3D printers affordable
The Best Cheap 3D Printers for 2022
While we'd hesitate to call 3D printing a mature technology, you might say it has reached its teenage years. Through their first decade-and-change, 3D printers have come down in price, grown easier to set up and operate, and become more reliable. And you may pay less than you expect: Many once-high-end features have migrated down to inexpensive models.
PC Labs has been reviewing 3D printers since 2013. Today, the state of 3D printing is strong, but that wasn’t always the case. For the first several years, it was often an adventure getting one of these printers up and running, let alone successfully through our testing regimen. Issues with filament-based—aka fused filament fabrication (FFF) or fused deposition modeling (FDM)—printers were abundant.
Filament feeders had to be coaxed into delivering filament from the spool to the extruder. Print beds had to be manually aligned. The extruder or hot end had to be positioned just right to minimize the gap between the nozzle and the build plate (the flat surface on which the object is printed). Objects frequently stuck to the build plate, and required careful, sometimes unsuccessful, efforts to pry them off. These and other issues required painstaking effort to resolve, often combined with calls to tech support.
Not so much anymore. While they can still be rebellious at times, 3D printers have grown up a lot, and achieving the 3D printer basics has gotten a lot less likely to end in a shouting match over small things. And they've gotten a lot more affordable, too, for curious DIY-ers and hobbyists to try.
If you're in the market for a beginner or low-cost 3D printer, it's important to know how lower-end models differ. Read on for mini-reviews of the top budget 3D printers we've tested. After that, we go into more detail on understanding the 3D printer specs and tech relevant to beginning buyers. Ready to take the plunge? Read on.
Original Prusa Mini
Best Overall Budget 3D Printer
4.5 Outstanding
Bottom Line:
It requires assembly and calibration care (plus shipping from the Czech Republic), but the Original Prusa Mini is a compact, open-frame 3D printer that consistently produces superb-quality output for a great price.
PROS
- Top-notch object quality
- Supports a variety of filament types
- Useful, professionally printed user guide
- Great support resources
- Versatile, user-friendly software
CONS
- First-layer calibration can be tricky
- Only includes starter packets of filament
- Requires monitoring if young children or pets are around
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prusa Research | $399.00 | $399.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Original Prusa Mini Review
XYZprinting da Vinci Mini
Best Budget 3D Printer for Schools, Community Centers
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
The XYZprinting da Vinci Mini is a consumer-oriented 3D printer that provides a winning combination of low price, ease of setup and use, solid print quality, and smooth, misprint-free operation.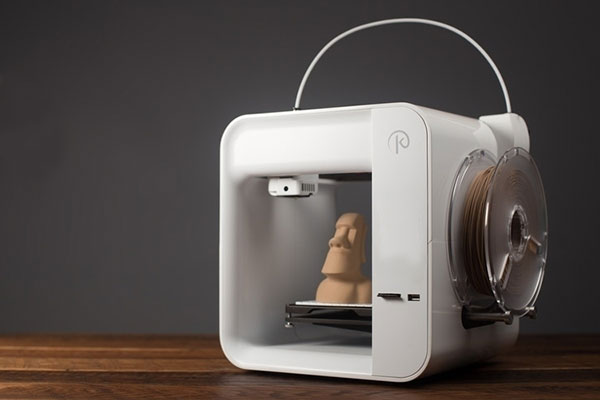
PROS
- Very low price.
- Reasonably priced filament.
- Good print quality.
- No misprints in testing.
- Easy setup and operation.
- Quiet.
- Prints over a USB or Wi-Fi connection.
CONS
- Occasional problems in trying to launch prints.
- Removing printed objects from the print bed is sometimes tricky.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walmart | $199.95 | $199.95 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Amazon | $199.95 | $199.95 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our XYZprinting da Vinci Mini Review
Toybox 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Children
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
The Toybox 3D Printer works well as a model designed for children, offering reliable printing from a browser or mobile device and a few thousand toys to print, plus creative options to output drawings or photos. Just bear in mind the tiny build area.
Just bear in mind the tiny build area.
PROS
- Reliable, misprint-free printing
- Easy setup
- One-touch operation
- Well-composed help resources
- Access to more than 2,000 printable toys and projects
- Lets you create your own printable designs
CONS
- Tiny build area
- Not ideal for importing 3D files created elsewhere
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299.00 | $299.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Toybox Labs | $379.00 | $299.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Toybox 3D Printer Review
Monoprice Mini Delta V2 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Beginners, Non-Techies
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
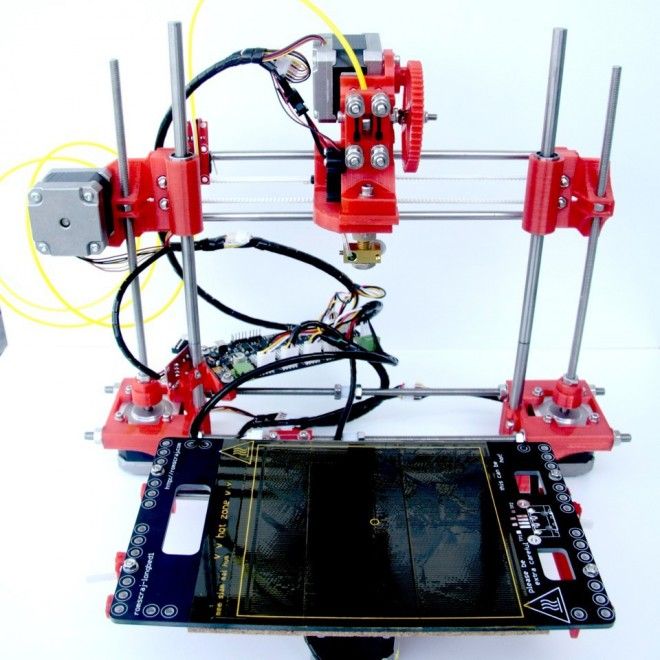
3D printing gurus will be intrigued by the Monoprice Mini Delta V2's use of the delta rather than Cartesian coordinate system, but beginners will just enjoy its low price, ease of use, and speedy printing.
PROS
- Sub-$200 price
- Quick, nearly misprint-free printing
- Easy setup and operation
- Sturdy steel-and-aluminum frame
- Supports multiple filament types
CONS
- Tiny build area
- So-so print quality
- Mere one-year warranty
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $179.99 | $179.99 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Monoprice Mini Delta V2 3D Printer Review
Anycubic i3 Mega S
Best Budget 3D Printer With an Open Design, Big Build Area
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Anycubic i3 Mega S, an inexpensive open-frame 3D printer, produced decent-quality prints in our testing. To get the most out of it, though, may require precise calibration.
PROS
- Modestly priced
- Large build area for an inexpensive printer
- Supports a variety of filament types
- Generally solid print quality
- Uses well-known Cura software
CONS
- Finicky print-platform alignment
- Supported coils of filament are small
- Poorly placed spool holder
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $229.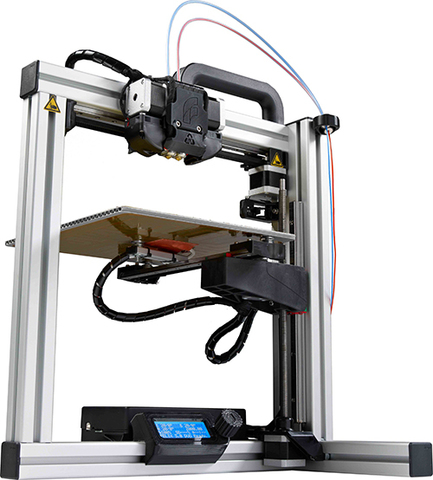 98 98 | $229.98 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
| AnyCubic | $279.00 | $279.00 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Anycubic i3 Mega S Review
Anycubic Vyper
Best Budget 3D Printer for the Biggest Build Area Possible
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
Anycubic's modestly priced Vyper whips up large 3D prints on its open-frame design, and provides automatic print-bed leveling. Just know that some minor assembly is required—and printed objects may require a bit of cleanup.
