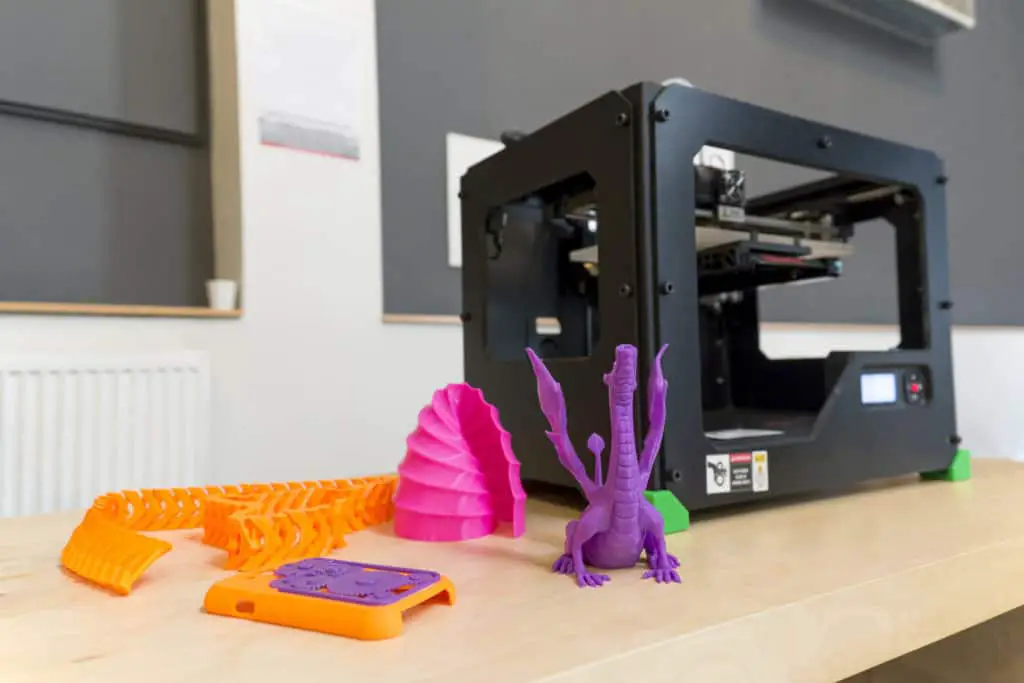
Anet a8 desktop 3d printer prusa i3 diy kit manual
[Discontinued] SAINSMART x Anet A8 Prusa i3 DIY 3D Printer – SainSmart.com
Brand: SainSmart SKU: 101-91-200
[Discontinued] SAINSMART x Anet A8 Prusa i3 DIY 3D Printer
SKU: 101-91-200 5 reviews UPC: 6959011562400 Product ID: 11073659348 Variants ID: 39375463415887
€187,95
SainSmart A8 is a a useful yet affordable 3D printer. It is an unassembled DIY kit, providing you an unforgettable step-by-step learning experience of the 3D printer from scratch.
【ENTRY-LEVEL】 For one-fifth of the cost of a new iPhone, SainSmart A8 is the best entry-level 3D printer for home or school use. At 8.66" x 8.66" x 9.45", A8 provides 6x more build volume than its competitors. You are also getting offline printing feature that is not found in other entry-level printers.
【STEM EDUCATION】A perfect gift for any teenagers and adults who are interested in Engineering. The challenging yet fun building experience makes an excellent course on electronics, mechanical engineering and 3D Printing.
【SUPPORT ALL FILAMENTS】 Unlike most other 3d printers in this price range, A8’s heated build plate and direct drive extruder is capable of printing all types of filaments, including PLA, ABS, Wood, dissolvable PVA, as well as the trending flexible TPU filaments.
【FREE SAMPLE TPU】A free spool of our best-selling Flexible TPU filament is included. You will be ready to create your own smart phone cases or GoPro mount right away.
You will be ready to create your own smart phone cases or GoPro mount right away.
【TRUSTED VENDOR】SainSmart is an established Maker hardware provider and a frequent Maker Faire exhibitor. We provide 6-month manufacturer warranty on all parts. Buy with confidence.
Default Title - Sold OutQuantity Only 0 in stock. Order now!
SainSmart A8 is a a useful yet affordable 3D printer. It is an unassembled DIY kit, providing you an unforgettable step-by-step learning experience of the 3D printer from scratch.
【ENTRY-LEVEL】 For one-fifth of the cost of a new iPhone, SainSmart A8 is the best entry-level 3D printer for home or school use. At 8.66" x 8.66" x 9.45", A8 provides 6x more build volume than its competitors. You are also getting offline printing feature that is not found in other entry-level printers.
At 8.66" x 8.66" x 9.45", A8 provides 6x more build volume than its competitors. You are also getting offline printing feature that is not found in other entry-level printers.
【STEM EDUCATION】A perfect gift for any teenagers and adults who are interested in Engineering. The challenging yet fun building experience makes an excellent course on electronics, mechanical engineering and 3D Printing.
【SUPPORT ALL FILAMENTS】 Unlike most other 3d printers in this price range, A8’s heated build plate and direct drive extruder is capable of printing all types of filaments, including PLA, ABS, Wood, dissolvable PVA, as well as the trending flexible TPU filaments.
【FREE SAMPLE TPU】A free spool of our best-selling Flexible TPU filament is included. You will be ready to create your own smart phone cases or GoPro mount right away.
【TRUSTED VENDOR】SainSmart is an established Maker hardware provider and a frequent Maker Faire exhibitor. We provide 6-month manufacturer warranty on all parts. Buy with confidence.
We provide 6-month manufacturer warranty on all parts. Buy with confidence.
Anet 3D Printer Most Common Mistakes And How To Fix Them
Updated on:
We participate in the Amazon affiliate program and may earn a commission if you make a purchase through links on our site. We also participate in other affiliate programs.
The Anet 3D Printer is quickly becoming one of the more popular and affordable 3D Printers in the industry. These DIY kits were originally cloned from the Prusa i3 style of 3D Printer.
These are some of the cheapest kits available which is probably why they are so popular and they are actually really decent 3D Printers. That is – when you know what you are doing.
That is – when you know what you are doing.
Here we will discuss some of the most common issues and mistakes I see Anet owners having.
Anet 3D Printer Installation Manual (it exists!)
Yes, there is actually an installation manual for Anet 3D Printers. What most people don’t do is check the SD Card that comes with the printer. That’s where they usually provide assembly instructions, STL models, and sometimes even software.
So don’t expect to get a printed installation manual and make sure to check your SD Card on your PC.
Unfortunately, most people won’t take that advice and will build their Anet before searching for instructions which can lead to the following issues.
Z-Coupler and Threaded Rods
I see this far too often with people thinking their threaded rods are too short.
This happens when the Z Couplers are not installed properly. When installing you want there to be a good distance between the shaft of the motor and the threaded rod. It’s recommended to insert the shaft and rod approx 5mm. This leaves enough distance for the flex coupler to you guessed it, flex.
It’s recommended to insert the shaft and rod approx 5mm. This leaves enough distance for the flex coupler to you guessed it, flex.
Y-Axis Belt Installation
This can be confusing when putting these parts together. Especially when you don’t know about the instruction manual on the SD Card.
