3D printing graphic design
Uses of 3D printing in graphic design and visual communication -
3D printing involves making things – 3 dimensional objects – which is generally not what most people think graphic designers do. However, graphic designers have actually been designing 3D objects since the early days of visual communication – from books and brochures through to signs, packaging, merchandise, folders, cards and advertising hoardings. The question is, will 3D printing have a role to play in visual communication? Will it change the solutions we design, or the way we design them?
Collaboration across design disciplines
Most current applications of 3D printing involve making parts or prototypes for everything from consumer products to medical prosthetics, architecture and machinery. Forbes’ article The State of 3D Printing, 2018 quotes research by Sculpteo that says the most popular applications of 3D printing are prototyping, production and proof of concept models. Graphic designers often work with product designers, architects and business clients, so to collaborate effectively they need to keep up with industry developments in 3D printing and related technologies.
3D topographic maps
Topographic model of Wilpena Pound, South Australia Topography and Bathymetry of New Zealand Topgraphic model of Yosemite National Park, USAThe examples above are from Thingiverse, which has thousands of 3D designs uploaded by users. The topographic map of Yosemite was generated via the handy Terrain2STL tool.
Information design and data visualisation
Complex data means nothing unless you can understand it! ‘Big data’ can sometimes be made more understandable using 3D modelling. The article How 3-D Printing is Revolutionizing the Display of Big Data explains how a translucent 3D-printed model is combined with coloured lights to enhance meaning and convey information.
3D printed model to explain a maths concept 3D flight map graphic 3D campus model with lighting
Typography
Complete typefaces are being developed for 3D, just as they are for print and screen use.
Business cards
Packaging
3D printing can be used to create prototype or small run packaging designs, and enables more complex shapes than some alternative methods.
Packaging prototypes Packaging prototypes Packaging productionThe above examples are just a few of the areas of visual communication where 3D printing is being used. Some other areas include signage, branding and education. As the technology develops, 3D printing is likely to be used in ways we can’t yet anticipate, especially if it reaches widespread use in the home and a wider range of materials (particularly eco-friendly materials) are available for everyday use.
<< back to Enhanced Design Tools index
How to Design for 3D Printing
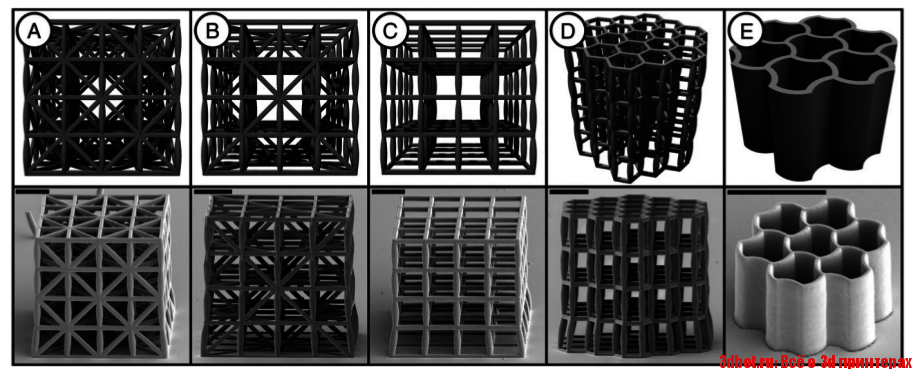
3D Printing is a revolutionary new technology that allows you to realize, well, just about anything. The most common form of 3D printers use a special form of plastic filament to print durable, hard ABS plastic components or items.
The most common form of 3D printers use a special form of plastic filament to print durable, hard ABS plastic components or items.
However, there are 3D printers—industrial mostly—that can work with materials like concrete, glass, titanium, steel and more. The tougher materials aren’t really necessary for design, but it’s still a great thing to know especially when you need to consider material design guidelines.
