Using solidworks for 3d printing
Should you use SOLIDWORKS for 3D printing?
Published on May 7, 2020 by Carlota V.
In industrial sectors and product design, SOLIDWORKS is a CAD solution many rely on. The software has been around since the mid 90s and the latest figures estimate that there are around 9.3 million active users across 80 countries. It is based on parametric modeling and is primarily used to create 3D models and assemblies. SOLIDWORKS has also been adopted in the world of additive manufacturing as it enables engineers to save their models in a STL format; the format needed for a 3D model to be processed by 3D printing software.
SOLIDWORKS was developed back in 1993 when John Hirschtick, a member of the MIT Blackjack Team, recruited a team of engineers to create the first accessible and affordable 3D modeling solution. At the time, AutoCAD, which had been released in 1989, was limited to the creation and editing of 2D geometry. Therefore, SOLIDWORKS was the first software to bring an accessible 3D modeling solution to the market. For many engineers, 3D modeling truly changed the way they could bring creations to life.
One of the first versions of the software
Soon enough the software became extremely popular and Dassault Systèmes decided to acquire it in 1997 for $320 million in stock. At the time, Dassault Systèmes was known for its CATIA solution, a product lifecycle management suite, which combines design, engineering, and manufacturing features used for automotive, aerospace and aeronautics. Essentially, SOLIDWORKS is a lighter version of CATIA.
Main Features of SOLIDWORKS
As mentioned, SOLIDWORKS is a CAD software based on parametric design. Parametric design is a process that clarifies the relationship between design intent and design response. One of the key features of parametric models is that attributes that are interlinked can automatically change their feature when one attribute is changed. This modeling process is great for projects with a lot of manufacturing requirements. 3D models can be created for high performance parts and assemblies used in sectors such as aerospace & defence or automotive.
3D models can be created for high performance parts and assemblies used in sectors such as aerospace & defence or automotive.
For example, the very popular AutoCAD solution from Autodesk is primarily a 2D CAD software that caters to architects, home builders and civil engineers. Even though it is possible to create basic 3D surface and solid modeling with AutoCAD, it is not its key feature, and definitely not as easy as working on a parametric modeling software. This is the key benefit of SOLIDWORKS.
It is primarily used to model parts or assemblies (as is the case here)
Furthermore, SOLIDWORKS also includes very beneficial features for a number of industrial applications such as simulation, rendering tools and CAM (computer-aided manufacturing) tools. You will be able to create solid models with SOLIDWORKS, but also import, create, and manipulate surfaces, view models in wireframe mode, and generate 2D drawings from the 3D solid models.
SOLIDWORKS Standard
SOLIDWORKS Standard will enable engineers and designers to create parametric parts, assemblies, production level drawings, as well as generating complex surfaces, sheet metal flat patterns, and structural weldments. Thanks to its parametric design feature, the models will automatically update with design changes. Conceptual design is also an important capability of the software as it allows to create layout stretches, apply motors and forces to check mechanism performance, etc. The Standard license costs $3,995 with an annual maintenance fee of $1,295.
Thanks to its parametric design feature, the models will automatically update with design changes. Conceptual design is also an important capability of the software as it allows to create layout stretches, apply motors and forces to check mechanism performance, etc. The Standard license costs $3,995 with an annual maintenance fee of $1,295.
SOLIDWORKS Professional
SOLIDWORKS Professional builds on the capabilities of SOLIDWORKS Standard to increase design productivity, with file management tools, advanced photo-realistic rendering, automated cost-elimination, design checking and a parts library. The Professional licence costs $5,490 with an annual maintenance fee of $1,495.
It can offer powerful simulation tools
SOLIDWORKS Premium
SOLIDWORKS Premium adds powerful simulation and design validation to the capabilities of SOLIDWORKS Professional, plus reverse engineering, and advanced wire and pipe routing functionality. ScanTo3D tools, available in SOLIDWORKS Premium, import mesh and point cloud data from which you can create surfaces and solid models. The Premium licence costs $7,995 with an annual maintenance fee of $1,995.