Also, be careful not to over-tighten your belt. Check and make sure you’re not flexing the acrylic frame. Pull the belt just enough to not sag and then use a Timing Belt Spring to tension the belt. These little springs are the safest way to tighten your belt without over-stressing the frame.1PCS GT2 2GT Timing Belt Locking Torsion Spring for 3D Printer Reprap Parts
Bed Leveling – Nozzle Height
This is probably the most critical part of 3D Printing. The theory is that you want a slight gap between your nozzle and print surface about the thickness of a standard piece of white paper.
Check out this great tutorial from Thomas Sanladerer to see how to properly level your bed.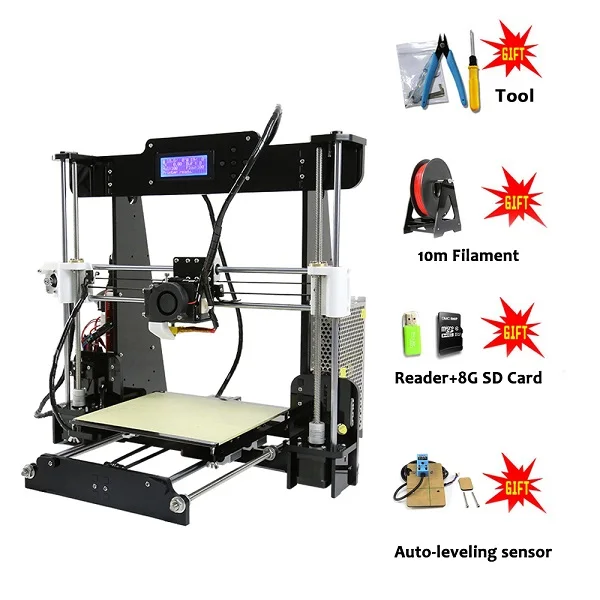
I also recommend adding some thread lock or Loctite to your bed screws to prevent vibrations from throwing off your dialed-in alignment over time.
Next, think about what you are printing on and what you need to make prints stick.
Sheet Metal Bed = Blue Painters Tape
Glass Bed = Elmer’s Glue Stick or Hairspray if your prints are not sticking
Other Bed Surface Types: PrintInZ Build Plate, Polyetherimide Ultem (PEI) Sheet, BuildTakBuildTak or other innovations.
Layer Shifting
Typically when your prints look like this the most common problems are Speed or Belt Tension.
Sometimes when the belts are too loose or the printer head is moving too fast this will cause the belts to slip off the gears and lose alignment.
Be sure to check that you have proper belt tension and that you’re not running your prints at too fast of a speed.
Under Extrusion and Clicking
This is another common issue I see that is sometimes hard to diagnose. The printer does not extrude a steady flow of filament or the Extruder Motor is skipping steps (clicking) preventing smooth extrusion.
The printer does not extrude a steady flow of filament or the Extruder Motor is skipping steps (clicking) preventing smooth extrusion.
This usually comes down to temperature settings. Try printing a temp tower test and see if the issue keeps happening…
Other possible issues are motor overheating, improper pot amps or other just a clogged nozzle.
3DPRINT.WIKI
If you are looking for more information on Anet A8 printers I suggest you check out https://3dprint.wiki/reprap/anet/a8
This is filled with great information that will address advanced improvements, upgrades and other useful things about your printer.
Garrett Dunham
A trained Mechanical Engineer and lifelong tinker, Garrett chose to attend Cal Poly San Luis Obispo's engineering proram because they had a 3D printer... back when they were called "rapid prototypers". "The first time I held something I designed and 3D printed, my mind exploded. Just hours earlier my idea was just a thought - and now it's a thing I'm holding. " Now, years later, Garrett brings his love of tinkering, inventing, engineering, and 3D printing to the Makershop community.
" Now, years later, Garrett brings his love of tinkering, inventing, engineering, and 3D printing to the Makershop community.
Instruction for beginners based on Anet A8
Introduction.
Often, when purchasing a 3D printer, we only know about 3D printing what we have read or seen online. For many, a 3D printer is something new, interesting, and exciting. However, despite the abundance of information on the global web, it can be confusing for a beginner, because there is no generalized information that would help you start printing without bumping into all sorts of nuances and pitfalls.
In this manual, we will try to cover the most common questions about 3D printing, collected on the Internet, and accumulated by personal experience. nine0003
An example for us is one of the most popular and affordable 3D printers Anet A8.
I.
What to do after assembly.
The moment has finally come when the assembly is finished. Hands itching to start typing.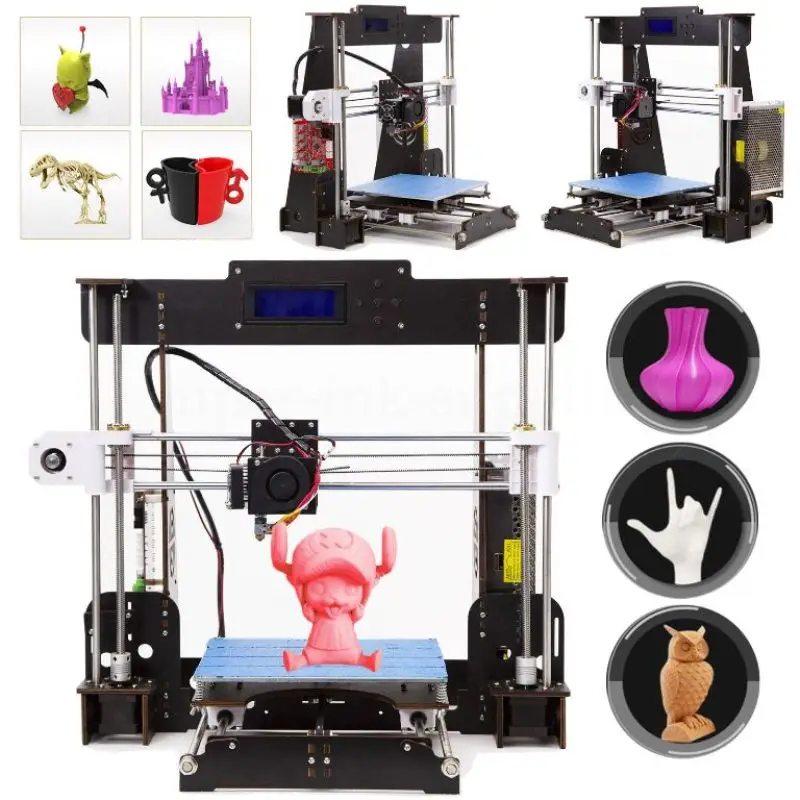 But in no case should you be in a hurry, otherwise printing may not start, for one reason or another.
But in no case should you be in a hurry, otherwise printing may not start, for one reason or another.
The first and main thing to do after assembly is to check that all screw connections are well tightened, we don't want the printer to fall apart after the first hour of operation, right? nine0003
Be sure to check that all wires are connected correctly to the control board. Only after these manipulations can the printer be connected to the network to check the operation of the device electronics.
Look at the display. Here is the main information menu of the printer.
Consider the readings on the display: The top line shows some numbers like 22.3/0 and 22/0. This is an indication of printer temperatures.
