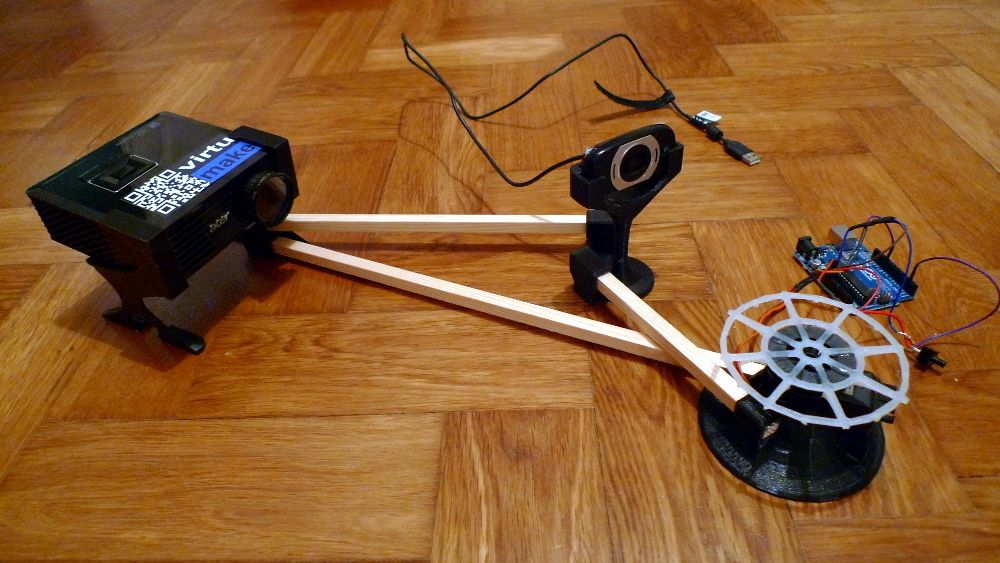
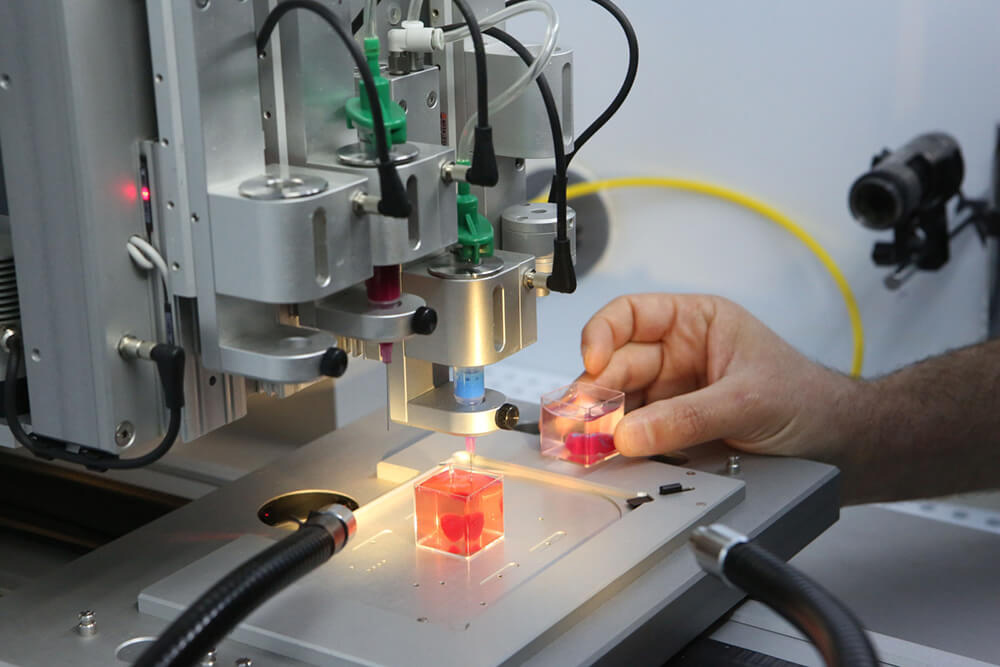
Tabletop 3d scanner
How to Choose the Best 3D Scanner to Use With Your 3D Printer
3D scanning has an important place at the beginning and end of 3D fabrication workflows. Engineers, product designers, and researchers use 3D scanners as a faster and more efficient way to start constructing digital models, whether by incorporating existing designs via reverse engineering, digitizing hand-sculpted clay designs, or referencing the exact shape of the human body.
After fabrication, 3D scanning can support quality control and help to verify the accuracy of a 3D printed part, or, after the part has been used, a scanner can reveal how it’s performed—a scan of a deformed part can show you where to reinforce the design in the next revision.
With such a wide range of product options from handheld 3D scanners to desktop 3D scanners, it can be difficult to choose the best 3D scanning system that’s right for your application and budget. In this post, we explore the most important factors to consider when purchasing a 3D scanner and showcase some of the key applications that are empowered by combining 3D scanning and 3D printing.
White Paper
3D scanning and 3D printing workflows can be applied to replication and restoration, reverse engineering, metrology, and more. Download our white paper to explore these applications and learn how to get started.
Download the White Paper
There are multiple scanning technologies currently on the market, all offering their own advantages and weaknesses.
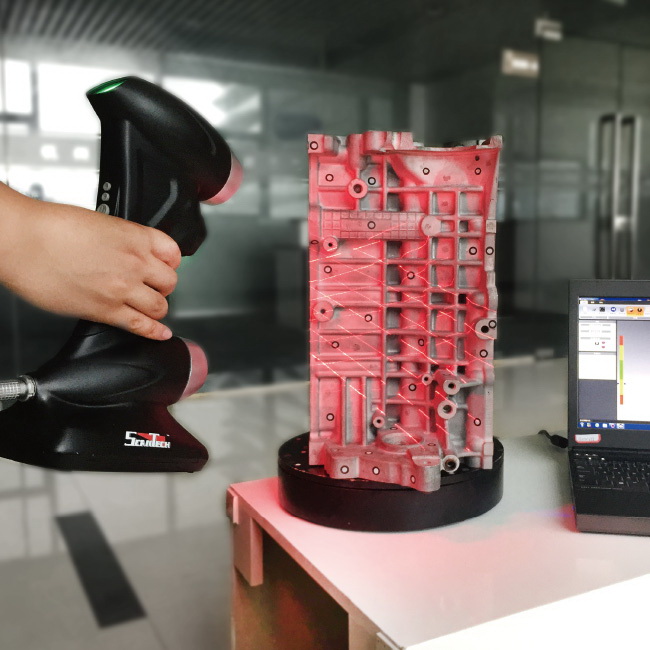
Laser triangulation uses light projected onto the object to take up to millions of measurements (dots) per second. The light reflected from the dots back into the scanner’s sensor to help it capture the geometry of the object. These types of scanners are often the most accurate, and are great for highly detailed parts that have opaque surfaces.
Laser triangulation scanners do have limitations. For example, this technology is not used in most portable scanners because the laser dots need to project from a stable source, and the source has to be kept a close distance from the scanned object. Laser triangulation scanners don’t always work on transparent or shiny surfaces either. Typically, they require reflective markers to be applied onto the object, which need to be removed after use and can be an obstacle depending on the object being scanned.
Laser triangulation scanners don’t always work on transparent or shiny surfaces either. Typically, they require reflective markers to be applied onto the object, which need to be removed after use and can be an obstacle depending on the object being scanned.