ScanTo3D tools, available in SOLIDWORKS Premium, import mesh and point cloud data from which you can create surfaces and solid models. The Premium licence costs $7,995 with an annual maintenance fee of $1,995.
SOLIDWORKS for 3D printing
As mentioned, SOLIDWORKS can be used for additive manufacturing technologies because you can save your 3D model as an STL file. This is the format needed to transform the data from the model into G-code that a 3D printer can work with. However, this is not the only way in which SOLIDWORKS is suited for additive manufacturing projects. When designing for additive manufacturing, there will be many design considerations to take into account. Anything from distortions, warping, and breaking can occur, which means a 3D model must be adjusted accordingly.
Topology Optimization is one of the design techniques possible on SOLIDWORKS
SOLIDWORKS has put in place tools that account for the special requirements of AM techniques, including support structures, and any distortion that can arise during printing. These features are extremely important, especially when working with expensive materials such as metals, where failed prints can be very costly. Finally, given the design freedom that 3D printing technologies allow, design techniques such as topology optimization can be applied to models. Another way to save material consumption and optimize a part! You can find more information HERE.
These features are extremely important, especially when working with expensive materials such as metals, where failed prints can be very costly. Finally, given the design freedom that 3D printing technologies allow, design techniques such as topology optimization can be applied to models. Another way to save material consumption and optimize a part! You can find more information HERE.
Do you use SOLIDWORKS? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages! Sign up for our free weekly Newsletter, all the latest news in 3D printing straight to your inbox!
How Do I 3D Print from SOLIDWORKS?
TriMech Video Tech Tips, 3D CAD, SOLIDWORKS, Tech Tips
By David Cano-Mejia on
As 3D printing becomes more common in the workplace, users are turning to SOLIDWORKS to better understand their designs in the context of 3D printing. SOLIDWORKS offers several 3D printing visualization and analysis tools and all of them can be accessed through the Print3D tool (File > Print3D). Let’s take a look!
SOLIDWORKS offers several 3D printing visualization and analysis tools and all of them can be accessed through the Print3D tool (File > Print3D). Let’s take a look!
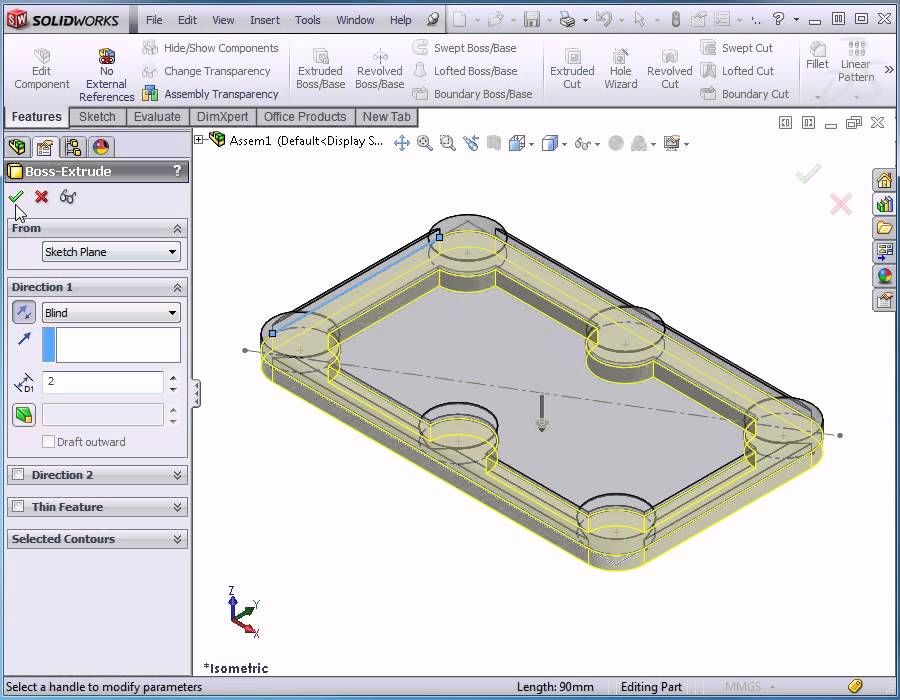
Does My Part Fit on My Printer?
