Pla 3d printer price
How much does 3D printing cost?
David Roberson21 September 2021
Guide
Once you understand how 3D printing works, it's important to talk money. A 3D printer should be a long-term asset for your organization that delivers value for years after you buy it. But how much does 3D printing cost?
This return on investment is a benefit that sets 3D printing apart from other solutions like outsourcing. But as with any long-term asset, it pays to be aware of all the associated costs that come with owning a 3D printer, and which expenses – including 3D printer material costs – you need to plan for into the future.
The list below should help you understand the costs involved, how they differ depending on the technology, and which are one-off or repeating. (Prices are indicative and subject to change – so we recommend doing your own research too.)
3D printer price
With products on the market for anyone from a home user to the R&D divisions of blue-chip companies, 3D printer prices vary a lot. Typically, FFF offers the greatest variation in price, from hobbyist machines costing a few hundred dollars to higher-performance desktop printers in the $2,000 to $6,000 range. Desktop SLA printers start from around $2,000 to $3,000, while an SLS printer typically costs $10,000 plus. Larger-scale industrial machines of any technology will cost significantly more.
Peripherals
These can add extra functionality, but also add extra expense your 3D printing costs. Post-processing peripherals are almost essential for SLA and SLS printers. For example, SLA prints will otherwise have to be manually washed in isopropyl alcohol and left in the sun to cure – so in practice, these printers often require purchase of post-processing stations unless that appeals to you! For FFF, peripherals can streamline workflows such as material handling, but are up to you depending on your needs.
Maintenance and service
Typically, this should only be the cost of replacing the odd consumable part over time. Check what support your seller includes as part of the price – they may offer installation and maintenance included. Some products also come with extended warranty options or an annual service plan. These plans can add certainty for some customers, but be sure to read the fine print in detail to understand the terms and exactly what support you get if something goes wrong.
Check what support your seller includes as part of the price – they may offer installation and maintenance included. Some products also come with extended warranty options or an annual service plan. These plans can add certainty for some customers, but be sure to read the fine print in detail to understand the terms and exactly what support you get if something goes wrong.
Energy
For regular use for an Ultimaker 3D printer, we calculated this to be around $50 per year. But if you want a more precise figure, check the power consumption specs of a 3D printer and make a calculation based on your likely usage and local energy prices.
Materials
Think of material costs like gas for your car. While not considerable in isolation, over the long-term it will be one of the biggest running costs. For FFF 3D printing, 3D printer filament prices (for an everyday material like PLA or PETG) are around $20 to $50 per kilogram, or $60 to $120 for specialized engineering or support filaments. Entry-level SLA resins cost around $50 per liter, and most professional options cost around $150 to $400. SLS powder can cost around $100 to $200 per kilogram.
Entry-level SLA resins cost around $50 per liter, and most professional options cost around $150 to $400. SLS powder can cost around $100 to $200 per kilogram.
Software
Most professional level 3D printers come with some software included, usually so you can prepare your prints and manage printers. Many cheaper 3D printers don’t come with adequate software, but luckily our Ultimaker Cura software is compatible with hundreds of machines and free to download. And if you really want to scale 3D printing in your business unit or even entire organization, consider an enterprise software plan with added features like direct support, online training courses, and cloud storage for your parts and projects.
You can learn more in our total cost of ownership white paper – available to download for free.
A 3D printer is part of an ecosystem that includes peripherals, materials, and software – either from the manufacturer or third parties
Need more info on 3D printing?
Explore the wider world of this incredible technology by reading our answers to these common questions:
What is 3D printing?
What can you make with a 3D printer?
How to use a 3D printer?
The Real Cost of Cheap 3D Printer Filament — 3D-Fuel
The Real Cost of Cheap 3D Printer Filament
One factor that many forget about when calculating the cost of the filament is wasted time and materials. Yes, you can get a 1kg spool of no-name filament for $20 – a cost of $0.020/gram. But, a spool at this cost usually has filler materials, inconsistent diameter and ovality, and poor spool winds. All of these factors can cause issues leading to failed prints, which then need to be started again. And a failed print costs you, in more ways than you may realize.
