Bulk 3d printing filament
Buying 3D Printing Filament in Bulk
3D Insider is ad supported and earns money from clicks, commissions from sales, and other ways.
One of our most favorite things about FDM printing is that it’s incredibly easy to swap one filament for another. If you’re tired of your plain old Natural PLA, then you take out that spool of colored ABS you’ve been keeping in storage.
However, some jobs benefit from sticking to a single roll of filament. When this situation comes up, you might want to have an extra-large roll of filament on hand. Recognizing this need, some filament manufacturers offer bulk or extra-large filament spools. Is it a good idea to buy filament in bulk?
Should you buy filament in bulk?
While most 3D printing filaments come in spools of 1 kilogram or less, the bulk filament can have as much as 15 kilograms of filament wound on a single spool. As you can tell, this can be a pretty big commitment. Before deciding to get an extra-large spool of filament, here are a couple of things you need to ensure:
You’re working on a large project
People often decide to buy filament in bulk when they expect to have to work on projects that are either exceptionally large or require a huge volume. A 3D printer that runs continuously can consume anywhere between two to four kilograms of filament in a day. If this kind of situation sound familiar to you, then an extra-large spool of filament seems like a practical option.
You’ve tested the specific filament brand before
As we’ve said, buying filament in bulk is a huge commitment. Not only are you going to be obliged to use up a lot of filament, but you’re likely going to pay $300 or more for a single spool. This is fine if you encounter no problems with your filament and it prints really well.
However, the opposite would be a huge headache. If you purchased filament in bulk from a brand you have not tested before, only to find problems with its quality and consistent, then you’re pretty much stuck with a huge amount of unprintable filament. This emphasizes the importance of due diligence – buy a smaller spool from a brand first before you decide to buy in bulk.
You have a suitable spool holder
Most 3D printers come with a spool holder located somewhere at its side or at the top. These are meant for the standard 3D filament spools that weigh 1 kilogram or less. However, you might need a more rugged spool holder if you intend to get bulk filament.
These are meant for the standard 3D filament spools that weigh 1 kilogram or less. However, you might need a more rugged spool holder if you intend to get bulk filament.
Make sure that your spool holder is rated for the weight of filament that you will be using. Some use a strong spool holder that can stand up on the desk beside the 3D printer. This filament holder from Creker is a good example. It basically acts as “feet” for the filament spool and has internal bearings that allow the spool to rotate freely.
For a space-saving solution, you can also wall-mount a spool holder. Screwing it in place is essential, especially if you’re buying a spool that weighs more than 10 kilograms.
You have storage space
Even if you’re working on a huge project, there is still a remote possibility that you will end up with leftover filament. The problem with extra-large spools of filament is that even the plastic spools are large, regardless of how much filament you have left. This makes storage somewhat challenging. If you’re buying large filament, make sure that you have vacuum bags large enough to fit its spool and that it will fit in your storage space.
This makes storage somewhat challenging. If you’re buying large filament, make sure that you have vacuum bags large enough to fit its spool and that it will fit in your storage space.
In summary, buying filament in bulk is a good idea if you have a big project for which you’ll use it for, you trust the brand you’re buying from, and you have the essential accessories to handle and store such a huge spool. This is not the kind of thing that you buy on impulse.
Pros and cons of buying filament in bulk
If you’ve made up your mind about deciding to buy an extra-large filament spool, then you would be pleased to know that it’s something that a lot of 3D printing professionals do. It certainly has its perks, but keep in mind that there are few drawbacks to using and keeping that much filament.
PROS:
Consistency
If you’re working on a single huge model or several smaller models using a single filament, then using just a single spool should provide a better assurance that your finished prints will be more consistent quality-wise. Consistency is often a problem when you need to change between filament spools in the middle of a print. Having a large filament ensures that this won’t ever be a problem again.
Consistency is often a problem when you need to change between filament spools in the middle of a print. Having a large filament ensures that this won’t ever be a problem again.
