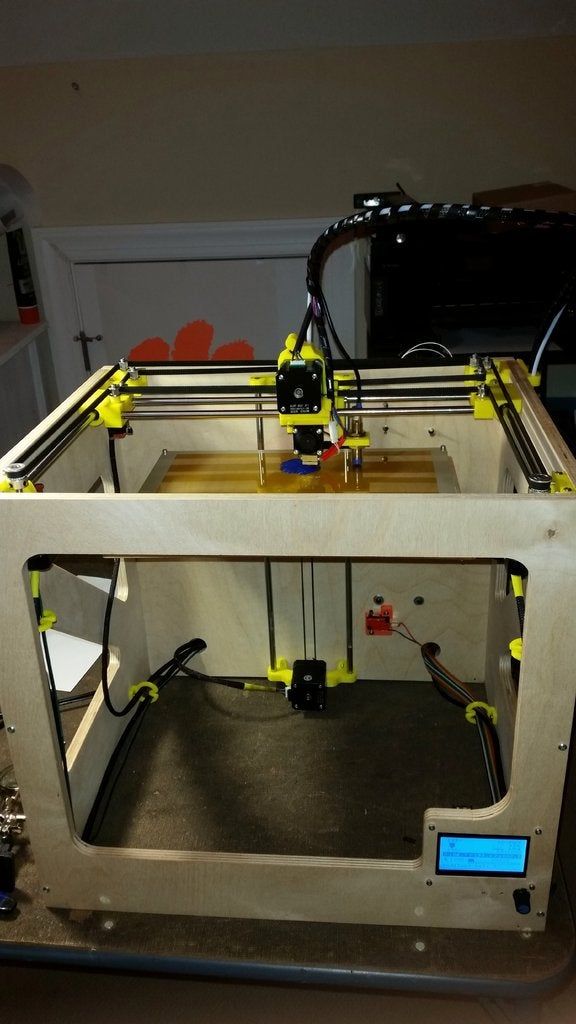
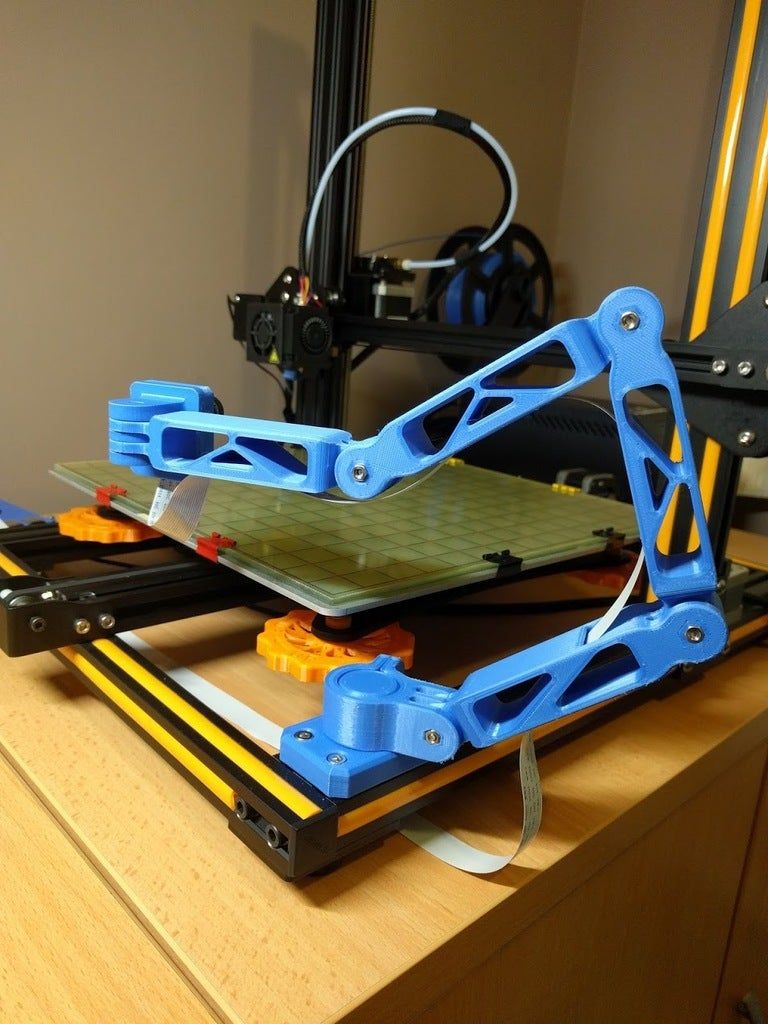
What is a delta 3d printer
How to Choose Between Cartesian and Delta 3D Printers — Fargo 3D Printing
In 3D printing, there are several different styles of printers. The two most common desktop 3D printer styles are Cartesian and Delta. These printers both use Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) technology but have different ways to navigate the print head through the 3D print space.
Cartesian
A Cartesian Printer.
From: All3DP
Cartesian printers are named after the Cartesian coordinate system that uses X, Y, and Z coordinates to plot points. This system of coordinates is used to determine the location of the print head and the extruder. Cartesian printers do this through a system of rails which are used to move the print head and the print bed to position the extruder anywhere in the 3D space.
Pros
One of the greatest advantages of Cartesian printers is their popularity. Since Cartesian printers are the most widely used type of printer, there is far more support for users of these printers than for users of Delta printers. It is easier to find parts and to repair Cartesian printers because of this solid market.
In addition, prints from a Cartesian printer tend to have a better surface finish than prints from a Delta printer. This is because Cartesian printers have more rigid axes, which allow less room for error when the print head moves within the 3D space.
Cons
There are no overall problems with Cartesian printers. Most issues that arise are specific to different brands. As such, any disadvantages of Cartesian style printers depend on the manufacturer. Check out our troubleshooting and guide pages to see common issues with various 3D printer brands and models.
Delta
A Delta Printer.
From: All3DP
Delta printers, like Cartesian printers, also work within the Cartesian plane. However, they use a different system to navigate and locate the print head within the 3D space.
A delta printer consists of three arms on rails that move up and down independently to move the print head. Delta printers use trigonometric functions based on the angles that these arms create to determine the precise location of the print head within the 3D print space.
Delta printers use trigonometric functions based on the angles that these arms create to determine the precise location of the print head within the 3D print space.
