Nylon 3d printer settings
How to 3D Print Nylon Filament Like a Pro – Ultimate Guide & FAQ – 3D Printerly
Learning how to 3D print with Nylon can pay off heavily when you want to make mechanically strong parts with diverse applications. However, Nylon is no easy filament to print with, and you’re definitely going to need to know what kind of settings and improvements you need to make for printing top-quality Nylon parts.
To 3D print Nylon, you should use a printing temperature between 225-270°C and a bed temperature between 70-90°C for the best results. Do not use cooling fans with Nylon and use a print speed that is between 25-50mm/s. Nylon is prone to absorbing moisture in the air, so store in an airtight container when not in use.
This article is going to be a simple, yet in-depth guide on how to 3D print Nylon filament just like the pros do, so stick around to see how it’s done and get your questions answered.
What is Nylon Filament for 3D Printing & What is it Made of?
Nylon filament or Polyamide in 3D printing is an exceptionally strong and durable thermoplastic filament that boasts high flexibility, great heat resistance, and even better toughness than ABS. It’s great for functional and mechanical parts that go through a lot of movement, like hinges and joints.
When we talk about what Nylon is made of, it is generally a synthetic polymer belonging to a family of polyamides. In a polyamide, many amides join with each other using a peptide bond. When several polyamides connect, Nylon is formed.
Nylon is an ideal choice for printing tools, RC cars, and everything of the like. It has a low coefficient of friction that makes it much more resistant to wear and tear than ABS, which is quite famous as well for such properties.
What Temperature Should You 3D Print Nylon?
The best nozzle temperature for printing Nylon is anywhere between 225-270°C depending on your 3D printer set up. Filament brands that manufacture Nylon also contain recommended temperature ranges. The eSUN ePA Nylon filament’s is 230-260°C while the OVERTURE Nylon’s is 250-270°C.
The best heat bed temperature for Nylon usually falls in the range of 70-90°C. You can try experimenting with different heat bed temperatures to figure out the perfect value that suits your Nylon filament and your 3D printer. Manufacturers will also send in their recommended bed temperature range for you to try out.
You can try experimenting with different heat bed temperatures to figure out the perfect value that suits your Nylon filament and your 3D printer. Manufacturers will also send in their recommended bed temperature range for you to try out.
A bed temperature of 60°C brought great results for one user who bought the taulman3D Nylon filament. Similarly, one customer remarked that a bed temperature of 110°C worked best for his Dremel Nylon filament.
Let’s now look at some top-rated Nylon filaments and their recommended nozzle and bed temperature ranges.
eSUN ePA NylonNozzle Temperature: 230-260°C
Bed Temperature: 70-90°C
Dremel Nylon
Nozzle Temperature: 230-250°C
Bed Temperature: 80-110°C
OVERTURE Nylon
Nozzle Temperature: 250-270°C
Bed Temperature: 25-50°C (though people report higher bed temperatures, around 80° C work better)
Taulman3D Nylon
Nozzle Temperature: 250-255°C
Bed Temperature: 55-70°C
What Printing Speed Should I Use for Nylon?
The recommended printing speed for Nylon is between 30-60mm/s.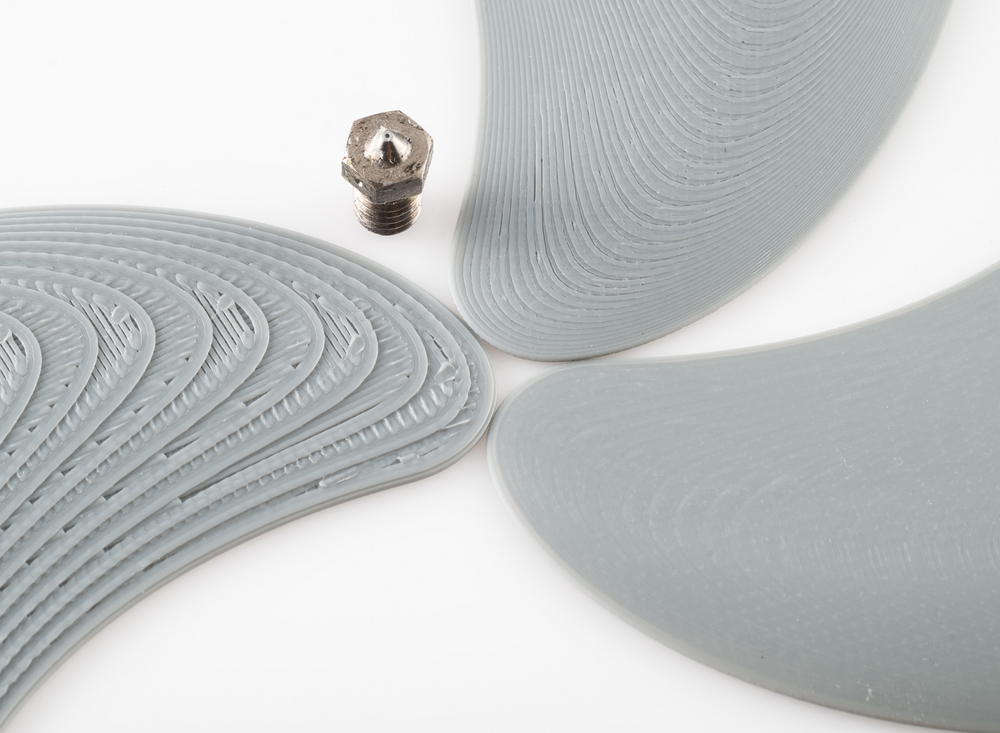 You can go beyond that, as long as your 3D printer is tuned up well and can handle faster speeds. Print quality usually declines when you go past 70mm/s for Nylon as it requires time to heat up and extrude evenly. Increasing printing temperature can help.
