Toughest 3d printing material
Strongest 3D Printing Materials: Impact Resistant Filaments
If you need to 3D print a part or object that has to withstand high impact or repetitive use, you’ll have to turn to some of the strongest 3D printing materials.
What makes a 3D printing filament strong? In this article, strength refers to materials that are able to withstand high impact and repeated use, and are durable. Some filaments have higher impact resistance, some better fatigue resistance or durability, and some have a combination of all three factors.
In this article, we’re reviewing 7 of the strongest 3D printing materials and how to choose between them for your next print.
7 Strongest 3D Printing MaterialsThe strongest 3D printing filaments are:
- ABS
- TPU
- PET-G
- PA
- PAHT CF15
- PP
- PP GF30.
The strength of these filaments vary, as some are more impact resistant, while others are structurally strong or even fatigue resistant. Let’s dive into the unique characteristics of each filament.
1. ABSABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is a stiff and impact-resistant thermoplastic material. It is a popular material that is mostly used for engineering purposes and technical prints. Compared to many other fiber filaments ABS is quite cost-effective, making it a great choice if you’re on a budget yet still need high strength. Along with being durable against impact and fatigue, ABS is also heat resistant and water-resistant.
- When To Choose ABS:
ABS is the perfect 3D printing material to use if your print will be used for a moving part, high mechanical stress, or for high-stress functionality. ABS is also a good option if your print will be an end-use product, as it has an attractive surface finish.
TPU (Thermoplastic polyurethane) is most well known for its flexibility, which is what makes this 3D printing material so strong. Along with being flexible, TPU is also highly durable, with strong resistance to impact, wear and tear, chemicals, and abrasion. TPU is an ideal 3D printing material to use for shock absorption.
- When to Choose TPU:
With the ability to extend up to 4.5 times its original size without breaking, TPU is your go-to choice for any prints that require high levels of flexibility and strength. TPU is commonly used to print parts like wheels, springs, shock absorbers, and other flexible objects.
3. PET-G3D printing beginners should turn to PET-G (Polyethylene terephthalate glycol-modified) when looking for a 3D printing material that is both strong and easy to print. PET-G is easier to print than ABS, yet stronger and more technical than PLA. PET-G is impact-resistant, abrasion-resistant, and also features some flexibility.
PET-G is impact-resistant, abrasion-resistant, and also features some flexibility.
- When to Choose PET-G:
Featuring a shiny finish and good levels of strength, PET-G is a great option for end-use parts. It is commonly used to print functional prototypes, mild-stress parts, and protective cases.
4. PAOne of the strongest 3D printing materials in terms of durability and heat resistance is PA (Polyamide). This semicrystalline plastic is used for prints that will undergo heavy-duty applications. PA has high strength, excellent impact resistance, and is fatigue-resistant, making it ideal for moving parts.
- When To Choose PA:
PA is commonly used to create washers, gears, jigs, sliding parts, and objects that undergo high fatigue. As one of the strongest 3D printing materials, it is resistant to abrasion, impact, and heat. When compared to ABS, PA has better impact strength and flexibility.
Another commonly used 3D printing material in the automotive industry is PAHT CF15 (High-Temperature Polyamide carbon fiber reinforced.) This filament packs a punch and it is the strongest 3D printing material on our list. PAHT CF15 is characterized by high levels of strength, heat resistance, stiffness, and impact resistance.
- When to Choose PAHT CF15:
Although it can be tempting to want to instantly use the strongest material you can find, this isn’t always the right choice. This strong 3D printing filament is best suited for the most demanding objects or parts. Reach for it when you need a material that needs to replace metal, or parts that will undergo extreme temperatures and high-stress environments.
6. PPPP (Polypropylene) is a lightweight and flexible material, but don’t let that fool you. In fact, PP is a very durable 3D printing material with great impact and fatigue resistance. PP is most well known for its heavy-duty resistance to most chemicals, including alkali, acids, and organic solvents.
In fact, PP is a very durable 3D printing material with great impact and fatigue resistance. PP is most well known for its heavy-duty resistance to most chemicals, including alkali, acids, and organic solvents.
- When to Choose PP:
While its lightweight nature may not make it as strong as other filaments on this list, its durability and resistance to impact while also maintaining an airy quality still make it a good option for parts that will undergo repetitive applications, such as packaging, pipes, and joints.
