3D colour printing
Guide to Color 3D Printers
Are you looking to 3D print parts in color or to create vibrant, multi-color parts? Over the last few years, multiple new methods have emerged to 3D print in color, and newer 3D printers have become more accessible, empowering any designer, model maker, or hobbyist to create objects in a range of hues.
In this guide, we dive into the several techniques you can use to produce colored 3D printed parts, as well as the technologies and applications of color 3D printing.
There are several options to produce colored 3D printed parts, from color mixing to color matching, full color 3D printing, painting 3D printed parts, and hydrographics.
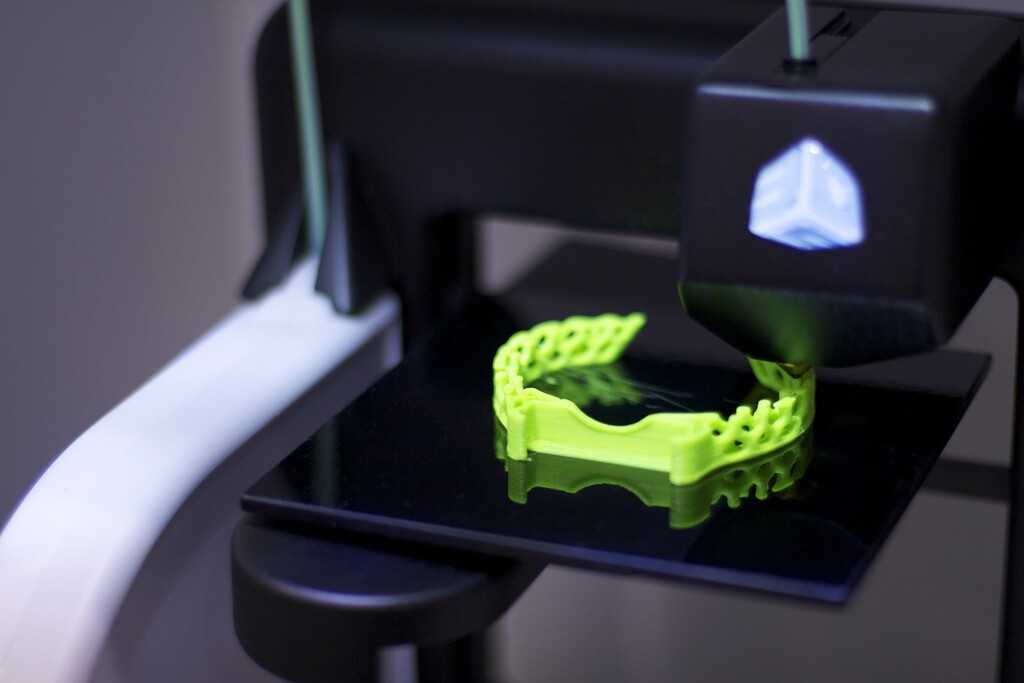
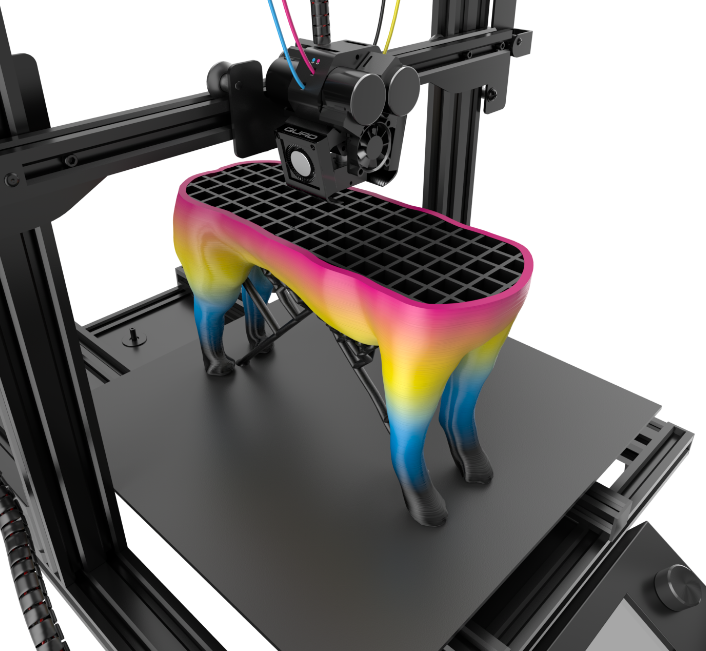
Direct color, also known as multicolor 3D printing is the most basic way to 3D print parts in multiple colors. It involves loading colored raw material into the printer. The most common way is using colored filaments with 3D printers that use fused deposition modeling (FDM) technology, which melts and deposits the filament onto the printer bed.