PROS
- Relatively large build area
- Automatic bed leveling
- Simple assembly
CONS
- Short (one-year) warranty
- Includes only a small starter filament coil
- Using Cura software with the Vyper requires tweaking a couple of settings
- Test prints showed some "hairy" filament residue
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $429. 99 99 | $429.99 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| AnyCubic | $369.00 | $319.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Anycubic Vyper Review
Creality Ender-3 V2
Best Budget 3D Printer for Tinkerers and DIY Types
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
Hands-on tweaking defines Creality's budget-price Ender-3 V2, an open-frame 3D printer that you build from a kit. It produces generally above-par prints, but its print bed can be tricky to keep leveled.
PROS
- Inexpensive
- Slightly above-average print quality
- Good-size build area for its price
- Supports several filament types
CONS
- Manual print-bed leveling can be tricky
- Setup instructions could be deeper, more legible
- Questionable quality control on some parts
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299.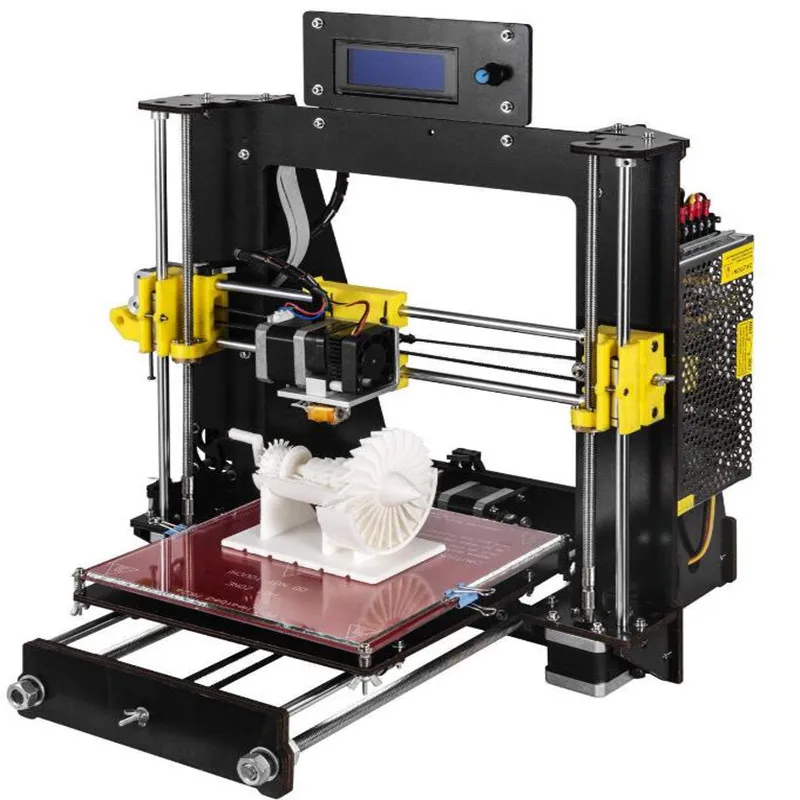 00 00 | $246.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Creality Ender-3 V2 Review
Flashforge Finder 3D Printer
Best 3D Printer for the Very Tightest Budgets
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Flashforge Finder 3D Printer is moderately priced and offers good print quality, but it proved tricky to get up and running in our tests.
PROS
- Quiet.
- Good print quality.
- Connects via USB 2.0 cable, USB thumb drive, or Wi-Fi.
- Reasonably priced.
CONS
- Some objects pulled off the platform during testing.
- Poor documentation.
- Modest build volume.
- Limited to printing with polylactic acid filament (PLA).
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $729.00 | $729.00 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Flashforge Finder 3D Printer Review
Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Dabbling in Small Objects
3. 5 Good
5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer is a compact, stylish 3D printer with above-par overall print quality, but, alas, a tiny build area for the money.
PROS
- Small, lightweight for a desktop 3D printer.
- Easy to set up and use.
- Supports PLA, PETG, and wood composite filaments.
- Multiple-color support.
- Wi-Fi camera monitors print jobs.
- Prints from USB drives, SD cards, or mobile devices.
CONS
- High price for its capabilities.
- Small build area.
- Too-brief warranty.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $699.00 | $699.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer Review
XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro
Best Budget 3D Printer With Closed Design, Roomy Build Area
3. 5 Good
5 Good
Bottom Line:
The XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro is a moderately priced closed-frame 3D printer with a large build volume and overall good performance, but a potentially balky filament-feeding system.
PROS
- Spacious build area
- Works with third-party filaments
- Self-leveling print bed
CONS
- Build plate is not heated
- Limited to PLA- and PETG-based filaments
- Guide tube is prone to detaching
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299.95 | $199.95 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Best Buy | $449.95 | $449.95 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro Review
Monoprice Voxel 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Cheap Filament
3. 0 Average
0 Average
Bottom Line:
The Monoprice Voxel is an under-$400 3D printer that's easy to set up and use. It exhibits generally good print quality, but it was unable to print two of our test objects.
PROS
- Easy to set up and use.
- Budget price for printer and filament spools.
- Supports PLA, ABS, and several composite filament types.
- Versatile software.
- Prints over Ethernet or Wi-Fi, or from a USB thumb drive.
CONS
- Frequent misprints on certain test objects.
- Slightly balky touch screen.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $449.99 | $369.26 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Walmart | $429.99 | $369.26 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Monoprice Voxel 3D Printer Review
Buying Guide: The Best Cheap 3D Printers for 2022
How to Buy a Cheap 3D Printer
The biggest changes to 3D printers over the last few years have come to the cheaper models. Nowadays, many of those classic, ornery 3D-printing issues have been resolved (most of the time, anyway), even for consumer and bargain-priced 3D printers. Automatic print-bed leveling is the norm, and you can usually remove 3D-printed objects from heated and/or flexible build plates with a minimum of coaxing. And most 3D printer manufacturers have either developed and refined their own software, or have adapted an open-source printing platform such as Cura(Opens in a new window).
Nowadays, many of those classic, ornery 3D-printing issues have been resolved (most of the time, anyway), even for consumer and bargain-priced 3D printers. Automatic print-bed leveling is the norm, and you can usually remove 3D-printed objects from heated and/or flexible build plates with a minimum of coaxing. And most 3D printer manufacturers have either developed and refined their own software, or have adapted an open-source printing platform such as Cura(Opens in a new window).
(Credit: Zlata Ivleva)
What separates more expensive 3D printers from cheap ones ("cheap" defined as $500 or less, for the purposes of this article) is often a select group of features. These include the build volume, the type of frame, the varieties of supported filament, the software, and the connectivity mix. Let's run through those in turn.
What's the Right Build Volume for a 3D Printer?
A 3D printer’s build volume is the maximum dimensions (HWD) of a part that it can print. (We say “a part” because a 3D-printed object can consist of multiple parts that are printed, then glued or otherwise pieced together.) While the smallest build volume of any 3D printer we have tested is 3.9 by 3.9 by 4.9 inches, we consider any build volume smaller than 6 by 6 by 6 inches to be small, any between that and 10 by 10 by 10 inches as medium, and any printer with at least one build dimension of more than 10 inches as having a large build volume.
(We say “a part” because a 3D-printed object can consist of multiple parts that are printed, then glued or otherwise pieced together.) While the smallest build volume of any 3D printer we have tested is 3.9 by 3.9 by 4.9 inches, we consider any build volume smaller than 6 by 6 by 6 inches to be small, any between that and 10 by 10 by 10 inches as medium, and any printer with at least one build dimension of more than 10 inches as having a large build volume.
(Credit: Molly Flores)
As a general rule, inexpensive 3D printers have small build volumes, while more expensive ones have larger build volumes. This depends in part on the type of printer. Closed-frame 3D printers—and most semi-open models, which have a rigid top, base, and sides but are open in front and, often, back—tend to have small build volumes, while open-frame printers, lacking as rigid a physical structure, often have relatively large build volumes for the price. You'll want to weigh the build volume against the kinds of objects you will print.
Should I Get an Open-Frame or Closed-Frame 3D Printer?