7. PP GF30PP GF30 (polypropylene 30% glass fiber) is like PP, but with a little extra boost. The glass fiber in PP GF30 allows this 3D printing material to have high levels of strength and rigidity while maintaining its lightness and high chemical resistance. This is one of the strongest 3D printing materials, and it is frequently used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
- When to Choose PP GF30:
Along with being lightweight, durable, and stiff, one of PP GF30’s most impressive qualities is its high resistance to hostile environments, including chemicals and weather conditions. If your 3D print will be placed outside or need to withstand harsh temperatures while maintaining structural strength, then PP GF30 will be a great choice.
The strongest 3D printer filament comes in all shapes, sizes, and definitions of strength. Whether you’re looking for durability, impact resistance, or fatigue resistance, this list is sure to lead you in the right direction.
What is the Strongest 3D Printer Filament? (2022) – Clever Creations
PEEK is the strongest 3D printer filament with an ultimate tensile strength of more than 7250 PSI. However, because PEEK requires high printing temperatures, Polycarbonate filament is an often preferred alternative that also offers high strength to your 3D prints.
The strength of your 3D printed part greatly depends on your filament material. In critical load-bearing applications, you must choose a strong 3D printer filament that is able to resist deformation. Knowing the strength of popular filaments will help you make better decisions in your designs and select the best material for your parts.
In this article, we’ll look at six different filaments and compare their strength and mechanical properties to determine which is the strongest 3D printer filament. We’ll also provide some tips on how you can use these filaments to create strong, long-lasting 3D printed parts.
What types of strength are there?
Tensile Strength
The tensile strength indicates the material’s ability to withstand deformation when stretched. It is used to test the strength of any material, and in our case, the strength of the 3D printed model. Tensile strength gives you an idea about how far you can load an object before it fails.
For example, the tensile characteristics of a carabiner will let you know if it’s safe to use for mountaineering. The strongest 3D printing filament should have a high tensile strength so that your models don’t fail or break easily.
PEEK, Polycarbonate, and Carbon fiber-infused filaments have some of the highest tensile strengths and are strong filaments apt for load-bearing applications.
Impact resistance
Impact strength is the measure of a material’s ability to withstand an impact without breaking or fracturing. The higher the impact strength of a filament, the less likely it is to break or fracture when subjected to sudden stress.
Polycarbonate, Nylon, and PEEK are all examples of 3D printing filament with excellent impact resistance. These materials can bear high sudden loads before they fracture and fail. These materials are typically used for tool housings, safety boxes, eyeglasses, and safety equipment.
Other considerations
Chemical resistance
Chemical resistance matters when your application involves chemical liquids and a harsh environment. Nylon and Polycarbonate have excellent chemical resistance. They’re useful for 3D printing objects that will come into contact with harsh chemicals. ABS is also resistant to some chemicals, but not as much as nylon and polycarbonate.
Nylon and Polycarbonate have excellent chemical resistance. They’re useful for 3D printing objects that will come into contact with harsh chemicals. ABS is also resistant to some chemicals, but not as much as nylon and polycarbonate.
UV resistance
Outdoor applications demand a 3D printer filament with high UV resistance. The UV exposure from sunlight weakens the material’s bonds and can cause your parts to fail. 3D printing filaments like ABS, ASA, and Nylon are most resistant to UV light. These are the ones you want to use for outdoor functional applications.
Temperature resistance
High-temperature applications will need 3D printing filament that does not soften at those temperatures. The strongest filament for these applications needs to have high heat resistance, as it must be able to perform under extreme conditions without any failure.
Nylon, PEEK, and Polycarbonate filaments have more heat resistance than other filaments, but keep in mind that they do need to be 3D printed at higher temperatures than others. This means you need to make sure that your 3D printer hot end can handle these temperatures.
This means you need to make sure that your 3D printer hot end can handle these temperatures.
What is the strongest 3D printer filament?
PolycarbonatePolycarbonate (PC) is known for its high-impact resistance, excellent toughness, and temperature resistance. It is one of the strongest filaments with transparent and lightweight qualities. A 2020 study concluded that polycarbonate filament has an Ultimate tensile strength of over 5200 PSI, making it one of the strongest 3D printer filaments on the market today.
Polycarbonate filament has good chemical and UV resistance too. Moreover, it can withstand high temperatures of up to 140 °C before softening. It is even used as an additive to enhance ABS filament’s properties to a great extent. Combined, these characteristics let you print protective equipment, medical instruments, and functional prototypes.
Yet, PC filament is tough to print, warps easily, and can absorb moisture from the air. To deal with this, an enclosed 3D printer and proper filament storage are recommended.
To deal with this, an enclosed 3D printer and proper filament storage are recommended.
Deal with these challenges successfully and you can enjoy Polycarbonate as the strongest 3D printer filament for durability and high-temperature applications.
