Lcd screen 3d printer
3D Printer Displays - 3DJake International
Sort byRelevanceBestsellersCustomer ReviewsPrice, Low to HighPrice, High to LowNew arrivalsHighest Discount
-
Phrozen LCD Screen 9 Model types- Original spare part
- From Phrozen
-
Anycubic LCD Screen 8 Model types- Original spare part
- By Anycubic
-
Elegoo LCD Screen 9 Model types- Original spare part
- From Elegoo
-
Creality Touchscreen Upgrade 3 Model types- 4.
3 inch HD colour screen
- 24-bit colour
- User friendly
- 4.
-
FLSUN Speeder Pad- 7-inch display
- 2-5x higher print speed
- Print monitoring in real time
-
Creality Sonic Pad- Open-source
- Runs with Klipper
- User-friendly installation
-
FLSUN Touchscreen 2 Model types- Original spare part
-
Creality 3D Pad- Better model preview
- Plug & Print
- Resume print function & filament sensor
-
Creality LCD Screen 3 Model types- Original spare part
- From Creality
-
Creality LCD Screen 26 Model types- Original spare part from Creality 3D
- Available for various 3D printers
-
BIGTREETECH Raspberry Pad 5- Responsive 5” HD touchscreen
- Broad connectivity - Many interfaces
- Design with BTB connector
-
Anycubic LCD Screen Protector 7 Model types- Original spare part
- From Anycubic
-
Creality Ender 3 Display Cables- Original spare part
- From Creality 3D
- For Ender 3 and Ender 3 Pro
-
Qidi Tech LCD Screen- Original spare part
- From Qidi Tech
-
Snapmaker Touchscreen- Original spare part
- User friendly
- Easily interchangeable
-
FlashForge Touch Screen 4 Model types- Original FlashForge
- High-quality
-
Zortrax Display Set- Original spare part
-
Zortrax LCD Screen for the Zortrax Inkspire 2 Model types- Original spare part
- For the Zortrax Inkspire
All prices incl.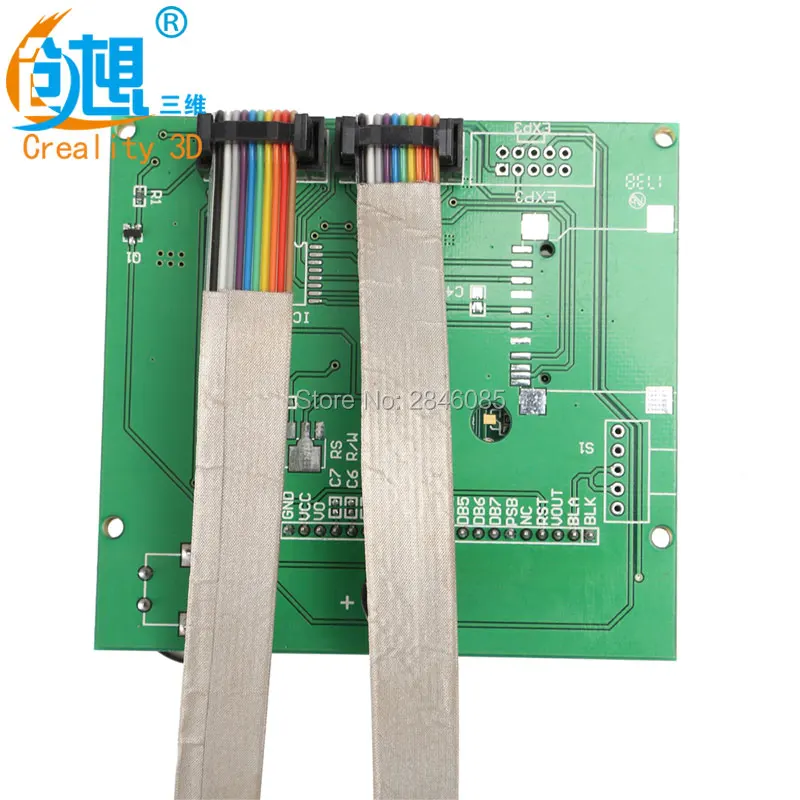 VAT.
