Second hand 3d scanner
Used CMM Equipment | Used 3D Scanners
Since we represent only the best brand manufacturers like Artec, Brown & Sharpe, Breuckmann, EnvisionTEC, Faro, GOM, Hexagon, Leica, Metronor, Mitutoyo, NDI, ProCon CT, Romer and Surphaser, we sell only the best used CMM equipment, used 3D laser scanners, CT industrial scanners and metrology equipment.
One of the more popular used 3D scanning equipment items we sell is a used CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine). This equipment is often found on a shop floor because it can be placed wherever your process needs it. We get requests for four types of a used CMM: 1) Used bridge CMM; 2) Used gantry CMM; 3) Used cantilever CMM; and 4) Used horizontal arm CMM. Your used CMM will measure the geometry of physical objects by sensing discrete points on the objects’ surfaces with a mechanical, optical, laser or white light probe.
Most of our inventory has only been used for a limited number of hours—so it operates as if it’s practically new.
If you don’t see “Exact-ly” what you’re interested in give us a call and we’ll try locating it for you. For example, if you’re looking for a used Zeiss CMM or a used Faro Arm, we may have access to one or something similar from another resource. And we always have more used scanning equipment in transit which simply hasn’t been processed yet for inclusion on our site.
Sell Us Your Used 3D Scanning Equipment
Exact Metrology is always looking to add to our Used Equipment Inventory. We’ll pay cash for any used equipment you might want to sell. Even if you don’t want to purchase any equipment from us, we’ll purchase from you.
Of course, if you are looking to upgrade your equipment, we would be happy to discuss a trade-in of your used 3D Scanning equipment as well.
Here are the types of used 3D Scanning Equipment purchases we are interested in:
- Used 3D Scanners
- Used CMM Equipment
- Used Laser Trackers
- Used Laser Scanners
- Used Long Range Scanners
- Used Probing Arms
- Used White Light Scanners
- Used Blue Light Scanners
- Used Portable CMMs
Contact Us to Sell Your Used Metrology Equipment
Equipment Financing
Giving businesses access to the financing they so desperately need is key to any healthy economy. But in our conversations with executives and business owners, we’re hearing that it’s still not easy for companies to find suitable financing options for 3D laser scanners, optical trackers, portable CMMs, long range scanners and other metrology and inspection equipment. And that kind of roadblock keeps them from the equipment required to expand their business.
But in our conversations with executives and business owners, we’re hearing that it’s still not easy for companies to find suitable financing options for 3D laser scanners, optical trackers, portable CMMs, long range scanners and other metrology and inspection equipment. And that kind of roadblock keeps them from the equipment required to expand their business.
That’s why Exact Metrology is doing more than just listening. We’re teaming up with financing companies that work hard to get you approved, companies that provide businesses in need of financing with credit terms that work for them rather than screen them out.
You’ll find great options including:
- 60-month financing
- Low annual interest rates
- No down payment
- No pre-pay penalty
Contact Us For More Information On Available Financing Services
Exact Metrology is an ISO 9001:2008 and AS9100 Certified Company
Exact Metrology, with facilities in Cincinnati, OH, Moline, IL and Milwaukee, WI and affiliated offices throughout the country, is a comprehensive metrology services provider, offering customers 3D and CT scanning, reverse engineering, quality inspection, product development and 2D drawings. The company also provides turnkey metrology solutions, including equipment sales and lease/rental arrangements.
The company also provides turnkey metrology solutions, including equipment sales and lease/rental arrangements.
Exact Metrology offers a complete line of portable scanning and measurement technologies as well as contract measurement for 3D laser scanning services, reverse engineering services, non-contact inspection, metrology services, and 3D digitizing. The company’s newest equipment includes a CT Scanner, the first in America being used for metrology rather than medical testing. Exact sells and rents metrology equipment solutions, in addition to providing testing as a service and application software training.
Visit exactmetrology.com
10 Best Cheap 3D Scanners in 2022 (That Work Well)
So you’re interested in getting into 3D scanning? First thing you’ll need: a 3D scanner. You could also make your own DIY 3D scanner, but this requires time, effort and skill, and many would prefer to buy their own affordable 3D scanner online and save the hassle.
But, you also don’t want to break the bank.
You don’t need a $20,000 professional piece of kit designed for precise prototypes and industry, you just want an easy-to-use, accurate and affordable 3D scanner you can use to scan your favorite miniatures and other fun designs, or even to scan you and your friends/family’s faces to 3D print them!
So, we’ve put together the absolute top picks for low-cost 3D scanners that still work great, from the lowest price range of $150 (though you have to build most of it yourself), to the $500-ish price range we recommend to get a good quality scanner – our Revopoint POP scanner is this price and we’re very happy with it – and also some more premium options for precise detail scanning.
What Makes a Good Cheap 3D Scanner?
- Price-performance ratio — offering bang for their buck
- Accuracy and resolution
- Versatility — are they portable, and can they be used both handheld and stationary?
- Ease of use — from simple setup, to software compatibility
BUDGET PICK
Revopoint POP
Has a grip for holding it to scan people/bodies, and turnstile and stationary object scanning
0. 3mm accuracy and 8fps scanning
3mm accuracy and 8fps scanning
Available at:
Revopoint hereMID-RANGE PICK
Matter & Form V2
Accurate 0.1mm scan quality
Powerful stationary scanner for intricate 25x18cm objects
Comes with Mfstudio scan software
Available at:
Amazon hereDynamism herePREMIUM PICK
Shining 3D EinScan SE
“Cheapest professional-level 3D scanner”
Scans 70x70x70cm objects to 0.1mm scan accuracy and can rotate objects
Available at:
Amazon hereDynamism here3DSourced is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more
| Name and brand | Type of 3D scanner | Price | Best price available at: |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revopoint POP | Stationary/Handheld | $500 | Revopoint 3D here |
| BQ Ciclop | Laser triangulation | around $165 | Amazon here |
XYZ 1. 0 Pro 0 Pro | Low cost handheld 3D scanner | $445 | Amazon here |
| Revopoint POP 2 | Stationary/Handheld/Color | $699 | Revopoint 3D here |
| Sol 3D scanner | Laser triangulation | $799 | Amazon here |
| Matter & Form V2 | Desktop 3D scanner | $749 | Amazon here |
| Shining 3D Einscan SE | Stationary 3D scanner | $1,199 | Amazon here |
| Scantech iReal 2E | Handheld 3D scanner | $3,980 | Scantech site |
| Shining 3D Einscan SP | Stationary 3D scanner | $2,599 | Amazon here |
Cheap 3D Scanners Under $500
Revopoint POP – Best Cheap 3D Scanner
- Price: around $500 — Available at Revopoint store here
- Resolution: 0.3 mm
- Max Scan Volume: 210 x 130 mm
- Technology: Structured light & infrared scanning
- Speed/Frame Rate: 8fps
The Revopoint POP is one of the best low-cost 3D scanners around, with a single frame accuracy of up to 0. 3mm, and the versatility to be used portably to scan faces, bodies and animals, as well as a stationary scanner for sculptures, prototypes and other objects.
