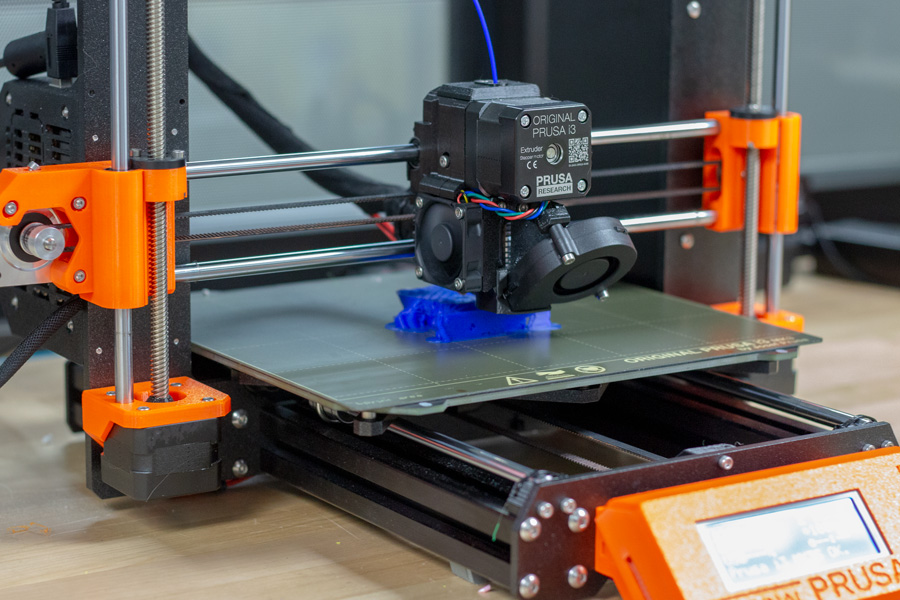
Stepcraft 3d printer
3D Print Head PH-40 | Stepcraft, Inc.
- Products
- 3D Print Head PH-40
STEPCRAFT Public Pricelist
/shop/10973-3d-print-head-ph-40-228
$ 599.00
$ 599.00 599.0 USD$ 599.00
This combination does not exist.
Add to Cart
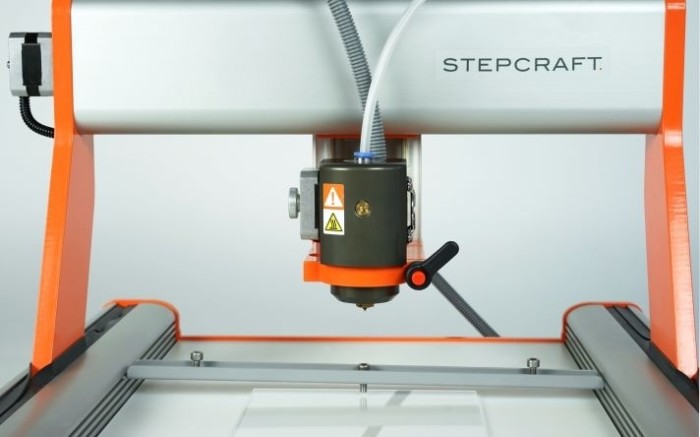
With the 3D Print Head PH-40 you can create high quality 3D models layer by layer. The variable temperature control makes it possible to use all filaments with a processing temperature of 150 to 265°C and a diameter of 1.75 mm. Additionally, the PH-40 contains numerous useful features, e. g. the quick release for the filament change, the automatic shutdown of the hot-end and the heating or the integrated active cooling of the hot-end, making 3D printing even more comfortable and safe.In order to start 3D printing, please export an STL-file from your CAD program or select one of the many templates you will find in the internet. Afterwards, this file needs to prepared for the STEPCRAFT CNC System in a slicing software like CURA. This is also where the most significant 3D print parameters, such as layer thickness, nozzle diameter and infill, are defined. You will find a download file with the most important parameters for CURA here. The created work file can be processed by the control software WinPC-NC, UCCNC or others.The control software WinPC-NC Starter does not support the operation of the 3D Print Head.
 Either an upgrade to the USB full version or the control software UCCNC is required.
Either an upgrade to the USB full version or the control software UCCNC is required.
