Micro 3d laser scanner
Desktop 3D Scanner for small objects
| Scanner type | Desktop | Handheld | Handheld | Handheld | Handheld |
| 3D point accuracy, up to | 0.01 mm | 0.05 mm | 0.1 mm | 0.1 mm | 0.1 mm |
| 3D resolution, up to | 0.029 mm | 0.1 mm | 0.2 mm | 0.5 mm | 0.2 mm |
| 3D accuracy over distance, up to | — | 0.05 mm + 0.3 mm/m | 0.1 mm + 0.3 mm/m | 0.1 mm + 0.3 mm/m | 0.1 mm + 0.3 mm/m |
| HD Mode | N/A | N/A | Yes | No | Yes |
| Hybrid geometry and texture tracking | N/A | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Data processing algorithms | Geometry based | Geometry and texture based | Geometry and texture based | Geometry based | Geometry and texture based |
| Working distance | — | 0. | 0.4 – 1 m | 0.4 – 1 m | 0.35 – 1.2 m |
| Volume capture zone | 324 cm³ | 2,000 cm³ | 61,000 cm³ | 61,000 cm³ | 160,000 cm³ |
| Ability to capture texture | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Texture resolution | 6.4 mp | 1.3 mp | 1.3 mp | — | 2.3 mp |
| Colors | 24 bpp | 24 bpp | 24 bpp | — | 24 bpp |
| 3D reconstruction rate for real-time fusion, up to | — | 7.5 fps | 16 fps | 16 fps | 22 fps |
| 3D reconstruction rate for 3D video recording, up to | — | 7.5 fps | 16 fps | 16 fps | 44 fps |
| 3D reconstruction rate for 3D video streaming, up to | — | — | — | — | 80 fps |
| Data acquisition speed, up to | 1 mln points/s | 1 mln points/s | 18 mln points/s | 2 mln points/s | 35 mln points/s |
| 3D exposure time | Customizable | 0. 0002 s 0002 s | 0.0002 s | 0.0002 s | 0.0002 s |
| 2D exposure time | Customizable | 0.0002 s | 0.00035 s | 0.00035 s | 0.0002 s |
| 3D light source | Blue LED | Blue LED | Flashbulb | Flashbulb | VCSEL |
| 2D light source | RGB LED | White 6 LED array | White 12 LED array | White 12 LED array | White 12 LED array |
| Interface | USB 3.0 | 1 × USB 2.0, USB 3.0 compatible | 1 × USB 2.0, USB 3.0 compatible | 1 × USB 2.0, USB 3.0 compatible | Wi-Fi, Ethernet, SD card |
| Supported OS | Windows 10 x64 | Windows 7, 8 or 10 x64 | Windows 7, 8 or 10 x64 | Windows 7, 8 or 10 x64 | Windows 7, 8, 10 x64 |
