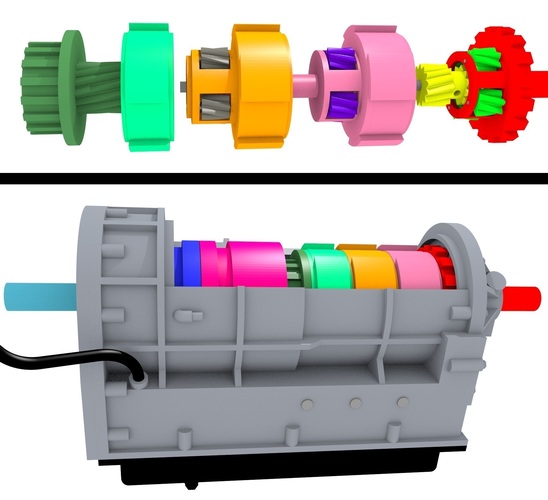
3D printed automatic transmission
Mechanical Engineer 3D Prints a Working 5-Speed Transmission for a Toyota 22RE Engine - 3DPrint.com
Who says that you can’t make anything useful on a desktop 3D printer? Sure, there are plenty of designs that you can find on 3D printing repository websites which make you question the motive of the designers — but at the same time, there are engineers and designers creating things that make you just stop and say, “WOW!”
One of these latter instances comes in the form of a 3D printed 5-speed transmission for a Toyota 22RE engine, created by a mechanical engineer named Eric Harrell of Santa Cruz, California. Not only does it look legitimate, but it also is completely functional.
You may recall a story that we did back in January about a 3D printed Toyota Engine. It was also designed by Harrell, after he completely reverse engineered a real Toyota 22RE engine. It received such a great reception from both Thingiverse users and the national media, that Harrell decided to take his creation one step further, providing this latest 3D printed transmission to complement the engine.
The two actually can be combined to create the ultimate piece of 3D printed machinery.
“I made the transmission due to the the success of my first upload, the 4 cylinder Toyota engine,” Harrell tells 3DPrint.com. “The overall number of people that were interested was overwhelming. I never thought that many people would be interested in it, yet actually print and build it, due to the shear complexity and print time involved. So far 8 people have made the engine and many more are in the process.”
In all, it will take about 48 hours of print time to print out all of the individual pieces needed to assemble the transmission. Once the pieces have all been printed, they will need to be assembled using the diagrams that Harrell provides. He admits that it’s not an easy task to put the transmission together once the parts have been printed, but welcomes questions from anyone who has difficulty doing so.
Transmission and engine mated together.
“If one was to build either my transmission or engine, they would have a pretty good idea of how to put an actual engine together since these are modeled after real parts,” Harrell tells us. “Which is great, because most people that are interested in 3D printing would never get the opportunity to actually rebuild an engine or transmission.”
While the majority of the transmission is 3D printed, there are some smaller parts which can not be printed on a desktop 3D printer, such as the 3mm rod, (18) 623zz bearings, (20) 3mm washers, and a few other small odds and ends like screws and bolts. At the same time, Harrell doesn’t ensure that all the parts will be ready to go off of the printer. Depending on the 3D printer used, some of them may need to be scaled up or down in order to fit together properly. Rather than scaling the parts, he also suggests that you could simply file them down where needed.
“The transmission works exactly like most manual transmissions found in any car or truck,” explained Harrell.
“However, I can barely explain how it works. It’s fairly hard to grasp unless you assemble one or see an animation of one opened up.”
Regardless of the time required for printing and assembly, this has to be one of the most incredible designs that we have come across yet on Thingiverse. Most incredibly, Harrell tells us that it could absolutely be used in a real vehicle, since it is a scaled down version of the real thing.
What do you think about this incredible 3D printed Toyota transmission? Have you, or will you be 3D printing your own? Discuss in the 3D Printed Toyota Transmission forum thread on 3DPB.com. Check out the video below of the 3D printed transmission in action.
Stay up-to-date on all the latest news from the 3D printing industry and receive information and offers from third party vendors.
Tagged with: 22re transmission • 3d printed engine • 3d printed toyota transmission • 3d printed transmission • 5-speed transmission • thingiverse • toyota 22re engine • toyota transmission • transmission
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.