You can go beyond that, as long as your 3D printer is tuned up well and can handle faster speeds. Print quality usually declines when you go past 70mm/s for Nylon as it requires time to heat up and extrude evenly. Increasing printing temperature can help.
Nylon isn’t like PLA that flows easily out of the nozzle and can be printed at higher speeds. You’ll have to go slow with Nylon if you intend to prioritize part quality.
That said, Delta 3D printers are capable of printing at more than 100mm/s as they are generally more speedy and stable when it comes to 3D printing.
When you have large 3D prints that don’t require the highest of detail, using faster print speeds should work out just fine with an increase in your printing temperature by 5-10°C. Smaller 3D prints with more detail should ideally use a print speed of around 40mm/s.
Does Nylon Need a Cooling Fan?
Nylon does not need a cooling fan to make successful 3D prints, though some people use low cooling fan settings with good results. It’s not usually recommended to use a cooling fan with Nylon since it is prone to warping due to being a high temperature filament. An enclosed print chamber is ideal when using cooling.
It’s not usually recommended to use a cooling fan with Nylon since it is prone to warping due to being a high temperature filament. An enclosed print chamber is ideal when using cooling.
Turning your cooling fans off when 3D printing Nylon tends to result in stronger parts, while low cooling fans can lead to better surface quality and textures.
People usually set their fan speed at 50% or even lower when printing with Nylon. This is a filament that likes constant, ambient temperature that’s best achieved within an enclosure.
However, cooling fans can be quite useful when you need to print overhangs, and bridges in your prints. An easy way to do this is by implementing scripts that can be found in the Cura slicer, so the cooling fans turn on at specific intervals.
While warping is a key issue for 3D printed parts, the temperature of your environment also matters drastically when printing with Nylon. Avoid printing in a cold room, and try to use an enclosure.
What Are Advantages of 3D Printing Nylon?
- Can give sharper detail than ABS or PLA
- Creates mechanically durable, strong, and tough parts that are second to none
- Highly flexible when printed thin
- Top-notch impact resistance
- Resistant to wear and tear, and abrasion as well
- Easy post-processing with dyes and paints due to its hygroscopic nature
- More UV and chemical resistant than ABS or PLA
- Offers low friction for making high-quality moving parts
- Great for display and aesthetic models
What Are the Disadvantages of 3D Printing Nylon?
- Difficult to print with and not recommended for beginners
- Works best with an enclosure and a heated bed, unlike PLA
- Being hygroscopic also means that it accumulates moisture quickly when not stored somewhere dry
- For the best results, Nylon requires pre-drying, which can be bothering at times
- Prone to warping due to its high melting point
- Parts can shrink during printing if it’s cooled
- The majority of Nylon brands have a low shelf life
- An all-metal hot end is used to print Nylon and not all 3D printers come equipped with it
What Bed Surface Should I Use for Nylon Filament?
The best bed surface for printing Nylon filament is glass. A heated glass build plate with a layer of PVA glue or blue painter’s tape on it works great for adhesion. You can also use other advanced bed surfaces like garolite or PEI. These surfaces are known to work well for Nylon 3D prints.
A heated glass build plate with a layer of PVA glue or blue painter’s tape on it works great for adhesion. You can also use other advanced bed surfaces like garolite or PEI. These surfaces are known to work well for Nylon 3D prints.
Getting Nylon to properly adhere to the build plate can be tricky. However, you can certainly use different bed surfaces to see which one performs the best for you.
Generally, a glass bed is known to work wonders for Nylon. That is when you pair the bed with heating, and an adhesive like glue, or tape.
Some users have even used poplar wood and cardboard as a build plate for Nylon. However, that is not the most ideal option to go with.
I’d recommend getting yourself a good quality garolite or PEI bed surface. You can find a good garolite build surface on MatterHackers.