FDM 3D printing in color. (source: 3Dnatives)
FDM 3D printers can print in a single color, using colored filament, in two colors, using a dual extruder, or in multiple colors and gradients using color mixing, depending on how many filaments feed through the printer simultaneously.
The main advantage of these multicolor 3D printers is that they're easy to use and affordable. However, the disadvantages are that it’s not possible to achieve a specific color tone, and the final part will likely have visible layer lines. Also, the more extruders an FDM printer has, the bigger the chance of print errors.
While direct color printing only offers off-the-shelf color options, color matching allows you to create 3D printed parts in almost any custom color.
SLA 3D printed parts in various custom colors.
As the first integrated color-mixing solution for stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing, Formlabs Color Kit mixes color pigments into the base material to create a full cartridge of customized color resin. The SLA 3D printing process then uses a laser to solidify the colored resin and 3D print parts in vibrant colors with a smooth surface finish and almost imperceptible layer lines.
The SLA 3D printing process then uses a laser to solidify the colored resin and 3D print parts in vibrant colors with a smooth surface finish and almost imperceptible layer lines.
Color Kit, the first integrated color-mixing solution for SLA 3D printing.
Sample part
See and feel Formlabs quality firsthand. We’ll ship a free sample part to your office.
Request a Free Sample Part
Full-color 3D printing is the most versatile color 3D printing method, as it produces objects in multiple colors at the same time, matching any tone and making realistic parts.
Unlike colored filaments or resin, the material used in full color printing is not pre-colored—the color is added to the base material during the printing process, similar to a color 2D printer.
Full-colored 3D printed part with binder jetting. (source: Hubs)
Technologies such as binder jetting and material jetting are able to produce full-color 3D prints. However, these processes have a high entry price, making them inaccessible to most users, while only one manufacturer offers a more affordable full color FDM 3D printer.
However, these processes have a high entry price, making them inaccessible to most users, while only one manufacturer offers a more affordable full color FDM 3D printer.
In certain cases, colored 3D prints may lack the detail or the vivid colors that an artist or designer aims for. Painting monochromatic 3D printed parts with acrylic, oil, or spray paint, while more time-consuming, offers an inexpensive and fully custom solution.
Side by side comparison on the before and after painting a dinosaur 3D printed SLA miniature.
Models that need a perfectly smooth finish or very fine features may require post-processing techniques, such as sanding, priming, or using a solvent prior to painting.
Sanding reduces imperfections in the surface, and primer fills in small cracks and holes. Additionally, some 3D printed parts may need an undercoat to diminish the neutral color of the primer before the paint application.
Watch or read our step-by-step guide on priming and painting 3D printed parts.
Hydrographics, also known as hydroprinting, water printing, or water transfer printing, is a common method for applying printed designs to three-dimensional surfaces. The process uses an inkjet printer to print an image on a polyvinyl alcohol film. The film gets submerged in water and receives an activator chemical spray. The color film then stretches over and adheres to the object as it’s slowly dipped through the floating film.
If you're interested in this process, read our guide about full color patterns to 3D prints with computational hydrographics.
The most used technologies in color printing are FDM, SLA, SLS/MJF, binder jetting, and material jetting. Let’s look at the pros and cons of each process.
FDM, or fused deposition modeling, is one of the most common and least expensive technologies in consumer 3D printing. FDM 3D printers build parts by melting and extruding thermoplastic filament, which a printer nozzle deposits layer by layer in the build area.
Filaments for FDM printing in various colors. (source: All3DP.com)
FDM is mostly used for direct color printing, with single extruder printers, or for color mixing 3D printing, with dual or multiple extruder printers.
FDM can now also be used for full color 3D printing with the da Vinci Color 3D printer. With a colorless filament that is dyed using CMYK inkjet cartridges right before being extruded, it produces colored parts in a similar way to a color 2D printer.
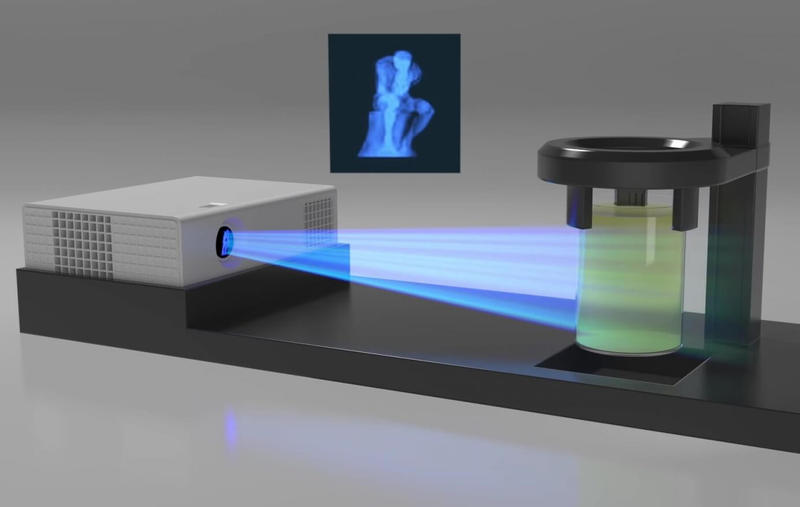
SLA, or stereolithography 3D printing, uses a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic in a process called photopolymerization. SLA parts have the highest resolution and accuracy, the clearest details, and the smoothest surface finish of all plastic 3D printing technologies.