Finally, the laser dots can be harmful to human eyes, so it is important to use extra safety precautions when scanning body parts with a laser triangulation system, or to check with your scanner manufacturer to make sure the device is eye-safe.
Structured light scanners (also known as white light scanners or blue light scanners) generally use a projector with two cameras at angles on either side. A pattern of light is projected and laid over the component being scanned, the cameras capture the ways in which the object deforms the light pattern, and then multiple images are integrated into a single 3D snapshot.
Structured light scanners are available in both stationary and portable format—the technology is the most commonly used process for handheld 3D scanners.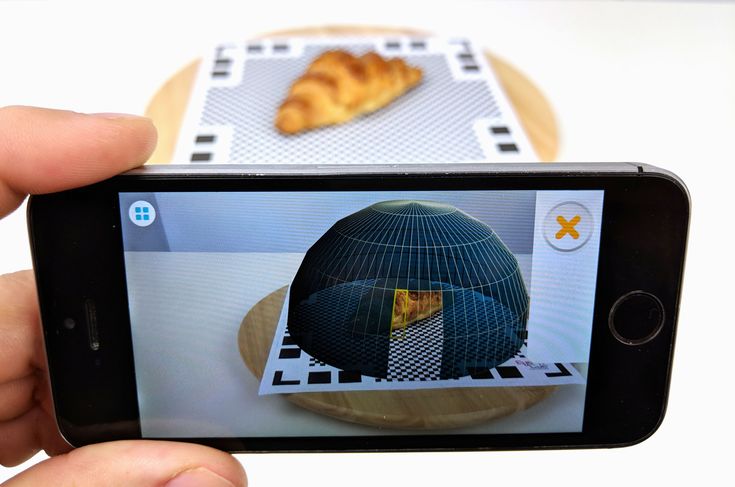 Structured light scanners are far more common in medical applications, since it is safe to use on both humans and animals and excels when an object is not perfectly still. Traditional white light scanners have been slower to scan than laser triangulation scanners.
Structured light scanners are far more common in medical applications, since it is safe to use on both humans and animals and excels when an object is not perfectly still. Traditional white light scanners have been slower to scan than laser triangulation scanners.
Structured light scanning is the most commonly used technology in handheld 3D scanners.
Depth-sensing cameras project a field of dots in infrared (IR) to sample a 3D scene. Depth-sensing cameras are simple to use and are the least expensive scanning option, but their accuracy and resolution are low, and fine details are sometimes lost. Large objects may be captured with depth-sensing cameras, but accuracy declines with increased distance from the subject and at steeper angles to the camera.
Photogrammetry means the act of deriving precise measurements from photographs. It involves taking a set of overlapping photos of an object, building, person, or environment, and converting them into a 3D model using a number of computer algorithms. This is the most commonly used method when creating a 3D scan with a smartphone, since modern phone cameras are capable of capturing and combining a large numbers of photos. Photogrammetry should be considered the least expensive and least accurate method for creating 3D prints, and is not suitable for serious business applications.
This is the most commonly used method when creating a 3D scan with a smartphone, since modern phone cameras are capable of capturing and combining a large numbers of photos. Photogrammetry should be considered the least expensive and least accurate method for creating 3D prints, and is not suitable for serious business applications.
LiDAR (light detection and ranging) sensors can be found on some higher-end smartphones and tablets, such as the latest versions of the iPhone Pro and the iPad Pro. This has made the iPhone and iPad viable scanners for those with only occasional scanning needs, offering performance a step above devices that only have access to photogrammetry. Applications that generate 3D mesh files via your smartphone’s or tablet's camera should be seen as the floor for entry-level scanning; users should expect additional work in their CAD software to remove gaps in meshes and improve the 3D model for applications like sending it to a 3D printer. Smartphones use fewer light points when scanning objects, resulting in less detail than a true, stand-alone scanner. iPhones are good substitutes for scanners if you have significant CAD design ability or need to transfer basic models into a digital space.
iPhones are good substitutes for scanners if you have significant CAD design ability or need to transfer basic models into a digital space.
WEBINAR
Watch this webinar with Peel 3D to explore how to integrate 3D scanners into your 3D printing workflow to elevate your product development process.
Watch the Webinar Now
Scan accuracy varies considerably between scanner technologies, and higher accuracy generally comes at a higher cost. The required tolerances of your final part can be a helpful guide for determining your accuracy requirements for a 3D scanner.
| High Price, Highest Accuracy ($15,000 and more) | More Affordable, High Accuracy ($12,000 and under) | Low price, Low Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Zeiss T-Scan Hawk Scantech Simscan EviXscan Optima+ M Creaform HandyScan 307 Silver Series | peel 3d peel 1, peel 2 & peel 2-S FARO Freestyle 2 Polyga Compact S1 | iPhone Pro and iPad Pro Structure Sensor Matter and Form 3D Scanner V2 Revopoint POP |
With accuracy in the range of 0. 1 mm or better, laser and structured light scanners are a good fit for professional applications and alongside high-resolution 3D printers. Formlabs stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers (such as the Form 3+) produce parts at a similar accuracy, and with a similar printable area, to the scan volume of many desktop 3D scanners.
1 mm or better, laser and structured light scanners are a good fit for professional applications and alongside high-resolution 3D printers. Formlabs stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers (such as the Form 3+) produce parts at a similar accuracy, and with a similar printable area, to the scan volume of many desktop 3D scanners.
Besides the accuracy between measured points and their actual location, scanners also vary in terms of resolution, which is the distance between captured points at a given scan distance. This means that details on the scanned object that are smaller than the scanner’s resolution won’t be captured. For example, a highly accurate 3D scanner with a lower resolution might detect the general shape of jewelry on a statue, but not clearly show individual details on a ring or necklace. Depending on your project requirements, this may or may not be a dealbreaker.
An easy way to remember these metrics is: accuracy is the measurement error between the part and digital value. Resolution refers to the density of measurements.
Resolution refers to the density of measurements.
Accuracy can mean slightly different things depending on the manufacturer and 3D scanning technology. For example, the accuracy of handheld scanners depends on the distance to the subject and the quality of scan reconstruction, while desktop scanners have consistent accuracy within the constrained scan volume. If you are considering buying a 3D scanner for precise measurement, make sure to compare like to like.
In general, structured light scanning provides the best resolution and accuracy when compared to laser scanning. For some artistic use-cases for 3D scanning you may need a lot of detail, while overall accuracy is less important—especially if you don’t require your part to fit precisely with other parts in an assembly. In these cases, photogrammetry is an excellent low-cost option to explore.
