D TPE Filament
Check Price at Amazon
Robotjoy Flex is a product of the USA. If you are looking for a US brand, in particular, this is it. This material is great for printing 3D parts that need to bend while maintaining its durability thanks to its rubber like properties. This TPE 3D printer filament brand is compatible with most 3D printers.
Robotjoy Flex is better compared to the typical filaments such as PLA. This is because it is flexible and excellent for prints that have to be soft while remaining strong. You can bend it and twist it and it won’t have any permanent damage on the print.
You can bend it and twist it and it won’t have any permanent damage on the print.
Check Price at Amazon
Go to top
3. eSUN Elastic TPE Flexible Filament
Check Price at Amazon
eSun has satisfied plenty of customers with the quality of their filaments. The prints you will get from eSun will be elastic and very flexible. Its shore hardness is at 85 while its tensile strength is at 30 MPa.
When 3D printing with eSun TPE filaments, you have to keep in mind that since the filament is soft, you will need to be careful in printing to make sure that the process runs smoothly. It is recommended that you print slowly at 20mm per second.
| Specifications | NinjaFlex | Robotjoy | eSun |
| Star Rating | 4 | 5 | 4.5 |
| Print Temperature | 210°C-225°C | 210°C-240°C | 210°C-230°C |
| Price | $96. 12 12 | $49.99 | $25.99 |
Check Price at Amazon
Conclusion
With the development of new materials, 3D printing becomes more exciting. If it is your first time to use TPE filament, don’t be afraid to make mistakes. As we’ve shared in the challenges of printing with this material, you may need to have several tries before you get the right settings.
📌You will learn more about the characteristics of this material the more you use it. So, start printing your designs and push this material further. Try and see what other designs you can print using a TPE 3D printer filament.
Other Sources:
3d printer filament review, PLA Filament amazon, PLA Vs. ABS, ABS Filament
Blog / Useful / Plastic types for 3D printer
09.04.2021
Content
Every year 3D printing becomes more popular and accessible. Previously, a 3D printer was more like a complex CNC machine, but now manufacturers are meeting users. Simplified and automated settings that many beginners drove into a stupor. Despite this, it can be difficult for a novice user to understand the variety of constantly appearing plastics for a 3D printer.
Previously, a 3D printer was more like a complex CNC machine, but now manufacturers are meeting users. Simplified and automated settings that many beginners drove into a stupor. Despite this, it can be difficult for a novice user to understand the variety of constantly appearing plastics for a 3D printer.
The choice of plastic for a 3D printer is very important, especially when the goal is to print a functional model with certain properties. It will be a shame if the printed gear breaks almost immediately, or the decorative model quickly loses its beauty.
It is important to understand whether the printer will be able to work with the selected plastic. Some materials (most often engineering) require certain conditions for successful printing.
First, decide which model you want to print. What properties should it have? Does the model need to be durable? Or is it a master model for further replication, in which the quality of the surface is important?
90% of 3D printers use 1.
75 diameter filament. 3mm diameter is rare, but it is better to check in advance which size is used in your printer.
PLA
PLA (Polylactide) is the most popular and affordable 3D printer plastic. PLA is made from sugar cane, corn, or other natural raw materials. Therefore, it is considered a non-toxic, biodegradable material.
Extruder temperature - 190-220 degrees. Table heating is not needed, but if the printer's table has a "heater" for better adhesion, you can heat it up to 50-60 degrees. PLA is very easy to work with. The only requirement is to blow the model. There is practically no shrinkage in this material. When printed, it is practically odorless, and if it smells, it smells like burnt caramel.
Pros:
-
Does not shrink. This makes it easy to build prefabricated or huge models without changing dimensions.
-
There are no specific requirements for a 3D printer. Any working 3D printer will do.
 PLA doesn't need a heated table or a closed case.
PLA doesn't need a heated table or a closed case. -
Non-toxic. Due to this, during printing it does not smell or has a barely perceptible aroma of burnt caramel.
-
Diverse color palette.
Cons:
-
PLA is poorly sanded and machined.
-
It begins to deform already with a slight heating (about 50 degrees).
-
Fragility. Compared to other materials, PLA is very brittle and breaks easily.
-
Decomposes under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Of course, it will not fall apart into dust, but it can become more brittle and fade.
PLA is perfect for making dimensional or composite models. For example, decorative interior items, prototyping, electronics cases, etc.
Recently, PLA+ has appeared on the market. It may differ from conventional PLA in improved performance.For example, more durable, with improved layer adhesion.
Dummy turbine
Decorative coasters
ABS
ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is the second most popular plastic for 3D printing due to its properties, availability and low price.