Colored SLA parts, 3D printed with Formlabs Color Kit and Standard Resins.
SLA offers the possibility for color matching almost any custom color using Formlabs Color Kit, the first integrated color-mixing solution for SLA 3D printing. Thanks to their smooth surface finish, SLA printed parts can also easily be post-processed, painted, and used for applying hydrographics.
Thanks to their smooth surface finish, SLA printed parts can also easily be post-processed, painted, and used for applying hydrographics.
White Paper
Looking for a 3D printer to realize your 3D models in high resolution? Download our white paper to learn how SLA printing works and why it's the most popular 3D printing process for creating models with incredible details.
Download the White Paper
Selective laser sintering is the most common additive manufacturing technology for industrial applications, trusted by engineers and manufacturers across different industries for its ability to produce strong, functional parts.
Dyed SLS 3D printed parts. (source: Hubs)
SLS 3D printers use white, grey, or black nylon powder as a raw material. While the parts cannot be directly printed in color, they can be dyed or painted in post-processing.
White Paper
Looking for a 3D printer to create strong, functional parts? Download our white paper to learn how SLS printing works and why it's a popular 3D printing process for functional prototyping and end-use production.
Download the White Paper
The binder jetting 3D printing technology is similar to SLS and MJF printing but uses a colored binding agent to bond powdered sandstone material instead of heat.
Parts produced with binder jetting have a porous surface and are very brittle, which means that this process is recommended only for static applications, such as creating full-color figurines and concept models.
Figurines printed with binder jetting. (source: Shapeways)
Material jetting 3D printers combine traditional inkjet printing with the use of photopolymer resins, by depositing droplets of the material on a build tray similar to 2D printers, which then gets hardened by UV light.
This process offers a myriad of color possibilities and can create photorealistic parts with vibrant colors. However, the parts have poor mechanical properties, are heat-sensitive, and the entry price for this technology is the highest of all color 3D printing options.
Color 3D printing with material jetting. (source: Hubs)
| FDM | SLA | SLS | Binder Jetting | Material Jetting | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Accuracy | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Surface Finish | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Ease of Use | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| Complex Designs | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| Description | The print head melts and extrudes thermoplastic filament | A laser solidifies liquid resin | A laser or light source sinters nylon powder | A binding agent bonds sandstone powder | An inkjet-like print head cures droplets of resin |
| Materials | Thermoplastic filaments | Varieties of liquid resin | Varieties of polymer powder | Sandstone | Varieties of liquid resin |
| Color 3D printing options | Direct color, color mixing, or full color | Color matching | None | Full color | Full color |
| Post-processing with colors | Painting (requires a lot of post-processing) Hydrographic printing | Painting Hydrographic printing | Dyeing Painting Hydrographic printing | Painting Hydrographic printing | Painting Hydrographic printing |
| Applications | Basic modelmaking | Rapid prototyping, miniatures and models, medical models | Rapid prototyping, end-use parts | Miniatures and models | Rapid prototyping, miniatures and models, medical models |
| Price | Budget printers and 3D printer kits start at a few hundred dollars. Higher quality mid-range desktop printers start around $2,000, and industrial systems are available from $15,000. Higher quality mid-range desktop printers start around $2,000, and industrial systems are available from $15,000. | Professional desktop printers start at $3,750, large-format benchtop printers at $11,000, and large-scale industrial machines are available from $80,000. | Professional benchtop printers start at $19,000. | Full color 3D printers start around $60,000. | Full color 3D printers start around $50,000 and large-scale machines are available from $100,000. |
Video Guide
Having trouble finding the best 3D printing technology for your needs? In this video guide, we compare FDM, SLA, and SLS technologies across popular buying considerations.
Watch the Videos
Color 3D printing empowers engineers and designers to save money and time with looks-like prototypes, movie makers to turn digital models into props, model makers to create vibrant miniatures, medical professionals to produce accurate anatomical models, and more.