NylonImage: AMFG
Nylon filament belongs to a class of Polyamide plastics. They’re known for their excellent mechanical strength and low coefficient of friction. Nylon is a common material in SLS 3D printing, but there are also plenty of FDM Nylon 3D printers that you can use to successfully 3D print with this material.
BCN3D’s testing of Nylon filament showed an impact strength of approximately 75 kJ/m2. This is higher than PLA, ABS, and PETG, making Nylon filament one of the best 3D printer filaments for high-impact applications. The low coefficient of friction and its high impact-resistant nature make Nylon a perfect material for gears, machine parts, hinges, and jigs and fixtures.
The downside of Nylon filaments are their hygroscopic nature and a tendency to warp easily, similar to Polycarbonate filament. You need a finely controlled printing environment to ensure that you can print Nylon without problems.
You need a finely controlled printing environment to ensure that you can print Nylon without problems.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) filament was one of the earliest 3D printing thermoplastics. It is still a relatively widely used material due to its versatility and low price, but both PETG and ASA filament are starting to be favored more and more over ABS because of their superior properties.
A 2019 study shows that ABS has an ultimate tensile strength of more than 4500 PSI. This gives ABS a lower tensile strength than polycarbonate filament, but its relative ease of printing and accessibility can still make it a better choice.
You can use ABS for functional prototypes, boxes, and automotive components. Its high melting temperature allows for better heat resistance than other 3D printing filaments. This is important for applications where the product needs to withstand higher temperatures, such as in a car that’s exposed to direct sunlight.
You can post-process your ABS 3D printed parts using Acetone. It’ll give your parts a smooth surface finish with a glossy look. This makes ABS filament suitable for printing aesthetic models and figures.
But, like other high-temperature thermoplastics, ABS filament tends to warp easily. Although you can print it on most budget 3D printers, it helps if you 3D print ABS filament inside of a 3D printer enclosure. This helps with containing 3D printing fumes as well, a common problem with ABS filament.
TPUImage: Creative Tools via Flickr, CC BY 2.0
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) filament is a flexible filament with excellent toughness and impact resistance. Its flexibility depends on the blends of materials. It can be varied by the manufacturer to offer high rigidity or high elasticity.
Devin from Make Anything tested various brands of TPU filament. He concludes that many TPU filaments can withstand high loads before they break. It is resistant to wear and tear due to abrasion and exhibits strong chemical resistance. It is suitable for printing protective gears, phone cases, prosthetics, and even footwear.
It is suitable for printing protective gears, phone cases, prosthetics, and even footwear.
TPU prints at lower temperatures and doesn’t need high-end 3D printers. But the flexible nature of TPU makes it difficult to 3D print with Bowden extruders. You need to print it at slow speeds to ensure that you do not jam the hot end. Another important thing to pay attention to is that setting a higher infill value with TPU parts will lead to stiffer 3D printed parts, and vice versa.
Recommended:
The Best Flexible Filaments for 3D Printing
PEEK
Image: 3DGence
PolyetherEtherKetone (PEEK) is the strongest 3D printer filament with a tensile strength of about 7250 PSI. PEEK is a strong filament with about 50% more strength than Polycarbonate. It makes PEEK a high-performance thermoplastic suitable for some very particular high-end applications.
PEEK also has an excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Its Young’s modulus is like that of a human bone, making it apt for medical applications. Its lightweight nature and high-temperature resistance are useful in aerospace industries. PEEK is used to print structural components and heat shields in these fields.
Its lightweight nature and high-temperature resistance are useful in aerospace industries. PEEK is used to print structural components and heat shields in these fields.
PEEK filament is a high-temperature thermoplastic and needs a specific printing setup to print well. It is also expensive compared to other thermoplastics and not easily accessible.
Usually, PEEK is reserved for industrial applications. However, with the right 3D printer and proper setup, you can achieve great results with PEEK at home.
Composite Materials
Carbon FiberCarbon fiber is used to add strength to various 3D printer filaments, like PLA, Polycarbonate, PETG, and Nylon. The resulting material consists of filament with short fibers of carbon ingrained. This increases hardness and abrasion resistance. Compared to parts printed with regular filament, carbon fiber filament parts can be made more lightweight and with increased stiffness.
Carbon fiber-infused Nylon filaments have high hardness. But the tensile strength remains like a regular Nylon filament. The increased hardness makes it suitable for machine parts and structural components. Typical applications would include 3D printed drone frames, tools, and support structures.
But the tensile strength remains like a regular Nylon filament. The increased hardness makes it suitable for machine parts and structural components. Typical applications would include 3D printed drone frames, tools, and support structures.
Because Carbon fiber has a high hardness and you will need stainless steel or a ruby-tipped nozzle. Regular bronze 3D printer nozzles will wear out in no time.
