Vacuum casting 3d printing
Vacuum Casting | 3D Printing Technology
Technology
Vacuum casting is a fast and cost-effective copying technique for producing high-quality plastic parts that are comparable to injection-molded components. Using two-component polyurethanes and silicone molds created from a 3D-printed master, this technique is especially suitable for fit and function testing, marketing purposes, or short series of end-use parts.
Why work with Materialise Manufacturing?
At Materialise, we can help you make a big impact with small series production. Our range of 26 carefully selected rubber-like, ABS-like, and PP-like polyurethanes provides an outstanding variety of properties. What's more, if you're looking for a specific finish, the teams at our dedicated vacuum casting center can match the exact finish you need for your parts.
Discover applications of vacuum casting
RHEA Compact, a compact airborne disinfection unit with a housing made from vacuum casting with a high-gloss painted finish
The housing of HOYA's Vision Simulator system is vacuum cast, allowing a fast initial time-to-market and cost-effective design upgrades.
Developed rapidly in response to COVID-19, Materialise's vacuum-cast NIP Connector offered an invaluable solution to overwhelmed hospitals.
Vacuum-cast RPU4, a rubber-like polyurethane with high elongation at break, was an ideal choice for creating this ergonomic ski pole handle.
Designed for use in demanding environments, this ACFM testing device features vacuum-cast rubber-like bumpers and an ABS-like vacuum-cast cover.
Vacuum casting is even used to create sports and leisure products, like this skateboard deck made from PE/PP-like polyurethanes.
Technical specifications
| Maximum build dimensions | The size of the mold is limited by the dimensions of the vacuum chamber (1,900 x 900 x 750 mm) and by the volume of the product (maximum volume: 10 liters) |
| Standard accuracy | ±0. |
| Minimum wall thickness | At least 0.75 mm to ensure the mold is filled properly; for best results, wall thickness of at least 1.5 mm is recommended |
| Surface structure | High-quality surface finish comparable to injection molding |
Materials
Choose from a broad selection of materials when you come to Materialise for your vacuum casting projects.
Material
Rubber-like Polyurethanes
Technology
Vacuum casting
Material
ABS-like Polyurethanes
Technology
Vacuum casting
Material
PE/PP-like Polyurethanes
Technology
Vacuum casting
Work with us: discover our products and services
Want to use vacuum casting in a future project? Discover the services that can help you do it.
Manufacturing services
Innovate and speed up your manufacturing in collaboration with our experts. Rely on our full range of in-house technologies suitable for all industries and applications.
Rely on our full range of in-house technologies suitable for all industries and applications.
Prototyping services
Transform your product development cycle and get the best possible products to market faster. Get unbiased advice and dedicated support from teams committed to your success.
Software
Build your success on a platform of software tools that efficiently manage and control the 3D printing process, allowing you to meet the highest standards of the most demanding industries.
Consultancy
Work with our experts to translate your business challenges into 3D printing opportunities and identify the applications that can help you meet your needs.
Get in touch
Would you like to ask a question or begin working on a project? We’d love to hear from you.
Talk to our team
Train and learn
Get more from your next project with helpful resources dedicated to vacuum casting.
Quick links
How to design for vacuum castingFind related trainingCASE STUDY
HOYA’s Vision Simulator and EyeGenius: 3D-Printed Eyecare Devices
3 min read
CUSTOMER STORIES
PAL Robotics Demonstrates the Perfect Synergy Between Robotics and 3D Printing
7 min read
CASE STUDY
HOYA’s Vision Simulator and EyeGenius: 3D-Printed Eyecare Devices
3 min read
CUSTOMER STORIES
PAL Robotics Demonstrates the Perfect Synergy Between Robotics and 3D Printing
7 min read
© Copyright Materialise 2022
Cookie Statement
Legal terms
Privacy notice
Ultimate Guide to Vacuum Forming 3D Prints
Download the full Guide
as a PDF!
The simple post-processing techniques presented in this guide are an excellent way for professionals to create low-cost silicone molds, threaded inserts for enclosures, vacuum formed parts, and more.
