Tpu filament 3d printing
3D Printing with TPU - NinjaTek
TPU filament is used to create flexible, durable 3D prints. You can stretch it and bend it, and it won’t break. NinjaTek® has been extruding TPU for over 50 years, bringing a level of expertise and knowledge unmatched by other companies.
What is TPU?
Uses & Applications
How to Print With TPU
Properties, Pros & Cons
FAQs About TPU
What is TPU 3D Printer Filament?
TPU, or Thermoplastic Polyurethane, is a flexible and durable 3D printing filament for beginners and pros alike. TPU has unique characteristics that make it elastic like rubber, yet durable like plastic.
TPU has qualities that other materials don’t have, such as vibration dampening, shock absorption and incredible elongation.
TPU Uses & Applications
TPU can be used in a number of industries across a variety of applications when you’re looking for high-performance materials. TPU’s shock absorption and vibration-dampening qualities make it the ideal material for prosthetics and orthotics (footwear inserts/insoles), as well as sporting goods and athletic equipment.
TPU’s soft, sleek feel lends itself well to the realistic texture needed for prosthetics. It’s even been used to make tracker-enabled turtle eggs to fool poachers.
Another advantage of TPU is its durability. It can take a beating. For example, when TPU is used to produce seals and gaskets, printed components hold up just as well as (if not better than) traditionally manufactured parts.
While durable, it’s also chemical resistant and non-marring. It can stretch around tools to protect them and other equipment from damage.
How to print with tpu
TPU can be somewhat tricky to print with because of its unique properties, but the prints you get have impressive quality and can withstand the test of time.
Temperature: TPU prints at moderate speeds and temperatures (225°C to 250°C).
Common issues: TPU has great elongation and stretchiness, but those properties can also cause some minor clogging and stringing. Check out our Troubleshooting Guide for common print issues and fixes.
Properties of TPU: Pros & Cons
Pros of TPU
- Flexible
- Stretchy like rubber
- Durable, shock- and impact-resistant
- Abrasion resistance
- Vibration dampening
- Huge variety of color and hardness options
Cons of TPU
- Can be a challenge to print for beginners due to its unique, high-performance properties
- Difficult to post-process because of its abrasion and chemical resistance
FAQs about TPU
Is TPU flexible?
Yes, TPU 3D printer filament is known for its flexibility, such as NinjaFlex® filament. There are some varieties of TPU filament with more rigid properties, like our Armadillo® filament. TPU is ideally suited for 3D printing applications where flexibility and durability are essential.
TPU is ideally suited for 3D printing applications where flexibility and durability are essential.
How soft is TPU filament?
TPU has a soft, smooth texture that lends itself to a number of applications. In addition to being soft, it has impact-resistant and elastic properties well suited for many industries, including healthcare and sports.
How fast can you print TPU?
TPU typically prints best at slower speeds. When combined with high heat, it will flow smoothly from the nozzle. If you’re looking for a quick-printing material that’s going to hold up with minimal issues, try our Cheetah® filament.
Which NinjaTek Filament Do You Need?
Compare hardness, elasticity, impact resistance and other properties of our 3D printer filaments.
Compare Products
Shop All Products
Related Resources
Shop Cheetah
Shop the fastest and easiest to print flexible filament on the market.
3D Printing by Industry
Fashion: Custom couture to cosplay costumes
Case Studies
Machinist designs protective covers for vise-grip pliers.
TPU 3D Printing: A Guide to 3D Printing Flexible Parts
Have you ever thought about 3D printing flexible parts? If so, Thermoplastic Polyurethane or TPU, as it’s commonly known, is definitely a material to add to your list.
TPU 3D printing offers unique possibilities that are otherwise unachievable with other 3D printing materials like ABS, PLA or nylon. Combining the properties of both plastic and rubber, TPU can produce elastic, highly durable parts that can be easily bent or compressed.
In today’s tutorial, we’ll explore the benefits and applications of TPU, the technologies that support the material, as well as a few tips to help you make 3D printing with TPU as easy and efficient as possible.