The LayerLock Garolite Bed Surface is a top-rated build plate that doesn’t require heating to print Nylon successfully. It is lamented with an epoxy resin for improved adhesion. You can also use 220 grit sandpaper on this bed to further improve the textured surface.
You can also use 220 grit sandpaper on this bed to further improve the textured surface.
In terms of a good PEI surface, these are available directly from Amazon for a competitive price. I’d recommend going for the Gizmo Dorks PEI 3D Printer Build Surface from Amazon.
In the following YouTube video, a user demonstrated how garolite works for Nylon.
How Strong is 3D Printed Nylon?
Nylon is popular for its durability and toughness. It’s more durable than ABS and boasts a high tensile strength of 7,000 psi. It is also highly flexible when printed thin, due to amazing impact and abrasion resistance. Military equipment such as tents, ropes and parachutes are made with this material.
Nylon is known to be ten times more impact-resistant than ABS. It’s on a whole new level than PLA in terms of toughness. Nylon is also flexible. Premium-grade cable ties are made out of Nylon and are extremely flexible.
If you’re printing Nylon with appropriate settings, you can count on it to tolerate significant impacts and abrasion. For that, make sure you’re using the right amount of infill and wall thickness.
For that, make sure you’re using the right amount of infill and wall thickness.
Best Nylon Filament to Buy for 3D Printing
Nylon has a reputation in the 3D printing space for its physical prowess and characteristics. Several manufacturers have this advanced filament up for grabs, but not all of them are worth the purchase.
Let’s have a look at some of the best Nylon filaments you can buy right now for 3D printing.
OVERTURE Nylon
OVERTURE Nylon is a high-class filament that promises to take away some complications associated with printing this material. It tends to warp lesser than other Nylon brands, and still offers the same excellent strength.
With a 4.5/5.0 overall rating on Amazon at the time of writing, OVERTURE Nylon is well-admired within its user base. 71% of the people who bought it have left a 5-star review lauded with praise.
It’s also priced conveniently at $31, and that’s even cheaper than the sub $55 cost of MatterHackers PRO Series Nylon. If you’re on a budget, there’s no other Nylon filament I’d rather recommend than this one.
If you’re on a budget, there’s no other Nylon filament I’d rather recommend than this one.
The manufacturer also includes a 200 × 200mm build surface for each spool of filament you buy from them. This surface is easily customizable to varying lengths to suit the size of your 3D printer.
One extremely satisfied customer was delighted to find out how easy it is to print with the OVERTURE Nylon. They even compared the ease-of-operation to PLA, minus the ventilation and temperature settings.
Buy OVERTURE Nylon directly from Amazon today.
SainSmart Carbon-Filled Nylon
SainSmart Carbon-Filled Nylon is an incredibly strong filament that has a formula built for rigidity and performance. It has a ratio of 75% Nylon to 25% Carbon Fiber, which is still easy to 3D print and provides an excellent surface finish.
For any projects that require some real resistance and strength, it would be a good idea to get yourself a spool of this filament.
It has a low shrinkage rate along with high strength and even less warping compared to normal Nylon filament. You can get some amazing dimensional accuracy, as well as solid functionality and stiffness for your 3D prints. Many people also enjoy how heat-resistant the filament is.
You can get some amazing dimensional accuracy, as well as solid functionality and stiffness for your 3D prints. Many people also enjoy how heat-resistant the filament is.
Some key examples of uses for this type of material would be things like prosthetics, cosplay, hinges, and even medical equipment. Do keep in mind that Carbon Fiber is an abrasive material, so it’s advised to use a hardened steel or stainless steel nozzle to handle it.
Using an enclosure is likely to give you the best results, since a constant ambient temperature is ideal.
Do be careful not to sand this material without using a respirator mask, as sanding it will create tiny dust particles that are irritating to breathe in. Additionally, it’s best to use spray paint and primer to paint SainSmart Nylon.
Buy SainSmart Nylon directly from Amazon today.
MatterHackers Pro Series Nylon
The MatterHackers Pro Series Nylon was one of the first filament brands to introduce a variety of colors for Nylon, which was previously known to be available in a few colors only.
This is a top-rated brand that has thousands of happy customers. You’re getting a cost-effective, insanely durable, and strong solution for all your functional and mechanical part requirements by purchasing this Nylon filament.
With an overwhelming majority of positive reviews, MatterHackers Pro Series Nylon is something that continues to deliver beyond expectations through accurate filament tolerance, and premium-grade build quality.
MatterHackers mentions that Kawasaki’s Supercross Racing Team Engineers also purchase the PRO Series materials from which this Nylon filament is made for their motorcycles.
If you require even tougher Nylon with extra resistance and durability, you have the MatterHackers PRO Series Carbon Fiber and glass-infused Nylon as well.
Check out the MatterHackers Pro Series of Nylon filaments on their official website store.
How Do You Dry Nylon Filaments?
