Hbd metal 3d printer
HBD Metal 3D Printer — 3D Printing Business Directory
Contact Details
| Name | HBD Metal 3D Printer |
| Founded | HBD |
| Legal Entity | HBD |
| ZIP code | 201109 |
| Full Address | China, Shanghai, Building #30, Jinlinggu Science Park, No. 525 Yuanjiang Road, Minhang District, Shanghai |
| Phone | +86 138 1639 2443 |
| Website | en.hb3dp.com |
| [email protected] |
Share This Listing
Profile Description
Contact Person: Nicolas YAO, yaofm@hb3dp. com
HBD is a manufacturer of metal 3D printers, providing proprietary additive manufacturing equipment, technical solutions, and OEM services with regard to selective-laser-melting metal 3D printing technology.
In 2007, the pioneers of HBD, who were engaged previously in laser technology, stepped into the metal additive manufacturing sector. With years of unremitting efforts and considerable investment on R&D, the first metal 3D printer created by HBD came into birth in 2013. Since then, HBD has become one of the well known brands in China’s metal 3D-print industry.
Today, HBD has obtained more than 200 technical patents, 20 software copyrights, and numerous other certificates and qualifications. Besides being connected to the most influential Chinese experts and market resources of additive manufacturing, HBD is authorized as Industry, University, and Research Base by Tongji University and Guangdong Industrial University, and work closely with many other universities including Shanghai Jiaotong University and Harbin Institute of Technology.
Rely on rich industrial resource and experience of market service as well as innovative modern management concept, HBD enjoys a fairly good market share and public praise in industries of aerospace, automobile, molding, dentistry, orthopedics, education and research, etc.
HBD is comprised of the two enterprises Shanghai Hanbang United 3D Tech Co., Ltd. and Guangdong Hanbang 3D Technology Co., Ltd.
Guangdong Hanbang 3D Tech Co., Ltd., known as Guangdong Hanbang, is located in Zhongshan City, concentrating on R&D and production of metal 3D printing machines. With 10-year assiduous research and accumulation of metal 3D printing technology, Guangdong Hanbang has innovated many successful series of metal 3D printers, software, control system, process parameters, and technical database in association with market demands.
Shanghai Hanbang United 3D Tech Co., Ltd., known as Shanghai Hanbang, is an international division of HBD in response to National Intelligent Manufacturing 2025 and National Strategy of “One Belt, One Road”. Favourably endowed by the international position of “Oriental Pearl”, Shanghai Hanbang is devoted to establish partnership with customers from all over the world, providing mutual development, technical solutions, customer experience, and after-sales services.
Favourably endowed by the international position of “Oriental Pearl”, Shanghai Hanbang is devoted to establish partnership with customers from all over the world, providing mutual development, technical solutions, customer experience, and after-sales services.
For more information, please visit the HBD website: en.hb3dp.com
Range of Services
- Metal 3D Printer
Address Details:
China, Shanghai
Phone: +86 138 1639 2443
Fax:
E-mail: [email protected]
Website: en.hb3dp.com
Opening Hours:
Company haven't yet any product.
h4D HBD Metal 3D Printers and Materials: Overview
In this article, we will tell you about SLM 3D printers and related materials from the China-based HBD company, also known as h4D HBD. Discover what models are available in the lineup, their specs and features, as well as in which industries they are utilized.
Discover what models are available in the lineup, their specs and features, as well as in which industries they are utilized.
To learn more about the manufacturer and examine application cases, read the following article.
HBD-150 3D Printer
- Galvo system SCANLAB
- Laser Power 200W
- Layer thickness 10–40 μm
- Oxygen content ≤100 PPM
- Printable materials Stainless steel, Cobalt-chrome alloy, Tool steel, Titanium alloy, High-temperature alloy, Hastelloy, some precious metals
- Scanning speed ≤10000 mm/s
- Scanning track width 40–80 μm
- Software HBD Build Expert, Materialise Magics (supported)
- Typical accuracy 0.
 05–0.1 mm
05–0.1 mm - Build volume φ159 x 100 mm
- Technology SLM
- Outer dimensions 1150 x 1150 x 1830 mm
- Weight 900 kg
Go to product
HBD-150 and 150D metal 3D printers are widely used in medicine, particularly for dental and orthopedic applications, including 3D printing of implants and surgical instruments, rapid prototyping, education and research. Designed primarily for printing of dentures, crowns, and jaw implants, the HBD-150D modification is equipped with two 200W lasers. Both models feature a compact build volume which allows printing small to medium items as a whole or smaller objects in batches.
Designed primarily for printing of dentures, crowns, and jaw implants, the HBD-150D modification is equipped with two 200W lasers. Both models feature a compact build volume which allows printing small to medium items as a whole or smaller objects in batches.