3mm, and the versatility to be used portably to scan faces, bodies and animals, as well as a stationary scanner for sculptures, prototypes and other objects.
Weighing just 200g, it’s portable and light, and can easily fit into any backpack or transporting equipment you have.
Whether you use iOS or Android, MacOS or Windows, it’s compatible with your smartphone, tablet or laptop, and connects seamlessly via USB to scan and export — and can export in STL, OBJ or PLY file formats. It comes with cables to connect to PC or Mac, as well as a portable stick that connects to your smartphone for previewing your scans in handheld mode.
For scanning faces, the infrared sensors (similar to more expensive 3D scanners like the Einscan H) makes for a zero-glare solution that doesn’t hurt your eyes, and helps with scanning darker features (though dark hair will still be a problem).
The entire kit includes a smartphone rig, mount and grip, LED light to support scanning, mini tripod, and a turntable for scanning stationary objects. Revopoint bundle the POP 3D scanner with their own software for editing and optimizing your scans, including multiple continuous splicing, making it a great all-around affordable 3D scanner workflow.
Revopoint bundle the POP 3D scanner with their own software for editing and optimizing your scans, including multiple continuous splicing, making it a great all-around affordable 3D scanner workflow.
Read more: Revopoint POP 2 3D scanner review
BQ Ciclop — Great Cheap 3D Scanner Under $200
- Resolution: 0.5mm
- Price: around $150 — Available on Amazon here
- Scan time: 2-8 mins
- Maximum scan volume: 200 x 200 x 205 mm
Most 3D printing experts will know of BQ’s 3D printer range. In addition to their printers, BQ also designed the Ciclop, an affordable 3D scanner that’s completely open-source. You can either build it yourself at home if you prefer a DIY project, or buy it pre-assembled online.
This nifty budget 3D scanner has a good scanning volume — up to 250 x 205 mm — so it’s no slouch for the price. It utilizes laser triangulation technology, so you don’t need to hold the scanner and move it around the object.
And since it’s open-source, you can modify it however you want — following the RepRap 3D printer philosophy. It’s a great cheap laser scanner, and one of the best value 3D scanners out there.
In terms of specs, it’s actually very good for the price — with resolutions between 0.3-0.5mm. You can easily scan to a free 3D software tool (the BQ Ciclop comes with Horus) via Bluetooth or USB, though experienced makers may prefer to work in a more professional 3D software package.
Overall, the BQ Ciclop is a plucky, low-cost 3D scanner that’s great for new makers looking to get 3D scanning. One drawback is that it isn’t the easiest 3D scanner to assemble, so less experienced DIY-ers may opt to buy it pre-assembled online.
XYZprinting Handheld 2.0
- Price – Check price on Amazon here
- Resolution: 0.2 mm – 1.5 mm
- Max Scan Volume: 100 x 100 x 200 cm
- Technology: Stereo imaging
- Speed/Frame Rate: 40 fps
Building on the success of its first low-cost 3D scanner, XYZ is back with the new XYZprinting 3D Scanner 2. 0, promising, rather grandly, 3D scanning for a new frontier. Much of the focus here is on wiping out the reliability issues of the original while also increasing the resolution substantially.
0, promising, rather grandly, 3D scanning for a new frontier. Much of the focus here is on wiping out the reliability issues of the original while also increasing the resolution substantially.
Powered by an Intel RealSense module, the XYZprinting 3D Scanner 2.0 leans on portability, fast scanning, and greater detail as its chief attributes. It employs two cameras equipped with stereo imaging technology to measure the depth, shape, and size of objects.
Housed in a light and compact shell (itself designed to fit comfortably in the hand or clip onto a laptop or PC screen) weighing a feathery 382 g are some impressive specifications. It features full-color scanning at up to 1920 x 1080p at 40 FPS and 640 x 480 at 30 FPS depth imaging.
Resolution sits at a decent 0.2 mm to 1.5 mm, far better than the original’s 1.0 to 2.5 mm. It has a 25-60 cm operating range and a scanning distance of 20-120 cm. Alongside it boasts a max scan size of 100 x 100 x 200 cm for quick scanning of relatively large objects or bodies.
Firing up the XYZprinting 3D Scanner 2.0 gives you three modes: one tuned to capture objects, one optimized for headshots and portraits, and the last designed for full-body scans. Scanning is the usual process of capturing an object from multiple angles. The scanner then creates a digital mesh model replica, exportable to STL, OBJ, PLY, and FBX file formats.
Overall, the XYZprinting Handheld 2.0 punches above its price point and is a sound investment for those that need an affordable 3D scanner. The only negative is that the scanner is tethered to a USB cable, which detracts a little from its overall portability as you’ll always need a computer to scan objects.
Low Cost 3D Scanners ($500+)
Revopoint POP 2 – Best Under $1000
- Price: $699 — Available at Revopoint Official store here
- Precision: 0.05 mm
- Scan Speed: 10 FPS
- Minimum Scan Volume: 20 x 20 x 20 mm
- Single Capture Range: 210 x 130 mm
- Working Distance: 150 – 400 mm
- Point Cloud Distance / Single-Frame Accuracy: 0.
 15 mm
15 mm
We already feature the Revopoint POP on our affordable 3D scanner review, but the newer upgraded version, the POP 2, improves in almost every area.
It’s one of the best, if not the best 3D scanner under a thousand dollars, and works superbly for stationary scanning (it comes with a movable turntable to scan all sides), handheld scanning of objects, faces, bodies and more, as well as accurate color scanning.Scanning a toy with the Revopoint POP 2 using the “fill holes” setting (often leave it off and sort any errors in post).However, you can’t scan black or shiny features unless you spray them to become visible to the camera.
If budget is important, then the standard POP is fine. But, if you want that extra quality, the POP 2 offers up to 0.05mm precision (vs 0.3mm for the POP), a faster 10fps scan speed (vs 8fps on the POP), and it can scan smaller parts, starting at 20mm³ vs the original POP’s 30mm³.During our test and review, the calibration showed an accuracy of around 0. 07mm.
07mm.