Speed
Speaking of changing over when a filament runs out, this step requires that you stop printing, clean out the residual filament, and feed the new filament into the printer. This can take a few minutes. For high-volume orders, you may need to do this step two or three times in a single day, slowing down the process significantly. By cutting down on delays due to changeover, you can finish the job a bit quicker.
Convenience
Having to swap spools in the middle of a print also means that you have to physically be there to do the job. A single 3D print takes several hours, and it’s not uncommon for users to walk away from the printer and do more productive things.
When a filament runs out, you pretty much have to drop what you’re doing and rush to replace the filament before the last layer that was printed starts to get cold. This is incredibly inconvenient, especially if you have to do it several times a day. You can consider an extra-large filament as a quality of life improvement that lets you wander away from your 3D printer for longer without worries.
This is incredibly inconvenient, especially if you have to do it several times a day. You can consider an extra-large filament as a quality of life improvement that lets you wander away from your 3D printer for longer without worries.
Cheaper
Theoretically, 3D printing filaments should follow an economy of scale. This means that they should cost less per gram when you buy more of them. For instance, a 1-kilogram spool of ABS filament from Gizmo Dorks costs about $20.95. A 5-kilogram spool of the same filament costs around $99.95. Granted that the savings aren’t so big in this particular example, but they should get bigger if you buy larger spools.
CONS:
Inherent risk
Whenever you buy anything in bulk, there is always an inherent risk of you ending up with a huge stock of low-quality products. The same can be said of 3D printing filaments. We would hate to buy a 10-kilogram spool only to find that it has issues with bubbles and size consistency. To avoid this, it’s very important to buy bulk filament only from brands that you can strongly vouch for. Otherwise, you could end up with a hundred-dollar paperweight.
To avoid this, it’s very important to buy bulk filament only from brands that you can strongly vouch for. Otherwise, you could end up with a hundred-dollar paperweight.
Difficult to mount
3D printers simply aren’t built to carry the weight of large filament spools. As we’ve mentioned, you can buy special filament holders that attach to the edges of spools to keep them upright. We prefer making a wall mount for the spool so it can still above the 3D printer, allowing for a smoother feed. In either case, you’re going to have to retrofit your setup to accommodate a super-sized filament roll.
Hard to keep dry
Most 3D printing professionals know that moisture is the number one enemy of plastic filaments. With enough moisture absorption, a filament can have micro-bubbles that expand and explode when exposed to heat. This could easily lead to ruined prints or jammed nozzles.
One issue to anticipate when buying large filament rolls is that they are also harder to dry because of their sheer volume. Simply put, more filament means more moisture retention. If you oven-dry your filament before use, then you’ll have to check if the filament will fit in your oven and determine how much longer you need to leave it inside.
Simply put, more filament means more moisture retention. If you oven-dry your filament before use, then you’ll have to check if the filament will fit in your oven and determine how much longer you need to leave it inside.
Moisture absorption is also a potential problem if you use a huge filament spool for extra-long printing sessions. Exposing the filament to the atmosphere for a few hours is one thing, but it’s a completely another thing to leave it the spool mounted near your 3D printer for several days.
In most cases, buying filament in bulk is a matter of convenience. You won’t need to buy filament as often, will change filament spools less frequently, and are assured of more consistent output quality. You may have to modify your practices and set-up to adapt to a larger filament, but the efforts are well worth the improvement in the quality of life.