Pros
Delta printers have circular print beds which gives them a more efficient use of the printing space, especially when printing circular prints. Additionally, many of the print beds are non-moving, which can be an advantage for some prints. Due to their design, Delta printers can also print taller objects than most Cartesian printers.
One of the main advantages of a Delta printer is its speed. These printers were designed for quick printing. Delta print heads are built to be as light as possible, which results in a quicker printing process.
Cons
However, this design’s focus on speed results in several disadvantages for the printer. One is the precision of the printer. As the speed of the printer increases, its precision decreases. Because of this, Delta printers tend to print with less detail and a rougher surface finish than Cartesian printers.
Another main disadvantage is the Bowden style extrusion. To reduce the weight of the print head, the stepping motor is removed and placed on the body of the printer. The filament is then fed to the print head using a Bowden tube. This style of extrusion limits the number of filaments that can be used and can cause binding within the tube itself. This is a problem that is currently being addressed by Zesty Technology and their new Nimble extruder drive, which is lighter than a standard extruder drive or stepping motor. Learn more about Bowden extrusion here.
Which One Should You Choose?
Diagram of a Cartesian Printer (left) and a Delta Printer (right).
From: Printspace3D
When choosing between them, you should consider what you want from the printer. Cartesian printers often come preassembled and work right out of the box. In addition, as they are more popular, there is more customer support for Cartesian printers. Delta printers often come in kits and need to be assembled before use. They are also very advantageous when making tall objects.
They are also very advantageous when making tall objects.
Get updates, deals, and more great posts by joining our community of over 6,000!
[sexy_author_bio]
What is a Delta 3D Printer? Pros, Cons, and Best Brands
3D Insider is ad supported and earns money from clicks, commissions from sales, and other ways.
3D printers are common enough nowadays that just about everyone has probably seen one in action at some point. Particularly popular are FDM printers, or those that print using plastic filament. However, not many may know that there are still several types of FDM printers, with each one having a set of advantages and drawbacks.
In this article, we turn the spotlight to Delta 3D printers. They are easy to identify with their triangular form factor. What is a Delta 3D printer, and how does it work? How does it compare to the “standard” 3D printer?
What is a Delta 3D printer, and how does it work?
Before diving into what a Delta 3D printer, let’s define what the “usual” 3D printer is so that we have a point of comparison.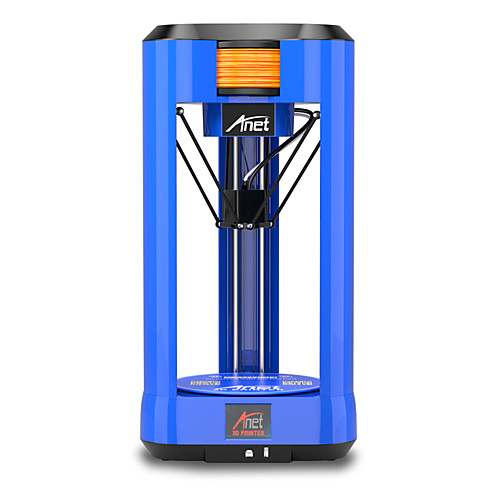 A large majority of the desktop 3D printers that you can see nowadays are what we call “Cartesian” 3D printers. This is so-called because the print head moves according to the Cartesian coordinate system – that is, the x, y, and z directions. A set of three unique numbers are assigned to every single point in a 3D model, which corresponds to its location in 3D space defined by Cartesian coordinates.
A large majority of the desktop 3D printers that you can see nowadays are what we call “Cartesian” 3D printers. This is so-called because the print head moves according to the Cartesian coordinate system – that is, the x, y, and z directions. A set of three unique numbers are assigned to every single point in a 3D model, which corresponds to its location in 3D space defined by Cartesian coordinates.
A Delta 3D printer takes a different approach to locate points in 3D space. Instead of a print head that moves along the forward-backward, left-right, and up-down axes, the print head is instead mounted on three moving arms. These three arms independently push and pull on the print head to control its position.
There is a sort of “gray area” when it comes to distinguishing between Cartesian and Delta 3D printers. This is because Delta 3D printers still plot points along the Cartesian coordinate system. However, the coordinates have to be translated to the specific angles that each of the three articulating arms need to be at. This translation is done via simple trigonometric functions.
This translation is done via simple trigonometric functions.
The three arms of a Delta 3D printer give it its distinct triangular frame, so identifying one is pretty easy. It typically has a stationary circular print bed. Delta 3D printers are thin and long, making them suitable for printing tall and narrow models. Cartesian and Delta 3D printers essentially use the same types of filaments, with special consideration going towards flexible filaments.
Aside from the two movement types of FDM printers that we have mentioned here, there are two others that are much less common. The first is the polar 3D printer, which has a print bed that moves and rotates relative to a stationary print head. The rarest type of FDM printers is the Selective Compliance Assembly Robotic Arm (SCARA) printer, a highly precise and incredibly compact 3D printer that looks like it came straight out of a science fiction movie.
Pros and cons of Delta 3D printers
On the surface, a Delta 3D printer seems like a very good alternative to the usual Cartesian 3D printer.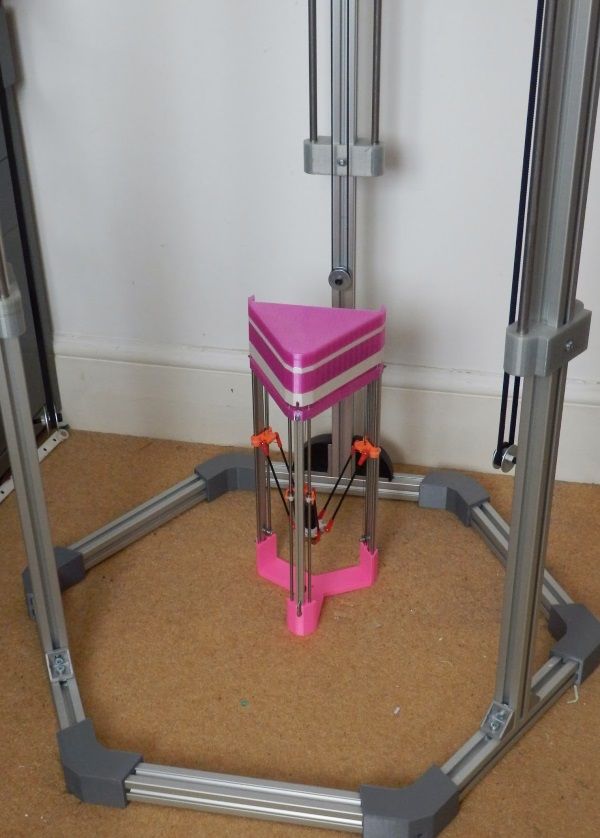 In some way, this is true. It’s not perfect, though. If you’re considering getting a Delta 3D printer, then here are the pros and cons to consider:
In some way, this is true. It’s not perfect, though. If you’re considering getting a Delta 3D printer, then here are the pros and cons to consider:
PROS
1. Fast
Delta 3D printers were built for speed. Each of the articulating arms is powered by a separate stepper motor, allowing them to move the print head very quickly. The print head itself is built to be very small and light. All Delta 3D printers use a Bowden extruder which moves a lot of the moving parts away from the print head.