| Recommended computer requirements | Intel Core i7 or i9, 64+ GB RAM, NVIDIA GPU with at least 3 GB VRAM, CUDA 3.5+ | Intel Core i7 or i9, 32 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM | Intel Core i7 or i9, 64+ GB RAM, NVIDIA GPU with 8+ GB VRAM, CUDA 6. 0+ 0+ | Intel Core i7 or i9, 32 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM | Intel Core i7 or i9, 64+ GB RAM, NVIDIA GPU with 8+ GB VRAM, CUDA 6.0+ |
| Minimum computer requirements | Intel Core i5, i7 or i9, 32GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM | Intel Core i5, i7 or i9, 18 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM | HD: Intel Core i7 or i9, 32 GB RAM, NVIDIA GPU with CUDA 6.0+ and at least 2 GB VRAM SD: Intel Core i5, i7 or i9, 12 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM | Intel Core i5, i7 or i9, 12 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM | HD: Intel Core i7 or i9, 32 GB RAM, NVIDIA GPU with CUDA 6.0+ and at least 4 GB VRAM SD: Intel Core i5, i7 or i9, 32 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAMA computer is needed only for data processing. Scanning does not require a computer. |
| 3D mesh | OBJ, PLY, WRL, STL, AOP, ASC, PTX, E57, XYZRGB |
| CAD | STEP, IGES, X_T |
| Measurements | CSV, DXF, XML |
| Power source | AC power | AC power or external battery pack | AC power or external battery pack | AC power or external battery pack | Built-in exchangeable battery, optional AC power |
| Dimensions, HxDxW | 290 x 290 x 340 mm | 190 × 140 × 130 mm | 262 × 158 × 63 mm | 262 × 158 × 63 mm | 231 × 162 × 230 mm |
| Weight | 12 kg / 26.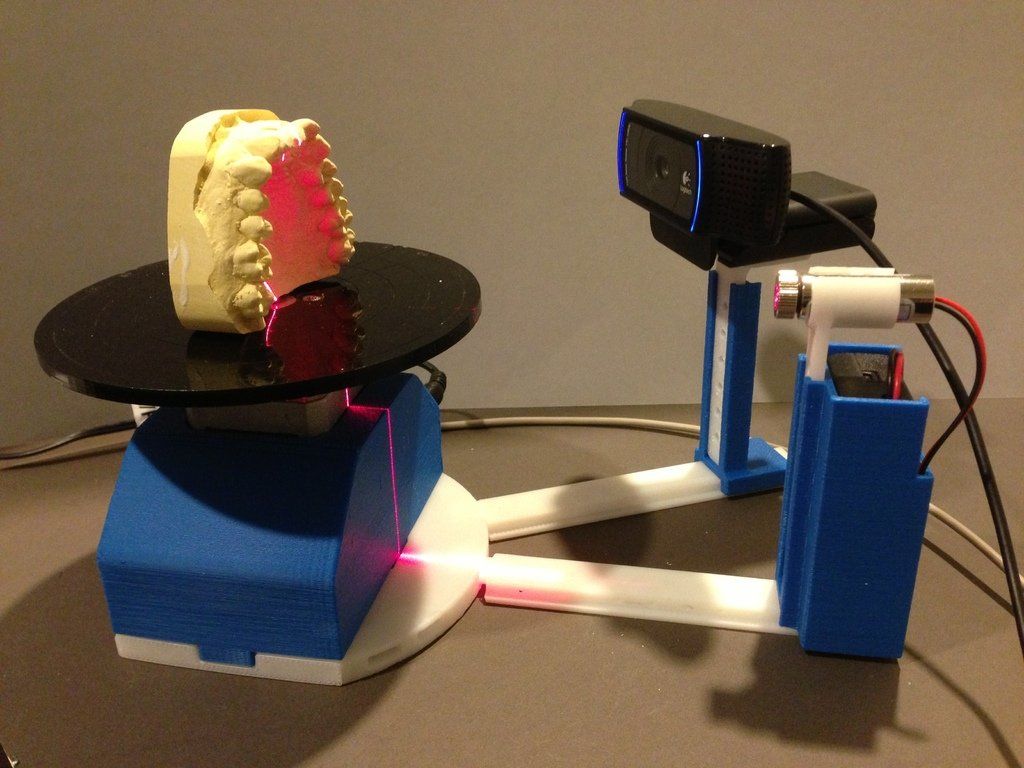 7 lb 7 lb | 0.8 kg / 1.8 lb | 0.9 kg / 2 lb | 0.9 kg / 2 lb | 2.6 kg / 5.7 lb |
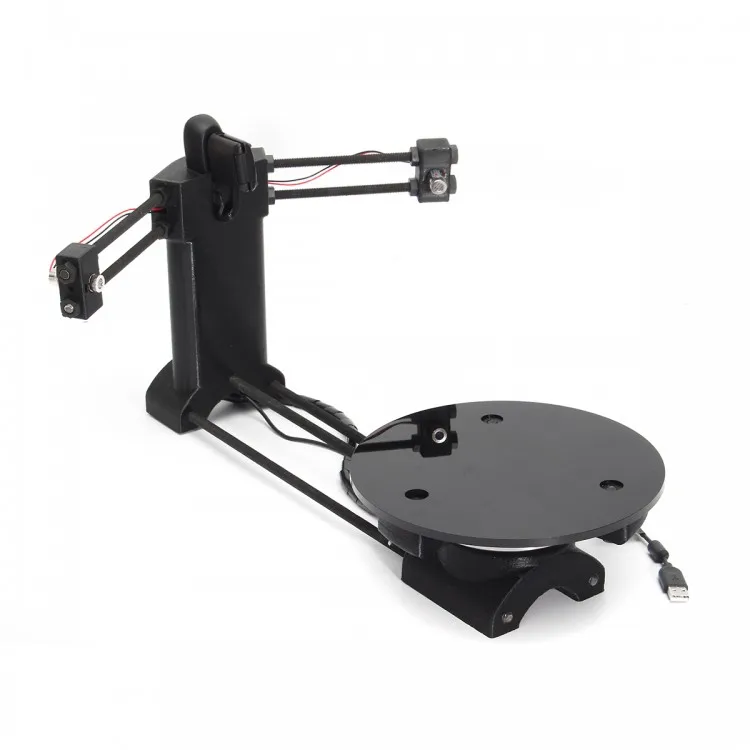
Artec Micro 3D Desktop Scanners
Artec Micro, is an automated, metrology-grade desktop 3D scanner. Equipped with cutting-edge twin cameras, Artec Micro is the company’s most accurate 3D scanner to-date. Complete with blue LED lights that are synchronized with the scanner’s dual axis rotation system, Artec Micro creates the perfect digital copy using minimal frames. With a single click, this fully-automated, industrial scanner springs to life to create a high-resolution color 3D scan that boasts an incredible point accuracy of up to 10 microns (0.4 thou), a tenth the size of a single grain of table salt. Resolution of .029mm (0.0011") and a 6.4 MP camera that allows for the capture of texture data.