Yes, you can get a 1kg spool of no-name filament for $20 – a cost of $0.020/gram. But, a spool at this cost usually has filler materials, inconsistent diameter and ovality, and poor spool winds. All of these factors can cause issues leading to failed prints, which then need to be started again. And a failed print costs you, in more ways than you may realize.
It Costs To Re-Print
Many 3D printer operators know and understand the problems that can come along with using that no-name $20 Filament, but it’s hard to pass up that price, right? Maybe not. Using cheap materials can cost less, but in many cases leads to a jam partway through the print, requiring the print to be restarted and the partial print discarded. Let’s use the example of a 21 hour print that should only use 252 grams of Filament.
Using that same low-price filament, let’s say the print fails at exactly 50%. Assuming it prints successfully the second me, at $. 020 per gram this print has now cost you $7.56 versus the original $5.04. A successful print will now take 31.5 hours versus the original 21 hours.
020 per gram this print has now cost you $7.56 versus the original $5.04. A successful print will now take 31.5 hours versus the original 21 hours.
It Costs To Un-Jam
When cheap filament inevitably jams your printer, it may take anywhere from 10 minutes to an hour to clear out. It may even take longer if the extruder has to be completely dismantled to clear the jam.
Assuming the jam is able to be cleared, this one failed print has already cost you an hour of hands-on me. On average, that’s half an hour of me you can’t get back and won’t be able to bill for. Some say time is more valuable than money, but let’s say you value one working hour at $50. With an hourly rate of $50, that’s $25 in lost revenue.
It Costs To Repair
In case the jam caused by that cheap filament is not able to be cleared, replacement parts will need to be purchased. A jam can even require the total replacement of an extruder or print head. A MakerBot Replicator 2 heater block assembly (a middle-of-the-road replacement part in terms of cost) costs $29. 95. Even a simple nozzle replacement will cost $7. Remember, you’ve valued one working hour at $50. Multiply that by how many hours you spend clearing a jam, replacing parts, and restarting prints.
95. Even a simple nozzle replacement will cost $7. Remember, you’ve valued one working hour at $50. Multiply that by how many hours you spend clearing a jam, replacing parts, and restarting prints.
Suddenly, that $20 filament is not such a bargain.
ARE YOU GETTING A REAL VALUE?
So how much more are you getting for your purchase from a high-quality PLA supplier? These filaments don’t contain filler materials, have consistent diameters and ovality, and are well wound spools. This is all better for your budget, your printer, and your finished product. But what are you getting for your money? One of the primary comparison points for 3D printing materials is the cost per gram. Take a look at the cost per gram of three different PLA suppliers.3D-Fuel • MakerBot • ColorFabb
A large spool of MakerBot PLA filament costs $48 and that spool contains 900g of filament.-black-kupit-v-soin-store.ru-2.jpg) That leads to a cost of $.053/gram.= $.053/gram That leads to a cost of $.053/gram.= $.053/gram |
| = 5.3¢/GRAM |
| ColorFabb filament spools cost $35.79. High quality, reputable filament for a decent price, right? Looking more closely, however, reveals that this filament spool only comes with 750g of filament per spool. That leads to a cost of $.047/ gram.= $.047/gram |
| = 4.7¢/GRAM |
| 3D-Fuel spools of Standard PLA are loaded with a full 1000 grams of filament for $29.99 – a cost of $.029/gram. That’s less expensive per gram than both MakerBot and ColorFabb filament. |
| = 2.9¢/GRAM |
Also consider that 3D-Fuel uses only genuine NatureWorks Ingeo™ PLA resin, with unparalleled low environmental impact and purity, and the real value is clear.
Filed in: filament, infographic, quality
Previous article 3D-Fuel and Raise3D Collaborate to Certify Pro PLA Filament Next article The Real Cost of Cheap 3D Printer FilamentFlexible TPU plastic for printing on a 3D printer in Moscow: 1.
-gold-kupit-v-soin-store.ru-2.jpg) 75 mm, weight 1 kg
75 mm, weight 1 kg Learn more
Only high-quality products
Learn more
Subscribe to newsletter
Be the first to know about discounts!
TPU plastic Description Parameters
for printing and
for post-processing Physical
mechanical characteristics
Material: TPU - thermoplastic polyurethane
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a modern polymer material based on polyesters. The elasticity of printed products is the main property that determines the use of this plastic.