By keeping the print head light and having it supported by three arms, Delta 3D printers eliminate the major speed limitation of Cartesian 3D printers. In a Cartesian 3D printer, the large of the weight of the print head generates a lot of momentum as it moves, making it prone to “overshooting” from its intended position. Any slight error will accumulate as the project proceeds, resulting in an almost unusable print.
Print speeds of up to 300 mm/s are not unheard of when using Delta 3D printers. Cartesian 3D printers typically print at about a fifth of that speed. If you are running a 3D printing business where quick turnover is valuable, then a Delta 3D printer would definitely be the better choice.
Cartesian 3D printers typically print at about a fifth of that speed. If you are running a 3D printing business where quick turnover is valuable, then a Delta 3D printer would definitely be the better choice.
2. Suitable for tall models
Due to the way that Delta 3D printers work, their build platform is limited to the area that lies between the three articulating arms. This is a very small area, so the manufacturers of Delta 3D printers compensated by adding quite a lot of height. The arms of a Delta 3D printer can move up and down along its columnar body, allowing for the printing of very tall models. Ornate columns and architectural models of towers are especially suited to Delta 3D printers.
CONS
1. Limited base size
Related to the item above is the fact that Delta 3D printers have a very small circular base compared to Cartesian 3D printers. If you’re working exclusively with a Delta 3D printer, it may be necessary to split models into separate parts.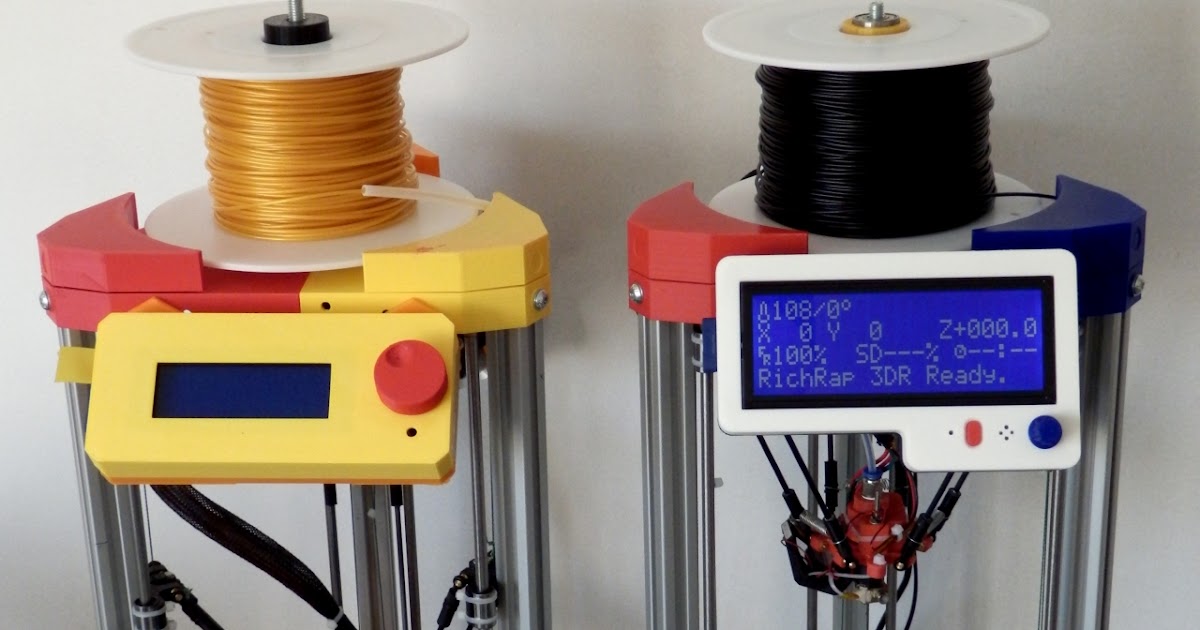 Obviously, this adds a bit of work and introduces more steps to the process where things can go wrong. If you have no plans of building particularly tall and narrow models, then a Delta 3D printer may not be a wise investment.
Obviously, this adds a bit of work and introduces more steps to the process where things can go wrong. If you have no plans of building particularly tall and narrow models, then a Delta 3D printer may not be a wise investment.
2. May not work well with flexible filaments
Delta 3D printers exclusively use Bowden extruders, both because it optimizes the rapid movement of its three arms and because a Direct extruder simply won’t fit inside the print’s narrow space. While the use of a Bowden extruder helps a Delta 3D printer operate rapidly, it also introduces complications if you have to use a flexible filament like TPU or TPE.
