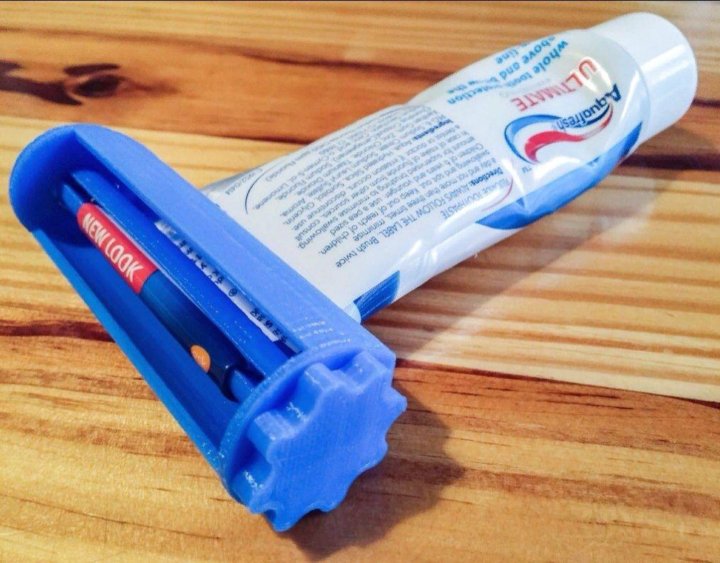
Toothpaste 3d print
Toothpaste best 3D printing files・Cults
Shrek bottle cap
€0.94
Toothbrush holder for bathroom
Free
ShockerToothpasteSqueezer
Free
toothpaste tube roll up clip
€0.57
Wall mountable Bathroom Organizer
Free
Oral-b stand
Free
Toothpaste holder
€1.49
Ultimate Toothpaste Squeezer
€1.65
Toothpaste-Toothpaste Tube Pusher
Free
toothpaste cup
Free
Toothbrush holder
€0.90
Toothpaste Doorstop
Free
Mustache Toothpaste Squeezer
Free
Tube roller
Free
giant toothbrush holder toothbrush holder house child
€0. 65
TOOTH BRUSH HOLDER / STORAGE
€5.73
Sink Caddy V3
€2.82
Yoda toothpaste
Free
Red Panda Toothpaste Squeezer
€1.88 -64% €0.68
Toothpaste and Toothbrush Wall Mount
Free
Toothbrush holders
€0.50
Toothpaste Holder
Free
Parametric Toothpaste and Toothbrush holder
Free
Toothbrush Holder/Organizer
Free
Halloween Pumpkin Toothpaste Topper
€3
2Brush 1Paste
Free
Jack-O-Lantern Toothpaste Tube Squeezer
Free
Economizer with Just Logo
€0. 94
94
Parametric Toothpaste Squeezer
Free
Toothpaste squeezer
€2
Electric Toothbrush Wall Caddy
€0.91
Emoji TOOTHPASTE
€0.89
Toothpaste squeezer and toothbrush holder
€1.91
Ratchet toothpaste tube squeezer
Free
Toothpaste Keyblade
Free
toothpaste - MOLD BATH BOMB, SOLID SHAMPOO - MOLD BATH BOMB, SOLID SHAMPOO
€1.41
Toothpaste Squeezer for tubes - simple robot face
Free
electric toothbrush holder + toothpaste
€1.50
Toothpaste Tube Squeezer, Fits Any Brand, Monkey
Free
Colgate or Fixodent tube Cap WITH Nozzle Options Full set
€2. 88
88
Charmander Toothpaste - toothpaste
€1.50
Spartan Toothpick Army (Then We 69)
Free
Fortnite Call toothpaste
€1.50
VENOM TOOTHPASTE CAP (Toothpaste cap)
€1.41
Simple Toothpaste Squeezer
Free
Toothpaste - Press
Free
Toothbrush holder
€0.55
toothpaste press
Free
Dick-head Toothpaste Topper Cap 3D Printable Digital Instant
Etsy is no longer supporting older versions of your web browser in order to ensure that user data remains secure. Please update to the latest version.
Take full advantage of our site features by enabling JavaScript.
Click to zoom
913 sales |
4. 5 out of 5 stars
5 out of 5 stars €10.53
Loading
VAT Included
Listed on Dec 16, 2022
641 favorites
Report this item to Etsy
Choose a reason…There’s a problem with my orderIt uses my intellectual property without permissionI don’t think it meets Etsy’s policiesChoose a reason…
The first thing you should do is contact the seller directly.