Which brings us to the frame "form factor" question: open-frame versus closed-frame. Closed-frame 3D printers are boxlike devices, with a rigid base, walls (with a see-through door in front), and top. Among their advantages? They muffle the operating noise, as well as reduce the odor from melted filament (which is potentially an issue with ABS plastic), and they provide some protection for people or pets who might inadvertently touch the hot extruder. A downside: They tend to have smaller build volumes than open-frame 3D printers, which have fewer (often, no) walls to constrict them.
(Credit: Zlata Ivleva)
Low-cost 3D printers include both open-frame and closed-frame models, as well as a few stereolithography printers. If a relatively large build volume is a priority, you’re likely to get more bang for the buck with an open-frame model. Open-frames do have some clear downsides by definition: They tend to be noisy, emit odors when certain plastics are melted, and provide little protection for someone who might touch the hot extruder.
(Credit: Molly Flores)
Also, recognize some potential negatives of open frames, depending on the model. Some require assembly, being essentially kits, and most require more setup care than a closed-frame printer, plus more maintenance to keep them running smoothly. Still, these very traits should not deter—and may even appeal to—hobbyists and DIY folks.
What Should I Look for in 3D Printer Software and Connectivity?
Gone are the days when tinkerers had to cobble together several different programs to get a 3D printer to run. Manufacturers either include their own 3D printing program or modify an existing platform such as the open-source Cura.
3D printing software performs three main functions: processing an object file (resizing, moving, rotating, and in some cases duplicating it), slicing it (into virtual layers, based on your chosen resolution), and printing it. These are almost universally combined into a seamless process. Some high-end printers have software that supports a wider range of settings you can tweak, but even the basic suites work at least reasonably well.
More likely to vary among the cheaper set is the array of connection options from model to model. Nearly all have a USB Type-A port to fit a thumb drive for printing from document files. Most also have a USB Type-B port for connecting directly to a computer, and some offer Wi-Fi, too (or as an alternative), while a handful let you connect via Ethernet to share the printer across a local network.
Some printers support storing 3D files on an SD or microSD card (which may also contain the printer’s system files). Most 3D printer manufacturers (even the discount ones) have a mobile app to launch and monitor print jobs, and a few provide access to cloud services from which you can print.
While high-end 3D printers tend to have an abundance of connection choices, discount models vary widely in their choices. Some are generous and some are basic, so it pays to assess what a given model offers.
What Should I Look for in Filament Support?
Filament support tends to be a key area that separates the cheaper models from the higher-end ones. (See our guide to understanding 3D printing filaments for more particulars.) Inexpensive 3D printers tend to support a limited number of plastic filament types, some of them only PLA and/or ABS.
(See our guide to understanding 3D printing filaments for more particulars.) Inexpensive 3D printers tend to support a limited number of plastic filament types, some of them only PLA and/or ABS.
Recommended by Our Editors
3D Printing: What You Need to Know
3D Printer Filaments Explained
(Credit: Molly Flores)
PLA (polylactic acid) is a biodegradable, plant-based polymer, while ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is the same tough plastic that Legos are made from. Objects printed from ABS are durable and nontoxic, though the material can be tricky to work with. ABS can emit an acrid, unpleasant odor during printing, and the bottom corners of objects being printed with it have a tendency to curl upward a bit, especially if you are using a non-heated print bed. This can lead to unsightly prints, and/or prints prematurely pulling off the build plate, ruining them.
Many entry-level and low-price 3D printers stick exclusively to PLA. If you want to experiment with a larger variety of filaments—which include water-soluble filament, wood- and metal-laced composites, and both tough and flexible varieties—you may have to pay more, although a few discount models support a wide range of materials.
If you want to experiment with a larger variety of filaments—which include water-soluble filament, wood- and metal-laced composites, and both tough and flexible varieties—you may have to pay more, although a few discount models support a wide range of materials.
Should I Consider a 3D Printing Pen Instead?
Although they aren’t printers per se, inexpensive 3D pens are close kin to 3D printers—using the same filament types and a similar extrusion system—and we include them in the 3D printing category. Rather than tracing out a programmed pattern, you use the 3D pen much like a normal pen, except that you draw with molten plastic. You can trace a pattern or draw freehand, and even draw in three dimensions as the plastic quickly solidifies and hardens once extruded.
(Credit: 3Doodler)
Most 3D pens cost less than $100, and some cost $50 or less. At a glance, 3D pens may appear to be toys, but some artists and craftspeople have taken to them, as it is possible to make quite complicated and beautiful objects with them. If your aim in 3D printing is something closer to freehand design and free expression than computer-centric, structured, and repeatable output, you might give one a try.
If your aim in 3D printing is something closer to freehand design and free expression than computer-centric, structured, and repeatable output, you might give one a try.
So, What Is the Best Cheap 3D Printer to Buy?
Buying a budget 3D printer needn’t mean a world of sacrifice. Plenty of capable and reliable models sell at less than $500, and while they may not be as feature-rich as their more expensive cousins, there's no sense in paying for things you don’t need.
Many casual 3D-printing experimenters will be fine with printing over a USB cable or from a thumb drive, and sticking to PLA may be the best choice for a starter 3D printer. If you focus just on the features you want, you may be pleasantly surprised at what you find. Below, check out a spec breakdown of the best under-$500 3D printers we have reviewed, paralleling our picks above. Also, for a look at the broader market, see our guide to our favorite 3D printers overall.
Best Budget 3D Printer: 8 Great Printers at a Price You'll Love
It costs less than ever to get into 3D printing, with printers available for under $200. The catch is that these budget machines usually require some tweaking to get right. You'll save money, but it's a rough-and-tumble way to get started. The best budget 3D printers have a healthy balance between cost and usability so that's what we are looking at in this list.
The catch is that these budget machines usually require some tweaking to get right. You'll save money, but it's a rough-and-tumble way to get started. The best budget 3D printers have a healthy balance between cost and usability so that's what we are looking at in this list.
3D printing -- or additive manufacturing to give it its scientific name -- has been around for a long time now. It's a fun way to create models that can be practical, or just for fun. You can print giant pieces of cosplay armor, or small statues to give as gifts. You can even buy a few printers, open your own Etsy store and make yourself a tidy profit.
These budget 3D printers all cost under $500 (though prices can drift a bit month to month), and some are better suited to beginners than others. Our list of picks for the best 3D printer overall covers a much wider range of choices, but these are excellent for getting started or for buying several at once!
James Bricknell/CNET
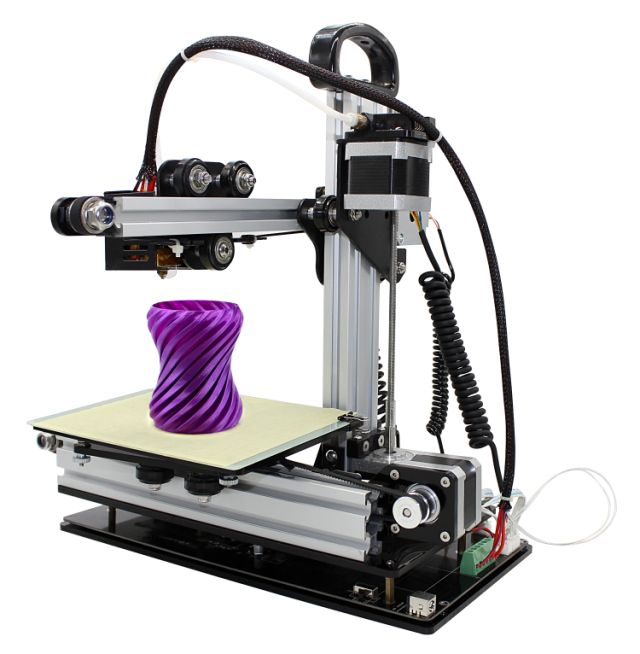
Elegoo Neptune 2
Keep it simple
The Elegoo is one of my favorite ultra-cheap printers. When testing it, I kept expecting it to fail and it just didn't. It produced amazing results for the price, and continues to do so every time I use it. It doesn't have auto bed leveling, but the Elegoo was easy to set up. And because it's based on the popular Ender 3, it has a lot of mods available to make it even better.
