Science 3d printer
Future of 3D Printing in Science Laboratories
When it comes to inventions that sound like science fiction, it doesn’t get more futuristic that 3D printing technology. Whilst 3D printing can sound like little more than a gimmick, its potential to change the world of scientific research is enormous. From bioprinting organs to printing t-shirts that will stop a bullet, the equipment for creating huge scientific advancement has never been so widely available as it is today.
- Changing Science with 3D Printing
- Advancing Medical Printing
- 3D Printing: What Next?
Hardware for the Price of Software
When it comes to setting up a science lab, something that discourages ambitious DIY scientists is the prohibitive cost of equipment. However, these barriers are being broken with the increasing availability of 3D printers, which can create equipment from designs shared online. One of the most popular 3D printers, the RepRap costs less than £1,000 and can reprint more versions of itself. These can then be used to create lab equipment that was previously far too expensive for individual scientists or small labs to purchase.
A centrifuge, for example, is pretty much essential for even the most basic lab experiments, yet to purchase one from the manufacturer can cost more than £10,000. Using a 3D printer and a free design from an open source hardware database, labs can now create several for a fraction of the cost to purchase one.
Scientists are now creating innovative designs for lab equipment that can be sold online and printed out affordably. This will make it possible to equip schools and third world labs with equipment that would never otherwise have been available to them, increasing opportunities for scientific advancement.
Rapid Prototyping
Widening availability of 3D printing is also revolutionising the production of prototypes, which used to cost thousands of pounds at each stage of development. Now, a designer who owns a 3D printer can print out prototypes at each stage, discovering what works and what doesn’t, at a small fraction of the cost.
Now, a designer who owns a 3D printer can print out prototypes at each stage, discovering what works and what doesn’t, at a small fraction of the cost.
Open source sharing sites allow teams to create new designs built out of printable parts that are available online, or to modify existing designs to achieve a different function. As 3D printing becomes more available, this kind of trial and error design will be possible in schools, in DIY labs, in people’s bedrooms, removing many of the barriers to innovation. 3D printing is likely to change the way we develop products and ideas forever.
Advancing Medical PrintingBespoke Cells and Organs
Some of the most exciting advancements in 3D printing are happening in the field of bioprinting. Scientists have successfully created 3D-printed liver cells that are able to function for more than 40 days. Whilst these cells are currently being used to test new pharmaceuticals, the advancement suggests we are on target to achieve 3D-printed organs within the decade, as experts predict.
In addition to liver cells, scientists have also successfully printed sheets of cardiac tissue and stem cells that can reproduce different kinds of human tissue. Similarly, a prototype for bioprinting cartilage has already been created, suggesting we are mere years away from being able to replace everything from an ear to an entire heart.
Surgical Tools
Bioengineering scientists have also had success in designing and 3D printing surgical tools, and other medical equipment. Bioengineering students from the University of British Columbia, for example, won a prestigious prize for a 3D-printed surgical smoke extractor they had designed. More basic tools, such as forceps and clamps, can also be 3D printed, with the added advantage of coming out of the printer sterile and costing just one tenth of their stainless steel equivalents.
Patch Repairs
As well as printing the tools for surgery, advancements in 3D printing are moving towards also providing the materials. Human cell heart patches, to repair heart tissue, have successfully been tested on rats. Additionally, artificial cardiac tissue that mimics the mechanical and biological properties of the human heart have also been successfully tested at this level. This use of 3D printing provides the hope of enormous medical advancement in the near future.
Human cell heart patches, to repair heart tissue, have successfully been tested on rats. Additionally, artificial cardiac tissue that mimics the mechanical and biological properties of the human heart have also been successfully tested at this level. This use of 3D printing provides the hope of enormous medical advancement in the near future.
Eliminating Organ Donors
One of the most exciting future possibilities of the medical advancements in 3D bioprinting is a world without organ donors. Researchers suggest we are likely to see the technology for printing complete workable organs within the next 10 years. This would mean that people who require lifesaving organ transplants will no longer have to wait for a suitable donor. Instead, the required organ will simply be printed out to meet their specifications.