In design and graphic art, you mostly work with hand sketches, digital content and imaging software, and flat, 2D-style designs. How would a 3D printer offer you anything new? Maybe you dabble in the occasional 3D modeling from time to time, or maybe you don’t. Whatever the case, the two mediums just don’t seem to correlate.
We’re going to explain some design tips you should be aware of and how that applies to your particular industry: graphic and visual design.
Major Brands Are Already Using 3D Printing for Design
A variety of large corporations and organizations have not only realized the potential of 3D printing technology — they’ve implemented it in their regular routines.
Nike, Nokia, Ittala, Coca-Cola and even Volkswagen have all been creating and designing with 3D printing tools. Nike even took their 3D printed concepts and rolled them into manufactured products, some of which you can buy on store shelves right now.
If the bigger companies and organizations are starting to adopt and utilize this technology, that will soon trickle down to smaller companies
The reason they’ve taken to this technology is because it streamlines their design and manufacturing processes. All product designs or prototypes can be constructed in-house, and then when it’s time to ship something, they can be manufactured internally as well.
This doesn’t relate to graphic design, but it does point out one obvious thing. If the bigger companies and organizations are starting to adopt and utilize this technology, that will soon trickle down to smaller companies, including you.
More companies will desire 3D printing compatible concepts and visuals, which means turning to professionals who can work with the necessary tools and software. If you haven’t already begun training with these technologies and tools, now is the ideal time.
If you haven’t already begun training with these technologies and tools, now is the ideal time.
Learn Printing Technologies
Before diving into the design process, you need to spend some time researching and getting to know the various 3D printing technologies and hardware you’ll be working with. Why? Because depending on the materials and the printer used, you’ll need to work with unique specifications.
ABS, alumide, polyamide, and rubber-like materials all allow you to create components and designs that incorporate interlocking parts. That is, you can build snap-together components that are incredibly easy to assemble. Unfortunately, this is not possible with materials like bronze, gold, silver and resin, but it’s not the consistency of the materials or even textures to blame. It’s really the hardware and 3D printers used during these processes. The latter materials aren’t compatible with the types of printers that can create interlocking parts.
In addition, the way in which these printers create components also differs depending on the material. Be sure to do the research so that you understand how they are all different and how this will influence your design.
Be sure to do the research so that you understand how they are all different and how this will influence your design.
Mind the Wall Thickness
When working with traditional 2D-based designs, dimensions are important, but you don’t necessarily have to worry about the thickness of your models. You can use specifications and number measurements to indicate true size, but you don’t actually have to design to scale — at least in many cases.
That’s not so with 3D printing, as you’ll always want to mind the wall thickness of the items you’re creating. Walls that are too thick can generate too much internal stress, causing the item itself to collapse or the surfaces to crack. If the walls are too thin, it can make the concept or prototype fragile and easy to break.
Considering you’ll likely be designing and planning the dimensions so that you end up with a durable, reliable product this is one feature you’ll want to brush up on.
File Resolution Is Still Important
With 3D printing, the designs are still parsed and transferred via digital files or blueprints, if you will. In graphic and visual design, file resolution is extremely important especially when working with larger products or prints.
In graphic and visual design, file resolution is extremely important especially when working with larger products or prints.
If you stretch a smaller resolution file too much, it ends up looking grainy and pixelated. That’s why it’s important you always design in larger environments and dimensions because scaling down is more accurate than scaling back up.
The common file format for 3D printing designs is STL, or standard triangle language format. The design—when printed—is translated into triangles in a wider 3D space, which makes it easier for the printers and related hardware to construct the resulting item.
Similar to visual design, you don’t want the resolution or file size of your blueprint to be too big, or too small. Too big means the internal content will be too much for machines and other designers to handle. Too small means no one will ever be able to get a quality print out of your STL.
The solution is to consider not just the file resolution, but something called “tolerance” in the world of 3D modeling.