If you’ve already done that, your item hasn’t arrived, or it’s not as described, you can report that to Etsy by opening a case.
Report a problem with an order
We take intellectual property concerns very seriously, but many of these problems can be resolved directly by the parties involved. We suggest contacting the seller directly to respectfully share your concerns.
If you’d like to file an allegation of infringement, you’ll need to follow the process described in our Copyright and Intellectual Property Policy.
Review how we define handmade, vintage and supplies
See a list of prohibited items and materials
Read our mature content policy
The item for sale is…not handmade
not vintage (20+ years)
not craft supplies
prohibited or that use prohibited materials
not properly labeled as mature content
Please choose a reason
Tell us more about how this item violates our policies.Tell us more about how this item violates our policies.
Frequently Asked Questions | 3D printing studio 3D Skill
Home » FAQ
- What is 3D printing and 3D printer?
-
3D printing is the creation (growing) of a virtual model in the form of a part.
 Simplified, this is like squeezing toothpaste out of a tube. The melted plastic is squeezed out of the nozzle and sticks to the table, layer by layer. nine0003
Simplified, this is like squeezing toothpaste out of a tube. The melted plastic is squeezed out of the nozzle and sticks to the table, layer by layer. nine0003 3D printer - is a printer that prints parts. The main characteristics of the printer: print area , layer thickness with which it can print, print precision .
Technically, the principle of operation of a 3D printer is that special control commands ( G-code ) generated by a special program ( slicer ) are loaded into it, then the printer executes them.
In terms of correct interpretation 3D printer is a CNC machine (with numerical control), that is, computer controlled.
The difference between a CNC machine and a 3D printer is that a CNC machine creates a product by cutting off excess from it with a cutter or other tool, and a 3D printer creates a model by growing it.
- Types of 3D printing
-
FDM printing (thermoplastic printing) - FDM printing.
 The printing material is various types of thermoplastic. Thermoplastic is a plastic that melts at 190-260 degrees. These are PLA, ABS, PET-G, SBS, Carbon, Flex . The advantages of printing are the ease of printing and the general availability of the material. Disadvantages - relatively low melting temperature of the material and low print detail. Used for prototyping and for most orders.
The printing material is various types of thermoplastic. Thermoplastic is a plastic that melts at 190-260 degrees. These are PLA, ABS, PET-G, SBS, Carbon, Flex . The advantages of printing are the ease of printing and the general availability of the material. Disadvantages - relatively low melting temperature of the material and low print detail. Used for prototyping and for most orders. SLA\DPL\LCD printing (printing with photopolymer) - printing with polymerization (hardening) of photopolymer using a laser or light. Advantages - very high detail, the possibility of obtaining transparent forms, coloring before printing. Disadvantages - the high cost of the material, its fragility and low printing speed. It is used in jewelry and medicine. nine0006 ABS-Like is a type of photopolymer that is similar in properties to ABS, allowing precise and fine details to be printed with the durability of plastic.
Gypsum polymer printing (gypsum printing) - printing by gluing powdered gypsum and applying a pattern to its surface.
 Advantages - the consumption of the amount of material spent is not more than the volume of the model, no support is required, multi-color printing. Disadvantages - the high cost of equipment, the fragility of the part, the high cost of equipment. It is used in art and souvenir printing. nine0003
Advantages - the consumption of the amount of material spent is not more than the volume of the model, no support is required, multi-color printing. Disadvantages - the high cost of equipment, the fragility of the part, the high cost of equipment. It is used in art and souvenir printing. nine0003 SLS printing (printing with polyamide) - printing by fusion of powdered plastic using a laser. Advantages - the consumption of the volume of the spent material is not more than the volume of the model, no support is required. Disadvantages - high cost of equipment, low detail, poor surface quality. Used for prototyping.
- What is FDM printing?
-
FDM printing That is, the plastic enters the extruder, in which the gears capture it and direct it into a special (fluoroplastic) tube - a thermal barrier. From the tube, the plastic enters the nozzle in a heated hot end. And from the nozzle under pressure, the plastic is squeezed out, where it cools and sticks to the table.
 The movement of the nozzle is carried out by motors under the control of the program. nine0003
The movement of the nozzle is carried out by motors under the control of the program. nine0003 3d printer model
- Basic printing specifications. What is the print speed and thickness (height) of the layer, density and type of filling pattern of the model, overhang angle of the supports?