Rapid prototyping helps companies turn ideas into realistic proofs of concept, advances these concepts to high-fidelity prototypes that look and work like final products, and guides products through a series of validation stages toward mass production.
The development team at birdkids used SLA 3D printing to create prototypes in color.
Concept models in color can demonstrate an idea to stakeholders, create discussion, and drive acceptance or rejection using low-risk concept explorations.
At later stages, realistic looks-like prototypes in color can give a better idea of what an end product will look like and how the end-user will interact with it. Ergonomics, user interfaces, and overall user experience can be validated with 3D printed looks-like prototypes before spending significant design and engineering time to fully build out product features.
Color matching 3D printing or full color 3D printing also allows product development teams to experiment with different color options and run studies with customers before moving into production.
In the entertainment industry, 3D printed props and models are blurring the line between physical models and digital effects. Artists create realistic, detailed models using 3D modeling software and then bring them to life in a matter of hours using 3D printing. High-resolution 3D printing processes, like SLA, can reproduce even the most complex parameters of a design, such as skin texture.
A behind-the-scenes look at visual effects (VFX) and design studio Aaron Sims Creative’s process to design of Stranger Things’ Demogorgon.
Props masters, such as Russell Bobbitt for Marvel movies and Jaco Snyman for the Raised by Wolves series, as well as visual effects (VFX) and design studio Aaron Sims Creative for Stranger Things, have adopted the technology, as it significantly saves time in prop making and fuels creativity in the design process. The creation becomes more flexible and fluid, and props and models can be created in an efficient manner.
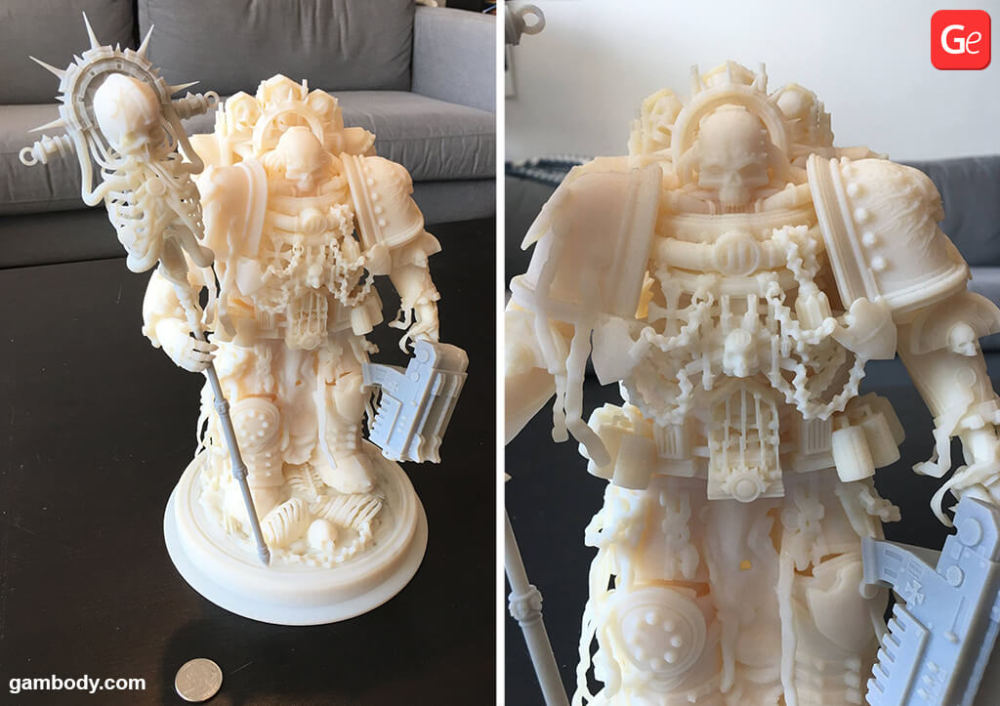
Without a doubt, 3D printing has revolutionized the creation of custom miniatures and figurines, whether for model making, tabletop games, collectibles, or other hobbies.
As full-color 3D printers are often out of budget for hobbyists and model makers traditionally hand-paint models anyway, the most popular way to create colorful models is to paint them after 3D printing.
For example, artists at Modern Life Workshop combine 3D modeling design with SLA 3D printing to create hyper-realistic celebrity portraits. The artists use the digital freehand sculpting software ZBrush to create detailed models on the computer. Then, they 3D print the designs on an SLA 3D printer and paint the parts by hand.
The artists from Modern Life Workshop create hyper-realistic sculptures with ZBrush and 3D printing.
In gaming, online communities have sprung up around tabletop games like Dungeons & Dragons, for which gamers use 3D printers to create one-of-a-kind D&D 3D printed miniatures, figurines, terrains, landscapes, and other board game accessories.