Nylon filaments can be dried by heating them in an oven or leaving them to dry in any moisture-free container. You can also purchase a dedicated filament dryer to eliminate unwanted moisture from your Nylon filament. If you have a food dehydrator at home, you can use that too to keep Nylon dry.
You can also purchase a dedicated filament dryer to eliminate unwanted moisture from your Nylon filament. If you have a food dehydrator at home, you can use that too to keep Nylon dry.
One of Nylon’s most undesirable traits is its tendency to take up moisture from the air at an alarming rate if not stored in a dry place. This alone can make a day and night difference when printing with Nylon.
The following video is a brief explanation of printing with wet Nylon filament vs a dry one.
I recommend opting for something more professional if you want to make high-quality Nylon prints. The SUNLU Upgraded Filament Dryer is an excellent option that you can purchase right now from Amazon.
It allows you to get rid of all the built-up moisture in your filament in a few hours, offering better quality and consistent prints. As the dryer comes fully assembled, you don’t have to put any effort into setting it up.
As the dryer comes fully assembled, you don’t have to put any effort into setting it up.
One of the best features of this filament dryer is its ability to allow 3D printing when the filament is being dried. This attributes to a productive experience and top-notch Nylon prints.
How Do You Smooth Nylon 3D Prints?
To smooth Nylon 3D prints, you want to use a combination of sanding with low and high grit sandpaper, then polishing with an epoxy resin. You should start with a coarse sandpaper (50-100 grit), then work your way up to finer sandpaper (300-600 grit). Finish by applying epoxy resin for a shiny surface.
If there are any gaps or holes, the epoxy resin can also fill them in.
You cannot use methods like acetone smoothing with Nylon since it is extremely chemical resistant. Your best bet is to sand it for smoothing out Nylon 3D prints.
How to Dye, Paint, or Polish 3D Printed Nylon
The best way to dye or paint 3D printed Nylon is to use an RIT fabric dye. People usually submerge their Nylon print in a tank containing hot water and the fabric dye for about 5 minutes, and then cool the print down in another tank full of cold water. This locks in the dye on the print and brings amazing results.
People usually submerge their Nylon print in a tank containing hot water and the fabric dye for about 5 minutes, and then cool the print down in another tank full of cold water. This locks in the dye on the print and brings amazing results.
You can also use a combination of primer and spray paint to paint 3D-printed Nylon.
Nylon is notorious for quickly absorbing moisture from the air and getting wet in a matter of minutes. This is obviously bad news for makers and enthusiasts, but Nylon’s hygroscopic nature also lends it a plus point.
You can easily post-process Nylon as primers, spray paints, and dyes tend to stick to it well. Where PLA and ABS would take many coats of paint for a great, shiny look, Nylon demands considerably fewer.
MatterHackers has created this highly useful video to illustrate how to dye Nylon 3D printed parts.
The following items are required to dye Nylon prints:
- A Nylon 3D printed part
- A container to hold water at a high temperature
- An RIT dye (works best for Nylon and is easy to get as well)
- Another container filled with cold water
- Pliers or anything similar to handle the dye
- Weight of some sort to keep the filament submerged inside the container
- A thermometer to measure the temperature of the water
- A stove or a hot plate
- Some tissues or paper towels
Before you dye your Nylon filament, the first thing to do after creating a Nylon 3D print is to clean it up, remove any support structures using an X-acto knife or Flush Cutters (Amazon), and smooth it for the best results.
Begin with coarse sandpaper that’s somewhere between 50-100 grits to eliminate large print artifacts and imperfections.
After you’ve plucked out the big ones, continue to finer sandpaper of 200-400 grits for smoothing the surfaces of your Nylon part. It’s recommended to use wet sandpaper for a more refined experience.
The Austor 102 Pcs Wet & Dry Sandpaper Assortment (60 to 3,000 Grit) from Amazon is a great choice to go with for your 3D prints.
In addition, be sure to clean out the bottom of the part for any residual glue, hairspray, or tape. Once done, take any cloth or toothbrush to take care of any visible dust. Now that your Nylon part is all ready, it’s time to dye the filament.
First, you’ll have to tie your model with the weight and set it down inside the container to measure how much water it’s going to take. Then, simply take out the model, fill in water at the specified level, and then add the dye.
You’ll now place this container on your hot plate or stove and start heating it. A temperature of 70°C is known to work best.
A temperature of 70°C is known to work best.
Side by side, you’ll take your second container and fill it with cold water. This will be later used to maximize the effects of the dye and lock them in.
It’s advised to first use test prints for dyeing to see how much time they take to catch the dye in the hot water container.
5 minutes is known to work for most people, but you can also use 3-5 test prints, and submerge them each with 30-second increments to evaluate the best time for your Nylon model.
After leaving your part submerged in your hot water and dye tank for the desired time, take it out using pliers, and sink it inside the cold water container.