Transmission best STL files for 3D printer・Cults
Skip to contentDriveshaft for custom diecast / model kit - 1/43
€3.38
Car cupholder manual transmission fidget toy
Free
COMPLETE SET OF SKODA, VOLKSWAGEN GEARBOX BUSHINGS (without gearbox joint)
€10
Axial 3 gear transmission to modify
Free
FUNNY CAR TOP FUEL Bellhousing N Clutch N Driveshaft
€6.13
Automatic transmission, double planetary gearset, Ravigneaux
€1.90 -70% €0.57
spur-helix rack and pinion transmission-simple
Free
Hobbed bar, hyena v1.0
Free
1/24 MAZ 537 Transmission
€4.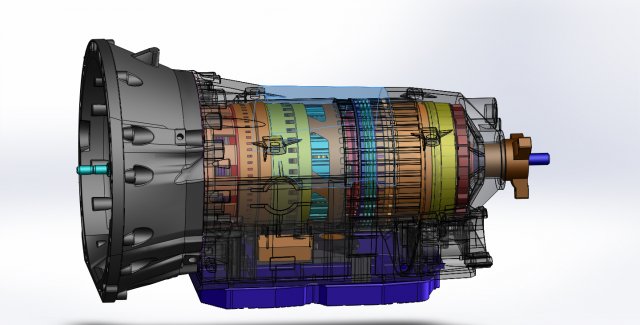 82
82
High voltage pole
€2.36
Crown Kyosho Rc Module 08, 59 Teeth
€1
Marble machıne
€4.99
2 speed dogbox transmission (working prototype)
Free
Reciprocating thing
Free
LMR400 Coax Holder for Transmitting Loop 36.5mm Length
Free
Marble machıne
€4.99
Marble machıne
€4.99
Marble machıne
€4.99
SHIFTER 4 FOR CUSTOM DIECAST / RC / SLOT / MODEL KIT - DRAG - PRO MOD
€5.12
Brinn Gen 1 Transmission 1/24th Scale
€4.09
Peugeot 206cc Automatic Gear(Shift) Knob Panel(Grille)
€12.50
GasGas / Rieju / motorbike transmission oil filler / funnel
€0. 54
54
PEUGEOT 508 HIH CUP PHONE HOLDER LIFT AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
€15.20
Tatra 813 1/8 scale high-end-project (incomplete!!) - PART A: wheel transmission
€4.95
Shaper quick return mechanism (Simple edition)
€0.50
Shaper quick return mechanism
€0.70
1966 Chevrolet C10 Custom Trans Kit
€163.71
Losi Mini Jrx2 XX Retrofit style Transmission case WIP
Free
Spiral bevel gear
€2.05
M.2 NVMe & SATA SSD Key Storage Drive Case Container Box
Free
Planetary gearing
€0.50
SHIFTER 3 FOR CUSTOM DIECAST / RC / SLOT / MODEL KIT
€4.40
PRO TOURING MCS Low-Pro Chassis Driveline N Transaxle
€6.13
1/24 Scale Saginaw 341, 3-Speed Manual Transmission 3-Pack
€4.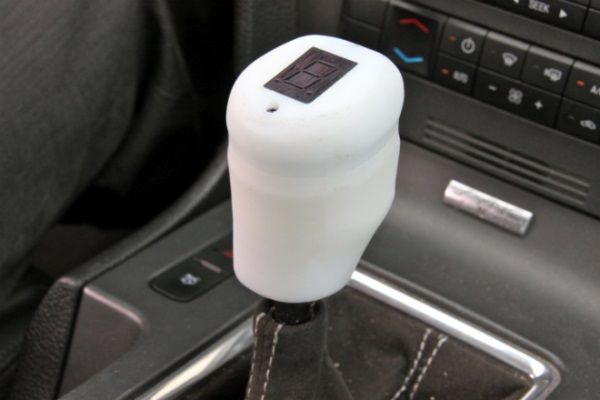 09
09
Cylindrical gear - paired - z100 m2 D204 d30
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z100 m2 D204 d25
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z100 m2 D204 d20
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z99 m2 D202 d30
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z99 m2 D202 d25
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z99 m2 D202 d20
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z98 m2 D200 d30
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z98 m2 D200 d25
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z98 m2 D200 d20
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z97 m2 D198 d30
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z97 m2 D198 d25
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z97 m2 D198 d20
€0. 50
50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z96 m2 D196 d30
€0.50
Cylindrical gear - paired - z96 m2 D196 d25
€0.50
How to calculate the cost of printing on a 3D printer
For some ideas, 3D printing is the fastest and easiest solution. In some situations, purchasing your own 3D printer can be a good solution, but sometimes it is much more profitable and faster to order the necessary product from a company specializing in 3D printing. Yes, and many owners of a 3D printer are thinking about how to “monetize” their hobby, but how to correctly calculate their costs?
Despite the fact that it is customary to indicate the price per gram of working material, simply multiplying the weight of the model by the cost of 1 gram will be wrong. In addition to the cost of consumables, many more, at first glance, non-obvious costs are added to the price of the product.
Each 3D printing technology uses its own consumables. Let's analyze the most popular and affordable of them.
Let's analyze the most popular and affordable of them.
Available technologies and key differences
Currently, a huge number of 3D devices have appeared, from small desktop ones that fit on the desktop to huge industrial machines. Among the most affordable, 2 technologies can be distinguished - FDM and photopolymer printers (LCD / DLP / SLA).
FDM 3D printing
Today, the most affordable 3D printing technology is FDM. A variety of materials and 3D printers allow FDM to be applied to a wide range of applications.
Schematic operation of FDM printer
A large selection makes it easy to choose a 3D printer for a specific task or find a universal device.
The material for printing is a plastic thread - filament. On the market you can find filament for various tasks, for every “taste” and budget. These can be very inexpensive ABS and PLA plastics or specific ones - conductive, burnable, etc.
Pros:
Cons:
Despite the fact that FDM allows you to print a wide range of plastics with different properties, the technology has some limitations. For example, it is impossible to obtain a perfectly smooth surface, to produce miniature and very thin elements, or to produce parts with very complex internal geometry with high accuracy.
Photopolymer printing
Photopolymer printers can work on one of 3 technologies - SLA, DLP or LCD. These devices will come to the rescue if you need to make a small but very detailed model with many small details.
How photopolymer printers work
As a consumable material, a photopolymer resin hardened by UV radiation is used. Now there is a wide variety of photopolymer resins for every taste. From particularly strong and precise engineering or jewelry resins to soft flexes.