As anyone who has ever used flexible filaments before, they are highly prone to deforming inside the extruder assembly. The design of Bowder extruder extends the path of the filament between the extruding gears and the nozzle. This extra room increases the chances of deformation of the filament, especially if you haven’t keyed in the perfect printing parameters.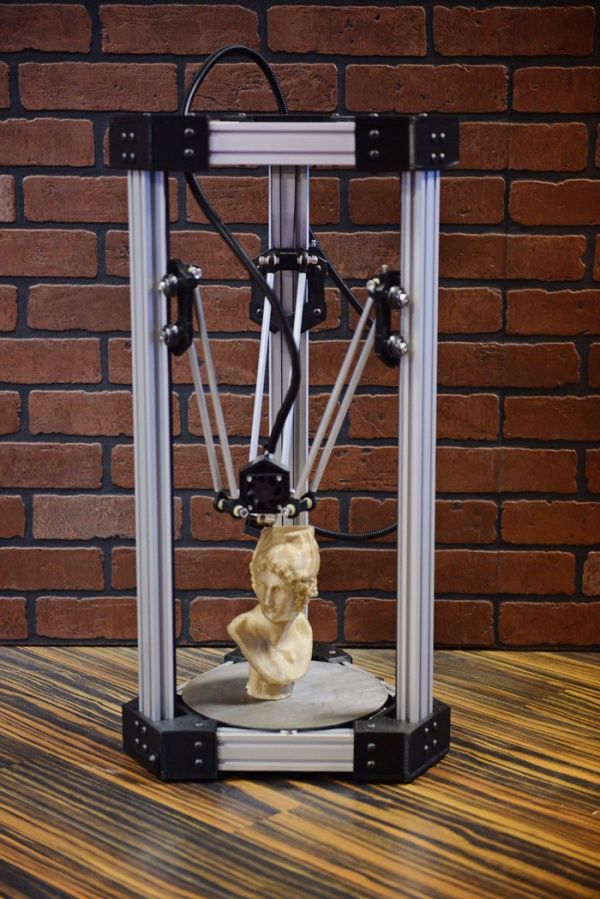 A deformed filament can lead to extrusion problems, or worse, clogging of the nozzle.
A deformed filament can lead to extrusion problems, or worse, clogging of the nozzle.
This does not make printing with flexible filaments impossible with a Delta 3D printer. It only means that there’s going to be a bit more work involved, and you’ll have to anticipating things going wrong more often.
3. Difficult to use and troubleshoot
The major advantage of Cartesian 3D printers becoming so popular is that they are now more user-friendly than ever. Not only can they be purchased fully assembled, but there are also thousands of online communities, help pages, and video tutorials that can help you develop your skill or troubleshoot any problems. In many ways, a Cartesian 3D printer is perfect for a beginner.
The same cannot be said for Delta 3D printers. These printers typically come in separate components that need to be assembled. With more motors and moving parts, there’s also a lot more that could go wrong with a Delta 3D printer. This is doubly difficult as there aren’t a lot of users of Delta 3D printers, and its communities aren’t quite as thriving.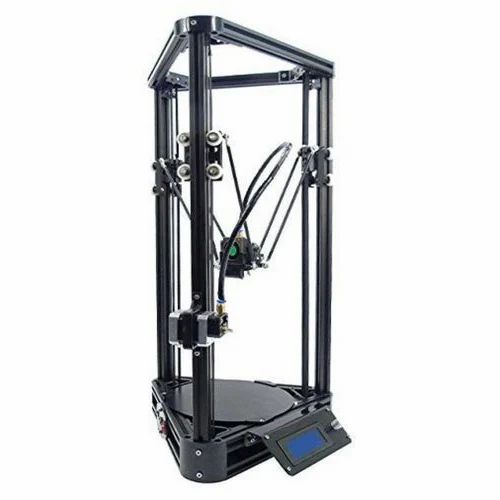 Before you buy a Delta 3D printer, you must already have a deep understanding of the mechanics of 3D printers and be ready to DIY just about everything.
Before you buy a Delta 3D printer, you must already have a deep understanding of the mechanics of 3D printers and be ready to DIY just about everything.
Delta 3D printers can be very useful in certain situations, but they are not going to absolutely replace Cartesian 3D printers. If you’re just starting out, then a Cartesian 3D printer may still be a better option. However, those looking to upgrade both their equipment and their skills would certainly recognize the appeal of a Delta 3D printer.
The top 3 best Delta 3D printers available today
1. Best overall: Monoprice Delta Pro 3D Printer
For the best in desktop Delta 3D printers, it would be a challenge to find a model that’s better than the Monoprice Delta Pro. As its name implies, this is the professional-grade Delta printer from popular 3D printing brand Monoprice. This printer has a huge build area that measures 270 millimeters across and 300 millimeters high. Despite the size, it is delivered fully assembled.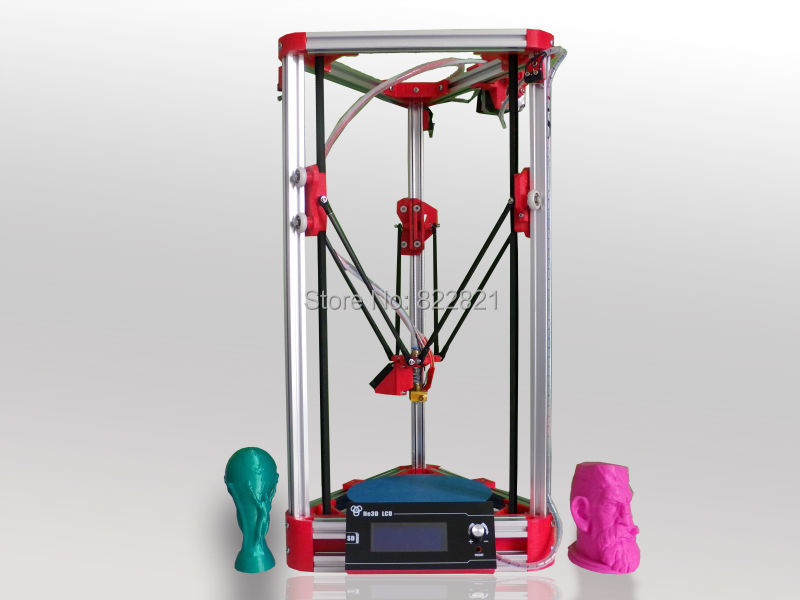 It has an all-metal construction with components that fit together perfectly, leaving no room for wobbling or warping during operations.
It has an all-metal construction with components that fit together perfectly, leaving no room for wobbling or warping during operations.
The Monoprice Delta Pro is a very smart 3D printer. The PID controller keeps the printing temperature very stable, even when the printer is subjected to changing environmental conditions. The extruder temperature can go as high as 310 °C, while the bed can be heated up to 100 °C. High-temperature filaments like PETG, Nylon, and ABS are perfectly suited to the Monoprice Delta Pro.