Press parameters:
Print temperature: 175-190 ° C
Table temperature: 50 ° C
Table cover: clean glass, glue BF-2, glue for 3D printing
speed speed prints: 15-20 mm/s.
Cooling: is recommended to be printed using efficient, annular airflow.
Density: 1.25 g/cm3
Features of TPU plastic and handling:
- Elasticity is the main property that determines the application.
- High resistance to deformation in both compression and tension.
- High strength, very soft. Shore hardness 75A
- No smell when printed.
- Excellent interlayer adhesion.
- The print speed is slow.
- Resistant to most solvents, fats, oils. Relative resistance to gasoline.
- Machining is very difficult due to the specific properties of the plastic.
- Wide operating temperature range.
- Bar accuracy ± 0.05 mm (reduced geometry tolerance).
- The FDM extruder head needs to be modified to eliminate gaps and cavities in the path of the bar from the feed gear to the hot zone of the print head. The use of bowden tube extruders is difficult due to the very low hardness of the material.
- Machining of TPU plastic products is difficult.

- Chemical treatment not applicable.
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a unique material, one of the most sought after polymeric materials. Operational and chemical properties have provided this material with a wide distribution in all industries with high requirements for the quality of materials.
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) combines wear resistance, lightness and elasticity, the ability to not change its color during its use. The material is resistant to low temperatures. rupture and aggressive environments, adheres well to the surface, restores shape when deformed, is able to perfectly resist punctures, has slip resistance.
TPU plastic is the first flexible, Flex-plastic in the line of plastics produced by the Moscow FDplast plant. Possessing excellent structural and technological properties, thermoplastic polyurethane is used in various industries, ranging from winding power cables, use in the development of the design of the bottom of shoes, the manufacture of protective accessories for electronic devices, and ending with a decorative overlay in the car interior.
Information on the properties of plastics and printing requirements can be found in the booklet "Flex for 3D printing FDplast".
Plastic storage
3D printing plastic must be stored in a dry place. Moisture and dampness greatly affect the filament, as a result, the plastic deteriorates, it becomes impossible to print from such plastic. There are no problems with the storage of plastic, it is practically not affected by the normal humidity of the ambient air. However, in order to obtain an ideal printing result, it is advisable to store the filament in a dry place, with silica gel.
3D Printing Tips
More >>
Download
Presentation. Plastic for 3D printing FDplast
Booklet. Plastic for 3D printing FDplast
Do you need a pipe? Call and we will help you!
Send an order to the Plant's e-mail and our managers will contact you as soon as possible!
Update form
Contacts
Moscow plant FDplast
Office in Moscow
Construction sites
How to calculate the cost of printing on a 3D printer
Main / Blog / Useful / The cost of 3D printing. Examples of models with prices
Examples of models with prices
06/21/2021
Content
-
- Available Technologies and the main differences
- FDM 3D PELIASTION
- Photopolymer Printing
- 057
- Examples of print
- Available Technologies and the main differences
- 3D Printing to order
- Commercial 3D print cost
- What is unprofitable to print
- Commercial Seal Examples
For some ideas, 3D printing is the fastest and easiest solution. In some situations, purchasing your own 3D printer can be a good solution, but sometimes it is much more profitable and faster to order the necessary product from a company specializing in 3D printing. Yes, and many owners of a 3D printer are thinking about how to “monetize” their hobby, but how to correctly calculate their costs?
