3D print tpe
TPE filament - learn everything about the TPE material for 3D printing
TPE filament - learn everything about the TPE material for 3D printingTPE material (Thermoplastic Elastomer) is a flexible material. In order to achieve the best possible outcome when 3D printing with TPE material you have to optimize the feed rate. It is recommended to print at a reduced layer height of around 0.1mm to 0.2mm range. As the height is lower, a reduced amount of plastic is required. This enables the extruder to use a reduced feed rate, easing the pressure on the filament.
The best results when printing with TPE will be seen when printing with a slow and consistent speed. As TPE has a high level of elasticity, it can mean that any sudden changes can cause a loss of control in the print speed. Fast print speeds can result in the filament compressing and will lead to a jam. Conluding: slow and steady is the best approach to take when printing TPE.
Specifications for TPE
| Features | |
| Durability | High |
| Strength | High |
| Flexibility | Very high |
| Resistance | |
| Abrasion resistance | High |
| Chemical resistance | Medium high |
| Fatigue resistance | Extremely high |
| Water resistance | Medium |
| Temperatures | |
| Nozzle temperature | 220 - 250 °C |
| Heated bed | up to 60 °C |
See all specs Hide specs
Download the full specsheet
Features of TPE material
Thermoplastic Elastomer has a wide range of features, making it a suitable choice for various applications when it comes to 3D printing.
Fatigue resistant
It is extremely fatigue resistant when it comes to flexing which makes it perfect for those applications where it will be required to flex. Due to its superb electrical properties, it is often found in applications where it is required to prevent electricity conduction such as wiring.
Tear resistant
Capable of heavy use, it is resistant to tear, abrasions and high impact. TPE material is also capable of withstanding temperatures as low as -30 degrees Celsius and as high as 140 degrees Celsius.
For businesses that are looking to enhance the way in which they work and improve the impact on the environment, Thermoplastic Elastomer is a specifically good material as it is recyclable.
Down points of TPE filament
TPE is more difficult to print compared to other filament materials, mainly due to its flexibility.
- ✓ Extremely fatigue resistant
- ✓ Very flexible
- ✓ Good resistances
5 Tips for 3D printing with TPE
Using TPE as a 3D printing material offers a wide range of benefits but there are some issues worth considering before printing with the material. Too much filament can cause a wide range of problems. For example it can result in an increase in pressure on the drive gear, which then causes more filament to feed through. Excessive friction before and after the drive gear can cause problems. So when printing with Thermoplastic Elastomer, it is important to remember that there are some requirements that have to be met in order to obtain a successful outcome.
Too much filament can cause a wide range of problems. For example it can result in an increase in pressure on the drive gear, which then causes more filament to feed through. Excessive friction before and after the drive gear can cause problems. So when printing with Thermoplastic Elastomer, it is important to remember that there are some requirements that have to be met in order to obtain a successful outcome.
-
1. Slow and consistent printing speed
As mentioned, the slower the print speed, the better the result. So, printing at 35 mm/sec or less will deliver better results. It is not required to use a heated build platform. When using a heated build plate, do not set the temperature higher than 60 degrees Celsius because this will negatively influence the adhesion.
-
2. Avoid using rafts and use a negative tolerance
When 3D printing with TPE material, it is important to avoid the use of rafts. Because the base layers of the raft often have an increased extrusion rate and that could lead to potential problems. With regard to 3D prints where the finished product will need to fit on top of another object, a negative tolerance should be used between the parts. This will ensure that the flexible part will have the ability to stretch over the other object in order to fit tightly.
With regard to 3D prints where the finished product will need to fit on top of another object, a negative tolerance should be used between the parts. This will ensure that the flexible part will have the ability to stretch over the other object in order to fit tightly.
-
3. Shorten the distance
If there is a gap between the extruder drive gear and the entry hole of the hot end, then the filament could buckle. If this occurs then the filament will seek another way out. If left unattended, it can cause a so-called bird’s nest or spaghetti, resulting in a jam. To experience the best results the distance between the drive gear and the melt zone of the hot end should not be too long. This ensures that the filament can be fed into the nozzle efficiently. Even more important is that there should also be tight tolerances along the pathway that the filament will travel, in order to prevent kinking and coiling.
When using TPE it is possible to obtain good results by using both Bowden type extruders and direct drive extruders. When switching between materials, it is crucial to purge thoroughly before 3D printing.