Vacuum forming is a manufacturing process by which a sheet of plastic is heated and pressed over a form to create a part.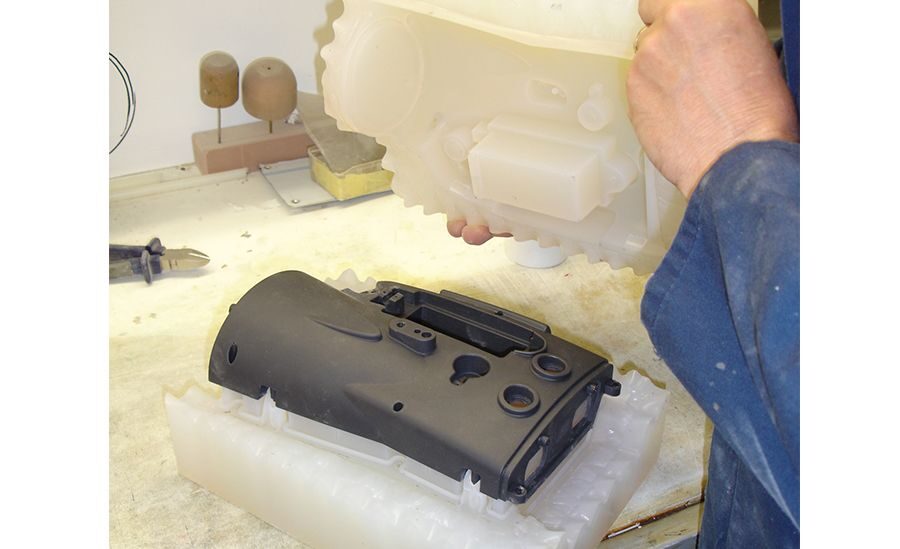 This process is used to create many of the products in your home such as plastic containers, tubs, sink units, and electrical enclosures.
This process is used to create many of the products in your home such as plastic containers, tubs, sink units, and electrical enclosures.
3D printing is a great way for manufacturers to create low cost molds for low volume manufacturing or prototyping.
While we used an industrial vacuum forming machine to achieve our application, you can also build one at home to achieve the same effect.
While working time will vary, this process took us about 1 hour from start to finish.
Supplies
Vacuum forming machine
Sheets of vacuum forming plastic
3d printed mold
Mold mounting fixture
Cutting tool
Eye protection
Heat resistant gloves
Need some of these products? We've curated an Amazon wish list for you.
STEP 1: OBTAIN YOUR MOLD
In order to vacuum form you will need a mold to vacuum form around. Your final parts will be nearly exact replicas of your mold.
You can download molds from sites such as GrabCAD, but we chose to design ours.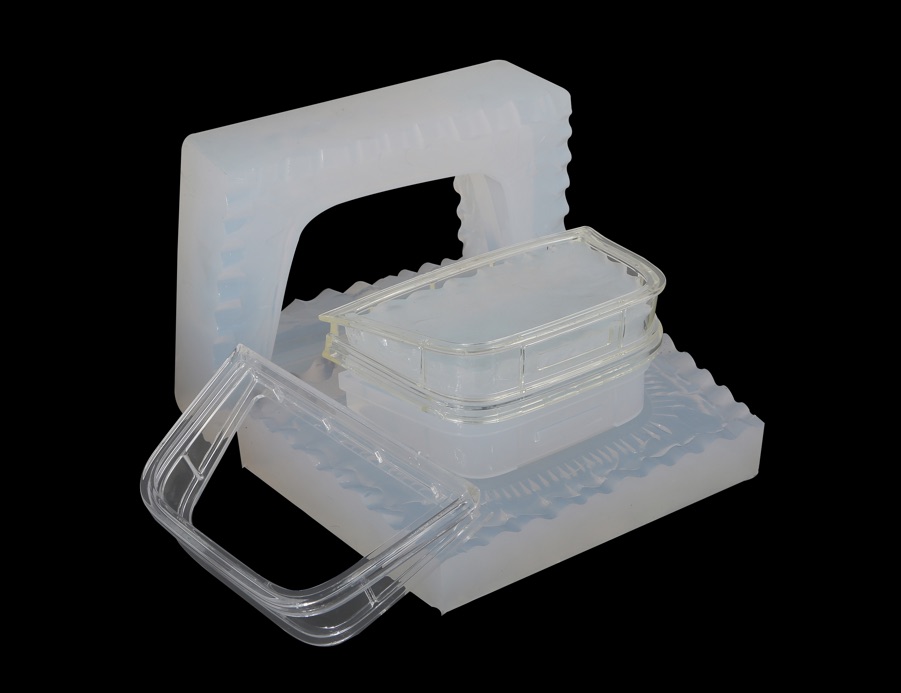 For our model, we designed a common taxi sign used to show whether or not cars are available for service.