Pros:
-
High print precision
-
Good surface quality
-
A wide variety of printers and consumables
Minuses:
Photopolymer printers have shown themselves well in a variety of industries that require a perfectly smooth surface and high accuracy.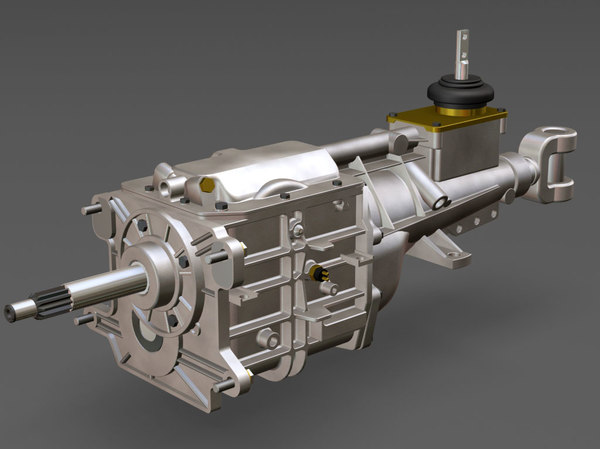 They are used in dentistry, the jewelry industry, for making miniature master models for casting, and much more.
They are used in dentistry, the jewelry industry, for making miniature master models for casting, and much more.
Industrial printers
These are already industrial machines, which require a separate room and sometimes certain requirements for ventilation, etc. In this article, we will not analyze these devices in detail, but briefly consider the most popular technologies.
FDM
In addition to desktop devices using FDM technology, industrial printers that work on the same principle are common.
This category includes devices with a large print area (from 30x30x30 cm and more). For example, Raise Pro2 with a print area of 30x30x30 cm.
Raise Pro2
Or machines designed for printing with refractory materials (eg PEEK). Such 3D printers usually have an active thermal chamber, and the extruder can be heated above 400 degrees.
CreatBot F160-PEEK designed to work with refractory plastics
Photopolymer printers
Industrial photopolymer devices usually have a much larger working area, compared to their "home" brothers. In addition, many processes have been optimized and automated for faster operation. On such printers, you can quickly and accurately produce a small batch of models, a large prototype or a master model.
In addition, many processes have been optimized and automated for faster operation. On such printers, you can quickly and accurately produce a small batch of models, a large prototype or a master model.
Prismlab Large Area Industrial Resin Printer Family
3DP
3DP - Three-Dimensional Printing (translated as three-dimensional printing) is a logical continuation of conventional two-dimensional printers. Printing is done using nozzles that selectively apply a binder to the material (usually gypsum). A dye can be added to the binder and the model will be colored.
Colored plaster model
Since the plaster model is fragile, a similar principle is used for printing with metals. Only the finished product needs to be treated in an oven to remove the binder and improve strength. But despite the processing, such metal prints will still be inferior in strength to cast products.
MJM
This is a proprietary technology of 3D Systems. MJM is a mix of FDM, 3DP and sometimes SLA (depending on material chosen). Printing is done using a variety of small nozzles (from 96 to 488) located on the head of the machine. The accuracy and quality of the surface of models made in this way is in no way inferior to photopolymer printers.
Models made with MJM technology
Such devices can work with photopolymer resins, wax or thermoplastics. You can combine several materials at once - for example, for complex models, you can use wax as a support.
SLM
SLM is the layer-by-layer sintering of metal powder using a powerful laser. There are several similar technologies - SHS/SLS. The principle of operation is the same, only a thermal print head is used instead of a laser beam.
SLM Turbine
As a material for printing, you can use powders of various metals - gold, stainless steel, aluminum, various alloys, etc.
During printing, the working chamber is filled with an inert gas to prevent oxidation of metals. This allows printing even with titanium powder.
Models made by this method are in no way inferior, and sometimes even superior, to cast products. SLM allows you to produce models with complex internal geometry that cannot be produced by another method (casting or milling).
Cost of 3D printing
The cost of a model usually consists of several factors.
-
Equipment depreciation. The printer, like any machine, requires maintenance and periodic replacement of some parts. During operation, belts gradually stretch, bushings or linear bearings wear out. For example, when bushings or linear bearings are worn; shafts may wear out and need to be replaced.
Cost of materials
The main cost item for a 3D printer is, of course, the printed material.;
FDM (plastic filament)
Since FDM technology is by far the most common, the choice of filaments is very diverse.
-
Engineering plastics are usually nylon with various fillers added to improve the physical characteristics of the finished model. Special cost. plastics starts from 2000r per coil and above. It all depends on the manufacturer and filler (carbon fiber, fiberglass, etc.).
-
Decorative plastics are used to imitate various materials. Plastic can simply be unusually colored (luminous, transparent plastics) or a special filler is added to it (plastics with metal powder). The cost of decorative plastics starts from 1500 rubles per coil and more, depending on the filler.
A big advantage of FDM is the diverse choice of materials to work with. This allows, having one printer, to produce almost any product - from a child's toy to a complex engineering prototype.
Photopolymers (resin)
Photopolymer resin printing technology is becoming more and more accessible. There are many different resins.
-
The cost of ordinary colored resin starts from 2500 rubles per 0.5 kg (volume +/- 0.5 l). You can find a smaller volume of resin (250 gr) on sale. You can buy several different resins in small containers and find out in practice which one is best for a particular model.
-
Engineering resins are resins with increased strength. They can be used not only for printing decorative items, but also for making functional prototypes and models. The cost for 0.5 kg starts from 5900r and above.