The first 22.3/0 means the current temperature of the extruder, usually it represents the ambient temperature. nine0003
The second 22/0 indicates the current bed temperature, however, due to the larger surface area, the bed temperature may differ slightly from the extruder temperature. Zero in this case displays the set temperature, that is, by default, after turning on the printer, it should not heat the extruder and the table, therefore the default temperature is 0.
Zero in this case displays the set temperature, that is, by default, after turning on the printer, it should not heat the extruder and the table, therefore the default temperature is 0.
Line below Z : 0.00 Buf : 0. The first value is the position of the extruder along the Z axis At the moment, the printer has no information about exactly where in space the nozzle is located, so the display shows 0.00. Buf : 0 is the memory buffer busy indication. Usually, during printing, the value changes from 0 to 16.
Third line Mul:100 Flow:100. The first value is the percentage of bar feed speed. The second value is the percentage of print speed. Both values show 100% - this means that the printer will execute all commands coming from GCODE with 100% accuracy. You can change these settings if you wish.
Well, the fourth line says "Printer ready", which means "Printer ready". Depending on the situation, the line may change to other inscriptions, announcing the execution of the operation. nine0003
nine0003
II.
How to insert the filament.
In this case, everything is simple. It is necessary to observe a number of conditions for the correct installation of a plastic thread in an extruder. First you need to decide what kind of plastic will be printed. This is necessary to determine the temperature to which the nozzle must be heated.
Each plastic has its own melting point. Consider PLA plastic. The melting point of this plastic is in the range from 190 to 220 degrees.
Let's set approximately average temperature to 210 degrees. To do this, enter the printer menu by pressing the central button of the joystick. We need the "Extruder" item. Select this item by pressing the right button. Before us are two lines “Bed Temp.: 0C” and “Temp. 0 : 0C", The first line is responsible for the temperature of the table, the second for the temperature of the extruder. Accordingly, we need a second one. Select the second line by pressing the right button of the joystick. The square next to the line will become filled. This means that we have entered the temperature setting mode. Now, by pressing the top button, we raise the temperature to the desired 190 degrees.
The square next to the line will become filled. This means that we have entered the temperature setting mode. Now, by pressing the top button, we raise the temperature to the desired 190 degrees.
Now, while the extruder is heating up, we need to prepare the plastic itself. The printer comes with cutting pliers. With this tool, you need to cut the plastic thread at an acute angle, so that you get an impromptu needle. This operation will allow the filament to pass freely through the thermal barrier channel to the melting zone and then to the nozzle. To make it easier to insert the thread into the guide hole, it is better to gently straighten a small section of it with your fingers, to such an extent that the thread becomes approximately straight. nine0003
So, the extruder has warmed up, the thread is ready, it remains only to fill the plastic into the extruder. The A8 and A6 printer models use the so-called "Direct" extruder.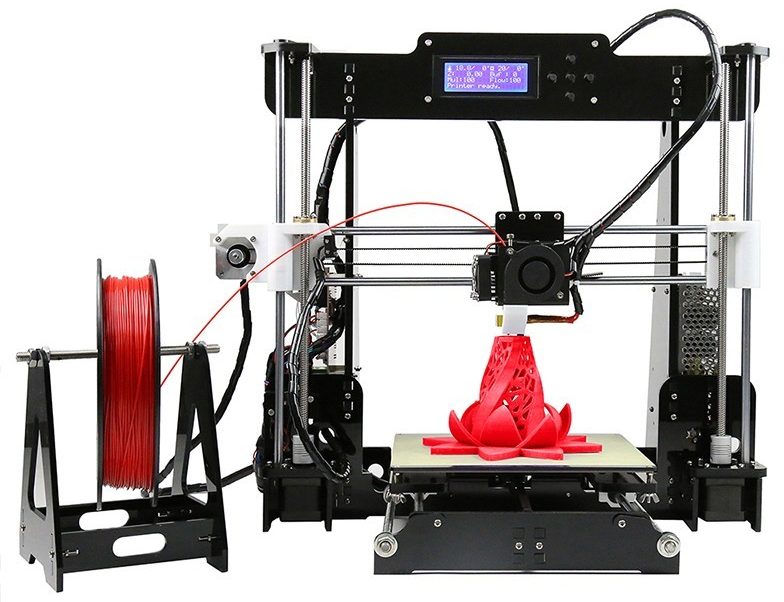 This means that the motor responsible for supplying plastic to the nozzle is located as close as possible to the thermal barrier and is mounted on a movable axle or axles. The extruder motor is equipped with a mechanism consisting of fasteners, a spring, a clamping bearing and a gear. This mechanism is designed for controlled supply of plastic into the thermal barrier channel. nine0003
This means that the motor responsible for supplying plastic to the nozzle is located as close as possible to the thermal barrier and is mounted on a movable axle or axles. The extruder motor is equipped with a mechanism consisting of fasteners, a spring, a clamping bearing and a gear. This mechanism is designed for controlled supply of plastic into the thermal barrier channel. nine0003
To correctly insert the filament into the extruder, press on the mount from the spring side. The pressure bearing will go to the side. In the meantime, insert the filament into the upper hole in the mount, draw it between the gear and the pressure bearing, and push it further, trying to get into the thermal barrier channel, until the filament melt appears from the extruder hole. Then we release the mount. Plastic installation is complete.
III.
Which plastic to choose and how to print it. nine0003
The choice of plastic depends on many factors. Here we will look at which plastic is right for you.