Technical Specification (Control Unit):
- Temperature control between 150 to 265°C (equals 300 to 500 degree Fahrenheit)
- Integrated system control to handle print temperature and temperature of the heating bed
- Continuous speed control of the optional workpiece fan
- Automatic shutdown of hot-end and heating bed when printing is finished
- 2-row LC-Display
- Language setting (German, English, French, Spanish)
- 15-Sub-D plug to connect control box to STEPCRAFT CNC System (Plug-and-Play)
- External power supply with 30 V 120 W
- Integration on other CNC routers possible due to documented interface (see operating instruction)
- Dimension: L 200 mm x W 165 mm x H 64 mm
Technical specification (Printing Head):
- Possible diameter of filament: 1.75 mm
- Filament material can be any material with a processing temperature between 150 to 265°C (equals 300 to 500 degree Fahrenheit)
- Nozzle diameter 0.
 4 mm, optional nozzle diameters available (0.3, 0.5, 0.7 and 1.0 mm)
4 mm, optional nozzle diameters available (0.3, 0.5, 0.7 and 1.0 mm) - Integrated active cooling for the hot-end
- Continuously adjustable pressure on the pinch roller for the feed of filament
- Quick release for the filament exchange
- Integrated connector socket for optional workpiece fan
- 43 mm mounting collar
- 40 Watts heating cartridge (hot-end)
- Length of flexible hose connection: 0.8 m
- Easy change of printing nozzle
- Dimension: L 80 mm x W 55 mm x H 110 mm
Scope of Delivery:
- 1 x control box with print head PH-40 and 0,4 mm nozzle
- 1 x power supply
- 1 x 15-Sub-D connection cable
- 1 x acrylic printing table 150 x 250 mm (unheated)
- 1 x filament tray (assembly kit)
- 1 x operating manual with various download links
- 1 x first steps manual
System Requirements:Additional 4th axis module to control the 3D Print Head is not required for operation via USB-interface. The control software of the STEPCRAFT must be UCCNC or Win PC-NC as a full version, newest release with 3D printing functionality Existing Win PC-NC installations can be easily updated free of charge Any other CNC control software with 4th axis capability can be used.
The control software of the STEPCRAFT must be UCCNC or Win PC-NC as a full version, newest release with 3D printing functionality Existing Win PC-NC installations can be easily updated free of charge Any other CNC control software with 4th axis capability can be used.
Support:
3D Printing |
c
Why my 3D printer head (Ph50) goes into Stand-By mode while working
Why my 3D printer head (Ph50) goes into Stand-By mode while working
The printers are going into standby and eventually shutting off because they are not receiving the correct signal from UCCNC that the machine is running. This is a very simple fix outlined below.
1.) Define pin outs in UCCNC –> CONFIGURATION –> I/O SETUP. On the left hand side you have “Current hi/low”. Those two pins should read “16” and “1”.
2.) Define pin outs in UCCNC –> AXIS SETUP –> SPINDLE. Bottom Left you have “M3 relay pin”. Change those values to “0” and “0” and uncheck the “spindle relay output enabled” if it is checked.
Bottom Left you have “M3 relay pin”. Change those values to “0” and “0” and uncheck the “spindle relay output enabled” if it is checked.
Categories: 3D Print Questions, Common Pre-Purchase Questions, Software Troubleshooting, STEPCRAFT Attachments and Accessories
c
What software is needed if I purchase the 3D Printer attachment?
What software is needed if I purchase the 3D Printer attachment?
You do not need any additional software. The 3D Printer attachment comes with Repetier Host slicing software to create the GCode for the the 3D print files. That file is then run in UCCNC which comes with the STEPCRAFT CNC machine.
Category: 3D Print Questions
c
What is the maximum project height I can 3D print?
What is the maximum project height I can 3D print?
The maximum print height is as follows:
STEPCRAFT 420, 600 and 840 – 120mm (4.72″)
STEPCRAFT 300 – 92mm (3. 62″)
62″)
If you are using the STEPCRAFT Heated Bed, then you need to subtract 17mm (.67″) from the total print height.
Categories: 3D Print Questions, Common Pre-Purchase Questions, STEPCRAFT Specifications
c
What are the Parameters for the Stepcraft PH-40 Printing Head in Cura?
What are the Parameters for the Stepcraft PH-40 Printing Head in Cura?