Videos
Artec Micro is a new member in the family of Artec 3D scanners
| Technical Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Scanner type | Desktop |
| 3D point accuracy, up to | 0.01 mm |
| 3D resolution, up to | 0.029 mm |
| 3D accuracy over distance, up to | – |
| Working distance | – |
| Volume capture zone | 324 cm³ |
| Linear field of view, HxW @ closest range | – |
| Linear field of view, HxW @ furthest range | – |
| Angular field of view, HхW | – |
| Ability to capture texture | Yes |
| Texture resolution | 6.4 mp |
| Colors | 24 bpp |
| 3D reconstruction rate for real-time fusion, up to | – |
| 3D reconstruction rate for 3D video recording, up to | – |
| 3D reconstruction rate for 3D video streaming, up to | – |
| Data acquisition speed, up to | 1 mln points / sec. |
| 3D exposure time | Customizable |
| 2D exposure time | Customizable |
| 3D light source | Blue LED |
| 2D light source | RGB LED |
| Position sensors | – |
| Display / touchscreen | USB streaming through an external computer |
| Multi-core processing | On external computer |
| Interface | USB 3.0 |
| Internal hard drive | – |
| Computer Requirements | |
|---|---|
| Supported OS | Windows 7, 8 or 10 x64 |
| Minimum computer requirements | i5 or i7 recommended, 32GB RAM |
| Not supported: Windows XP, Windows Vista, 32-bit OS, AMD FirePro M6100 Fire GL V Not recommended: Xeon or AMD processors, NVIDIA SLI or AMD CrossFire configurations NVIDIA Quadro and Intel cards are officially supported starting from the release of Artec Studio 11.  | |
| Output formats | |
|---|---|
| 3D mesh formats | OBJ, PLY, WRL, STL, AOP, ASC, PTX, E57, XYZRGB |
| 3D point cloud formats | BTX, PTX |
| Formats for measurements | CSV, DXF, XML |
| Power source and dimensions | |
|---|---|
| Power source | AC power |
| Dimensions, HxDxW | 290 x 290 x 340 mm |
| Weight | 12 kg / 26.7 lb |
scopes and overview of models / Sudo Null IT News
3D laser scanning - creating a digital model of a physical body using a laser beam. The technology is non-contact, works at close and long distances, eliminates damage to objects during scanning. The principle of operation of 3D laser scanners: a directed laser beam is reflected from the surface of an object, forming a cloud of points. Each point has its own coordinates in space. The software identifies them and creates a finished 3D digital model based on this data.
Each point has its own coordinates in space. The software identifies them and creates a finished 3D digital model based on this data.
From the overview you will find out where laser scanning is used and what equipment is used to solve related problems.
Purpose of laser scanners
Source: newequipment.com
In comparison with traditional measurement methods, laser scanners have an important advantage - they can digitize objects with complex surfaces and work in hard-to-reach places for humans. The main areas of application of devices are input and output quality control in production, inspection of working devices in order to prevent and eliminate defects, reverse engineering and other areas.
Construction, renovation and renovation of objects
Source: ellisdon.com
During the preparation of the building design, it is necessary to evaluate the features of the site and the cost of the forthcoming works. With the help of 3D laser scanners, a landscape model is created, on the basis of which further work is carried out. During the construction process, intermediate control of the geometry of future buildings is required: walls, corners, openings, etc. Laser scanning copes with this task more accurately and faster than conventional measuring technologies.