Recommendations for bulk filament
There aren’t many filament brands that outright offer extra-large filaments in their standard product line.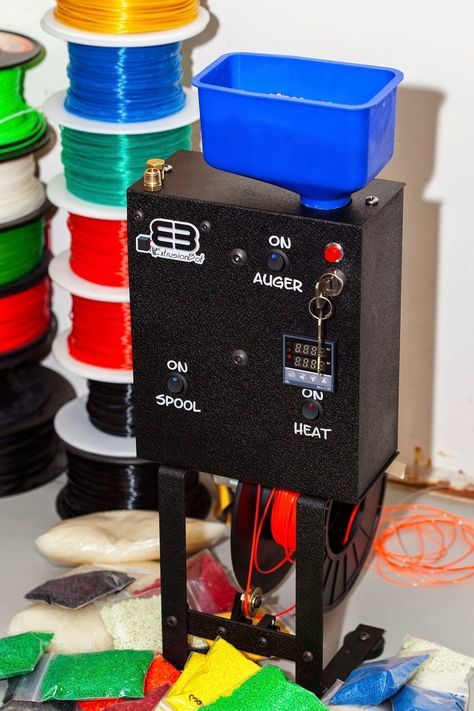 Perhaps this is a testament to how little the demand is for filaments in bulk. However, they usually accept custom orders for larger spools depending on what you need. If you have a favorite filament brand, then the best option would be to call them or shoot them an e-mail.
Perhaps this is a testament to how little the demand is for filaments in bulk. However, they usually accept custom orders for larger spools depending on what you need. If you have a favorite filament brand, then the best option would be to call them or shoot them an e-mail.
However, it’s not impossible to find larger than usual filament spools that are being sold directly. The following are a few of the best options we’ve stumbled upon:
1. Gizmo Dorks PLA Filament 5 kg.
Quality is very important when buying extra-large filament spools, so we’re quite partial to the popular filament brands Gizmo Dorks. They have been around for a long time and their filaments are some of the most reliable in the market. This assurance of quality is enough to justify this moderately expensive spool of PLA filament.
2. Tianse 3D Printer PLA Filament 5 kg.
If the 5-kilogram PLA filament from Gizmo Dorks feels a bit too expensive for you, then you can save around $15 with this spool from Tianse. It weighs the same and has the same color. The only difference is that it comes from a less popular brand. Despite being less expensive, the Tianse PLA filament has proven to be consistent enough for 3D printing professionals to finish whole 5-kilogram rolls.
It weighs the same and has the same color. The only difference is that it comes from a less popular brand. Despite being less expensive, the Tianse PLA filament has proven to be consistent enough for 3D printing professionals to finish whole 5-kilogram rolls.
3. Gizmo Dorks HIPS Filament 5 kg.
Both PLA and ABS are old hats when it comes to 3D printing, so large-sized spools of these two filaments are pretty commonplace. This 5-kilogram spool of HIPS filament from Gizmo Dorks simply illustrates that it’s also possible to get extra-large spools of more exotic filament types. If you haven’t used HIPS before, its primary use case is as a support material that is most compatible with PLA. If you need to print a large model using PLA, then having 5-kilogram spools of PLA and HIPS printing on a multi-extruder system sounds like a winning combination.
Final thoughts
Having a huge selection of different filament types and colors is well and good until you need just one particular filament and find that you have no spares.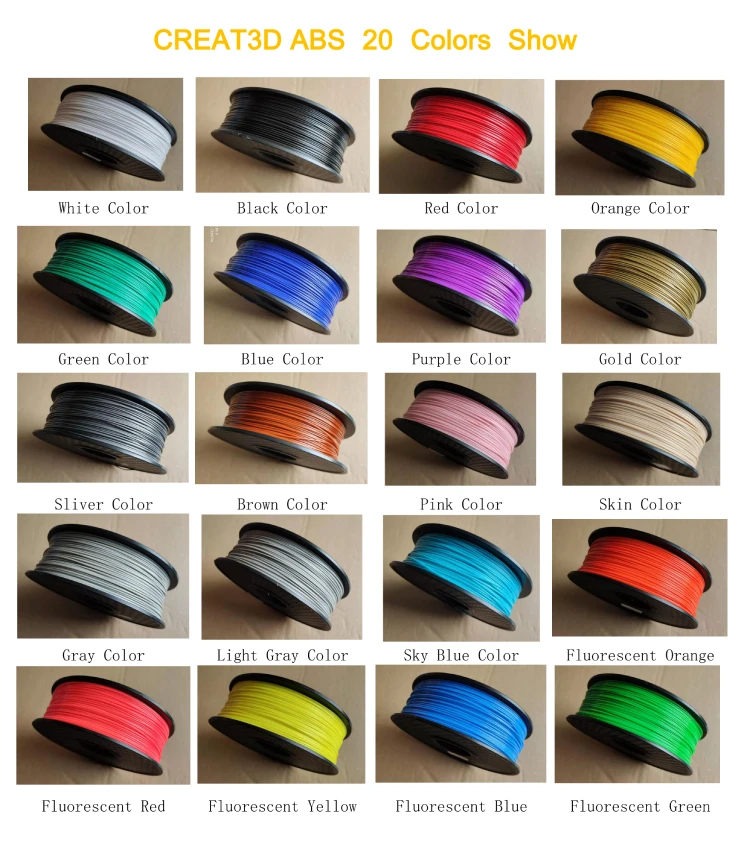 If you anticipate doing huge jobs soon, then buying a large filament may be the more prudent move.