For our model, we designed a common taxi sign used to show whether or not cars are available for service.
When designing a mold for vacuum forming consider drafting angles. Drafting angles allow your molded part to be removed from the mold. They should typically be anywhere from 3-5 degrees from 90 on any vertical surface.
STEP2: PREPARE AND PRINT MODEL
When preparing a model for vacuum forming in MakerBot Print, there are some print settings that should be taken into account.
We printed our model with 4 shells at 25% infill.
Next, print your model. We printed our model on the MakerBot Replicator Z18 because of the large size of our model.
Increase shells and infill settings to create a strong mold that will withstand the pressures of vacuum forming.
Because we used an industrial vacuum forming machine we needed to secure the mold to an additional fixture. This holds the mold in place against the various forces that occur when operating the machine.
A. Drill or tap holes in an inconspicuous place on the underside of your print & attach to Small plate or MDF board
B. Mount board to vacuum forming machine
The 2021 Guide to 3D Printing Materials
Learn about polymers, composites, and metals all available for 3D Printing!
STEP 4: LOAD AND HEAT PLASTIC
A. Load your plastic.
We started with 12 x 24 inch sheets of white polystyrene plastic about .75mm thick and worked up to ¼ inch thick sheets of PET-G.
When choosing plastic sheets for vacuum forming, consider the thickness of the plastic and the size of the sheet as well. Thicker sheets will need to be heated to higher temperatures and will require a higher power vacuum.
B. Heat plastic to desired temperature.
Because we used an industrial vacuum forming machine, our plastic was heated automatically to temperature based on the type of plastic, thickness, and density.
While 400 degrees fahrenheit is close to the melting point of PLA, only the sheet is heated and not the form. This means the heat is not necessarily a concern in low volume production or prototyping.
This means the heat is not necessarily a concern in low volume production or prototyping.
Choose thinner sheets of plastic if your vacuum forming machine does not create large amounts of consistent heat or suction.
Typically plastics will be heated somewhere around 400 degrees fahrenheit.
STEP 5: PRESS PLASTIC OVER FORM
Once plastic is heated, it is pushed over the form.
At this point you will notice that the vacuum suction will pull all of the air out from under the heated plastic sheet and it will be forced down over your mold.
The plastic will begin to cool instantly.
Once all of the air has been removed from under the plastic and it has been formed over your mold, remove the formed part and set it aside to cool.
The mold is not removed from the machine between shots
This process can be repeated to produce many of your desired product.
If you notice that over time your 3D printed mold becomes deformed due to heat or pressure, it might be time to print another.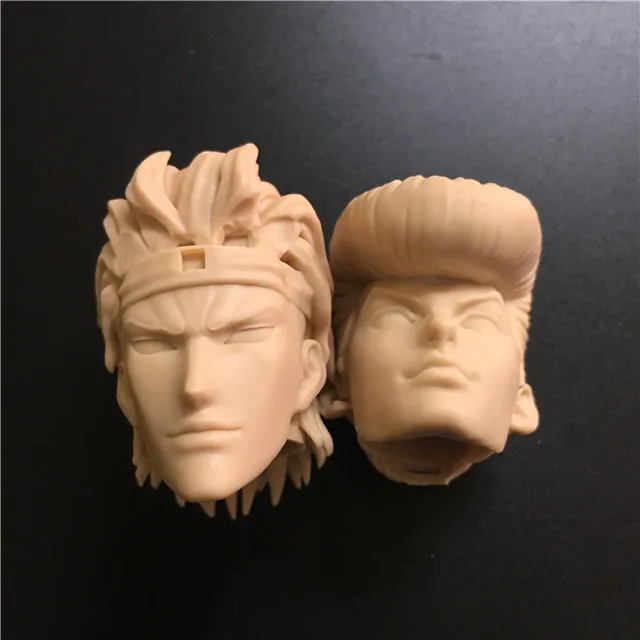
Because printing is such an inexpensive option for mold production, producing 2-3 spares up front is not cost or time prohibitive.