3D Printing Is Not So Different
At a glance, it seems as though 3D printing, and designing for the medium, are much different than the current work you do in graphic and visual design. That’s not necessarily the case though, as both forms of design require you to have working knowledge of modern digital software and tools.
Sure, you might use a different tool to design say, an infographic or visual model than you would a 3D STL file, but the concepts and mechanics are similar.
As long as you mind the tips discussed here, you should do just fine. If you haven’t already started learning how to work with 3D modeling and design tools, you might want to get on that as soon as possible.
The market for additive and manufacturing products and services—which will call for reliable designers and visual artists—is predicted to increase by as much as seven times the current rate by 2020. At that time, the market value is expected to surpass $20 billion.
Featured image via Unsplash
Business using a desktop 3D printer, is it real?
Home » Articles » 3D printers, 3D scanners and CNC machines » Business using a desktop 3D printer, is it real?
Business using a desktop 3D printer, is it real?
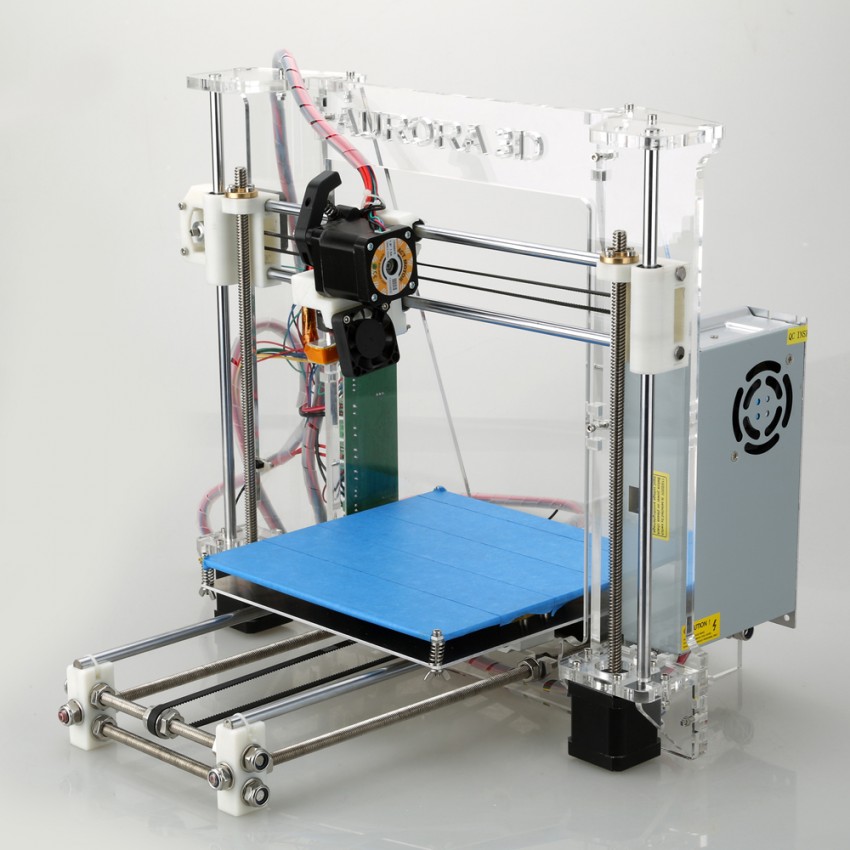
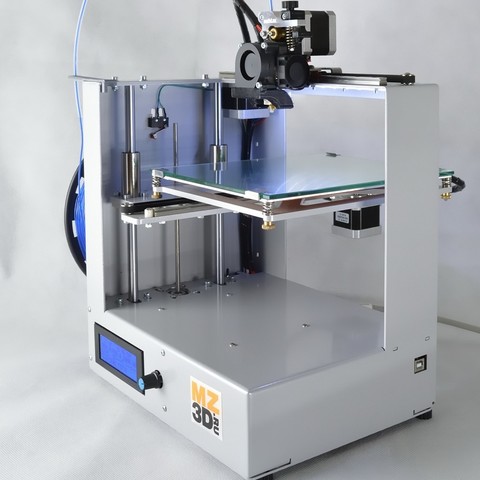
3D printers have firmly entered our lives and have taken their rightful place in it. These units are designed for 3D modeling of various objects: from toys and souvenirs to complex parts and high-precision tools. With their help, you can create a model of any product. This explains their demand and popularity. 3D printers these days are actively used not only for amateur purposes. For businesses, professional additive installations with FDM technology are purchased, which involve the use of various types of materials for 3D printing. And these will not necessarily be bulky expensive devices, the operation of which requires separate laboratories with forced ventilation. Today, even open source desktop 3D printers are equipped with FDM technology. They allow anyone who wants to start their 3D business not just from scratch, but in a constantly changing market.