The first step in analyzing your design for 3D printing is to ensure that it will fit inside the print area. Under Printer, you can select the 3D printer that you will be using. If this is your first time using the Print3D command, you will need to add your printers to your favorites list. Click on Manage Favorites to browse all available 3D printers. SOLIDWORKS has added a comprehensive list of 3D printers with up-to-date envelope information so you can quickly find your most used printers and add them to your Favorites for easy access. If for some reason your 3D printer is not listed under this library, you can define a Custom Printer by manually inputting the print volume dimensions.
Under Print Bed Location select a plane, or planar face, to be defined as the bottom plane of the model. This will automatically orient your model on the print bed. If the model is larger than the print volume, the geometry outside the print volume will be highlighted in red and you will not be able to print. If you need to change the orientation of the model, you can use the translation controls, manually type in the desired print bed angle and offsets in the Print3D PropertyManager, or click Orient to Fit to let SOLIDWORKS orient your part or assembly for you.
This will automatically orient your model on the print bed. If the model is larger than the print volume, the geometry outside the print volume will be highlighted in red and you will not be able to print. If you need to change the orientation of the model, you can use the translation controls, manually type in the desired print bed angle and offsets in the Print3D PropertyManager, or click Orient to Fit to let SOLIDWORKS orient your part or assembly for you.
Under Scale, you can also choose to print your design at a scale other than 1, which is the current size of the model in SOLIDWORKS. To do so, type a value for the scale factor. The new value is saved as a document property in the SOLIDWORKS file so if you print the model again, the saved value is used still there. The Scale to Fit option sets the scale to the largest value that will still fit inside of the print volume.
Can I Analyze My 3d Print?
Sure! You just have to switch over to the Preview tab in the Print3D PropertyManager.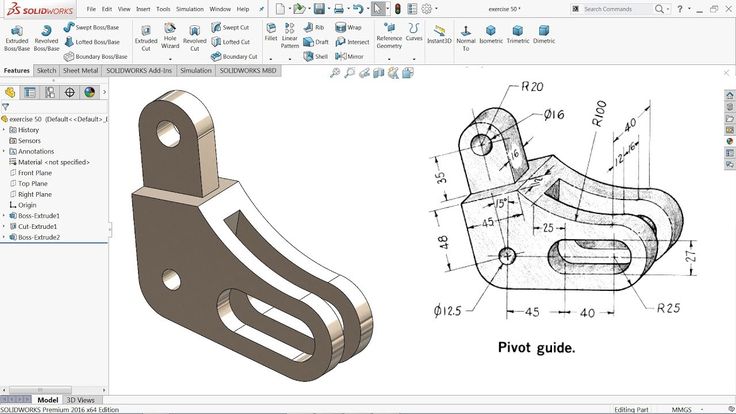 There are several analysis tools that you can use to get a better understanding of the design to be printed.
There are several analysis tools that you can use to get a better understanding of the design to be printed.
- Build Analysis
- This allows you to preview the faces of your model that may require supports. Depending on the printer being used, at a certain overhang angle, the print quality is greatly affected unless supports are used. Type in the maximum angle for the faces that will require support. I recommend changing the Support face color to red and checking Show As Transparent to make it easy to visualize all of the faces that will need support.
- Layer Height
- This option lets you visualize the height of each print layer in order to determine whether the print resolution is sufficiently fine to produce the desired print. Type in a layer height and turn on Show Striation Lines in order to get a preview.
- If you are planning on exporting your file as a .3MF (3D Manufacturing Format), you can choose to let SOLIDWORKS generate the slices for the 3D print and embed those into the .
 3MF file instead of slicing the model using the printer’s slicer software
3MF file instead of slicing the model using the printer’s slicer software
- Thickness/Gap Analysis
- If you are using FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) for your prints, this calculates the ideal wall thickness/gap based on the material that you set and the layer height.
How Do I Export the File to Be 3D Printed?