STEP 8: POST PROCESSING
After you have produced the desired number of parts, cut away any spare plastic.
You can cut away spare plastic using a manual cutting tool, or with a CNC. If you’re using a CNC, 3D printing is a good solution for creating custom fixtures.
Here, you can see what successfully vacuum formed plastic sheets look like.
Visit one of our other applications pages for tips on how to take your print even further.
We recommend that you visit our pages on:
Sanding
Painting
Silicone Molding
Last but not least, remember to share your work with us on Thingiverse and social media @MakerBot.
We can’t wait to see what you make!
Contact Us
Special thanks to our friends at COMCO Plastics for all their help.
Powered by MakerBot Learning.
Vacuum molding into elastic molds
Vacuum molding into elastic molds is a process for the production of plastic products or rubber products, as well as copies of plastic parts. These can be prototypes, prototypes, as well as small batches of plastic parts of almost any complexity and dimensions without the use of expensive metal equipment. The mold is made by pouring silicone into the formwork with the master model located inside. After polymerization of silicone, molding into silicone molds is carried out.
These can be prototypes, prototypes, as well as small batches of plastic parts of almost any complexity and dimensions without the use of expensive metal equipment. The mold is made by pouring silicone into the formwork with the master model located inside. After polymerization of silicone, molding into silicone molds is carried out.
Characteristics of products when casting into molds
The largest possible dimensions of the form
60x12x5 cm
 The texture completely repeats the texture of the original, down to fingerprints.
The texture completely repeats the texture of the original, down to fingerprints. Benefits of silicone mold casting
-
In the production of plastic products by casting into silicone molds, the properties of silicone are used. It perfectly reproduces the dimensions and surface texture of the master model.
-
Casting in a vacuum avoids the occurrence of porosity and the formation of surface defects in castings.
-
Casting in silicone molds allows you to get products of almost any complexity. In this way it is possible to produce complex shaped cast parts that cannot be extracted from conventional metal molds. The possibility of casting each product is determined by engineers.
-
Finished products can be with different physical and mechanical properties - rigid, imitating the properties of ABS, semi-rigid, elastic, heat-resistant, transparent, and also combined.
 If necessary, you can even pour in metal components.
If necessary, you can even pour in metal components. -
Polyurethane
-
Polyurethane is classified as a structural material (CM). The mechanical properties of this material make it possible to use it in the details of machines and mechanisms that are subjected to power loads. Very serious requirements are imposed on this type of material in terms of resistance to aggressive external environment.
Applications
Manufacture of impact-resistant housings, covers and other products
- imitates ABS and PVC;
-
- very hard, very high impact strength;
-
- stained with dyes;
-
- high bending strength.