With the help of 3D laser scanners, a landscape model is created, on the basis of which further work is carried out. During the construction process, intermediate control of the geometry of future buildings is required: walls, corners, openings, etc. Laser scanning copes with this task more accurately and faster than conventional measuring technologies.
The basis for an exterior or interior renovation is often an accurate digital model, on the basis of which changes and additions to the current interior or exterior are planned. Laser scanners are also indispensable in this area.
Road networks and transport
Source: autodesk.com
Laser scanning is becoming an integral part of the planning and creation of urban and suburban road networks, tunnels, pedestrian sections, railways, ports. The technology is used to assess the current state of coatings, plan and estimate the cost of repairs, to obtain models of perennial structures, such as bridges. The equipment is involved in the design, manufacture, repair and tuning of cars, air transport and ships.
The equipment is involved in the design, manufacture, repair and tuning of cars, air transport and ships.
Public utilities
Source: 3dscanner.es
With the help of 3D laser scanners, it became possible to quickly digitize and document engineering communications. Scanning significantly saves time during maintenance and reconstruction. The devices work remotely, minimizing the risks of people when working in adverse conditions and in hard-to-reach areas.
Oilfield installations
Source: ramboll.com
Oil production complexes located in the water require constant monitoring of work processes. Objects are regularly exposed to adverse and changeable environmental influences: winds of different strengths and directions, currents, temperature changes, etc. 3D laser scanning is becoming an integral part of the inspection of oil production installations.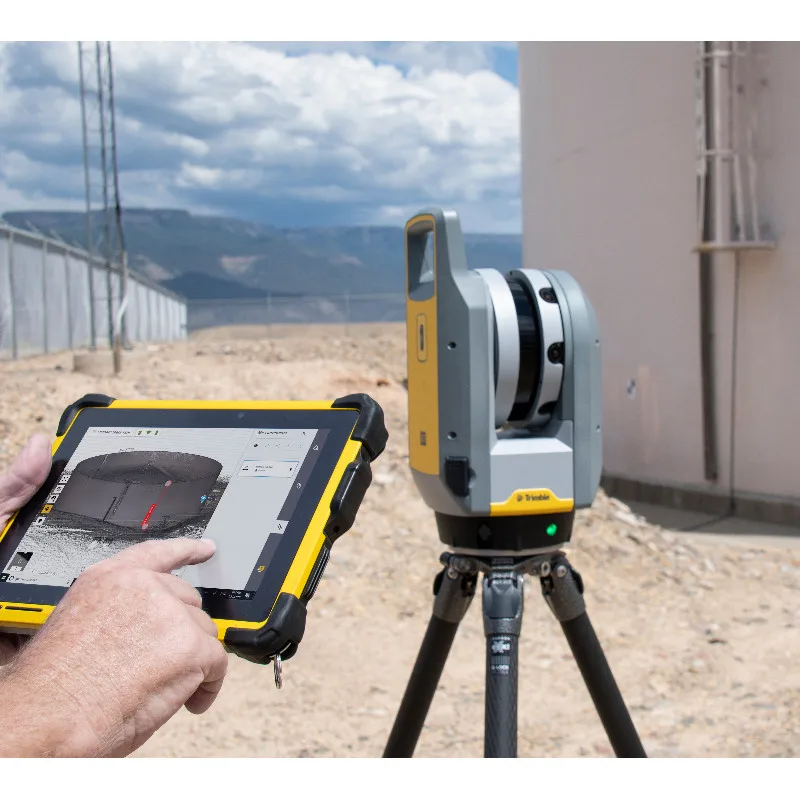 The equipment allows you to quickly identify and fix deformations and other damage, control wear, calculate the timing of scheduled maintenance, and prevent accidents.
The equipment allows you to quickly identify and fix deformations and other damage, control wear, calculate the timing of scheduled maintenance, and prevent accidents.
Forensic examination
Source: faro.com
Photographs and manual measurements in investigative processes and forensic examinations are being replaced by 3D laser scanning. The devices create three-dimensional models of scenes of incidents with accurate fixation of the location of objects and the distances between them. The data is used in the process of pre-trial and litigation.
Other applications
Source: news.microsoft.com
3D laser scanners facilitate and optimize workflows in the following areas:
- In cartography and geodesy - when creating terrain plans, maps, geographic information systems (GIS).