Both depth-sensing cameras and photogrammetry are a good solution for scanning large objects in order to create 3D printed scale models and also offer enough accuracy for capturing the shape of the human body.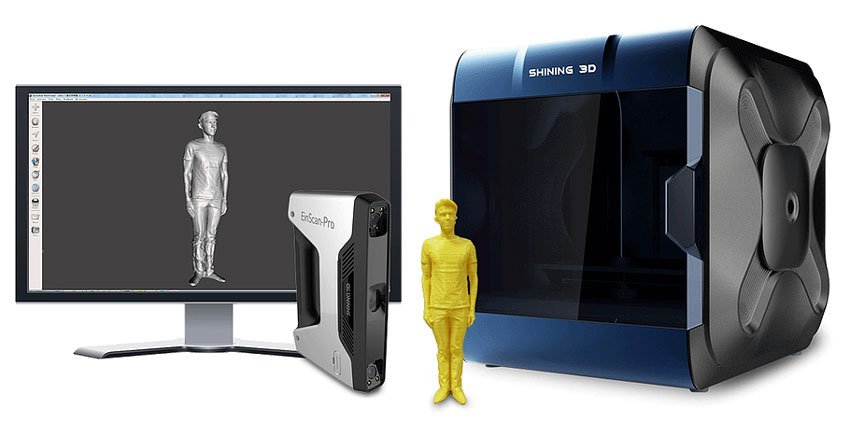
Several entry-level laser scanners are available using technology similar to higher-end systems. These scanners are a great way to start replicating small objects at 1:1 scale. As one would expect, the accuracy of entry-level laser 3D scanners is lower than a high-end scanner, but they can easily provide enough detail to replicate small decorative objects and figures where accuracy is not critical.
If you only have occasional 3D scanning needs, digitization services can scan your object, as well as perform CAD translation and accuracy inspection.
The area that a 3D scanner can capture varies significantly between scanners. Find a scanner that fits your size and resolution requirements without too much overhead, as cost typically increases with scan volume.
Handheld scanners can be manually moved around the object and have fewer size constraints than desktop models. Most inexpensive handheld scanners can capture objects from the size of a basketball to an entire room. High-end handheld scanners have an even wider range, and fill the niche for all objects that require precise measurements, but cannot fit in a desktop scanner. Handheld scanners are also able to capture objects nearly instantaneously, which makes them well-suited for taking human measurements (where the subject is not perfectly still) for ergonomics and medical applications.
High-end handheld scanners have an even wider range, and fill the niche for all objects that require precise measurements, but cannot fit in a desktop scanner. Handheld scanners are also able to capture objects nearly instantaneously, which makes them well-suited for taking human measurements (where the subject is not perfectly still) for ergonomics and medical applications.
If the area of the model can’t be seen by the scanner, it will cause a gap in the model. You can automatically repair small missing sections with most scan software programs to create a 3D printable model. However, repaired holes are rarely accurate to the original object. For parts that demand close to perfect accuracy, auto-repair of gaps or holes will not be sufficient. Read our MeshMixer tutorial for advanced tips to edit and repair 3D files for 3D printing.
Many scanners use turntables to increase what the scanner can see. The sophistication of a scanner’s turntable affects how easily and completely the object is captured: some scanners have the ability to move the object around multiple axes, imaging the object from more angles. This feature is important when reverse engineering plastic parts with deep recesses and ribs, which are impossible to capture from a single angle.
This feature is important when reverse engineering plastic parts with deep recesses and ribs, which are impossible to capture from a single angle.
Scanners may rotate the object to capture occluded areas. Red regions are occluded and will be missing in the scan. Areas with deep relief are difficult for a single axis turntable to fully capture due to occlusion.
Cost concerns are straightforward; how much you are willing to spend on a scanner will reflect your business’s budget and how often the scanner is going to be used. Higher cost scanners will be able to capture small objects and create highly-detailed meshes that don’t require significant touch-ups in CAD software. Handheld scanners are also often on the higher end of the price range, due to their portable nature. The low-cost scanning market offers a wide range of options, but you have to know what to look for.
Use this flowchart to determine what scanner you need based on accuracy, scan volume, and budget.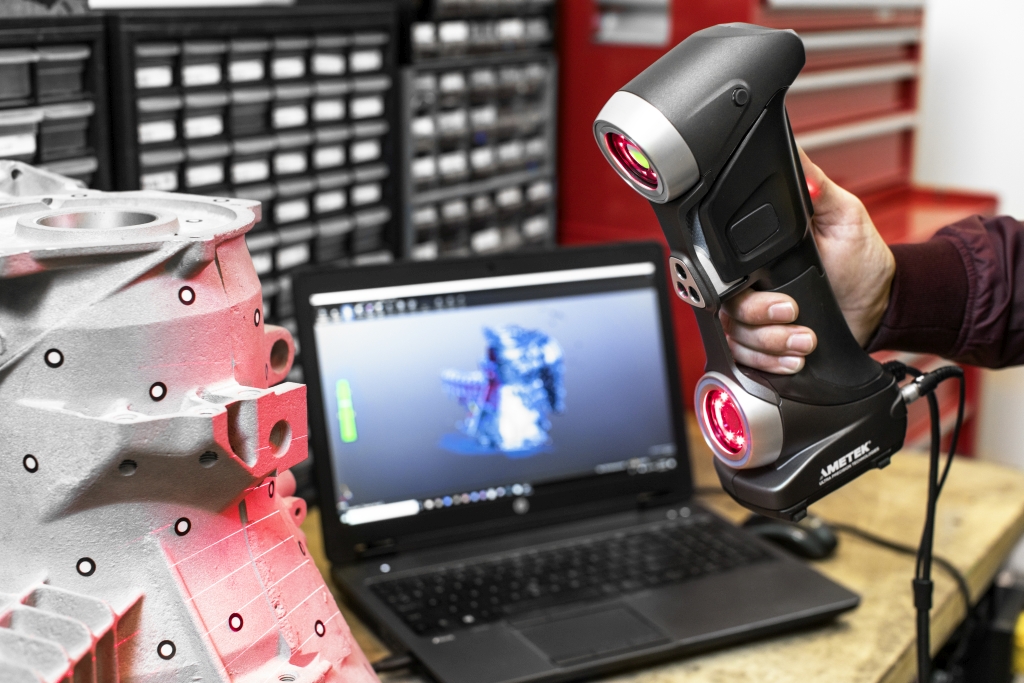
Download the high-resolution version of this infographic here.
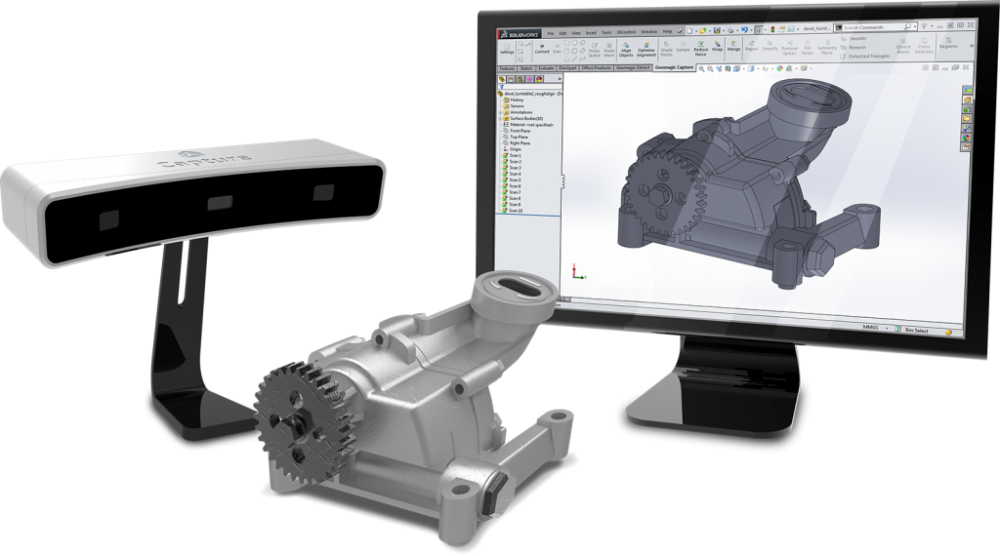
A 3D scanner expands the capabilities of a 3D printer, allowing you to replicate the shape of almost any object. Together, the two technologies create a powerful, digital workflow that can simplify and sophisticate processes in a range of industries.