First of all, you need to decide whether you have experience in 3D printing, this is a decisive factor. If not, then of course you will need PLA plastic. This plastic is primarily suitable for beginner 3D printers due to its ease of use. It is made from vegetable raw materials and is safe to use. PLA has practically no shrinkage, it keeps well on the printer's desktop even without heating, when printing with this plastic, no toxic substances are released, and the finished model made of this plastic is easy to machine. However, this plastic has a number of disadvantages - the finished model cannot be heated, at 50 degrees the plastic softens and deforms. Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation and the environment, PLA plastic is structurally destroyed, and after a while, products made from it become unusable. nine0003
For those who already have experience in 3D printing, it is no secret that there are some difficulties with ABS plastic, and before switching to this type of plastic, a number of problems should be solved.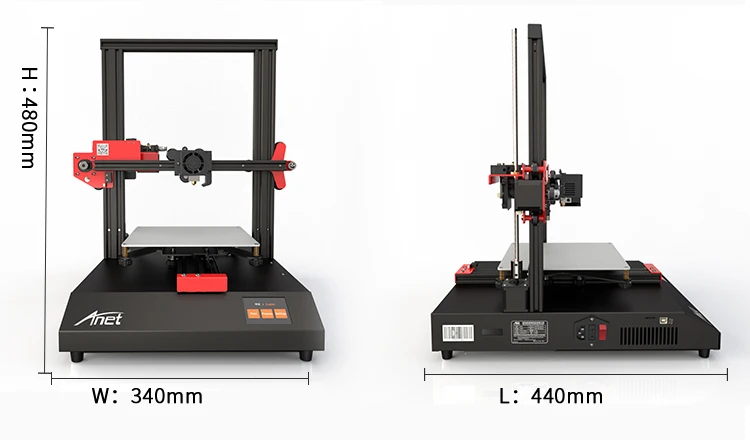 But let's go in order, first the pluses - it is good to print from ABS plastic, for example, gears, because ABS tolerates mechanical loads well. Also, ABS plastic shows good impact, tensile and fracture strength. That is why ABS plastic is used to produce housings for household appliances, car parts, and battery housings. This plastic is very easy to process both mechanically and chemically. nine0003
But let's go in order, first the pluses - it is good to print from ABS plastic, for example, gears, because ABS tolerates mechanical loads well. Also, ABS plastic shows good impact, tensile and fracture strength. That is why ABS plastic is used to produce housings for household appliances, car parts, and battery housings. This plastic is very easy to process both mechanically and chemically. nine0003
An excellent solvent for ABS plastic is regular acetone. We will describe how to process printed models in chemicals in the following articles. Models printed from ABS plastic are durable and can last for decades. This is due to the fact that our atmosphere has practically no effect on ABS plastic, but you should not keep a model made of this plastic in the sun for a long time. And now the most interesting - the disadvantages of ABS plastic: The first and main disadvantage is toxicity when heated. The problem is that ABS plastic is produced from 3 monomers, one of which is styrene. Under normal conditions, plastic is safe because all its components are bound and in a stable state, but as soon as it is heated, toxic styrene and poisonous acrylonitrile begin to be released.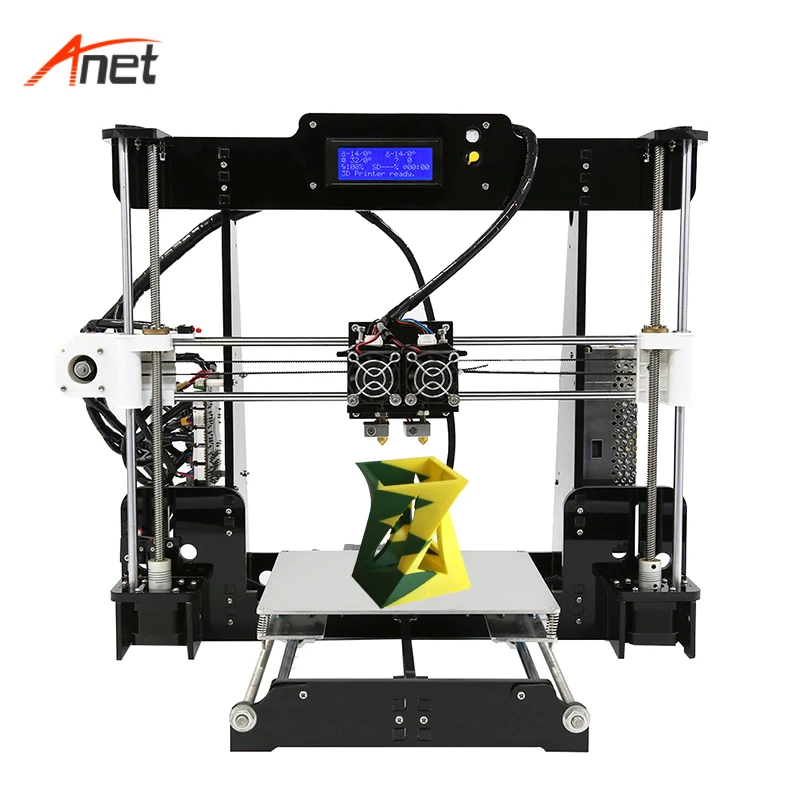 Therefore, it is necessary to observe safety precautions when working with this plastic. nine0003
Therefore, it is necessary to observe safety precautions when working with this plastic. nine0003
Also, ABS plastic has a monstrous shrinkage, so printing with this plastic on a cold table is simply not realistic, and simple heating to 100 degrees is unlikely to help. But that's not all, because of the same terrible shrinkage, a model that has not yet been printed can crack due to the temperature difference between the middle of the model, the hot table and the nozzle.
So printing with ABS is only recommended if you have experience with printing, want to create something durable and can secure the place where you print. nine0003
Next on the list is SBS plastic. Strictly speaking, SBS is not exactly plastic. If you look at the plastics that are described above, then their common name is thermoplastics, but SBS is a thermoplastic elastomer. Thermoplastics are polymeric materials that can reversibly change into a highly elastic or viscous fluid state when heated. (According to wikipedia). Elastomers are polymers with highly elastic properties and viscosity. Rubber or elastomer refers to any resilient material that can stretch to dimensions many times its original length (elastomeric filament) and, importantly, return to its original size when the load is removed. (According to the same wikipedia) A Thermoplastic elastomers are materials that behave like elastomers at room temperature, but when heated, they can be processed like plastics. nine0003
Elastomers are polymers with highly elastic properties and viscosity. Rubber or elastomer refers to any resilient material that can stretch to dimensions many times its original length (elastomeric filament) and, importantly, return to its original size when the load is removed. (According to the same wikipedia) A Thermoplastic elastomers are materials that behave like elastomers at room temperature, but when heated, they can be processed like plastics. nine0003
This is all theory, but in practice SBS plastic has limited properties of both rubber and plastic. The plastic itself is quite soft and elastic, in its pure form it is transparent, although there are also non-transparent rods. Its stretch factor can be up to 250%, but unlike rubber, it will remain stretched and will not return to its original shape. As for the properties of the plastic, in the hardened state it is very stable, not brittle, not brittle, but it is quite easy to crush or stretch. As a printing material, it is well suited for printing vases, ceiling lamps, plates, large gears, electronics cases. It is mechanically processed quite easily, but due to viscosity it quickly clogs the skin or file. Chemistry is processed perfectly and cheaply. The solvent is a conventional petroleum solvent. You don’t need to rest any baths, just apply it with a brush on the model and it will almost immediately acquire gloss and a smooth surface. nine0003
It is mechanically processed quite easily, but due to viscosity it quickly clogs the skin or file. Chemistry is processed perfectly and cheaply. The solvent is a conventional petroleum solvent. You don’t need to rest any baths, just apply it with a brush on the model and it will almost immediately acquire gloss and a smooth surface. nine0003
And finally PETG. As they say, the best last. We deal with this plastic every day. Containers are made from it, tires are reinforced, dishes, bottles, canisters are cast, it is used in medicine, instrument making and household appliances, used in the production of films, fibers and fabrics based on PET, and much more.
PETG is the same PET but with glycol added. This additive does not allow the polymer to crystallize during solidification, and gives the plastic the necessary viscosity, unlike PET. nine0003
This plastic is ideal for printing, adheres very well to the table, interlayer adhesion (adhesion) is very strong, is not afraid of drafts, is not afraid of sunlight and the atmosphere, and is excellent mechanically processed. Chemical processing is somewhat difficult due to the characteristics of the polymer, but is also possible. Chemically processed with boiling acetone (which is not recommended), or dichloromethane vapor (which is recommended), but for a long time.
Chemical processing is somewhat difficult due to the characteristics of the polymer, but is also possible. Chemically processed with boiling acetone (which is not recommended), or dichloromethane vapor (which is recommended), but for a long time.
IV.
How to calibrate the table. nine0003
In fact, everything is quite simple, just do not be afraid. There are many ways to calibrate your printer online. In most cases, it is recommended to calibrate the printer using a piece of paper as a gauge. This is not a bad way if you do not have accurate calibers at hand, but it has a number of disadvantages. However, consider this method as a guide to calibrating the printer.