- In archeology - in the restoration and preservation of ancient artifacts.

- In paleontology, to create missing parts of excavated skeletons.
- In medicine, including plastic surgery and dentistry.
Overview of models and manufacturers
FARO Focus
Source: ifworlddesignguide.com
FARO is one of the popular manufacturers of laser scanning devices. The new Focus3D S-series instruments stand out from other scanners in lightness and compact size, as well as the ability to work in bright sunlight and keep in touch with the location using GPS.
The FOCUS 3D S 150 scanner works at a distance of up to one hundred and fifty meters, with an accuracy of up to ±2000 microns at a maximum distance. The device is used in design, architecture and construction, for digitizing equipment and other objects.
You can learn more about this model on the website.
Source: youtube.com
Focus3D S 350 scans with the same accuracy as the previous device, but the distance to the measurement object is increased to 0. 35 km. The device is designed for outdoor use.
35 km. The device is designed for outdoor use.
Source: kkgeosystem.blogspot.com
SHINING 3D
Source: shining3d.com
FreeScan is a line of well-known Chinese manufacturer of digital equipment SHINING 3D. These are universal laser handheld 3D scanners FreeScan X5 (X5+), FreeScan X7 (X7+) weighing up to 1 kg, with an excellent set of professional features.
Basic parameters:
Specifications
Creaform
Source: foundry-planet.com
Creaform's SCAN 3D range is characterized by high scanning quality combined with ease of use. Portable laser scanners HandySCAN 3D, MetraSCAN 3D have a clear interface, do not require special skills and complex user training.
Instrument features:
ScanTech
Handheld range
Source: cmmxyz. com
com
The HandHeld Prince series uses blue and red laser beams to scan large and small objects with high accuracy. Scanners can operate in bright sunlight and low light conditions. Due to its compact size, high speed and detail, the equipment is widely used in reverse engineering, quality inspection, digitization of museum, archaeological and other objects.
Key features:
Composite series
Source: twitter.com
In addition to the dual scan mode, the KSCAN20 is equipped with a photogrammetry system, thanks to which the working area of the device is 2.5 m * 3 m with an accuracy of 35 µm / m.
Blue and red lasers provide high-speed scanning of up to 650,000 measurements per second with a resolution of 0.01 mm.
Key Features:
3D Laser Scanner Applications
Reduce construction costs and time with FARO Focus
Source: autodesk. com
com
US construction company Gilbane invested $60,000 in the purchase of a FARO Focus-S 350 laser scanner, software and employee training. At first glance, the amount seems too large for a small-scale firm. But, after making calculations, the company's management came to the conclusion that the investments would pay off in the shortest possible time.
According to Gilbane's director of 3D design, John Tocci Jr., after introducing the expensive new technology, the company began to use the equipment even in areas where it was not originally planned. The specialists managed to save $30,000 for one hour of Focus-S 350 and Autodesk Revit software.
Source: autodesk.com
Building a digital model of air ducts and other systems made it possible to avoid errors during the installation of physical objects, which could take several weeks. The use of FARO Focus in the assembly of plumbing, electrical and mechanical installations helped to optimize costs at all stages of work
Case “Modernization of the building of the University of Miami”
Source: elevar. com
com
At the time of the start of work, the architects had drawings made 85 years ago, and a little more than 4.5 thousand square meters of the old building. Using a 3D laser scanner, Gilbane digitized the training areas in one day. Modernization of load-bearing structures, as well as the main utility systems: plumbing, electrical and ventilation, was based on data obtained from scanning.
Quality Inspection with ScanTech
Source: 3d-scantech.com
The advantage of metal stamping over forging and casting is the lower weight and thickness of the resulting parts. The use of molds gives high accuracy and maximum compliance of the obtained parts with the specified characteristics, but does not completely exclude deviations and deformations. Which, in turn, can lead to difficulties in assembling finished products and reducing product quality. Therefore, constant quality inspection is a necessary part of production.
Having understood the problems of the manufacturer, ScanTech experts proposed to check the quality of stamped parts using the PRINCE laser scanner. The ability to switch blue and red laser modes allowed the device to combine the functionality of traditional portable and metrological 3D scanners. The mode of operation with an active beam of a red laser provides fast digitization of objects. In the case of increased requirements for accuracy and detail, turn on the blue laser beam mode.