When you are done analyzing and visualizing your design, you are ready to export the 3D print files. You can export part and assembly files to STL (.stl), 3D Manufacturing Format (.3mf), or Additive Manufacturing File Format (.amf) files.
- STL (*.stl)
- This ASCII or binary format file describes only the surface geometry of a 3D object as a raw, unstructured triangulated surface.
- 3D Manufacturing Format (*.3mf)
- This is a 3D focused file format that contains 3D model, material, and property information for sharing full-fidelity 3D models to other applications, platforms, services, and printers.

- This is a 3D focused file format that contains 3D model, material, and property information for sharing full-fidelity 3D models to other applications, platforms, services, and printers.
- Additive Manufacturing File (*.amf)
- This xml-based file lets you select export options that store the color, scale and materials of the object to be 3D printed in the .AMF file, as well as the geometry of the model.
Under Save To File, select your desired format and click Save File. Once you have one of these files, you can import it into your printer’s slicer software to generate the G-code that the printer will use to print your design.
Can I Print Directly From SOLIDWORKS?
Yes, but only if your 3D printer manufacturer uses the SOLIDWORKS 3D Print API. As soon as you finish using the Print3D command and click OK , the 3D printing rapid prototyping dialog box will open to ensure that your printer’s build area is empty. The printer will start to warm up get ready to print. If your 3D printer does not use the SOLIDWORKS 3D Print API, you can still export the file as described above and import it into your printer’s slicer software.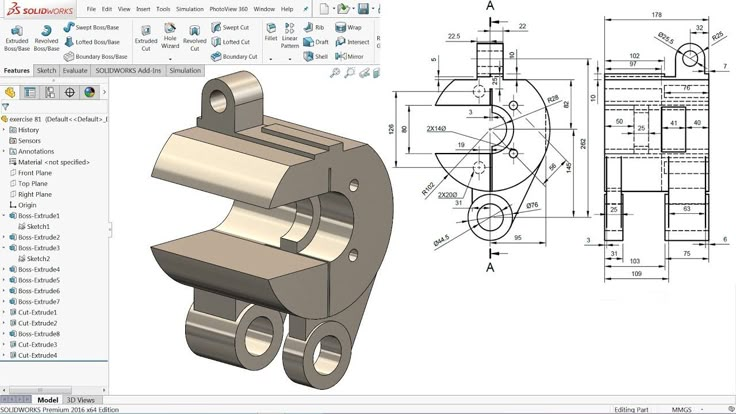
How Do I Set My 3D Printing Options?
If you are planning on printing directly from SOLIDWORKS, you can set the 3D printing options that you would typically set in the slicer software. Job Quality corresponds to the print layer height and is the printer’s approximation to match that resolution. Infill Percentage lets you select the percentage of the part that is solid. You can select between 0%, 10%, 40%, 70%, and 100%. Infill percentage can greatly affect print times and part strength. Include Raft builds the print output on top of a raft of disposable material that you can remove after printing. This option is cleared by default. Include Supports adds supports for model faces that are in open space with no part of the model supporting the face. This option is selected by default and resets to the default each time that you open the Print3D PropertyManager.