The output from a 3D scanner is a mesh of triangles representing the surface of an object at a real-world scale. In some cases, the scan can be used directly to replicate objects without any CAD work. A hybrid workflow can also be powerful, where solid CAD models are combined with scanned 3D models. For example, customized ergonomics capture a physical imprint of a part of the human body, and integrate them with a mechanical design.
3D scanners are also valuable tools for measuring the accuracy of manufactured objects. Many factors affect 3D print accuracy, and metrology-grade 3D scanners provide a clear picture of how a material performs for demanding applications.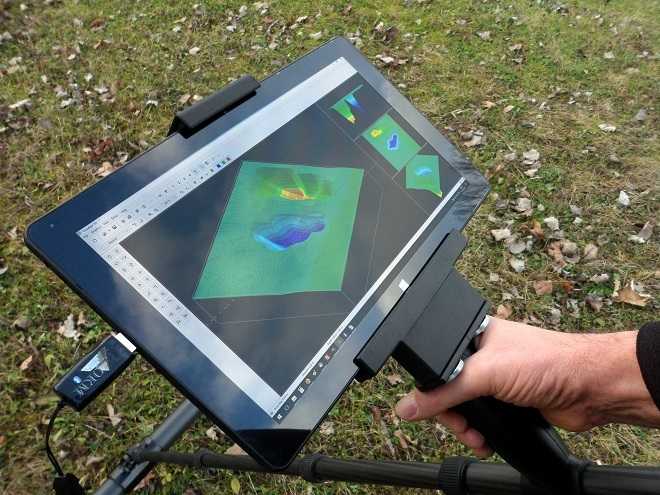
A variety of powerful workflows are enabled by combining a 3D printer and a 3D scanner:
- Reverse engineering to create replacement parts, products with custom ergonomics, and more.
- Replication and restoration of parts, especially in art and jewelry.
- Consumer audio for creating custom earpieces.
- Dental and medical applications, and how 3D scanning is enabling patient-specific workflows.
- Metrology to validate and measure the accuracy of manufactured objects.
Webinar
Watch this webinar for a detailed look at how to start using 3D scanning to improve part design and production when paired with reverse engineering CAD and 3D printing.
Watch the Webinar Now
3D scanners and 3D printers are essential parts of digital workflows across industries. Download our white paper or watch our webinar to get a detailed look into how to start using 3D scanning to improve part design and production and learn how to pair 3D printing and 3D scanning to empower a variety of workflows in engineering, product design, and more.
Learn more about the 3D printer side of the equation: get to know stereolithography (SLA) and selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing technologies and see Formlabs advanced 3D printing materials for yourself with a free sample 3D printed part.
Explore Formlabs 3D PrintersRequest a Free Sample Part
Best 3D Scanner - The Top 10 3D Scanners for 2022 [Reviews]
Much like a regular scanner, laser scanning 3D uses various methods to analyze a physical object and then relay that data to a computer to create digital 3D models. The 3D digitizer process might be automatic or users might need to complete the model to their requirements by using software. The aim is usually to get an accurate model to the right standard and format, ready for 3D printing, for virtual reality applications or other purposes.
Such scanners are used in many professional industries, but with advances in home 3D printing, there are now also a good variety of home options. They are sometimes called portable 3D scanners or handheld scanners if they’re designed as such. These allow you to easily scan small to medium-sized objects for 3D printing.
They are sometimes called portable 3D scanners or handheld scanners if they’re designed as such. These allow you to easily scan small to medium-sized objects for 3D printing.
Some come completely assembled while others, like 3D printers themselves, you’ll have to put them together by yourself. The benefit for those that are good with that type of thing is it reduces the price and allows for easier upgrades and modifications.
Scanning is typically done using laser triangulation or various forms of structured light to surround the object and measure its 3D dimensions or ‘geometry’. High-quality 3D scanner camera lenses also capture the color and surface texture of the object. Using accompanying or third-party software, the model can then be scaled up or down, or completely modified.
It’s never been easier to scan 3D objects!
How Do 3D Scanners Work?So, how do you scan 3D objects into a computer? Whether it’s on an industrial scale, at a small business, or on a desk at home, 3D scanners all share similar characteristics in the way they work.
The majority use laser and/or white light technology and cameras. The physical object is placed in a bed, tray, or suitable location. Electromagnetic light bounces off the object, measuring its circumference, full dimensions, and all its finer details.
Depending on the scanner it may use multiple light sources, cameras, and other tech to aid this process. The collected data is called a point cloud, which refers to the number of points captured by the laser.
The more points collected the more accurate the scan. A high-resolution scanner can capture hundreds of thousands of points in seconds and reach millions overall. The whole process only takes a few minutes.
While the light tends to be a measure of the object’s geometry, HD cameras tend to capture the surface detail and color.
The data recorded can then be fed into a computer-aided design program or similar software for inspection and manipulation.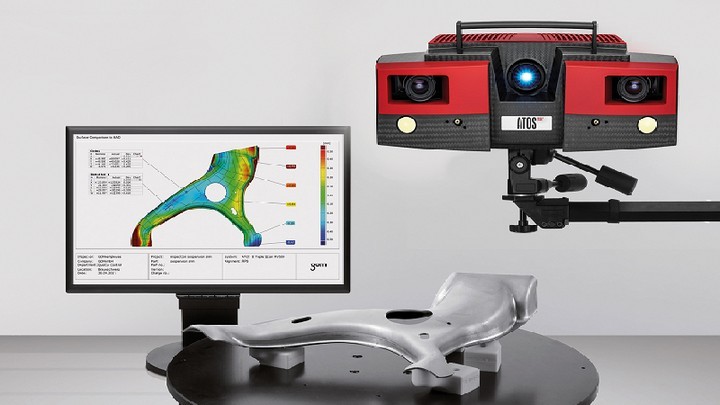 E.g. if you’re planning to use it for 3D printing, the model might need scaling up or down, hollowing, have added support structures, be re-colored or have brightness/contrast changes, etc.
E.g. if you’re planning to use it for 3D printing, the model might need scaling up or down, hollowing, have added support structures, be re-colored or have brightness/contrast changes, etc.
There are, of course, different types of 3D scanner and scanning technology. So, let’s take a closer look at each one:
Types of 3D ScannersThere are several 3D scanner types. Before making your decision check out the section below:
Handheld vs StationaryHandheld and stationary 3D scanners often use the same technology and can overlap in their functions. The difference lies mainly in the design.
A handheld scanner has a grip and lets the user move around the object themselves to capture it at every angle.
A stationary scanner has to be positioned in front of the object, which is typically placed on a rotating plate and captures it as it spins 360 degrees.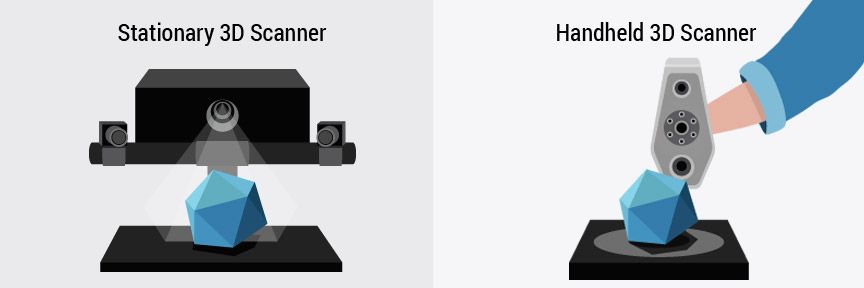 The user may have to reposition the object several times to capture every angle.