Professional model-making companies, like DM-Toys, also use 3D printing to accelerate prototyping and production cycles of custom models.
Global play and entertainment company Hasbro also uses the technology to create Hasbro Selfie Series figures—a groundbreaking endeavor to use 3D printing to manufacture personalized action figures at scale. For the first time, fans are now able to scan their face with a smart device and have a custom-made look-a-like action figure delivered to their door.
In healthcare, radiologists, surgeons, and biomedical professionals are increasingly turning to 3D printing to create accurate 3D models of anatomical features that can be used as reference tools for preoperative planning, intraoperative visualization, and education.
3D printing empowers medical professionals to create complex models with intricate details that would be impossible to produce with other technologies.
A fully colored pancreas model that was produced with SLA 3D printing and then painted with acrylic.
High-detailed color models are excellent in resident education programs, where each blood vessel or organ can be directly 3D printed or painted in different colors for easy classroom viewing.
Furthermore, patient-specific surgical models that are based on patient scan data are becoming increasingly useful tools in today’s practice of personalized, precision medicine.
Whether it is color matching to create 3D printed parts in almost any custom color, or printing high-resolution parts that can be painted to create hyper-realistic models, SLA 3D printing delivers incredible detail and seamless performance at an affordable price point.
Start 3D printing your own 3D printed parts on the Form 3 and bring your biggest ideas to life with the Form 3L.
See the Form 3See the Form 3L
Color 3D printing: What are your options?
3D Learning Hub
See all categories
Contents:
- Introduction
- Direct color 3D printing
- Indirect color 3D printing
- What is your next color 3D printing project?
Introduction
Direct color 3D printing
Direct color 3D printing allows you to use a colorful filament to 3D print your models. It works with FDM technology. You can achieve bright colors and nice details, depending on the 3D printer and the quality of filament you buy. Direct color 3D printing, however, won’t allow you to mix the colors, so the effect won’t be photo-realistic.
It works with FDM technology. You can achieve bright colors and nice details, depending on the 3D printer and the quality of filament you buy. Direct color 3D printing, however, won’t allow you to mix the colors, so the effect won’t be photo-realistic.
FDM: single extruder
It is possible to achieve colorful prints even if the FDM printer has just a single extruder. What do you need to do to achieve that? When you send your 3D files for 3D printing, set multiple tasks using your slicing software. The software will produce a g-code with instructions for the 3D printer to stop at a certain level. Then you switch out the filament and the printing job is restarted.
While it’s the most obvious way, it can be quite time-consuming and a bit risky. But there are also solutions where you use one extruder to combine multiple filaments. Then, your model needs to contain information about which parts use certain colors, and the device outputs the colors into the extruder. The video below shows this case of multicolor 3D printing.
The video below shows this case of multicolor 3D printing.
FDM: multiple extruders
Another solution for direct color 3D printing is 3D printers with multiple extruders. This is not such a new development, a dual extruder is used especially for printing dissolvable supports. But you can also use them to print with two colors of filaments. There are different devices available on the market, some with even 4 extruders.
Indirect color 3D printing
Indirect color 3D printing applies the color from an external source during the printing process. This technology is much more precise and allows for a more realistic appearance of the 3D prints, but in most cases, the process requires professional knowledge. It is important for you to remember that indirect color 3D printing uses CMYK color mode and you need to take that into consideration when preparing your model.
ColorJet technology
With ColorJet technology you have a choice of 36 000 colors! Your 3D files need to carry the color and texture information before it’s sent for multicolor 3D printing. During the 3D printing process, fine, sandstone-like powder is used. A layer of the material is spread, then the printing heads apply color that adheres to the layer. The next layer is spread and the process repeats.
The results are pretty impressive! Thanks to the wide range of colors, you can achieve so much more than with direct color 3D printing. This solution is especially interesting for designers to present proof of concepts to their clients, architects to produce visual models, and for game character production.
PolyJet technology
PolyJet technology works with liquid resin and prints at impressive 16 microns which assures very fine detail and good surface finish of your 3D models. In between the layers, color is applied and cured with UV light. This technology lets you adjust even the level of transparency of the colors.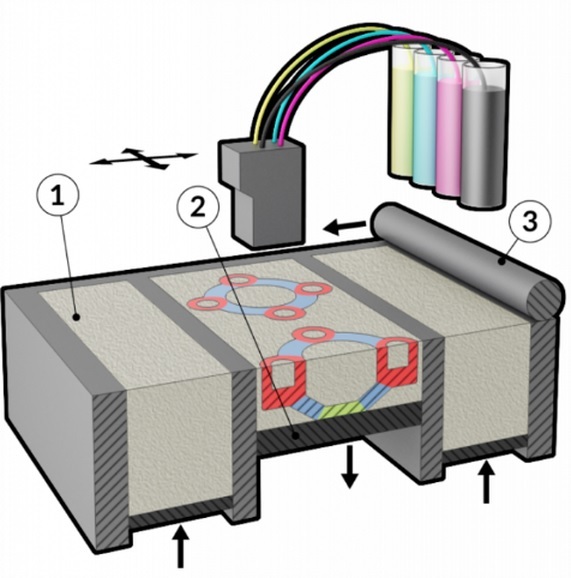
HP Jet Fusion
HP’s 3D printing solutions are revolutionary in the world of Additive Manufacturing. HP’s engineers started by studying light and how to use it in order to produce evenly colored 3D printing, at the quality of regular 2D printers.