The Delta Pro can print at resolutions of up to 50 microns and a maximum printing speed of 150 millimeters per second. It comes with an easy-to-use touchscreen interface and can be loaded with 3D models via USB or SD card.
The drawback of the Delta Pro, which is quite common with Delta 3D printers, is that it’s obviously not designed for beginners. It doesn’t come with a lot of documentation, so even setting it up might prove to be frustrating. It’s also quite expensive compared to the other entries in this list, but it also still costs less than $1000. That is not a bad price tag for a Delta 3D printer that claims to have professional-grade quality.
That is not a bad price tag for a Delta 3D printer that claims to have professional-grade quality.
2. Best budget: Monoprice Mini Delta 3D Printer
At less than $200, the Monoprice Mini Delta is an amazing bargain. This is a compact and lightweight 3D printer that even comes with a carrying handle so you can move it around the house. It comes with the usual polished and minimalist design as some of Monoprice’s much pricier models. With black all-metal frames and a pre-built form factor, the Monoprice Mini Delta looks much more professional than most of the other 3D printers in the sub-$200 price range.
Like its more expensive counterparts, the Monoprice Mini can print at resolutions of up to 50 microns. The nozzle can be heated up to 260 °C and the heated bed up to 60 °C. The maximum heated bed temperature is quite problematic, as it may not get hot enough to avoid warping of high-temperature filaments like ABS and Nylon. This is a massive limitation that we cannot overlook.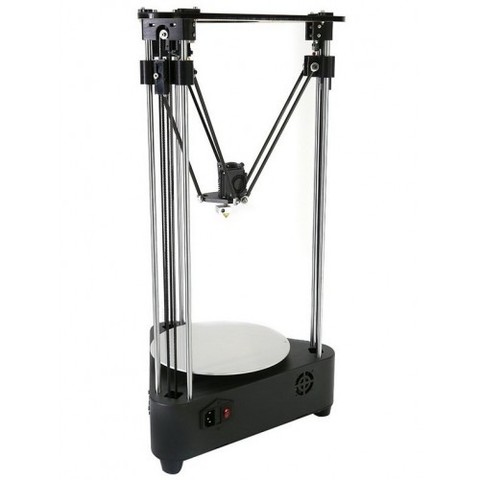 Fortunately, the Monoprice Mini is still a very fast 3D printer that can print at speeds of up to 150 millimeters per second.
Fortunately, the Monoprice Mini is still a very fast 3D printer that can print at speeds of up to 150 millimeters per second.
As you would expect from such a small 3D printer, the build size of the Monoprice Mini is also limited. The build area measures 100 millimeters across and 120 millimeters high – basically the size of an action figure. This build size is fine if you’re just doing 3D printing for fun, but there aren’t many professional uses for the Monoprice Mini.
The Monoprice Mini has a touchscreen user interface which makes navigation easier. 3D models can be loaded via micro USB, a microSD card, or a WiFi connection. We suggest sticking with the microSD card to ensure that your print does not get interrupted.
3. Best value: FLSUN QQ-S Pre-Assembled Delta 3D Printer
If you can spend a little more than the cost of the Monoprice Mini, then you can get the FLSUN QQ-S Delta 3D Printer which is much more versatile. It’s a better Delta 3D printer almost across the board with a bigger build area and a more extensive temperature range.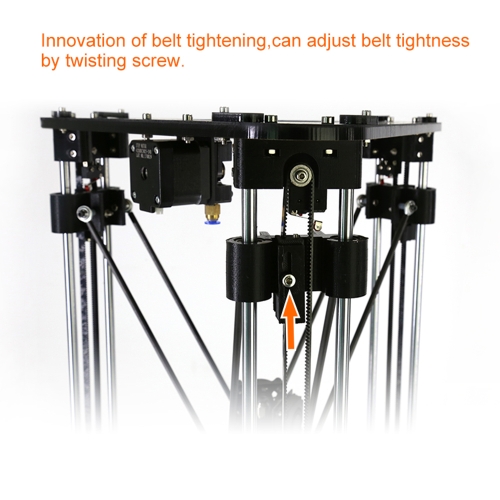 It also still costs less than $500, so you won’t exactly be spending a fortune.
It also still costs less than $500, so you won’t exactly be spending a fortune.
The FLSUN Delta 3D Printer features an all-metal frame and requires a small amount of assembly upon delivery. A spool holder sits at the top of the 3D printer which also doubles as a handle if you need to carry it around. It’s a little less portable than the other entries on this list. However, this isn’t an issue if you have no need to move the printer regularly.
The build area of the printer measures 255 millimeters across and 300 millimeters high, which is almost as big as the Monoprice Delta Pro. It can print features as small as 50 microns and has a maximum printing speed of 300 millimeters per second. Its nozzle temperature goes as high as 270 °C, which should be hot enough for printing with ABS or Nylon. This is perfectly complemented by a bed that can be heated up to 100 °C. Although this still falls short of the recommended bed temperature for some high-temperature filaments, it’s certainly much more manageable with the help of some adhesives.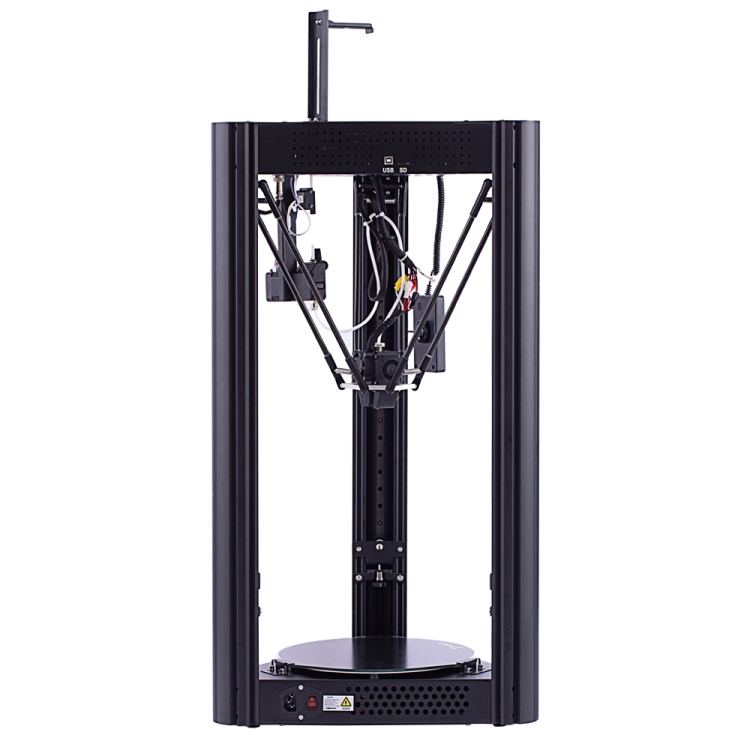
You’ll need to have some amount of mechanical knowledge to set up the FLSUN QQ-S, but it’s an incredibly reliable piece of machinery once it gets going. For its price, it provides incredible value.