If you anticipate doing huge jobs soon, then buying a large filament may be the more prudent move.
Before you spend a hundred dollars on some large filament spool, make sure that you’re getting it from a brand you trust and that you have the necessary accessories to handle it. With just a little planning, you may be convinced to never go back to those tiny 1-kilogram spools.
Warning; 3D printers should never be left unattended. They can pose a firesafety hazard.
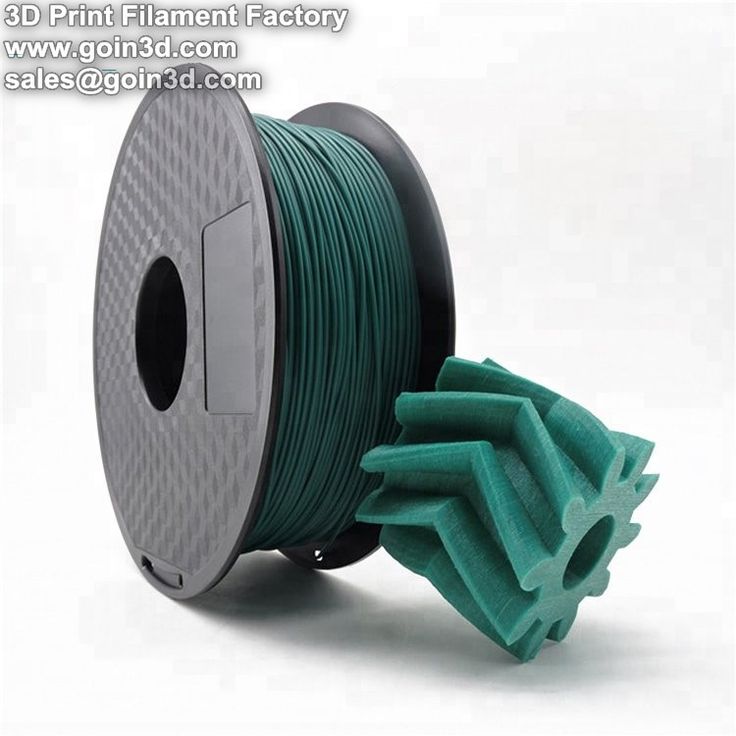
Aurarum PLA bulk spool 2-5kg (ch FDM / SLA / DLP 3D printing resin / filament
Aurarum PLA 3D Printer Filament – Bulk 3-5Kg (Choose Size And Colour)
AUD90.95 – AUD275.95Inc GST
Aurarum PLA is the easiest material to print with ? A good starting point for a successful print is to have your hot end around 200 degrees and your hot bed around 55 degrees.
All AURARUM filaments are 100% Australian made right here in Melbourne, Victoria.
Support a local Australian business supporting Aussie families.
please note even though we often have bulk spools in stock it might take 1-2 weeks to make more.
SKU: 697478832174 Categories: Bulk Spools, Bulk spools Tags: bulk, Filament, PLA, Wholesale
- Description
- Brand
- Additional information
Description
Aurarum PLA 3D Printer Filament – Bulk 3-5Kg (Choose Size And Colour)
About PLA
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is by far the most popular material used in 3D printing today.