Take a look at other guides on 3D printing plastics:
3D Printing with ABS Plastic: All You Need to Know
PLA 3D Printing: All You Need to Know
FDM 3D Printing: Comparing ASA, PETG, and PC Filaments
Nylon 3D Printing: All You Need to Know
ULTEM & PEEK: The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance 3D Printing Materials
What is TPU?
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) belongs to the family of thermoplastic elastomers and combines the best properties of thermoplastics and rubbers (thermosets).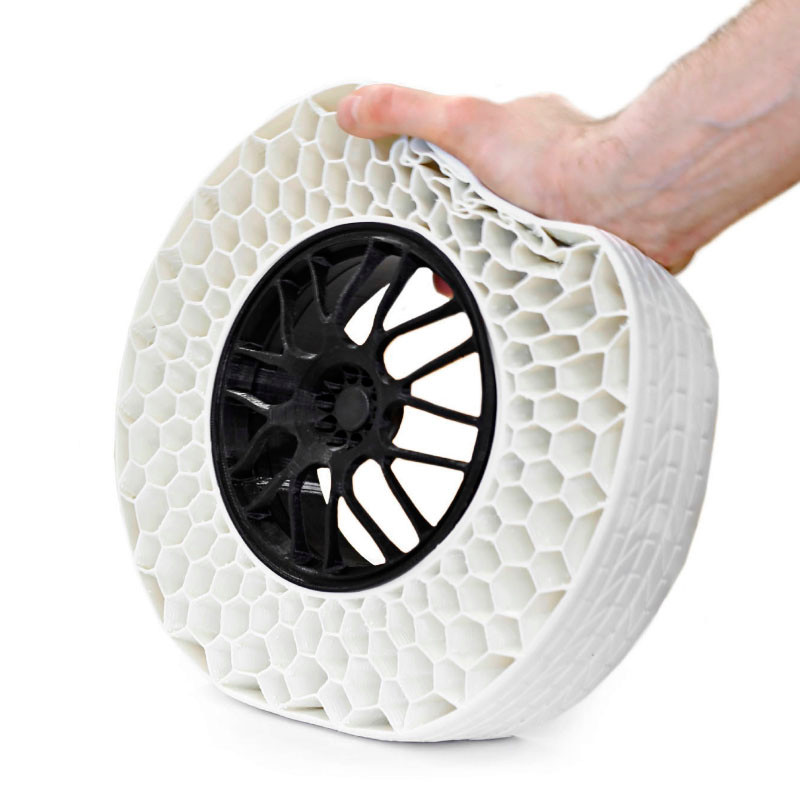
You may be more familiar with the term TPE — or ThermoPlastic Elastomer. Formerly the go-to material for flexible 3D printing, TPE is a very soft, rubber-like plastic that can be bent or stretched without deformation. However, its softness makes TPE a very challenging material for machine extruders to 3D print.
TPU, on the other hand, can be thought of as the newer version of TPE. TPU possesses rubber-like elasticity, high tear and abrasion resistance, high elongation at break as well as thermal stability.
In addition to this, TPU is also resistant to oils, greases, and a variety of solvents. Being firmer than TPE, TPU is therefore also much easier to 3D print with.
| Pros | Cons | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic and soft material | Hygroscopic | Sporting goods |
| Can be very stretchy depending on the elongation at break | Prone to stringing and clogging | Protective cases |
| Low warpage and shrinkage | Needs to be printed at low temperatures | Automotive bushings |
| Chemical-resistant | Difficult to post-process | Vibration-damping components |
| Good impact-resistance | ||
| Good vibration damping and shock absorption | ||
| Available in a range of colours |
Applications
TPU has a wide range of applications. For example, it is a good option for 3D printing flexible functional prototypes or end-use parts that need to be bent and compressed.
For example, it is a good option for 3D printing flexible functional prototypes or end-use parts that need to be bent and compressed.
Consumer goods
For consumer goods, TPU is ideal for producing accessories, such as phone cases, and footwear components.