Despite the fact that it is customary to indicate the price per gram of working material, simply multiplying the weight of the model by the cost of 1 gram will be wrong.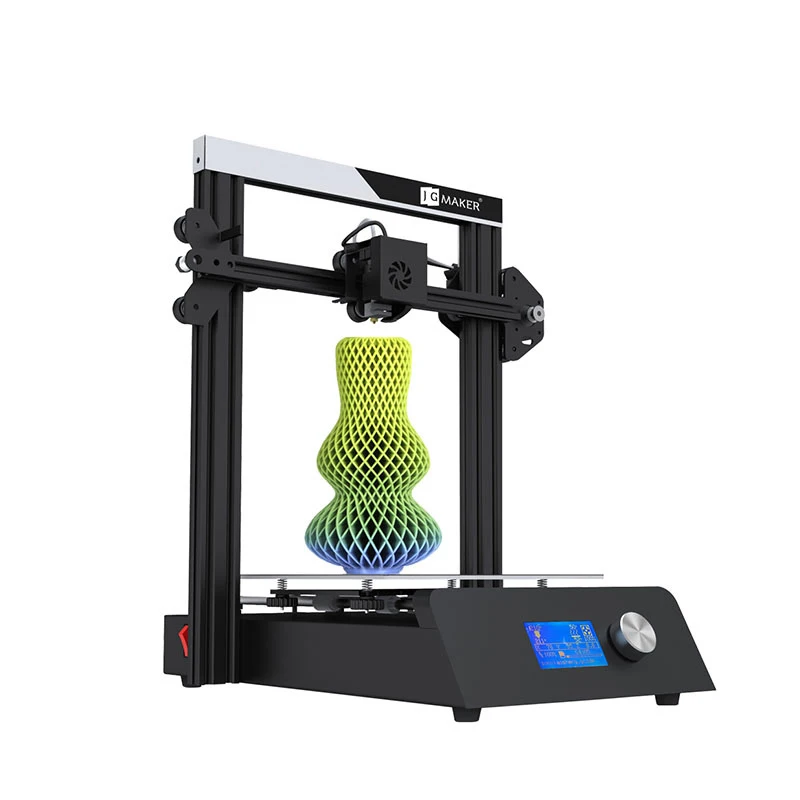 In addition to the cost of consumables, many more, at first glance, non-obvious costs are added to the price of the product.
In addition to the cost of consumables, many more, at first glance, non-obvious costs are added to the price of the product.
Each 3D printing technology uses its own consumables. Let's analyze the most popular and affordable of them.
Available technologies and key differences
Currently, a huge number of 3D devices have appeared, from small desktop ones that fit on the desktop to huge industrial machines. Among the most affordable, 2 technologies can be distinguished - FDM and photopolymer printers (LCD / DLP / SLA).
FDM 3D printing
Today, the most affordable 3D printing technology is FDM. A variety of materials and 3D printers allow FDM to be applied to a wide range of applications.
Schematic operation of FDM printer
A large selection makes it easy to choose a 3D printer for a specific task or find a universal device.
The material for printing is a plastic thread - filament. On the market you can find filament for various tasks, for every “taste” and budget. These can be very inexpensive ABS and PLA plastics or specific ones - conductive, burnable, etc.
On the market you can find filament for various tasks, for every “taste” and budget. These can be very inexpensive ABS and PLA plastics or specific ones - conductive, burnable, etc.
Pros:
Cons:
Despite the fact that FDM allows you to print a wide range of plastics with different properties, the technology has some limitations. For example, it is impossible to obtain a perfectly smooth surface, to produce miniature and very thin elements, or to produce parts with very complex internal geometry with high accuracy.
Photopolymer printing
Photopolymer printers can work on one of 3 technologies - SLA, DLP or LCD. These devices will come to the rescue if you need to make a small but very detailed model with many small details.
How photopolymer printers work
As a consumable material, a photopolymer resin hardened by UV radiation is used. Now there is a wide variety of photopolymer resins for every taste. From particularly strong and precise engineering or jewelry resins to soft flexes.
From particularly strong and precise engineering or jewelry resins to soft flexes.
Pros:
-
High print precision
-
Good surface quality
-
A wide variety of printers and consumables
Minuses:
Photopolymer printers have shown themselves well in a variety of industries that require a perfectly smooth surface and high accuracy. They are used in dentistry, the jewelry industry, for making miniature master models for casting, and much more.
Industrial printers
These are already industrial machines, which require a separate room and sometimes certain requirements for ventilation, etc. In this article, we will not analyze these devices in detail, but briefly consider the most popular technologies.
FDM
In addition to desktop devices using FDM technology, industrial printers that work on the same principle are common.
This category includes devices with a large print area (from 30x30x30 cm and more). For example, Raise Pro2 with a print area of 30x30x30 cm.
Raise Pro2
Or machines designed for printing with refractory materials (eg PEEK). Such 3D printers usually have an active thermal chamber, and the extruder can be heated above 400 degrees.