Extruder temperature - 220-240 degrees. The temperature of the table is 80-100 degrees. For printing, a heated table is required at the printer. It is desirable to have a closed chamber, because ABS "does not like" drafts. Due to a sharp temperature drop, it can “unstick” from the table or crack in layers. ABS can smell bad when printing, so it is recommended to use the printer with a closed chamber and filters, or print in a well-ventilated area.
Pros:
-
Good strength characteristics allow the production of functional prototypes from ABS.
-
Simple mechanical and chemical processing.
 ABS is easy to sand and drill, and with an acetone bath you can achieve a perfectly smooth surface.
ABS is easy to sand and drill, and with an acetone bath you can achieve a perfectly smooth surface. -
It is currently the most inexpensive type of plastic for 3D printing.
-
Large selection of colors and shades.
Cons:
-
High shrinkage. Because of this, it can be problematic to manufacture overall products.
-
Printing requires a heated bed and a closed chamber. Without this, the ABS may peel off the table or crack in layers.
-
During the printing process, ABS can smell bad. Therefore, it is recommended that you print in a ventilated area or use the printer with a sealed chamber and filter.
ABS is an engineering plastic. It is suitable for the manufacture of simple functional products.
ABS after chemical treatment in an acetone bath
RU model made of ABS
ABS+ differs from conventional ABS in improved strength characteristics (elasticity, rigidity, hardness), less shrinkage and sometimes resistance to certain oils and solvents (eg gasoline).

HIPS
HIPS (high impact polystyrene) - originally conceived as a soluble support plastic for materials with high printing temperatures. For example for ABS or Nylon.
The extruder temperature is 230-260 degrees. The temperature of the table is 80-100 degrees. It is desirable to have a closed camera for a 3D printer.
Pros:
-
Less shrinkage than ABS.
-
Ease of machining.
-
The matte surface looks very advantageous on decorative products.
-
Food contact allowed (but be sure to check with a specific manufacturer for certificates)
Cons:
-
For printing, you need a printer with a heated table and a closed chamber.
-
More flexible and less durable than ABS. Because of this, it will not be possible to produce functional products.
-
Small palette of colors.

Most often, HIPS is used for its intended purpose for printing on 2x extruder printers as a support for ABS. It dissolves perfectly (though not very quickly) in limonel.
Sometimes HIPS is used as an independent material. Products from it are not very durable, but this plastic is loved for easy post-processing. HIPS can be used for models that will subsequently come into contact with food (not hot).
Using HIPS as a Soluble Support
Decorative vase made of HIPS
PVA
PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) is a material that was developed as a water-soluble support for PLA.
Extruder temperature - 190-210. Table heating is not required. PVA is a slightly "capricious" material, it is not recommended to overheat it and print at high speeds.
PVA is very hygroscopic and dissolves in plain water. Therefore, it is only used as a support for PLA or other plastics with print temperatures close to PVA.
Soluble PVA Support
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Tiger3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Tiger3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Esun |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Esun |
PETG
PETG (polyethylene terephthalate) combines the best properties of PLA and ABS. It is easy to work with, it has a low percentage of shrinkage and excellent sintering of the layers.
Extruder temperature - 220-240 degrees. Table temperature - 80-100 degrees. During the printing process, the model must be well blown.
Pros:
-
Excellent sinterability of layers.

-
PETG is very strong and wear resistant. Good impact resistance.
-
Virtually no smell when printing.
-
Non-toxic.
-
Little shrinkage.
Cons:
PETG is perfect for printing functional models. Due to its low shrinkage, it is often used to make large or composite models. Due to its low toxicity, PETG is often used for products that will come into contact with food.
Cookie cutters and patterned rolling pin
SBS
It is a highly transparent material. At the same time, it is durable and resilient. SBS is a low toxicity plastic. It can be used to print food contact models.
Extruder temperature - 230 -260 degrees. Table temperature - 60-100 degrees. You can print without the closed case on the printer.
Pros:
-
slight shrinkage
-
Transparency.
 After treatment with solvent, limonel or dichloromethane, beautiful transparent products with an almost smooth surface can be obtained.
After treatment with solvent, limonel or dichloromethane, beautiful transparent products with an almost smooth surface can be obtained. -
Easily processed mechanically or chemically.
-
Allowed contact with food.
Cons:
SBS is excellent for translucent vases, children's toys and food containers. Or functional things that require transparency, such as custom turn signals for a motorcycle or car, lamps or bottle prototypes.