VAT.
5 Things You Need to Know When Choosing LCD screen – mSLA/LCD 3d printers.
Table of content
- LCD STRUCTURE AND WORKFLOW
- LCD SCREEN SIZE AND PIXEL
- RESOLUTION & PPI
- BRIGHTNESS AND CONTRAST RATIO
- TRANSMISSION AND LIFESPAN
1.LCD structure and work flow
LCD screen(Liquid Crystal Display) plays an important role in the mSLA/LCD resin printers. In this article, I am going to introduce some knowledge bases about the LCD panel to help you learn more about resin printers.
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical devices that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly, instead of using a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome. and it is usually made by professional manufacture such as Sharp;JDI;BOE; Samsung etc.
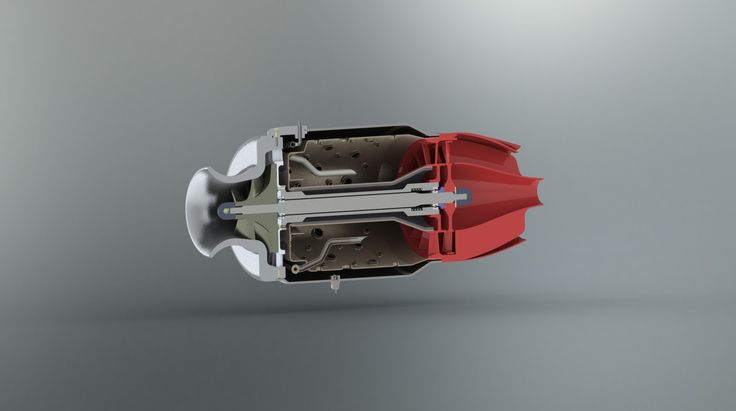
This picture shows the structure inside LCD, you can see there are many complex modules and electronics.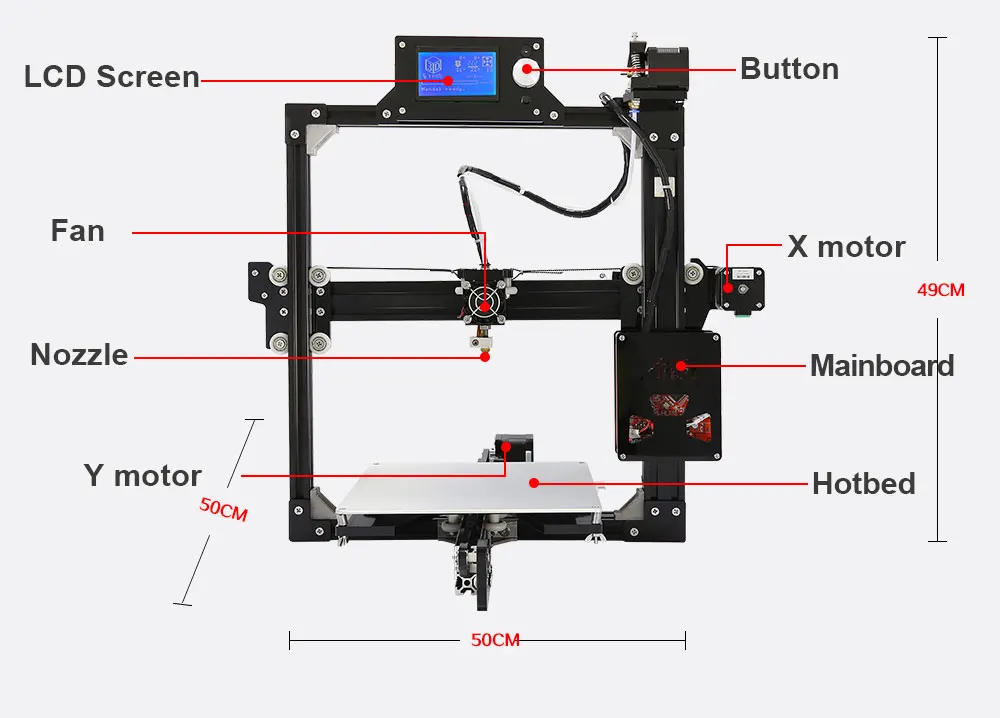
There is a YouTube video that explains very detailed info about how LCD works. different from the original LCD, the LCD used in resin printers don’t need a backlight, because we use the UV LED as a light source.