Cura does not come with the Stepcraft PH-40 as a pre-configured printer, and thus requires creating a custom printer profile (please see the PH-40 First Steps UCCNC manual for more information). Below is a PDF containing the parameters for your Cura profile. Please note that the nozzle diameter setting is dependent on what size nozzle is fitted to the print head.
Stepcraft PH-40 Cura Printer Settings
Category: 3D Print Questions
c
How Do I Level My Heated Bed for the 3D Printer?
How Do I Level My Heated Bed for the 3D Printer?
The following video will show you how to level your heated bed for your 3D printer…
Categories: 3D Print Questions, Maintenance
c
Does the Laser DL445 use the same port on the STEPCRAFT as the 3D Printer and HF500 spindle?
Does the Laser DL445 use the same port on the STEPCRAFT as the 3D Printer and HF500 spindle?
Yes, they both use the same serial port on the back of the machine. You would need to disconnect the cable and reconnect the attachment that you wish to use. STEPCRAFT also offers a Switchbox which allows you to connect everything and simply turn the dial to select the attachment you wish to use. This is very handy if you are constantly changing attachments.
Categories: 3D Print Questions, Laser Cutter/Engraver Questions, Spindles and Routers, STEPCRAFT Attachments and Accessories
c
Does the 3D Printer come with filament?
Does the 3D Printer come with filament?
No, it does not. We suggest that you purchase filament from www.matterhackers.com. You will need standard 1.75mm filament.
We suggest that you purchase filament from www.matterhackers.com. You will need standard 1.75mm filament.
We can run any PLA, ABS, Custom PLA (flexible, conductive, wood, brass, etc) as well as HIPS
Category: 3D Print Questions
c
Does the 3D Printer attachment fit all size machines?
Does the 3D Printer attachment fit all size machines?
Yes, it will work with all Version 1 and Version 2 STEPCRAFT CNC machines.
Categories: 3D Print Questions, Common Pre-Purchase Questions
c
Do I need to buy additional software if I am only buying the Machine and 3D Printer attachment?
Do I need to buy additional software if I am only buying the Machine and 3D Printer attachment?
No, since UCCNC is included with the machine to run the G Code and the 3D Printer attachment comes with Repetier-Host slicing software. Those two programs are all you need if you are just going to use your STEPCRAFT CNC for 3D printing. If you are going to use the machine for cutting (spindle, laser, drag knife, etc.) then you need to have a CAM software program as well.
If you are going to use the machine for cutting (spindle, laser, drag knife, etc.) then you need to have a CAM software program as well.
Categories: 3D Print Questions, Common Pre-Purchase Questions
c
Can I use a 3D scanner to create 3D models to carve as well as 3D print?
Can I use a 3D scanner to create 3D models to carve as well as 3D print?
Yes, models created with a 3D Scanner are typically saved in common 3D formats like a .stl. These files can be imported into CAM programs like Vectric Cut 3D, Vectric V Carve and Deskproto where they can be assigned tool paths to carve the object out of a material. This is commonly done with two tool paths: Roughing and Finishing, using a standard end mill and a ball nose end mill, respectively.
These files created from a 3D scanner can also be used for a 3D printer.
Here is a good article with a list of the best 3D scanners for 2017: https://pinshape.com/blog/the-11-best-3d-scanners-on-the-market/
STEPCRAFT also has a 3D Touch Probe which can be used for 3D scanning. The following videos show how that works:
The following videos show how that works:
Categories: 3D Print Questions, Common Pre-Purchase Questions, Touch Probe, Vectric Software (Cut 2D, Cut 3D, V Carve)
c
Can I connect my HF-500/MM-1000 spindle and 3D printer to the STEPCRAFT at the same time?
Can I connect my HF-500/MM-1000 spindle and 3D printer to the STEPCRAFT at the same time?