It scanned color images well when we tested it on some kids toys and a multi-color Rubik’s cube, and scanned faces accurately (but don’t select the “fill holes” setting as it will create deformed faces by creating a mesh cloud that includes background noise).
Overall, it’s probably the best cheap 3D scanners around – standard scanning, face scanning, color, or entire body scanning, it’s good for all uses.Color scanning and editing test.
Read the full review: Revopoint POP 2 hands-on test and review
Compare: Revopoint POP vs POP 2 and MINI
Sol 3D scanner — Low cost laser scanner
- Price: $799 — Available on Amazon here
- Resolution: up to 0.1 mm
- Scan volume: up to 170 x 170 mm
- Scan speed: 10 min in Turbo mode, 20 min normally
Costing under $1,000, the Sol 3D scanner is an affordable laser scanner capable of scanning small and medium-sized objects with strong accuracy. For small parts or objects, it has a specialized Near Mode option, and for larger objects, you can use Far Mode.
For small parts or objects, it has a specialized Near Mode option, and for larger objects, you can use Far Mode.
Specialized 3D scanning software comes with the Sol scanner, easily enabling you to export object scans in either STL or any other file formats, for either 3D printing in a 3D slicer, or importing into a 3D CAD software tool for editing and optimizing.
The scanner is positioned towards hobbyists as well as entrepreneurs looking to expand their product range presentation.
With Facebook now letting anyone upload 360-degree images of their products that customers and fans can view, it has never been more important to have 3D scans of your best-sellers, with the Sol perfectly suited for this.
Overall, it’s a great low cost 3D scanner for effective scanning of small and medium objects.
Matter & Form V2 3D Scanner
- Price: $749 — Available on Amazon worldwide here / Available on Matterhackers here
- Scan volume: 250 x 180 mm
- Accuracy: within 0.
1 mm
- Scan speed: up to 65 seconds
Featuring very accurate scanning at up to 0.1mm due to its 2 lasers and HD-CMOS sensor, the Matter & Form V2 is up there as the most precise cheap 3D scanner under $1,000.
Like many of these desktop 3D scanners, the Matter & Form comes with its own 3D software tool for editing and transferring files, and comes with Mfstudio and Quickscan for fast 65-second scanning.
If you’re looking to 3D print your scans, you can seamlessly import them into your 3D printer software and either print remotely via WiFi, or slice and export to a USB or SD card.
The only thing that may rule it out for some people is its relatively small maximum scanning size. Because it sits stationary when scanning, it can only scan objects that fit on its scanning platform (up to 25cm tall and 18cm diameter), so those who plan on scanning people or larger objects will prefer a handheld scanner instead.
Apart from that, it’s a fantastic, very precise 3D scanner perfect for scanning intricate, small objects.
Shining 3D EinScan-SE — Best value 3D scanner
- Price: $1,199 — Available on Amazon worldwide here / Available on Dynamism Store here
- Scan accuracy: a single shot is within 0.1 mm
- Scan range: single scan – 200 x 150 mm / maximum scan range – 700 x 700 mm
- Scan speed: a single shot under 8 seconds
Proclaimed the “cheapest professional level 3D scanner” by Shining 3D, their EinScan SE model is their entry-level 3D scanner. Some of their other scanners, for example the Einscan Pro 2X can cost upwards of $7,000, though just because it’s their cheapest scanner doesn’t mean the EinScan SE isn’t impressive.
It can scan up to 70 x 70 x 70 cm, which should be enough for your printing needs unless you’re scanning entire cars, or people. Moreover, it’s accurate to 0. 1mm so scan quality will absolutely not be a problem.
1mm so scan quality will absolutely not be a problem.
You can either have the object being scanned rotate, or do so yourself, the EinScan-SE supports a variety of options. Overall, it’s impressive for the price and a very strong 3D scanner.
iPhone With LiDAR Scanner
- Price: Check price on Amazon here
- Technology: LiDAR sensor
- Compatible Devices: iPhone 13 Pro Max, iPhone 13 Pro, iPhone 12 Pro Max, iPhone 12 Pro, iPad Pro
You may already have one of the best cheap 3D scanners in your pocket right now – an iPhone. The latest additions to Apple’s iPhone lineup, namely the iPhone 12 and 13 Pro family, along with the iPad Pro, feature a LiDAR sensor integrated into the camera assembly.
Light Detection And Ranging, or in simple terms, 3D laser scanning, beams light onto an object and then measures the time it takes for the light to reach back to the sensor to capture the size, shape, and other characteristics. It does not just scan objects but also 3D spaces.
It does not just scan objects but also 3D spaces.
The sensor is chiefly equipped to boost the iPhone’s ability to capture crisp and clear images in less than ideal light conditions, but when paired with an appropriate app becomes a decent 3D scanner. The results aren’t quite on par with what you’d get with a dedicated 3D scanner, but they aren’t half bad for a device with a cheap LiDAR scanner you likely already own.
A growing number of apps make full use of the iPhone LiDAR sensor to scan and create 3D models, ready for export in various popular formats, which you can then edit in CAD software. Apps like Canvas, 3D Scanner, and Polycam are excellent starting points. Most are free, too, meaning you can 3D scan for no extra cost if you’re already the owner of one of the latest iPhones.
iReal 2E color 3D scanner
- Price: $3,980 – More info at Scantech store here
- Resolution: up to 0.2 mm
- Accuracy: up to 0.
 1 mm
1 mm - Weight: 850g
While not as cheap as some other options, Scantech’s iReal 2E is one of the most cost-effective professional handheld color 3D scanners on the market, capable of extraordinary accuracy and precise 3D object scans.
It’s specially designed for 3D scanning medium and large objects and human body scanning, equipped with four scanning modes: features, texture, markers, and mixed, giving you great flexibility for scanning different types of objects.
It features a large 580 x 550 mm field of view making it easy for beginners to operate, and a long 280 – 1000 mm scanning distance, ideal for larger items that lower-cost 3D scanners simply can’t manage.
Additionally, the iReal 2E color 3D scanner adopts infrared structured light technologies, with key advantages across invisible light scanning, environment/material adaptability (such as performing well on human hair, dark objects or under strong sunlight), and so many more.
Above all, if you are looking for a reasonably priced 3D scanner that can handle professional applications, this could be perfect for you.
It’s powerful and with the scanning modes and large field of view, it’s also very versatile. The iReal 2E is particularly useful for:
- Human body modeling — customization and re-creation of artistic portraits, film, video, game, VR, AR and other CG character modeling, medical rehabilitation, human body parts customization
- Art and design — medium and large-sized sculptures, cultural relics, college art training, clothing design, creative design, and derivative product development, etc
- Reverse engineering — castings, forgings, sanitary ware and other products with low precision requirements
- 3D printing
Shining 3D EinScan-SP
- Price: $2,599 — Available on Amazon worldwide here / Available on Dynamism Store here
- Scan range: single scan – 200 x 150 mm / max scan range – 1200mm³
- Accuracy: single-shot accuracy under 0.