With huge advancements being made in the development of artificial tissue, these organs could be tailored to match their recipient biologically, preventing the body from rejecting the new organ. This will be a major milestone in modern medicine’s ability to treat illnesses and save lives.
This will be a major milestone in modern medicine’s ability to treat illnesses and save lives.
Innovative Materials
From human stem cells to graphene, a substance 100 times stronger than steel, the materials that are suitable for 3D printing are becoming more diverse. Combining these innovative materials with 3D printing technology opens up the possibility of creating products beyond our wildest imagination.
Take graphene, for example, which is incredibly strong, but also flexible and transparent. Using 3D printing technology, it could be possible to create a bulletproof graphene outfit for professions such as the police which perfectly fits its wearer’s body.
Beyond simply printing customised organs, it may be possible in the future to create biological materials which release medication over time, directly targeting the problem area. Uses for these kinds of materials, combined with 3D-printed technology are infinite, and they have the potential to completely change the world as we know it.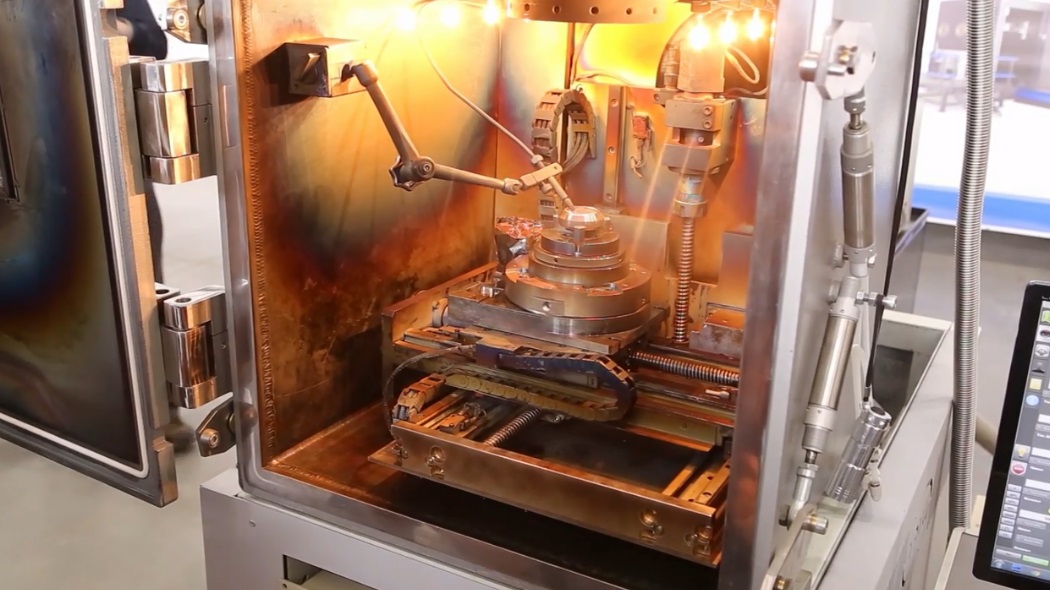
InterFocus is a leading team of research suite suppliers and fitters. If you want more information about redesigning or fitting a laboratory, visit our homepage or call us on 01223 894 833.