Their color 3D printer uses an innovative binding agent to fuse the plastic powder locally. The color is applied at a level of 3D printing DNA called the ‘’voxel’’, a three-dimensional pixel. Thanks to that you can achieve color 3D printing even with very complex objects.
Mimaki
https://mimaki.com/special/3d_print/gallery.html
This company is a true champion of color 3D printing. When we talk about full-color 3D printing, they are a real winner, bringing to the market machines capable of using over 10 million colors! Their technology is based on UV light which was originally developed for regular, paper printers.
A layer of powder material is spread, and then pigmented resin is dropped with the inkjet head of the 3D printer. The next step is UV curing the resin into a solid-state. The process repeats and your 3D prints are produced in great, vibrant colors.
Desktop 3D printers for indirect color 3D printing
Some companies take yet another take on indirect color 3D printing in order for it to be reachable from your desk. There are a few ways to deal with that. One of them is actually using paper. CMYK inks are dropped on the paper and then the layer of paper is die-cut and fused with the next one. The downside is a risk of the ink spreading or bleeding.
Another solution is the ink absorbent filament. FDM 3D printer lays a layer of the filament and before the next layer is applied, it drops CMYK ink. This technology is impressive, although the results can be quite soft and translucent. Check out Da Vinci Color to discover more.
What is your next color 3D printing project?
There are plenty of opportunities for you to start using color 3D printing. From FDM printers to industrial-grade machines, multicolor 3D printing is available for you right now. Depending on your project, one of the technologies will surely meet your needs.
From FDM printers to industrial-grade machines, multicolor 3D printing is available for you right now. Depending on your project, one of the technologies will surely meet your needs.
Do you already have a color 3D printing project in mind? Don’t wait any longer! Achieve the best quality with an online 3D printing service like Sculpteo. Simply upload your STL files or contact us in case of any questions.
Related Topics
- Return to Top
Get the latest 3D printing news delivered right to your inbox
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter to hear about the latest 3D printing technologies, applications, materials, and software.
3D color printing - how it works