When testing it, I kept expecting it to fail and it just didn't. It produced amazing results for the price, and continues to do so every time I use it. It doesn't have auto bed leveling, but the Elegoo was easy to set up. And because it's based on the popular Ender 3, it has a lot of mods available to make it even better.
$170 at Amazon
Prusa Research
Prusa Mini Plus
Small but mighty
The Mini Plus is one of the best small-footprint printers you can buy. It has everything you would expect from a Prusa machine: Auto bed leveling, crash detection and great print quality, all for under $450. Building it with my son gave us a lot of good insights into how a 3D printer works, and potentially how to fix one.
$429 at Prusa Research
Creality
Creality Ender 3
Community favorite
The Ender 3 is one of the bestselling 3D printers of all time. Its under-$200 price removes a huge barrier to entry for anyone looking to spend as little as possible for their first machine.
Its under-$200 price removes a huge barrier to entry for anyone looking to spend as little as possible for their first machine.
Its popularity means there is a huge community of people to help you get it set up and working -- it's not exactly plug-and-play -- and you may need to spend a fair amount of time tweaking the Ender 3 to get it to print as well.
$199 at Amazon
You're receiving price alerts for Creality Ender 3
Anycubic
Anycubic Kobra Go
Entry level kit
The latest entry-level printer from Anycubic is surprisingly good. It comes in kit form, which gives you a chance to learn a little bit more about the machine. While that makes the setup more complicated, the printing is much easier with auto bed leveling, something I have never seen in a $200 printer. It makes everything easier, believe me.
If you are looking to get into 3D printing and want to learn what each of the parts does, this is a great way to find out.
$200 at Amazon
Flashforge
Flashforge Finder 3
Excellent out of the box
I've recently been working with the Finder 3 and I'm impressed with the quality it was able to produce straight from the box. It is easy to set up and comes with a flexible build plate that you can replace the glass bed with. It makes it far easier to remove builds.
On my CNET torture test, the Finder 3 coped really well with overhangs, as well as the points of the towers. Ringing was minimal, though it did struggle with bridging.
Overall, the Finder 3 is a great printer for the price. It's perfect for a teacher in the classroom as the enclosure makes it stable, and the slicer can control multiple printers at once via Wi-Fi.
$400 at Amazon
$369 at Flashforge
You're receiving price alerts for Flashforge Finder 3
Dan Ackerman/CNET
Creality Ender 3 S1
Direct drive with advanced features
As Dan Ackerman said in his review of the Creality Ender 3 S1 "At $399, the S1 version of the Ender-3 is about $100 more than older versions but includes so many upgrades and quality of life features that it qualifies as a great beginner-friendly, plug-and-play printer. "
"
It's also a great budget-friendly Direct Drive printer, making it easier to use for materials such as TPU.
$399 at Amazon
You're receiving price alerts for Official Creality Ender 3 S1 3D Printer with Direct Drive Extruder CR Touch Auto Leveling High Precision Double Z-axis Screw Silent Board Printing Size 8.6X8.6X10.6in, Upgrade Ender 3 V2 for Beginners
Resin 3D printers for beginners
Most beginner printers use a plastic filament to create models, but there are plenty of affordable resin 3D printers, too. Liquid resin is a little more difficult to use than standard 3D printing material and requires safety equipment. But it also produces amazingly detailed results.
Elegoo
Elegoo Mars 3
The best starter resin printer
This small resin printer is Elegoo's latest model in its popular Mars line. Because of the 4K monochrome LCD (these printers use light from an LCD to cure liquid resin) it can print much faster than older printers.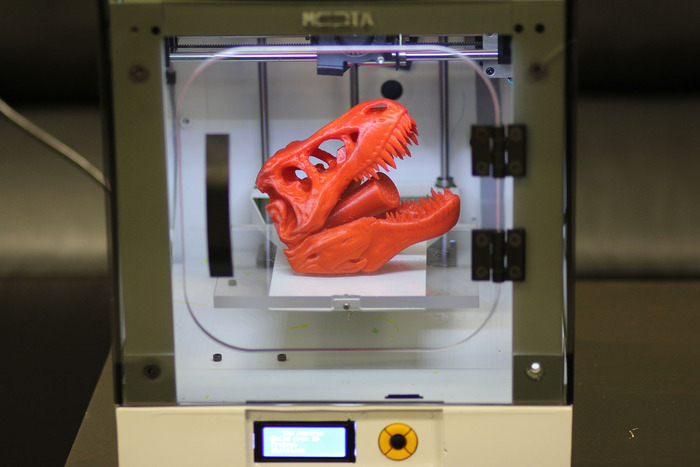 The level of detail on models is something that standard 3D printing simply can't reproduce. At this price, the Elegoo Mars 3 is the best resin printer for the money.
The level of detail on models is something that standard 3D printing simply can't reproduce. At this price, the Elegoo Mars 3 is the best resin printer for the money.
$259 at Amazon
You're receiving price alerts for Elegoo Mars 3
James Bricknell/CNET
Anycubic Mono X
When you need it bigger
This is expensive for a budget printer, but well worth it if you want a large enough print area to make something special. I have been using this as my main resin printer and it can handle anything I throw at it, from a D&D miniature army to highly detailed sculptures.
$580 at Amazon
James Bricknell/CNETFrequently asked questions
What material should I use to print with?
Most home 3D printers use PLA or ABS plastic. Professional printers can use all sorts of materials, from metal to organic filament. Some printers use a liquid resin, which is much more difficult to handle but offers sharper details. As a beginner, use PLA. It's non-toxic, made mostly of cornstarch and sugarcane, handles easily, and is inexpensive. However, it's more sensitive to heat, so don't leave your 3D prints on the dashboard of a car on a hot day.
Professional printers can use all sorts of materials, from metal to organic filament. Some printers use a liquid resin, which is much more difficult to handle but offers sharper details. As a beginner, use PLA. It's non-toxic, made mostly of cornstarch and sugarcane, handles easily, and is inexpensive. However, it's more sensitive to heat, so don't leave your 3D prints on the dashboard of a car on a hot day.
What settings should I use?
Most 3D printers include or link to recommended software, which can handle converting 3D STL or other files into formats supported by the printer. Stick with the suggested presets to start, with one exception. I've started adding a raft, or bottom layer of filament, to nearly everything I print. It has cut down dramatically on prints that don't adhere to the bed properly, which is a common issue. If you continue to have problems, rub a standard glue stick on the print bed right before printing.
What are supports?
Your 3D models probably need some help to print properly, as these printers don't do well with big overhangs -- for example, an arm sticking out from a figure. Your 3D printer software can usually automatically calculate and add supports, meaning little stands that hold up all those sticking-out parts of the model. After the print is done, clip the supports off with micro cutters and file down any nubs or rough edges with hobby files.
Your 3D printer software can usually automatically calculate and add supports, meaning little stands that hold up all those sticking-out parts of the model. After the print is done, clip the supports off with micro cutters and file down any nubs or rough edges with hobby files.
How we test
Testing 3D printers is an in-depth process. Printers often don't use the same materials, or even the same process to create models. I test SLA, 3D printers that use resin and light to print, and FDM, printers that melt plastic onto a plate. Each has a unique methodology. Core qualifiers I look at include:
- Hardware quality
- Ease of setup
- Bundled software
- Appearance and accuracy of prints
- Repairability
- Company and community support
A key test print, representing the (now old) CNET logo, is used to assess how a printer bridges gaps, creates accurate shapes and deals with overhangs. It even has little towers to help measure how well the 3D printer deals with temperature ranges.
Testing resin requires different criteria so I use the Ameralabs standard test -- printing out a small resin model that looks like a tiny town. This helps determine how accurate the printer is, how it deals with small parts and how well the UV exposure works at different points in the model.
Many other anecdotal test prints, using different 3D models, are also run on each printer to test the longevity of the parts and how well the machine copes with various shapes.
For the other criteria, I research the company to see how well it responds to support queries from customers and how easy it is to order replacement parts and install them yourself. Kits (printers that come only semi-assembled) are judged by how long, and how difficult, the assembly process is.
How much does a 3D printer cost?
3D printing is a one-stop solution for a wide range of applications, from high-resolution model production to rapid prototyping, rapid tooling for traditional manufacturing processes, production of aids and end-use models.