It is also recommended to print carbon fiber-infused filament at low speeds. This reduces the chances of clogs and offers a more consistent print quality.
PRILINE Carbon Fiber Polycarbonate 1KG 1.75 3D Printer Filament,...
1,166 Reviews
Check Price Polycarbonate BlendsImage: Javelin Tech
As stated earlier, Polycarbonate has excellent toughness and is resistant to impact loads. It is not easy to 3D print, however. This is why many users cannot take advantage of the material’s properties. To overcome this, filament manufacturers introduced Polycarbonate composite filaments blended with ABS materials.
In the Polycarbonate study mentioned above, researchers also tested a PC-ABS blend filament. They found that it has a significantly higher tensile strength of upwards of 6000 PSI, compared to ABS’s 4500 PSI. This means that the parts produced using PC-ABS filament can deform more before failure, giving PC-ABS filament an edge over regular ABS filament.
Polycarbonate also increases the part’s chemical and high-temperature resistance. This blend is an excellent alternative if you need high-strength parts that are easy to print.
Polymaker PC-ABS Filament 1.75mm White Polycarbonate Filament 1.75mm...
372 Reviews
Check PriceWhat is the strongest 3D printer resin?
3D printer resin is inherently brittle and breaks easily under the slightest loads. A lot of resins are catered toward 3D printing miniatures and other small, high-detailed models that do not require a lot of strength. Some resins, like tough and engineering resins, are specifically formulated for high-strength applications.
In his video experiments, Stefan from CNC Kitchen conducted tests on various resin materials. He found that Siraya Tech Blu tough resin exhibited increased toughness properties. The strength of the printed parts was like ABS and PETG 3D prints with excellent layer adhesion.
Regardless of which strong 3D printing resin you choose, you will need the best resin 3D printers to get the highest-quality 3D printed parts.
Siraya Tech Blu 3D Printer Resin Tough Clear Resin 3d Printing with...
956 Reviews
Check PriceFrequently Asked Questions
What is the most durable 3D printing material?
The most durable 3D printing filament is polycarbonate. It has a high degree of toughness and resistance to wear, making it perfect for use in a wide range of applications. It also has a high resistance to impact, and is resistant to UV rays, making it ideal for use in 3D printing applications that require durability and toughness.
What filament is stronger than PLA?
There are a few different filaments that are stronger than PLA. One of the most popular is PETG, which is a strong and durable plastic that is ideal for prototyping. Polycarbonate and PEEK are also both very strong materials that are often used for industrial applications.
One of the most popular is PETG, which is a strong and durable plastic that is ideal for prototyping. Polycarbonate and PEEK are also both very strong materials that are often used for industrial applications.
Which is stronger, PETG or ABS?
Comparing PETG vs ABS, if we’re talking about overall filament strength, then PETG is the stronger 3D printer filament. It has a higher ultimate tensile strength and lower Young’s Modulus (which measures rigidity), meaning that it can resist external forces better. So if you need a material that can withstand a lot of wear and tear or impact, PETG is the better choice.
Is ABS or PLA stronger?
PLA is a stronger 3D printer filament than ABS. However, the lower melting temperature of PLA makes it unsuitable for some applications. PLA is also more brittle than ABS. Depending on your application, one or the other may be better suited.
For example, if you need a strong, rigid material that can withstand high temperatures, PLA wouldn’t be a good choice. On the other hand, if you need a material that’s easy to work with and doesn’t require high temperatures to melt, PLA would be a better option.
On the other hand, if you need a material that’s easy to work with and doesn’t require high temperatures to melt, PLA would be a better option.
Recommended:
PLA vs ABS: Which Filament is Better?
Is PLA or resin stronger?
Parts that are printed with popular 3D printer filaments, like PLA, ABS, PETG, and Nylon are nearly always stronger than those printed with resin. Not only do they have higher tensile filament strength, but they also are more resistant to impact.
Resin 3D prints are notoriously brittle, and unless you are 3D printing with specially formulated strong resin, you will find that your FDM printed parts have higher strength.
Recommended:
Resin vs Filament 3D Printers: What’s the Difference?
Conclusion
The studies mentioned above and test results prove that PEEK is the strongest 3D printer filament. It has an excellent strength-to-weight ratio and is suitable for high-performance applications. It is expensive and not easily accessible, limiting it for special industrial applications.
Polycarbonate, Nylon, and composite filaments like Carbon fiber-infused filament are the other alternatives. They show a high level of strength for many applications. These strong filaments have excellent stiffness and toughness while printing with relative ease. They’re more suited toward prosumer applications and are available in various mixes.