These units are designed for 3D modeling of various objects: from toys and souvenirs to complex parts and high-precision tools. With their help, you can create a model of any product. This explains their demand and popularity. 3D printers these days are actively used not only for amateur purposes. For businesses, professional additive installations with FDM technology are purchased, which involve the use of various types of materials for 3D printing. And these will not necessarily be bulky expensive devices, the operation of which requires separate laboratories with forced ventilation. Today, even open source desktop 3D printers are equipped with FDM technology. They allow anyone who wants to start their 3D business not just from scratch, but in a constantly changing market.
Risk or not?
Own business is always a certain risk, to a greater extent it is present at the stage of formation. In order not to burn out immediately after launch, you should already have a developed working strategy based on:
- Budget allocated for business development;
- Existing 3D modeling skills;
- Features of a 3D installation that provides business.

If you're only looking to buy a desktop 3D printer for professional use and make money with it, don't be fooled by the low cost. A good thing, a priori, cannot be cheap. Keep in mind, however, that the price of desktop additive rigs has come down significantly in recent times.
Buying a 3D printer will not be your only investment in your own business. As it develops, the need for additional investments will also increase. Therefore, the more powerful and functional the additive installation you bought, the less money will be required to refine the parts performed on it. A high-quality 3D printer will ensure high-quality products, an expansion of the customer base and a rapid increase in orders, which guarantees a quick return on investment.
Business options using a desktop 3D printer
With a desktop 3D printer, you can realize a number of business ideas that will bring not only good income, but also satisfaction from what you do.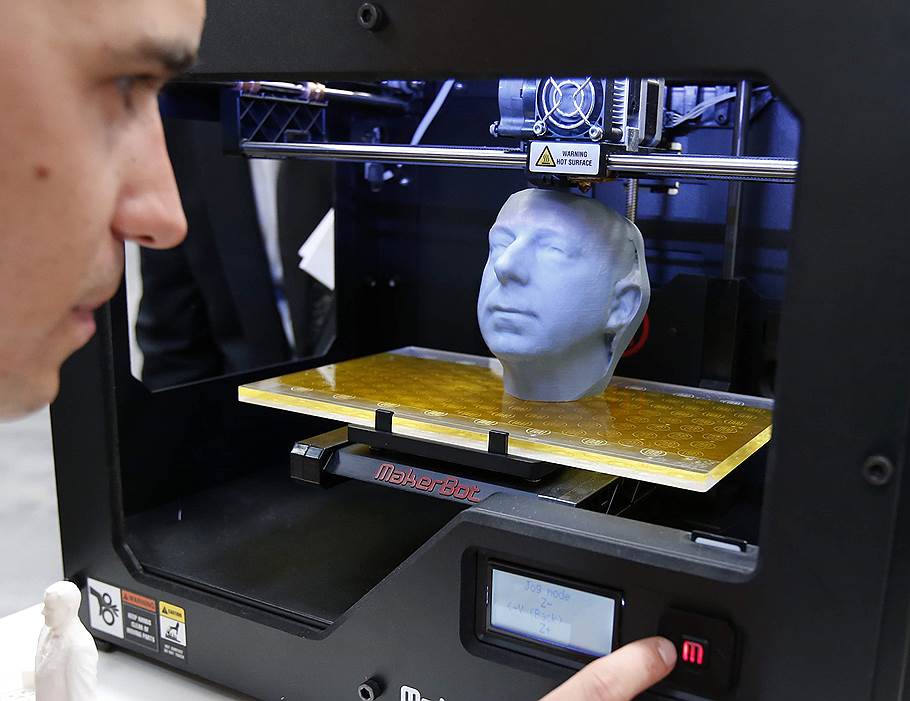 Even a small additive installation will allow you to make unique things. This will be the #1 idea for your business.