Final thoughts
A Delta 3D printer is just one of several movement types developed for FDM printers. It may not have the far-reaching popularity and versatility of Cartesian 3D printers, but it definitely serves a purpose. They may have limited build size, but they make up for it with pure speed.
3D printing professionals know how valuable printing speed can be, especially if you need to create several prints, and you don’t have a lot of time. The good thing about Delta 3D printers is that they achieve very high printing speeds without compromising on quality. If you want good-looking 3D prints made quickly, then you should consider getting a Delta 3D printer.
Warning; 3D printers should never be left unattended. They can pose a firesafety hazard.
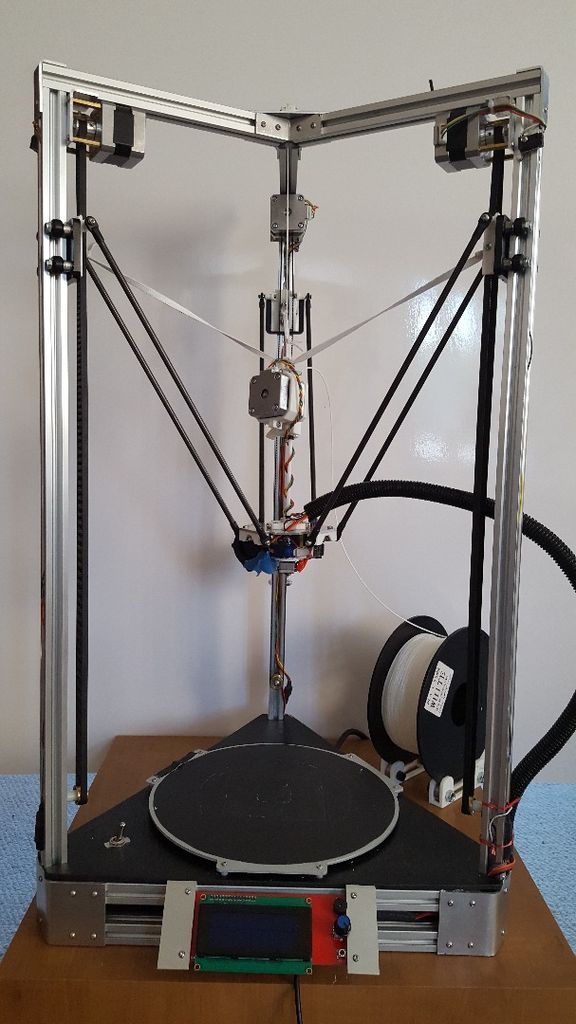
delta printer
Reviews
FLSUN 3D Metal Frame Kossel Delta Kit Anycubic Kossel linear plus FLSUN 3D Metal Frame Large Print Area 3D Printer
The Delta Printer is a 3D printer with Cartesian kinematics (Delta - kinematics) operating in the XYZ coordinate system.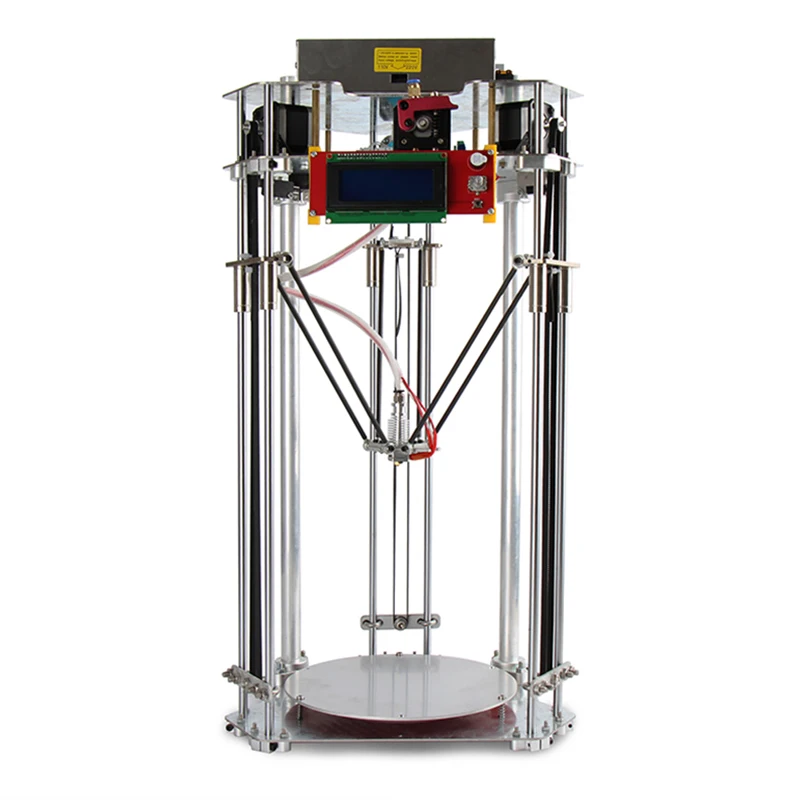 They differ from counterparts with other types of kinematics, higher printing speed, a fixed platform, which avoids “wobble” and the likelihood of distortion, and a large print height along the Z axis due to the vertical arrangement of the rails.
They differ from counterparts with other types of kinematics, higher printing speed, a fixed platform, which avoids “wobble” and the likelihood of distortion, and a large print height along the Z axis due to the vertical arrangement of the rails.
Anycubic Kossel and Anycubic Prediator, very popular in the Russian market, were discontinued and Anikubik did not offer any alternative. But to the delight of fans of fast and beautiful 3D printing, a young and successfully developing Chinese company FLSUN from Shenzhen took advantage of this and offered the market a line of 3D printers Delta . In the sale of the 3DSN store there are models from a warehouse in Russia and on order, wholesale lots.