-
Print speed
Print speed is one of the most important characteristics, it is the speed of the printer nozzle, measured in mm/s. Naturally, the higher the speed, the worse the adhesion of the layers and the worse the print quality. nine0003
At high speed, the plastic does not have time to harden and take the required shape, inertial forces of the print head occur, resulting in deformations, distortions, print skips and other print defects.
Layer thickness (height)
Important to know! For most printers, the optimum average print speed is between 45 and 65 mm/s, depending on the design of the printer and the media being used.
nine0002 When printing, the plastic is squeezed out by a “thread”, the thickness (diameter) of which is the thickness (height) of the layer , measured in mm or microns (1 micron - 0.01 mm).
Important to know! The thickness (height) of the layer is not equal to the diameter of the plastic thread (for example, 1.75 mm) and the diameter of the nozzle (for example, 0.3 mm), as it becomes thinner due to the tension of the thread.
The thicker the layer, the more layers are visible on the printed model and the rougher and worse the print quality will be. Modern printers can print with a layer thickness of 0.05 mm, the minimum value for satisfactory quality is 0.25 mm. nine0003
Print quality versus layer thickness
Fill density
To reduce plastic consumption and at the same time maintain durability when printing, the inside of the model is made not with a solid fill, but with a certain structure - honeycombs.
 The strength of the model remains the same, and the weight can be significantly reduced, and hence the plastic consumption. The structure of the internal cells can be different, by default it represents squares. This is the fastest filling method. But in terms of strength, a structure resembling a honeycomb is considered the best. The parameter that determines all this is filling density . In most cases, 20% filling density is sufficient.
The strength of the model remains the same, and the weight can be significantly reduced, and hence the plastic consumption. The structure of the internal cells can be different, by default it represents squares. This is the fastest filling method. But in terms of strength, a structure resembling a honeycomb is considered the best. The parameter that determines all this is filling density . In most cases, 20% filling density is sufficient. Fill Types Model
Supports
If the model has some parts overhanging at a certain angle, then they can be deformed under the action of gravity. To prevent this from happening, supports are built - "pillars" supporting overhanging elements of the part.
Example of building a model with supports
The angle of overhang and the density of supports differ for different plastics. For example, ABS requires tighter supports and a lower overhang due to greater fluidity during printing and a slow cure rate.

If the printer allows printing with two nozzles, then a support material different from the main plastic is used to create supports. This allows one to be used as support material that can be easily removed. For different plastics, certain combinations of such materials are used, since if you choose the wrong one, there will be no normal adhesion between the materials..
Resin ABS uses HIPS , which dissolves after dip printing in Limonene .
And for plastic PLA , PVA is used (actually PVA glue in solid form), which dissolves after printing in ordinary water.
PLA printed example with PVA supports
Wall thickness
The wall thickness of the part can be adjusted. A minimum thickness of at least 0.8 mm is recommended for strength and quality. nine0003
- Basic plastics: ABS, PLA, Flex
-
Since the nozzle heating temperature is maximum 260 degrees, certain types of plastics are required for FDM printing.
 Usually they use ABS, PLA, Flex.
Usually they use ABS, PLA, Flex. Plastic ABS ( acrylonitrile butadiene styrene ) is one of the most common plastics, produced from oil, often used in the automotive industry as plastic products (bumpers, dashboards) and for printing cases, parts and parts of highly loaded mechanisms. It is durable, it has a relatively high melting point, but due to its physical and thermal characteristics, printing with this plastic requires a heated platform and more deformations occur during printing than when printing with other plastics. nine0003
Plastic PLA (polylactide) - biodegradable, made from sugar cane and corn. More brittle than ABS, but it has the advantage that it does not require a heated bed to print and does not warp as much as ABS.
Plastic Flex - flexible, used for printing "rubber" products, when printing they require a slow print speed.
You can get acquainted with all the important physical and technical characteristics of plastics in the table.
 nine0003
nine0003 - Default print settings
-
The default settings are the settings for the most important and basic print settings that significantly affect plastic consumption, print speed and print quality. The cost of printing is calculated based on the default settings. If printing with other settings is required, the customer must inform which print settings should be changed.
Thickness (height) of the layer - 0.25 mm. nine0003
Wall thickness - 1.0 mm. Minimum part wall thickness without voids to form part walls without through holes
Fill density - 20% .