Yes you can with the use of the of the STEPCRAFT System Attachment Switch Box. To use the Switch Box, you simply plug a serial cable from the Switch Box to the serial port on the CNC and then you plug the 3D Printer and the HF500 Spindle into the respective ports on the back of the box. Then you can just rotate the dial to select the attachment that you would like to use and mount that attachment into the tool holder on the STEPCRAFT.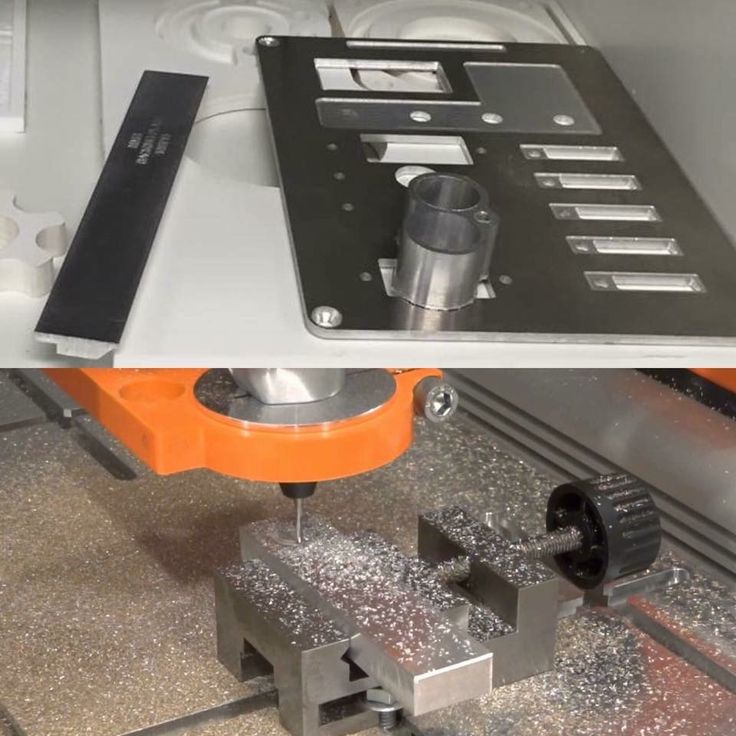
Categories: 3D Print Questions, Spindles and Routers, STEPCRAFT Attachments and Accessories
c
Are there any specific 3D Scanners that work best with STEPCRAFT, or any other CNC?
Are there any specific 3D Scanners that work best with STEPCRAFT, or any other CNC?
Honestly, No. Most 3D scanners are capable of generating and saving files in common 3D file format. That is really all that is required for STEPCRAFT. The resolution will vary, though, from scanner to scanner and typically the more expensive they are, the better the scan resolution:
Here is a good article with a list of the top 11 3D scanners for 2017: https://pinshape.com/blog/the-11-best-3d-scanners-on-the-market/
Categories: 3D Print Questions, Common Pre-Purchase Questions, Project Design
how we taught 3D printers to print complex parts more economically and twice as fast .
6874 views
What is the idea
The most popular FDM 3D printers print the parts layer by layer.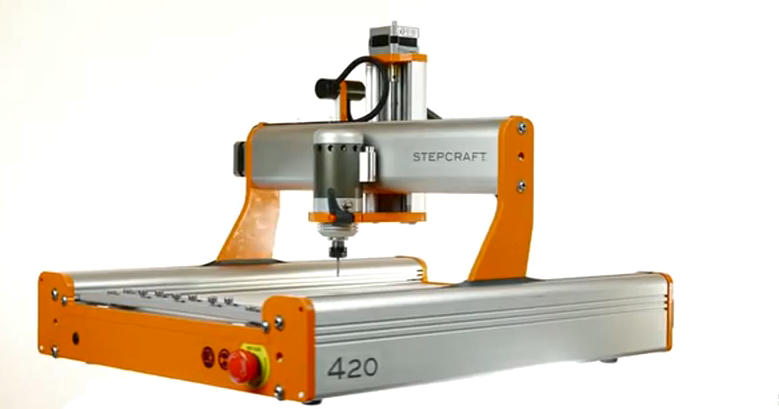 At the same time, in 70% of cases, “hinged” elements appear during printing - fragments that do not have support under them and hang over the desktop like visors. To fix such details, it is necessary to print special supporting structures (they can take up to 50% of the material).
At the same time, in 70% of cases, “hinged” elements appear during printing - fragments that do not have support under them and hang over the desktop like visors. To fix such details, it is necessary to print special supporting structures (they can take up to 50% of the material).
In addition, after printing, these supports must be removed: such processing is often time consuming and not always safe - the part may break in the hands due to insufficient strength, and then everything will have to be redone. And some designs are simply impossible to produce using this method: the supports will fill almost the entire space of the part.
I saw a solution that avoids this problem in the field of metalworking - five-axis milling machines have been used there for a long time. The idea is to equip the 3D printer with a turntable: with its help, the body of the model is always positioned during printing so that each subsequent layer is built based on the already printed elements of the model.