CreatBot F160-PEEK designed for use with refractory plastics
Photopolymer printers
Industrial photopolymer devices usually have a much larger working area, compared to their "home" brothers. In addition, many processes have been optimized and automated for faster operation. On such printers, you can quickly and accurately produce a small batch of models, a large prototype or a master model.
Large Area Prismlab Industrial Resin Printer Family
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | CreatBot |
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Raise3D |
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Prismlab |
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Prismlab |
3DP
3DP - Three-Dimensional Printing (translated as three-dimensional printing) is a logical continuation of conventional two-dimensional printers. Printing is done using nozzles that selectively apply a binder to the material (usually gypsum). A dye can be added to the binder and the model will be colored.
Printing is done using nozzles that selectively apply a binder to the material (usually gypsum). A dye can be added to the binder and the model will be colored.
Colored plaster model
Since the plaster model is fragile, a similar principle is used for printing with metals. Only the finished product needs to be treated in an oven to remove the binder and improve strength. But despite the processing, such metal prints will still be inferior in strength to cast products.
MJM
This is a proprietary technology of 3D Systems. MJM is a mix of FDM, 3DP and sometimes SLA (depending on material chosen). Printing is done using a variety of small nozzles (from 96 to 488) located on the head of the machine. The accuracy and quality of the surface of models made in this way is in no way inferior to photopolymer printers.
Models made with MJM technology
Such devices can work with photopolymer resins, wax or thermoplastics. You can combine several materials at once - for example, for complex models, you can use wax as a support.
You can combine several materials at once - for example, for complex models, you can use wax as a support.
SLM
SLM is the layer-by-layer sintering of metal powder using a powerful laser. There are several similar technologies - SHS/SLS. The principle of operation is the same, only a thermal print head is used instead of a laser beam.
SLM Turbine
As a material for printing, you can use powders of various metals - gold, stainless steel, aluminum, various alloys, etc.
During printing, the working chamber is filled with an inert gas to prevent oxidation of metals. This allows printing even with titanium powder.
Models made by this method are in no way inferior, and sometimes even superior, to cast products. SLM allows you to produce models with complex internal geometry that cannot be produced by another method (casting or milling).
Cost of 3D printing
The cost of a model usually consists of several factors.
-
Equipment depreciation. The printer, like any machine, requires maintenance and periodic replacement of some parts. During operation, belts gradually stretch, bushings or linear bearings wear out. For example, when bushings or linear bearings are worn; shafts may wear out and need to be replaced.
Cost of materials
The main cost item for a 3D printer is, of course, the printed material.;
FDM (plastic filament)
Since FDM technology is by far the most common, the choice of filaments is very diverse.
-
Engineering plastics are usually nylon with various fillers added to improve the physical characteristics of the finished model. Special cost. plastics starts from 2000r per coil and above. It all depends on the manufacturer and filler (carbon fiber, fiberglass, etc.).
-
Decorative plastics are used to imitate various materials. Plastic can simply be unusually colored (luminous, transparent plastics) or a special filler is added to it (plastics with metal powder).
 The cost of decorative plastics starts from 1500 rubles per coil and more, depending on the filler.
The cost of decorative plastics starts from 1500 rubles per coil and more, depending on the filler.
A big advantage of FDM is the diverse choice of materials to work with. This allows, having one printer, to produce almost any product - from a child's toy to a complex engineering prototype.
Photopolymers (resin)
Photopolymer resin printing technology is becoming more and more accessible. There are many different resins.
-
The cost of ordinary colored resin starts from 2500 rubles per 0.5 kg (volume +/- 0.5 l). You can find a smaller volume of resin (250 gr) on sale. You can buy several different resins in small containers and find out in practice which one is best for a particular model.
-
Engineering resins are resins with increased strength. They can be used not only for printing decorative items, but also for making functional prototypes and models. The cost for 0.5 kg starts from 5900r and above.

-
Special resins - burnable, dental, soft flexes, etc. Depending on the resin, the price for 0.5 kg can start from 4800 rubles and more. It all depends on the characteristics of the resin.
Photopolymer resins have not yet reached such a variety as FDM filaments, but they are surely catching up. Although due to the fact that a liter of resin costs significantly more than a spool of filament, the cost of the product is much higher.
Print examples
FDM
Mag Pull for G3 magazines.