The signal interface is also different with different size LCD, there are MIPI, RGB, EDP, and LVDS. In the current resin printer market, most screens are come with MIPI(small size) and eDP(large size) interface.
With the same interface, you will also need to know if need an adaptor to connect the screen to the board sometimes. Like Sharp04 to 03interface on board(Original Photon board only support 03 interface, you will need a MIPI to MIPI adaptor to work with current Sharp04 screen)
The ChiTu L series use the MIPI interface, you can connect directly with a small size LCD panel.
The ChiTu L HDMI series use the HDMI interface, you will need an HDMI to eDP adaptor to work with a large-size LCD panel.
2.LCD Screen size and Pixel
The screen size is the size of the diagonal measurement.
The Pythagorean theorem also work on this: width²+height²= (diagonal measurement)²
For example, a 5.5inch 2K Sharp04(LS055R1SX04) screen’s LCD active area is 68.04mm(H)x120.96mm(V), which marks as 120*68 printing size in the printer’s specification.
68.04mm²+120.96mm²=138.78mm²
1inch=2.54cm=25.4mm
138.78mm/25.4mm=5.46≈5.5 inch
Aspect ratio refers to the width of the screen in relation to its height
In the width and height, there are the same ratio of pixels,
For example, 5.5inch sharp04 is 2K=1440pixels x 2560pixels=9:16
Here is a video introducing how different aspect ratio affects.
3.Resolution & PPI
The resolution of an LCD is expressed by the number of columns and rows of pixels (e.g., 1440×2560).
The resolution is actually the size of pixel,below is the specification of 5.5inch 2K Sharp04(LS055R1SX04) screen, which used on most 5.5inch printers such as ELEGOO Mars; Mars pro and Creality LD-002R; EPAX X1; Wanhao D7 etc. And Sharp03(LS055R1SX03) for photon and photon S, which can work with sharp04 with a 04 to 03 adapter.
Sharp04 LS055R1SX04
Resolution = pixel size= Active area/ Pixels
68.04(H)/1440(H)=120.96(V)/2560(V)=0.04725mm=47.25μm
PPI(Pixels per inch) is the pixels in an inch. It is also using the Pythagorean theorem to calculate. Higher PPI means better resolution.
Each pixel is usually composed of 3 sub-pixels, a red, a green, and a blue one. This had been one of the few features of LCD performance that remained uniform among different designs.
This had been one of the few features of LCD performance that remained uniform among different designs.
Each sub-pixels can reach 256 different brightness to change the mixed color, 256x256x256=16,777,216 colors are the value that an LCD can archive.
4.Brightness and Contrast Ratio
Contrast ratio is the ratio of the brightness of a full-on pixel to a full-off pixel.
The LCD itself is only a light valve and does not generate light; the light comes from a backlight that is either fluorescent or a set of LEDs. Brightness is usually stated as the maximum light output of the LCD, which can vary greatly based on the transparency of the LCD and the brightness of the backlight. In general, brighter is better[citation needed], but there is always a trade-off between brightness and power consumption.
5.Transmission and lifespan
As we know now there are so many complex modules and electronics inside the LCD panel, most of the light will be blocked,
The LCD manufacture said that the transmission is around 1% for normal RGB LCD under 405nv UV LED light source. The lifespan is also very shorter work with UV light,
The lifespan is also very shorter work with UV light,
To solve this issue, LCD manufacture is trying hard to improve the transmission such as increasing the aperture ratio, also there comes out a monochrome LCD screen that can reach about 6% transmission, With better lifespan and better printing speed.
If your LCD panel is dead, feel free to get one from ChiTu online store.