It comes in many colours, blends and is usually very easy to print with.
??
Best settings for successful printing:
| Printing / Extrusion temperature | 185 to 220 degrees |
| Bed Temperature | 20 to 60 degrees |
| Printing Speed | 40-100mm/s |
PLA is biodegradable material made using cornstarch or sugarcane. ? It is renewable and is much safer than something like ABS for example.
? It is renewable and is much safer than something like ABS for example.
PLA can be printed on a much cooler heated bed or if you have a well levelled bed maybe even no heat at all.
| Strength | 6/10 |
| Detail level | 9/10 |
| Smooth Finish | 9/10 |
| Transparency (colour dependent) | 2/10 to 8/10 |
| Flexibility | 1/10 |
Like any 3D printing a well ventilated space is preferred and good storage is the key to a good shelf life of your filament.? All our filament is shipped in a vac sealed bag containing a small desiccant satchel.? When opening your bag a clean cut along the top edge will allow you reuse that bag again if you do not finish the entire reel in 1 go.
| Reel Size | 200h x 65w |
| Weight / metres | 1kg / 340 metres (approx) |
| Filament width | 1.75mm +/- 2mm |
| Spool | Plastic, Vacuum packed |
One of the best things about PLA is the ease of post processing. ? Sanding and painting is made simple making it easy to get a very finished and polished look even from the roughest of prints.
? Sanding and painting is made simple making it easy to get a very finished and polished look even from the roughest of prints.
Aurarum PLA is printer agnostic and as such is suitable for all brands including Flashforge, RepRap, Creality, Artillery, MakerBot, Ultimaker, Makergear, Up! ? and many others.
Brand
Aurarum
Aurarum is a true Australian manufacturer that is here to support and provide you with 3D printer supplies. We manufacture and sell 3D printer filament that will fulfil your 3D printing needs.
Among our 3D printer supplies, we can offer you 3D printer filament, Flashforge and ideaPrinters 3D printer and other 3D printer spare parts and parts required for your DIY project.
Even though we are a manufacturer we welcome business, retail and wholesale customers.
Apart from our 3D printer supplies, we can offer you a 3D printing service.
No job is too small for us.
Friendly and welcoming service will make sure that you are 100% satisfied with our service and we will see you back again.
Our Australian made 3D printer filament is of the highest quality and yet with affordable price. The price is a lot lower than what you would expect to pay for a quality product.
In our assortment, you will find PLA, ABS, Nylon, TPE and HIPS 3D printer filaments. Our colour range is wide as well it has 20 standard colours ranging from natural to something like safety yellow and safety orange that are quite bright compared to the other colours. On top of our standard colours, we can offer 4 glow in the dark colours Blue, Green, Violet and Aqua Blue.
Using quality 3D printing supplies saves you time and money.
As part of our services we can offer OEM service, where we would produce your branded filament. To the architects and everyone else we can offer colour matching service – the colour of the filament can be matched to the item that you have.
So if you are after quality 3D printer supplies, 3D printing or a 3D printer look no further. We are here to help you with all your needs.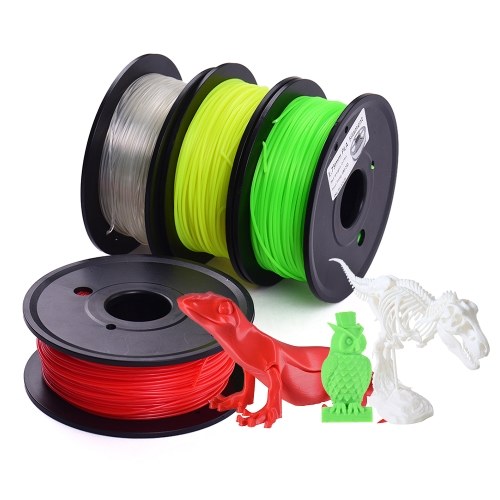
How can you print objects on a 3d printer
12/11/2015
3D printing technology is rapidly entering the life of modern society. If earlier it was used mainly in the field of photography, cinematography and animation, today its scope has expanded significantly.