The user may have to reposition the object several times to capture every angle.
Newer designs are becoming smaller and more easily portable.
Laser TriangulationThe most common technology used in 3D scanning is laser trigonometric triangulation. It records millions of different points on the surface of the object to build an accurate overall polygon mesh. These are common in handheld options and industrial-grade scanner machines. They can also work long-range and for laser-tracking objects.
Structured-Light 3D ScannersSimilar and often used interchangeably with laser triangulation, structured light or ‘white light’ projects itself in a grid-like pattern over an object. It can then measure the structure of that grid as it applies to the object by using sensors/3D scanner cameras and triangulation.
Long RangeLonger range scanners use phase shift or pulse technology that can capture millions of points while rotating 360 degrees with the aid of mirrors.![]() This is more commonly used to scan large objects like cars or buildings.
This is more commonly used to scan large objects like cars or buildings.
They might also use ‘time of flight’ technology that measures the distance of an object in relation to the speed of light and the time it takes for it to return to a sensor.
This is less relevant for everyday 3D scanning and printing.
3D Scanning ApplicationsThere are many different applications for 3D laser scanning - from those for 3D printing at home, to prototyping, industrial scale medical supply production and even architecture.
Hobbyist 3D printingCheaper 3D scanners are typically used by home users for scanning simple objects and 3D printing them for fun.
MedicalThe medical field and dentistry commonly use 3D scanning to create implants and aids to serve their patients’ needs. For example, scanning people’s feet with a high-quality 3D scanner allows for the creation of orthotics (shoe inserts). It is also used in the creation of prosthetics.
It is also used in the creation of prosthetics.
Industrial 3D scanners are used both in the creation and quality control of cars, planes, and even aerospace. It ensures existing parts are as accurate as their original models and that new viable parts are made.
Reverse Engineering and RepairsFrom the home computer desk to the manufacturing floor, 3D scanning allows users to reverse engineer or copy existing objects. Saved models also allow for the reconstruction of damaged objects.
Virtual RealityFrom creating realistic 3D worlds to the people that occupy them, 3D scanning devices are integral to the growing virtual reality industry. This ranges from AAA video games, virtual cinematography, and computer-generated imagery (CGI), to virtual tours and office meetings. It is also a side industry to motion capture.
ForensicsCSI has come a long way. Forensic experts nowadays don’t just have to rely on memory, photos, and evidence of a crime scene. They can capture the entire location in a full 3D model for closer inspection and for running through different scenarios.
Forensic experts nowadays don’t just have to rely on memory, photos, and evidence of a crime scene. They can capture the entire location in a full 3D model for closer inspection and for running through different scenarios.
From museums to libraries, 3D scanning is being used to log and preserve everything from artifacts to digitizing books. This also gives experts and the public remote access.
Architecture3D scanning can also help architects map the areas they will be designing their buildings in, take inspiration from existing architecture, and aid in building miniatures/prototypes.
What Should I Know Before Buying a 3D Scanner?Before you buy a 3D scanner, there are several things to consider:
- your budget
- what you’ll actually be using it for
- it’s speed and accuracy
- the device’s other features.

3D laser scanner price ranges vary greatly. On the cheaper end, you may be able to pick one up for home for just shy of $300, like the XYZprinting 3D Scanner 1.0 A. However, if you want the highest overall quality and the ability to scan small and large objects. Or, if you’re a professional and need a 3D part scanner in a field like medical implants or automotive parts, you’re looking at anywhere between $3,000 and $35,000.
Typically, it’s best to look for 3D scanners for sale online where you can find the best selection and prices.
3D PrintingWhile a dual 3D printer scanner combo is rare, if you want to scan models for 3D printing, you will need to make sure it has good accuracy and resolution. The software also must be able to export to a usable format. You will need to check your 3D printer and its own software to see what file types it accepts and then choose your scanner accordingly.
Fortunately, almost all of our 3D scanner reviews include devices that can export in common file types like OBJ and STL.
It’s typically only the more expensive scanners that are good for other applications, like VR, full-body scanning, architecture, and engineering.
Handheld vs StationaryWe already explained the difference, but basically, a handheld scanner is mobile, while the stationary one will require you to move and adjust the object. Neither is necessarily better than the other, it’s all down to your needs.
SpeedHow fast is the scanner? Do you have a lot of spare time or require the job to be done as fast as possible? All 3D scanners will take a few minutes to complete, while many scanning complex objects in high resolution can talk half an hour or longer.
Accuracy and ResolutionAccuracy refers to how close to the object being scanned your digitized model will be, measured in millimeters.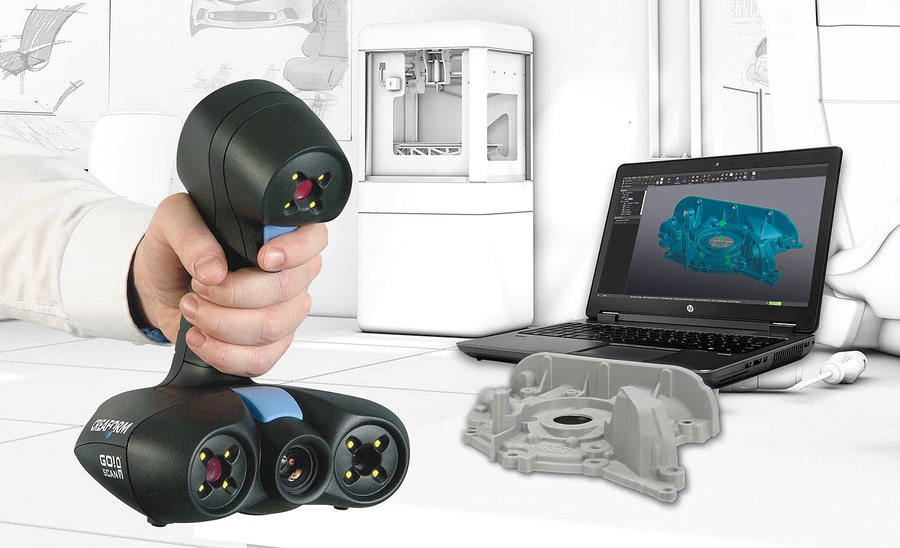 Therefore, the smaller the better. The term resolution may be used interchangeably with accuracy or refer to the resolution of any cameras being used as part of the scanning process.
Therefore, the smaller the better. The term resolution may be used interchangeably with accuracy or refer to the resolution of any cameras being used as part of the scanning process.
Generally, the lower the millimeter, the better. Other factors also play a role in overall quality, such as lighting conditions, color, and depth.
Object Size and SpaceSome types of 3D scanners excel at scanning small objects while others are better at medium to large. Others are all-rounders. Before buying a scanner, you should decide the general size of the items you will be scanning.
You will also need to make room for the scanner. Although all the products on our list are small and relatively portable, stationary scanners at least need a table to work from. Likewise, there will be a minimum and maximum distance the scanner must be in relation to the object being scanned.