Industry applications
Dentistry: 50%
Education: 30%
Implantation: 20%
HBD-200 3D Printer
- Galvo system SCANLAB
- Laser Power 200W×2
- Layer thickness 10–40 μm
- Oxygen content ≤100 PPM
- Printable materials Stainless steel, Cobalt-chrome alloy, Tool steel, Titanium alloy, High-temperature alloy, Hastelloy, some precious metals
- Relative density Nearly 100%
- Scanning speed ≤10000 mm/s
- Scanning track width 40–80 μm
- Software HBD Build Expert, Materialise Magics (supported)
- Typical accuracy 0.
 05–0.1 mm
05–0.1 mm - Build volume 270 x 170 x 120 mm
- Technology SLM
- Outer dimensions 1780 x 1380 x 1900 mm
- Weight 1100 kg
Go to product
The HBD-200 is equipped with two fiber lasers and a dual galvanometer increasing its productivity and accuracy. The printer features a long build platform of 270 mm with a rather low height of the build chamber, which significantly reduces its cost, providing the possibility to build fairly large parts of small height.
The printer features a long build platform of 270 mm with a rather low height of the build chamber, which significantly reduces its cost, providing the possibility to build fairly large parts of small height.
Industry applications
Dentistry: 40%
Orthopedics: 30%
Prototypes: 20%
Education: 10%
HBD-350 3D Printer
- Galvo system SCANLAB
- Laser Power 500W / 500W×2
- Layer thickness 30–100 μm
- Oxygen content ≤100 PPM
- Printable materials Stainless steel, Cobalt-chrome alloy, Tool steel, Titanium alloy, High-temperature alloy, Aluminum alloy, Hastelloy, some refractory metals like Tungsten and Tantalum
- Relative density Nearly 100%
- Scanning speed ≤10000 mm/s
- Scanning track width 70–200 μm
- Software HBD Build Expert, Materialise Magics (supported)
- Typical accuracy 0.
 05–0.2 mm
05–0.2 mm - Build volume 325 x 325 x 400 mm
- Technology SLM
- Outer dimensions 1850 x 1250 x 2350 mm
Go to product
The HBD-350 is available in single and dual-laser configurations and features an efficient and reliable powder feeding system. Engineered with a closed automatic powder circulation system, it ensures a high safety level and control of the printing process. The unique multi-stage purification system of the HBD-350 meets the continuous production requirements and is suitable for 3D printing of press and injection molds, aerospace parts, automotive components, etc.
Engineered with a closed automatic powder circulation system, it ensures a high safety level and control of the printing process. The unique multi-stage purification system of the HBD-350 meets the continuous production requirements and is suitable for 3D printing of press and injection molds, aerospace parts, automotive components, etc.
Industry applications
Spare parts: 30%
Aviation: 30%
Molds: 10%
Aerospace: 10%
Machine building: 20%
HBD-E500 3D Printer
- Galvo system SCANLAB
- Laser Power 500W×2 / 500W×3
- Layer thickness 30–100 μm
- Oxygen content ≤100 PPM
- Printable materials Stainless steel, Cobalt-chrome alloy, Tool steel, Titanium alloy, High-temperature alloy, Aluminum alloy, Hastelloy, some refractory metals like Tungsten and Tantalum
- Relative density Nearly 100%
- Scanning speed ≤10000 mm/s
- Scanning track width 70–200 μm
- Software HBD Build Expert, Materialise Magics (supported)
- Typical accuracy 0.
 05–0.2 mm
05–0.2 mm - Build volume 430 x 520 x 520 mm
- Technology SLM
Go to product
Depending on the version, the HBD-E500 can be equipped with up to three lasers, featuring an intelligent powder recoating monitoring system. The printer can print large, high-quality and precise parts for the most demanding industrial and aerospace applications. The HBD-E500 is used to print unique products based on generative design and topological optimization, which allows producing lightweight parts maintaining their strength properties while reducing material consumption.
The HBD-E500 is used to print unique products based on generative design and topological optimization, which allows producing lightweight parts maintaining their strength properties while reducing material consumption.
Industry applications
Spare parts: 25%
Aviation: 20%
Aerospace: 25%
Machine building: 20%
Automotive: 10%
HBD-1000 3D Printer
- Galvo system SCANLAB
- Laser Power 500W×4 / 1000W×4
- Layer thickness 30–120 μm
- Oxygen content ≤100 PPM
- Printable materials Stainless steel, Cobalt-chrome alloy, Tool steel, Titanium alloy, High-temperature alloy, Aluminum alloy, Hastelloy, some refractory metals like Tungsten and Tantalum
- Relative density Nearly 100%
- Scanning speed ≤10000 mm/s
- Scanning track width 70–200 μm
- Software HBD Build Expert, Materialise Magics (supported)
- Typical accuracy 0.