And we have a UV meter that can help you test if the screen is dead.
ChiTu Aliexpress Store
CBD-Tech team has been working with all the partners in resin printing for the long term, we will keep moving and try the best to provide a better solution with ChiTu system and CHITUBOX.
Next week we will talk about detail about the advantages of monochrome screen.
Useful information
There is a wide variety of 3D printers on the market today. LCD, DLP and SLA 3D printers use photopolymer resins. But which ones are best for your needs?
Today we will focus specifically on the aforementioned photopolymer 3D printers. We'll take a look at the pros and cons of each type of printer and compare their resolution, accuracy, clarity, speed, and cost.
We'll take a look at the pros and cons of each type of printer and compare their resolution, accuracy, clarity, speed, and cost.
A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF LCD 3D Printers nine0003
LCD 3D printers use a liquid crystal screen to project a specific light pattern, which is then used to cure a photopolymer resin in a bath. The LED lamp is used as the light source, while the LCD screen controls the light pattern. The light is emitted by an LED lamp. Then it passes through the liquid crystal screen and is absorbed by the resin. The image of each layer is generated on the LCD screen and at the same time it is completely solidified. nine0003
Phrozen LCD 3D printers use ParaLED technology, in which an array of LED chips projects light through an LCD screen, which is then evenly distributed over the print area.
A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DLP 3D Printers
DLP 3D printing, or digital light processing, uses a digital projector to flash ultraviolet light in the area to be printed and immediately cures the resin layer.
The optical pattern for DLP 3D printing is mainly generated by a digital micromirror device (DMD) inside the projector lens. The DMD itself is made up of many tiny mirrors that control the pattern of light being projected. Light is reflected from its surface, located at an angle to the liquid resin. nine0003
A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF SLA 3D Printers
SLA 3D printing, or stereolithography, uses lasers as a light source for 3D printing. The resin hardens as the laser beam prints each dot in a particular layer.
When a laser beam is reflected from a computer-controlled mirror, it is directed by the mirror to various coordinates that are in the resin and cures it in layers.
COMPARISON PERMISSIONS nine0003
Resolution is related to 3 dimensions: XY resolution and Z resolution.
The Z resolution is mainly determined by the specification of the 3D printer motor, motor driver, and lead screw. The Z resolution refers to the minimum layer height. For daily printing, we will use the average layer height, for example 30-100 µm, for printing instead of the minimum layer height.
For daily printing, we will use the average layer height, for example 30-100 µm, for printing instead of the minimum layer height.
For example, the Z resolution of the Sonic 4K Phrozen printer is 10 µm, but we usually print at a layer height of 30-100 µm. The lower the layer height, the longer it will take to print the model. This means that as the number increases, the printer will print faster. Please note that the layer thickness can be preset on each 3D printer. nine0003
Keep in mind that the resolution of the STL file itself will also affect the resolution of the final print.
For each type of 3D printer, the XY resolution is defined as follows:
LCD 3D printers: For LCD 3D printers, the XY resolution is determined by the pixel size.
LCD 3D printers can produce higher resolution 3D prints, depending on the pixel size of the printer's LCD display.
nine0003
For an LCD screen, you can calculate the pixel size by dividing the length of the LCD by the number of pixels along its length. Take Phrozen's Sonic 4K as an example, its X-axis resolution (pixel size) is 134.4 mm / 3840 pixels = 0.035 mm.
Take Phrozen's Sonic 4K as an example, its X-axis resolution (pixel size) is 134.4 mm / 3840 pixels = 0.035 mm.
Phrozen's Sonic 4K allows you to print in 4K at 35µm resolution and 722 PPI (the highest PPI on the market). PPI stands for Pixels Per Inch. The higher the PPI of the printer, the more detailed the 3D model will be. nine0003
DLP 3D printers:
For DLP 3D printers, the XY resolution is also determined by the pixel size. Although the difference is that the pixel size of DLP 3D printers depends on the size of the small mirrors on the DMD.