Print speed - 65mm/s
Support Density - 15%
Angle of overhang of supports - 75 degrees Angle of a part of the part, above which the slicer will build supports so that the overhanging elements do not deform under the action of gravity.
 nine0076
nine0076 Position on the platen - at the discretion of the operator. The print operator chooses the position of the part himself based on minimizing plastic consumption, the highest possible quality of the front surfaces, minimizing supports and taking into account his own experience.
- Printing cost calculator
-
The website price is for cm 3 . The price of 1 cm 3 is indicated on the page of our promotions
In the case of FDM printing , the volume is calculated based on the actual consumption of plastic for 3D printing, since the default model is 20% filled and the wall thickness of the part is -1 mm, then the consumption in most cases is less than the volume of the model. So the calculation is done individually? based on the wishes of the customer and the features of the model.
In the case of SLA printing, the volume is calculated from the volume of the part plus the volume required to build the supports.
 In most cases, the additional volume for building supports is 10-20% of the model volume. For a more accurate calculation, it is required that we calculate the required volume. Sometimes you can reduce material consumption by making the model hollow
In most cases, the additional volume for building supports is 10-20% of the model volume. For a more accurate calculation, it is required that we calculate the required volume. Sometimes you can reduce material consumption by making the model hollow Otherwise, the required volume is equal to the part volume.
- SLA\DLP\LCD printing with photopolymer.
-
The principle of printing of SLA is that a laser beam guided by a lens system hits a liquid photopolymer resin, which hardens (polymerizes) under the influence of light. In this way, point by point and layer by layer, the model model is grown, attaching to the platform and previous layers.
Important to know! And for such printing, supports are also required, but there are fewer such supports than with FDM printing and it is easier to remove them.
SLA printing principle
- Printing program.
 Slicer.
Slicer. -
Slicer (from the English slicer - slicer) - a program that creates a file with printer commands to print based on print settings.
We load the model into the program, set the print parameters and settings that determine the nuances of printing, after which the program calculates the amount of material, print time and creates a control code for the printer (G-code). nine0311
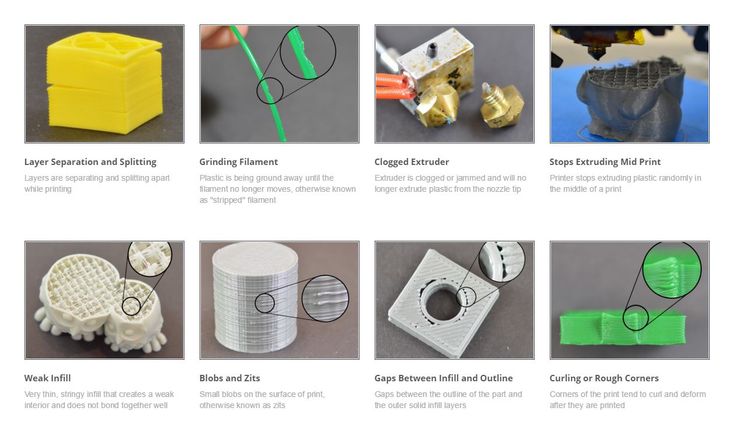
- Print defects. Shrinkage, deformation
-
Printing errors often occur:
- shrink;
- lamination;
- small item failure;
- defects after removal of supports.
Shrink
One of the most frequent defects is shrinkage of . What is shrinkage? When printing, cooling plastic shrinks, i.e. decreases in size from 1 to 5% of the total volume. Most often, this manifests itself in the fact that on large (from 10 cm) parts, the edges are torn off the table and the part is deformed.
 nine0311 Shrinkage depends on the type of plastic and the filling density. Some plastics - ABS, PC, Neylon have strong enough shrinkage, so it is not easy to print with such plastics, the result can be unpredictable and it is desirable to print with low shrinkage plastics: PLA, PETG, Carbon, SBS. It is also recommended to use 3D printers with closed chambers and an additional border when printing.
nine0311 Shrinkage depends on the type of plastic and the filling density. Some plastics - ABS, PC, Neylon have strong enough shrinkage, so it is not easy to print with such plastics, the result can be unpredictable and it is desirable to print with low shrinkage plastics: PLA, PETG, Carbon, SBS. It is also recommended to use 3D printers with closed chambers and an additional border when printing.
LayeringLamination
Since FDM technology is based on layer-by-layer deposition, the layers can be seen visually. This is critical when printing souvenirs, figurines, and when printing cases and small parts. nine0003
How to reduce layering?
Reduce layer thickness (height). The thinner the layer, the less layers are visible. But the smaller the layer thickness, the longer it takes to print.