 05 mm
05 mm - Speed: single shot speed of under 4 seconds
Having included the EinScan-SE, we had to also include its bigger brother, the EinScan-SP, as they’re both such standout 3D scanners. It’s not as cheap, and in fact, $2,500 is a lot of money, but compared to some industrial 3D scanners that can cost $50,000 plus, it’s comparatively inexpensive!
Whereas the EinScan-SE is accurate to 0.1mm, the SP is accurate to 0.05mm, an astonishing level of precision. This will result in clean, accurate and crisp 3D scans that can in turn be made into stunning 3D prints.
Additionally, it can scan larger objects, up to 120 x 120 x 120 cm, so unless you need to scan entire rooms or cars, you should definitely have enough space with the EinScan-SP.
What Makes A Good Cheap 3D Scanner – Buyer’s Guide
Portable
A handheld and portable cheap 3D scanner allows for more freedom of movement to capture scans of all shapes and sizes, even those located in hard-to-reach places. Better yet, a scanner that works in both stationary and handheld modes offers the best of both worlds. Furthermore, portability usually means lightweight, making scanning more manageable and less of a strain when capturing an object from multiple angles.
Better yet, a scanner that works in both stationary and handheld modes offers the best of both worlds. Furthermore, portability usually means lightweight, making scanning more manageable and less of a strain when capturing an object from multiple angles.
Resolution
Resolution determines the quality of the 3D model obtained after scanning an object. Around 1 mm to 2 mm is a good starting point, but go lower if possible; ideally, about 0.3 mm to 0.5 mm to give you the best possible results on a budget. You’ll find cheap 3D scanners like the Matter & Form V2 3D Scanner drop to as low as 0.1 mm, but these tend to carry a higher price tag.
Scan Volume
This determines the size of the maximum scannable area you can capture in one go. Lean towards cheap 3D scanners with large scan volumes if you plan to make full-body scans as these reduce the number of angles you’ll need for a complete scan.
Ease of Use
Though the technology behind 3D scanners is relatively complex, the actual scanning process doesn’t have to be. Look for scanners with one-touch scanning, multiple optimized modes, and user-friendly accompanying software.
Look for scanners with one-touch scanning, multiple optimized modes, and user-friendly accompanying software.
Export File Formats
A good cheap 3D scanner needs to offer the ability to export scans to file formats that will be useful to you and compatible with CAD software. STL, OBJ, and PLY are generally available on most budget 3D scanners but check beforehand if you need a less standard format.
What You Can Do With a Cheap 3D Scanner – Uses and Applications
- Education and Schools – For developing 3D CAD modeling skills, design lessons, and general STEM education.
- 3D Printing – Scan real-world objects and convert them into 3D printed objects. Especially useful for those that don’t want to create 3D models from scratch in CAD software.
- Design – Rough, rapid prototypes based on real-world objects.
- 3D Room Scans – Renovation, digital real estate house viewings, interior design.
- AR and Animation – game development, app development, digital art.
FAQ
Which Is the Best Cheap 3D Scanner?
Revopoint POP is one of the most versatile cheap 3D scanners, thanks to both stationary and handheld modes, along with the tripod and turntable that ships alongside the scanner.
Among the best cheap stationary 3D scanners for objects, the Matter & Form V2 3D Scanner is a solid option offering high-quality scans thanks to an excellent 0.1 mm accuracy and fast scan speeds.
If you’re looking for pure value and the lowest price, nothing beats the cost-effective offering of the BQ Ciclop.
Lastly, if you need a scanner capable of higher quality results, the Shining 3D EinScan-SE is a value-packed professional 3D scanner at a mid-range price.
Who Makes the Best Low-Cost 3D Scanners?
Shining 3D is among the best 3D scanner manufacturers, as exemplified by the excellent EinScan-SE. If we drop in price, Revopoint’s versatile POP 3D scanner is largely unmatched when it comes to bundling a broad range of scan options into a lightweight, compact, and affordable device. Also worthy of mention is XYZprinting and their 3D scanner range, notably the refreshed and updated XYZprinting Handheld 2.0, which offers excellent resolution at a great price.
If we drop in price, Revopoint’s versatile POP 3D scanner is largely unmatched when it comes to bundling a broad range of scan options into a lightweight, compact, and affordable device. Also worthy of mention is XYZprinting and their 3D scanner range, notably the refreshed and updated XYZprinting Handheld 2.0, which offers excellent resolution at a great price.
Other articles you may be interested in:
- Professional 3D scanners buyer’s guide
- DIY 3D scanner kits you can build at home
- The best 3D scanners – ranked
- Top 3D scanner apps (for iOS and Android)
3D Printing Knowledge Base
“Calibration Cubes, or How to Train a 3D Printer”
If immediately after launching FDM/FFF, the 3D printer produces arbitrary shapes that the best abstract artists would envy, do not rush to panic. Most likely, the equipment just needs to be calibrated, and we’ll tell you how to do it under the cut.
Continue reading →
"Buying a used 3D printer: how to save money and not get into trouble"
Used FDM 3D printers are a good option, especially when more capable or modern hardware is needed but the budget leaves a lot to be desired. In this article, we will share tips for purchasing 3D printers in the secondary market and tell you what you need to pay attention to before buying.
In this article, we will share tips for purchasing 3D printers in the secondary market and tell you what you need to pay attention to before buying.
Continue reading →
“Painting products after FDM 3D printing”
Nowadays, there are enough 3D printers with multiple extruders or filament switching systems, but if this is not enough, you can increase the presentability, and often the durability of 3D printed products painting. In this article, we will deal with the main points of coating and pigmentation.
Continue reading →
"Ten Interesting Hobby 3D Printing Projects"
We can talk about the possibilities of additive technologies as much as we like, but it's better to see once than hear a hundred times. Better yet, print your own! We offer a selection of interesting projects that can be implemented using a home 3D printer.
Continue reading →
Support structures in FDM 3D printing
Supports are a necessary evil: they cause a lot of inconvenience, but often it is simply impossible to get products without them, especially when it comes to 3D printing models with hinged structures. In this article, we will talk about supports - what they are, how to avoid them and what to do if you cannot do without supports.
In this article, we will talk about supports - what they are, how to avoid them and what to do if you cannot do without supports.