-
Special resins - burnable, dental, soft flexes, etc. Depending on the resin, the price for 0.5 kg can start from 4800 rubles and more. It all depends on the characteristics of the resin.
Photopolymer resins have not yet reached such a variety as FDM filaments, but they are surely catching up. Although due to the fact that a liter of resin costs significantly more than a spool of filament, the cost of the product is much higher.
Print examples
FDM
Mag Pull (quick release loop) for G3 magazines.
The model was downloaded for free from an open source (the file can be downloaded here). Printing with engineering carbon-filled plastic (price per spool from 4700 rubles). The weight of the model with support is about 25 grams. Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished model is 250 rubles.
Plastic fastener
The file was downloaded from an open source (can be downloaded here). Plastic - carbon-filled nylon (price per coil from 4700r). The weight of the finished product is about 20 grams. Print without post-processing. The total cost is 200 rubles.
Model watch
The model is modeled to order (the cost of modeling is from 1000 rubles). The product is printed on an industrial printer using soluble support. Print without post-processing. The cost of the finished product - from 700 rubles per piece (depends on the number of required products).
Print without post-processing. The cost of the finished product - from 700 rubles per piece (depends on the number of required products).
Traction prosthesis
The model is taken from an open source (you can download the modified version of the prosthesis here). The weight of the used material is about 600 gr, printed with ABS plastic (the cost of the coil is from 800 r). After printing, post-processing and assembly took place. The total cost of the product - from 3000 r (depends on the print material, support material, filling, etc.).
Pedal layout
Production of a 3D model according to the drawing (from 1000 r). The weight of the finished model is about 200 gr. The product was printed with engineering carbon-filled plastic (the cost of the coil is from 4700 r). Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished product is about 3000 rubles.
Photopolymer printers
Model jaws for crowns
Files for printing were obtained using a 3D scanner and finalized in a 3D editor (the cost of scanning is from 3000 r, the cost of manual revision is from 1000 r). Printing on an industrial photopolymer printer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is from 80 r per gram.
Printing on an industrial photopolymer printer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is from 80 r per gram.
Burnout resin rings
The model is made to order. Printing on a desktop SLA printer with a burnable polymer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is 200 rubles per product.
Miniatures
The models were bought on the myminifactory website (the cost of the model is from $2). Made with a desktop DLP printer. Post-processing was not required. The cost of the finished figurine is from 70 r per gram.
Custom 3D printing
Many owners of 3D printers are thinking about monetizing their hobby. But you should understand that the price of 3D printing “for yourself” and the price of commercial printing are very different.
When starting to print to order, it is better to have several printers working on different technologies.

Cost of commercial 3D printing
In addition to the cost of the model, to the commercial production of products, you can add:
-
Modeling. Often the client needs not only to make a part, but to pre-model it. It can be a simple cogwheel that doesn't take long to model, or it can be a complex sculpture that takes more time to model than it does to make.
-
Model post-processing. This can be simply the removal of supports, with cleaning of the place of their contact with the product, or a complete processing cycle (puttying, surface grinding, painting, etc.).
It should be borne in mind that it is not always possible to print the model the first time. Sometimes it may take several attempts. And these are additional costs.
What is unprofitable to print
Despite the wide possibilities of 3D printing, there are models that are unprofitable to make on a 3D printer.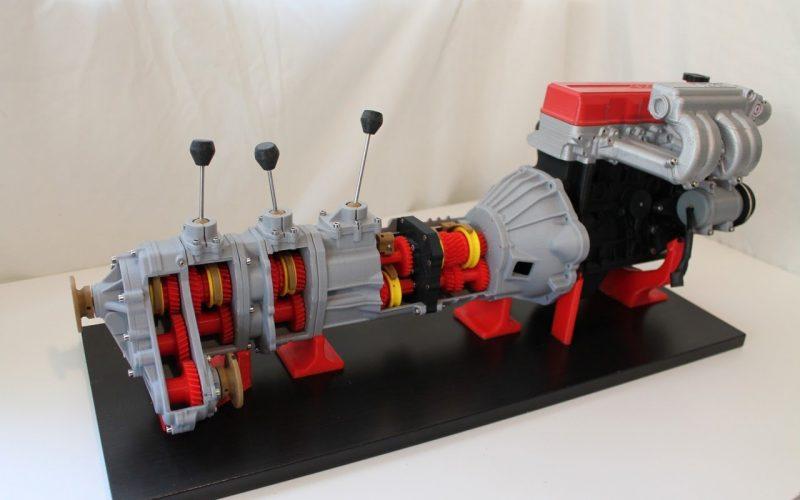 For such models, it is better to use other manufacturing methods.
For such models, it is better to use other manufacturing methods.
Commercial print examples
Jewelry for further casting
Manufacture of promotional items and souvenirs
Piece miniatures or master model for further casting
3D printed model
Profitable to print on a 3D printer:
-
If the item is only sold as an assembly. For example, a small gear broke in the mechanism, but the mechanism is sold only “assembly”. It is much cheaper to make the desired gear on a 3D printer than to buy the entire mechanism.
-
A small batch of parts. Small batches, especially models with complex geometry, are more profitable to produce on a 3D printer than by casting or other methods.
Totals
If you need several models or a small project, sometimes it will be more expedient to outsource manufacturing. After all, in addition to buying equipment and materials, you will have to understand the nuances of the settings and the characteristics of various materials.