Each layer is seen as square pixels and light is projected according to the size of the pixel.
DLP 3D printers use the same concept as LCD 3D printers; you can calculate the pixel size by dividing the length of the small mirrors by the number of pixels present on the DMD. nine0003
SLA 3D printers: For SLA 3D printers, the XY resolution will depend on the average spot size of the laser beam and the amount of steps that the laser beam is driven.
The size of the laser spot can be adjusted according to the size of your print. Some may also define its resolution in different ways, such as scan speed or beam size at minimum power.
Due to differences in methods, SLA 3D printers should be treated as a separate case when compared to DLP and LCD 3D printers. nine0003
Comparison of measurement accuracy.
LCD 3D Printers: With a wide variety of LCD 3D printers on the market, companies are now rushing to create LCD 3D printers that are far more accurate than previously possible. This means that LCD 3D printers are approaching the accuracy of traditional SLA 3D printers with the proper calibration components.
Phrozen 3D printers use ParaLED technology to provide the most parallel angle of UV light emission. This is to ensure that each resin layer receives an equal amount of UV light during the printing process, improving the efficiency of light passing through the LCD screen while projecting each pixel size accurately and accurately. nine0003
nine0003
DLP 3D printers:
DLP 3D printers tend to be less accurate than SLA and LCD 3D printers.
This is because DLP printers use the projector lens to project light from a small source to a wider source, which increases the chance of pixel distortion due to spherical aberration.
Some professional DLP 3D printers try to improve this slight distortion by building floor standing 3D printers to increase projection length to reduce the effect of spherical aberration. nine0003
SLA 3D printers:
Because SLA printing uses lasers, 3D models printed using this technique are generally accurate. SLA 3D printers print models with a flat and smooth surface as the laser travels in a continuous path, slowly drawing out each layer.
Although SLA 3D printers can print smooth models, the purchase price of such a device can be 3-5 times higher than LCD 3D printers. In addition, printing on an SLA 3D printer takes much longer, we will talk about this later. For those who want to print miniatures and other similar models at home, it would make more sense to purchase an LCD 3D printer. nine0003
For those who want to print miniatures and other similar models at home, it would make more sense to purchase an LCD 3D printer. nine0003
Speed Comparison
LCD 3D printers:
LCD 3D printers are similar to DLP 3D printers in that the entire resin layer cures at once, which means it can also print much faster than SLA 3D printers and print out a collection of 3D models in one go.
Print speeds can vary from 20mm/hr for Phrozen's Shuffle XL Lite to 80mm/hr for our Sonic 4K, depending on whether the 3D printer uses a single crystal screen. nine0003
Monocrystalline screens last much longer and print much faster than regular color LCD screens.
This is because monochrome LCD screens are designed to provide higher light transmission and higher thermal resistance. Thus, 3D printers using Mono-LCD screens can cure resin with shorter layer exposure time and have a longer life than color LCD screens.
In comparison, color LCD screens take longer to cure the resin, as the LCD panel has a lower light transmission rate than Mono-LCD screens.
Being ahead of the curve, Phrozen pioneered Mono-LCD display technology in the world of 3D printing.
DLP 3D Printers: Because the entire resin layer is cured with UV light at the same time, this means you can print a large number of tiny models at the same time when using a DLP printer. This process will be much faster than with an SLA 3D printer and even some LCD 3D printers. nine0003
DLP printers can print between 20 and 140mm/hr, but they lose resolution and produce smaller print sizes than LCD 3D printers.
SLA 3D printers:
Since SLA 3D printers use lasers to trace the pattern of one layer before moving on to the next layer, it takes much longer to print each individual model using this type of printing technique.
The printing speed can vary from 14mm/hour to 36mm/hour. nine0003
Because SLA 3D printers use a different printing technique, it cannot be fully compared to the printing methods of DLP or LCD 3D printers. If you want to print models at high speed, it would be better to purchase LCD 3D printers as SLA 3D printers print very slowly.
If you want to print models at high speed, it would be better to purchase LCD 3D printers as SLA 3D printers print very slowly.