Science best 3D printer models・Cults
6mm modern/sci fi army (Global Protection Agency)
€5
6mm modern/sci fi army (Brotherhood of MAD)
€5
buck rogers belly bomber
€9
Set of 3 Science Laboratory cookie cutters STL files
€2.76
heart DNA (big version)
€1
Heart DNA
€0.70
Junk Cart
€7
Deadly
Free
Sci-Fi Industrial Utility Cart
€2. -25% €2.07 75
75
Sci-Fi Crate
Free
Quantum Beacon (Ant-man and the Wasp: Quantumania)
€6.49 -20% €5.19
Ruesis combat robot (17) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Hidos combat robot (15) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€2.90
Hedon combat robot (11) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Wakldir combat robot with pilot (18) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€2.90
Cudmos scorpio combat robot (16) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€2. 90
90
Amus combat robot (14) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Thelstus combat robot (13) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Phydon combat robot (12) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Oveyar combat robot (10) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Childir combat robot (9) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Unos combat robot (8) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€2.90
Cistia combat robot (7) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€2.90
Munos combat robot (6) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€2. 90
90
Rhistus combat robot (4) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€2.90
Tuhbium combat robot (5) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€2.90
Imperium Faction Barricade for Kill team
€3 -20% €2.40
Fumenar combat robot (3) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Isarus combat robot (1) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€2.90
Mobile satellite guidance antenna turret (6) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Rocket turret with four quadruple baskets (5) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1. 90
90
Robotic turret with double ion cannons (4) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Ion gun turret with shield (3) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.50
Wybus dinosaur combat robot (2) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Turret with double laser cannon and missile launcher (2) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Supercharged machine gun turret (1) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€1.90
Usg Ishimura
€27.02 -15% €22.96
Graze Death Hound Custom Part Set
€3. 75
75
Custom Computer and Chairs for 3.75in & 6 Star Wars and Sci-Fi Diorama
€3.99
Gothic Sci Fi City Scatter Terrain Pack A
€5.07
Mercurialis spaceship (40) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€2.90
Agelastus spaceship (39) - Future Sci-Fi SF Post apocalyptic Tabletop Scifi
€2.90
Great Harbinger of Lust
€16.59
Pantherturm Style Bunker
Free
Enforcer APC
€14.42
Cursed Earth Judiciary Enforcers
€11.66
SPACE ZOMBIE ROBOTS - OBSIDIAN DESTROYER - 28MM MINIATURE - TABLETOP WARGAME
€5
3" cube Sci-fi modular terrain 9 - 3x3 pieces
Free
ADAPT AND CREATE A MODULAR 3D PRINTER
Please use this identifier to cite or link to this item: http://hdl.  handle.net/10995/117484
handle.net/10995/117484
| Title: | Adaptation and creating a modular 3D printer | |
| Authors: | Moshkin, G. P. Grachev, A.V. Tumanina, P.D. Aminev, T.R.0009 | Nizhny Tagil Institute of Technology (branch) of the Ural Federal University |
| Citation: | ADAPTATION AND CREATION OF A MODULAR 3D PRINTER / G. P. Moshkin, A. V. Grachev, P. D. Tumanina, T. R. Aminev. - Text: electronic // Youth and science: materials of the international scientific and practical conference of high school students, students and graduate students (May 27, 2022): in 2 volumes. - Nizhny Tagil: NTI (branch) UrFU, 2022. - Volume 1. - P. 269-271. | |
| Abstract: | This article describes the process of developing and creating a modular 3D printer, provides the information and reference materials necessary for this. A detailed analysis of the market for 3D printers with similar characteristics was carried out.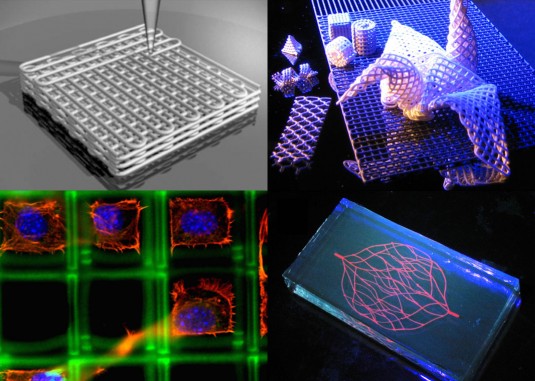 The process of development and development of additive technologies is considered, the first printing technologies are described. The text also provides the goals and objectives of the research work, describes the main structural elements of the finished printer and the development of its own components, presents a unique modular system, describes its relevance, features and prospects for possible use in industry and at home. A comparative analysis of existing belt systems, kinematics and 3D printing technologies was carried out. 3D printing is one of the most promising directions in the development of science and technology in our time. The developed modular system allows 3D printing with a wide range of different materials. It is based on the possibility