3D printers are used to create all kinds of layouts and prototypes of finished products, in small-scale production of exclusive items, in the printing industry to create advertising and souvenir products, in medicine they use prostheses and implants made of biocompatible materials. 3D printers have appeared in the construction industry that print blocks and even entire buildings using a special concrete mixture with the addition of polymers and special hardeners.
What is 3D printing?
First, a three-dimensional model of the future object is created in 3D modeling programs. The next step is the processing of the digital model by the "slicer" program, which "cuts" the object into many horizontal lines and creates a code that is understandable to the 3D printer. On the basis of a given program, the printer "cultivates" the object using the method of layer-by-layer deposition of the material. The action takes place until the product is completely ready. The use of 3D technology is a serious alternative to classical printing; it allows you to create three-dimensional physical objects.
On the basis of a given program, the printer "cultivates" the object using the method of layer-by-layer deposition of the material. The action takes place until the product is completely ready. The use of 3D technology is a serious alternative to classical printing; it allows you to create three-dimensional physical objects.
Materials for 3D printing
The range of materials that 3D printers work with is large and constantly expanding. There are quite exotic options, but the most common raw materials are thermoplastics. The most popular brands are ABS and PLA. ABS is a durable and reliable plastic, it can be used to make parts of machines and mechanisms, but it is destroyed by exposure to direct sunlight. PLA - polylactide, is made from natural materials: corn, soybeans, sugar cane. Due to its natural origin, products made from such plastic are completely biocompatible and can be used for the production of dishes, food packaging and even implants.
The following materials are also used:
- cement polymers, similar in properties to concrete, but more durable;
- chocolate, caramel and other edible ingredients;
- fusible metals with special impurities for lower melting temperatures;
- wood used in pulp solutions;
- paper which, in combination with glue, is used for laminating products;
- dry powder plaster;
- photopolymers capable of changing properties when exposed to light.
3D printer filament production
Features of 3D printing technology do not allow the use of polymer raw materials in the form of powder or granules. Existing limitations make it necessary to give the thermoplastic the shape of a fiber; for this, special equipment is used - an extruder for a 3d thread. An industrial extruder for 3d filament is an expensive, large-sized equipment that has a capacity of several tens of kilograms per hour. In addition, desktop models for small businesses and personal use are widely used, the price of which starts at $ 1000, and the productivity is several kilograms per hour.
In addition, desktop models for small businesses and personal use are widely used, the price of which starts at $ 1000, and the productivity is several kilograms per hour.
Making filament for a 3D printer is not a particularly difficult process. It is important to strictly observe the processing temperature and the proportions of the components.
Main production steps:
- Preparation of raw materials. The finished granules are thoroughly dried to completely eliminate the ingress of moisture. Then, if necessary, a coloring pigment is added, the mass is mixed and fed into the extruder.
- In the extruder hopper, the mixture is heated, mixed and, having melted to a homogeneous consistency, is forced by a screw mechanism through a nozzle of the required diameter.
- After the extruder, the filament enters a container of water where the plastic cools and hardens.
- Drying - the cooled plastic is transferred to a special chamber with the help of a roller system, where it is dried with hot air.

- Measuring the thickness of the thread and packaging - the dried material is wound on a spool or collected in skeins of a given weight.
The use of modern equipment, strict adherence to technology and control at each stage make it possible to obtain high quality filaments for a 3D printer and the required parameters.
| The material was helpful |
3D printing laboratory - All about plastics - education, technology, perspectives
Prototyping and modeling using 3D printers has recently become more and more widespread. This is due not only to the development and cheapening of equipment for creating three-dimensional models, the emergence of new polymeric materials for three-dimensional printing, but also the emergence of the need for such modeling for medical products, aircraft parts, instrumentation, automotive and aircraft manufacturing, as well as souvenirs. and other areas. The use of polymeric materials for structural purposes for prototyping made it possible to produce not only models, but also small batches of technical products.