When switching between materials, it is crucial to purge thoroughly before 3D printing.
-
4. Placement of the spool
Tweaking the material spool can make a huge difference. Naturally, the extruder will pull the filament into the nozzle, resulting in the filament spool that is mounted on your 3D printer to unwind a small amount of plastic. However, the elasticity of TPE filament will mean that the filament will be stretched out when it is pulled in by the extruder leading to under-extrusion. So, try mounting the spool above the printer so that the filament unwinds downwards which can lead to a reduced level of resistance.
Industries that use TPE material in 3D Printing
TPE filament is flexible. As a result it can be stretched to twice their length when they are at room temperature. Once the material has been stretched, it will return to its original size. For that reason it’s now being used more frequently in the 3D printing process.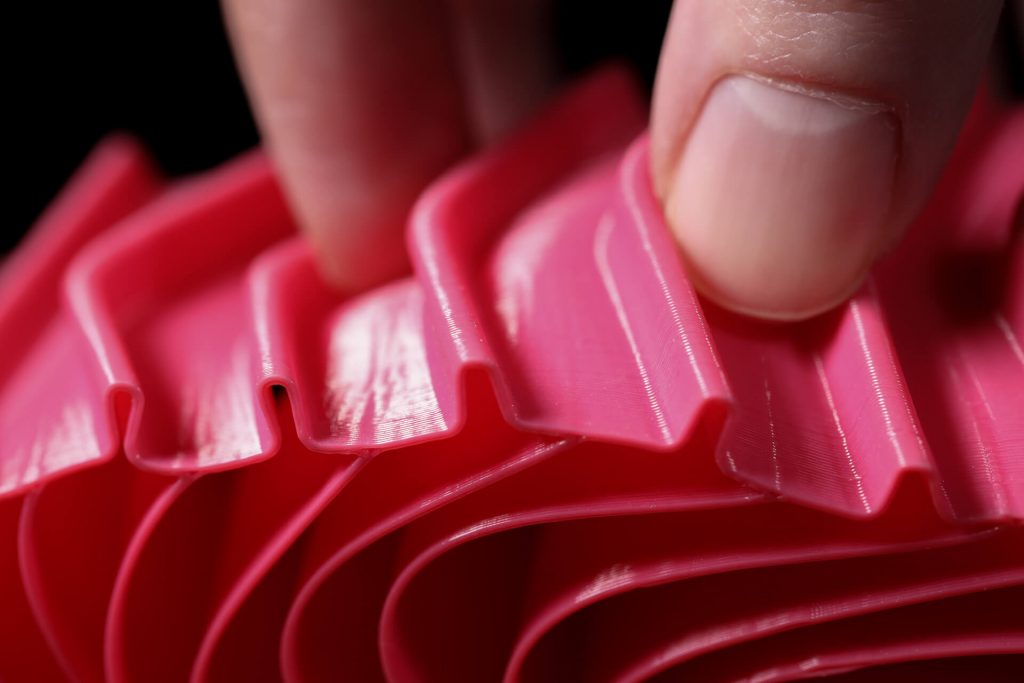 In fact, it is now a material that is beginning to replace traditional rubbers due to its wide range of benefits and uses. There are many different industries that use Thermoplastic Elastomer because its features offer them a number of advantages.
In fact, it is now a material that is beginning to replace traditional rubbers due to its wide range of benefits and uses. There are many different industries that use Thermoplastic Elastomer because its features offer them a number of advantages.
Food Contact TPE
The filament has been food-contact approved. Therefor it will often be found in baby spoons and toddler cup spouts. This is because it is free from concern-causing chemicals.
Medical and Healthcare
As a result of the high regulations regarding safety in this industry, TPE material is the perfect choice. Due to the fact it can be sterilized by using autoclaves and even gamma radiation. They can also be designed so that they can be biocompatible with high levels of purity and low levels of leachable substances. In some instances, they can be used in place of latex and even silicone.
Industries that use seals
There are many industries that use seals such as the marine and automotive industry. Traditionally, sealing rings have been developed using thermoset rubbers. Now TPE makes it possible to create two-component sealings that are colored and co-moulded . There is an increased level of efficiency when using TPE material, which means that seals can be produced quicker than thermoset rubbers.
Traditionally, sealing rings have been developed using thermoset rubbers. Now TPE makes it possible to create two-component sealings that are colored and co-moulded . There is an increased level of efficiency when using TPE material, which means that seals can be produced quicker than thermoset rubbers.