Which one do you think would give you the best strength for your applications? Let us know your experience with these filaments. If you have anything else to add, feel free to comment below.
What is the most durable material for 3D printing?
3DPrintStory 3D printing process What is the most durable material for 3D printing?
While the 3D printing process seems like a great alternative to traditional manufacturing methods, the parts produced can be fragile and unusable. As a rule, this is the result of using standard materials that are not designed for strength and durability. But there is a solution: use durable materials! Durable 3D printing materials can greatly enhance your options, as you can print parts and assemblies for small projects without fear of breakage.
As a rule, this is the result of using standard materials that are not designed for strength and durability. But there is a solution: use durable materials! Durable 3D printing materials can greatly enhance your options, as you can print parts and assemblies for small projects without fear of breakage.
In this article, we'll take a look at the three most durable types of 3D printing materials. However, before that, we will take a closer look at what strength means in terms of filament materials.
What is strength and how do we evaluate it?
The strength of a material can be measured and evaluated in different ways. In this article, we will mainly use tensile strength (stress before something breaks). We will list the tensile strength of each 3D printing material in pounds or pounds per square inch (PSI).
Despite the obvious number of pounds the material can support, there is still a margin of error depending on how the part was printed. We've compiled research from a variety of sources to make sure these three materials are the strongest.
You must also understand that the material itself is not the only factor that affects the strength of the finished product. The design itself, post-processing and the 3D printing process also affect the strength of the part.
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate (PC) is considered by many manufacturers and reviewers to be the strongest 3D printing filament available. In particular, it is possible to achieve high strength of polycarbonate products by 3D printing with an all-metal hot end and a 3D printer in a case that is isolated from the influence of the external environment.
Some Numbers
Airwolf 3D has come to the conclusion after many filament tests that polycarbonate is the best choice of durable filaments for desktop 3D printers. They were able to hang up to 685 pounds on a polycarbonate printed hook and found that this material had a tensile strength of 9800 psi. In contrast, the same part printed in PLA could only support 285 pounds.
Using a similar test, MatterHackers studied the tear strength of this type of thread, as well as a number of other materials. They were able to hang an average of 409 pounds on the polycarbonate hook, while the PLA parts had a significantly lighter average weight of just 154 pounds.
Finally, renowned 3D printing YouTuber Thomas Sunladerer reviewed several polycarbonate materials and gave very positive feedback on the strength of the material.
3D printing with polycarbonate
It is worth noting that the quality of 3D printing with polycarbonate is not very good. Compared to other materials, protrusions and small details may not turn out as well as using the same PLA.
According to Rigid.Ink, polycarbonate is mostly sold in clear. This 3D printing material has excellent heat resistance as well as impact resistance. But note that you will have to print at high temperatures. As mentioned above, it is better to use an enclosed 3D printer and a solid metal hotend.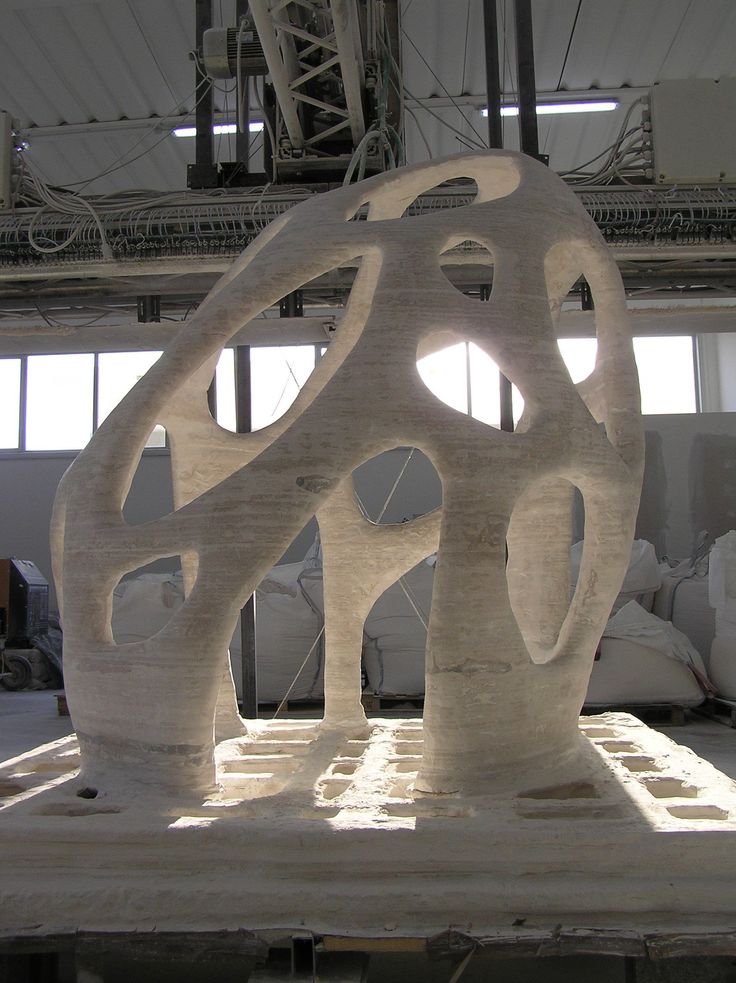
Pros of polycarbonate : extra strong, excellent thermal and impact resistance.