After all, in addition to buying equipment and materials, you will have to understand the nuances of the settings and the characteristics of various materials.
Buying a 3D printer for commercial use is justified if you can fully load it with work or then it can be used for other purposes.
To print to order, you need to have several printers working on different technologies. It is better to get several devices with a smaller print area than to buy just one printer, albeit with a large working area.
Top 20 Free 3D Printing and 3D Printing Software
Looking for 3D printing software? We've rounded up the top 20 software tools for beginners and professionals alike. Most slicers are free.
What is a slicer? This is a program for preparing a digital model for printing. Models for 3D printing are usually distributed in STL files. To turn an STL file into G-code (a language that a 3D printer understands), a slicer program is required.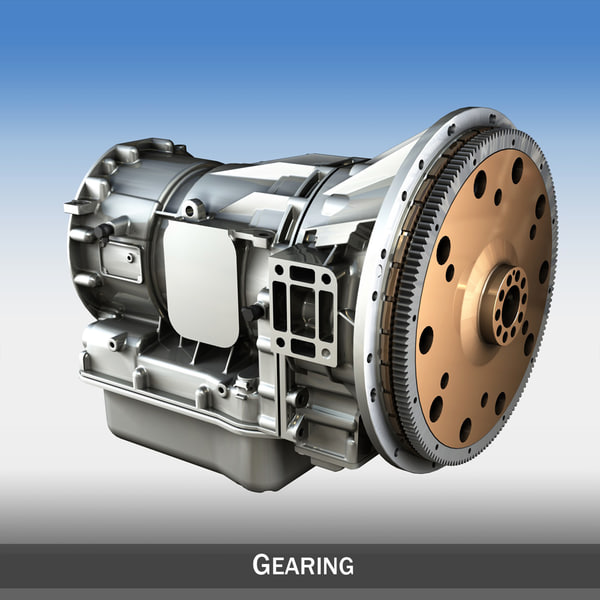 It is called a slicer because it cuts (to slice - English) a 3D model into many flat two-dimensional layers, from which a 3D printer will add a physical object.
It is called a slicer because it cuts (to slice - English) a 3D model into many flat two-dimensional layers, from which a 3D printer will add a physical object.
Which slicer should I choose? In this article, we will tell you which slicer is best for 3D printing for each stage of your work. Which one is better for preparing a 3D model for printing? But what if you need to create a 3D model from scratch? And if you are only taking the first steps in 3D?
Don't be afraid: we've answered all of these questions, including the required skill level for each program and where you can download it. The great thing is that most of these programs are completely free and open source.
- Cura
- CraftWare
- 123D Catch
- 3D Slash
- TinkerCAD
- 3DTin
- Sculptris
- ViewSTL
- Netfabb Basic
- Repetier
- FreeCAD
- SketchUp
- 3D Tool
- Meshfix
- Simplify3D
- Slic3r
- Blender
- MeshLab
- Meshmixer
- OctoPrint
#1: Cura
For beginners who need a slicer to prepare STL files for 3D printing
Cura is the default slicer software for all Ultimaker 3D printers, but can be used with most others , including RepRap, Makerbot, Printrbot, Lulzbot and Witbox.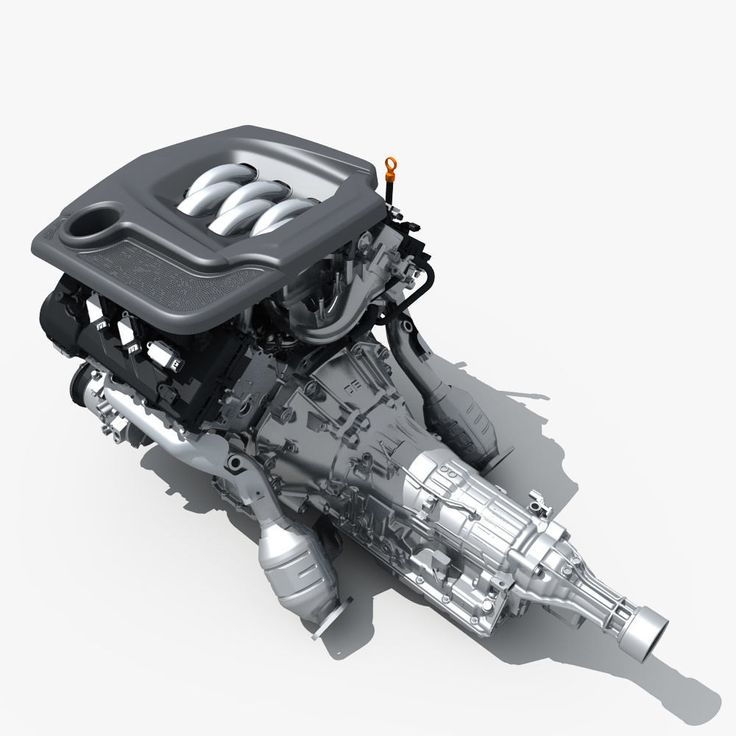 The program is completely open source, its capabilities can be extended using plugins.
The program is completely open source, its capabilities can be extended using plugins.
This program is very easy to use and allows you to manage the most important 3D printing settings through a clear interface. Start in Basic mode to quickly get up to speed and change print quality settings. If finer control is required, switch to Expert mode.
Cura can also be used to directly control the printer, but then the printer and computer must be connected to each other.