According to the recent study “3D Printing Market (2013-2020)” published by Markets and Markets (“M&M”), between 2013 and 2020, the annual growth of the 3D printing market will be 23%, resulting in will grow to 8.4 billion US dollars by 2020 (http://www.orgprint.com/wiki/3d-pechat/obzor-tehnologij-3D-pechati).
3D printing is a technology for creating three-dimensional objects from a digital sample (CAD) by layer-by-layer application of additive materials. 3D printing methods include stereolithography (SLA), powder laser sintering (SLS), electron beam melting (EBM), layer-by-layer printing with molten polymer thread (FDM), formation of three-dimensional models from layer-by-layer sheet material (LOM) and others.
Initially, 3D printing was used exclusively for prototyping objects, but recently a radical step has been taken towards production. Automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer products are among the industries that are actively embracing 3D printing. According to M&M, 3D printing in medicine and aerospace will grow exponentially in the near future. 3D printing has significant growth potential, it is indispensable where piece production of personalized products is needed.
3D printing has significant growth potential, it is indispensable where piece production of personalized products is needed.
This article touches upon some aspects of 3D printing, which is carried out by layer-by-layer printing with a melted polymer thread (rod).
Layer-by-layer printing with molten polymer thread , also known as Fused Deposition Modeling or simply FDM, is used to obtain single products that are close in their functional characteristics to serial products, as well as for the manufacture of investment molds for metal casting.
The main polymer materials used in FDM technology in Russia are ABS plastic, PLA (polylactide), to a lesser extent polyamide (PA-12 or PA-11), TPU, PET-G and a number of other polymers. Almost all polymeric materials are imported.
High impact polystyrene (HIPS) is used as support polymers. This material is used for printing ABS plastic, PMMA, PET-G. Polyvinyl alcohol PVA (PVOH, PVA or PVAL) is also used as a support polymer, however, due to the water solubility of this polymer, it is more difficult to obtain a thread from it, modification of the standard technology is required.
At the Interplastica-2018 exhibition, work was announced on the synthesis of special grades of structural polymer materials for 3D printers at the Kabardino-Balkarian State University (PSU, PFS, etc.). In the report of KNRTU (Kazan), the topic of using PP filament for 3D printing was mentioned, which is not surprising, since in the Republic of Tatarstan a wide range of PP grades is produced by Nizhnekamskneftekhim PJSC. The problem with polyolefins in printing is associated with poor adhesion to the 3D printer substrate and high shrinkage when cooled.
FDM printing technology is as follows: a polymer thread is fed into a heated head with a controlled temperature, in the head it is heated to a melt state and the resulting thermoplastic modeling material is fed with high precision in thin layers onto the working surface of a 3D printer. The layers are applied on top of each other, joined together and cooled, gradually forming the finished product.
The diameter of the nozzle through which a thread with a diameter of 3 or more often 1. 75 mm is fed is 0.3-0.4 mm in the first case, and 0.1-0.3 mm in the second case. Therefore, the requirements for a polymer thread should be quite stringent in terms of sizing (thickness variation), stability of rheological properties (melt flow), melt purity (presence of impurities or contaminants).
75 mm is fed is 0.3-0.4 mm in the first case, and 0.1-0.3 mm in the second case. Therefore, the requirements for a polymer thread should be quite stringent in terms of sizing (thickness variation), stability of rheological properties (melt flow), melt purity (presence of impurities or contaminants).
1 shows the scheme of printing polymer thread FDM
1. Flow chart of 3D printing by FDM polymer filament printing.
The production of thread (rod) for FDM technology is carried out on extrusion plants for extruding rod, including a dryer, an extruder, usually a single-strand extrusion head, a calibrator (if necessary), a cooling bath, a gauge for the thickness (diameter) of the thread, 2 (rarely 4 -x positional) bar winder on the coil. There is a lot of information on the Internet about homemade filament extruders, as a rule, of low productivity and low quality filament. However, the production of thread must be carried out on specialized extrusion lines.
A diagram of such a line is shown in fig.










.jpg)