 05–0.2 mm
05–0.2 mm - Build volume 600 x 600 x 1000 mm
- Technology SLM
Go to product
One of the most productive h4D HBD 3D printers, the HBD-1000 can be equipped with four 1000W or 500W lasers and features a closed automatic powder circulation system, an independent long-term multi-stage purification system, and integrated post-processing unit. The machine boasts a large build chamber making it suitable for almost any manufacturing industry, from aircraft to automotive.
The machine boasts a large build chamber making it suitable for almost any manufacturing industry, from aircraft to automotive.
Industry applications
Aerospace: 60%
Aviation: 30%
Other: 10%
HBD-1200 3D Printer
- Galvo system SCANLAB
- Laser Power 500W×2 / 1000W×2
- Layer thickness 20–120 μm
- Oxygen content ≤100 PPM
- Printable materials Stainless steel, Cobalt-chrome alloy, Tool steel, Titanium alloy, High-temperature alloy, Aluminum alloy, Hastelloy, some refractory metals like Tungsten and Tantalum
- Relative density Nearly 100%
- Scanning speed ≤10000 mm/s
- Scanning track width 70–200 μm
- Software HBD Build Expert, Materialise Magics (supported)
- Typical accuracy 0.
 05–0.2 mm
05–0.2 mm - Build volume 460 x 460 x 1500 mm
- Technology SLM
Go to product
The HBD-1200 is designed to print models of up to 460 x 460 x 1500 mm, which allows building large structural metal parts for aerospace, aviation, and heavy engineering. With one of the largest build chambers among metal 3D printers, the HBD-1200 meets all the basic needs of the aerospace and aviation industries. The device is available in two versions — with two 500W or 1000W lasers.
The device is available in two versions — with two 500W or 1000W lasers.
Industry applications
Aerospace: 80%
Aviation: 20%
Materials
Aluminum alloy AlSi10Mg
Aluminum powder pre-alloyed with silicon and magnesium has good casting properties and high strength and is used for printing thin walls and complex structures.
Stainless steel 316L
316L austenitic stainless steel has high strength and corrosion resistance, withstands wide-range low temperatures, and its overall performance is better than that of 310 and 304 steel. It also features good erosion resistance against chlorine compounds.
Nickel alloy Ni718
Ni718 is a nickel-based superalloy in a powder form with good aging resistance and high tensile and breaking strength, even at temperatures up to 700 °C. It has excellent corrosion resistance in a variety of aggressive environments.
Titanium alloy Ti6AlV4
Titanium-aluminum-vanadium alloy is characterized by high mechanical properties and good biocompatibility. Among other applications, it is used in medicine for 3D printing of endoprostheses.
Among other applications, it is used in medicine for 3D printing of endoprostheses.
Cobalt-chromium CoCr alloy
An original mixture of pre-alloyed powders, designed for printing parts with cobalt-chromium-molybdenum superalloy. The alloy is characterized by excellent mechanical properties as well as corrosion and heat resistance. It is used for various purposes, for example, 3D printing of dental crowns.
Maraging (martensitic-aging) steel
Maraging steel is a powdered martensitic hardened steel of high strength, toughness and ductility which is easily processed. The hardness of printed parts after heat hardening does not exceed 55 HRC. It is used where other high-strength steels and alloys are too brittle due to their higher hardness.
Bottom line
h4D HBD provides complete metal 3D printing solutions, offering not only high-end SLM 3D printers with various build volumes and smart features, but also metal powders with different compositions and final part properties, meeting all the requirements of industrial metal 3D printing.
The cost-efficiency and high quality of HBD products are proved by numerous industrial companies which have purchased more than 500 company’s SLM 3D printers. Learn more about the application cases from this article.
Hardware Overview: HBD
Metal 3D PrintersIn 2007, the Chinese company Shanghai Hanbang United 3D Tech Co., Ltd, known under the trademark HBD, entered the metal 3D printing industry. Having experience in the development of equipment and technical solutions, the company brought to the market a new generation of equipment for SLM printing, as well as its own software. HBD has obtained more than 60 technical patents and copyrights for 9programs and today has powerful resources of expert development. Rich experience in the service market and an innovative management concept allowed the company to conquer the market and gain public recognition.