Wires and Cables
TPE material is used in industries that use wire and cable, fibre optic and electrical applications. TPE offers a wide range of functionalities, it can be customized and it is perfect for engineering and prototyping.
TPE 3D printers
Other 3D filaments
Copyright 2020 Terms of agreement Privacy statement
What is the difference between TPE and TPU in 3D printing? – Beamler
Rubber or materials with rubber-like properties are widely used for a great range of applications where the elastic properties of rubber are required. Since 3D printing with rubber was long not thought possible (rubber is a thermoset material), manufacturers started looking for a 3D printing alternative to rubber. The first one came through flexible PLA materials.
The first one came through flexible PLA materials.
Nowadays, 3D printing with TPE and TPU is growing in popularity due their great properties. But what is the difference between TPE and TPU?
Share on linkedin
Share on facebook
Share on google
Share on email
TPE and TPU are thermoplastic elastomers, or rubber-like materials. They have been around since the 1950’s. TPE’s and TPU’s are used to make rubber-like cases, lids, panels, soles for footware, etc. Recently both materials became available as 3D printable materials for the additive manufacturing industry.
So what is the difference between the two materials? How do you decide for 3D printing in TPU or TPE? What is the difference to other types of rubber-like materials, like flexible PLA? Are TPU and TPE a good 3D printing alternative to rubber?
Difference between TPE and TPU
Before 3D printable TPE and TPU was available, the market looked at flex or soft PLAs to mimic the rubber-like qualities.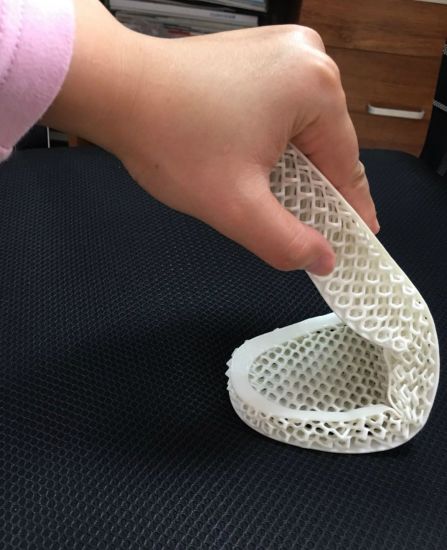 But these are of lower quality in terms of wear and elastic properties than TPE and TPU. For industrial applications, there is no doubt that 3D printing with TPE or TPU offers much better results than with PLA. That is the main reason why Beamler does not offer these elastic PLAs.
But these are of lower quality in terms of wear and elastic properties than TPE and TPU. For industrial applications, there is no doubt that 3D printing with TPE or TPU offers much better results than with PLA. That is the main reason why Beamler does not offer these elastic PLAs.
When to choose for 3D printing with TPU over TPE and vice versa? We have already seen that TPU is a type of TPE. For that reason, it is safe to say that TPE is more common than TPU since it has been available as a 3D printing material for a longer period of time. TPU is a newer variant of 3D printable thermoplastic elastomers. When 3D printing with TPU you can expect your part to be firmer than the ones manufactured with TPE.
Thus, the real difference is not in the name but in available hardness grades. So your choice between TPU and TPE purely depends on the hardness that your 3D printed part requires.
First, what is TPE and what is it an abbreviation of? TPE stands for Thermoplastic elastomer It is a thermoplastic rubber, with both thermoplastic and elastomeric properties, in essence a combination of rubber and plastic.
Applications of TPE
TPE is used in the automotive and medical industries. But TPE can also be found in electronics as the cable jacket and around some headphone cables or any other application where rubber-like qualities are required.
3D Printing with TPE
TPE materials are available as filament for FDM and powder for use in SLS machines. EOS, CRP Technology, Roboze and Sintirit all offer TPE material for 3D printing and are available via the Beamler platform.
EOS already launched their TPE material for SLS in 2013 under the name of PrimePart ST (PEBA 2301).
CRP Technology offers TPE SLS-powder under the name: Windform® RL.
Also Sintirit has TPE powder in their portfolio.
If you are looking for TPE filament: Roboze has a TPE filament in their portfolio called FLEX, for use in their Roboze FDM printers.
All of them are great options for engineers interested in 3D printing with TPE due to outstanding quality of the printed parts.
TPE Windform by CRPtech
Curious about the cost for TPE 3D printed parts?