The tools available inside of the Print3D command are easy to use and set up.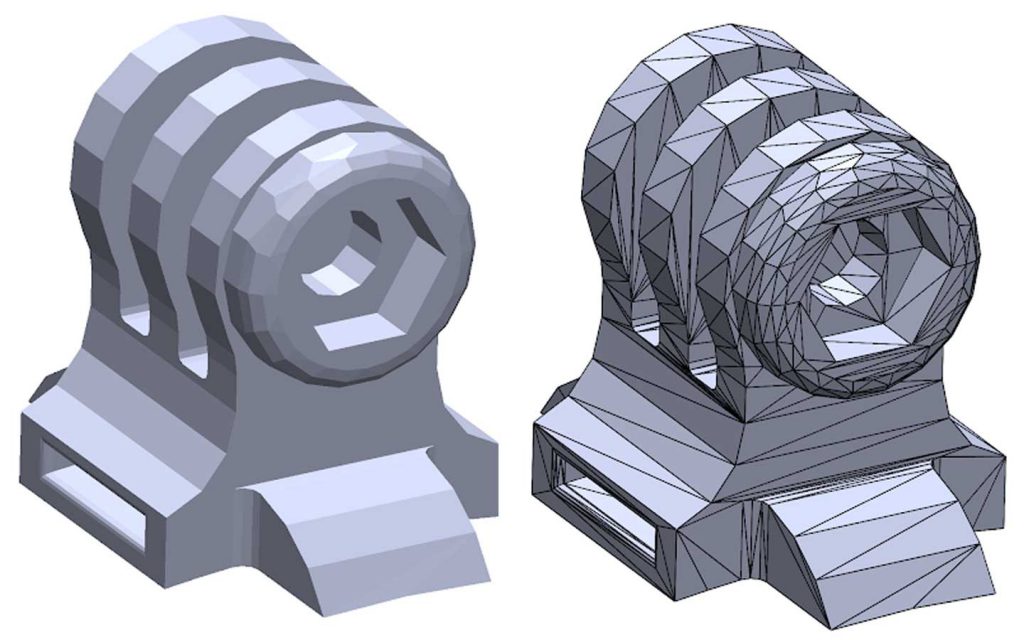 Even if a different slicer software ends up being used to send the model to the printer, these tools can serve as a great starting point to understand the 3D printing requirements that your specific design may have.
Even if a different slicer software ends up being used to send the model to the printer, these tools can serve as a great starting point to understand the 3D printing requirements that your specific design may have.
Ready to learn more about SOLIDWORKS? Explore the different training options that we have to offer.
Preparing a model for 3D printing in SolidWorks
by 3DAdmin · 10/09/2016
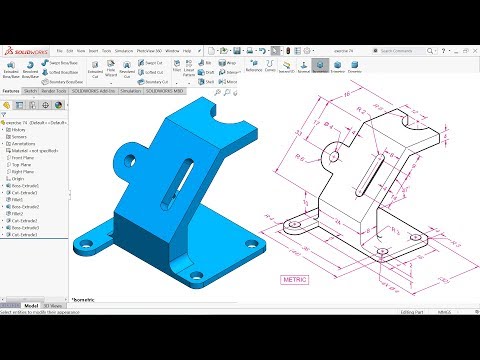
In this article, you will learn how to create and prepare a model for subsequent 3D printing in SolidWorks.
The process of building a three-dimensional model of the part:
- Open the SolidWorks program, create a document “Part”.
- Open the Design Tree, click on the Top View icon.
- Orient this plane perpendicularly in the View Orientation panel.
- On the "Sketch" toolbar, click on the "Rectangle" icon and draw this shape in the sketch.
- With the left mouse button (LMB), click on any free space in the drawing window. The rectangle will turn blue, indicating that no dimensions have been set.
- Click on one of the sides of the rectangle and delete it.
- In place of the remote side, draw an arc using the “Arc through three points” function.
- The next step is to relate the origin to the sketch elements. You can do this by activating "Add Relationship".
- Between the center of the arc and the starting point, we establish the relationship “Coincidence”.
- After that, open the window and set the dimensions of the sketch.
- Click LMB on any point of the figure, and then on any free space outside the drawing. This activates the "Automatic Dimensioning" function.
- Create a solid element.
- Click on the “Extruded Boss” icon, set the extrusion. We activate the function.
- Create a cylinder.
- Activate the top face of the base with LMB.
- Click on the “Create Sketch” icon and call the “Perpendicular” function.
- Activate the “Circle” icon.
- Move the cursor to the starting point and click LMB. Move the cursor away from the center and press the button again to designate the second point.
- Set the circle size on the SolidWorks toolbar. Activate the "Automatic dimensioning" function.
- Click on the “Extruded Boss” icon and extrude the circle by 30mm.
- Building a square cutout.
- Activate the top face of the base. Click on the “Create Sketch” icon and orient it perpendicularly.