Before starting to calibrate the table, it is necessary to use a ruler to determine the relative alignment of the motors of the Z axis. To do this, use the ruler to set the same distance between the two carriages of the Z axis.
The table itself is spring-loaded and rests on a metal table holder with springs. Through all four springs located at the corners of the table, screws are passed, on which, in turn, “lambs” are screwed. It is with their help that we will calibrate the printer. In order to completely exclude the nozzle from touching the table, we twist the “lambs” to such an extent that the springs are completely compressed at all four corners of the table. Then, you need to determine by eye the line between the Z-axis limit switch button and the table horizon, and fix the Z-axis limit switch approximately 5-7 mm above the imaginary table horizon line. nine0003
Through all four springs located at the corners of the table, screws are passed, on which, in turn, “lambs” are screwed. It is with their help that we will calibrate the printer. In order to completely exclude the nozzle from touching the table, we twist the “lambs” to such an extent that the springs are completely compressed at all four corners of the table. Then, you need to determine by eye the line between the Z-axis limit switch button and the table horizon, and fix the Z-axis limit switch approximately 5-7 mm above the imaginary table horizon line. nine0003
Then you need to turn on the printer, and enter the menu by pressing the center button. We are interested in the line "Position". Select this line by pressing the right button. Before us is the positioning menu. We are interested in the line "Home All". After selecting this function, the printer will start moving along the axes, in the direction of the limit switches. First along the X-axis, then along the Y-axis, and finally along the Z-axis.
After finishing the positioning of the printer, turn off the power to the motors. To do this, again enter the printer menu by pressing the central button. This time we need the line "Quick Settings" this is the quick settings menu. There are many lines in this menu, we need the latest "Disable stepper". Press the bottom button until we get to this line. After activating this function, the power to the motors will be turned off. nine0003
Now we proceed directly to the calibration of the table. Manually move the extruder nozzle to the front left edge, take a piece of paper, put it on the table, and begin to unscrew the “lamb” until the nozzle touches the piece of paper. The spring must be released to such a limit that a sheet of paper passes between the nozzle and the table with little effort. This procedure must be repeated on all four corners of the table.
For a more accurate calibration, send the printer back to the "home" position using the "Home All" function. Turn off the power to the motors again, using the "Disable stepper" function. This time you can move the extruder to a few arbitrary points on the table, and check the distance between the table and the nozzle using a piece of paper. If necessary, you can release or tighten the table springs. nine0003
Turn off the power to the motors again, using the "Disable stepper" function. This time you can move the extruder to a few arbitrary points on the table, and check the distance between the table and the nozzle using a piece of paper. If necessary, you can release or tighten the table springs. nine0003
V.
What to print on
So far there is no comprehensive answer to this question. Let's just list the methods, implementation, and result.
Separately, it should be mentioned that printing on a bare table is not worth it. There are several reasons for this. Firstly, it can damage the surface of the table, which will lead to its deformation and even failure. Secondly, even PLA plastic does not adhere well to a bare table, not to mention other types of plastic.
Let's start over. The heated table comes with the printer. By default, the table is pasted over with paper tape. This is done so that the plastic sticks better to the surface of the table, so you do not need to peel it off.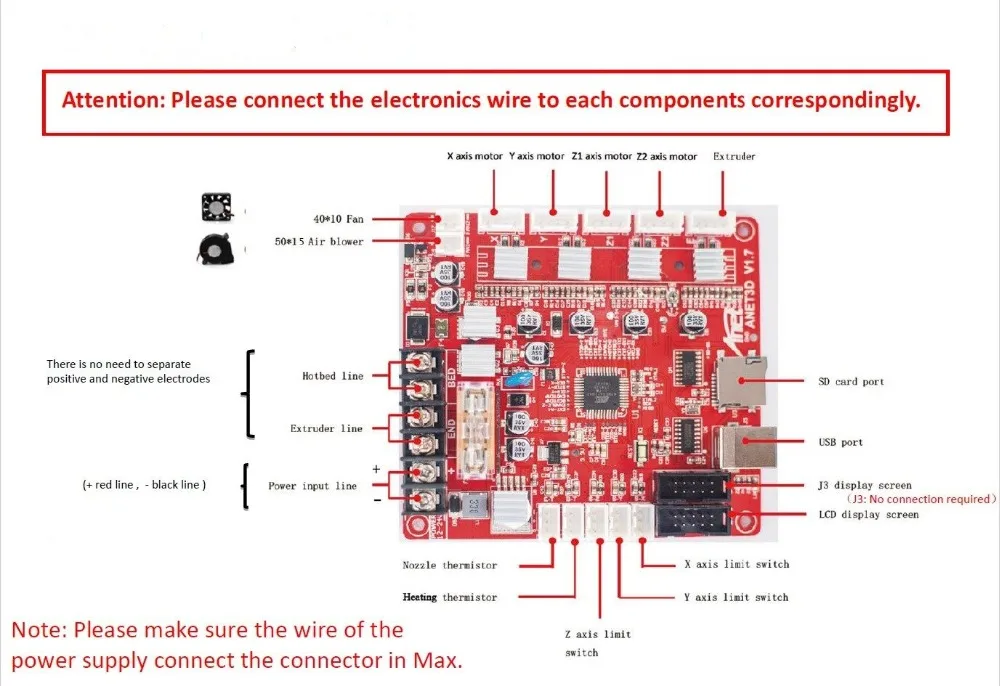 However, this measure is only valid for a few types of plastic, such as PLA and SBS. They do not need high adhesion to the table, since these plastics have practically no "shrinkage". So, if you are going to print only PLA and SBS, this method will be enough. nine0003
However, this measure is only valid for a few types of plastic, such as PLA and SBS. They do not need high adhesion to the table, since these plastics have practically no "shrinkage". So, if you are going to print only PLA and SBS, this method will be enough. nine0003
There is a special, self-adhesive, table cover. This coating is quite suitable for printing on plastics such as PLA, SBS, ABS and PETG. With the proviso that ABS plastic can print small area models. Otherwise, the models will peel off the table surface, ruining the final model.
Some print on Kapton tape. This is also a perfectly acceptable, albeit expensive, option. Nevertheless, it is possible to print ABS plastic on Kapton, again, models of a small area. PLA, SBS and PETG plastics adhere well to Kapton, but not as well as self-adhesive surfaces. nine0003
Many 3D printers use glass or mirror to print. There are many advantages to such a decision. Firstly, the surface of the glass is smoother than the surface of the table, and the surface of the mirror is smoother than the surface of the glass. But just like that, printing on glass or a mirror will not work. For good adhesion, "adhesive compounds" must be used. And here the most interesting begins. There is a lot of information on the net about how to cover glass. Among them are sugar syrup, burnt sugar, dark beer, hairspray, glue stick, liquid glass (nails), titanium glue, etc. And there is also a composition that is well suited for adhesion, this is BF2 glue and ethyl or isopropyl alcohol. BF2 is diluted with alcohol in a proportion of 12 - 13, to a liquid state. nine0003
But just like that, printing on glass or a mirror will not work. For good adhesion, "adhesive compounds" must be used. And here the most interesting begins. There is a lot of information on the net about how to cover glass. Among them are sugar syrup, burnt sugar, dark beer, hairspray, glue stick, liquid glass (nails), titanium glue, etc. And there is also a composition that is well suited for adhesion, this is BF2 glue and ethyl or isopropyl alcohol. BF2 is diluted with alcohol in a proportion of 12 - 13, to a liquid state. nine0003
VI.