Terem3D is the official distributor of HBD equipment in Russia.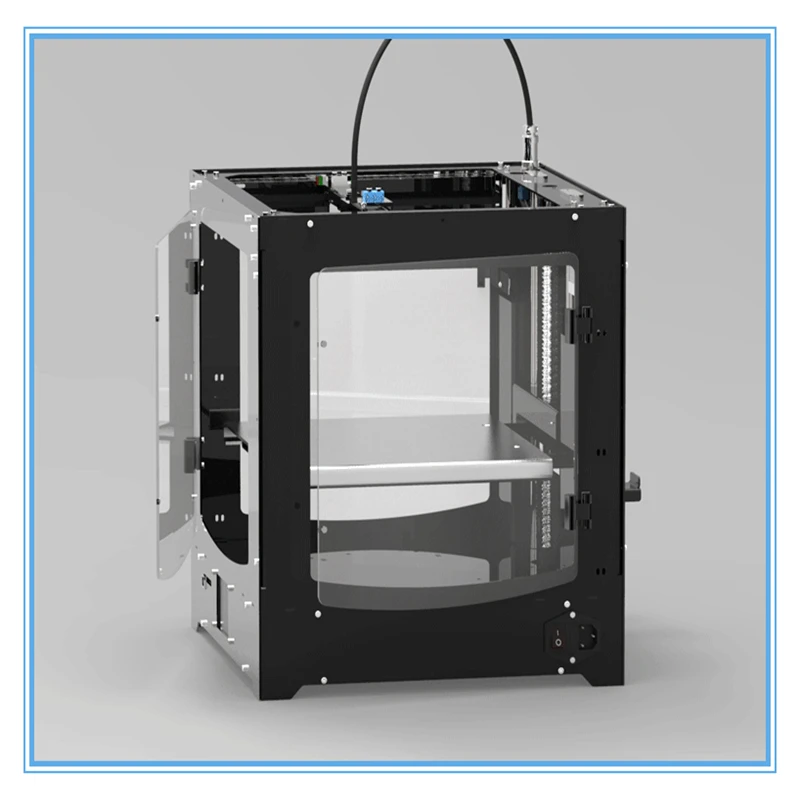
Today, HBD 3D printers are used in areas such as engineering, medicine and education. They are successfully used in the jewelry and even in the aerospace industry.
HBD works with many well-known medical institutions that use 3D printers to print surgical templates, metal implants, bone plates, instruments and other products, the need for which is obvious and growing every day. HBD plans to provide the healthcare industry with the latest digital technology solutions.
Additive technologies make it possible to shorten certain production cycles in the engineering industry, improve the physical and mechanical properties of the product, and get away from warehouse logistics and assembly lines. Already now, modern production facilities have fully automated production lines using additive technologies. These technologies have already firmly entered the life cycle of modern production.
Modern education of a designer, technologist, jeweler and many other professions is impossible without an understanding of modern production methods. Metal additive machines are part of the modern production process, and specialists working with this equipment begin their journey in educational institutions with the development of this technology. HBD metal additive machines are used both in production and in the educational process, which allows an employee, having received an education, to immediately be introduced into work.
Metal additive machines are part of the modern production process, and specialists working with this equipment begin their journey in educational institutions with the development of this technology. HBD metal additive machines are used both in production and in the educational process, which allows an employee, having received an education, to immediately be introduced into work.
Applications of HBD 3D printers:
1.Production of products with unique cooling and filtration channels
2.Medical products
3.Functional products
4.Building of products with a complex structure of topological optimization
5.Scientific research
6.Prototypes and spare parts
Advantages of HBD 3D Printer:
1. Reduction of production time:
- titanium products;
- products with a complex configuration;
- products that cannot be manufactured by other technologies.
2. Product weight reduction:
- weight reduction due to topological optimization;
- design.
3. HBD metal printers work with 90% metals and alloys.
4. HBD additive machines use open 3D printing technology. In other words, if the production process requires the use of metal with which the 3D printer has not yet worked and it lacks the appropriate settings for working with this particular material, the technologist will be able to independently select the mode for it and prepare the equipment for further work. Not all manufacturers of metal 3D printers provide this opportunity. Even the giants of metal 3D printing prefer to do their own hardware customization at the request of customers. On the contrary, HBD not only sells additive machines, but also trains manufacturing specialists to work autonomously with them.
5. Affordable price of HBD additive machines compared to their American and European counterparts. At the same time, HBD buys components for them in Europe, the USA and Japan.
6. Support in Russia. "Terem3D" is the official representative of HBD in Russia and always provides high-quality and prompt assistance to its customers. ■
■
, HBD additive machines, 3D printing technologies, metal 3D printers, HBD metal printers, Shanghai Hanbang United 3D Tech Co., Ltd, 3D metal printing, SLM printing
Other materials:
- Demo
- Comprehensive support and turnkey solutions for additive manufacturing
- Strengthening the Russian technology market with CNC machines
- Additive manufacturing: what's new?