3D color printing - how it worksColor 3D printing - how it works
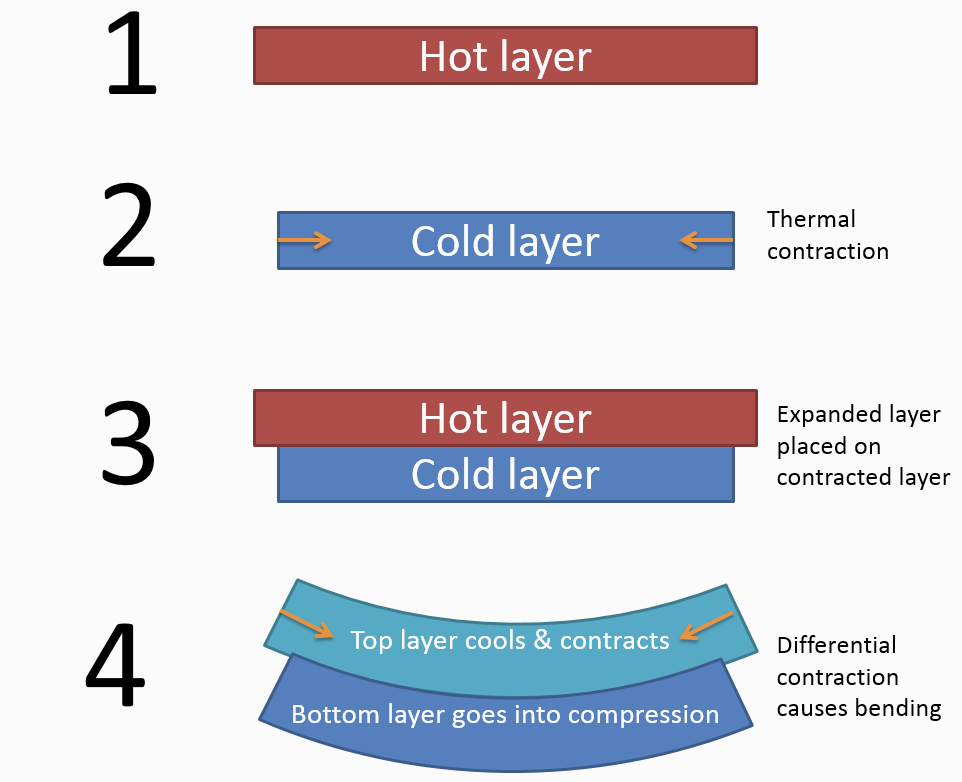
3D printing is a layer-by-layer method for virtually anything, from simple figurines to jewelry, weapons, and aerospace parts.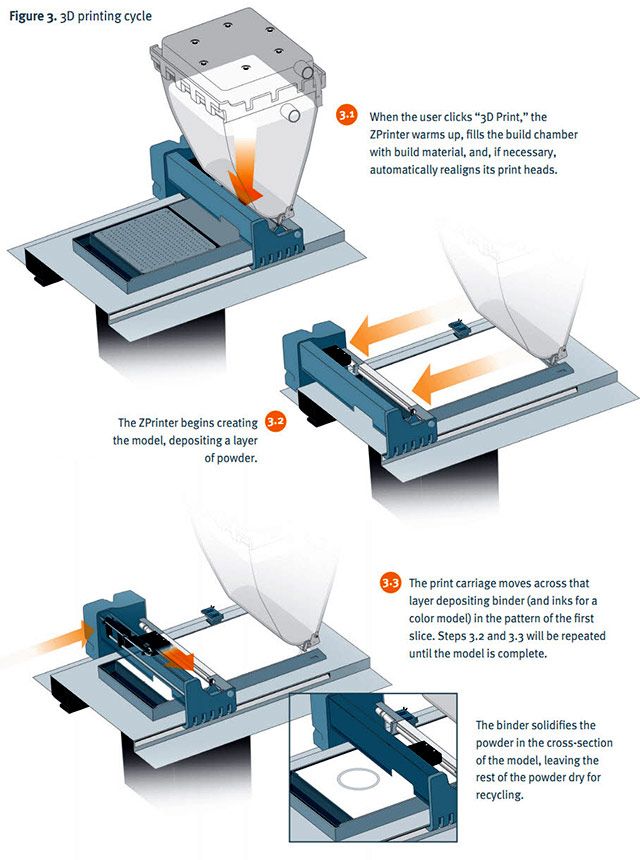 Three-dimensional printing has long been an integral part of the creation of complex architectural and technological objects. Now 3D printing is actively developing and reaching the user level - fast and high-quality production of objects gives 3D technologies significant competitive advantages over traditional production methods. And color 3D printing opens up a lot of opportunities for creating various products in all their color diversity.
Three-dimensional printing has long been an integral part of the creation of complex architectural and technological objects. Now 3D printing is actively developing and reaching the user level - fast and high-quality production of objects gives 3D technologies significant competitive advantages over traditional production methods. And color 3D printing opens up a lot of opportunities for creating various products in all their color diversity.
Today, the most commonly used color 3D printing material is gypsum, a material that allows printing photorealistic color models at a resolution of 600×540 dpi. Gypsum is ideal for 3D printing figurines, figurines, game characters, artwork, decorative and art objects, architectural models, corporate souvenirs and more. In general, the material can be described as hard, hard, brittle and slightly rough, perfect for stationary models.
The color 3D printing process is as follows:
- First, a 3D model is created using special software such as: SolidWorks, Maya, Sketchup, Blender or any other similar software.

- The model is then sliced into separate images corresponding to each printed layer. The starting material for printing is gypsum powder, which is applied in an even layer on the base surface.
- The printheads move in a horizontal plane, layer by layer, applying a glue-like substance and a tint of a predetermined color to a certain area of the future model. The cycle is repeated until the 3D model is "grown".
- After printing is completed, the finished product is carefully removed from the printer and cleaned of excess powder using a jet of compressed air.
- Next, the object is completely immersed in glue, which fills all the micro-holes of the model, giving it the final hardness, color saturation and gloss. And the unused powder is automatically recycled and can be reused for 3D printing.