Vases are perfectly printed with a thick nozzle (0.7-0.8) in one pass (printing in 1 wall or spiral printing in a slicer).
Models of bottles after chemical treatment
Nylon
Nylon (polyamide) is considered the most durable material available for home 3D printing. In addition to good abrasion resistance and strength, it has a high slip coefficient.
Extruder temperature - 240-260 degrees. The temperature of the table is 80-100 degrees. Nylon is a very capricious and hygroscopic material - it is recommended to dry the coil with plastic before use. For printing, you need a printer with a heated table and a closed chamber, without this it will be difficult to print something larger than a small gear.
The temperature of the table is 80-100 degrees. Nylon is a very capricious and hygroscopic material - it is recommended to dry the coil with plastic before use. For printing, you need a printer with a heated table and a closed chamber, without this it will be difficult to print something larger than a small gear.
Pros:
-
High strength and wear resistance.
-
High slip factor.
-
Heat resistance compared to other 3D printing plastics.
-
High resistance to many solvents.
-
Good for mechanical processing. Perfectly polished and drilled.
Cons:
Nylon is perfect for making wear-resistant parts - gears, functional models, etc. Sometimes nylon is used to print bushings.
Nylon gear
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Tiger3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Tiger3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Esun |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Bestfilament |
Soft plastics
FLEX (TPU, TPE, TPC) is a material similar to silicone or rubber. It is flexible and elastic, but at the same time tear-resistant. For example, TPE is a rubbery plastic, while TPU is more rigid.
It is flexible and elastic, but at the same time tear-resistant. For example, TPE is a rubbery plastic, while TPU is more rigid.
FLEX are printed at a temperature of 200-240 (depending on the material). A heated table is not required. On printers with direct material feed (feed mechanism on the print head), there are usually no problems with printing. On a bowden feeder (the feed mechanism is located on the body), printing with very soft plastics can be difficult. Usually it is necessary to additionally adjust the clamping of the bar. The main nuance is the very low print speeds - 20-40mm.
Pros:
Cons:
Depending on the type of FLEXa, the models can be flexible or rubber-like. This material, depending on its softness, can be used to print gaskets, insoles, belts, tracks or other models that require flexibility or softness.
FLEX belt
Trainers with flexible soles
Wheel for switchgear model
Decorative plastics
Decorative plastics are PLA plastics with various fillers (wood or metal shavings). Or with dyes selected to imitate different materials. Since the base of the plastic is PLA, it is very easy to print.
Or with dyes selected to imitate different materials. Since the base of the plastic is PLA, it is very easy to print.
Extruder temperature - 200-220 degrees (depending on the manufacturer). A heated table is not required.
Pros:
Cons:
-
Some fillers (eg clay) are abrasive. For such plastics, the standard brass nozzle cannot be used. Will have to buy a harder steel nozzle.
-
Some decorative plastics can clog the small nozzle (0.4 or less). For them, you need to use a “thicker” nozzle.
Depending on the filler, different material properties are obtained. Plastics that use only dye do not require additional processing. Materials with "fillers" may sometimes require additional post-processing.
Plastics with metal fillers after printing must be processed with a metal brush. Then the Metal content will show through and the model will resemble a metal casting.
Plastics with metallic powder
These plastics are often used for printing key chains, decorative models and interior details.
If the plastic has a high content of wood dust, then it is recommended to use a larger nozzle diameter (0.5 or more), a smaller nozzle can quickly become clogged during printing.
Wood-filled plastic ground
Plastic key rings with copper dust
Engineering plastics
These are nylon-based plastics with fillers that improve strength, heat-resistant and other characteristics, help to achieve less shrinkage of the material. For example - carbon fiber, carbon fiber or fiberglass.
Extruder temperature - 240-300 degrees (depending on the manufacturer). Table temperature - 90-110 degrees. Since plastics are based on nylon, the requirements for printing are similar. This is a heated table and a closed printer case.
Pros:
-
Hardness and strength.
-
Low flammability or non-combustibility.
-
High precision due to low shrinkage.
Cons:
3D printers use brass nozzles, some plastics can quickly “waste” it during printing. For such materials it is recommended to use steel nozzles.
These are highly specialized plastics used for a specific task, depending on the filler. For example, functional parts that do not lose their shape when heated, are resistant to many solvents, etc.
Functional Carbon Fiber Composite Prototype
Composite frame
Polycarbonate ashtray
Totals
This is of course not the whole list of materials for 3D printing. There are many highly specialized engineering and decorative plastics for specific tasks.