- Development project
Attention!
We accept news, articles or press releases
with links and images. [email protected]
Metal 3D Printing - The Essential Guide
There is no hotter trend in 3D printing today than metal. We will talk about metal printing at home, how it is done on an industrial scale, about technologies, applications, printers, processes, prices and materials.
Metal 3D printing has grown in popularity over the past few years. And this is quite natural: each material offers a unique combination of practical and aesthetic qualities, can be suitable for a wide range of products, prototypes, miniatures, decorations, functional details and even kitchen utensils.
The reason metal 3D printing has become so popular is because the printed objects can be mass-produced. In fact, some of the printed parts are just as good (if not better) than those made with traditional methods.
In traditional production, working with plastic and metal can be quite wasteful - there is a lot of waste, a lot of excess material is used. When an aircraft manufacturer makes metal parts, up to 90% of the material is simply cut off. 3D printed metal parts require less energy and waste is reduced to a minimum. It is also important that the final 3D printed product is up to 60% lighter than a traditional part. Billions of dollars could be saved in the aviation industry alone—mainly through weight savings and fuel savings.
So, what do we need to know about metal 3D printing?
Metal 3D printing at home
where to start if you want to print metal objects at home? Given the extreme heat required for true metal 3D printing, a conventional FDM 3D printer will not be able to do this.
It is unlikely that in this decade it will be possible to print with liquid metal at home. Until 2020, you probably will not have a printer specialized for this purpose at home. But in a few years, as nanotechnology advances, we may see significant developments in new applications. This can be 3D printed with conductive silver, which will emit in much the same way as it does in 2D home printers. It will even be possible to mix different materials like plastic and metal in one object.
Materials for metal 3D printing at home
Even though you can't print actual metal objects at home, you can turn to plastic filament that has metal powders added to it.-kupit-v-soin-store.ru-4.png) ColorFabb, ProtoPasta and TreeD Filaments all offer interesting metal-PLA composite filaments. These filaments, containing a significant percentage of metal powders, remain pliable enough to be printed at low temperatures (200 to 300 Celsius) on virtually any 3D printer. At the same time, they contain enough metal to make the final object look, feel, and even weigh like metal. Iron-based filaments even rust under certain conditions.
ColorFabb, ProtoPasta and TreeD Filaments all offer interesting metal-PLA composite filaments. These filaments, containing a significant percentage of metal powders, remain pliable enough to be printed at low temperatures (200 to 300 Celsius) on virtually any 3D printer. At the same time, they contain enough metal to make the final object look, feel, and even weigh like metal. Iron-based filaments even rust under certain conditions.
But you can go further. Typically, up to 50 percent metal powder is added to 3D printing filament. Dutch company Formfutura says they have achieved 85 percent metal powder with 15 percent PLA. These filaments are called MetalFil Ancient Bronze and Metalfil Classic Copper. They can be printed even at "moderate" temperatures from 190 to 200 degrees Celsius.
Metallic 3D Printing Filament Spools, in this case from SteelFill and CopperFill colorFabb (Steel and Bronze), Ancient Bronze (Ancient Bronze) from Formfutura
Here are the key points about metal printing at home
- Gets a unique metal surface and look
- Ideal for jewelry, figurines, housewares, replicas
- Durability
- Objects are not flexible (structure dependent)
- Objects do not dissolve
- Not considered food safe
- Typical print temperature: 195 - 220°C
- Extremely low shrinkage on cooling
- No table heating required
- Printing complexity is high, requires fine tuning of nozzle temperature, feed rate, post-processing
Preparing your home printer for metal 3D printing
Since getting metal 3D prints is more difficult than usual, you may need to upgrade your 3D printer nozzle, especially if you are an entry-level printer. The metal filament wears it out quickly. There are hard-wearing hot-ends (like the E3D V6) that are themselves made of metal. They can withstand high temperatures and fit most printers. Be prepared for the fact that the nozzles will have to be changed frequently, because the metal filament is very abrasive.
The metal filament wears it out quickly. There are hard-wearing hot-ends (like the E3D V6) that are themselves made of metal. They can withstand high temperatures and fit most printers. Be prepared for the fact that the nozzles will have to be changed frequently, because the metal filament is very abrasive.
You will also need to take care of the final finishing of the surface (cleaning, grinding, oiling, waxing or priming) so that the printed metal object shines as it should.
How much does metal filament for 3D printing cost?