Which files are accepted by the printer.
The printer, like most CNC machines, only accepts GCODE files. But let's figure out where they come from and why they are needed at all.
There are several 3D printing software available. All these programs are called slicers - from the English word slice - a piece, layer, part or slice. That is, the literal translation of slicer is a slicer. It turns out that the 3D printing program is a slicer, and it really is. The program, as it were, cuts the loaded model into the layers specified in the program. This is the main principle of the slicer, and at the same time the main printing parameter. Each slicer allows you to adjust various print settings such as layer thickness, nozzle and bed temperature, print speed, etc. nine0003
The program, as it were, cuts the loaded model into the layers specified in the program. This is the main principle of the slicer, and at the same time the main printing parameter. Each slicer allows you to adjust various print settings such as layer thickness, nozzle and bed temperature, print speed, etc. nine0003
Usually, STL files are loaded into the slicer, but there are programs that read OBJ format. In turn, these formats are saved from programs for 3D modeling, but we will not consider them here. Files in STL and OBJ format are a cloud of points that make up the 3D model itself. Depending on the settings, the slicer fills the model from wall to wall, and cuts it into layers. At the moment when the user is confident in all the settings of the slicer, it's time to save the results or send the finished code to the printer. In both cases, the information from the slicer becomes a GCODE file. Basically GCODE is a set of commands for 3D printer electronics. On a computer, you can open it with a regular notepad. nine0003
nine0003
VII.
First print from flash drive.
In order to print from an SD card, you need to learn how to compile GCODE. In this guide, we will look at how this is done through the Cura program version 15.04.03. So let's get started.
Loading the installed program. Before us is the working area of the printer, and on the left is the print settings menu window. In the upper right corner of the program there is a drop-down menu "File". After clicking on the “File” menu, a tab will drop out and a lot of inscriptions, we are interested in the very first line - “Upload model file”. Select this menu item. The directory selection window will open. We need an STL file of the model we want to print. nine0003
The same operation can be done more easily. In the upper left corner of the printer's working area, you can see the folder icon. After clicking on it, a directory selection window will also open.
After selecting the model we need, it will be displayed in the working area of the printer. After that, you can proceed to the settings for future printing.
After that, you can proceed to the settings for future printing.
So, we have set all the settings necessary for printing, and now we need to turn to the familiar File menu. In the drop-down window, we are interested in the line "Save GCode ...". Click on this line. The directory selection window appears. To avoid errors, or file loss, when writing to an SD card, it is best to save the GCODE file to the computer's desktop, and only post it to the SD card. nine0003
Next, you need to put the SD card into the printer's card reader. You need to press the center button of the joystick. The selection menu appears on the display. We need to find 2 lines to choose from "Print file" or "SD card". If "Print file" is selected, the file selection menu will immediately appear. You need to select the GCODE format file you just saved. If you select "SD card" a selection menu will appear in front of you, we need the line "Print file".
The printer will start preparing for printing - it will warm up the desktop, the extruder, and after the end of the warm-up it will go to the "home points" - first along the X axis, then Y then Z in turn.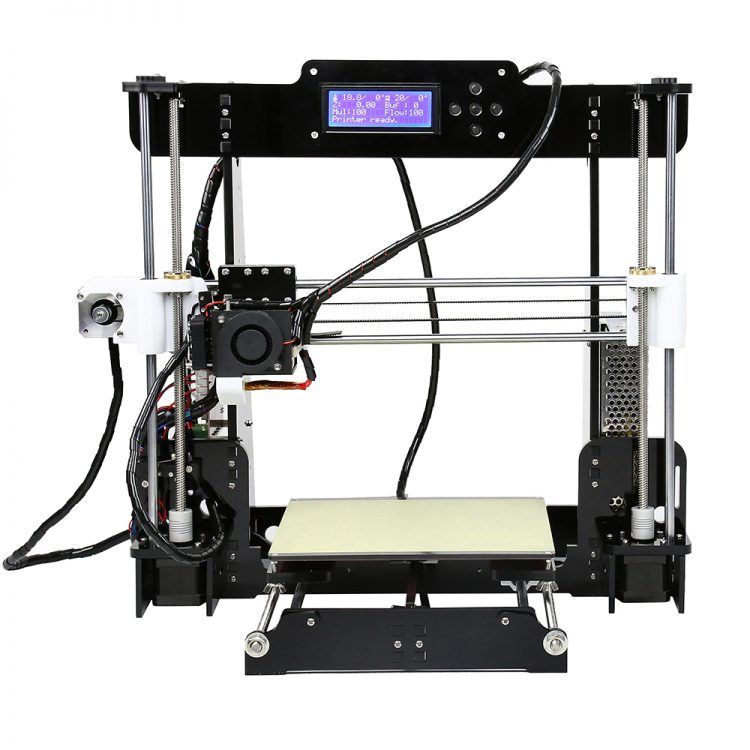 After completing all the preparatory operations, the printer will start printing. nine0003
After completing all the preparatory operations, the printer will start printing. nine0003
VIII.
First print via computer.
Printing from a computer is somewhat easier than from an SD card. However, you must install the Ch440G driver from the SD card before printing. This is USB-COM port support driver. After installation, you need to connect the printer with a USB cable. Next, we load the Cura slicer version 15.04.03, as in the above example. We need the Printer drop down menu. In the "Printer Settings..." drop-down menu. The printer settings window will open. In the lower right corner, the item "Communication Settings". On the opposite line "Serial port", you need to set COM # - where # is the port number on which the Ch440G driver is installed. On the opposite line "Baud rate" you need to set the speed to 115200.
After completing the print settings and connecting the printer to the computer, in the upper left corner of the workspace, the central icon with a “diskette” will change to another icon with the inscription USB. After clicking on this icon, the computer and printer connection status window will appear. By clicking on the print button you start the printing process. The printer will start heating the bed and then the extruder. After the temperature has been set, printing will begin.
After clicking on this icon, the computer and printer connection status window will appear. By clicking on the print button you start the printing process. The printer will start heating the bed and then the extruder. After the temperature has been set, printing will begin.
IX.
Where to get new print files and how to prepare them. nine0003
Many ready-made files can be downloaded from the Internet. There are a huge number of both paid and free sites. But if creativity does not give rest, or you need to carry out an individual project, there are a number of 3D editors that can save files in the STL format.
We discussed in detail how to prepare files for printing in the section “What files the printer accepts” and “First printing from a USB flash drive”.