Continue reading →
"Best 3D Printers of 2022"
Today's additive market is saturated with all kinds of 3D printing equipment, and sorting through all this variety can be very difficult. We have prepared a list of a dozen of the most interesting, in our opinion, FDM and photopolymer 3D printers for amateurs and professionals.
Continue reading →
FDM 3D Printer Basics
Thinking about buying a 3D printer and don't know where to start? Then you are welcome under the cat: in this article we will try to explain as clearly as possible what FDM 3D printing is and how to work with FDM 3D printers.
Continue reading →
"How to deal with deformations in 3D printing"
Any production process that involves cooling polymers or metals will be accompanied by shrinkage of materials, whether it is plastic injection molding, metal casting or 3D printing. In this article, we will share tricks to help combat the unwanted effects of shrinkage - deformation, cracking and peeling off.
In this article, we will share tricks to help combat the unwanted effects of shrinkage - deformation, cracking and peeling off.
Continue reading →
“How to clean the nozzles of FDM 3D printers”
The nozzle is one of the simplest and at the same time the most critical parts of an FDM 3D printer, since the ability of the equipment to lay material depends on the correct operation of the nozzle. In fact, everything is not so simple: a lot depends on the material from which the nozzle is made, the filaments used, the operating temperature, the shape and even the diameter. In addition, the nozzles are often clogged. In this article, we will figure out how to correctly identify problems and take care of a small but important detail.
Continue reading →
"Top Ten Parameters of FDM 3D Printing"
In the last article, we talked about the best 3D printing software in 2022. Today we will talk about preparing a 3D model for printing. Slicers are used to prepare 3D models for 3D printing. These programs not only convert digital models into machine code, but also allow you to adjust all the parameters of the FDM 3D printers. The key settings will be discussed in this article.
Today we will talk about preparing a 3D model for printing. Slicers are used to prepare 3D models for 3D printing. These programs not only convert digital models into machine code, but also allow you to adjust all the parameters of the FDM 3D printers. The key settings will be discussed in this article.
Continue reading →
"Best 3D printing software in 2022"
3D printing is a multi-step process, because you first need to design a 3D model, check it for errors, convert it to machine code, and only then into it's a 3D printer. In this article, we will share examples of programs that can help at every stage of preparatory work and directly during 3D printing.
Continue reading →
"G-Code Basics: Basic Command Reference for FDM 3D Printers"
G-code or Gcode is machine code, that is, a sequential set of commands for 3D printers generated by slicers. At the same time, the G-code often has to be edited manually if the slicer does not have the appropriate functionality or the user simply needs to change the behavior of the 3D printer. In this article, we will share a list of the most widely used commands.
In this article, we will share a list of the most widely used commands.
Continue reading →
Getting Started with FDM 3D Printing: A Beginner's Guide
Especially for those who are just starting to comprehend the basics of 3D printing, we offer a selection of useful tips to solve the most common problems when working with FDM 3D printers.
Continue reading →
"The best programs for 3D modeling for 3D printing"
the most popular free and commercial programs of different levels of complexity and functionality.
Continue reading →
"The most popular slicers for FDM 3D printing and more"
What is a "slicer"? This is a program that converts digital 3D models (usually in STL, OBJ, or M3F formats) into machine code (G-code), a series of commands that a 3D printer understands. Do not even try to make the 3D printer figure out what is required of it from the 3D model. Instead, use one of the solutions on our list, especially since most of them are free.
Instead, use one of the solutions on our list, especially since most of them are free.
Continue reading →
"PrusaSlicer: overview of the program, functionality and basic settings"
PrusaSlicer is a free, feature rich slicer from Prusa Research based on the Slic3r system by Alessandro Ranellucci. The slicer was originally called Slic3r PE (Prusa Edition), but as it moved more and more away from the source, Prusa officially renamed it in May 2019 to avoid confusion. Since then, PrusaSlicer has continued to evolve and be updated every few months.
Continue reading →
"Who and how makes money on 3D printing"
Are you ready to make money with direct hands and a 3D printer? Okay, but before diving head first into the business, it would be nice to understand exactly how 3D printing is changing the face of the industries around us in order to find its niche. Let's watch.
Continue reading →
"The Best Professional Storage Solutions for 3D Printing Plastics"
3D printing results.
Continue reading →
"PEEK: how to print, characteristics and properties"
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK, PEEK) is a special polymer with outstanding properties, which in some cases can replace metals, for example in the production of aircraft parts or implants.
Continue reading →
“How to properly (and not) dry filaments for 3D printers”
As we found out in the previous article, the best option is not to let the filaments absorb moisture at all, but in practice this is almost unrealistic. So, before 3D printing, it is advisable to play it safe and start drying the plastic. We'll talk about this under the cut.
Continue reading →
“Post-processing of 3D FDM printed products”
In most cases, 3D printed models do not need post-processing, but this applies mainly to functional products. In many cases, surfaces are required to be processed to a finished look using various tools, and in this article we will look at the basic techniques.
In many cases, surfaces are required to be processed to a finished look using various tools, and in this article we will look at the basic techniques.
Continue reading →
"The most common extrusion 3D printing problems and solutions"
FDM/FFF A 3D printer is a complex machine, and plastics for 3D printing can vary greatly in properties. As a result, it may be difficult for a novice user to identify the causes of defects in printed products. Especially for such cases, we have prepared a guide with a list of the most common problems and solutions.
Continue reading →
"How to properly store 3D printer filaments"
When it comes to storing 3D printing plastic, it's better to be safe than sorry. If you protect filaments for FDM 3D printers from moisture and dirt, you can count on better and trouble-free 3D printing, and this is not at all difficult to do. We tell you how and why.
Continue reading →
"Resin 3D printing in industry"
In this article, we will look at the industrial use of extrusion 3D printing technologies with polymers and composites. No whistles and gnomes, only serious application!
Continue reading →
"Top 10 3D Model Sites for 3D Printing"
If you already have a 3D printer and 3D printing plastic, all you have to do is find digital models. Do-it-yourself 3D modeling is interesting, but mastering this skill will take a lot of time. In the meantime, we suggest looking for something interesting on the sites in our selection.
Continue reading →
Selecting Plastic for 3D Printing: A Guide to REC Materials and Applications
This article collects basic information on commercial 3D printing plastics and composites under the REC brand.
Continue reading →
REC Multi-Material 3D Printing Guide
Especially for those who practice 3D printing of composite products and soluble supports on FDM 3D printers, we have prepared a handy guide to help predict results in terms of adhesion and shrinkage when working with two different materials at the same time.