- Budget Delta Printer - 3D printer Flsun Q5 Delta (Kossel)
Compact budget Delta 3D printer with a modular structure. It has simple assembly, maintenance and convenient operation.
Ø 200 x 200 mm build area
Auto leveling
32-bit motherboard with TMC2208 drivers
High speed 3D printing up to 120mm/s.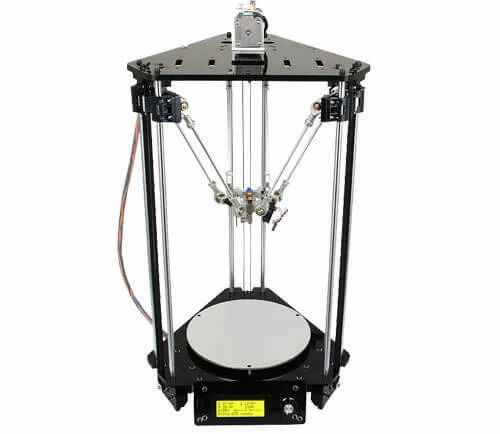
- 3D printer Flsun QQ S PRO Delta Kossel
The FLSUN QQ S PRO 3D Printer (Delta Kossel) is an affordable delta 3D printer offering a fairly large build volume of 255 x 365mm diameter and easy to use features such as automatic bed leveling and the ability to remotely control the printer via Wi-Fi connection -Fi.
Working chamber Ø 255x365 mm
Nozzle working temperature - up to 270 ℃
Heating table temperature - up to 110 ℃
Automatic leveling
Noise level 50 dB
Feeding system: Bowden drive
Filament diameter: 1.75 mm
Nozzle diameter: 0.4 mm
Interface: SD card, Wi-Fi, USB
Size: 286x348x0703 mm
Weight: 13 kg. Equipped with linear rail guides. Glass coated with a special layer for better adhesion.
Construction material: aluminum alloy 6063
Nozzle temperature: ≤ 240 ℃
Table temperature: ≤ 100 ℃
Leveling type: automatic
Motherboard: 32bit
mm/s - 5020mm with
Maximum idle speed: 300 mm/s
Extruder cooling: double fan
Print size: 260x330 mm
Printer size: 440x390x960 mm
Package size: 88x42x20. 5 cm0003
5 cm0003
Weight: 16.5 kg
More interesting articles
2
Subscribe to the author
Subscribe
Don't want
Dreambot 3D printers are reliable high performance devices for professional use....
Read more
0
Subscribe to the author
Subscribe
Don't want
Good afternoon!
In this review, we will introduce the readers of the 3dtoday portal to a line of 3d pro...
Read more
nk.xcfg
Loading
05/10/2016
38285
117
Follow author
Follow
Don't want
“A good tester won't even launch the app. ” (heard at work) Based on real...
” (heard at work) Based on real...
Read more
calibration, setting up a delta 3d printer, which one is better (pros and cons)
3D printers with delta kinematics stand out from other models with a high printing speed of very complex parts. Such devices are quite expensive, but they can be assembled independently. Consider the assembly steps, configuration and nuances of using a delta printer.
Which 3D printer is better - delta or cartesian?
Cartesian (also called Cartesian) and delta printers use the same filaments for printing. In addition, they have the same working parts (extruder, platform, motor), but their location is different.
For Cartesian 3D printers, the extruder or platform moves along the rods of the X, Y and Z axis (Cartesian plane). That is, work items move left, right, forward, backward, up, and down.
Delta 3D printers are based on a different movement system. The machine is equipped with three brackets that support the extruder.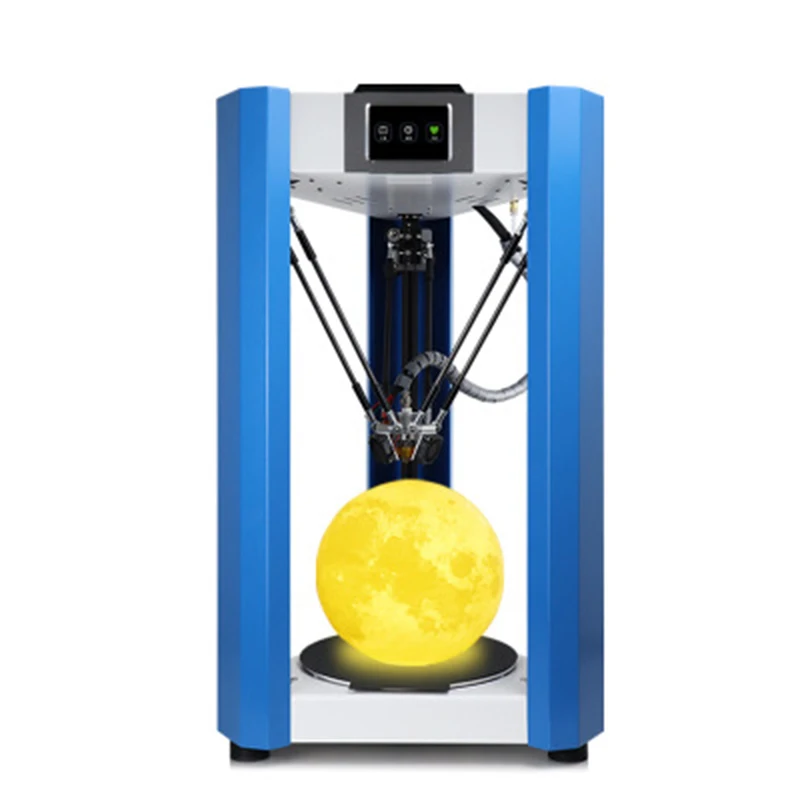 The brackets themselves are attached to three vertical posts, which are arranged in the shape of a triangle. The extruder on a delta printer can move in all directions, and each arm can only move vertically up and down.
The brackets themselves are attached to three vertical posts, which are arranged in the shape of a triangle. The extruder on a delta printer can move in all directions, and each arm can only move vertically up and down.
Considering the structural features of both types of equipment, you can determine which one will be better used for certain purposes. To do this, we highlight the advantages and disadvantages of the Cartesian and delta printers.