However, when you consider investing in a 3D printer, the viability of a solution usually boils down to a simple question: Is it cost-effective for your business? How much does a 3D printer cost and how much time and money can it save your business? nine0003
3D printer prices range from $200 to $500,000 depending on the printing process, materials, and complexity of the solution.
In this guide, we'll break down 3D printing costs by technology, compare outsourcing versus in-house manufacturing, list factors to consider when calculating the cost of each model, and look at what else to look for when comparing different solutions. for 3D printing and other production methods. nine0003
Interactive
This interactive ROI tool will help you find out how much time and money you can save by 3D printing with a Formlabs 3D printer.
Calculate Your Costs
The three most well-known plastic 3D printing technologies today are Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).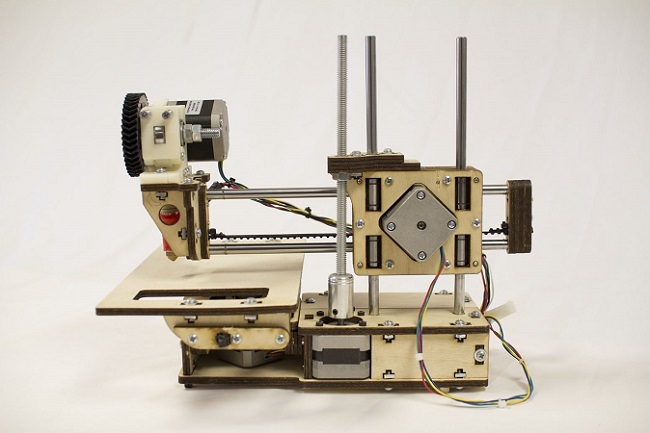
Each technology has its advantages and disadvantages - take a look at the infographic:
Download this high resolution infographic here. Interested in learning more about FDM, SLA and SLS 3D printing technologies? Check out our detailed guide.
Prices for 3D printers have dropped significantly in recent years, and today all three technologies are available in compact, low cost systems.
FDM generally produces models at a lower cost if you only print relatively simple prototypes in limited numbers. SLA technology offers higher resolution and quality, as well as a wide choice of 3D printing materials at a slightly higher price. But this difference is quickly offset when you print complex designs or larger batches due to the less labor-intensive post-processing process. Finally, SLS technology is the most cost effective for medium to high volume production of high quality functional models. nine0003
Comparing the total cost of different 3D printers by price tags alone will not give you a complete picture of how the cost of a 3D printer and a printed model will compare. The cost of 3D printing materials and labor significantly affects the cost of a model, depending on the application and your production needs.
The cost of 3D printing materials and labor significantly affects the cost of a model, depending on the application and your production needs.
Let's look at the different factors and costs for each process.
FDM, also known as Fused Filament Manufacturing (FFF), is a printing method where the parts of a model are made by melting and extruding a thermoplastic filament, which the printer's nozzle applies layer by layer onto the model being made. nine0003
FDM is the most popular form of consumer grade 3D printing, fueled by the proliferation of hobbyist 3D printers. However, professional and industrial FDM printers are also popular among professionals.
The cheapest 3D printers are FDM printers. DIY kits for FDM 3D printers start at $200. However, most of these models are more like toys or DIY projects that take a significant amount of time to build, set up and calibrate. The quality of the print largely depends on the success of these operations. In addition, machines require repairs and regular maintenance to keep them working, so they are more suitable for people with a higher engineering education who have a lot of time and patience. nine0003
nine0003
Hobbyist FDM 3D printers cost between $500 and $1,500, come pre-assembled or unassembled, require less setup, but have the same disadvantages as the cheapest 3D printers. More expensive models are capable of large print volumes and work with a wide variety of materials besides low temperature ones such as PLA.
Professional 3D FDM printers start at $2,500 and large format professional FDM printers are available from $4,000. The cost of the most modern industrial FDM printers can exceed 10,000 US dollars. Most of these printers come pre-assembled and calibrated in the box, or they can be automatically calibrated. Printers in this category offer better print quality, a wider range of media, higher print volumes, improved reliability, and ease of use and maintenance. In addition, professional 3D printer manufacturers offer customer support services for troubleshooting. nine0003
Material costs for FDM 3D printing range from $50 to $150/kg for most standard and engineering filaments, and $100 to $200/kg for auxiliary materials. There are also cheaper alternatives, but they are of lower quality.
There are also cheaper alternatives, but they are of lower quality.
In addition, FDM printing can be very labor intensive. Successful printing of complex models requires support structures that must be removed manually or dissolved in water. To obtain a high quality surface and remove layer lines, lengthy manual post-processing of models, such as sanding, is necessary. nine0003
SLA 3D printers use the process of photopolymerization, that is, the conversion of liquid polymers into hardened plastic using a laser. SLA is one of the most popular processes among professionals due to its high resolution, accuracy and material versatility.
Models printed on SLA printers have the highest precision, sharpest detail and smoothest surface possible of any plastic 3D printing technology. But the main advantage of the SLA method is its versatility. SLA polymers have a wide range of optical, mechanical and thermal properties that match those of standard, engineering and industrial thermoplastics. nine0003
nine0003
SLA 3D printers can handle a wide range of resin materials for a wide variety of applications.
SLA used to be used only in large and complex industrial 3D printers costing over $200,000, but the process is now much more affordable. With the Formlabs Form 3+ Printer, businesses can now use industrial quality SLA printing for as little as $3,750. With Form 3L, large format SLA printing starts at just $11,000. nine0003
Stereolithographic 3D printers will be shipped in a box assembled and calibrated. These are professional tools that are highly reliable and require virtually no maintenance. Technical support is also always available. It provides troubleshooting in a critical situation (but its probability is extremely small).
Most standard and engineered polymers for SLA technology cost between $149 and $200 per liter. nine0003
SLA printers are easy to use and many workflow steps such as rinsing and final curing can be automated to reduce labor costs. Printed models have a high quality surface immediately after printing and require only simple post-processing to remove supporting structures.
Printed models have a high quality surface immediately after printing and require only simple post-processing to remove supporting structures.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printers use a high power laser to sinter fine polymer powder particles. The unsprayed powder supports the model during printing and eliminates the need for special support structures. This makes SLS ideal for complex geometries, including internal features, grooves, thin walls, and negative taper. nine0003
Models produced using SLS printing have excellent mechanical characteristics - their strength can be compared with the strength of injection molded parts. As a result, SLS technology is the most popular plastic 3D printing process for industrial applications.
SLS printed nylon models are ideal for a range of functional applications, from consumer product design to healthcare applications.
Like SLA, SLS was previously only available in large format, complex 3D printing systems costing $200,000 or more. With the Formlabs Fuse 1 stereolithography printer, businesses can now solve industrial-scale tasks with SLS technology starting at $18,500. The complete kit, which includes the post-processing and powder recovery system, costs $31,845.
With the Formlabs Fuse 1 stereolithography printer, businesses can now solve industrial-scale tasks with SLS technology starting at $18,500. The complete kit, which includes the post-processing and powder recovery system, costs $31,845.
As with SLA printers, stereolithographic printers are shipped assembled and calibrated in the box. They are reliable and can operate 24/7. The package includes in-depth training and fast technical support. nine0003
SLS nylon print materials cost about US$100/kg. SLS does not require supporting structures and unused powder can be reused, reducing material costs.
SLS is the least labor-intensive plastic 3D printing process in the production environment, because the printed models are of high quality right away, and to remove excess powder, they simply need to be cleaned.
There are several processes for 3D printing not only plastics but also metals. nine0003
Metal FDM printers are similar in design to traditional FDM printers, but use extruded metal rods held together by a resin binder. The finished parts of the model are sintered in an oven to remove the binder.
The finished parts of the model are sintered in an oven to remove the binder.
SLM and DMLS printers are similar to SLS printers, but instead of polymer powders, they fuse metal powder particles layer by layer using a laser. SLM and DMLS-based 3D printers create strong, precise, and complex metal products, making the process ideal for the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. nine0003
Prices for metal 3D printers have also begun to decline, ranging from $100,000 to $1 million today. However, these systems are still out of reach for most businesses.