Continue reading →
"Composite materials for 3D printing"
Over the past few years, the intensive development of additive technologies has allowed the introduction of 3D printing in most industries, and this, in turn, has led to new requirements for 3D printers and the emergence of brand new, customized consumables. The expansion of the line of consumables mainly affected the most popular and affordable 3D printing technology — FDM/FFF.
Continue reading →
"Adhesion and 3D printing: everything you need to know"
@media screen and (min-width: 991px){ .mobil{ display: none; } Many 3D printer owners experience parts coming off the table during 3D printing. Let's take a look at the causes and solutions.
Continue reading →
"X-Line UltraX - printing parameters, characteristics and material properties"
UltraX is an engineering thermoplastic capable of withstanding high loads. This composite material is based on structural polyamide-6 filled with short carbon fibers.
This composite material is based on structural polyamide-6 filled with short carbon fibers.
Continue reading →
"PETG Biocide - material description, print settings and properties"
REC Biocide PETG is a special composite material that has disinfecting properties due to additives in the form of special nanoparticles distributed over the polymer matrix.
Continue reading →
"X-Line FormaX - print parameters, material properties and tips"
Formax is an engineering thermoplastic based on ABS with the addition of carbon fibers (up to 15%), capable of withstanding heavy loads and high temperatures.
Continue reading →
“Flex to flex: what are flexible filaments and how to work with them on a 3D printer”
Flex is just a general name for 3D printing materials with a characteristic flexibility. This group includes a variety of filaments with a wide variety of compositions, so disputes on the topic “which flex is better” are often meaningless. We decided to approach the practical side of the matter and collect in one article useful information on the options that are produced under our brand, that is, REC, and at the same time explain how to work with them.
We decided to approach the practical side of the matter and collect in one article useful information on the options that are produced under our brand, that is, REC, and at the same time explain how to work with them.
Continue reading →
REC PP+: print parameters, features and properties
REC PP+ is a modified polypropylene filament that allows you to print strong and durable products with high chemical and impact resistance. Continue reading → Main advantages and disadvantages of REC PP+ Polypropylene is one of the most common polymers due to a number of positive characteristics. This polymer is non-toxic and has a low specific gravity (with the same volume, polypropylene is about a third lighter than the popular PLA plastic), excellent resistance to abrasion, shock loads and mechanical...
"PVA - print parameters, characteristics and properties"
REC PVA is a special filament capable of facilitating the 3D printing of complex parts. It is a specialized support material that is soluble in water and does not require mechanical processing.
It is a specialized support material that is soluble in water and does not require mechanical processing.
Continue reading →
«REC Friction: printing parameters, characteristics»
REC Friction is a structural composite in the form of a wear-resistant glass-filled filament based on polyamide-12.
Continue reading →
"5D printers, description, features, types"
A five-axis 3D printer or 5D printer is the next generation of conventional 3D printers. Their difference is that they have five axes of mobility, which means many new possibilities in printing.
Continue reading →
"PMMA-plastic (REC Cast): printing parameters, properties and characteristics"
REC Cast is a specialized material designed for 3D printing of burnt foundry master models.
Continue reading →
"TPU plastic (REC Easy Flex): how to print, characteristics and properties"
TPU filament (REC Easy Flex) makes it possible to print flexible, elastic and durable TPU parts.
Continue reading →
"Flex plastic: how to print, characteristics and properties"
REC Flex is a material that resembles hard silicone in performance and is suitable for the manufacture of durable flexible parts suitable for outdoor use.
Continue reading →
"REC Rubber: print settings, description and specifications"
synthetic rubber filament.
Continue reading →
"ASA (REC Eternal): description, advantages, printing options"
Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA, ASA), offered by our company under the name REC Eternal, is a close relative of ABS plastic, but with a number of advantages, the most important of which is the possibility of long-term operation in the open air.
Continue reading →
«HIPS: description, printing parameters, storage and post-processing of the material»
In modern industry, polystyrene is one of the most common polymers used in the production of household appliances, household supplies, packaging and containers, including food. In 3D printing, polystyrene plays another important role as a support material for the popular ABS plastic.
In 3D printing, polystyrene plays another important role as a support material for the popular ABS plastic.
Continue reading →
"PLA plastic: characteristics, print settings, tips"
Polylactide (PLA, PLA) is a biopolymer that is very popular among 3D printing enthusiasts for two main reasons.
Tags: PLA plastic
Continue reading →
"PETG: material overview, 3D printing settings and troubleshooting tips" wide temperature range of application (from -40°С to +70°С). The letter G in the name means that the material has been modified with glycol to prevent crystallization and maintain transparency when cooled.
Continue reading →
"ABS plastic: characteristics, advantages and printing parameters"
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS, ABS) is one of the most popular materials for 3D printing due to its relative cheapness and a successful combination of physical, mechanical and chemical characteristics.
Continue reading →
"How to print on a 3D printer from a computer, flash drive and Wifi"
There are many different ways to transfer information, namely uploading your 3D model to a 3D printer. We will tell you what types of downloads are available and how to use them. Types of printing: from a computer via a USB cable from a flash card / usb flash drive via Wi-Fi via local network
Continue reading →
3D printing test models
Test models for 3D printers are required for: When you bought a new printer and need to test it on your favorite materials When you have purchased new material and need to check the print specifications When you have been using the material for a long time, but do not know its strength limits We will talk about the 8 models most used for testing in 3D printing. 1. 3D Benchy 3D Benchy is one of the most popular 3D printer test models. The boat figurine perfectly demonstrates the capabilities of FDM printers in any price category. Such a model will help you exactly...
The boat figurine perfectly demonstrates the capabilities of FDM printers in any price category. Such a model will help you exactly...
"Filament storage"
3D printer filament requires special storage conditions. For the most common PLA, ABS, PETG and TPU filaments, the main requirement for storage is the absence of moisture. Also important is the absence of dust and solid particles during storage of the thread. Let's take a closer look! What's So Dangerous About Humidity? Most materials used in FDM 3D printing can be considered hygroscopic, meaning that they absorb water molecules rather than repel them. This does not mean that the plastic filament will act like a sponge, but if you leave it on...
"Drying Plastic"
All 3D printing plastics are hygroscopic (they like to absorb moisture) and therefore must be dealt with. It is advisable to store the filament in closed and airtight packages, then it is less likely that they will absorb moisture and stop printing well. If, nevertheless, the plastic was stored without packaging, then most likely it will need to be dried before printing. How can you tell if plastic is wet? Most often, the signs are the same for different plastics: When the plastic comes out of the heated nozzle and the sounds of bursting bubbles are heard Strange outer surface, on...