-
Physical and mechanical characteristics of the final product (approximate data)
Biresin® VG280 resin
Linear shrinkage, at a thickness of 4-5 mm
ext. test
%
 35*
35* * value after heat treatment: 1 hour/70°С
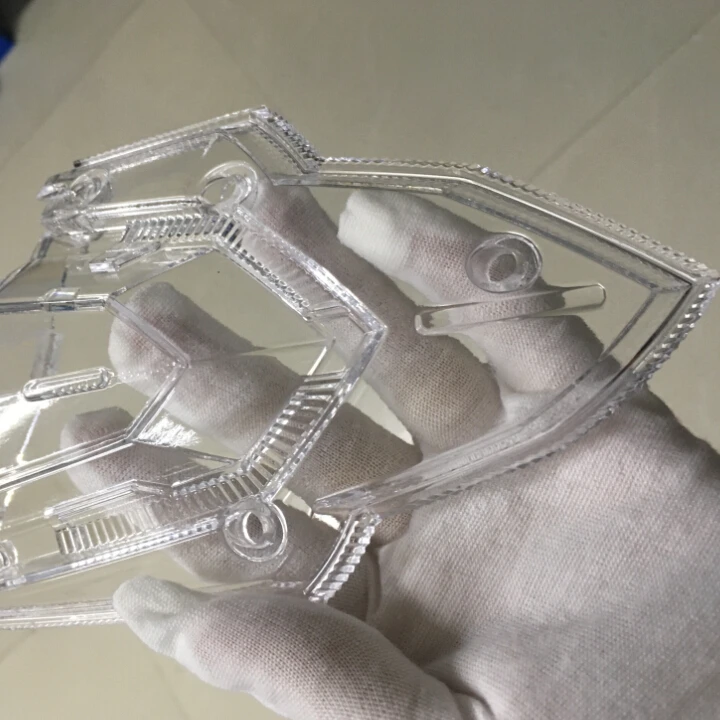
Transparent plastic
It is a two-component aliphatic polyurethane of optical transparency. It is used when absolute transparency of the material and resistance to ultraviolet radiation is required.
Optical transparency;
Application
This polymer gained worldwide popularity when casting souvenirs, prototypes, creating prototypes, copying sculptures, casting decorative elements, various optical transparent products for industrial use, in jewelry, in medicine - when casting prototypes and lenses, in the film industry - in the production of special effects, creation of special props, imitation of ice products, etc.
Physical and mechanical characteristics of the final product (approximate data)
| Specifications | Unit rev.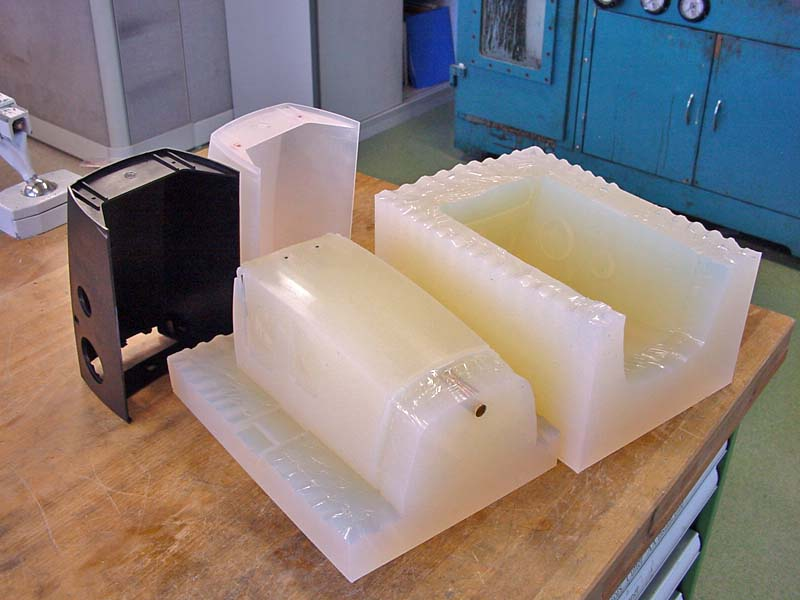 | Crystal Clear 200 |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Shore D | 80 |
| Ratio (A/B) | by weight | 100A : 90V |
| Color | Transparent | |
| Lifetime | 20 minutes. | |
| Curing time at room temperature (depending on casting thickness and configuration) | 16 hours | |
| Maximum casting thickness | cm | 1.27-7.62 |
| Mixture viscosity | sp | 600 |
| Mix Density | g/cm3 | 1.036 |
| Specific volume of the mixture | cm3/g | 0.97 |
| Tensile strength | MPa | 17.24 |
| Tensile modulus | MPa | 504.7 |
| Shrinkage (depends on casting weight) | % | 0. 254 254 |
| Elongation at break | % | ten |
| Modulus of elasticity | MPa | 137.9 |
| Bending strength | MPa | 73.43* |
| Compressive strength | MPa | 44.02* |
| Compressive modulus | MPa | 275.8 |
| Refractive index | At 20°C | 1.49962 |
| At 25°C | 1.49894 | |
| Thermal distortion temperature (distortion) | °C | fifty |
| Electrical strength | kV/cm | 102.36 |
| Dielectric constant at 25°C and 100 Hz | 3.36 | |
| Dielectric constant at 25°C and 1 kHz | 3.36 | |
| Dissipation factor at 25°C and 100 Hz | 0. 00 00 | |
| Stray coefficient at 25°C and 1 kHz | 0.01 | |
| Volume resistivity at 25°C | ohm/cm | 1.4x1015 |
* - the indicator was measured after the post-curing of the material
Polyurethane rubber
New industrial polyurethane with a hardness of 70 and 90 Shore A (optional).