Five Axis 3D Printer
Why do we need a five-axis 3D printer and who are our customers
The 5-axis 3D printer allows you to print complex parts quickly without wasting material on supporting structures and saving time in post-processing. In essence, we allow you to reduce costs and increase productivity: according to our estimates, one machine can replace two previous generation 3D printers.
The 5-axis printer allows you to print parts with complex geometries, such as live piping layouts that companies need during the design phase. Printing this on a conventional 3D printer will not work, and creating it using conventional methods will take a lot of time and effort. In addition, products printed on a five-axis printer are much stronger than conventional ones. When printing, new layers of matter are not just layered on top of each other, but are printed "overlapped" at different angles - it is much more difficult to break such details.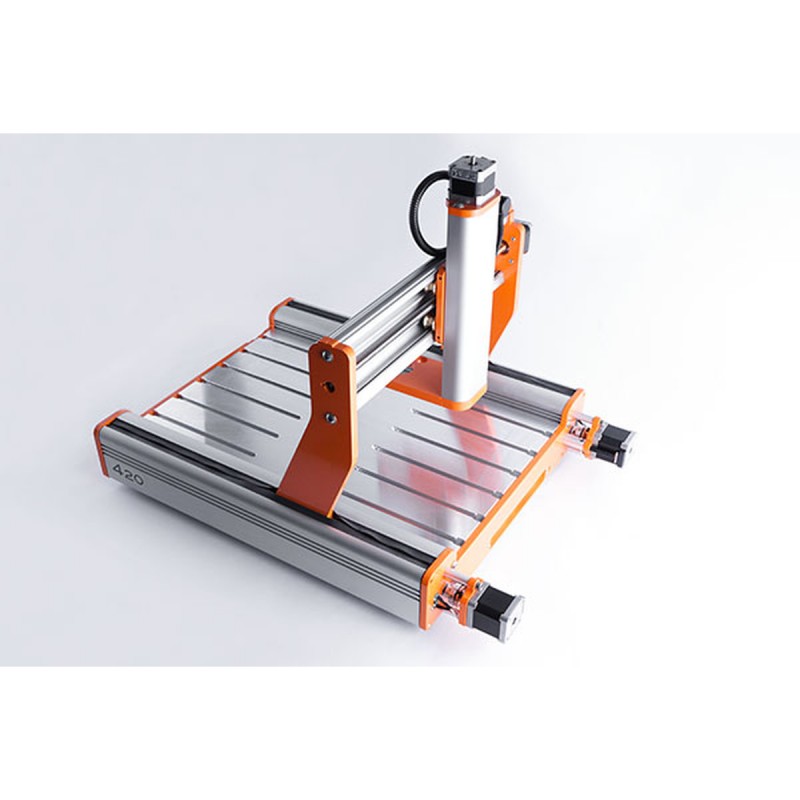
Of course, not everyone needs to print complex and durable products: potential buyers of the Epit 5.1 5-axis 3D printer are 3D printing service companies, industrial design studios and design departments of manufacturing enterprises. That is, our machine is needed specifically for industrial use.
How we got into this topic
Seven years ago I worked in a company that produced plastic automotive components, responsible for marketing and creating new business lines.
Back then, for one of the projects, it was necessary to make a prototype of a new part: it was expensive and time consuming to do it with traditional methods (I would have to create a mold), so I decided to contact a company that was engaged in 3D printing. At that time, this direction was on the hype, and everyone talked about the fact that soon 3D printers would be in every kitchen and garage.
But the reality turned out to be completely discouraging. With our task, we turned to several companies that were engaged in 3D printing in Naberezhnye Chelny, but no one was able to make the part according to our request: it turned out to be too complicated.
Since I am a designer by education, I began to think and look for solutions to the problem myself - and did not find anything similar on the market.
Creating a team proved to be more difficult than finding funding. Initially, I focused on the "iron" component of the project and did not think about the software that is necessary for the efficient operation of a 3D printer, so I began to look for developers.
An expert I knew then told me: “You need people who, like you, do not understand what they are getting into” - because developing software for such a printer turned out to be a rather specific and long task.