If, nevertheless, the plastic was stored without packaging, then most likely it will need to be dried before printing. How can you tell if plastic is wet? Most often, the signs are the same for different plastics: When the plastic comes out of the heated nozzle and the sounds of bursting bubbles are heard Strange outer surface, on...
3D printing technologies for metal casting / 3D printing / Services:
Share:
Source
About casting
The end product of foundry production is castings - future parts or blanks. Their mass can range from a few grams to several hundred tons.
This is how it is done in a machine tool factory.
The following features of the use of casting in production can be distinguished:
- the ability to obtain products with a mass of several grams to hundreds of tons, with complex geometry and various mechanical and operational properties;
- the possibility of obtaining products whose materials or dimensions make it impossible or unprofitable to create them by other methods;
- castings are as close as possible, in size and shape, to finished products, in contrast to blanks obtained by volumetric hot stamping or forging.

Comparison with conventional technology
In the traditional casting process, the master model can be made by hand or by machining. Some forms cannot be implemented manually. For the manufacture of master models, five-axis CNC machining centers are used, which significantly increases the possible variety of shapes, but the cost of such a stencil or master model increases markedly. This way of obtaining a casting is relevant for mass production; in small and medium series, it is most often not economically feasible - here the use of 3D printing is more rational.
The graph of the dependence of the cost of the model on the number of copies produced shows the effectiveness of the use of additive technologies.
Algorithm of the casting process using additive technologies
One of the tasks facing the technologists of any foundry is to minimize labor-intensive operations for the machining of workpieces. It is solved by the fact that the castings should be as close as possible to the parameters of the required part, which also saves money and time. Here, innovations come to the rescue, in the form of additive technologies, which allow speeding up the technical process, bypassing the traditional first steps in casting manufacturing technology. The manufacturer can obtain the required casting model or mold in one operation.
It is solved by the fact that the castings should be as close as possible to the parameters of the required part, which also saves money and time. Here, innovations come to the rescue, in the form of additive technologies, which allow speeding up the technical process, bypassing the traditional first steps in casting manufacturing technology. The manufacturer can obtain the required casting model or mold in one operation.
In the red area - the traditional casting process, in the green and blue - casting using additive technologies - production time is reduced by 2-6 times.
Direct printing of a product, which is already implemented in many modern industries, is more expensive than traditional casting from an economic point of view. Therefore, 3D printing of models for melting and burning, as well as the synthesis of molds and cores ready for casting, is of particular interest.
AM injection molding is more cost effective than direct printing.
Applications
3D-printed master models and injection molds are used in jewelry factories, in the production of dental and orthopedic products, in design offices, for R&D, in training centers and prototyping centers.
Geometrically complex castings resulting from the use of additive technologies are used in film and television, where unusual props of complex shape are required to be quickly produced.
The 007 Aston Martin 1960 DB 5 model for the movie “Coordinates: Skyfall” was created using additive technologies to preserve the original car in stunt scenes.
Decorations cast using sand molds printed on a 3D printer.
3D printers and 3D printing technologies for foundry models
To obtain injection models, 3D printing is used using FDM (FFF), SLS, SLA, DLP technologies. These technologies make it possible to print the necessary model for subsequent melting or burning out of the injection mold formed around it. Wax is used for investment models, PMMA, CAST plastic and special photopolymers are used for burnt models.
These technologies make it possible to print the necessary model for subsequent melting or burning out of the injection mold formed around it. Wax is used for investment models, PMMA, CAST plastic and special photopolymers are used for burnt models.
The main advantage of using such a solution is the absence of the need to prepare special equipment, such as molds, and the low ash content of materials during burnout. The prepared 3D model is immediately sent to print and, after a little post-processing, is ready for use.
FDM (FFF): layer by layer welding
A 3D printing method widely known to professionals and amateurs of additive technologies that does not require additional description.
The filament material for FDM printing of burnt-out models is a special plastic or a composite with a high wax content.
Principal device FDM (FFF) - printer.
FDM 3D printing process.
PICASO 3D Designer X
PICASO 3D Designer X is a 200x200x210 mm FDM printer that can print materials such as ABS, PLA, HIPS, PVA, ULTRAN 630, ULTRAN 6130, ASA, ABS/PC, PET , PC, FRICTION, CAST, RELAX, ETERNAL, FLEX, RUBBER, SEALANT, PETG, AEROTEX, CERAMO, WAX, SBS, SBS PRO, PROTOTYPERSOFT, PRO-FLEX, TOTAL PRO, NYLON and PEEK at speeds up to 100 cm³/h and with a layer thickness of 10 µm.
SLS – Selective Laser Sintering
It is used for the manufacture of master models of complex shapes, moderate accuracy and relatively large dimensions.
How it works: in a working chamber filled with an inert gas such as nitrogen, a roller rolls polystyrene powder with a particle size of 50-150 microns onto the platform. The new layer is sintered with a CO2 laser (with a temperature of 100-120 °C) along the section of the “body” of the CAD model. Further, the working platform is lowered by 0.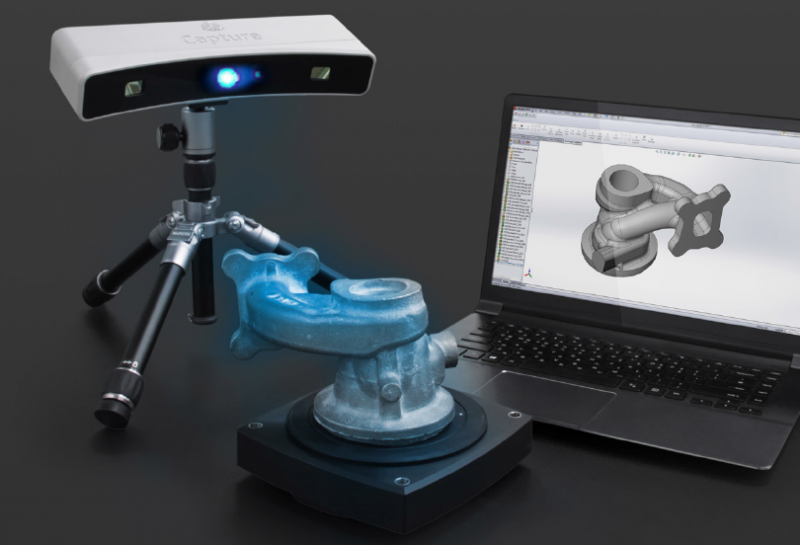 1-0.3 mm, after which the next layer is printed.
1-0.3 mm, after which the next layer is printed.
Basic structure of the SLS printer.
The printed model does not require support, because the material itself - the surrounding powder - serves as a support. Unused material is reused.