High quality 70 Shore A polyurethane, resistant to abrasion, very durable. Ideal for creating industrial applications. It is also used to create rubber mechanical parts of various configurations (gaskets, wheels, pulleys) and for the production of bushings for ball mills and impact pads.
90 Shore A polyurethane has been specially formulated for industrial applications as a compound with high tensile and tear strength, as well as excellent impact and wear resistance. The most suitable material for the production of various kinds of industrial products, such as: elastic dies, making injection molds for concrete, gypsum and similar compounds.![]() This material is also used for the manufacture of various parts of mechanical products (industrial cylinders and tapes), as spacers between mechanical parts and as a bonding material with metal surfaces.
This material is also used for the manufacture of various parts of mechanical products (industrial cylinders and tapes), as spacers between mechanical parts and as a bonding material with metal surfaces.
Physical and mechanical characteristics of the final product (approximate data)
| Shore A hardness | 70 | 90 |
| Weight ratio | 2A:1B | 2A:1B |
| Color | transparent amber | transparent amber |
| Life time, min (at 23 °С) | thirty | thirty |
| Curing time, hour (depending on model size) | 16 | 48 |
| Density | 1.04 | 1.07 |
| Viscosity cP | 3000 | 3000 |
| Tear strength, kH/M | 35. 03 03 | 52.54 |
| Elongation at break, % | 750 | 550 |
| Tensile strength, MPa | 5.17 | >13.79 |
| Modulus of elasticity at 100% elongation, MPa | 1.72 | 4.41 |
| Shrinkage 24 hours after molding, % | less than 0.3 | less than 0.3 |
| All readings obtained after 7 days at 23°C | ||
The technology makes it possible to obtain small (from 1 to 1000 pieces) batches of plastic products in a few days due to the speed of tooling manufacturing.