And what about metal filament for 3D printing? - you ask. Here are some examples:
- ColorFabb's 750 gram Bronzefill spool is $56.36
- ColorFabb 750g Copperfill Coil $56.36
- Protopasta's Polishable Stainless Steel PLA Composite is $56 for 56 grams of
- Rustable Magnetic Iron PLA Composite from Protopasta is $34.99 for 500 grams of
Industrial metal 3D printing
But what if you want a better result or even full metal 3D printing? Should a real "metal" 3D printer be purchased for business needs? We wouldn't recommend it - unless you're going to be doing it every day. A professional metal 3D printer is expensive: EOS or Stratasys devices will cost you 100-500 thousand dollars. In addition, the costs will be even greater, since you will have to hire an operator, a worker to maintain the machine, as well as to finalize the printouts (polishing, for example). Just a note: In 2016, an affordable metal 3D printer didn't exist.
A professional metal 3D printer is expensive: EOS or Stratasys devices will cost you 100-500 thousand dollars. In addition, the costs will be even greater, since you will have to hire an operator, a worker to maintain the machine, as well as to finalize the printouts (polishing, for example). Just a note: In 2016, an affordable metal 3D printer didn't exist.
Lowering Metal 3D Printing Costs
If you are not going to open a metal 3D printing business, but still need a professionally 3D printed metal part, it is better to contact the appropriate company that provides such services. 3D printing services like Shapeways, Sculpteo and iMaterialise offer direct metal printing.
They currently work with the following metal materials in 3D printing:
- aluminum
- steel
- brass
- copper
- bronze
- sterling silver
- gold
- platinum
- titanium
If you are a jeweler, you can also order wax models for casting in precious metals.
If we talk about wax models, then in most cases they (with subsequent melting) are used when printing with metals (including gold and silver). Not all orders are carried out directly by these firms. They usually turn to other metal 3D printing companies to complete the order. However, the number of such services around the world is growing rapidly. In addition, metal 3D printing techniques are becoming more and more common in companies that offer such services.
The reason big companies love 3D printing so much is that it can be used to build fully automated lines that produce "topologically optimized" parts. This means that it is possible to fine-tune the raw materials and make the components thicker only if they must withstand heavy loads. In general, the mass of parts is significantly reduced, while their structural integrity is preserved. And this is not the only advantage of this technology. In some cases, the product turns out to be significantly cheaper and affordable for almost everyone.
Please note that metal 3D printing requires special CAD programs for modeling. It is worth paying attention to the recommendations of Shapeways - 3D printing metal guidelines. To delve further into the topic, check out Statasys’ information on related 3D printers and the nuances of metal 3D printing.
Here are some examples of Benchy test model prices for metal 3D printing:
- Metal plastic: $22.44 (former alumide, PLA with aluminium)
- Stainless steel: $83.75 (plated, polished)
- Bronze: $299.91 (solid, polished)
- Silver: $713.47 (solid, mirror polished)
- Gold: $87.75 (gold plated, polished)
- Gold: $12,540 (solid, 18K gold)
- Platinum: $27,314 (solid, polished)
As you might expect, solid metal 3D printing prices are quite high.
Metal 3D printing. Applications
GE LEAP aircraft engine parts 3D printed at Avio Aero (Photo: GE)
There are several industries already using 3D printers to make everyday objects - you may not even know that these objects are printed.
- The most common case is surgical and dental implants, which are considered the best option for patients today. Reason: they can be tailored to individual needs.
- Another industry is jewelry. Here, most manufacturers have abandoned resin 3D printing and wax casting, switching directly to metal 3D printing.
- In addition, the aerospace industry is becoming more and more dependent on 3D printed metal objects. The Italian company Ge-AvioAero was the first to do all-metal 3D printing. It manufactures components for LEAP aircraft engines.
- Another industry targeting metal 3D printing is the automotive industry. BMW, Audi, FCA are seriously considering this technology, not only for prototyping (3D printing has been used for this for quite some time), but also for making real parts.

Before metal 3D printing really takes off, however, there are some hurdles to overcome. And first of all, this is a high price, which cannot be made lower than during molding. Another problem is the low production speed.
Metal 3D printing.
Technologies
Most metal 3D printing processes start with an “atomized” powder
You can talk a lot about “metal” 3D printers, but their main problems remain the same as any other 3D – printers: software and hardware limitations, material optimization and multimateriality. We won't talk too much about the software, we'll just say that most of the major specialized software companies, such as Autodesk, SolidWorks and solidThinking, try to emphasize as much as possible the fact that as a result of the 3D metal printing process, you can get any shape you want.
In general, printed metal parts can be as strong as parts made by traditional processes. Parts made using DMLS technology have mechanical properties equivalent to casting. In addition, the porosity of objects made on a good "metal" 3D printer can reach 99.5%. In fact, manufacturer Stratasys claims that 3D printed metal parts perform above industry standards when tested for density.