I began to apply to the universities of Tatarstan and neighboring regions - to look for students who are ready to take on a non-trivial task. But the students who responded could not move forward in the solution, and as a result, I found Mikhail Ivanov in Innopolis, who became a developer and my partner in a startup.
The second person who was needed in our business was someone who understands electronics, a specialist in the field of digital program control. Unlike a programmer, such a specialist cannot work remotely, so I was looking for a person in Naberezhnye Chelny.
Unlike a programmer, such a specialist cannot work remotely, so I was looking for a person in Naberezhnye Chelny.
Having spent a lot of effort and nerves, I found only two people who had the necessary level of knowledge and were able to realize my ideas, and fortunately one of them, Pavel Kozhevnikov, took up the project.
Getting funding, finding a team, and working on a printer went gradually - and in April of this year we created an MVP.
What we are doing now
In the spring of 2020, we entered the Pulsar Venture Capital accelerator and are now working on a project together with the company's experts. Acceleration made me run faster, spend even more time on the project, and constantly refine something.
On the other hand, due to quarantine, we work remotely, and for me it turned out to be even more convenient - I stayed in the familiar atmosphere with the opportunity to work on the product.
Now we have a finished product, the first pre-orders for it, and an understanding of how we will bring it to the market, how to position it. In addition, during the acceleration we have expanded the horizons of thinking and now we are looking not only at Russia, but also at the global market - this has ceased to seem like an impossible task.
In addition, during the acceleration we have expanded the horizons of thinking and now we are looking not only at Russia, but also at the global market - this has ceased to seem like an impossible task.
We assessed the economics of the business and set the price for the printer at around $7,000, which is an adequate price for a printer with such a wide range of capabilities, because it allows you to get prototypes of products quickly and with high quality.
I see how 3D printer owners are increasingly thinking about equipment efficiency and the ability to do more. In response to these requests, in recent years, the number of developments in the field of creating a new generation of 3D printers has been growing, and this is encouraging - it means that the topic is really in demand and the market will actively develop.
For example, the scientific community is working on the creation of algorithms and principles for processing models. The new generation of 3D printers is being made by our competitors from Europe and Asia, but so far they have not announced the launch of mass production.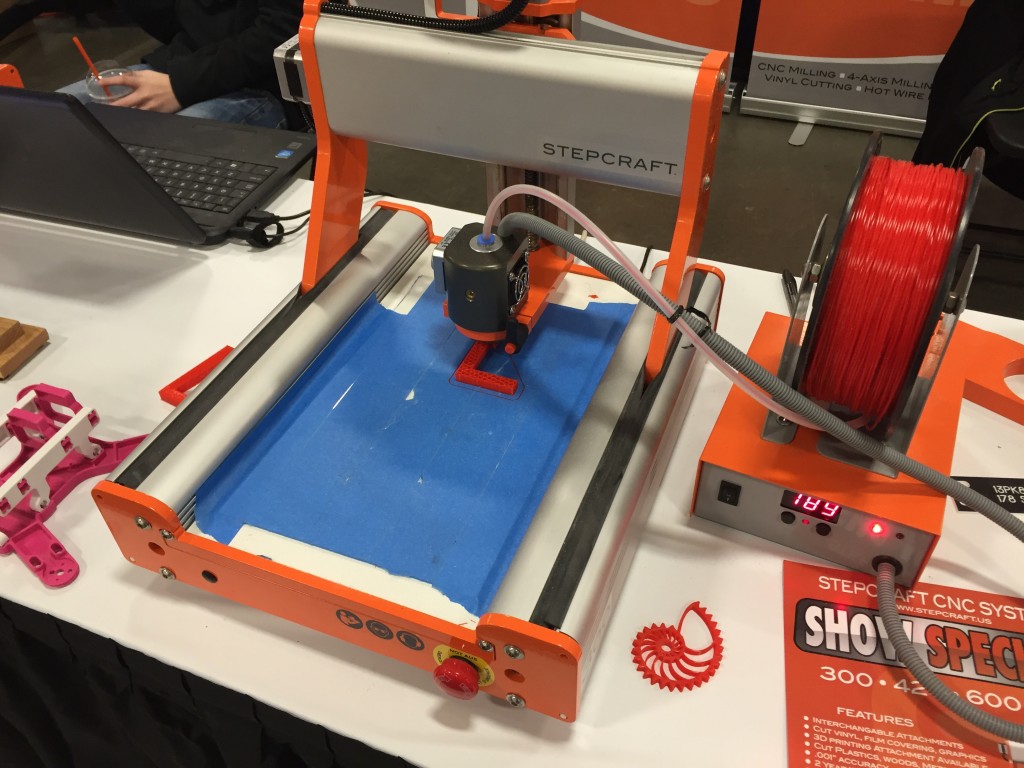
Therefore, it will be great if we, Russian companies, manage to become market leaders in the creation of third-generation 3D printers that can work even more efficiently and change attitudes towards additive manufacturing.