- Click on the “Rectangle” icon, draw a square and enter its dimensions from the edges of the part.
- Activate the "Extruded cut" function, enter a value of 20 mm.
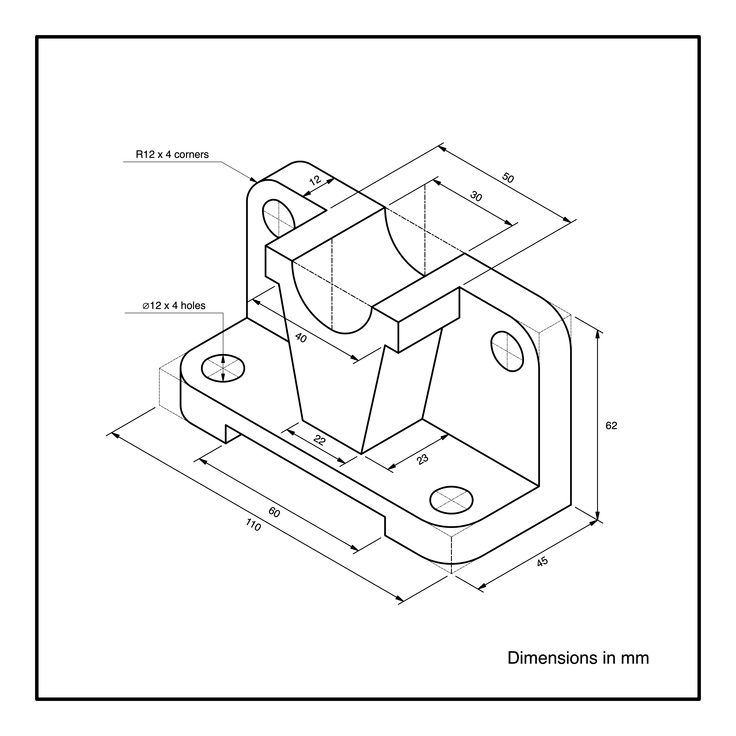
- Click on the “Slope” icon, enter the parameters. “Tilt angle” - 15 mm, “Neutral plane” - the bottom of the square cutout.
- In the “Slope faces” window, double-clicking the LMB, we write the side faces of the square cutout.
- Click on the “Rounding” icon, enter the value of the rounding radius -10 mm.
- Create a cutout. Orient the sketch plane perpendicularly.
- Select the "Polygon" icon. Click LMB on the place where the polygon will be located. Click again with LMB and specify the position of one of the vertices.
- Activate "Add Relationship". Click LMB on one of the edges of the polygon and set the relationship “Vertical”.
- Enter the edge size - 10 mm.
- Set the size of the position of the center of the figure.
- We establish a relationship between the starting point and the center of the polygon.
- Activate the "Extruded cut" and set the value to 150 mm (inside the part).
And so, we have created a 3D model. And now the most important part - preparing the model for 3D printing.
And now the most important part - preparing the model for 3D printing.
- In order to be able to print a 3D model, it must be “water tightness” (i.e. solid, forming a closed volume). If blue surfaces are visible on the model, then more layers should be added so that this color is not visible. Each edge should have no more and no less than two layers, if this is not the case, then the extra surfaces should be removed. The most common errors when modeling in SolidWorks:
- Internal surfaces
- Holes
- Keep in mind that if your model consists of several objects (for example, letters), they must be combined into one object using a slicer.
- It is desirable that the base of the model be flat. If it is not so, delamination may occur, as a result of which the coordinate axes may shift. If it is not possible to make the base flat, you should print the model on a raft.
- If your model has a lot of overhanging structures, make a support for each.
 In order to successfully print the model, the angle of inclination of the walls should be no more than 45 degrees.
In order to successfully print the model, the angle of inclination of the walls should be no more than 45 degrees. - If the model has many small parts, they must be larger than the nozzle diameter. Otherwise, the 3D printer will not be able to print them.
- If your model is large, it is better to print it in parts. To do this, it should be cut, and then connected with glue. However, it will be better if you immediately foresee this and make secret connections.