3D printing is much faster than standard production technologies, and the products produced by professional 3D printers are of high quality, high precision and have a wide range of applications.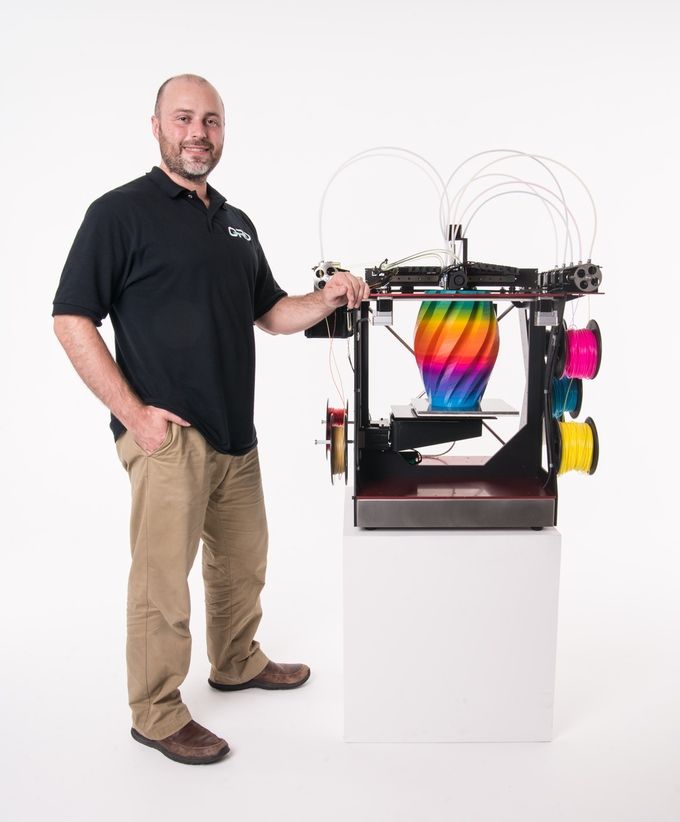
This video demonstrates how the CubicPrints 3D printing service creates colorful objects on the Zprinter 650 professional 3D printer.
Color 3D printing - technology and equipment features
Today, printing of three-dimensional objects is available to everyone. Even at home, you can create three-dimensional models on compact 3D printers from a variety of materials. Color 3D printing works on the same principles as the method of building products in a single color. The availability of equipment has brought technology into the category of practical, original entertainment. However, multi-color 3D printing is also used to solve research problems and implement global projects.
Application areas for color 3D printing
3D printing is rapidly progressing, as the rapid and high-quality creation of prints gives the technology significant advantages over classical production methods. Most printers work with only one color, which is enough when prototyping or building engineering projects. When it comes to the artistic use of 3D equipment, color or combined 3D printing is needed. The technique also helps designers to simultaneously analyze the aesthetics of the design and its functional characteristics.
Most printers work with only one color, which is enough when prototyping or building engineering projects. When it comes to the artistic use of 3D equipment, color or combined 3D printing is needed. The technique also helps designers to simultaneously analyze the aesthetics of the design and its functional characteristics.
Full-color 3D printing provides a wide range of possibilities for producing objects in a wide variety of shades and halftones.
The advantages of the technology were evaluated in various industries:
• construction and architecture - to build demonstration models of buildings;
• Medicine - for students to practice on realistic models of human internal organs, doctors test new techniques, develop devices for the disabled;
• education - for teaching on practical visual aids that reflect the features of a particular subject;
• fashion and design - well-known couturiers already offer entire collections printed on a 3D printer;
• Jewelery - to replace hand-made stencils, printed;
• Art and Hobbies - to create exclusive figurines or mass-produce copies of famous masterpieces.
Features of working with color
Creation of color models is possible on devices operating on ColorJet Printing (CJP) full-color inkjet 3D printing technology. Today it is the most common method of growing volumetric objects.
Two-color 3D printing and construction in various colors takes place in several stages:
1. Creation of a three-dimensional model using special software.
2. The model file is cut into thin layers corresponding to the printed layers.
3. The gypsum powder is placed on the work platform in an even layer.
4. The printhead moves in a horizontal plane, applying adhesive plus color to specific areas.
5. The cycle is repeated until the complete construction of the 3D object.
6. The finished object is removed from the chamber, cleaned of powder residues with a stream of compressed air.
7. The model is completely immersed in a special compound that fills micro-holes, giving greater strength and color intensity.
8. Unused powder is recycled and reused.
The resulting products are distinguished by precision, high surface quality and a wide range of applications.
Two-color printing on a 3D printer can also be performed using FDM technology. The consumable resource in the form of a polymer rod is sent to the extruder, where it is heated. The molten mass through the nozzle is placed in layers along the established trajectory, forming the final model. The difficulty lies in the need to install a new plastic when you need to change the color of a 3D print. The calibration procedure is complicated, so fused filament printers are much less in demand.
Professional color 3D printers are divided into categories according to the purpose of operation, the complexity of operation, the required level of skill of the operator who controls the process. Equipment modification affects not only the quality of the final product, but also the price of the 3D printing service.
Conclusion
Multicolor printing is an interesting, useful technology that is constantly evolving.