Conclusion
The article turned out to be voluminous and we hope that it will be useful for many novice users. Because in 3D printing, you don’t even assemble a printer, but prepare it for printing, achieve ideal settings, etc.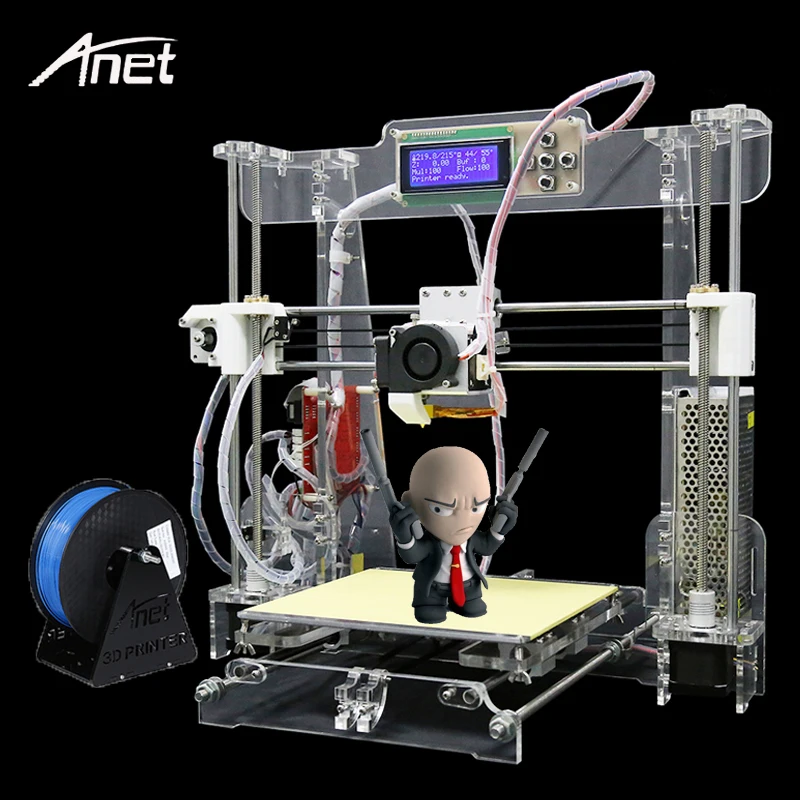 nine0003
nine0003
We have tried to summarize most frequently asked questions in one article. Next, we will continue to tell you in more detail about the different types of plastic, how they are processed, and much more. Thank you for reading to the end.
Bye everyone!
User manual for 3D printer Anet A8
User manual
3D printer Anet A8
What to do before starting0165 Be sure to check that all wires are connected correctly to the control board
.
Only then can the printer be connected to the network in order to check the operation of the
device electronics.
Look at the display. Here is the main information menu of the printer.
The top line shows some numbers like 22.3/0 and 22/0. This is
printer temperature indication. The first 22.3/0 means the current temperature of the extruder,
as a rule it displays the ambient temperature. The second 22/0 means the current
table temperature.
The line below Z : 0. 00 Buf : 0. The first value is the position of the extruder in the Z axis. Buf : 0 -
00 Buf : 0. The first value is the position of the extruder in the Z axis. Buf : 0 -
is the memory buffer busy reading.
Third line Mul:100 Flow:100. The first value is the percentage of bar feed speed
. The second value is the percentage of print speed.
The fourth line reads "Printer ready".
How to insert a filament.
1.
First you need to decide what plastic will be printed. Need it
to determine the temperature to which the nozzle should be heated.
2.
Each plastic has its own melting point. Consider PLA plastic.
The melting point of this plastic is in the range from 190 to 220 degrees.
3.
Let's set approximately average temperature to 210 degrees. To do this, you need to enter
in the printer menu by pressing the central button of the joystick. We need item
"Extruder". Select this item by pressing the right button. We have two
lines "Bed Temp.: 0C" and "Temp. 0 : 0C", The first line is responsible for the temperature of the table,
the second for the temperature of the extruder. Accordingly, we need a second one. We select the second
Accordingly, we need a second one. We select the second
line by pressing the right button of the joystick. The square opposite the line will become
filled in. This means that we have entered the temperature setting mode. Now
by pressing the top button we raise the temperature to the desired 190 degrees.
4.
Now, while the extruder is heating up, we need to prepare the plastic itself. In set with
cutters come with the printer. With this tool, you need to cut the plastic
thread at an acute angle, so that you get an impromptu needle. This operation
will allow the filament to pass freely through the thermal barrier channel to the melt zone and then
to the nozzle. In order to make it easier to insert the thread into the guide hole, a small section of it
is better to gently straighten it with your fingers, to such an extent that the thread becomes
approximately straight.
5.
So, the extruder has warmed up, the thread is ready, it remains only to fill the plastic into the extruder. nine0165 To correctly insert the filament into the extruder, press on the mount from the side of the spring.
nine0165 To correctly insert the filament into the extruder, press on the mount from the side of the spring.
Thrust bearing will go to the side. In the meantime, insert the filament into the upper hole in the mount, pass
between the gear and the pressure bearing, and push it further, trying to get
into the thermal barrier channel, until the filament melt appears from the extruder hole. Then
release the mount. Plastic installation is complete.
How to calibrate the table.
1.
2.
Before proceeding with the calibration of the table, it is necessary to use a ruler to determine the relative alignment of the
motors of the Z axis. To do this, use the ruler to set the same distance
between the two carriages of the Z axis. springs on a metal table holder. Through all
four springs located at the corners of the table, screws are passed, on which, in turn,
“lambs” are screwed. It is with their help that we will calibrate the printer.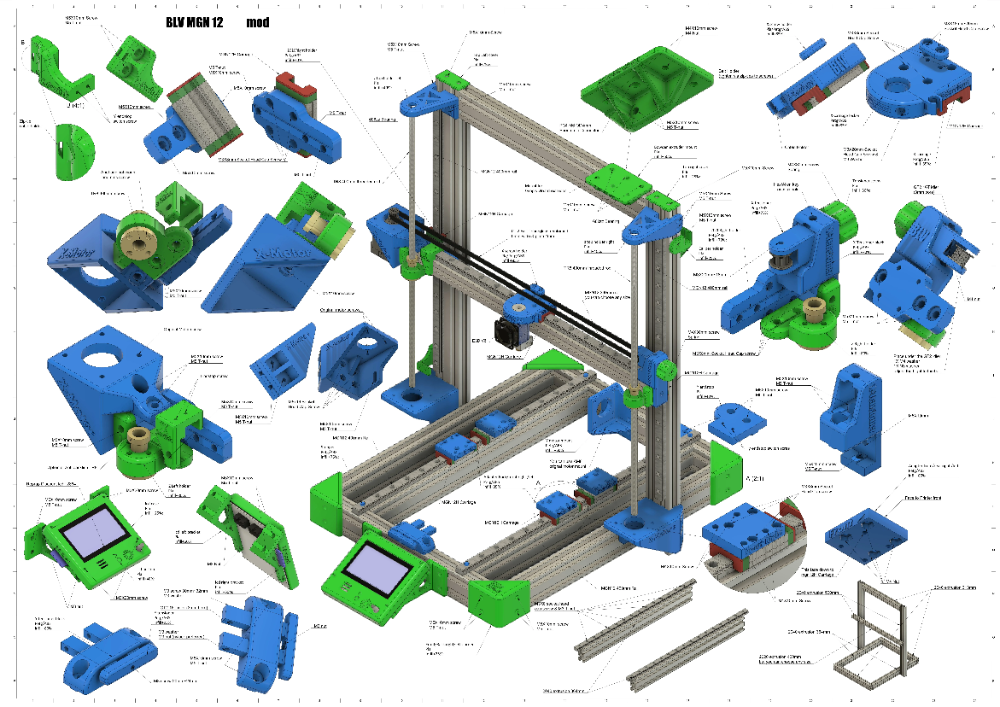 order
order
in order to completely prevent the nozzle from touching the table, we twist the “lambs” to such an extent that
the springs are completely compressed at all four corners of the table. Then, you need to determine by eye the line
between the button of the Z-axis limit switch and the table horizon, and fix the Z-axis limit switch approximately 5-7
mm above the imaginary table horizon line.