Upload your files to get prices and lead times. It's free and easy.
Get quote
TPU than, stands for thermoplastic polyurethane, and is a form of TPE or thermoplastic elastomer.
TPU was invented by BF Goodrich in 1959 (now operating under the name of Lubrizol Advanced Materials.) It is a thermoplastic elastomer belonging to the polyurethane class of plastics. TPU’s hardness can be customized resulting in material ranging form soft (rubber-like) to hard (rigid plastic). TPU comes in different colors aswell as transparent. The surface can be smooth or rough as to provide grip.
Applications of TPU
TPU can be found in many applications: automotive instrument panels, sporting goods, medical devices, soles of footwear, inflatable rubber rafts, mobile phone cases and TPU is the plastic around wire and cables.
3D Printing with TPU
TPU is available as filaments for use in FDM machines. TPU is a thermaplastic and is suitable for material extrusion processes: the material can be melted, cooled and hardened.
TPU is a thermaplastic and is suitable for material extrusion processes: the material can be melted, cooled and hardened.
TPU filament for FDM machines is offered by Stratasys as FDM TPU 92A . This material was introduced in November of 2018.
But 3D printing with TPU powders can also done through SLS machines.
Polish material manufacturer offers TPU powders by the brandname FLEXA .
TPU 92A FDM by Stratasys
The German chemical and materials company BASF has a large portfolio of materials, among which a selection of TPU’s, branded under the name of Ellatollan, but it is only recently that the started offering TPU materials for additive manufacturing.
BASF is an ambitious new player in the field. BASF moved into AM in 2017 with the aim of building a portfolio of high quality materials for additive manufacturing. They created a subsidiary, BASF 3D Printing Solutions GmbH, dedicated to additive manufacturing that will initially focus on the automotive, aerospace and consumer goods sectors. BASF is rapidly becoming a reference by providing outstanding materials for 3D printing with TPU.
BASF is rapidly becoming a reference by providing outstanding materials for 3D printing with TPU.
Their rapidly growing material porfolio for AM includes: filaments (Ultrafuse and Innofil3D) and powders (Ultrasint and Adsint) and Advanced Photopolymers and Inks (Ultracur3D).
Their additive manufacturing portolio has two TPU powders. One, Adsint TPU 90 flex, designed for Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) technology the other UtrasintTM TPU01 for HP Multi Jet Fusion printers. The materials were developed by Advanc3D Materials, a company acquired by BASF in 2018.
Adsint TPU 90 flex (thermoplastic Polyurethane) is a powder developed for SLS printing technology. Parts printed with Adsint TPU 90 flex have high elongation, excellent physical properties, rubber-like elasticity and good abrasive and chemical resistance. Typical applications are hard-soft systems, sport footwear, orthopedic models, hoses and tubes, sealings and wheels. BASF claims Adsint TPU 90 flex has been tested on most common SLS printers and can be used on machines of all sizes.
UltrasintTM TPU01 is the second TPU material in the additive manuacturing materials portfolio of BASF. This material is suited for use in HP Multi Jet Fusion printer.
Curious about the cost for TPU 3D printed parts?
Upload your files to get prices and lead times. It's free and easy.
Get quote
New kid on the block: Silicone Printing
TPE and TPU are rubber-like plastic materials, and already of better quality the rubber-like PLA. But what about rubber itself? Printing with rubber itself was long thought not possible, because it is a thermoset material, but recently 3D printing in silicone, a rubber-type material has become available. Read the article Is 3D printing with silicone possible? to learn more about it.
Silicone printing, compared to printing with TPU and TPE, has much better elastic qualities and feels more like rubber, then the rubber-like materials that feel more like plastic. It is more expensive, but depending on your needs and requirements a very interesting option to consider.
Conclusion
TPE and TPU, both inventions of the 1950’s have a wide range of applications and are widely used in the manufacturing industry, where rubber-like properties are required. Recently they have become available as 3D printing materials, as a better alternative to the previously available flexible PLA’s. Both TPE’s and TPU’s are offered at Beamler.
Flexible plastics TPE and TPU
3DPrintStory 3D printing process Flexible plastics TPE and TPU - what's the difference
TPE and TPU are thermoplastic elastomers that allow the finished product to easily stretch or flex. Before we get into the details of these two types of materials that are used in 3D printing, let's talk about flexible materials in general and why they are used.