Pros and cons of the delta printer
The main advantages of the delta printer are:
- very fast printing of complex objects;
- high detail of thin and small parts of the product;
- easy replacement of the extruder.
Along with the advantages of the delta printer, it also has the following disadvantages:
- a small amount of information about the operation, assembly and configuration of the device;
- complex assembly, adjustment and calibration for the correct functioning of the printer;
- Difficulties with the selection of parameters and settings when printing complex objects at high speed.

Pros and cons of a Cartesian printer
Traditional printers based on the Cartesian coordinate system have a number of advantages when used:
- stable print result in mass production;
- a large amount of free information about the structure, operation, configuration and maintenance of the printer on thematic forums;
- the size of the created product is not limited, since the model for printing on a Cartesian printer can be divided into its component parts.
The main and significant drawback of the Cartesian printer is a much slower print speed than that of the delta device. This is because the Cartesian printer spends a lot of time accelerating and decelerating the system. Because of this, the print head moves more slowly to the desired point.
How to make a Delta 3D printer with your own hands: step by step instructions
Before you start assembling a delta printer, you must select all the parts correctly.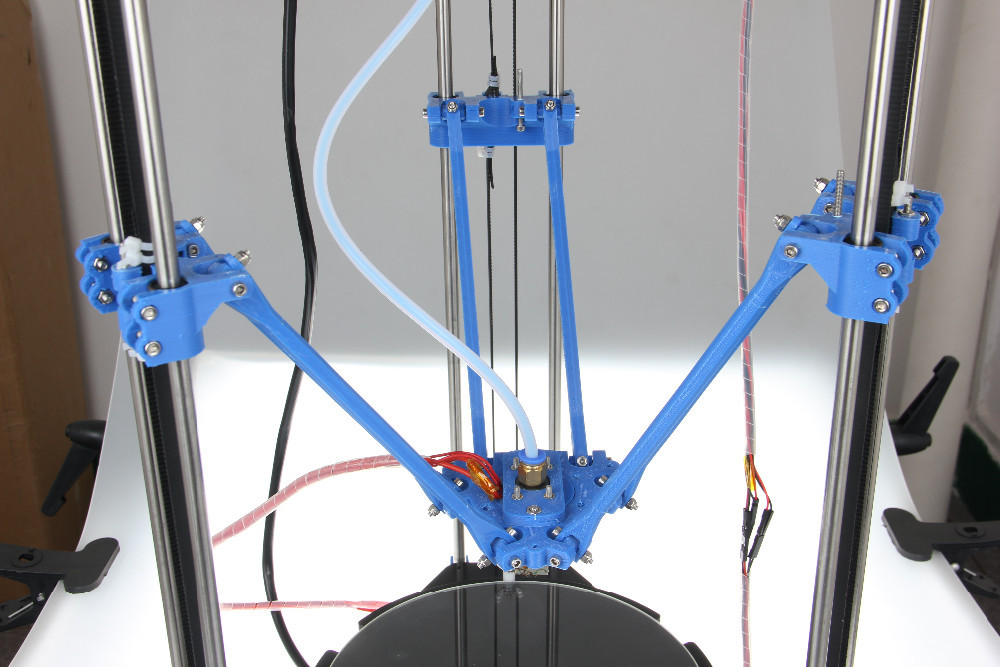 To construct a workable device, the following components are required:
To construct a workable device, the following components are required:
- frame with plastic bushings;
- guide rollers;
- heated table;
- stepper motors;
- RAMPS 1.4 expansion board;
- mechanical stops;
- microcontroller Arduino Mega 2560 R3;
- Threaded rods M5 format;
- step-down voltage regulator;
- power supply 12 V;
- extruder;
- optical limit switches;
- filament spool;
- two coolers (for blowing parts and for blowing drivers).
- display and button with 220V terminal.
Delta 3D printer is assembled in the following order:
- First, the frame and end supports are designed. The lead screws at the top remain free.
- The voltage regulator is soldered to the power input. A microcontroller is installed and a regulator is attached to it from behind.
- The expansion board is then soldered separately to the legs.
 Mechanical stops are set in the direction of correct polarity.
Mechanical stops are set in the direction of correct polarity. - Before setting up the firmware, the printer is connected to electronic components and optical ends. They also install a table, an extruder, coolers and a material reel.
- Firmware for the printer is configured based on its size. Also, when installing, it is important that all the rods are the same length.
Help. To make rods of equal length, it is necessary to screw the hinges on equally cut pieces of the stud on both sides. After that, you should install neodymium magnets on the finished bar and rotate the pin until the hinges are clearly in the middle of the magnet. After adjusting all the rods, it is necessary to fix the thread at the hinge with glue.
Setup and calibration
The most convenient way to calibrate the delta printer is with the OpenDACT utility or Pronterface. These programs will auto-calibrate the equipment by electrical contact between the metal nozzle and the table. This procedure is carried out in three stages:
This procedure is carried out in three stages:
- Aluminum adhesive tape is applied to the work table.
- One end of the wire is crimped into a block, the other two ends are fixed on the radiator and on aluminum tape. After the three ends of the wire are connected to the 3D printer.
- The printer is then connected to a computer from which the auto-calibration program is launched. The whole process can take a long time, as it requires you to select all the necessary geometry parameters.
After or before calibrating the printer, you must also calibrate the device desktop. This will achieve maximum print accuracy. Table calibration is performed as follows:
- Heat the table to +90 °C, tighten the screws and move the print head to the center of the table. A sheet of white paper is placed directly under the extruder nozzle. It should not be strongly pressed down by the nozzle, but it should not “walk” under it either.

- After adjusting the central part of the table, move the sheet to the corners of the work surface and calibrate the table in the same way.
Errors during creation and tips on how to avoid them
When assembling and setting up the delta printer on your own, the user can make a number of errors that will negatively affect the operation of the device:
- Incorrect printer calibration. It will lead to backlash and deviations in the geometry of the structure. And these problems will cause serious distortion of the part when printed.
- Rods slipping off the magnets. It can lead to deformation of the printed product. You can avoid slipping of the rods from the magnets by providing clamps for the rubber bands. They will not allow the hinge to come off the magnet.
- The product cannot be printed to the full working height of the printer. This problem occurs because the print head is not properly positioned. It must be provided with a separate space in the printer that does not take up useful working space.

Learn more