You’ll need more room when scanning larger objects in full.
All 3D scanners need to be connected to a computer or device to help monitor the process and for saving the digital model. This is usually done via a USB or HDMI cable. You will need to check that your computer or laptop meets the minimum requirements for the scanning and modeling software. Also, make sure that you have a tablet to make real-time monitoring easier.
SoftwareYour device will either come with its own software or a popular third-party program to aid the process and to help touch-up the model once it’s scanned. Different 3D printing software is better suited to different skill levels. Some programs have a lot of features for experienced users and others do most of the basic tasks automatically. Check our 3D scanner reviews to see the software each device comes with and how advanced and easy to use it is.
Wrap UpWhether you’re looking for a tool for your home or something more on an industrial scale for your business, our 3D scanner reviews have something for everyone. From handheld devices to structured lightboxes with turntables, you’ll be creating 3D models or reverse engineering parts in no time. Perhaps you’ll even do a 3D selfie or two!
From handheld devices to structured lightboxes with turntables, you’ll be creating 3D models or reverse engineering parts in no time. Perhaps you’ll even do a 3D selfie or two!
If you’re still unsure about 3D printing after reading our reviews and guides, check out our answers to your most commonly asked questions below.
Desktop 3D Scanners - EinScan Multifunctional 3D Scanner
Get a quote
Please fill out this form to receive a free quote within 24 hours (during working days).
AfghanistanALAND ISLANDSAlbaniaAlgeriaAmerican SamoaAndorraAngolaAnguillaAntigua And BarbudaArgentinaArmeniaArubaAustraliaAustriaAzerbaijanBahamasBahrainBangladeshBarbadosBelarusBelgiumBelizeBeninBermudaBhutanBolivia, Plurinational State OfBosnia And HerzegovinaBotswanaBouvet IslandBrazilBritish Indian Ocean TerritoryBrunei DarussalamBulgariaBurkina FasoBurundiCambodiaCameroonCanadaCape VerdeCayman IslandsCentral African RepublicChadChileChinaChristmas IslandCocos (Keeling) IslandsColombiaComorosCongoCook IslandsCosta RicaC?te D'IvoireCroatiaCubaCyprusCzech RepublicDenmarkDjiboutiDominicaDominican RepublicEcuadorEgyptEl SalvadorEquatorial GuineaEritreaEstoniaEthiopiaFalkland Islands (Malvinas)Faroe IslandsFijiFinlandFranceFrench GuianaFrench PolynesiaFrench Southern TerritoriesGabonGambiaGeorgiaGermanyGhanaGibraltarGreeceGreenlandGrenadaGuadeloupeGuamGuatemalaGuernseyGuineaGuinea-BissauGuyanaHaitiHeard Island And Mcdonald IslandsHoly See (Vatican City State)HondurasHong KongHungaryIcel andIndiaIndonesiaIran, Islamic Republic OfIraqIrelandIsle Of ManIsraelItalyJamaicaJapanJordanKazakhstanKenyaKiribatiKorea, Republic OfKosovoKuwaitKyrgyzstanLao People'S Democratic RepublicLatviaLebanonLesothoLiberiaLibyan Arab JamahiriyaLiechtensteinLithuaniaLuxembourgMacaoMadagascarMalawiMalaysiaMaldivesMaliMaltaMarshall IslandsMartiniqueMauritaniaMauritiusMayotteMexicoMicronesia, Federated States OfMoldova, Republic OfMonacoMongoliaMontenegroMontserratMoroccoMozambiqueMyanmarNamibiaNauruNepalNetherlandsNetherlands AntillesNew CaledoniaNew ZealandNicaraguaNigerNigeriaNiueNorfolk IslandNorthern Mariana IslandsNorwayNORTH KOREAOmanPakistanPalauPalestinian Territory, OccupiedPanamaPapua New GuineaParaguayPeruPhilippinesPitcairnPolandPortugalPuerto RicoQatarReunionRomaniaRussian FederationRwandaSaint BarthélemySaint HelenaSaint Kitts And NevisSaint LuciaSaint MartinSaint Pierre And MiquelonSaint Vincent And The GrenadinesSamoaSan MarinoSao Tome And PrincipeSaudi ArabiaSenegalSerbiaSeychel lesSierra LeoneSingaporeSlovakiaSloveniaSolomon IslandsSomaliaSouth AfricaSpainSri LankaSudanSurinameSvalbard And Jan MayenSwazilandSwedenSwitzerlandSyrian Arab RepublicTaiwan, Province Of ChinaTajikistanTanzania, United Republic OftestThailandTimor-LesteTogoTokelauTongaTrinidad And TobagoTunisiaTurkeyTurkmenistanTurks And Caicos IslandsTuvaluUgandaUkraineUnited Arab EmiratesUnited KingdomUnited StatesUruguayUzbekistanVanuatuVenezuela, Bolivarian Republic OfViet NamVirgin Islands, BritishVirgin Islands, U.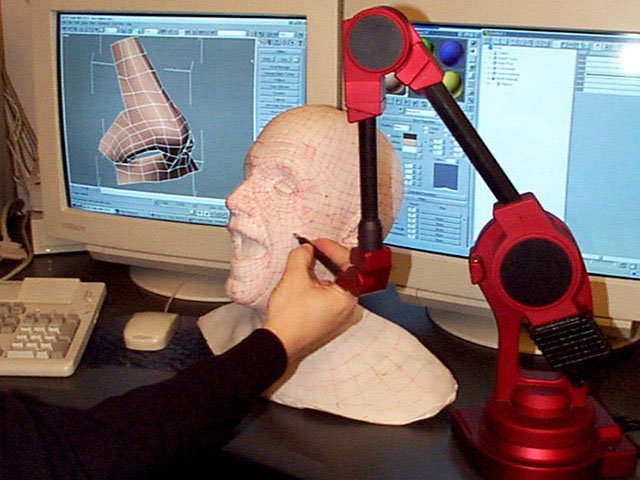 S.Wallis And FutunaWestern SaharaYemenZambiaZimbabweMACEDONIASOUTH GEORGIADemocratic Republic of the Congo
S.Wallis And FutunaWestern SaharaYemenZambiaZimbabweMACEDONIASOUTH GEORGIADemocratic Republic of the Congo
* Which product are you interested in?* Desktop 3d scanner* Hybrid light source handheld 3d scanner* Multifunctional handheld 3d scanner* Multiple scan range 3d scanner* Other Products and Service
submit...
choose the best in 2022 in our field
In order to expand the user audience, SHINING3D offers universal solutions - the same 3D scanner is able to satisfy the needs of ordinary consumers and be in demand in industrial production. Based on the feedback and reviews of device owners, the developers have improved the line of models, making 3D digitization and additive technologies even more accessible. nineOl000 Transcan C
EinScan Series 3D Scanners
For Beginners, Designers or Educational Entities
Small object scanning applications require precision and advanced settings in the capture software. The first thing users are guided by is the scanning area. Using two models - EinScan-SP and EinScan-SE - it will be possible to scan an object from 30 × 30 mm.
The first thing users are guided by is the scanning area. Using two models - EinScan-SP and EinScan-SE - it will be possible to scan an object from 30 × 30 mm.
EinScan-SP and EinScan-SE are useful for beginners, designers and educational users. Desktop scanners SE and SP are the easiest to learn.