In 2015, New Balance created running shoes with TPU 3D-printed midsoles. Using 3D Systems’ DuraForm Flex TPU, 3D printing and generative design, the footwear giant was able to achieve a high level of flexibility in its midsoles, as well as strength, optimal weight and durability.
Medical
Another interesting application of TPU is in the medical sector. For example, the material can be used to create orthopaedic models. In 2016, US-based company Graphene 3D Lab introduced a conductive TPU filament, suitable for producing flexible electronics, including wearable medical devices like wristbands.
Automotive
With its high chemical resistance to oils and greases, TPU is ideal for automotive applications like seals, gaskets, plugs, tubes and protective applications.
One innovative example is a 3D printed electric car produced by Chinese startup XEV Limited. The car is made up of around 100 parts, many of which were 3D printed with TPU alongside PLA and nylon.
Available TPU Materials| Material Manufacturer | Material Brand Name | Shore A hardness | Key properties | Technology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Systems | DuraForm TPU Elastomer | Shore A hardness can be varied | Abrasion and tear resistant Easy to process Elongation at break 200% | SLS |
| Prodways | TPU-70A | 70A | High resolution Elongation at break above 300% | SLS |
| Advanc3D | Adsint TPU 80 shA | 80A | Good abrasive and chemical resistance Elongation at break 600% | SLS |
| Sinterit | Flexa Soft | 40-55A | Elongation at break 137% | SLS |
| Sinterit | Flexa Black | 80-90A | Elongation at break 155% | SLS |
| Sinterit | Flexa Grey | 70-90A (adjustable) | Elongation at break 137% | SLS |
| Sinterit | Flexa Bright | 79A | Elongation at Break 317% | SLS |
| LUVOCOM | LUVOSINT® TPU 92 Shore A | 88A | High strength and high abrasive resistance Elongation at break 500% | SLS |
| Lubrizol | Estane® 3D TPU F70D-045TR UV | 70D | Low-temperature flexibility and UV stability | FFF, SLS, Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) |
| Lubrizol | Estane® 3D TPU F50D-045SR GP | 50D | High stiffness with excellent chemical and oil resistance | FFF, SLS, MJF |
| Lubrizol | Estane® 3D TPU F98A-030CR HC | 98A | Excellent mechanical properties, low warpage and shrinkage | FFF, SLS, MJF |
| Lubrizol | Estane® 3D TPU F75D-035 TR UV | 75D | Offers high modulus and excellent processing attributes | FFF, SLS, MJF |
| Ninjatek | Ninjaflex TPU | 85A | Abrasion resistance 20% better than ABS and 68% better than PLA Resistant to chemicals Elongation at break 660% | FFF |
| Ninjatek | Cheetah TPU | 95A | Great impact strength Abrasion resistance 40% better than ABS and 76% better than PLA | FFF |
| Ninjatek | Armadillo TPU | 75D | Rigid, abrasion resistant, tough Excellent bridging capabilities and virtually no warping | FFF |
| Polymaker | PolyFlex™ TPU95 | 95A | Easy to process Elongation at break 330% | FFF |
rigid. ink ink | rigid.ink TPU | 94A | Tough and durable Elongation at break 500% | FFF |
| MatterHackers | MatterHackers PRO TPU | 95A | Resistant to abrasion, grease and oil | FFF |
| Fillamentum | Flexfill TPU | 92A and 98A | Oil resistant with excellent inter-layer adhesion | FFF |
If you want to explore 3D printing with this flexible material, there are two main technologies to choose from: Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM).
Let’s delve into the possibilities of each.
Selective Laser SinteringSelective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a powder bed fusion 3D printing technology that uses a laser beam to selectively melt and fuse powdered material.
SLS offers many advantages for industrial manufacturing, as the technology is capable of producing functional parts with great mechanical properties. Furthermore, SLS requires no support structures, allowing free-form parts without any support removal marks. However, parts will require some form of post-processing to achieve a better surface finish.
Furthermore, SLS requires no support structures, allowing free-form parts without any support removal marks. However, parts will require some form of post-processing to achieve a better surface finish.