Download: Cura
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#2: CraftWare
For beginners to prepare STL files for 3D printing 3D printers by the Hungarian startup CraftUnique to support their CraftBot crowdfunding machine. However, the program works with other printers.
Like Cura, CraftWare allows you to switch from "Easy" to "Expert" mode, depending on how confident you feel. It's a colorful app that features a visual G-code visualization with each function represented by a different color. But the most outstanding feature is the individual support service. As far as we know, only the paid program Simplify3D has this.
But the most outstanding feature is the individual support service. As far as we know, only the paid program Simplify3D has this.
Please note, however, that this program is still in beta, so bugs may occur.
Download: CraftWare
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#3: 123D Catch
-systems, smartphones and tablets, which allows you to convert images of objects into a 3D model. Pictures can be taken with a smartphone/tablet or digital camera.
You need many photos of the object from different angles - the more the better - after which they will be compiled into a 3D model.
123D Catch is more of a fun app than a professional 3D printing tool, but after some tambourine dancing, you can get good results, especially when paired with an STL editor like MeshLab or Meshmixer.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Android, iOS, Windows Phone
#4: 3D Slash
and surprisingly simple, and refreshingly new. With 3D Slash, you can design 3D models using your dice skills.
With 3D Slash, you can design 3D models using your dice skills.
You can start with a large block and, like a virtual sculptor, remove small cups from it with tools such as a hammer or drill, or start from empty space and build a model from cubes and other shapes. You can paint with flowers or use template pictures.
Other features worth mentioning are tools for creating logos and 3D text. The Logo Wizard imports an image and creates a 3D model, while the Text Wizard allows you to enter and format text, and then turn it into 3D.
Recommended!
Download: 3dslash.net
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux, Browser
#5: TinkerCAD
- A computer-aided design (CAD) system for 3D printing, which is a good starting point for beginners. Since its capabilities are limited compared to Blender, FreeCAD and SketchUp, many users switch to more powerful tools after some time.
As in 3D Slash, here you can build models from basic shapes. At the same time, unlike 3D Slash, TinkerCAD allows you to create vector shapes in 2D and convert them into three-dimensional models.
At the same time, unlike 3D Slash, TinkerCAD allows you to create vector shapes in 2D and convert them into three-dimensional models.
Come in: Autodesk TinkerCAD
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#6: 3DTin
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
another easy and intuitive online tool choice for beginners in 3D modeling. All you need is a Chrome or Firefox browser with WebGL enabled.
Choose from a huge library of 3D shapes and add them to your sketch. All sketches are stored in the cloud, access to them is free if you honor the Creative Commons license. Everything can be exported to STL or OBJ formats.
Enter: 3DTin
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#7: Sculptris
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
clay. This is a fantastic 3D modeling program if figurines are your main task. For example, you can make a bust of your favorite video game or comic book character.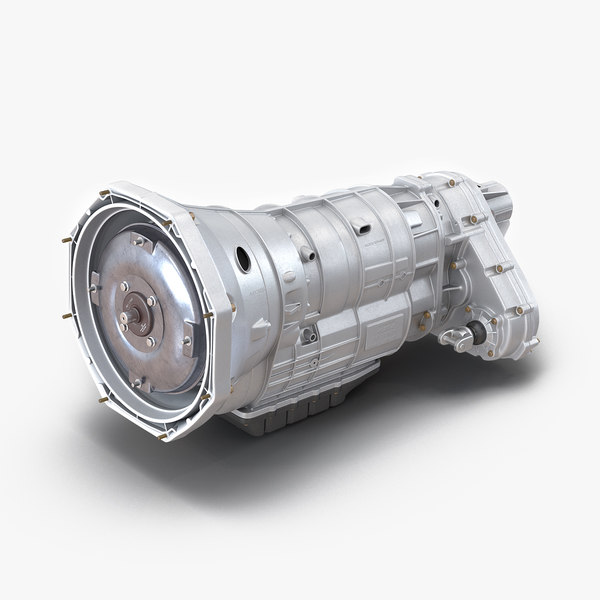 Sculptris is completely free and bills itself as a stepping stone to the more complex (and expensive) ZBrush tool.
Sculptris is completely free and bills itself as a stepping stone to the more complex (and expensive) ZBrush tool.
Download: Pixologic Sculptris
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#8: ViewSTL
For beginners who want to view STL files
Using ViewSTL is the easiest way to view STL files . Simply open a web page and drag the STL onto the dotted box.
The STL online viewer allows you to display the model in one of three views: flat shading (for a quick view), smooth shading (for a high-quality image), and wireframe.
Enter: ViewSTL
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#9: Netfabb Basic
some nice features that allow you to analyze, "repair" and edit STL files before moving on to the model cutting stage.
A good choice if you need more than just a slicer and want to be able to quickly fix STL files without having to learn programs like MeshLab or Meshmixer.
Don't let the 'Basic' in the name fool you, Netfabb Basic is actually a very powerful 3D printing tool. It's "basic" only in the sense that it doesn't cost €1,500 like Netfabb Professional!
It's "basic" only in the sense that it doesn't cost €1,500 like Netfabb Professional!
Download: netfabb.de
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
No. 10: Repetier
For advanced to prepare STL files for 3D printing
9002 the next level of 3D printer slicer software, but if you want to stay open source, you should look into Repetier. It is the great grandfather of 3D printing software and a favorite of the RepRap community.Today the program is moving by leaps and bounds from the level for beginners to advanced users. Packaged in an all-in-one configuration, it supports up to 16 extruders, multi-slicing via plug-ins, and virtually every fusing 3D printer on the market. Get ready to tinker!