The model was downloaded for free from an open source (the file can be downloaded here). Printing with engineering carbon-filled plastic (price per spool from 4700 rubles). The weight of the model with support is about 25 grams. Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished model is 250 rubles.
Plastic fastener
The file was downloaded from an open source (can be downloaded here). Plastic - carbon-filled nylon (price per coil from 4700r). The weight of the finished product is about 20 grams. Print without post-processing. The total cost is 200 rubles.
Plastic - carbon-filled nylon (price per coil from 4700r). The weight of the finished product is about 20 grams. Print without post-processing. The total cost is 200 rubles.
Model watch
The model is modeled to order (the cost of modeling is from 1000 rubles). The product is printed on an industrial printer using soluble support. Print without post-processing. The cost of the finished product - from 700 rubles per piece (depends on the number of required products).
Traction prosthesis
The model is taken from an open source (you can download the modified version of the prosthesis here). The weight of the used material is about 600 gr, printed with ABS plastic (the cost of the coil is from 800 r). After printing, post-processing and assembly took place. The total cost of the product - from 3000 r (depends on the print material, support material, filling, etc.).
Pedal layout
Production of a 3D model according to the drawing (from 1000 r). The weight of the finished model is about 200 gr. The product was printed with engineering carbon-filled plastic (the cost of the coil is from 4700 r). Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished product is about 3000 rubles.
The weight of the finished model is about 200 gr. The product was printed with engineering carbon-filled plastic (the cost of the coil is from 4700 r). Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished product is about 3000 rubles.
Photopolymer printers
Model jaws for crowns
Files for printing were obtained using a 3D scanner and finalized in a 3D editor (the cost of scanning is from 3000 r, the cost of manual revision is from 1000 r). Printing on an industrial photopolymer printer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is from 80 r per gram.
Burn-out resin rings
The model is made to order. Printing on a desktop SLA printer with a burnable polymer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is 200 rubles per product.
Miniatures
The models were bought on the myminifactory website (the cost of the model is from $2). Made with a desktop DLP printer. Post-processing was not required. The cost of the finished figurine is from 70 r per gram.
Made with a desktop DLP printer. Post-processing was not required. The cost of the finished figurine is from 70 r per gram.
Custom 3D printing
Many owners of 3D printers are thinking about monetizing their hobby. But you should understand that the price of 3D printing “for yourself” and the price of commercial printing are very different.
When starting to print to order, it is better to have several printers working on different technologies.
Cost of commercial 3D printing
In addition to the cost of the model, to the commercial production of products, you can add:
-
Modeling. Often the client needs not only to make a part, but to pre-model it. It can be a simple cogwheel that doesn't take long to model, or it can be a complex sculpture that takes more time to model than it does to make.
-
Model post-processing. This can be simply the removal of supports, with cleaning of the place of their contact with the product, or a complete processing cycle (puttying, surface grinding, painting, etc.
 ).
).
It should be borne in mind that it is not always possible to print the model the first time. Sometimes it may take several attempts. And these are additional costs.
What is unprofitable to print
Despite the wide possibilities of 3D printing, there are models that are unprofitable to make on a 3D printer. For such models, it is better to use other manufacturing methods.
Commercial print examples
Jewelry for further casting
Manufacture of promotional items and souvenirs
Piece miniatures or master model for further casting
3D printed layout
Profitable to print on a 3D printer:
-
If the item is only sold as an assembly. For example, a small gear broke in the mechanism, but the mechanism is sold only “assembly”.
 It is much cheaper to make the desired gear on a 3D printer than to buy the entire mechanism.
It is much cheaper to make the desired gear on a 3D printer than to buy the entire mechanism.
-
A small batch of parts. Small batches, especially models with complex geometry, are more profitable to produce on a 3D printer than by casting or other methods.
Totals
If you need several models or a small project, sometimes it will be more expedient to outsource manufacturing. After all, in addition to buying equipment and materials, you will have to understand the nuances of the settings and the characteristics of various materials.
Buying a 3D printer for commercial use is justified if you can fully load it with work or then it can be used for other purposes.
To print to order, you need to have several printers working on different technologies. It is better to get several devices with a smaller print area than to buy just one printer, albeit with a large working area.
#Useful
Expert in additive technologies and 3D printing with over 5 years of experience.