3.
4.
Then turn on the printer and enter the menu by pressing the center button. We are interested in the
line "Position". Select this line by pressing the right button. We have menu
positioning. We are interested in the line "Home All". After selecting this function, the printer will start
moving along the axes, in the direction of the limit switches. First along the X-axis, then along the Y-axis, and finally along the Z-axis.
After finishing the positioning of the printer, turn off the power to the motors. To do this, again
enter the printer menu by pressing the central button. This time we need the line "Quick
This time we need the line "Quick
Settings" this is the quick settings menu. There are many lines in this menu, we need the latest
"Disable stepper". Press the bottom button until we get to this line. After
activation of this function, the motors will be powered off.
5.
6.
Now we proceed directly to the table calibration. Manually move the extruder nozzle to the
front left edge, take a piece of paper, put it on the table, and begin to unscrew the “lamb” until
until the nozzle touches the piece of paper. The spring must be released to such a limit that the sheet of
paper passes between the nozzle and the table with little effort. This procedure must be repeated for
in all four corners of the table.
For more accurate calibration, send the printer back to the "home" position, using the
"Home All" function. Turn off the power to the motors again, using the "Disable stepper" function. At
this time you can move the extruder to a few arbitrary points on the table, and
check the distance between the table and the nozzle using a sheet of paper. If necessary, loosen
If necessary, loosen
or tighten the table springs.
Which files the printer accepts.
The printer, like most CNC machines, only accepts GCODE files. nine0165 But let's figure out where they come from and why they are needed at all.
There are several programs for 3D printing. All these programs are called slicers -
from the English word slice - a piece, layer, part or slice. That is, the literal translation of the slicer is
slicer. It turns out that the 3D printing program is a slicer, and it really is.
The program, as it were, cuts the loaded model into the layers specified in the program. This is
the main principle of the slicer, and at the same time the main printing parameter. Every 9The 0165 slicer allows you to adjust various print settings such as layer thickness,
nozzle and bed temperature, print speed, etc.
Usually, STL files are loaded into the slicer, but there are programs that read
OBJ format. In turn, these formats are saved from programs for 3D modeling,
but we will not consider them here. Files in STL and OBJ format are
Files in STL and OBJ format are
point clouds that make up the 3D model itself. Depending on the settings, the slicer fills
model from wall to wall, and cuts it into layers. At that moment, when the user is confident
in all the settings of the slicer, it's time to save the results or
send the finished code to the printer. In both cases, the information from the
slicer becomes a GCODE file. Basically GCODE is a set of commands for 3D
printer electronics. On a computer, you can open it with a regular notepad.
First print from flash drive.
In order to print from an SD card, you need to learn how to compile
Gcode. In this guide, we will look at how this is done through the Cura program version
04/15/03. So let's get started.
Loading the installed program. Before us is the working area of the printer, and on the left
the print settings menu window. In the upper right corner of the program there is a drop-down menu
"File".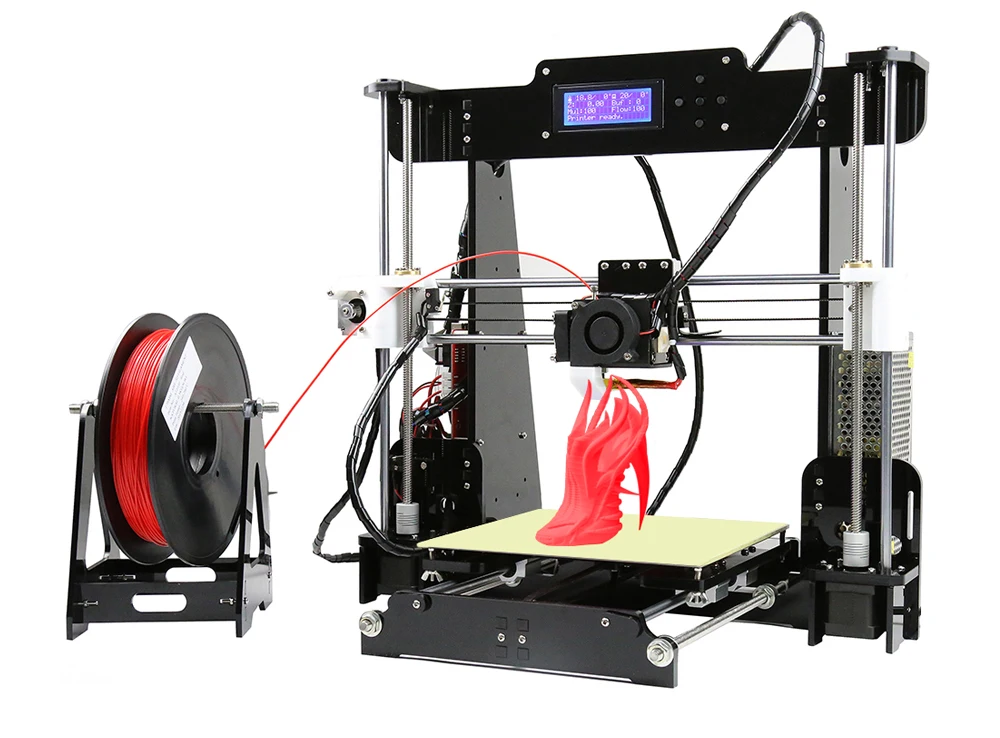 After clicking on the “File” menu, a tab will drop out and a lot of inscriptions, we are interested in
After clicking on the “File” menu, a tab will drop out and a lot of inscriptions, we are interested in
the very first line - “Download model file”. Select this menu item. The
directory selection window opens. We need a file of the model we want to print in format
STL.
The same operation can be performed more simply. In the upper left corner of the
printer's workspace, you can see the folder icon. After clicking on it, the
directory selection window will also open.
After selecting the model we need, it will be displayed in the working area of the printer. After
, you can proceed to the settings for future printing.
So, we have set all the settings necessary for printing, and now we need to turn to the menu
familiar to us "File". In the drop-down window, we are interested in the line "Save GCode ...". Click on this line. Appears
directory selection window. To avoid errors, or file loss, when writing to an SD card, it's best to
save the GCODE file to the computer's desktop, and only post it to the SD card.
Next, you need to put the SD card into the printer's card reader. It is necessary to press the central button
of the joystick. The selection menu appears on the display. We need to find 2 lines to choose from "Print file" or "SD
card". If "Print file" is selected, the file selection menu will immediately appear. You need to select the newly saved
GCODE format file. If you select "SD card" a selection menu will appear in front of you, we need
line "Print file".
The printer will start preparing for printing - it will warm up the desktop, the extruder, and after the end of the warm-up,
will go to "home points" - first along the X axis, then Y, then Z in turn. After completing all
preparatory operations, the printer will start printing.
First print via computer.
Printing from a computer is somewhat easier than printing from an SD card. However, the Ch440G driver must be installed from the SD card before printing
. This is USB-COM port support driver.