Leave it there for about 5-7 minutes and after taking it out and drying for a couple of minutes, enjoy a beautifully colored Nylon 3D print.
Does Nylon Filament Emit Fumes? Is It Toxic?
Yes, Nylon emits fumes as it melts at a high temperature. It is known to emit a volatile organic compound called Caprolactam and Styrene, both of which are dangerous upon inhalation and can cause headaches and breathing problems. It’s highly advised to print Nylon with an enclosure and a proper ventilation system.
It’s highly advised to print Nylon with an enclosure and a proper ventilation system.
Nylon is one of the most toxic 3D printer filaments out there. It does not emit foul-smelling odors during printing, but can pose a health risk when printed without precautionary measures.
You can check out my article called 3D Printer Enclosures: Temperature & Ventilation Guide, which goes through some of the key information that you’ll want to know.
Is Nylon Hard to Print With?
Nylon is an advanced filament that is known to be hard to print with due to a number of reasons. It has a high melting point that most 3D printers cannot achieve without an all-metal hot end. It is also extremely hygroscopic and will absorb moisture from the air quickly if not stored somewhere dry.
Ideally you should have an enclosure and a heated bed to 3D print Nylon successfully.
It can take a fair amount of time to get the hang of printing Nylon without running into print failures.
You also want to have the right settings, a capable 3D printer with an all-metal hot end, a suitable printing environment, and a place to store your filament and prevent it from getting dry.
Following the settings and process in this article should make Nylon easier to 3D print with.
Once you get everything right, your chances of getting amazing Nylon prints will increase dramatically.
Does Nylon Need an Enclosure?
Yes, it’s highly recommended to print Nylon with an enclosure. Nylon has a high melting point that makes it vulnerable to warping. Using an enclosure minimizes the chances of warping and provides Nylon the constant, ambient temperature that it needs to thrive and make stunning prints.
An enclosed print chamber increases print quality and keeps the temperature generated from the nozzle and the bed regulated with minimal fluctuations. Therefore, using an enclosure when printing with Nylon can bring great results.
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With Nylon
Learn how to 3D print Nylon like a pro. Nylon is a stronger and more durable alternative to PLA or ABS and easy to 3D print with using these Tips and Tricks.
Nylon is a stronger and more durable alternative to PLA or ABS and easy to 3D print with using these Tips and Tricks.
Updated on November 14, 2022
by
MatterHackers
Everyone with a 3D printer is familiar with PLA and ABS.
If you’ve 3D printed with PLA, you probably know that while it’s fairly strong, it’s also very brittle. You can’t leave parts out in the sun or anywhere that the temperature gets above 100°F.
If you’ve 3D printed with ABS, you know it’s much more durable than PLA, but 3D printed ABS parts don’t have the strength of injection molded parts, and often aren’t strong enough for functional parts.
Enter Nylon.
Nylon filament is an incredibly strong, durable and versatile 3D printing material. Flexible when thin, but with very high inter-layer adhesion, nylon lends itself well to things like living hinges and other functional parts. Its low friction coefficient and high melting temperature make it an excellent choice for a variety of everyday items such as 3D printed tools, gears, RC cars and more.
Check out our tips below on how to successfully 3D print with nylon filament.
From achieving excellent bed adhesion to proper filament storage, this guide prepares you with the knowledge and tools you will need to succeed when printing with nylon.
Not All HotEnds Are Created EqualMost 3D printers come standard with hotends that use PEEK and PTFE. Both PEEK and PTFE begin to breakdown above 240°C and will burn and emit noxious fumes. When successfully printing with nylon filament, you'll want a hotend that reaches temperatures of at least 250°C. If you aren’t sure if your hot end is setup for 3D printing nylon, send us an email or check with your printer manufacturer and we can let you know.
Most 3D printers can easily be upgraded with an all-metal hot end in order to print at temperatures above 240°C (extrusion temperature). We use the E3D V6 All Metal HotEnd on our machines due to the all-metal design that allows temperatures to safely reach up to 300°C. They are excellent hot ends that we highly recommend. Before replacing your current printer's hotend, make sure to print the correct mount to attach the E3D V6 hotend to your 3D printer.
They are excellent hot ends that we highly recommend. Before replacing your current printer's hotend, make sure to print the correct mount to attach the E3D V6 hotend to your 3D printer.
E3D V6 All Metal HotEnd is the go-to for Nylon 3D printing. You can find them pre-installed on many printers, including our own Pulse 3D Printers.
Bed Surface Matters: Garolite, Glass and PVA GlueLike with any other type of filament, the bed surface you choose to print nylon on can be the make or break between warping and successful 3D printing. For nylon, garolite sheets and glass plates are two build surfaces we've seen produce the most consistent successful results. With the addition of a PVA glue stick, both surfaces provide the bed adhesion necessary to bind prints to the build surface for a smooth 3D printing experience.