Making Industrial 3D Printing Cheaper / Sudo Null IT News0001
Most people have already encountered 3D printing in one way or another, but there is still a myth that you can print anything on a 3D printer. But this is far from true. And as a result, 3D printing cannot be widely used in the production chains of large companies. The main technological problem of 3D FDM printing is the use of unfilled polymers (polylactite, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) as a processed material, which significantly limits the scope of products obtained using FDM printing.
This problem is largely due to the fact that for the materials of polymer rods (filaments) there are rather “strict” requirements for physical and mechanical properties, melt viscosity - processability, thermal and physical properties, adhesion to various surfaces, etc. Thus, a filament for 3D - printing is a full-fledged polymer product. However, the production of 3D prototypes based on such functional filaments is an extremely difficult task due to the need to achieve high parameters in terms of mechanical, thermal, electrical and other properties of the final products obtained by 3D printing using the FDM method, and at the same time comply with the technological requirements for the filament, which is used to make the final product.
Thus, a filament for 3D - printing is a full-fledged polymer product. However, the production of 3D prototypes based on such functional filaments is an extremely difficult task due to the need to achieve high parameters in terms of mechanical, thermal, electrical and other properties of the final products obtained by 3D printing using the FDM method, and at the same time comply with the technological requirements for the filament, which is used to make the final product.
In other words, obtaining a “filament” from highly filled materials (heat-conducting, high-strength, chemically resistant, etc.) is an extremely difficult and, in some cases, completely impossible task. If the “filament” is obtained, then it is not possible to print it on conventional 3D printers.
In general, the use of polymer composite materials in FDM 3D printing is associated with a number of limitations and problems: requiring consideration of the properties of both the resulting products and the properties of consumables;

The solution to this problem is the rejection of polymer rods and the use of granules and powders as consumables for 3D printing, which are widely used for industrial injection molding.
For these purposes, a unique 3D printer with a screw-plunger extruder was developed, which allows processing low-flow polymer-composite materials in the following technological windows:
2. Operating temperatures: 25 - 450 °C;
3. Heat chamber temperature: 120 °C
3. Print volume 350×350×350mm;
4. Printing speed up to 30cm3/min;
5. Positioning accuracy from 0.05 mm.
Processed materials:
- Thermoplastics and thermoplastic elastomers: ABS copolymer, LDPE, PP, PVA, PET, PMMA, PSt, 1,2-SPB, SBS, thermoplastic polyolefin elastomers, thermoplastic elastomers;
- High-strength engineering plastics: polyphenylsulfide, polyetheretherketone, polycarbonate, fluoroplastic;
- Biodegradable polymers: polylactides, polyhydroxyalkanoates.

As short reinforcing agents, for three-dimensional prototypes, a variety of polymeric and inorganic fibers can act:
- Monofilaments: glass fiber, carbon, viscose, polyester; polyamide, copper, nickel, aluminum and silver fiber;
- Hybrid fibers: metal-textile, metal-glass and metal-polymer fibers;
- Biodegradable fibers: viscose, collagen, hydrogel and polysaccharide fibers.
The presented technology will make it possible to create products from composite materials with the widest scope, and not only prototypes, but ready-made functional products, which is relevant in the context of growing trends in the introduction of composite materials into large-scale industry and the expectations of the additive technologies market.
Compared to “filament” 3D printers, this technology has a number of advantages:
- a wide range of recyclable materials - opens up the possibility of using those materials that were previously available only to users of expensive Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) technology, as well as hitherto unsuitable for 3D printing in principle;
- reduction of material costs by 5-10 times;
- increased throughput of the extruder and, as a result, higher printing speed;
- preservation of the original properties of the material in the final product;
- the ability to experiment with filling the material directly during printing;
- the ability to test new materials directly in the form of the final product.

Learn more