Parts made using DMLS technology have mechanical properties equivalent to casting. In addition, the porosity of objects made on a good "metal" 3D printer can reach 99.5%. In fact, manufacturer Stratasys claims that 3D printed metal parts perform above industry standards when tested for density.
3D printed metal can have different resolutions. At the highest resolution, layer thickness is 0.0008 - 0.0012" and X/Y resolution is 0.012 - 0.016". The minimum hole diameter is 0.035 - 0.045".
However, let's look at what metal 3D printing technologies are. formed layer)
The metal 3D printing process used by most relevant large companies today is called Powder Bed Fusion. This name indicates that some source of energy (a laser or other energy beam) melts an "atomized" powder (i.e., a metal powder that is carefully ground into spherical particles), resulting in layers of a printed object.
There are eight major manufacturers of metal 3D printers in the world that already use this technology; while we are talking here, there are more and more such companies. Most of them are in Germany. Their technologies are called SLM (Selective Laser Melting - selective laser fusion) or DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering - direct metal laser sintering).
Most of them are in Germany. Their technologies are called SLM (Selective Laser Melting - selective laser fusion) or DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering - direct metal laser sintering).
Metal 3D printing No. 2:
Binder Jetting (spraying the binder)
at 3DP technology of Exone metal objects are printed by binding the powder before its binding in the mining (photos : ExOne)
Another professional approach that also uses a powder base is called Binder Jetting. In this case, the layers are formed by gluing metal particles together and then sintering (or fusing) them in a high-temperature furnace, just like it is done with ceramics.
Another option, which is similar to working with ceramics, is mixing metal powder into metal paste. A pneumatically extruded 3D printer (similar to a syringe bioprinter or an inexpensive food printer) forms 3D objects. When the required shape is reached, the object is sent to the furnace, i. e. in the mountains
e. in the mountains
This approach is used in the Mini Metal Maker, apparently the only inexpensive "metal" 3D printer.
Metal 3D printing process #3: 9Metal Deposition This is not entirely true. Of course, on some desktop device, simply fusing metal threads onto the base will not work. However, very large steel companies can do it. And they do. There are two options for working with "metal surfacing".
One is called DED (Directed Energy Deposition) or Laser Cladding. Here, a laser beam is used to melt the metal powder, which is slowly released and solidifies as a layer, and the powder is fed using a robotic arm.
Normally the whole process takes place in a closed chamber, but the MX3D project used conventional 3D printing techniques to build a full-size bridge. Another option for metal fusion is called EBAM (Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing - additive electron beam technology), which is essentially soldering, in which a very powerful electron beam is used to melt 3 mm titanium wire, and the molten metal forms very large finished structures. As for this technology, its details are known so far only to the military.
As for this technology, its details are known so far only to the military.
Metal 3D printing. Metals
3D Printing Metal #1: Titanium
Pure titanium (Ti64 or TiAl4V) is one of the most commonly used metals for 3D printing and is definitely one of the most versatile, strong and lightweight. Titanium is used both in the melting process in a preformed layer and in the process of spraying a binder and is used mainly in the medical industry (for the manufacture of personal prostheses), as well as in the aerospace industry, automotive and machine tools (for the manufacture of parts and prototypes). But there is one problem. Titanium is very reactive and explodes easily in powder form. Therefore, it is necessary that titanium 3D printing takes place in a vacuum or in an argon environment.
3D printing metal #2: Stainless steel
Stainless steel is one of the cheapest 3D printing metals. At the same time, it is very durable and can be used in a wide range of manufacturing and even artistic and design applications. The type of steel alloy used also contains cobalt and nickel, is very difficult to break, and has a very high elasticity. Stainless steel is used almost exclusively in industry.
The type of steel alloy used also contains cobalt and nickel, is very difficult to break, and has a very high elasticity. Stainless steel is used almost exclusively in industry.
3D Printing Metal #3: Inconel
Inconel is a superalloy manufactured by Special Metals Corporation, its registered trademark. The alloy consists mainly of nickel and chromium and is very heat resistant. Therefore, it is used in the oil, chemical and aerospace (for black boxes) industries.
3D Printing Metal #4: Aluminum
Due to its lightness and versatility, aluminum is very popular in 3D printing. Aluminum alloys are commonly used.
3D Printing Metal #5: Cobalt Chrome
gap). It is most commonly used in the manufacture of turbines, dental and orthopedic implants, where 3D printing has become the dominant technology.
3D printing metal #5. Copper and bronze
With some exceptions, copper and bronze are used in wax melting processes, rarely in layer melting. The fact is that these metals are not very suitable for industry, they are more often used in the manufacture of works of art and crafts. ColorFabb offers both metals as the basis for a special metal filament.