Our personal favorite surface to use with nylon filament is LayerLock Garolite Build Surface. Made out of fiberglass linen cloth laminated with epoxy resin, this surface has high stability over temperature so it easily withstands the 60°C recommended for successful nylon bed adhesion on a heated bed. Another perk of using a garolite surface is its strong adhesion quality that lasts for thousands of prints with sandpaper. Using a sheet of 220 grit sandpaper, lightly sand down the top of the garolite to remove any blemishes and reveal a more textured, even surface. This allows nylon to achieve a better grip on the bed for a successful flat first layer, leading to a successful nylon 3D print overall for years to come.
Another perk of using a garolite surface is its strong adhesion quality that lasts for thousands of prints with sandpaper. Using a sheet of 220 grit sandpaper, lightly sand down the top of the garolite to remove any blemishes and reveal a more textured, even surface. This allows nylon to achieve a better grip on the bed for a successful flat first layer, leading to a successful nylon 3D print overall for years to come.
LayerLock Garolite Build Surface is designed to succeed with nylon, nylon-based filaments like NylonX, and other 3D printing materials.
We trust in the success of garolite so much that we offer it as the stock bed surface for our Pulse XE, the 3D printer designed to succeed with 3D printing nylon and nylon-based filaments (on top of standard filaments). For maximum success, PVA glue and sandpaper are also included with LayerLock Garolite Build Surfaces for additional adhesion and minimal maintenance for longevity. To learn more about printing on garolite, check out our "How To: 3D Print Nylon on Garolite Print Beds" article.
Nylon filament is incredibly hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs water from the air. Nylon can absorb more than 10% of its weight in water in less than 24 hours which is why it is best to not leave hygroscopic filaments sitting out in the open. When you 3D print with nylon filament that isn’t dry, the water in the filament explodes causing air bubbles during printing that prevents good layer adhesion, greatly weakens the part and ruins the surface finish. No doubt about it; successful 3D printing with nylon and nylon-based materials require dry filament.
Dry nylon, on the other hand, prints buttery smooth and has a glossy finish.
Desiccant helps keep filaments dry, but packets of desiccant are nowhere near enough to actually extract the moisture from your 3D printing materials. MatterHackers' preferred tool for drying Nylon is the PrintDry system. Just place the spools in the PrintDry chamber, set the system to 75c, and leave to dry for 8-12 hours.
Another way to dry nylon filament is by placing it in an oven at 160°F - 180°F for 6 to 8 hours. Keep in mind that most all convection and household ovens do not regulate their temperature well at these lower temperatures and can easily warp your spool or soften the plastic causing it to deform and even adhere the filament stands together.
After drying, either immediately print with it in a room that isn't cold or drafty or store it in an airtight container with desiccant to use for later. If using a system like the PrintDry, you can leave the spool in the unit and print directly from it, keeping moisture at bay while on those long prints. To learn more about desiccant as well as some useful 3D printing tools, click here.
Dry 3D printed nylon on the left, wet 3D printed nylon on the right
While kitchen ovens are capable of drying filament, we highly recommend using a PrintDry PRO Filament Drying System instead. PrintDry is a safe, desktop-friendly machine engineered specifically for removing moisture from filaments.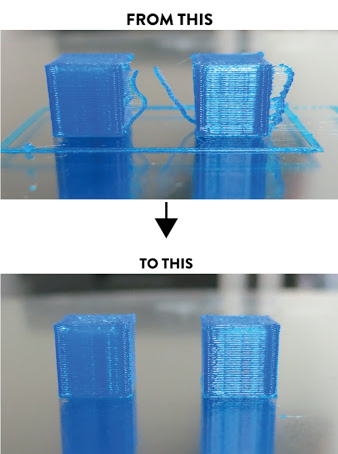 With its compact, transportable design, you can simply place the PrintDry PRO next to your 3D printer and feed dry filament into it while it's printing. If you are unable to feed the filament in the PrintDry PRO directly into your printer, this filament drying system still works very well for simply drying filament and then storing it in an air-tight container for later. To get the best quality prints possible, filament drying systems like the PrintDry are a 3D printing accessory we highly recommend for consistent success.
With its compact, transportable design, you can simply place the PrintDry PRO next to your 3D printer and feed dry filament into it while it's printing. If you are unable to feed the filament in the PrintDry PRO directly into your printer, this filament drying system still works very well for simply drying filament and then storing it in an air-tight container for later. To get the best quality prints possible, filament drying systems like the PrintDry are a 3D printing accessory we highly recommend for consistent success.
To learn more about the benefits of drying filaments, check out our article here.
Filament drying systems like PrintDry are highly recommended to remove moisture from hygroscopic filaments for maximum strength and durability in your 3D prints.
Nylon Can WarpWe've found 3D printing nylon can warp about as much as ABS.