Even a small additive installation will allow you to make unique things. This will be the #1 idea for your business.
1. Manufacturing
Making rare and unique gizmos with a 3D printer may well become your additional income. This idea should be used by those who already have their own well-known brand. The additive device will allow you to produce a series of rare products in a limited edition in a unique design and with non-standard design elements. It can be souvenirs, jewelry, accessories, toys, reduced copies of cars, planes, spaceships and much more.
2. Prototyping
Having a desktop 3D printer will allow you to forget about time-consuming manual modeling that takes a lot of effort, money and energy. Using this device, you will produce high-precision three-dimensional models that are in demand in various sectors of the national economy - mechanical engineering, shipbuilding and aircraft building, dentistry and cosmetology, light industry, etc.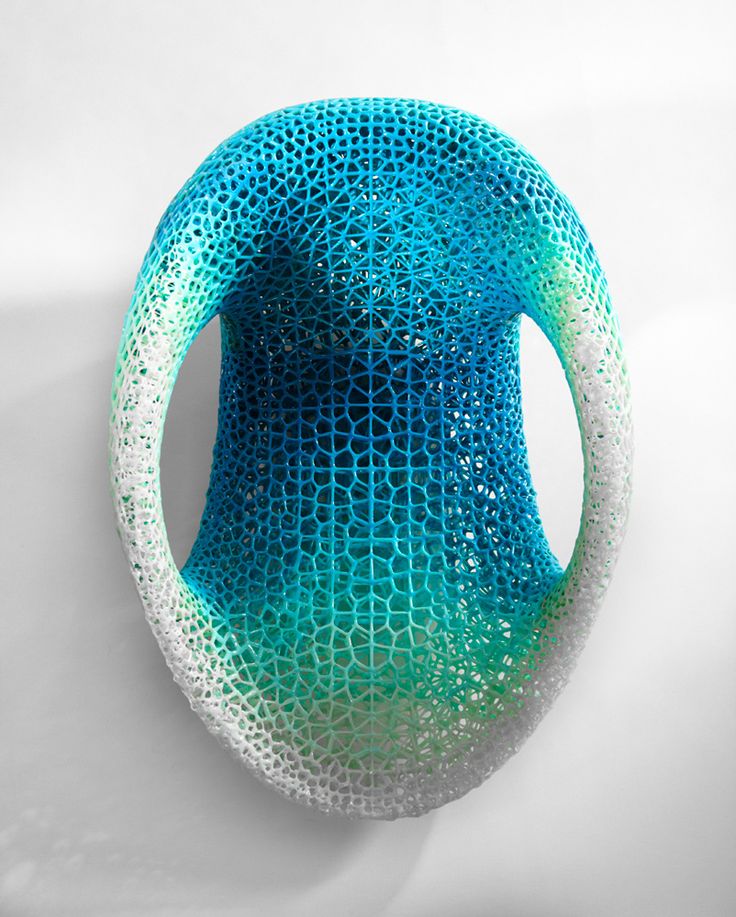 They will be a worthy alternative to plaster and clay models, which are used less and less these days.
They will be a worthy alternative to plaster and clay models, which are used less and less these days.