The photo shows the stages of work:
1. Installing markers - takes about two minutes.
Source: 3d-scantech.com
2. Digitizing a part takes about three minutes.
Source: 3d-scantech.com
Source: 3d-scantech.com
3. Identification of deviations - lasts 3 minutes.
Source: 3d-scantech.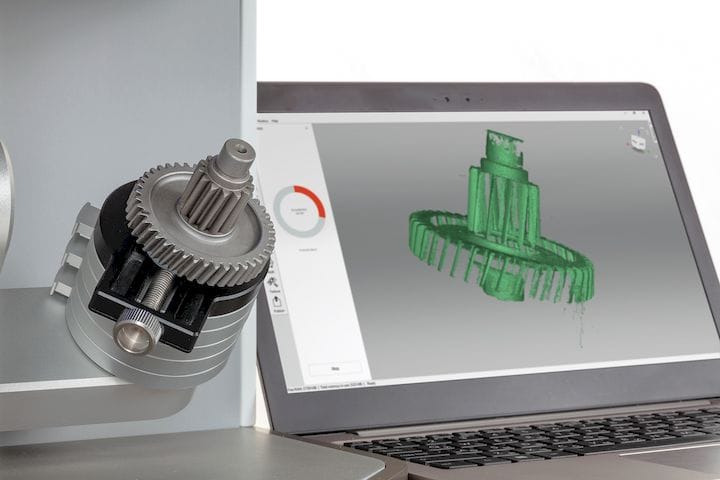 com
com
The digital model demonstrates the parameters and deviations, allows you to correct errors at the design stage. The case clearly shows that the process required a minimum of time and effort.
Using FARO 3D scanners on Justin Timberlake's world tour
Source: disguise.one
Timberlake's "Man of the Woods" program features scenery brought to life on stage. First, the ScanLAB team digitized a number of corners of the forest in the US state of Oregon. Laser projectors then directed images over the auditorium and stage, painting amazing pictures of the Portland landscape on translucent canvases suspended in the air.
Source: faro.com
Two Faro Focus X 330 laser scanners, Faro Scene 6.2 software were used to prepare visual effects. In total it took 40 digital copies and 1 working day in the concert hall.
Source: www. esa.int
esa.int
Considering the limited preparation time, the large surface areas for displaying the image and the corresponding need for high image resolution, creating visual effects in a short time without using the chosen technology was impossible.
Selection guide for 3D laser scanners
In the review, we introduced you to the equipment of market leaders with an excellent reputation. All the devices described have high performance, so we recommend that you pay attention to these devices for use in various fields:
FARO Focus: Focus3D S350, Focus 3D S150.
Creaform: MetraSCAN 350 (350 Elite), MetraSCAN 750 (750 Elite), HandySCAN Black (Black Elite).
SHINING 3D: FreeScan X5 (X5+), FreeScan X7 (X7+).
ScanTech: KSCAN20, PRINCE 775, PRINCE 335.
Results
Source: 3d-scantech.com
The cases discussed clearly prove that the use of 3D laser scanning optimizes workflows in many areas.![]() The range of tasks solved with the help of 3D laser scanners is constantly expanding.
The range of tasks solved with the help of 3D laser scanners is constantly expanding.
Buy a professional 3D laser scanner in Top 3D Shop — experienced specialists will help you choose the most suitable equipment, software for your business, and offer a project to modernize production.
3D ground laser scanning
Point cloud examples
Despite the fact that the first terrestrial 3D scanners appeared in the last century, there is no reason to state that 3D laser scanning technology is widely used in geodesy. The main reasons, probably, are the still high cost of such systems and the lack of information on how to use them effectively in various applications. Nevertheless, interest in this technology and its demand in the market of geodetic equipment are growing exponentially every year.
What is a 3D laser scanner?
According to the type of information received, the device is in many ways similar to a total station. Similar to the latter, the 3D scanner uses a laser range finder to calculate the distance to an object and measure vertical and horizontal angles to obtain XYZ coordinates. The difference from a total station is that daily shooting with a ground-based 3D laser scanner is tens of millions of measurements. Obtaining a similar amount of information from a total station will take more than one hundred years ...
Similar to the latter, the 3D scanner uses a laser range finder to calculate the distance to an object and measure vertical and horizontal angles to obtain XYZ coordinates. The difference from a total station is that daily shooting with a ground-based 3D laser scanner is tens of millions of measurements. Obtaining a similar amount of information from a total station will take more than one hundred years ...