Cons of polycarbonate : does not cope well with protrusions and small details of a 3D model, requires a body and an all-metal hot end, a limited number of colors.
Nylon
Next on our list of durable 3D printing materials is nylon. This material is considered by many to be the most reliable for desktop 3D printers. Nylon is inferior in strength to polycarbonate, but still clearly stronger than other competitors such as PLA and ABS.
Some numbers
A hook printed with nylon (910) thread had a breaking strength of 7,000 psi, while the same ABS hook only had a strength of 4,700 psi, according to Airwolf 3D. Airwolf 3D also noted that the nylon filament-printed clip holds 485 pounds.
MatterHackers posted similar results and noticed that a hook printed with their NylonX material can hold an average of 364 pounds before it breaks.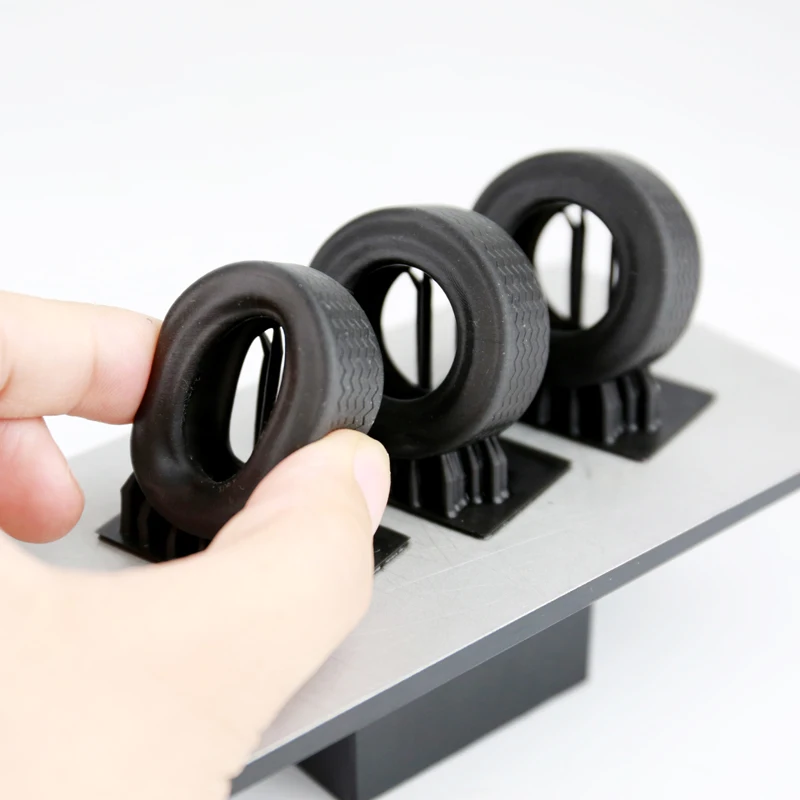 Rigid.Ink also reviewed some nylon threads and gave them a four out of five rating for strength and a five for durability. For comparison: the strength and durability of PLA is three conventional units.
Rigid.Ink also reviewed some nylon threads and gave them a four out of five rating for strength and a five for durability. For comparison: the strength and durability of PLA is three conventional units.
Nylon 3D printing
Nylon is slightly easier to print than polycarbonate, but it's still not PLA. Nylon filament is quite hygroscopic, so it must be kept dry and requires a high printing temperature of 220-270°C. This material is prone to slight warpage, but is also resistant to impact, fatigue, and high temperature.
Nylon pros: impact resistance, fatigue resistance, heat resistance, easier to print than polycarbonate.
Nylon 9 cons0042 : hygroscopic, warping, very high hot end temperature required.
Composites
Finally, composite threads, although not essentially a single material, can be extremely strong. Composites are threads with certain additives that affect the properties of the material, including to increase strength. The names of these threads usually have the words "pro", "reinforced" (reinforced) or "infused" (infused), since they are usually a mixture of different materials.