What's more, Repetier Host works remotely via Repetier Server, so that the 3D printer can be controlled via a browser, tablet or smartphone.
Download: Repetier
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#11: FreeCAD
The program is a great option for developing your design skills.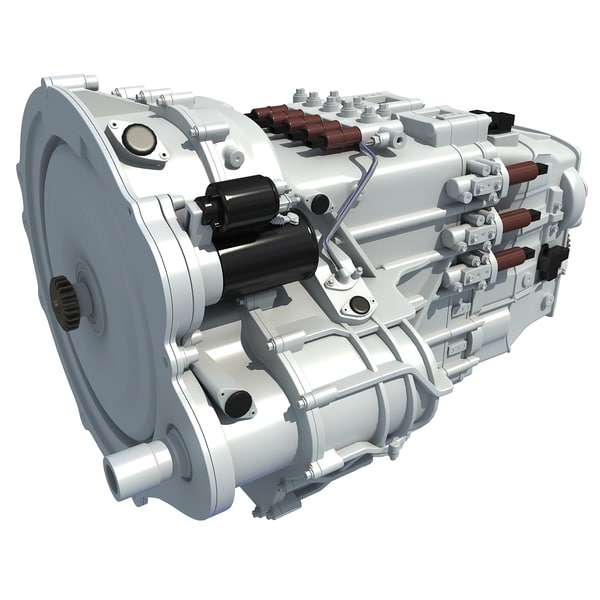 More technically, this parametric 3D modeling program allows you to easily change the project by rolling back through the history of the model and editing the parameters.
More technically, this parametric 3D modeling program allows you to easily change the project by rolling back through the history of the model and editing the parameters.
Download: freecadweb.org
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#12: SketchUp
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
SketchUp is the perfect combination of simplicity and the perfect combination functionality, with a user-friendly interface and a relatively flat learning curve (i.e., as experience grows with the time spent), the ideal program for developing three-dimensional models.
The Make SketchUp version is free and will have everything you need for 3D modeling if you also download and install the free STL exporter. There is also a professional edition for architects, interior designers and engineers.
Download: sketchup.com
Price: Free (SketchUp Make), $695 (SketchUp Pro)
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#13: 3D-Tool Free Viewer
view and check STL files
3D-Tool Free Viewer is a sophisticated tool that, among other things, allows you to check the structural integrity and printability of your file.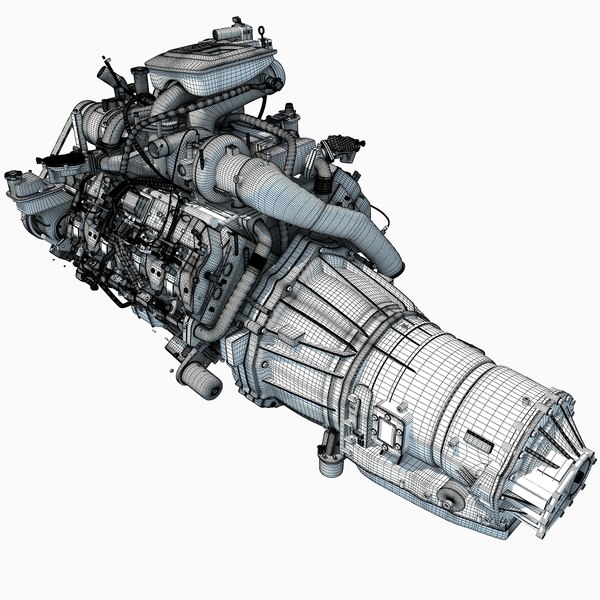 With the Cross-Section function, for example, you can look at the model from the inside and check the wall thickness. Very useful if you want to check your STL file for killer errors before printing.
With the Cross-Section function, for example, you can look at the model from the inside and check the wall thickness. Very useful if you want to check your STL file for killer errors before printing.
Download: 3D-Tool
Price: Free
Systems: PC
#14: Meshfix
your model for errors.
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#15: Simplify3D
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing print. A flexible algorithm checks the model for problems, fixes them, shows a preview of the printing process (ideal for identifying potential problems), and then slices it.