Finishing (smoothing) with special solvents or sanding
Using a non-laminated printing technology such as photo-half dimensional printing or using non-laminated material such as Carbon.

Small items not printing
If the model has elements (parts) less than 5 mm, then the slicer simply will not be able to create the correct control commands to print such elements. To remedy the situation, reduce the layer thickness and print speed.
But it is better in this case to change the printing technology to, for example, photopolymer printingDefects after removal of supports
When supports are used for printing, defects are sure to remain after their removal. Why? Supports are connected to the part so that the plastic does not leak and an uneven surface forms in these places. Also, since the supports have a gap and a small percentage of filling, the plastic partially flows through them and forms "snot"
- Postprocessing
-
The printed part is often not a finished product, but requires post-processing, that is, processing after printing.
Such processing is not included in the cost of printing and its cost depends on the complexity of the operations.
Remove supports. Support must be removed after printing. This removal of supports requires experience in order not to damage the product. But in most cases, this is a fairly simple procedure.
nine0002 Creates a smooth and glossy surface. Sanding and/or solvent treatment (acetone, dichloromethane) is most commonly used to remove lamination.Painting and priming. Since in most cases printing is carried out in one color, if multi-color printing is required, then after printing the part is processed, primed and painted by professional artists.
Fdm technology in 3d printing and its features
Extrusion - what is it? Think about the tube of toothpaste you squeeze onto your toothbrush every morning before brushing your teeth. Now imagine that this toothpaste has the properties of a thick adhesive and dries after 5-6 seconds, forming a solid structure. Now imagine that you are squeezing this toothpaste onto some drawing, a circle, for example, applying toothpaste right along its perimeter, along the ring, making circular movements, layering the paste one layer on another. And if you continue squeezing out this toothpaste for as long as possible - until it runs out, for example, then you will get a tube with a diameter equal to the diameter of the circle on the perimeter of which you squeezed the paste and with walls formed by dried toothpaste. nine0003
And if you continue squeezing out this toothpaste for as long as possible - until it runs out, for example, then you will get a tube with a diameter equal to the diameter of the circle on the perimeter of which you squeezed the paste and with walls formed by dried toothpaste. nine0003
Naturally, if you squeeze out the paste not in a circle, but, say, along the perimeter of the cross, then you will get a kind of complex tube that has the shape of a cross in plan.
An extrusion 3d printer extrudes melted plastic in the same way - ABS plastic or PLA plastic, or some other plastic with a given thickness of the extruded layer around the perimeter of the model that you are currently manufacturing, creating a finished part before your eyes .
A Extrusion - extrusion, in English, this is extrusion. nine0003
In the process of developing a new product, whether it be a toothbrush or a new Formula 1 car, designers at some point in time inevitably face the need to feel the projected object live. Drawings are certainly not bad, but even a three-dimensional computer model of the designed thing will not give the designer the fullness of sensations that he can get just by touching it. Or at least its prototype. At such moments, it immediately becomes clear where which protrusion will work and which will not; where to add and where to remove; where it is convenient and where it is not. We can say that this moment is the moment of truth for the engineer: it immediately becomes clear to him where his miscalculation is, and where is his creative success. And so the process of making a prototype is considered an integral part of the design work. But here's the problem: until recently, the processes of manufacturing prototypes using traditional methods: cutting, milling, turning, casting, stamping, molding, etc., entailed significant, sometimes incomparable with the expected benefits, losses. To make a prototype, let's say, a car, it is necessary to sculpt a plasticine model, then manually tap the body panels on it, fit them to each other, sculpt the interior, manually make a frame, glass, etc.
Drawings are certainly not bad, but even a three-dimensional computer model of the designed thing will not give the designer the fullness of sensations that he can get just by touching it. Or at least its prototype. At such moments, it immediately becomes clear where which protrusion will work and which will not; where to add and where to remove; where it is convenient and where it is not. We can say that this moment is the moment of truth for the engineer: it immediately becomes clear to him where his miscalculation is, and where is his creative success. And so the process of making a prototype is considered an integral part of the design work. But here's the problem: until recently, the processes of manufacturing prototypes using traditional methods: cutting, milling, turning, casting, stamping, molding, etc., entailed significant, sometimes incomparable with the expected benefits, losses. To make a prototype, let's say, a car, it is necessary to sculpt a plasticine model, then manually tap the body panels on it, fit them to each other, sculpt the interior, manually make a frame, glass, etc.