SLA 3D printing is available as an alternative for casting workflows that allow metal models to be produced cheaper and faster than traditional methods and provide greater design freedom.
Technical report
Get design guides for 3D printing samples, see the step-by-step direct investment casting process, and study guides for indirect investment casting and sand casting.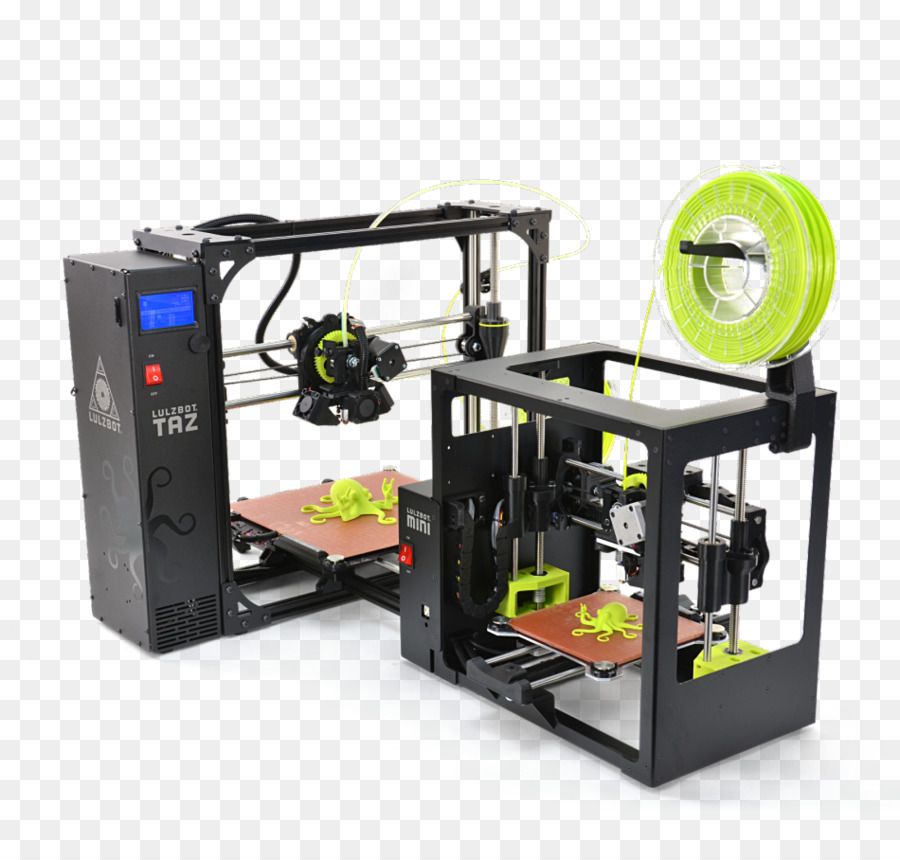
Download white paper
Different plastic and metal 3D printing processes have unique qualities that make them suitable for different applications. Below is a comparison of different printing technologies.
| Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) | Stereolithography (SLA) | Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | Metal FDM Printing | Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Direct Metal Sintering (19008) 9008 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permission | ★☆ | ★ opa ★ ution | ★ opa | ★cle | ★cle ★ MyQUTION | SUMPLE | 1112 HICE | ★ opa ☆ | 1111111 ☆☆☆ | 1 ☆ | ★ opa |
| Ease of use | x 300 x 600 mm (Desktop and Workshop 3D printers) | Up to ~300 x 335 x 200 mm (Desktop and Workshop 3D printers) | Up to 165 x 165 x 300 mm (3D - workshop printers) | Up to 300 x 200 x 200 mm | Up to 400 x 400 x 400 mm |
| Price range | DIY kits for 3D printers start at $200 and hobby printers cost $500-1500. Professional 3D FDM printers start at $2,500, while large format professional FDM printers are available from $4,000. Professional 3D FDM printers start at $2,500, while large format professional FDM printers are available from $4,000. | Professional desktop printers start at $3,750 and high-volume large format desktop printers are available from $11,000. nine0112 | Workshop industrial printers start at $18,500 and traditional industrial printers start at $100,000. | Metal FDM printers start at $100,000, but complete solutions including an oven are much more expensive. | DMLS/SLM solutions start at around $200,000. These printers require special infrastructure conditions, which can further increase costs. |
| Cost of materials | US$50-150/kg for most standard and engineering yarns and US$100-200/kg for auxiliary materials. | US$50-150/L for most standard and engineering polymers. | US$100/kg for nylon. SLS does not require supporting structures and unused powder can be reused, reducing material costs. | Depends on material and technology. Significantly higher than plastic. Significantly higher than plastic. | Depends on material and technology. Significantly higher than plastic. nine0112 |
| Labor | Manual removal of support structures (soluble support structures may be used in some cases). Long post-processing is required to obtain a high quality surface. | Washing and final polymerization (both can be automated). Simple post-processing to remove supporting structures. | Easy cleaning to remove excess powder. | Washing and sintering (both can be automated). It is possible to use mechanical processing and other types of surface treatment. nine0112 | Stress relief, support structure removal, heat treatment, and mechanical and other surface treatments. |
| Materials | Standard thermoplastics such as ABS, PLA and their various blends. | Various polymers (thermosetting plastics). Standard, engineering (similar to ABS and PP, similar to silicone, flexible, heat resistant, rigid), injection molding, dental and medical (biocompatible). nine0112 nine0112 | Engineering thermoplastics - typically nylon and its composites (nylon 12 biocompatible + sterilizable). | Stainless steel, tool steel, inconel, copper, titanium. | Stainless steel, tool steel, titanium, cobalt-chromium, copper, aluminium, nickel alloys. |
| Applications | Basic experimental models, low cost rapid prototyping of simple parts. | Prototypes with a high level of detail requiring close tolerances and smooth surfaces: molds, tooling, templates, medical models and functional parts. nine0112 | Complex geometries, functional prototypes, low volume production or limited trial production. | Strong and durable models, tools and production aids. | Strong and durable models with complex geometries; ideal for the aerospace, automotive and medical industries. |
When calculating the cost of one model, the cost of ownership of equipment, material costs and labor costs are usually taken into account..jpg) It is important to understand the factors that affect each of these cost components, as well as the questions to ask in order to evaluate alternative production methods and uncover hidden costs. nine0003
It is important to understand the factors that affect each of these cost components, as well as the questions to ask in order to evaluate alternative production methods and uncover hidden costs. nine0003
Hardware ownership costs are fixed costs: 3D printer price, service contracts, installation and maintenance. These amounts must be paid whether your printer is idle or produces dozens of models per week.
Add up all projected fixed costs over the lifetime of the equipment, then divide by the number of models you plan to make. As a rule, the higher the performance and efficiency of your 3D printer, the lower the cost of ownership of equipment per model. nine0003
In recent years, desktop 3D printers have shown excellent results in reducing the cost of ownership of equipment. With a price 10 to 100 times lower than traditional industrial 3D printers and the ability to produce thousands of models over a lifetime, the cost of ownership can be negligible.
Questions:
-
Are there installation, training or additional initial costs other than the cost of the machine itself? nine0003
-
Do I need to sign a (mandatory) service contract? What does it include?
-
What accessories and tools are needed to make the final models?
-
What kind of maintenance is required for the machine to function properly? What is the expected annual maintenance cost? Will it change with an increase in production volumes?
The 3D printing raw materials and consumables you need to create models at an affordable price. These costs largely depend on the number of models you produce. nine0003
These costs largely depend on the number of models you produce. nine0003
When calculating the cost of materials, determine how much material is required to create one model, and multiply this figure by the cost of the material. Count the amount of waste and any other consumables. As production grows, the cost of ownership of equipment decreases, and the cost of 3D printing materials tends to become more balanced.
Be sure to check what materials you need to create specific models, as the cost of 3D printing consumables can vary greatly. Please note that some 3D printers only work with their proprietary materials and thus limit your ability to use third party materials. nine0003
Questions:
-
What is the cost of each type of 3D printing material?
-
How much material is required to create one particular model, including waste?
-
What is the shelf life of the materials?
-
Do I need other consumables to create models?