Initially, the technology was used with various types of nylon but with recent advancements in material research, it’s now possible to sinter TPU powder.
Currently, there are a few manufacturers on the market that offer TPU powder with various degrees of shore hardness:
– 3D Systems offers its proprietary DuraForm TPU Elastomer, which is compatible with its Pro 60 HD-HS 3D printer.
– French AM specialist Prodways has TPU-70A in its material portfolio with an elongation at break of more than 300%. With TPU-70A, shore hardness can be adjusted based on energy input.
– In 2017, German material manufacturer Advanc3D introduced the Adsint TPU 80 shA material, said to be the stretchiest material commercially available for SLS technology.
Minimum wall thickness
1.5 mm is the minimum wall thickness when using TPU powder. Parts 3D printed with 1.5 mm walls will be very flexible but you can also make your part more rigid by increasing the wall thickness to 3 mm.
Minimum feature size
When designing details for your TPU part, ensure that they are minimum 0.5 mm in size. For the visibility of embossed and engraved details, their height and width should not be smaller than 1.5 mm.
Complex designs
As a powder bed technology, SLS can create enclosed and interlocking parts, eliminating the need to assemble individually printed components. For this to be successful, keep in mind that the clearance between parts should be minimum 1 mm. For large objects, the clearance should be increased.
Escape holes
Hollowing your part may be useful, as it reduces printing time and saves material. However, when doing so, don’t forget to factor into your design holes with a diameter of at least 1. 5 mm to help remove the powder stuck inside your part after the printing process.
5 mm to help remove the powder stuck inside your part after the printing process.
FDM technology can also be used with TPU filaments.
There are two major benefits of using FDM instead of SLS when manufacturing TPU parts: firstly, FDM is less expensive and secondly, it is typically faster to produce TPU parts with filaments rather than with powders.
On the other hand, 3D printing with TPU filaments using FDM will result in a less dimensionally accurate part, with visible print layers that cannot be smoothed. Additionally, since TPU is a soft material, particularly when compared to ABS and PLA thermoplastics, TPU filaments can flex in the extruder mechanism, resulting in coiling of the filament and clogging of an extruder. However, the softness of the material is what makes the layer to layer adhesion in TPU prints strong and durable.
5 Tips for 3D printing with TPU filaments
Basic printer requirements:
- Extruder temperature: 225-250°C
- Type of the extruder: Direct Drive extruder is recommended
- Heated print bed: 50 ±10 °C
- Cooling: part cooling fan is recommended (medium or high setting)
- Enclosure: not necessary
- Build Surface: Kapton tape (PEI), blue painter’s tape
Printing Temperature
The recommended extrusion temperature range is between 225-250°C depending on the type of a 3D printer and a TPU filament you have.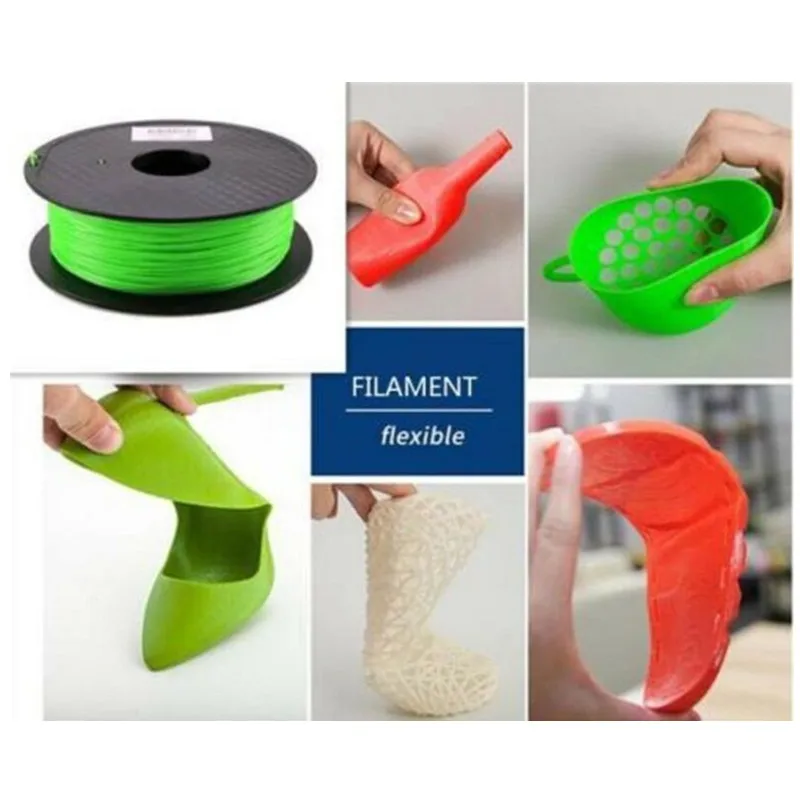 However, keep in mind that printing with higher temperatures will allow the filament to melt faster and to flow easier from a nozzle.