The names of these threads usually have the words "pro", "reinforced" (reinforced) or "infused" (infused), since they are usually a mixture of different materials.
For this reason, it is impossible to assess where the composite fibers are compared to the two previous materials. Some composites, such as Carbonyte, can compete with nylon threads for strength, while some composites are less durable.
It all depends on what the composite thread consists of. Durable is usually a high strength material such as nylon impregnated with another high strength material such as carbon fiber or glass.
Speaking of carbon fiber, this is also a very strong filament that is sometimes used for 3D printed bicycles. However, some composite fibers are stronger than many pure carbon fibers, so they are not in the top three, but deserve special mention as composite fibers.
Some numbers
We will use carbon fiber nylon and glass fiber nylon threads as examples. MatterHackers has determined that hooks printed on these materials can hold an average of 349and 268 pounds respectively.
Rigid.Ink gave the fiberglass nylon filament four out of five ratings for strength and five for durability. They also gave the carbon fiber nylon a five out of five rating for both strength and durability. In comparison, PLA and ABS were in the top three for strength.
3D printing with composites
Composites vary in the way they are 3D printed, but they are generally relatively similar to their base material. Durable composite fibers are usually made from nylon, so you'll have to print at fairly high temperatures. These threads are also quite expensive.
Advantages of composites : This is a combination of several materials to achieve the best possible properties, durable.
Cons of composites: Expensive, requires high 3D printing temperatures.
3D printing material comparison
3D printing material comparison
3dunitprint2022-02-07T14:43:04+03:00
3dunitprint Knowledge base 0 comments
ABS - PLASTIC
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is one of the most popular plastics. It is an easily accessible, durable and lightweight material. ABS plastic comes in a wide range of colors. Its strength and ease of processing have led it to become the most popular of the engineering polymers.
It is an easily accessible, durable and lightweight material. ABS plastic comes in a wide range of colors. Its strength and ease of processing have led it to become the most popular of the engineering polymers.
Manufacturing techniques: FDM
- Rugged
- Flexible
- Easy to process
- Resistant to everyday chemicals
- Temperature resistant
- High print shrinkage
- "Plastic" smell when printed
- Not suitable for food contact
Strength
90%
Cost
20%
Moisture resistance
70%
Stability to ultraviolet
9000%Chemical resistance
40%
PLA - PLASTIC
The raw material for the production of PLA plastic is corn starch (but you can also find varieties of sugar cane and tapioca), which makes it biodegradable. This is a simple material for 3D printing, when heated, it releases a pleasant sweet aroma. For this reason, many people prefer its ABS.
For this reason, many people prefer its ABS.
Manufacturing techniques: FDM
- Eco-friendly, biodegradable
- Food contact
- Hard, durable
- Low shrinkage
- High surface quality
- Low softening point 50°C
- Narrow temperature range (-20 to +40°C)
- Short-lived
- Fragile
Durability
75%
Cost
20%
Moisture resistance
20%
UV resistance
25%
Chemical resistance
45%
PETG, PET, PETT - PLASTIC water. This material is the second alternative to ABS, it does not emit caustic fumes when melted, while remaining strong and flexible.
Manufacturing techniques: FDM
- Odorless printing
- UV resistance
- Wide operating temperature range.
- Good slip and impact resistance
- Non-toxic, can be printed on articles intended to come into contact with food.

- Lower strength and softening point than ABS.
- High printing temperature quickly destroys the PTFE insert in the hot end
- Scratches more than ABS.
- Absorbs moisture from the air
Strength
90%
Cost
30%
Moisture resistance
75%
Ultraviolet
9000%Chemical resistance
9000,000 (polycarbonate) is a high strength material designed for harsh environments and engineering applications. It has extremely high thermal deflection and impact resistance. Polycarbonate also has a high glass transition temperature of -150° Celsius. This means that it will maintain its structural integrity up to this temperature, parts made with this material show significantly improved mechanical strength compared to ABS and PLA.Manufacturing techniques: FDM
- Impact resistance
- High temperature resistant
- Naturally transparent
- Flexibility
- Durability
- Tendency to warp
- Very high print temperature required
- High tendency to shrink during printing
- Absorbs moisture from the air, which can cause print defects
Strength
90%
Cost
45%
Moisture resistance
55%
Ultraviolet
9000%Chemical resistance
%HIPS - Plastic
HIPS (BDYARIROLRIL) is a dissolvable support material commonly used with ABS. When used as a support material, it can be dissolved in d-Limonene leaving the print free of any defects caused by the removal of supports. HIPS has many of the same printing properties as ABS, making it a logical partner for dual extrusion. This material is more stable and slightly lighter than ABS, making it an excellent choice for parts that wear quickly or are used to print lighter products.