-
Can the machine work with third-party materials?
While 3D printing can replace complex traditional manufacturing methods and provide significant time savings, depending on the 3D printing technology, it can still be quite labor intensive. nine0003
nine0003
Professional desktop 3D printers are generally optimized for ease of use. DIY kits for 3D printers and hobby printers often require additional effort to adjust settings, while regular maintenance or material changes on traditional industrial machines can involve time-consuming tasks that require the assistance of a skilled operator.
Post-processing workflows vary depending on the 3D printing process, but in most cases involve cleaning models and removing support structures or excess material. However, there are solutions to automate some specific tasks. For example, Formlabs Form Wash and Form Cure simplify the wash and finish process for Formlabs SLA 3D printers, while Fuse Sift offers a turnkey post-processing and powder recovery system for the Fuse 1 SLS printer. nine0003
More complex processes such as SLA and SLS do not take long to achieve high quality models, while FDM models require lengthy manual post-processing to improve quality and remove layer lines.
Questions:
-
What is the whole model production workflow? What specific steps are required to set up printing, change materials, and post-process models?
nine0298 -
How long does it take to post-process one specific model?
-
Are there any tools or devices available to automate some of these tasks?
Outsource production orders to 3rd party service bureaus or labs when you use 3D printing only occasionally or to produce large models in non-standard materials. Typically, the bureau has several in-house 3D printing processes such as SLA, SLS, FDM, as well as metal 3D printers. They can also provide advice on a variety of materials and offer additional services such as design or improved finishes. nine0003
The main disadvantages of outsourcing are the high cost and duration of production. One of the main advantages of 3D printing is its speed compared to traditional production methods. But it is noticeably reduced if the delivery of the model produced by the involved organization takes several days or even weeks.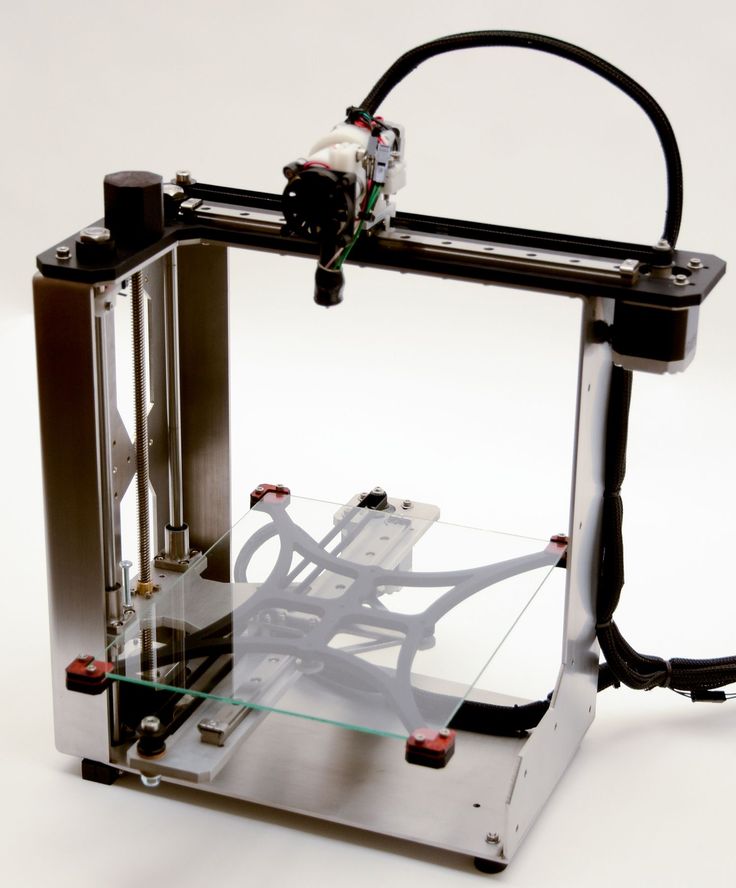 And as demand and capacity grow, the costs of outsourcing are rising rapidly.
And as demand and capacity grow, the costs of outsourcing are rising rapidly.
Desktop 3D printers are the perfect solution for fast model production. Depending on the number of parts needed and the volume of prints, the investment in a professional 3D printer can pay for itself in just a few months. nine0003
With desktop and workshop printers, you can pay for the capacity that matches your business needs and scale your production by adding more devices as demand grows, without the heavy investment of a large format 3D printer. Using multiple 3D printers also allows you to print models from different materials at the same time. But if there is a need for the production of large parts or the use of non-standard materials, service bureaus can come to the rescue. nine0003
Investment, material and labor costs are relatively easy to calculate. But what about indirect costs and hard-to-calculate factors that affect your business? Let's look at some of the main considerations when comparing a desktop 3D printer to outsourcing or other manufacturing methods.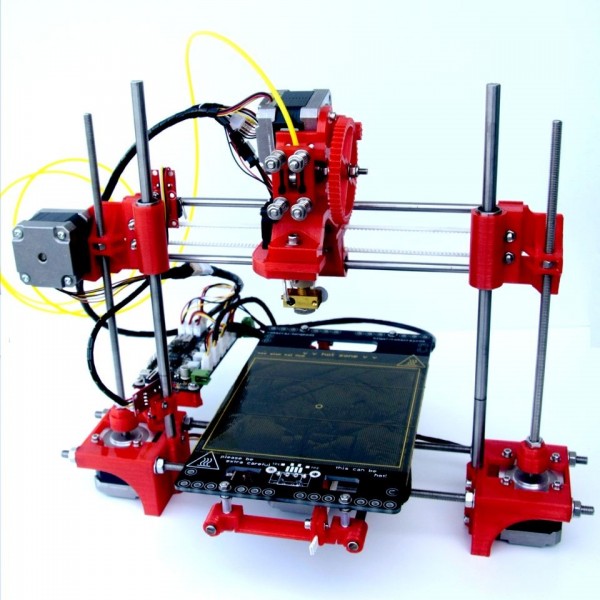
Save time: What if you could get products to market a few months faster? Or reduce the delivery time of your products by a few days or weeks? 3D printing simplifies traditional prototyping and manufacturing workflows, helping you save time and stay ahead of the competition. nine0003
Top results: 3D printing allows you to create more iterations, overcome failures faster, and produce better end products. Troubleshooting a design early on also helps avoid costly redesign and the use of additional tools.
Interaction: Having high-quality prototypes and models allows you to communicate more effectively with customers, clients, suppliers and other stakeholders. Avoid misunderstandings and costly mistakes. nine0003
Intellectual Property Protection: Do you work with confidential information? Making your own models means you don't have to transfer intellectual property (IP) to third parties, reducing the risk of IP leakage or theft.
Usually, calculating cost per part, lead time, and comparing alternatives to see if a solution is right for your business is a tedious task of creating a complex spreadsheet in an attempt to collect all of the often hidden information from a manufacturer. nine0003
Use our simple online tool to calculate cost per model and order lead time when printing with a Formlabs stereolithographic 3D printer and compare time and cost savings with other manufacturing methods.
Calculate the cost and time
The most expensive 3D printers in the world
- home
- News AT nine0298
- World
- The most expensive 3D printers in the world
Various technologies do not stand still, they are constantly developing. This article proposes to consider the evolution of industrial 3D printers today, which are the most expensive in the world and why.
3D printers are unique in terms of the variety of different 3D printing methods, materials used and their applications. You can spend as little as $100 to get a reliable 3D printer to make a huge variety of parts from affordable plastic material. On the other hand, you can spend over a million dollars to buy a 3D printer to 3D print parts with large and complex construction geometries. They can be used in the aerospace industry, the production of space satellites or miniature biocompatible devices for medical purposes. The most expensive 3D printers on the market today use 1 to 12 powerful lasers to fuse metal powder, sinter polymer materials, or polymerize resin, and 3D printing from a given 3D model occurs by applying the powder layer by layer, which is a process additive manufacturing. nine0003
It can be noted that the size of the 3D printer does not determine how expensive the 3D printer will be. Today, the price often depends on advanced patented technologies and features that allow a 3D printer to produce fast and high-quality 3D-printed parts without requiring special technical knowledge from the operator.