of changing the carriage with extruders. The carriage can be quickly adapted to a given extruder and manufactured using FDM (Fusion Deposition Modeling) technology. Thus, the system allows 3D printing with any existing printheads of small dimensions and weighing no more than 100 g. The process of development and development of additive technologies is considered, the first printing technologies are described. The text also provides the goals and objectives of the research work, describes the main structural elements of the finished printer and the development of its own components, presents a unique modular system, describes its relevance, features and prospects for possible use in industry and at home. A comparative analysis of existing belt systems, kinematics and 3D printing technologies was carried out. 3D printing is one of the most promising directions in the development of science and technology in our time. The developed modular system allows 3D printing with a wide range of different materials. It is based on the possibility of changing the carriage with extruders. The carriage can be quickly adapted to a given extruder and manufactured using FDM (Fusion Deposition Modeling) technology. Thus, the system allows 3D printing with any existing printheads of small dimensions and weighing no more than 100 g. | |
| KEYWORDS: | 3D Printer Modular system Development 3D printer Modular 3D printer Additative technologies | |
| URI: | http://hdl.handle.net/11748484/117484000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 : | info:eu-repo/semantics/restrictedAccess |
| Conference name: | International scientific and practical conference of high school students, students and graduate students "Youth and Science" | |
| Conference Date: | 05/27/2022 | |
| ISBN: | 978-5-9544-0131-8 978-5-9544-0132-5 (t. 1) | |
| Origin: | Youth and science. - Volume 1. - Nizhny Tagil, 2022 | |
| Appears in Collections: | Conferences, seminars |
Show full item record Google Scholar
Items in DSpace are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated. nine0005
nine0005
3D printer - technology of the future
Bibliographic description:
Mikhailova, A. E. 3D printer is the technology of the future / A. E. Mikhailova, A. D. Doshina. - Text: direct // Young scientist. - 2015. - No. 20 (100). - S. 40-44. — URL: https://moluch.ru/archive/100/22467/ (date of access: 01/31/2023).
This article will focus on new technology for creating objects and objects - 3 D printer. The history of occurrence is described, the basic principles and device operation technologies are indicated. 3 D printer application in Rostov-on-Don, and highlights the problems and prospects for using this technology in different areas of life.
Keywords: 3 D printer, 3 D printing, stereolithography, SLA technology, SLS technology, DLP technology, EBM technology.
3D entered our everyday life at the beginning of the new millennium. Naturally, we associate this definition with film art or animation. But this technology covers much more spectrums of our life. So, what is a 3D printer, and what is printing on such a device? nine0005
A 3D printer is a device that creates an image in three dimensions. But first, let's take a look at the history.
Origin of
3D printing technology has been around since 1984. CharlesHull has developed 3D printing technology to create objects using digital data. In 1986, this technique was patented and given the name stereolithography.
The same company, CharlesHull, developed the first industrial 3D printer. And at 19In 1988, 3DSystem developed a 3D printer for printing at home - SLA-250.
Solidscape was founded in 1993. It starts mass production of inkjet-based 3D printers at low cost.
And finally, in 2005, the first color 3D printer appears - the Spectrum Z510. The credit for this advancement in the development of 3D printers belongs to ZCorporation (ZCorp).
The credit for this advancement in the development of 3D printers belongs to ZCorporation (ZCorp).
nine0187 Working principle 3 D printing
The principle of forming a figure from three-dimensional printing is called additive (from the word Add (English) - add). To begin with, a computer model of the future object is created. This can be done either with the help of a three-dimensional graphic editor of a CAD system (3D StudioMax, SolidWorks, AutoCAD), or by scanning the entire object in 3D. Then, with the help of a special software product, it splits the scanned object into layers and generates a set of commands that will determine the sequence in which layers of material will be applied during printing. nine0005
Further, the 3D printer forms the object in layers, gradually applying portions of the material (Fig. 1). By positioning the print head on an X and Y coordinate system, the printer deposits material layer by layer according to a simulated electronic circuit. When the platform is moved one step along the Z axis, the construction of a new level of the object begins.