Manufacturers are constantly trying to replenish the range of materials for 3D printing. Already familiar materials are improved for more comfortable printing. There are many interesting decorative plastics imitating different materials - ceramics, clay, wood, metals.
And of course, the assortment of engineering plastics is constantly updated. Now there are many interesting materials for highly specialized tasks - for example, burnable plastic with a low ash content for subsequent casting in metal.
Burnout plastic
Before buying a coil, read the information on the website of the manufacturer or seller. There you can find some nuances of printing for a particular plastic. The manufacturer indicates the recommended temperature range on the box. Sometimes, for quality printing, it is recommended to print several tests to adjust the temperature settings, retract, etc.
Try to store the started coil in silica gel bags. It is recommended to additionally dry high-temperature plastics before printing to remove excess moisture.
It is recommended to additionally dry high-temperature plastics before printing to remove excess moisture.
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Tiger3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Esun |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Esun |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | FlashForge |
#Useful
Expert in additive technologies and 3D printing with over 5 years of experience.
Share
all materials
Do you have any questions?
Our specialists will help you with the choice of 3D equipment or accessories, consult on any questions.
Ultrafuse 316L Metallic Filament for FDM (FFF) 3D Printing - SMARTPRINT
Composite Metallic Filament with Stainless Steel for FDM (FFF) 3D Printers
Ultrafuse® 316L is an innovative filament for the production of 3 parts from stainless steel grade 61.
[button target="_blank" hover_type="default" text="Buy Ultrafuse® 316L 1.75mm" margin="15px 0px 0px 0px" link="https://3dsmart.com.ua/shop/materials/basf- ultrafuse-316l-175″][button target="_blank" hover_type="default" text="Buy Ultrafuse® 316L 2.85mm" margin="15px 0px 0px 0px" link="https://3dsmart.com.ua /shop/materials/basf-ultrafuse-316l-285″]
Material Details
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-download' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation= » icon_animation_delay=» link=» target='_self'] Product Brochure
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-download' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color =" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Data Sheet
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-download' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link= » target='_self'] User Manual
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-download' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin= » icon_animation=» icon_animation_delay=» link=» target='_self'] Debinding Simulation Guide
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-download' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Processing Guide
Description
It is designed for maximum ease of use on conventional FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) 3D printers. The BASF Ultrafuse® 316L combines greater design freedom with a lower total cost of ownership—printing metal parts is easier, faster and more affordable. Parts printed with Ultrafuse® 316L develop their final properties, including hardness and strength, through a catalytic debinding and sintering process. The catalytic debinding technology was developed and implemented by BASF and has become the industry standard.
The BASF Ultrafuse® 316L combines greater design freedom with a lower total cost of ownership—printing metal parts is easier, faster and more affordable. Parts printed with Ultrafuse® 316L develop their final properties, including hardness and strength, through a catalytic debinding and sintering process. The catalytic debinding technology was developed and implemented by BASF and has become the industry standard.
Benefits at a Glance
=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Easy and Affordable Metal 3D Printing
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Fast material change and easy handling
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] For all open source FFF printers
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color =" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Produces 316L stainless steel parts.
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Uniform particle distribution improves mechanical properties
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] The high flexibility of the filament allows it to print successfully on any FFF printer.
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Compatible with both Bowden and direct drive extruders
Use Cases
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Snap
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link= » target='_self'] Fixtures & Fixtures
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin =" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Function Prototypes
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color =" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Limited edition
Process Brief
Easy and cost-effective 3D printing of metal parts with Ultrafuse® 316L
We developed Ultrafuse® 316L to produce high quality metal parts and high productivity. This state of the art metallic filament is suitable for use with any conventional Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) printer. Once printed, the final properties of the part are achieved through a debinding and sintering process developed by BASF that has become the industry standard.
This state of the art metallic filament is suitable for use with any conventional Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) printer. Once printed, the final properties of the part are achieved through a debinding and sintering process developed by BASF that has become the industry standard.
Ultrafuse® 316L is economical, easy to process and meets MIM industry standards for catalytic debinding and sintering. This innovative industrial metal-polymer composite supports a wide range of applications, including tools, fixtures and fixtures, small-scale production, functional parts, prototypes, and even jewelry.
Ultrafuse® 316L contains thermoplastic binders with 90 weight percent fine metal particles. Our filament has a non-slip surface that allows it to be used in most Bowden or direct drive extruders. Due to its high flexibility, it can be fed through sophisticated idlers and multiple filament transport systems in printers – no additional drying required. Metal-polymer composite as a filament does not have any of the production hazards and safety risks associated with handling fine metal powders, making 3D printing of stainless steel parts affordable, simple and safe.