When printing on glass or garolite, a heated bed is required with nylon filament. A PVA based glue stick applied to the bed is the best method of bed adhesion. Elmer’s or Scotch permanent glue sticks are inexpensive and easily found at a reasonable price.
Elmer’s or Scotch permanent glue sticks are inexpensive and easily found at a reasonable price.
We've found that a bed heated to 75°C with a thin layer of glue applied in a cross-hatch pattern works best for glass plates.
When printing on a garolite surface, a build plate is required with nylon filament. Whether it's directly on a heated bed, a sheet of glass, PEI glass or a FlexPlate System, we recommend the garolite sheet be attached to some kind of build plate that is able to transfer heat to this build surface. Like printing on glass, a PVA based glue stick applied to the bed can be helpful with bed adhesion for garolite build surfaces. We recommend Elmer's glue sticks for this surface. If more adhesion is needed, use 220g sandpaper to lightly sand all across the garolite for a textured, even surface that the print can grab onto.
For bed temperature, we recommend anywhere between 55°C - 65°C depending on what type of brand and nylon or nylon-based filament you're printing with. If it's NylonX, we recommend 60°C. If it's NylonG, we recommend 65°C.
If it's NylonX, we recommend 60°C. If it's NylonG, we recommend 65°C.
Do not use layer cooling fans and avoid drafty or cool rooms for best results. If you can't avoid placing your printer in drafty or cold rooms, consider either make shifting your own printer enclosure or purchasing one of the 3D printer enclosure kits sold here.
3D Printed Nylon Surfboard Fins Reinforced with Carbon Fiber using the MarkForged 3D Printer
Recommended Nylon 3D Print Settings:- Extruder Temp.: 240°C - 260°C
- Start printing at 250°C and adjust in increments of 5°C until you find the right temperature that produces a strong, durable print with a beautiful finishing surface
- The right temperature may vary between nylon and nylon-based filaments
- The right temperature may vary between brands of nylon and nylon-based filaments
- Bed Temp.: 55-65°C
- This is for garolite surfaces with PVA based glue
- Bed Temp.
 : 70-80°C
: 70-80°C - This is for glass and other surfaces with PVA based glue
- Speed: 30-60 mm/s
- 0.2 mm - 0.4 mm layer heights
- 0% Layer Cooling Fan
We hope this helps you succeed with 3D printing Nylon. If you have any further questions hop on our forum full of helpful posts and fellow makers working together towards a successful 3D printing experience.
If you are looking for a machine that prints nylon right out of the box, check out some of the following printers below:
- Ultimaker S5
- LulzBot TAZ 6 / LulzBot TAZ Workhorse / LulzBot TAZ Pro
- Pulse XE / Pulse DXE
- Raise3D Pro2 / Raise3D Pro2 Plus
- BCN3D Sigma R19 / BCN3D Sigmax R19
- MAKEiT PRO-M / MAKEiT PRO-L
Happy Printing!
Produce strong, durable prints with a variety of vibrant colors from our line of MatterHackers Series PRO Series Nylon filament.
Article Tags
- 3D Printing
- Firmware
- 3D Design
- MatterControl
- Press Releases
- Small Business
- Automotive
- E3D
- Jewelry Making
- Engineering
- Entertainment Industry
- MatterControl Touch
- ESD Materials
- NylonX
- BCN3D
- Open Source
- Crafty Pen
- Digital Fabrication Anatomy
- How To
- Hardware and Upgrades
- Tips and Tricks
- Weekend Builds
- Top Ten
- Education
- Tech Breakdown
- Women in 3D Printing
- Project Ideas
- Advanced Materials
- Reference
- Pulse Dual Extrusion
- Product Spotlight
- Aerospace
- Jobs
- Military & Government
- Multi-Tool Machines
- Getting Started
- Healthcare
- How To Succeed With Any 3D Printing Material
- Creality3D
- Architecture
- 3D Printer Reviews
- Hacker of the Month
Related Products
View all related productsNylon printing
Article applies to printers:
Felix 3. 0 1X MakerBot Replicator 2X WANHAO Duplicator 4X
0 1X MakerBot Replicator 2X WANHAO Duplicator 4X The tips in this article will teach you how to print nylon ( Nylon ) like a pro. Nylon ( Nylon ) is a stronger and more durable alternative to materials such as PLA and ABS plastics.
Everyone who has ever printed on a 3D printer is familiar with materials such as PLA and ABS plastics. If you've printed PLA with plastic, you probably know that while it's quite strong, it's also a very brittle material. You cannot leave the parts in the sun or in any other place where the temperature rises above 54*C.
If you've printed ABS plastic, you know it's much stronger than PLA, but 3D printed ABS parts don't have the strength of molded parts, and often aren't strong enough for functional parts.
Trying Nylon ( Nylon).