There are several reasons why you should consider using TPE or TPU plastics for 3D printing. These may be the need for vibration damping and damping, high impact strength and good tear and wear resistance, high resistance to chemicals, and high or low temperatures. With all these advantages, it should be noted that printing with flexible materials is not as easy as we would like. As a rule, the softer and more flexible the material, the more difficult it is to use for 3D printing.
Now let's talk more about TPE and TPU materials and clarify the differences between them. In the article, we will also look at advanced 3D printing techniques and offer you some 3D models that you should try printing with TPE or TPU plastics.
Two TP plastics
TPE
TPE stands for thermoplastic elastomer. It is a mixture of hard plastic and soft rubber, so it has both thermoplastic and elastic properties. TPE covers a wide range of flexible materials including thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), thermoplastic copolyester (TCP), thermoplastic polyamide (TPA).
TPU
TPU stands for thermoplastic polyurethane. This is the most common type of TPE and is in the group of flexible materials with greater rigidity.
Clearing Up the Confusion
Since the terms TPE and TPU are often confused, it's worth clarifying.
- TPE is known as a soft material and has been available for several years. On the other hand, TPU has only recently entered the market, so it is new to the market.
- TPE is a non-specific term for flexible material whereas TPU material refers to a stiffer but still flexible material.
Now that we know the basics about these 3D printing materials, let's take a closer look at their differences.
Similar but different
TPE and TPU can be classified according to their hardness, which is measured by the material's resistance to deformation. As we know, TPU is harder than TPE, and TPU Shore hardness is from 60A to 55D with a high elastic range (typically 600 to 700%).
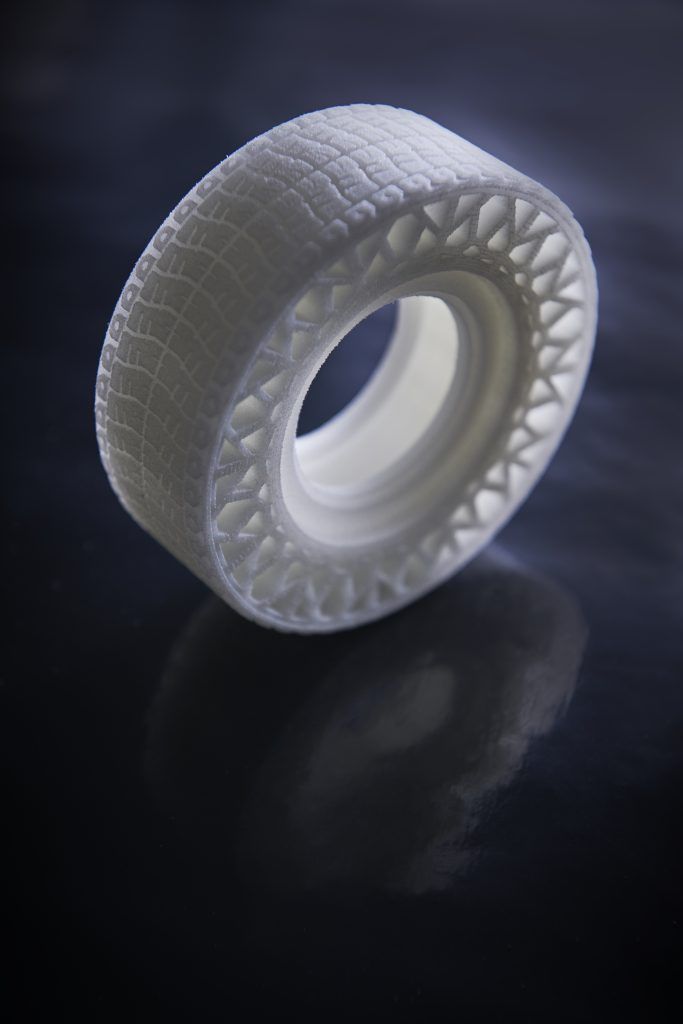
Logically, TPE has a wider hardness range than TPU. Differences in the chemical composition of TPE means that some types of TPE are partially hard and suitable for 3D printing something like a car tire, while other types are very elastic, comparable to a rubber band in their properties.
Compared to TPE, TPU exhibits greater rigidity, which should not be confused with hardness. Stiffness characterizes the ability of a material to bend, indicating the tendency of a material to return to its original shape after being subjected to a load.