The initial result of the 3D laser scanner is a point cloud. In the process of shooting, three coordinates (XYZ) and a numerical indicator of the intensity of the reflected signal are recorded for each of them. It is determined by the properties of the surface on which the laser beam falls. The point cloud is colored depending on the degree of intensity and after scanning looks like a three-dimensional digital photo. Most modern models of laser scanners have a built-in video or photo camera, so that the point cloud can also be painted in real colors.
In general, the operation of the device is as follows. The laser scanner is mounted opposite the object to be filmed on a tripod. The user sets the required point cloud density (resolution) and survey area, then starts the scanning process. To obtain complete data about an object, as a rule, it is necessary to perform these operations from several stations (positions).
The laser scanner is mounted opposite the object to be filmed on a tripod. The user sets the required point cloud density (resolution) and survey area, then starts the scanning process. To obtain complete data about an object, as a rule, it is necessary to perform these operations from several stations (positions).
Then the initial data received from the scanner is processed and the measurement results are prepared in the form in which they are required by the customer. This stage is no less important than field work, and is often more time-consuming and complex. Profiles and sections, flat drawings, three-dimensional models, calculations of areas and volumes of surfaces - all this, as well as other necessary information, can be obtained as the final result of working with a scanner.
Where can laser scanning be used?
Main applications of 3D scanning:
- industrial enterprises
- building and architecture
- road shooting
- mining
- monitoring of buildings and structures
- documentation of emergencies
This list is far from complete, since every year users of laser scanners perform more and more unique projects that expand the scope of technology.
Laser Scanning from Leica Geosystems - History of Laser Scanners
The history of Leica laser scanners began in the 90s of the last century. The first model 2400, then under the Cyra brand, was released in 1998. In 2001, Cyra entered Leica Geosystems into the HDS (High-Definition Surveying) division. Now, after 14 years, Leica Geosystems introduces a line of two scanning systems on the market.
As mentioned above, 3D laser scanning is used in completely different areas, and there is no universal scanner that would effectively solve all problems.
For shooting industrial facilities where a long range is not required, but the model must be very detailed (that is, an accurate high-speed device is needed), the Leica ScanStation P30 laser scanner will be optimal: range up to 120 m, speed up to 1,000,000 points per second.
Completely different requirements are imposed on the scanner when it comes to shooting opencast mines and storages of bulk materials in order to calculate volumes. Here, centimeter accuracy of the rangefinder is enough, and the shooting range and protection from weather conditions and dust come to the fore. The ideal tool for scanning in such conditions - Leica HDS8810 with a range of up to 2,000 m and IP65 dust and water resistance. In addition, this device is the only one on the market of scanning systems that operates in the temperature range from -40 to +50 degrees. That is, the HDS8810 is a laser scanner that works in all weather conditions.
Here, centimeter accuracy of the rangefinder is enough, and the shooting range and protection from weather conditions and dust come to the fore. The ideal tool for scanning in such conditions - Leica HDS8810 with a range of up to 2,000 m and IP65 dust and water resistance. In addition, this device is the only one on the market of scanning systems that operates in the temperature range from -40 to +50 degrees. That is, the HDS8810 is a laser scanner that works in all weather conditions.
The key model of Leica Geosystems' HDS division is the Leica ScanStation P40 . The famous and most popular ScanStation line in the world, whose history began in 2006, was replenished in April 2015 with the P40 scanner. The P40 inherited the accuracy and speed from the previous model, but has become more long-range, and the data quality has become even better. In terms of the range of tasks to be solved, this device is truly a leader in its segment. It is no coincidence that despite the "youth" of this model, it has already gained wide popularity in the world.
Laser Scan Data Processing Software (Point Clouds)
It is impossible not to say a few words about the software for processing data received from the scanner. Potential customers pay undeservedly little attention to this component of the 3D laser scanning system, although data processing and obtaining the final result of the work are no less important stages of the project than field work. The range of Leica HDS software is truly the widest on the laser scanning market.
The main element of the spectrum is, of course, the Cyclone complex. This modular software system is rightfully considered the most popular in the world and has a large package of tools for processing data obtained using a scanner. Leica also has a number of more highly specialized programs. For those who are accustomed to working in traditional CAD, there is a series of software products Leica CloudWorx embedded in AutoCAD, MicroStation, AVEVA and SmartPlant, which allows users of these programs to work directly with point clouds.