The fact is that these metals are not very suitable for industry, they are more often used in the manufacture of works of art and crafts. ColorFabb offers both metals as the basis for a special metal filament.
3D printing metal #6. Iron
Iron, incl. magnetic, also mainly used as an additive to PLA-based filaments, which are produced, for example, by ProtoPasta and TreeD.
3D printing metal #7. Gold, Silver and Other Precious Metals
Most preformed melt process companies can 3D print precious metals such as gold, silver and platinum. Here, along with the preservation of the aesthetic properties of materials, it is important to achieve optimization of work with expensive starting powder. Precious metal 3D printing is required for jewelry, medical applications and electronics.
Metal 3D printing. Printers
Do not even hesitate - the purchase of a metal 3D printer will not pass without a trace on your budget. It will cost at least 100-250 thousand dollars. Here is a list of a variety of "metal" printers, some of which can be found in firms providing 3D printing services.
It will cost at least 100-250 thousand dollars. Here is a list of a variety of "metal" printers, some of which can be found in firms providing 3D printing services.
Metal 3D Printer #1:
Sciaky EBAM 300 - metal filament printing
If you need to print really large metal structures, Sciaky's EBAM technology is your best bet. By order, the device can be built in almost any size. This technique is used mainly in the aerospace industry and the military.
Sciaky's largest production printer is the EBAM 300. It prints objects in a volume of 5791 x 1219 x 1219 mm.
The company claims the EBAM 300 is also one of the fastest industrial 3D printers on the market. A three-meter-sized titanium part for an aircraft is printed on it in 48 hours, while the material consumption is about 7 kg per hour. In general, forged parts that usually take 6-12 months to complete can be made in 2 days with this 3D printer.
The metal layers are first cut and then ultrasonically welded. The largest Fabrisonic 7200 printer operates in a volume of 2 x 2 x 1.5 m. The metal powder 3D printer is the Concept Laser XLine 1000. It has a modeling volume of 630 x 400 x 500 mm and is the size of a house.
Its German company, one of the main suppliers of 3D printers for aerospace giants like Airbus, recently introduced a new machine, the Xline 2000.
This machine uses two lasers and has a working volume of 800 x 400 x 500 mm. Uses LaserCUSING laser technology (a variant of selective laser fusion) from Concept Laser, which allows you to print alloys of steel, aluminum, nickel, titanium, precious metals and even some pure substances (titanium and stainless steel).
Metallic 3D printing. Services
There are more than 100 companies worldwide offering metal 3D printing services. We list the most popular services for consumer needs.
#1 Metal 3D Printing Service: Shapeways
The world's most popular 3D printing service, Shapeways offers two types of services. As a consumer, you can choose from a wide range of professionally designed objects, customize them, and then have them printed to your specifications. Like other 3D printing services, Shapeways offers a platform for designers to sell and print their work. Shapeways is also a good place for rapid prototyping: customers benefit from industrial-grade printers (EOS, 3D Systems) and personal technical support.
As a consumer, you can choose from a wide range of professionally designed objects, customize them, and then have them printed to your specifications. Like other 3D printing services, Shapeways offers a platform for designers to sell and print their work. Shapeways is also a good place for rapid prototyping: customers benefit from industrial-grade printers (EOS, 3D Systems) and personal technical support.
3D printing metals: aluminium, brass, bronze, gold, platinum, precious metal plating, silver, steel. There are also wax molds for jewelry purposes.
Metal 3D Printing Service #2: Sculpteo
Like Shapeways and i.materialise, Sculpteo is an online 3D printing service that allows anyone to upload 3D models and send them to fabrication in a wide range of materials . Like its competitors, Sculpteo provides a platform for hobbyists and professionals to showcase and sell their designs. The stable of Sculpteo printers includes highly professional machines from 3D Systems, EOS, Stratasys and ZCorp. Extensive technical documentation will help identify design flaws and select the right material for the project.
Extensive technical documentation will help identify design flaws and select the right material for the project.
3D printing metals: alumide (plastic with aluminum particles), brass, silver.
Metal 3D Printing Service #3: iMaterialise
Materialise is a company that works with industrial customers to prototype 3D printed products. For casual users and designers, Materialize offers an online 3D printing service called i.materialise. As with Shapeways, this service allows anyone to upload their 3D designs and print them out. Once an object has been uploaded and successfully printed, a designer can list it for sale either in the gallery of the i.materalise online store or by embedding some code into their website.
3D printing metals: alumide (plastic with aluminum powder), brass, bronze, copper, gold, silver, steel, titanium.
Metal 3D Printing Service #4: 3D Hubs
Through 3D Hubs, you can search for individuals and companies that offer 3D printing services in your area, upload STL files (which are immediately evaluated for defects ) and contact service providers directly to get the job done.