Some of the most expensive printers are not even for sale. Carbon 3D's 3D printers are available for rent only, which allows them to be used by many users. Others use their 3D printers on a project-by-project basis, such as the Vulcan construction printer from homebuilder Icon 3. nine0003
Stargate, the world's largest metal 3D printer built by Relativity Space to 3D print rockets, it's not for sale, but if it was, it would definitely be on our list. Many of the most exciting technologies in 3D printing can only be used for custom 3D printing, not for purchase. (Source: Relativity Space)
Let's look at the criteria that affect the cost of a modern industrial 3D printer.
Features 3 D -Printers affecting their price:
- The uniqueness of the technology when creating
- How automated the processes in 3D appintering
software
- Numerous controls and adjustments
- Controlled environment inside the working chamber (use of inert gas, the possibility of heating/cooling the working platform)
Breaking down these features:
Features that drive up the price of 3D printers include software tuned to a specific printer technology, real-time 3D printing control systems, and anything that automates processes that sometimes are performed manually in cheaper systems (layer leveling, subsequent post-processing or powder sieving) or processes that require knowledge of metallurgy or polymers.
Production technology requiring a vacuum chamber in a 3D printer, filling the working chamber with an inert gas, or printers that are certified for use in clean rooms and having these characteristics are significantly reflected in the final price of this equipment.
The materials used in the 3D printing process also have a significant impact on the final cost of a 3D printer. Many 3D printers only work with proprietary materials that have been developed by the manufacturer for that 3D printer. They can be metal powder, special resins filled with carbon fiber particles, and unique polymer powders. At this point in time, it is possible to 3D print anything from pure gold to advanced engineering plastics on 3D printers, even in the harsh environment of space. nine0003
There are 3D printers that can 3D print multiple materials in one job, and there are multi-color 3D printers that are also in the higher price segment.
THE MOST EXPENSIVE 3 D -PRINTERS
The 3D printer manufacturers discussed below are reluctant to publish exact prices for their products. This is due not only to competition, but also to the fact that 3D printers have a basic package, as well as a package with additional options according to customer requirements. That said, with that in mind, below is a look at some of the most expensive 3D printers available today - all costing over half a million US dollars - and what they provide. nine0003
This is due not only to competition, but also to the fact that 3D printers have a basic package, as well as a package with additional options according to customer requirements. That said, with that in mind, below is a look at some of the most expensive 3D printers available today - all costing over half a million US dollars - and what they provide. nine0003
E-PLUS3D EP-M450H
3D printer EP-M450H LPBF (Source: E-Plus 3D)
Chinese company E-Plus3D produces industrial metal 3D printers with a large construction of construction for additive manufacturing for various industries in the country. These 3D printers are used in the aerospace, automotive, electronics, and engineering industries to produce not only large-sized parts such as heavy-duty molds, but also mass-produced parts. nine0003
The EP-M450H Metal 3D Printer is the company's largest 3D printer with a build chamber of 456 x 456 x 1080 mm, producing 99. 9% density metal parts from a wide range of materials at a speed of 55 cm³ per hour.
9% density metal parts from a wide range of materials at a speed of 55 cm³ per hour.
XJet Carmel 1400C
Israeli company XJet has developed a unique ceramic 3D printing technology. NanoParticle Jetting (NPJ) technology allows the production of metal and ceramic parts with a high level of detail, smooth surface roughness and geometric accuracy. The high cost of this 3D printer is not only due to the technology itself, patented materials that make this printer a serious investment, but also to the advanced automation of the 3D printer itself, which makes it easy to use. nine0003
Carmel 1400C, equipped with one of the largest 1,400 cm² work platform in the industry, which allows the production of several ceramic parts at the same time.
SLM Solutions NXG Xll 600
NXG XII 600 Large Metal 3D Printer (Source: SLM Solutions) range of printers, but its NXG Xll 600 is what the company says is a revolution in industrial additive manufacturing. The NXG XII 600 was designed for high-volume additive manufacturing and features the industry's first 12 1,000W lasers with a 600x600x600 build chamber. Lasers provide high build speed up to 1000 cm 3 /h and capacity not available for other machines.
The NXG XII 600 was designed for high-volume additive manufacturing and features the industry's first 12 1,000W lasers with a 600x600x600 build chamber. Lasers provide high build speed up to 1000 cm 3 /h and capacity not available for other machines.
In addition to lasers, the NXG Xll 600 has all the benefits that SLM Solutions customers have been asking for over the years, including automatic start-up, laser focusing, closed powder feeding and material screening, and other latest developments.
UpNano NanoOne Bio
The Austrian company UpNano has developed a two-photon 3D printer using hydrogel-based bio-ink, which allows direct printing of 3D structures containing living cells, both at the meso- and microscale. The NanoOne Bio printer is based on the NanoOne line of laser printers capable of creating structures of 12 orders. The new hydrogel is the only commercially available resin that allows live cells to be embedded directly from culture plates into 3D printed structures for biological applications. nine0003
nine0003
UpNano claims that the combination of X Hydrobio INX U200 and NanoOne Bio opens up new possibilities in biomedical research and development, both in industry and academia, allowing pharmaceutical companies and research institutes to create cell models that mimic natural growth conditions in the body person.
Black Buffalo 3D
Black Buffalo's new 1G construction printer (Source: Black Buffalo)
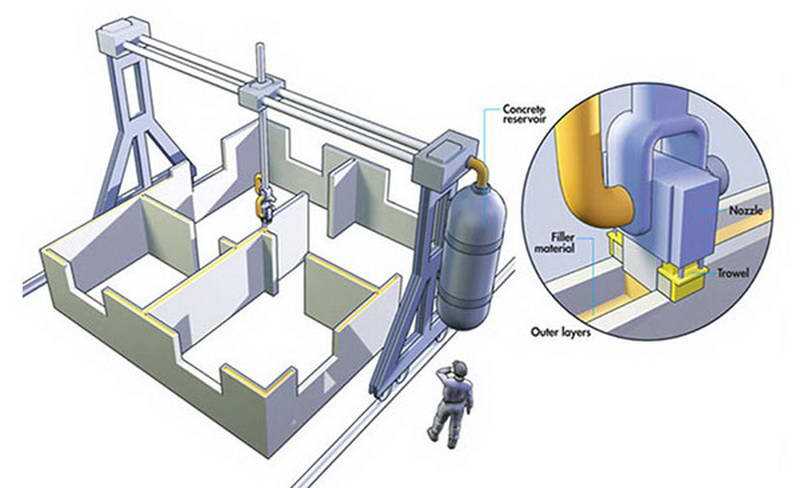
Black Buffalo 3D, an American company based in South Korea, officially unveiled its Nexcon 1G earlier this year, which is a 3D printer for building houses and other large concrete objects. The printer can create a 92.9 square meter structure in less than 20 hours. It uses Black Buffalo's patented cementitious material, the company calls it ink, that can be dyed to a chosen color and is also customizable to 3D print locally according to the temperature, humidity and altitude conditions of the area. nine0003
The Nexcon 1G is a modular 3D construction printer that can be extended along the X, Y and Z axes to scale up (or down) a project up to three stories high. The 1G printer is unique in that users can reposition the base rails and move the printer to a new printable area without having to remove the X or Z axis.
The 1G printer is unique in that users can reposition the base rails and move the printer to a new printable area without having to remove the X or Z axis.
Optomec LENS 860
Energy Deposition (DED), which allows the recovery of large titanium components, such as those used in aircraft engines. Optomec offers several models of 3D printers that have large build chambers like 860x600x610 and laser power of 3 kW. nine0003
The LENS 860 machining systems are ideal for the fabrication, repair or coating of medium to large metal parts.
ExOne S-Max Pro
While many ExOne printers (now owned by Desktop Metal) are still very affordable given that high volume 3D printers can cost quite a few zeros.
3D printers are used to 3D print complex and detailed sand molds and cores for foundries producing large metal parts for industrial use. The S-Max Pro features a 1,260 liter build chamber for fast 3D printing of sand molds and cores. A new automated print head enables fast 3D printing, while improved sand compaction ensures the density and strength of complex sand mold designs.