Key benefits:
- Easy device setup with Plug and Play technology;
- Russian software interface;
- the ability to scan objects of different sizes - from small to large; nine0020
- texture tracking.
- 1 second per shot;
- Russified software;
- automatic and fixed operation;
- Align scanned data with marks.
- 1 second per shot;
- 45 seconds for 360 degree AutoScan;
- Russified software;
- automatic alignment of multiple scans; nine0020
- API access service for 3D printers of any brand.

Scanners for objects of various sizes
aIn this category, models with the “H” index successfully demonstrated their capabilities: EinScan H , EinScan HX from the line of hybrid devices. The most affordable is the portable EinScan H.
Two of these models stand out from the SHINING3D product list with the presence of hybrid light sources:
- EinScan H - an infrared emitter has been added to the LED illumination;
- EinScan HX - white LED light combined with a blue laser.
This high-tech solution makes it possible to use these two professional scanners. Manual mode allows you to scan objects of different sizes - medium and large.
Photo of 3d scanner EinScan HX- Structured emission of LED source and scanner laser;
- In Laser Scan mode, object scan accuracy is 0.04 mm; nine0020
- Minimum point distance 0.05 mm;
- High performance in fast scan mode - 1,200,000 points/s;
- Full color copy.

Copying accuracy is so great that when scanning objects of works of art, it is possible to obtain a perfect replica. For medical institutions, this is also a worthy find. Separately, it should be noted the presence of a built-in color camera.
3D scanning of people and their faces
Special scanning technology is required to work with living objects. You can get a digital copy of a fragment of a human body, face and hair using EinScan H hybrid models - thanks to two light sources and a color camera, they produce an ideal 3D model with texture preservation. nine0003
- Two scanning technologies - LED and invisible infrared light, combined in one device;
- Scanning people (portrait, full-length) and other living objects;
- High accuracy of scanned data up to 0.05 mm and volumetric accuracy of 0.1 mm/m;
- Fast scanning and large FOV scanning 420*440 mm.
HX is a universal scanner model, and Einscan Pro HD/Einscan pro 2x 2020 are multi-functional scanners that have the ability to perform tasks in various industries.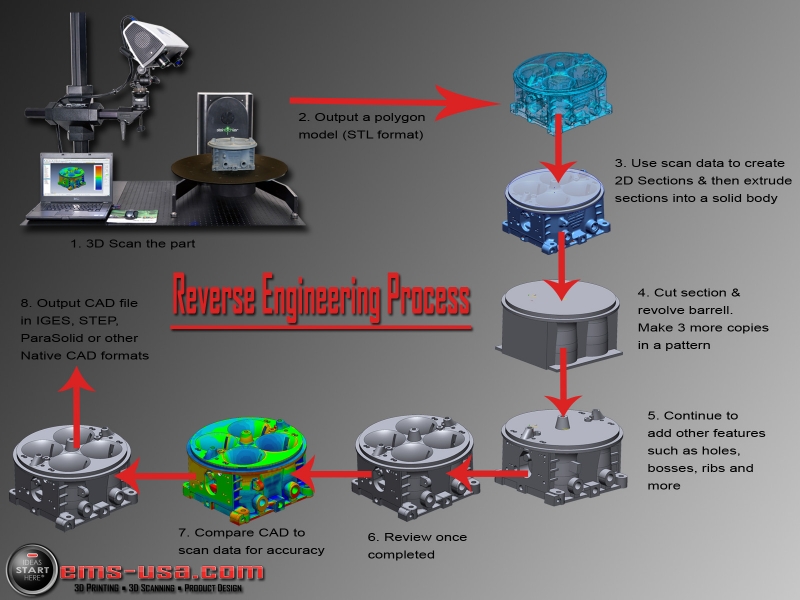 nine0003
nine0003
The EinScan Pro HD is an upgraded scanner from the older model of the Einscan Pro 2x series, thanks to its ergonomic and high quality design. Models in this range can be used with a special tripod.
This professional 3D scanner provides high precision scanning of objects in both operating modes: up to 0.045+0.3 mm/m.p. in manual mode and up to 0.04 mm. in fixed scan mode.
Manual object scanning has two submodes: Rapid and HD, the latter providing a higher level of detail. nine0003
The maximum possible scanning speed for this scanner is 3 million points per second. Even aside from the specification, you can see that the device is extremely fast in real-life scenarios. For example, a 220 x 71 cm low relief sculpture can be fully digitized in color in less than a minute.
Scanning of human bodies is also possible with this device, it provides decent quality. Last but not least, the device can scan color materials, including even textured images.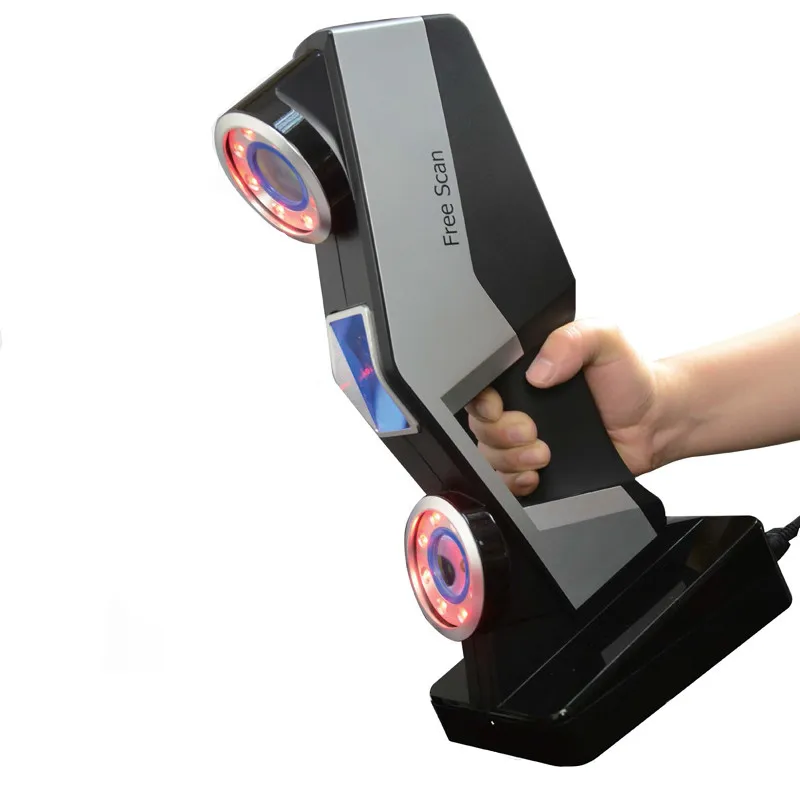 This feature is available as a paid option called the Color Pack. nine0003
This feature is available as a paid option called the Color Pack. nine0003
The EinScan HX is more expensive than the EinScan H scanner, and professional scanners, which include the EinScan Pro HD, are traditionally more expensive than other "classmates" and therefore are available to large additive manufacturers.
EinScan Pro 2X 2020 3D Scanner
Portable and versatile handheld 3D scanner for high-precision results
The EinScan Pro 2X 2020 3D scanner is an excellent option for scanning small, medium and large objects. nine0003 3D scanner EinScan Pro 2X 2020
The updated scanner model has improved the main characteristics, added new 3D scanning algorithms. Thus, Einscan Pro 2x 2020 has become a more affordable version of Einscan Pro HD, retaining the advantages and features of the old model.