When the platform is moved one step along the Z axis, the construction of a new level of the object begins.
Rice. 1. Printing with a 3D printer
For printing, metal alloys, plastic, paper, photopolymers, mineral mixtures can be used as a material in additive manufacturing. Some types of 3D printers are able to work simultaneously with different materials, both in terms of properties and color. nine0005
There are a lot of 3D printing technologies. They differ in the principle of formation of layers and their connections. Consider the main production technologies.
Core technologies (SLA, SLS, DLP, EBM, HPM)
Printing on 3D printers can be done in different ways, depending on the material used.
SLA technology. This technology allows the fastest construction of objects. The technology uses a photopolymer, on which a laser beam is directed, after which the material hardens. After hardening, the product can be easily processed (glued, painted, etc. ). nine0227 SLS technology. Represents the sintering of powder reagents under the influence of a laser beam. This is one of the technologies that allows the production of molds for metal and plastic casting.
). nine0227 SLS technology. Represents the sintering of powder reagents under the influence of a laser beam. This is one of the technologies that allows the production of molds for metal and plastic casting.
DLP technology. This is a relatively new technology that uses stereolithographic printing machines. Printers of this type use digital light processing. This technology uses photopolymer resins and a DLP projector to create three-dimensional figures. nine0005
EBM technology. This technology uses electron beam melting to create three-dimensional objects. For the layer-by-layer deposition of high-precision parts, a special material was developed - metal clay. This material is made from a mixture of organic glue, metal shavings and water.
HPM technologies. Allows the production of final models from structural and high performance thermoplastics. This is the only technology that provides mechanical, thermal and chemical strength of parts. nine0005
nine0005
Nowadays, another interesting device has appeared that is used for manual printing - pens for drawing 3D objects. Pens are made in the same way as printers. The plastic thread is fed into the pen, where it melts to the right temperature and is squeezed out through a small nozzle.
Applications 3 D printing
- Building. There is an assumption that in the future the process of erecting buildings will be much faster thanks to 3D printing. nine0253
- Medicine. Thanks to 3D printing, doctors have been able to create replicas of the human skeleton. 3D printers are widely used in dental prosthetics.
- Architecture and design. Creating layouts of interior elements, buildings and districts allows you to evaluate the ergonomics, functionality and appearance of the prototype.
- Marketing and advertising allow you to demonstrate the benefits of a new product.
 nine0253
nine0253 - Education. 3D models are excellent visual materials for teaching at all levels of education.
- Automotive. Such a method as 3D modeling allows you to test the car at the development stage.
- Modeling. Production of packaging materials, toys and souvenirs.
- Light industry. Manufacture of various elements of consumer goods. nine0253
- Manufacture of clothes and shoes. Such clothes and shoes are used only at shows. The material here is polyurethane, rubber and plastic.
- Jewelry business. 3D modeling technologies allow you to create full-fledged products from metal powder.
- History and anthropology. Models are created on the basis of archaeological finds and allow assessing the reliability of scientists' guesses. nine0253
In all other areas not mentioned above, 3D modeling is gradually finding its way. Slowly but surely, it is crowding out other ways of representing an object.
Study of using 3 D printer in city of Rostov-on-Don
We conducted a market research on 3D printing services in the city of Rostov-on-Don.
Here are the results: There are about 10 3D printing service points in this city, as well as several 3D scanning points. About 80% of customers deal with the tasks of manufacturing accessories, parts for personal projects. 8% try this technology by heart, the remaining 7% use 3D printing directly for work. Also, there is another group that uses 3D printing to create global personal projects. This group is only 5%. This percentage includes such a project as a “touching museum”. A group of students from Rostov-on-Don plans to create a network of museums in Russia using 3D printing and crowdfunding (crowd funding). The idea is to print on a 3D printer the world's works of art that can be touched not only by ordinary people, but also by those who have visual impairments. nine0005
To find out people's awareness of 3D printing, a survey was conducted among residents of Rostov-on-Don.