3. Graphic design
This area of 3D modeling is rapidly developing these days. In order to succeed in it, you need to have good taste, be diligent, painstaking and accurate, as well as have computer skills and basic knowledge in the field of 3D modeling. Graphic design is used to create sketches of 3D layouts and models grown on a 3D printer.
To practice graphic design skills, you can use one of the free programs that are available on the World Wide Web. The software installed on the PC, with the accumulation of experience, knowledge and practical skills, can be improved with the help of additional plug-ins. Not a single 3D printing is complete without graphic design, so this line of business in the field of 3D is guaranteed to become popular and successful.
4. Courses and master classes in 3D modeling
If you are sure that your knowledge and skills are enough to teach the intricacies of three-dimensional modeling to other people, then this line of business is especially for you. You can organize training courses on the basics of 3D or modeling techniques known to you, conduct master classes and trainings, participate in competitions held in this area. This will allow you not only to do your favorite thing at a professional level, while receiving a good income, but also to constantly improve your own level of knowledge, hone your skills, develop and grow to become a true expert in the field of 3D and a leader in your niche.
You can organize training courses on the basics of 3D or modeling techniques known to you, conduct master classes and trainings, participate in competitions held in this area. This will allow you not only to do your favorite thing at a professional level, while receiving a good income, but also to constantly improve your own level of knowledge, hone your skills, develop and grow to become a true expert in the field of 3D and a leader in your niche.
5. Engineering design
This line of business in the field of 3D will be of interest to "techies" who prefer to study three-dimensional modeling "from the inside". It involves the design and creation of new 3D printers and their components, the improvement of existing ones. This niche has not yet been fully occupied, and not only in our country, but throughout the world, so the prospects that will open before you will be simply colossal.
7. 3D printing services
Similar services in major cities of our country are growing like mushrooms after rain. Therefore, if you decide to offer 3D printing services to consumers, be prepared to offer them something new and interesting in order to beat the competition. Fresh ideas in the field of 3D will allow you to stand out among similar companies and attract the interest of the target audience. This will help you become a leader in your niche and regularly make good profits.
Therefore, if you decide to offer 3D printing services to consumers, be prepared to offer them something new and interesting in order to beat the competition. Fresh ideas in the field of 3D will allow you to stand out among similar companies and attract the interest of the target audience. This will help you become a leader in your niche and regularly make good profits.
If high competition does not scare you, and you intend to get into the provision of 3D printing services, be prepared for the fact that this business will require significant investments from you at the initial stage. You will not only have to purchase a high-tech desktop 3D printer, but also a number of additional installations, as well as high-quality materials for growing three-dimensional parts, otherwise you will not achieve success in your business.
8. Software development for 3D printing
Despite the fact that there are a huge number of 3D printing programs on the World Wide Web, both paid and free, new, improved software will never be superfluous. To create it, of course, professional skills and knowledge are needed. If you have them, go ahead. Your startup can bring you a solid income with a minimum investment in its development.
To create it, of course, professional skills and knowledge are needed. If you have them, go ahead. Your startup can bring you a solid income with a minimum investment in its development.
9. Organization of a fab lab
Fab labs are popular among those who are just learning the basics of 3D modeling, but are already showing good skills in this area. In them, novice users can hone their professional skills on the latest high-tech equipment with specialized technical support. To organize a fab lab, you need funds and special permissions.
And in conclusion, I would like to write that a desktop 3D printer can be used to develop your business. It, together with your skills and knowledge, will bring you a stable income and very tangible benefits to consumers.
Directions of 3D graphics - interiors, animation, special effects, game design, 3D printing
Directions of 3D graphics - interiors, animation, special effects, game design, 3D printing game development. Even now, when there are many lessons, video tutorials and books, it will not be so easy for a beginner to understand what's what.
Even now, when there are many lessons, video tutorials and books, it will not be so easy for a beginner to understand what's what. Interior visualization
Let's imagine that you decide to open your own coffee shop, but not just any, but with an individual design so that each chair and light bulb fits into the interior. You can, of course, try to turn on your imagination, or throw something in Photoshop, but, most likely, in the end you will go to the interior visualizer, because. it is better to see the interior that has not yet been realized in 3d, and understand how it will all look and, perhaps, correct something, and remove something.