Nylon is an incredibly strong, durable and versatile 3D printing material. Flexible when thin, but with very high interlayer adhesion, Nylon ( Nylon) well applicable in the manufacture of models such as movable hinges or other functional parts and mechanisms. Low friction and high melting point Nylon Nylon is an excellent choice for printing things like gears.
Low friction and high melting point Nylon Nylon is an excellent choice for printing things like gears.
Here's what you need to know to get started printing with nylon ( Nylon).
1) Nylon melting point - 240C and above, make sure your printer's extruder can be heated to at least 260C.
2) Nylon must be dry.
Nylon is very hygroscopic. This means that it easily absorbs water from the air. Nylon can absorb more than 10% of its weight in water in less than 24 hours. Dry filament is required to achieve successful printing with nylon filaments. When printing with Nylon that is not dry, the water explodes the filament, causing air bubbles during printing, which prevents good layer adhesion and greatly weakens the model. It becomes fragile.
Dry Nylon is printed with a buttery smooth or glossy finish. In order to dry Nylon (Nylon), it must be placed in an oven with a temperature of 80-95C for 6-8 hours. After drying, store in an airtight container, preferably with a desiccant (silica gel).
After drying, store in an airtight container, preferably with a desiccant (silica gel).
Model printed with dry nylon on the left, wet nylon on the right.
3) Nylon may warp.
We have found that Nylon deforms about the same as ABS.
When printing with Nylon, a heated bed printer is required. And a PVA-based glue stick applied to a heated table is the best way to adhere. Glue or scotch tape is a fairly inexpensive consumable and is quite easy to find. We have found that a heated bed up to 75C, together with a thin layer of adhesive, works great when printing with Nylon.
Do not use layer cooling fans.
For best 3D printing results, avoid drafts or cool places.
Recommended printing parameters:
Extrusion temperature - 240-260C (each type of Nylon filament is slightly different. Follow manufacturer's recommendations).
Heated bed temperature - 70-80C (use PVA glue)
Print speed: 30-60mm/s
Layer height: 0. 2 - 0.4 mm
2 - 0.4 mm
dedicated to developing innovative materials for 3D printing. To date, 3 types of nylon are available under the Taulman3D brand.
Taulman3D 618 Nylon is specially designed for 3D printing, its features are good bonding, high water resistance, good tear resistance and ink absorption. Models printed with this material have a natural white color with a transparent surface. Plastic can also be easily dyed, both before and after printing.
Taulman3D 645 Nylon has unique characteristics. Expected tensile strength is 16.533 psi (114 MPa), tensile strength is 120%. Taulman3D 645 Nylon has all the same features as Taulman3D 618 Nylon but with improved performance. Recommended printing temperature is ~230°C to 265°C.
Taulman3D 645 Nylon - is the company's latest development with improved intercoat adhesion and increased strength.
You can buy Taulman3D products in our online store.
Techno Print 3D Company
This is our first review of the most popular and inexpensive 3D printers for 2020. The list will include the best-selling devices in two price ranges (up to 30 tr and up to 60 tr). Printers working with both plastic filament (FDM) and photopolymers (LCD/DLP) will be presented. This list will always be up to date, as it is periodically updated and supplemented. Read more→
The list will include the best-selling devices in two price ranges (up to 30 tr and up to 60 tr). Printers working with both plastic filament (FDM) and photopolymers (LCD/DLP) will be presented. This list will always be up to date, as it is periodically updated and supplemented. Read more→
The Chinese company Dazz3D announces the launch of the project on KickStarter and accepts pre-orders for Dazz3D Basic and Dazz3D Pro 3D printers. These revolutionary new devices are aimed at both the professional and amateur markets. Read more→
We all know that accurate calibration of the 3D printer desktop is the foundation and the key to successful printing on any FDM printer. In this article we will talk about the main and most popular ways to level the "bed". So, as mentioned above, 3D printing without desktop calibration is impossible. We face this process Read more→
It's hard to go through a day today without hearing about 3D printing technology, which is bursting into our lives at an incredible speed. More and more people around the world are becoming addicted to 3D printing technology as it becomes more accessible and cheaper every day. Now almost anyone can afford to buy a 3D printer, and with the help of Read more→
More and more people around the world are becoming addicted to 3D printing technology as it becomes more accessible and cheaper every day. Now almost anyone can afford to buy a 3D printer, and with the help of Read more→
The FormLabs Form 2 and Ultimaker 3 are perhaps the most popular 3D printers today, capable of high quality printing with incredible surface detail. Moreover, these two devices use completely different technologies, and therefore, there are a lot of differences between them. Many will say that it is wrong to compare them or Read more→
XYZprinting, best known for its daVinci line of desktop 3D printers, is bringing five new devices to the professional and industrial environment. One will use laser sintering technology, the second full color inkjet printing and three DLP machines. First of all, the novelties will be of interest to dentists and jewelers. Read more→
Cleaning the nozzle of a 3D printer is a fairly common process that any user of such a device has to deal with.