Price
LCD 3D Printers: Compared to other 3D printing methods, LCD 3D printers are designed as an affordable alternative to their 3D printing counterparts. These 3D printers use a liquid crystal panel for printing, which can be easily replaced. Also, LCD printers can be small, so most LCD 3D printers are desktop-sized, making them easy to store. nine0003
LCD printers can cost anywhere from $500 to $3,000, such as the Sonic Mini Phrozen, which costs around $500, and our Sonic XL 4K, which costs $3,100.
Phrozen 3D printers produce models with high efficiency, providing high resolution printing to capture all the fine details of your 3D models. Phrozen offers a wide range of 3D printers for personal use, dental applications, jewelry and more. nine0003
DLP 3D printers:
DLP 3D printers are more expensive than LCD 3D printers because this printer requires the use of a digital micromirror device (DMD), which also tends to be expensive.
The price of DLP 3D printers typically ranges from $5,000 to $100,000.
SLA 3D printers:
In terms of cost, SLA printers tend to be more expensive than their counterparts: DLP printers and LCD 3D printers. This is because SLA printers include machines and lasers, which tend to be more expensive. nine0003
Depending on the brand and type of SLA 3D printer you decide to purchase, the price can range from $5,000-$7,000 for a basic SLA 3D printer to several hundred thousand dollars for an industrial SLA 3D printer.
While DLP 3D printers print the fastest, they produce lower resolution models, and they are also more expensive than LCD 3D printers. 3D models can also be easily distorted due to the use of a projector lens.
SLA 3D printers print products with fairly high accuracy using a laser, although it prints very slowly. These 3D printers also tend to be much more expensive, making them less accessible to the average user. nine0003
Although LCD 3D printers do not print as fast as DLP 3D printers, they print with precision using an LCD screen and UV light, producing extremely high resolution 3D models.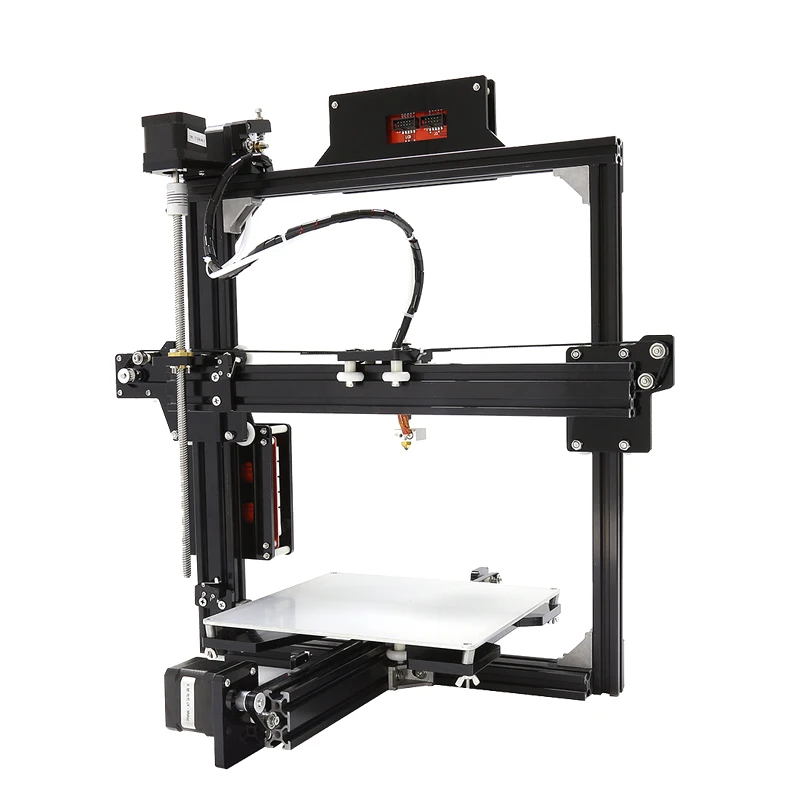 At the same time, the cost of LCD-3D printers, especially Phrozen LCD-3D printers, remains very affordable.