The main improvements of the new model:
- A new principle of 3D scanning of the device in manual HD mode, which allows scanning without the use of markers (as Einscan Pro HD does).
 The old model could not scan without markers in this mode. The quality and detail of scans have also been improved. nine0020
The old model could not scan without markers in this mode. The quality and detail of scans have also been improved. nine0020 - Higher device scanning accuracy in manual HD mode, improved volumetric accuracy for scanning large objects
- Higher scanning speed in manual HD mode
- Increased 3D scanning area
- Added alignment modes in manual HD mode: alignment by markers, alignment by geometry , hybrid alignment. This expands scanning capabilities and efficiency in a wider range of tasks and areas.
Einscan Pro 2x 2020 3D scanner is compact and lightweight, you can take it anywhere with you. It has a comfortable grip and is light weight, and if you need HD mode accuracy, put the scanner on a tripod. The scanner is connected via USB 3.0 to a computer or laptop. nine0003
The latest developments in data capture and optimized algorithms make the Einscan Pro 2x 2020 3D scanner truly groundbreaking, reaching up to 1,500,000 points per second (at 30fps) in manual scanning mode.
If you need to expand the functionality of the scanner, Shining 3D offers several options:
- Color Pack 3D Scanning Module - an additional camera that allows you to scan with color and texture; nine0020
- Industrial Pack - turntable and tripod. Suitable for high quality scanning of small objects in the studio.
Transcan C
3D ScannerThe Transcan C 3D Scanner is a professional scanning grade scanner capable of capturing “extraordinarily” accurate high-resolution scans of small to medium-sized objects thanks to two 12-megapixel color cameras with adjustable scanning range and the ability to switch between multiple permission levels within a single project. nine0003
The 3D scanner has a sliding design that allows you to easily switch the scanning range between 150mm x 96mm and 300mm x 190mm for different sizes of objects. The multi-resolution fusion algorithm allows you to mix high, medium and low resolutions in the same project, making the scanner much more efficient, and its two cameras can capture a 24-bit color map for detailed 3D color data. The
The
Transcan C features a structured light scanning mode with an automatic turntable that, in combination with the scanning software's stitching algorithm, allows “efficient 3D model acquisition without manual intervention. nine0003
What other indicators do you need to understand in order to choose what you need? - ease of setup and others. Of course, the properties are considered in a complex: the most important parameter is considered as a basic one, the rest are considered as auxiliary, but at the same time mandatory. nine0003
3D Scan Accuracy
The degree to which the copy matches the original is perhaps the most important indicator. The technical characteristics of scanners indicate the maximum allowable deviation of the scan size from the real object. The smaller the number, the more accurate the 3D scan will be. But the deviation in reality can be greater, since it is quite difficult to create ideal conditions for the device to work, the result is affected by:
- characteristics of the object;
- user qualification; nine0020
- scanner settings.

The use of professional 3D scanners in metrology
3D scanners cope with the process of measuring the dimensions and shapes of models in a matter of minutes, unlike traditional coordinate measuring machines. The non-contact mode of operation allows the device to scan surfaces of complex shapes (internal corners and edges), recesses and other hard-to-reach places.
After receiving all the necessary data, they are transferred to the computer for processing. The program performs a comparison of indicators in order to identify deviations - a mismatch in shape and size, the presence of chips, cracks and other deformations caused by mechanical stress or corrosion processes. nine0003
Innovatively adapted blue laser 3D scanning technology
For metrology purposes for scanning a small object, we recommend the OptimScan-5M, 3M and AutoScan Inspec Scanner-Inspector. All these devices to some extent belong to the same price niche, are multitasking, provide an opportunity to obtain high-quality digital 3D models for comparison with reference samples, demonstrating:
- the highest accuracy;
- the ability to upload scans to processing programs; nine0020
- compatible with CAD/CAM technologies;
- work with objects of various sizes and shapes, including those with complex geometry;
- texture tracking and color imaging.

Professional, they are also industrial, 3D scanners help to perform the following tasks:
- reverse engineering;
- ultra-precise 3D quality control;
- implementation of intermediate stages of the technological chain of additive manufacturing; nine0020
- faster prototyping and other operations.
3D scanning in mechanical engineering
Integration of 3D scanning technologies into production processes gives undoubted preferences. Properties of modern industrial scanners:
- high speed;
- ultra-precise measurement and digital copy saving;
- processing of objects regardless of the size and complexity of the form;
- possibility of implementation in automated production systems. nine0020
Numerous processes can be carried out with the help of 3D scanners and specialized software:
- reverse engineering, or reverse engineering;
- metrological control;
- test measurements of geometric parameters for the purpose of quality control and detection of defects;
- creation of archives of digital models.

Reverse engineering
Reverse engineering of complex shapes is one of the areas of industrial engineering. A physical sample is converted into a digital copy using a 3D scanner. The resulting polygonal model is converted into a CAD format. The digital copy is modified and modified to achieve the specified parameters. Unlike traditional design, work takes many times less working time. The finished object becomes the basis for serial production. nine0003
Quality control
Metrological 3D scanners make it possible to obtain a point cloud of the test sample, on the basis of which an ultra-precise 3D model of the part is formed. It is compared with a digital copy of a reference sample or with an existing CAD model.
Benefits of 3D quality control:
- Absolutely accurate data for reference comparison;
- measurement of millions of surface points;
- high speed operation;
- possibility of automatic operation. nine0020
The obtained data can be used for reverse engineering.
For quality control, scanners from the metrological category are recommended.
FreeScan UE Handheld 3D Laser Scanner
Shining 3D FreeScan UE is the latest addition to the FreeScan line of high performance 3D scanners. The device uses the patented blue laser technology and features high accuracy and stable repeatability.
Sunny Wong, product manager of Shining 3D, states: “Innovative adaptation of blue laser 3D scanning technology, high precision and stable repeatability, and easy and convenient operation of hardware and software, enable FreeScan UE to effectively and accurately upgrade digital workflows in engineering and inspection tasks”. nine0003
The Metrology Grade FreeScan UE system provides 0.02 mm accuracy and 0.02 mm + 0.04 mm/m volumetric accuracy. With a maximum scan area of 510 x 520mm, users get a field of view suitable for large-scale reverse engineering projects.
AutoScan Inspec High Accuracy Stationary 3D Scanner AutoScan Inspec
- user friendly interface;
- the accuracy of the 3D model reaches the metrological level with an error of 10 µm; nine0020
- the device can be used for non-contact measurement and quality control;
- the process is fully automated.

Works with native software developed by SHINING 3D programmers for industrial applications.
OptimScan-5M 3D Metrology Scanner
OptimScan-5MProfessional 3D Metrology Scanner OptimScan-5M delivers the best consumer performance just right for 3D inspection:
- accuracy - 15 microns;
- two 5-megapixel cameras;
- high processing speed;
- blue light scanning technology.
AutoScan Inspec Desktop Scanner is a two-in-one scanner-inspector that works in automatic mode. The scanner performs 3D scanning with the highest precision and 3D inspection of objects. This is one of the best devices for working with complex shapes and tiny elements:
Dental Solutions
In dental orthopedics, 3D scanners – intraoral and dental – have become indispensable assistants for orthopedists and dental laboratory specialists. The former are used for scanning, creating digital impressions and then manufacturing perfectly fitting prostheses, crowns, veneers and other dental restorations using a 3D model using CAD / CAM technology.