This slicer offers the best infill pattern options in the competition. For models that require supports, Simplify3D will create the appropriate structures on its own and give you full control over their placement. For printers with a dual extruder, when printing with different materials, the Dual Extrusion wizard will help, as a result of which, for example, it will be easier to remove the dissolving filament.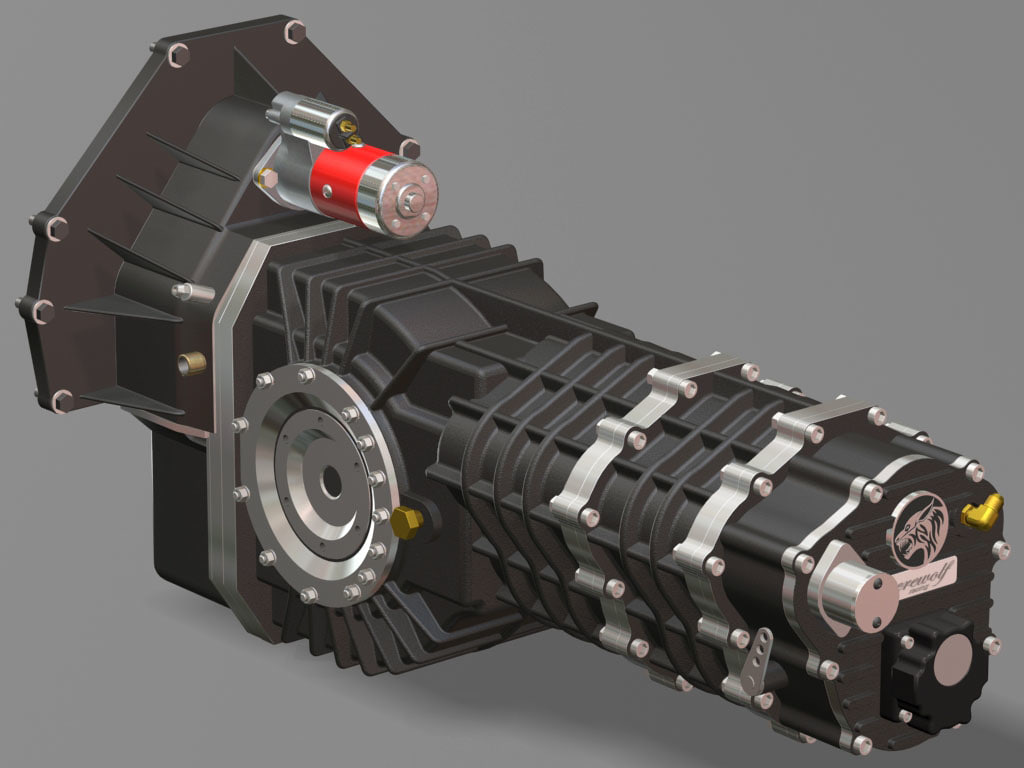
Simplify3D supports 90% of today's commercially available desktop 3D printers and is compatible with Marlin, Sprinter, Repetier, XYZprinting, FlashForge, Sailfish and MakerBot firmware. Simplify3D can also be used to directly control the printer, but then the printer and computer must be connected to each other.
Download: simplify3d.com
Price: $149
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#16: Slic3r
source code, which has a reputation as a carrier of super new functionality, which you will not find anywhere else. The current version of the program is able to show the model from multiple angles, so that the user gets a better preview experience.
There's also an incredible 3D honeycomb infill, the first of its kind that can extend over multiple layers rather than repeating itself like a stamp. This significantly increases the strength of the internal filling of the model and the final printout.
Another option is direct integration with Octoprint. Once the files on the user's desktop are sliced, they can be directly uploaded to Octoprint with one click.
Once the files on the user's desktop are sliced, they can be directly uploaded to Octoprint with one click.
Download: Slic3r
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#17: Blender
For professionals who want to create 3D printable models
Blender is a popular computer-aided design (CAD) system with a steep learning curve. Not at all the best choice for beginners, but what you need if you are quite experienced and need something more complex for modeling and printing.
In short, Blender is one of the most powerful tools in existence. Its community is always ready to help, there are a lot of educational materials. It's also open source, so enthusiasts often write extensions to make it even better and more powerful.
Download: blender.org
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#18: MeshLab
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing
MeshLab - advanced editor.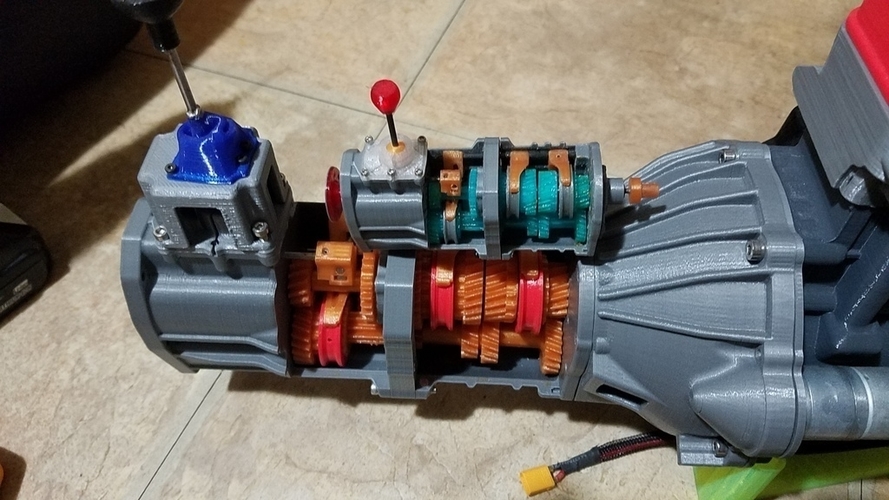 It allows you to remove parts of a 3D model, merge two models into one, patch holes. If you need a program to modify models for 3D printing or some kind of "repair" work, MeshLab is the right choice.
It allows you to remove parts of a 3D model, merge two models into one, patch holes. If you need a program to modify models for 3D printing or some kind of "repair" work, MeshLab is the right choice.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#19: Meshmixer
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing files. It's especially good for identifying potential problems and fixing them automatically. For example, it will show paper-thin walls that can lead to problems with 3D printing. Meshmixer is part of the Autodesk family of 3D printer software, so it should work well with tools like TinkerCAD.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#20: OctoPrint
start, pause or interrupt 3D print jobs. Combined with Wi-Fi capable devices, it makes for a great monitor for remotely monitoring the 3D printing process.
Octoprint understands the G-codes of almost all 3D printers and slicers and includes a gCodeVisualizer to visualize this code before or during printing.