A different age contingent and different social groups were interviewed. As a result, according to a survey of 348 people, data was obtained: many residents (92%) are aware of the existence of 3D printing. Young people under the age of 30-35 are more aware in this area. Older residents of the city, if they know about such technology, do not dare to try it. Only 19% of the population knows that 3D printing exists not only from plastic, but also from metal. 45% of respondents are aware of the capabilities of a 3D printer and printing materials. But at the same time, only 15% of respondents used this service at least once in their lives, of which 3% used it often. Which suggests that 3D printing is not yet in great demand. But 80% of those respondents who had not heard of 3D printing became interested in this technology and expressed their desire to learn more about this technology. About 51% of respondents had heard of a 3D pen, but the majority had not used it. But quite a lot of people are ready to entrust their lives to new technologies. 50% of those surveyed would trust their lives to such technology. nine0005
Young people under the age of 30-35 are more aware in this area. Older residents of the city, if they know about such technology, do not dare to try it. Only 19% of the population knows that 3D printing exists not only from plastic, but also from metal. 45% of respondents are aware of the capabilities of a 3D printer and printing materials. But at the same time, only 15% of respondents used this service at least once in their lives, of which 3% used it often. Which suggests that 3D printing is not yet in great demand. But 80% of those respondents who had not heard of 3D printing became interested in this technology and expressed their desire to learn more about this technology. About 51% of respondents had heard of a 3D pen, but the majority had not used it. But quite a lot of people are ready to entrust their lives to new technologies. 50% of those surveyed would trust their lives to such technology. nine0005
Details are shown below.
Problems and prospects for using this technology in different areas of life
3D printing technology is not yet perfect. There are several problems that can lead to some rather unexpected results. For example, a printer printing several parts at the same time can print them linked together. Another problem is that due to the layered construction of the part, the lower layer may not withstand the weight of the upper layers, and then the part is destroyed. Before printing, it is necessary to carefully work out a computer model so that the result is the way it is expected to be. nine0005
There are several problems that can lead to some rather unexpected results. For example, a printer printing several parts at the same time can print them linked together. Another problem is that due to the layered construction of the part, the lower layer may not withstand the weight of the upper layers, and then the part is destroyed. Before printing, it is necessary to carefully work out a computer model so that the result is the way it is expected to be. nine0005
3D printing is the technology of the future. Every day this printing technology finds itself in new areas. Such a service is interesting in the field of entertainment: anyone can make a scan of their body and get their own miniature copy. In the field of medicine, the manufacture of shoes, insoles, and headphones is gradually coming into use, ideally repeating the shape of certain parts of the body or detailed parts for the functioning of the body, for example, a section of the human cranial cortex. The size of parts is gradually increasing, and the choice of materials for printing is also expanding.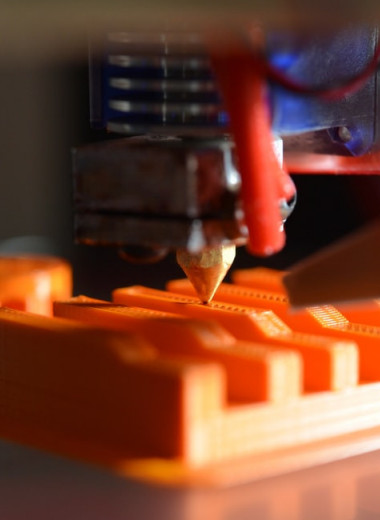 nine0005
nine0005
Conclusion
Summing up, it is worth noting that the use of 3D printers allows you to completely eliminate manual labor and the need to make drawings and calculations on paper, and eliminate the identified shortcomings not in the process of creation, but directly during development. In creating models using a 3D printer, there is no restriction on design and complexity of form, which allows you to fully use your imagination and make an individual and original product. Products are very light, and at the same time, their production time is minimal. nine0005
This technology is only gaining momentum in its development and distribution. This can be seen in the city that was chosen for the study - Rostov-on-Don. Most of the orders belong to the group of personal interest in the new technology and nothing more. But it is also impossible not to notice that the process of using 3D printing technology in large and useful projects for society is already underway.