When used as a support material, it can be dissolved in d-Limonene leaving the print free of any defects caused by the removal of supports. HIPS has many of the same printing properties as ABS, making it a logical partner for dual extrusion. This material is more stable and slightly lighter than ABS, making it an excellent choice for parts that wear quickly or are used to print lighter products.
Manufacturing techniques: FDM
- Low cost
- Impact resistant
- Waterproof
- Light
- Soluble with d-limonene
- Heated deck required
- Closed chamber recommended
- High Print Temperature
- Ventilation required
Strength
80%
Cost
10%
Moisture resistance
80%
Ultraviolet 60005
70%
Chemical resistance
25%
FLEXIBLE - plastic
FLEXIBLE (FLOOK FIRS) (TPE), which are a mixture of hard plastic and rubber. This material is elastic in nature, which allows it to stretch and flex easily. There are several types of TPE, with thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) being the most commonly used among 3D printing filaments. The degree of elasticity of the plastic depends on the type of TPE and the chemical composition used by the manufacturer. For example, some threads may be partially flexible, like a car tire, while others may be elastic and fully flexible, like a rubber band.
This material is elastic in nature, which allows it to stretch and flex easily. There are several types of TPE, with thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) being the most commonly used among 3D printing filaments. The degree of elasticity of the plastic depends on the type of TPE and the chemical composition used by the manufacturer. For example, some threads may be partially flexible, like a car tire, while others may be elastic and fully flexible, like a rubber band.
Manufacturing techniques: FDM
- Flexible and soft
- Excellent vibration damping
- Long shelf life
- Impact properties
- Hard to print
- Difficulty removing supports
- Not suitable for all 3D printers
Strength
80%
Cost
60%
Moisture resistance
80%
Persistence to ultraviolet
70%
Chemical resistance
70%
Photopolymers
Photopolymers are liquid resins, they usually consist of epoxy resin or a combination . When exposed to UV radiation, these monomers quickly form molecular bonds with each other and turn into a solid polymer. The main modern technologies where photopolymers are used are SLA/DLP and PolyJet. Resin 3D printing is also an additive process, just like FDM printing. This means that the process is based on a layer-by-layer building process, where one layer forms molecular bonds with the next layer. This process is repeated until the entire model is recreated.
When exposed to UV radiation, these monomers quickly form molecular bonds with each other and turn into a solid polymer. The main modern technologies where photopolymers are used are SLA/DLP and PolyJet. Resin 3D printing is also an additive process, just like FDM printing. This means that the process is based on a layer-by-layer building process, where one layer forms molecular bonds with the next layer. This process is repeated until the entire model is recreated.
Crafting Technologies: SLA/DLP , Polyjet
- High Detail
- Smooth surface
- Faster printing process
- Finished product uniform in all axes
- High material cost
- More labor-intensive removal of supports
- More limited choice of materials
Strength
80%
Cost
75%
Moisture resistance
80%
Ultraviolet
9000%Chemical resistance
9000%Polymide (powder)
Poliamide (nylon) is one of the most popular 3D printing materials used by professional 3D printing companies. Polyamide is the reference material in the technology of SLS-laser sintering of plastic powder. This technology is used for rapid prototyping and rapid production. With this technology it is possible to create complex three-dimensional objects that can be used as prototypes or as functional parts.
Polyamide is the reference material in the technology of SLS-laser sintering of plastic powder. This technology is used for rapid prototyping and rapid production. With this technology it is possible to create complex three-dimensional objects that can be used as prototypes or as functional parts.
Given its flexibility and strength, nylon is an indispensable material for a wide range of applications from engineering to art. Nylon (polyamide) parts have a rough surface that can be polished to a smooth finish. Nylon is stronger than all other types of plastics, making it an ideal material for 3D printing products that require good tensile strength and mechanical strength.
Manufacturing techniques: SLS
- High detail
- High strength
- Finished part flat surface
- Supports not required
- Fast printing process
- High material cost
- Rough surface (can be removed with post-processing)
- Limited materials
- Available in one color (white)
Strength
90%
Cost
90%
Moisture resistance
65%
Ultraviolet resistance
80%
Chemical resistance
80%
Metals (powders)
Metal powder (steel, aluminum, aluminum, aluminum, aluminum, aluminums, aluminums, aluminums, aluminums, aluminums, aluminums, aluminums, and aluminums, aluminums, aluminums, aluminums nickel, titanium) are metals that are ground to particles and are pre-base materials for most 3D printing processes that produce metal parts.