At the same time, the cost of LCD-3D printers, especially Phrozen LCD-3D printers, remains very affordable.
DLP and LCD 3D Printers: What's the Difference?・Cults
Resin 3D printing is a popular technology in the 3D printing industry, and every market has a number of these 3D printers in its product range. It finds wide application in various industries and its development is a priority to improve print quality, financial viability and access to a wider user group. nine0003
DLP and LCD are two of the most prominent technologies in resin 3D printing. Both work on a similar principle and are comparable in many ways. However, there are also some obvious differences that users should be aware of before purchasing a resin 3D printer.
In this blog, we will focus on DLP and LCD 3D printers. We will discuss the main technologies used, their individual advantages and disadvantages, and how they suit your specific 3D printing needs.
Resin 3D printing belongs to the broad category of vat light curing, which is considered one of the main types of 3D printing technologies.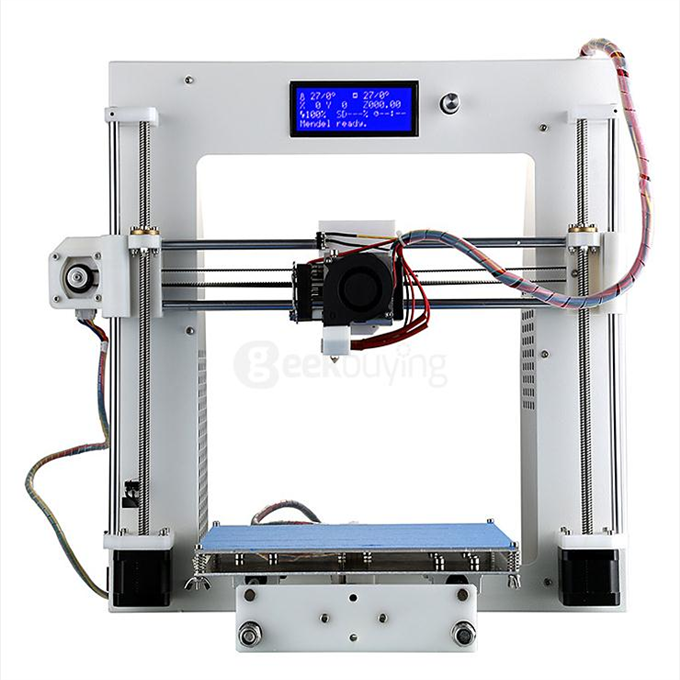 The concept is based on the ability of light-sensitive resins in the liquid phase to solidify under the influence of light radiation.
The concept is based on the ability of light-sensitive resins in the liquid phase to solidify under the influence of light radiation.
Resin 3D Printing uses this ability to create 3D objects from liquefied resins that are selectively exposed to light to cure desired areas of the resin. Only those parts of the resin that have solidified under the influence of the light source become part of the 3D printing, while the rest remain liquid. nine0003
A typical configuration for resin 3D printing includes a tray, or reservoir (in technical terms), that is filled with liquid resin, a light source, and a mechanism for directing the light source to a specific point in the resin to be cured.
In addition, there is a build platform that can move up and down inside the tank with amazing precision. For each new layer, the building platform is lowered to the bottom of the tank, leaving only a tiny gap (0.5 mm in most cases) in which the layer adjacent to the platform is built. For subsequent layers, the platform continues to rise slightly each time, while each new layer fits into the resulting gap and is bonded to the top layer. The 3D printed resin model is built upside down as light passes through the bottom of the tank. nine0003
The 3D printed resin model is built upside down as light passes through the bottom of the tank. nine0003
That's what resin 3D printing is all about! Now let's move on to two interesting technologies that we want to talk about.
Digital Light Processing, or DLP, uses a digital light projector as a light source to cure resins. This light source is characteristic of this technology and is the main difference between it and LCD displays.