Vacuum casting to order in Moscow
The spread of three-dimensional technologies has greatly simplified the manufacturing process, making it more economical and flexible. 3d scanning and virtual modeling allow the most accurate measurement and reproduction of the required shape in the form of a digital model, 3D printing provides fast and inexpensive production.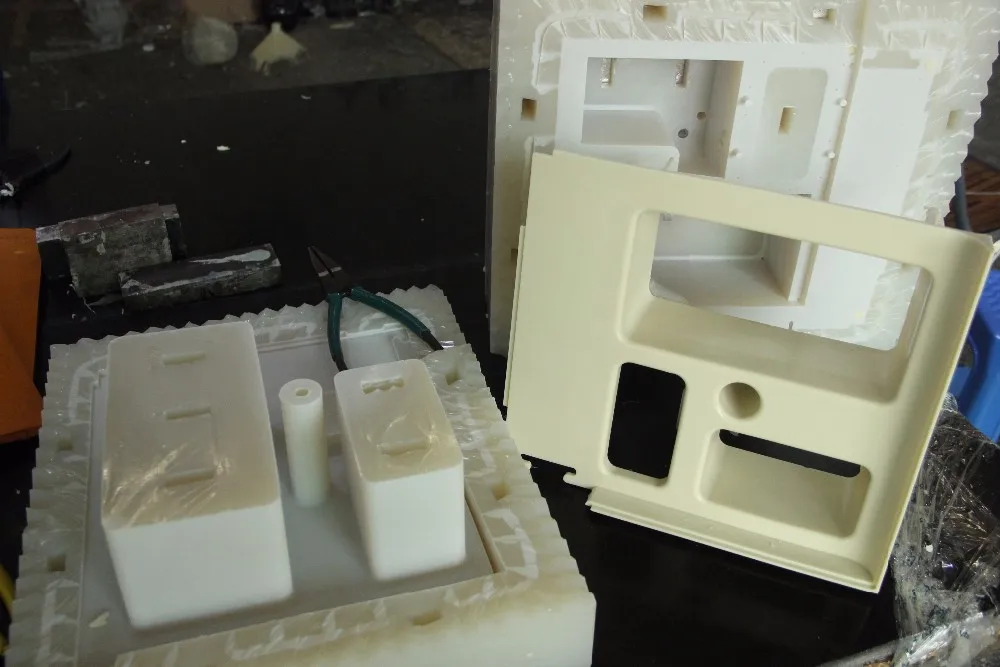 In some cases, it is more profitable for the customer to prefer 3D printing vacuum casting. It will cost less, for example, in cases where you want to make a small or medium series of plastic or polyurethane products according to an existing sample.
In some cases, it is more profitable for the customer to prefer 3D printing vacuum casting. It will cost less, for example, in cases where you want to make a small or medium series of plastic or polyurethane products according to an existing sample.
Compared to factory production, vacuum molding into silicone molds is a much faster, and again, cheaper way to get the right amount of product. The silicone mold costs less than regular tooling; it is suitable for repeated use - depending on the subject, the form can withstand from 20 to 50 fillings.
In what cases should you consider vacuum casting as a way to fulfill your order?
- If a small or medium batch is required, as already mentioned above. Of course, you can make one copy.
- If prototypes are needed. Perhaps you want to evaluate the design of a product, test parts for assembleability, test before making traditional tooling, examine the performance of a design. Or a sample is needed for research.

- If the products you need have a complex geometry, a metal tool (or a mold) will cost more than a silicone version.
- If there is a need to conduct a consumer study with an evaluation of a pilot product.
- If the deadline is running out and the batch must be ready within a few days.
Vacuum casting in silicone provides an exact copy of the master model, that is, exact dimensions. At the same time, the products will not differ from those produced using a conventional injection molding machine.
Casting of plastics and polyurethanes in silicone molds to order in Moscow. Circulation from 1 copy. Quick cost calculation. A wide range of materials with different properties and colors. Dimensions up to 500*500*800 mm.
To perform vacuum injection molding of plastic, the following sequence of operations is required:
- Master model preparation. This can be an existing product / part or a prototype made using 3d printing or other technologies.
 You can provide drawings or a sketch, we will perform 3d modeling and manufacture the product by layer-by-layer synthesis or milling.
You can provide drawings or a sketch, we will perform 3d modeling and manufacture the product by layer-by-layer synthesis or milling. - Silicone mold or die casting. Silicone is poured into the formwork with the master model placed inside - a vacuum mixer and an oven are used in the process to polymerize the silicone.
- Trial casting and finishing. At this stage, the quality of the pilot version of the product is studied and, if necessary, the matrix is adjusted.
- Manufacture of articles by pouring material into a mould. The range of plastics and polyurethanes in different colors allows you to choose the right ones. You can also choose the texture: it can be smooth or rough, glossy or matte. Combining different materials, it is possible to achieve the required physical and mechanical properties: the required level of impact resistance, heat resistance, flexibility and other characteristics.
By casting, plastic cases, souvenirs, toys, parts, packaging, including for the food industry, and much more are made.

 3% (with a lower limit on ±0.3 mm on dimensions smaller than 100 mm)
3% (with a lower limit on ±0.3 mm on dimensions smaller than 100 mm)