However, keep in mind that printing with higher temperatures will allow the filament to melt faster and to flow easier from a nozzle.
Speed
TPU typically prints best at slower speeds. It is a good practice to set half of the average speed (15 mm/s – 20 mm/s) to ensure high-quality prints.
Extrusion multiplier
Extrusion Multiplier is 3D printer’s setting which allows you to control how much filament comes out of the nozzle or simply the extrusion flow rate. As TPU filaments can improperly extrude during the printing process, resulting in improper bonding of layers and perimeters. One way of dealing with this issue is to slightly increase your extrusion multiplier.
Retraction
Retraction is the mechanism in a 3D printer, which pulls the filament backwards into the extruder as a means of preventing the oozing of the melted filament. This feature is very useful with rigid filaments like PLA and ABS, however, with TPU filaments, retractions can be challenging and can result in clogging. That’s why it is highly advisable to disable retraction to prevent stretching and compressing of the flexible filament in the nozzle.
That’s why it is highly advisable to disable retraction to prevent stretching and compressing of the flexible filament in the nozzle.
Rafts and skirts
A raft is a throwaway horizontal surface on top of which a part is printed, and it is used to prevent warping. However, since TPU parts usually do not warp, rafts are not recommended when 3D printing with TPU, not at least because they can cause additional printing issues due to high printing speeds. In contrast, it would be wise to print a skirt — a few loops of material around the print — to check the flow of the filament and ensure the success of the first few layers.
Conclusion
TPU is a highly useful material, providing unique properties and a wide range of possible applications.
However, 3D printing with TPU can be tricky due to the unique properties of the material, which is why it’s important to understand the possibilities and limitations of TPU before printing. With this guide, we hope that you’re now well on the way to successfully producing your 3D-printed TPU parts.
All you need to know about TPU for 3D printing
You are here
Home
So-called thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a type of elastomer that is highly flexible and durable when processed. Its properties are due to the presence of alternating sequences of hard and soft segments, that is, by varying the proportion of these segments, we can change the hardness and flexibility of the material. It also affects the transparency of the final parts, the softness to the touch or the adhesion of the parts. In general, we can say that TPU is a very diverse polymer that provides a very interesting set of part characteristics. In addition, this makes it possible to apply it to create 3D printed flexible models. But what should we consider when using TPU?
In the additive manufacturing industry, this material opens up many opportunities for different markets such as footwear, elastic soles, or the automotive industry for tires and shock absorbers. TPU is ideal for end-use parts, functional prototypes, concept models and custom components. This type of material is widely used to make mobile phone cases, for example, as it protects the device from bumps and cracks. Let's now look at the outstanding properties of this flexible material.
TPU is ideal for end-use parts, functional prototypes, concept models and custom components. This type of material is widely used to make mobile phone cases, for example, as it protects the device from bumps and cracks. Let's now look at the outstanding properties of this flexible material.
Due to its flexibility, TPU can be used to make phone cases.