It is worth noting that now it is gaining momentum VR-visualization of interiors , this is when you can put on virtual reality glasses and almost live look at the interior, which is not there yet. It looks much more spectacular, but it also costs more, because. spend much more time on development.
Photorealism is important in interior visualization .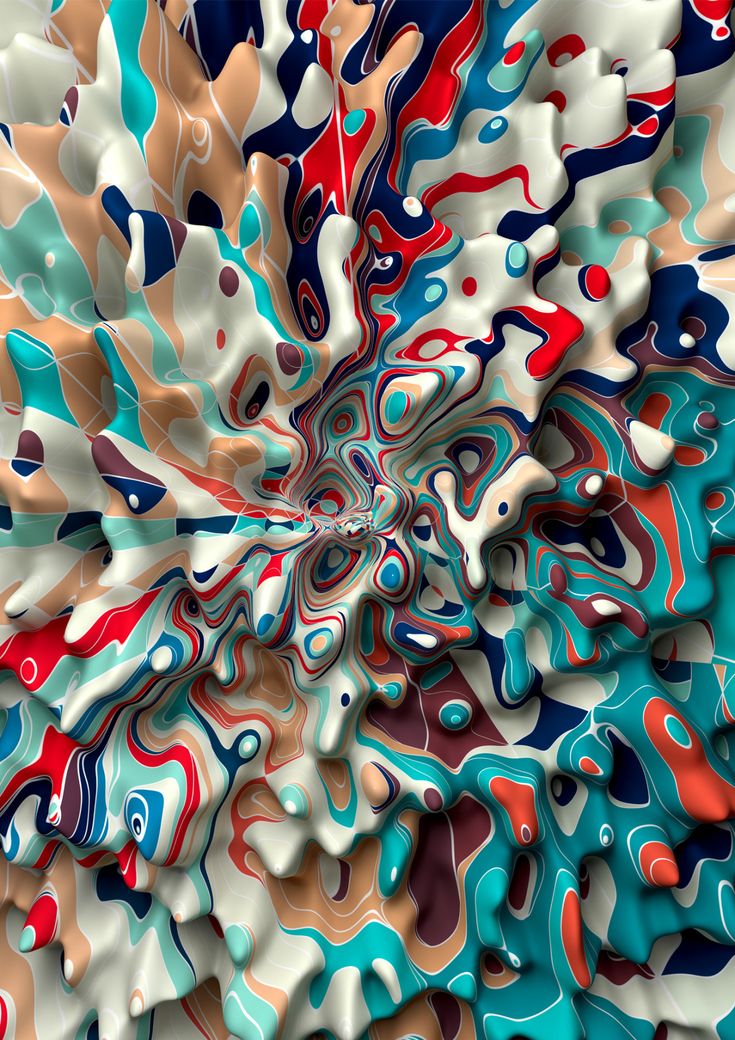 In fact, the models are static, they are not animated, for these purposes a bunch of 3d max + some kind of visualization program, such as VRAY or CORONA, is often used. Lights, textures and effects are modeled in 3D Max, and rendering is already done in the visualization program.
In fact, the models are static, they are not animated, for these purposes a bunch of 3d max + some kind of visualization program, such as VRAY or CORONA, is often used. Lights, textures and effects are modeled in 3D Max, and rendering is already done in the visualization program.
Landscape modeling
Landscape modeling (here, not the interior is visualized, but what is outside). For example, you need to build a residential complex from high-rise buildings and fit the picture into the building site. Before the era of 3D, you had to do everything by hand - create layouts. This labor-intensive method was replaced by 3D modeling. Physical layouts are still being made, but with the help of 3d printing.