The projector projects light onto a unique device called a DMD (Digital Micromirror Device), which consists of a very large number of very small mirrors, each of which is capable of deflecting light from the projector in different directions. For each layer, these mirrors are arranged in a specific orientation that reflects the digital light beam from the projector onto the tank in the exact shape of the printed layer/layer. nine0003
Mirrors cannot change the nature of the light source in any way, they only direct it. This means that the number of pixels produced on the build platform is the same as the number of pixels on the projector. So if the layer is slightly smaller than the projector's beam, the image is actually slightly sharper and more accurate than what is being projected! However, this also has a downside. The opposite happens if the printed piece is larger than the projector screen. In this case, the resolution is reduced, and there is also a risk of distortion at the edges, since the light is refracted too far (like an elephant's foot when printing with filament). nine0003
So if the layer is slightly smaller than the projector's beam, the image is actually slightly sharper and more accurate than what is being projected! However, this also has a downside. The opposite happens if the printed piece is larger than the projector screen. In this case, the resolution is reduced, and there is also a risk of distortion at the edges, since the light is refracted too far (like an elephant's foot when printing with filament). nine0003
Modern, more expensive DLP 3D printers use advanced technology to minimize this distortion problem and maintain layer quality despite being enlarged. As a result, these DLP 3D printers can safely be considered professional products.
DLP technology has been around for a long time due to the age of the light source: projectors are century old devices widely used in movie theaters. Therefore, the technology is tried and tested.
LCD 3D printing, also known as MSLA 3D printing, is a relatively new technology compared to DLP technology. As mentioned above, it uses a non-DLP light source: UV LEDs that shine through the LCD screen. nine0144 Although LCD also creates full layers at the same time as DLP 3D printers, the quality of the layers depends on the screen resolution. The higher the pixel density of the LCD screen, the better the print quality. In addition, there are no problems with distortion, as the print created on the LCD is transferred to the resin unchanged without deviation. Since the original projection size on the LCD screen does not change, the print area is limited by the screen area, so larger prints require a larger screen.
Cost is a tricky issue when it comes to LCD 3D printers. The material is cheap because the LCD screens used in these devices are practically the same as in smartphones. The problem, however, is that they need to be replaced frequently to maintain quality. The idea that LCD 3D printers are cheap is true, but you need to be aware of the running costs involved.
DLP and LCD are similar in many ways: technology, print quality, speed, applications, etc. Are they the same? But are they the same? No. nine0003
Are they the same? But are they the same? No. nine0003
There are a few things to consider before choosing one or the other. First, let's talk about print quality. As mentioned above, it is comparable for both 3D printers. The finish is smooth, the layers are indistinguishable. However, DLP has an edge in this regard. Cheaper options compare well with LCD printers, but if you consider mid-range DLP 3D printers (which support layer distortion and warp), the build quality is much more detailed and subtle. nine0003
In terms of cost, LCD is the cheapest option. Even if the screen has to be changed, the technology itself is so accessible and cheap that DLP is still more expensive. But this comes at the expense of quality, which must be known.
Compatibility with the resin material is another factor to consider. Most resins can be used with both DLP and LCD 3D printers, but some are only suitable for one or the other. It depends on the energy intensity of the light source. The LCD uses a low power light source, so resins that cure quickly are suitable. If any other resin is used, it will not cure properly and the structural integrity of the model will be compromised. Naturally, DLP is compatible with resins that take some time to cure due to the high density of the energy source. nine0003
If any other resin is used, it will not cure properly and the structural integrity of the model will be compromised. Naturally, DLP is compatible with resins that take some time to cure due to the high density of the energy source. nine0003
In general, it all depends on the specific application. People who require professional-grade quality and who have a large budget should always choose DLP as it is better suited for detailed work. Consumers who are just starting out or have low-precision tasks on a budget should consider LCD 3D printers, which are also very good in many ways.
This page has been translated using machine translation. Suggest the best translation nine0003
Previous
ShareNext
Similar publications
Known for its quality desktop 3D printers and high market share in the 3D printing industry, Creality 3D launched its revolutionary Infinite-Z 3D printer, the 3DPrintMill, on Kickstarter on November 19, 2020.