Features of TPU in 3D printing
In terms of properties, we need to know that these polymers have many advantages, such as high resistance to impact, wear, abrasion and cuts. In addition, they have a fairly high adhesion to the layer, which provides excellent mechanical uniformity of the manufactured parts, making them isotropic. However, this type of material has certain limitations that we must take into account. TPU does not adapt well to hot conditions. This factor is remarkable in that, despite the wide operating range, it does not withstand high temperatures.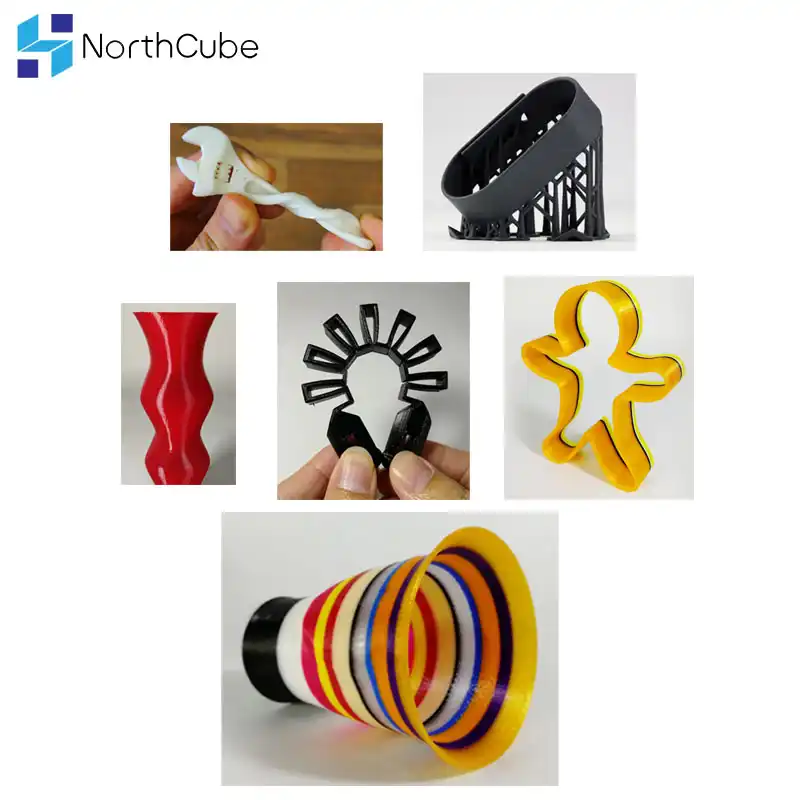 In addition, print settings should differ depending on the technology used.
In addition, print settings should differ depending on the technology used.
When printing parts with TPU using FDM, we suggest applying a thin layer of adhesive to the print bed to facilitate adhesion of the material. It is also recommended that the extrusion nozzle reach a temperature between 210 and 235°C to melt the filament (although this will vary by manufacturer). These are general tips, however, the success of a TPU will depend on each 3D printer's configuration and proper calibration; therefore it is recommended to perform small tests with this material before starting more complex prints.
Good layer adhesion results in excellent mechanical homogeneity.
In terms of stereolithography, TPU is not recommended for small, thin-walled models or models simulating high elongation materials. When setting up a model, it is recommended that the models have their final shape and be oriented close to the production platform, but not more than 20º. Thinner and taller parts will be more difficult to print, although additional supports can always be used for optimal results.
Thinner and taller parts will be more difficult to print, although additional supports can always be used for optimal results.
Which companies provide these materials?
In today's additive manufacturing market, we can find major players offering TPU for flexible parts. The giant Ultimaker has a filament called TUP 95A that is compatible with its Ultimaker S5, Ultimaker 3 and Ultimaker 2+ 3D printers. According to the company, the material can withstand up to 580% elongation at break; this thread is available in 4 different colors. Another big company is Formlabs, which introduced its so-called "elastic resin" for SLA technology last year. This resin has a hardness of 50 Shore A, in addition to high elongation and energy return. The elasticity and durability of this material allows it to be used in several cycles. In addition, the technology allows you to reduce costs and delivery times by printing directly on soft parts.