In order to create a really beautiful and unusual building, the architect first makes drawings, and the 3d artist creates a three-dimensional visualization. Also, in the future, animation can be performed.
Landscape modelingAnimation
Animation, if desired, in general, can be used in any direction, but most of all, of course, it is used in film production, animated films and games. Animation makes the model come alive.
Animation makes the model come alive.
If you are working with animation, you should already have a model ready, and in order to animate it, you may also need to do skinning, creating muscles and rigging.
Skinning is the process of creating a system of bones, that is, a skeleton, for models of people, animals, insects. The bones allow the 3D character to move. It is the creation of the skeleton that is the first step for normal animation.
Next comes muscle building. Another, simplified geometry is created that mimics the muscles under the skin. After that, the muscles are given their dynamic behavior, for example, they can sway and sway when the character moves, just like muscle mass does in living beings. After creating the muscles comes rigging. Its meaning is not to move each bone separately, but to control additional controls. According to a certain scheme, they control entire groups of bones.
Visual effects
Visual effects are used to create non-existent things.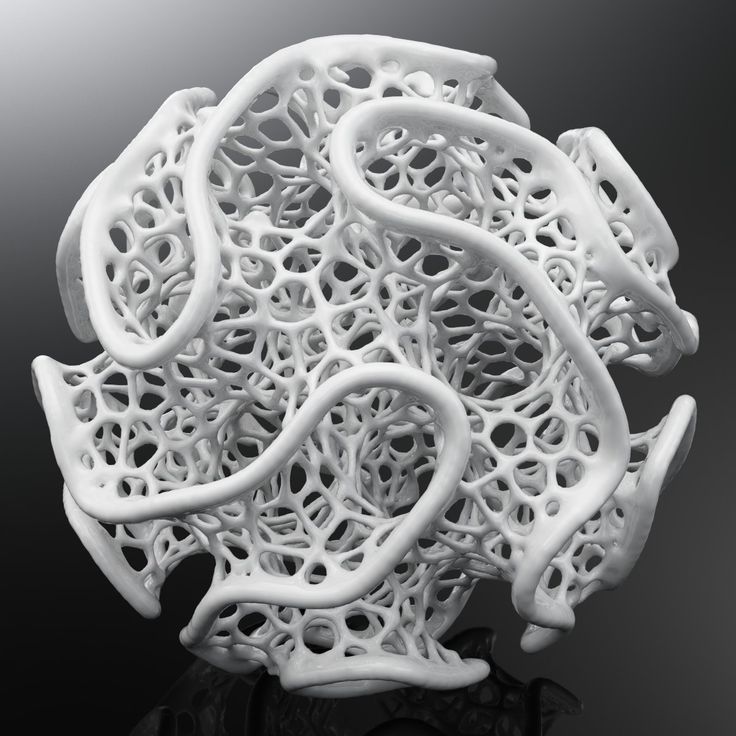 These include matt painting, compositing and particle simulation. Visual effects are used, for example, when you need to finish the rain in post-production, because it makes no sense to wait for rain for several days of shooting. Also, with the help of visual effects, you can, for example, increase the number of soldiers in the frame, because. it is not cost-effective to gather a crowd of thousands of people for several shooting days, but you can shoot a small group that is copied and filled with it all the space.
These include matt painting, compositing and particle simulation. Visual effects are used, for example, when you need to finish the rain in post-production, because it makes no sense to wait for rain for several days of shooting. Also, with the help of visual effects, you can, for example, increase the number of soldiers in the frame, because. it is not cost-effective to gather a crowd of thousands of people for several shooting days, but you can shoot a small group that is copied and filled with it all the space.
Another popular technology that is included in visual effects is motion capture. With its help, it is easier to recreate complex movements by the character. Sensors are fixed on the body of a live actor, after which his movement is transmitted to the program. This technology allows you to achieve greater realism of movements.
Visual effectsGame design (Content design)
Content design is the creation of characters, objects, animation, level design, level landscape.