The model obtained on such a printer is filled with mold material, from which it is then burned out in a roasting oven. During burning, combustible gases are released, which must be neutralized. There is a danger of clogging the mold with the ash of a burnt-out model, therefore, materials for its manufacture are taken with a low ash content, in hundredths of a percent.
Left - 3D printed polystyrene, right - cast aluminum
Sentrol SS600G
Sentrol SS600G - SLS 3D printer with a build area of 600x400x400 mm, printing at a speed of 26 cm³ / h, with an accuracy of 300 microns in XY and from 250 in Z.
SLA - Stereolithography Laser Apparatus
The printing process is similar to SLS, only instead of powder material - liquid. The UV laser acts on the material, which cures selectively and in layers.
Photosensitive resins and photopolymers are used as the material. The working platform is lowered or raised (depending on the location of the light source) and the liquid is polymerized by a laser at given points. Unused liquid material, as in the case of powders, can be reused for printing subsequent models.
SLA 3D printing process.
The resulting models have a high surface quality, which eliminates the need for further machining.
Plastic stereolithographic models of water jet impellers (top left), wax models made from them (bottom left) and finished metal casting (right).
Left - SLA model, right - cast in silver.
Zrapid iSLA1100
The Zrapid iSLA1100 laser 3D printer prints objects up to 600x1000x1000 mm at a speed of 100~230 grams/hour.
DLP - Digital Light Processing
To cure the photopolymer, a DLP projector on DMD chips is used. This is the main difference from SLA technology, which uses a UV laser. Another difference is that the entire layer is projected, all the pixels at the same time, and not drawn by a laser beam, which speeds up the process.
DMD chip with two micromirrors.
Models printed with this printer require support removal and UV treatment. That is, post-processing for models obtained using this technology does not differ from those that are printed using SLA technology.
DLP printing process.
DLP projector “spot” of light, depending on the specific layer being printed.
DLP printing produces a model faster but with a less smooth finish than an SLA printer.
SLA (left) and DLP (right).
Detail difference between SLA printing and DLP printing.
FlashForge Hunter DLP
FlashForge Hunter DLP is a DLP printer with a layer thickness of 25-50 microns and a print area of 120x67.5x150 mm.
Printed model and finished product made with FlashForge Hunter DLP printer.
Voxeljet
Voxeljet is a method of layer-by-layer bonding of plastic powder or sand, developed by the German company of the same name. Its analogue is Binder Jet, it works only with sand.
Such 3D printers appeared as a result of a combination of MJ and SLS technologies. Using PMMA as a material, it is possible to obtain burn-out models. PMMA - polymethyl methacrylate, if it is simpler - crushed plexiglass with a fraction of 85 μm. The printhead lays a layer of powder with a thickness of 100 to 150 microns on the working platform. Next, a binder is applied, on top of which a layer of powder is again laid. So the process is repeated until the complete production of the required model. In the case of sand, we get an injection mold.
PMMA - polymethyl methacrylate, if it is simpler - crushed plexiglass with a fraction of 85 μm. The printhead lays a layer of powder with a thickness of 100 to 150 microns on the working platform. Next, a binder is applied, on top of which a layer of powder is again laid. So the process is repeated until the complete production of the required model. In the case of sand, we get an injection mold.
As with SLA technology, the Voxeljet model is suitable for precision casting.
PMMA castings, no post-processing.
Voxeljet VX 1000
Voxeljet VX 1000 provides 1060 x 600 x 500mm print area, 100µm layer thickness, 0.3% accuracy and vertical speed up to 36mm/hr.
3D mold printers
You can quickly get a high-quality casting mold using Binder Jet and SLS technologies. 3D printers using these technologies print molds from special foundry sand.
3D printers using these technologies print molds from special foundry sand.
Binder Jet technology - binder application
This technology allows you to print a sand mold with a complex geometry without any additional processing. After printing, you can immediately start casting. The main advantage of Binder Jet technology is that there is no need for any special conditions for the operation of such a printer: printing is possible at room temperature.
Binder Jet printing process.
The material, in this case sand, is spread over the working platform by means of a roller. Next, the print head applies a bonding adhesive on top of the powder. The platform is lowered through the thickness of the model layer and the object is formed where the sand is associated with the liquid (i.e. glue). The unused material, by analogy with SLS technology, is a support for a future model.
Printer principle with Binder Jet technology.
Binder Jet printed molds.
Sentrol SB1000
Sentrol SB1000 3D printer prints using Binder Jet technology with layer thickness from 100 microns, XY accuracy from 0.0625 mm and model size up to 120x67.5x150 mm.
SLS mold printing
The main difference from the previously mentioned SLS technology is the use of foundry sand pre-clad with a polymer as a printing material. The material is laser sintered and then cleaned. The resulting form is placed in a calcining oven for curing, which takes place at a temperature of 300-350 ° C. The main difference from the Binder Jet is the higher detail of the finished mold. True, it takes more time to get the finished form, due to the need for additional processing.
True, it takes more time to get the finished form, due to the need for additional processing.
Solar 3D printing
By the way, there is another interesting sand printing technology - Solar Sinter. It was developed by a German engineer, designer and artist Markus Kaiser. Solar 3D printing is great for creating sand molds, albeit very low precision.
If you're going to print in the desert, you'll need to bring an office. Markus Kaiser offers a pyramid tent with a reflective coating - an excellent shelter from the hot sun.
If your business is located in the desert, this is the best option - sand and sunlight are all around, which are available on a standard nine-hour shift. You only need to bring your own printer with a computer. The printer is equipped with a Fresnel lens, which concentrates sunlight into a beam, which makes it possible to melt sand with a temperature of 1400-1600°C; a solar tracker that tracks the position of the sun and rotates the lens towards it; and photocells to power the electric drives of the installation. The main plus is saving on electricity, materials and rent of premises. But even more important, perhaps, is the concept.
The main plus is saving on electricity, materials and rent of premises. But even more important, perhaps, is the concept.
The process of printing on a solar 3D printer.
Such a printer, both due to the specifics of the application and due to the low accuracy of the resulting models, can hardly be used for industrial needs. But for artists and artisans, it will be a real find. Printing injection molds on it is perhaps a dubious occupation, but art objects are the very thing.
Removing the model from the working area of the solar 3D printer is done using a tablespoon. You can use a plug, but the speed will be slower.
Seriously, who knows where technology will go next? Sometimes crazy projects open up new possibilities.
Total
The introduction of 3D printing makes the casting process cheaper and faster, makes it possible to manufacture models and molds for casting with complex geometry and various dimensions, without losing the accuracy of the resulting casting.