Source: Formlabs
There are other companies that mainly develop these materials, such as Recreus, which offers a variety of 3D printing filaments. In particular, her famous thread FilaFlex.
In particular, her famous thread FilaFlex.
Source
Tags:
thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), additive manufacturing, 3D printed flexible modeling, 3D printing filament, Recreus, FilaFlex filament, Ultimaker, TUP 9 filament5A, Formlabs, "Elastic Resin" for SLA Technology
Other materials:
- Researchers determine the impact of powder processing on 316L
- Scientists ITMO University Scientists as part of megagram work under the University of Toronto
- Advantages of Materialise Magics when creating supports for 3D printing
- Vladimir Cheverikin: We register the patents of our own .
- How we taught the 3D printer to print with metal casting wax
Attention!
We accept news, articles or press releases
with links and images. [email protected]
TPU 3D Printer Filament - Applications & Features
3D Printer TPU Filament - Applications & Features
- Post category: 3D printing / 3D printing articles
Most of the models printed on the 3D printer are rigid models. It is important that the printed model hold its shape, be firm and resilient, especially if you need a case for some project or some kind of mechanical part, such as a gear. However, in some cases, 3D printer users do not need a model that is rigid and resistant to bending, but, on the contrary, is flexible, soft and returns to its original shape. And if you really need a model with such characteristics, then TPU thread is just what you need.
It is important that the printed model hold its shape, be firm and resilient, especially if you need a case for some project or some kind of mechanical part, such as a gear. However, in some cases, 3D printer users do not need a model that is rigid and resistant to bending, but, on the contrary, is flexible, soft and returns to its original shape. And if you really need a model with such characteristics, then TPU thread is just what you need.
TPU
thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU for short) has many industrial applications. From a microscopic point of view, this flexible material consists of two types of structures: long, deformable "soft" chains, and shorter, highly polarized "hard" chains. In fact, these two chains form one crystal structure. But, if we heat TPU , the crystalline "grid" will change its properties, and the material will become like rubber. Due to this property, TPU is used in the automotive industry, sports equipment, tool handles, etc. The use of polyurethane makes glass and mirrors more resistant to impact and cracking. Also, this material is used in the manufacture of phone cases.
The use of polyurethane makes glass and mirrors more resistant to impact and cracking. Also, this material is used in the manufacture of phone cases.
Key properties of TPU filaments
Thermoplastic polyurethane used as a consumable for 3D printers allows designers to create flexible 3D models . The TPU threads are like rubber. They guarantee high flexibility, and parts from them easily return to their original shape after compression. TPU filament models are abrasion resistant and highly wear resistant in contact with many chemicals, mainly oils and greases. They tolerate changing weather conditions very well. Models made of thermoplastic polyurethane do not shatter on impact. They also have the ability to dampen vibrations and shocks.
3D printing with TPU 9 filaments0003
When deciding whether to print with TPU filaments, there are a few key points to keep in mind. First, the 3D printer must be adapted to this type of material. Most printers in the amateur or semi-professional segment are equipped with bowden extruders, i.e. the filament travels a long way inside the Teflon tube to the nozzle. Unfortunately, in such designs, the TPU filament encounters a lot of resistance, which can lead to filament breakage. Therefore, it is necessary to check whether the given 3D printer model use flexible polyurethane.
Most printers in the amateur or semi-professional segment are equipped with bowden extruders, i.e. the filament travels a long way inside the Teflon tube to the nozzle. Unfortunately, in such designs, the TPU filament encounters a lot of resistance, which can lead to filament breakage. Therefore, it is necessary to check whether the given 3D printer model use flexible polyurethane.
Also, when printing with TPU filament, the user must have at least some experience with this material. Also, a lot depends on the specified print settings. TPU filaments typically require the nozzle to be heated to 210-240°C and the worktable (platform) to approximately 20°C to 80°C. Sometimes exact values need to be determined experimentally. An additional requirement is to set a lower 3D printing speed. TPU filament 3D model will take longer. Otherwise, there is a risk that the applied layers will not lie flat.
Conclusion
TPU filaments are the dream of many designers.