Other differences are that TPU will cause more problems during 3D printing because TPU is denser than the TPE group of plastics. TPU has a smooth surface while TPE usually has a more rubbery texture. TPU has greater wear and abrasion resistance than most TPE plastics, and TPU shrinks less than TPE.
Now that we've covered the differences between TPU and TPE materials, let's look at the recommendations for 3D printing with these flexible materials.
3D Printing Features for Flexible TPU and TPE Plastics
3D Printing with TPE Plastics
Printing with TPE plastics can cause problems due to elasticity. It is recommended to print with the following settings:
- Extruder temperature: 210 ºC - 260 ºC
- Bed temperature: unheated - 110 ºC
- 3D printing speed: 5-30 mm/s
- If 3D printing is too fast, it may cause a jam. TPE works best with a direct drive extruder, so be especially careful if you have a Bowden type extruder.
Prices of some popular brands of TPE materials: eSun TPE (about $42/kg), MatterHackers Pro Series TPE (about $55/0.5kg) and 3DXFlex TPE (about $68/0.5kg) .
3D printed TPU plastics
The good news is that TPU plastics are easier to print than TPE because it is relatively rigid. But compared to rigid materials such as PLA, 3D printing with TPU plastics is still more difficult. It is recommended to print with the following settings:
- Extruder temperature: 210 ºC - 230 ºC
- Bed temperature: unheated - 60 ºC
- 3D printing speed: 5-30 mm/s
- optimize the 3D printing process.

Prices of some popular brands of TPU materials: Kodak Flex TPU (about $50 / 0.75 kg), Ultimaker TPU (about $ 70 / 0.75 kg), MatterHackers Build series TPU (about $ 45 / kg ), Polymaker PolyFlex (about $55/0.75kg) and, one of the most popular, NinjaTek (about $55 for 0.5kg).
What to 3D Print with TPU or TPE Plastics
Now we know that TPU is a type of TPE. TPE plastics are generally softer than TPU, which means that TPU 3D printing is less of a problem. In general, if you want heavier, stiffer, and more durable items, choose TPU, but for lighter, softer, and more flexible items, choose TPE.
Here are some cool 3B models you can try printing with TPE or TPU plastics:
- phone case;
- bicycle grips;
- pencil holder.
eLastic (TPE-83A) - eSUN 3D Printing Materials
Request now
83A TPE flexible printing consumables are strong and durable; Printed models are softer than TPU-95A and eFlex, with a delicate and soft hand feel, as well as low friction on the surface.
Colour:
eLastic (TPE-83A) natural
eLastic (TPE-83A) black
Diameter size:
1.75mm
Net weight:
1 kg / coil
Personal purchase:
- Bulk purchases / Agency
Introduction
Parameter information
Notes
Download
- * Description:
-
Description
83A TPE flexible printing supplies are strong and durable; Printed models are softer than TPU-95A and eFlex, with a delicate and soft hand feel, as well as low friction on the surface.
Selling Point
Matte effect
Pleasant to the touch
Flexible and soft
Strong and durableHigh elasticity
High durability
High impact resistance
- * Application
-
Financial support Machinery
- * Print model
-
| Thread chart | |
|---|---|
| 3D PRINT FLAMETER | eLastic (TPE-83A) |
| Density (g/cm 3 ) | 1. 14 14 |
| Thermal distortion temperature (℃, 0.45MPa) | / |
| Melt flow index (g / 10 min) | / |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 32 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 420 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | / |
| Flexural modulus (MPa) | / |
| Impact strength ISOD (kJ /) | / |
| Durability | 9/10 |
| Printable | 6/10 |
| Recommended print settings | |
| Extruder temperature (℃) | 220 - 250℃ Recommended temperature:240℃ |
| Bed temperature (℃) | 45 - 60°C |
| Fan speed | 100% |
| Print speed | 20-50 mm / s |
| Heated bed | Optional |
| Recommended work surfaces | Paint paper, hard glue PVP, PEI |
| Feature | |
| Flexible | √ |
| Elastic | √ |
| Impact resistant | √ |
| Soft | √ |
| Composite | —— |
| UV resistant | —— |
| Waterproof | —— |
| Soluble | —— |
| Heat resistant | —— |
| Chemical resistant | —— |
| Fatigue resistant | √ |
| Need drying | —— |
| Heated bed required | —— |
| Print recommend | Drying at 55 ℃ /> 4 h, short radius extruder, slow printing |
1.