- You should also think about the strength of the model. It is better that the load is distributed across the layers. But if you make it across, the model will quickly unstick.
- It remains to decide on the file format. The most popular and convenient is STL. It is with him that most slicers work, including Repeater-Host and Cura.
Thus, we have learned how to create parts in the SolidWorks application and prepare them for subsequent printing on a domestic or industrial FDM 3D printer. Now try to apply the acquired knowledge and create your own unique model.
Now try to apply the acquired knowledge and create your own unique model.
Did you like it? Show your friends!
You will like it
Preparing models for 3D printing: Materialize Magics features
3D basics
Software
Author: Kirill Romanov
Author: Kirill Romanov
Materialize Magics: An all-in-one 3D printing program | What is included in the software | Magics RP Base Module Capabilities | Additional modules | Benefits of Magics
How models are prepared for 3D printing
Additive manufacturing starts with the modeling of objects, which is carried out in various programs such as CATIA, SketchUp, SolidWorks, Inventor, Siemens NX and others. In order to print a product, it is necessary to prepare its digital model, and this process can take up to 32% of the time of the entire additive manufacturing cycle, depending on the technology and complexity of the object.
To manufacture a part on a 3D printer, first of all, you need to get an STL file. To do this, we convert a rigid body to a polygonal model, and then perform the operations of correction, enhancement, editing, platform preparation, nesting, generation of supporting structures, measurements and analysis.
To do this, we convert a rigid body to a polygonal model, and then perform the operations of correction, enhancement, editing, platform preparation, nesting, generation of supporting structures, measurements and analysis.
The next stage is slicing (separation into layers), which consists in creating a control program for a 3D printer. The model is divided into layers with a certain step, and on each layer we get a closed contour, along which the extruder or printer's laser beam will pass. Each layer is usually a 2D DXF image.
Applying Materialize Magics Software to the Additive Manufacturing Cycle
Next, the object is printed and undergoes the necessary post-processing. The stages of work from converting to STL to slicing are performed in specialized software, which will be discussed in our review.
Attention! In the context of sanctions, VoxelDance will become a worthy analogue of the software of manufacturers who have left the Russian market.
 These are universal solutions for preparing models for 3D printing at a bargain price. Check out the overview and demonstration of work in the software product.
These are universal solutions for preparing models for 3D printing at a bargain price. Check out the overview and demonstration of work in the software product. Materialize Magics: Universal 3D Printing Software
The most flexible and comprehensive solution for these purposes is offered by Materialize, which has developed the Magics software product for 3D printing professionals. It allows you to create individual layers of components with high speed and accuracy based on 3D CAD data or 3D scan data. The software provides a full cycle of additive manufacturing - from data import (in STL and other formats) and quality analysis to platform preparation and post-processing.
Materialize Magics is unique in that it comes with the widest range of features available today. This is a kind of constructor, flexible and adaptable to almost any task of additive manufacturing. The software works with all types of 3D printers, and many manufacturers are building Magics into their hardware.
What's in the
softwareBase module RP
- Has a wide range of special functions for editing models.
- Works with a large number of import file formats.
- Quickly, accurately and geometrically correct errors in uploaded files.
- Keeps the original color, textures and textures of objects after the "treatment" of the downloaded files, depending on the settings.
- Provides convenient configuration of processes at all stages of preparation for printing.
Additional modules for specific functions
For example, the Import Module allows you to import many different formats; Structures allows you to design and print honeycomb structures and layers; Slice is used to transfer objects at the layer level in CLI, F&S, SLC, SSL formats; Tree Support is a set of supports, and so on.
Let's take a closer look at the capabilities of these software products.
Magics RP
The most important modeling step for a 3D printer is correcting errors. RP allows you to automatically correct errors in polygonal models, such as inverted normals, holes, open boundaries, noise, self-intersections of triangles, overlaps, etc.
RP allows you to automatically correct errors in polygonal models, such as inverted normals, holes, open boundaries, noise, self-intersections of triangles, overlaps, etc.
Software functions:
- One-click auto-correction of the most common geometry problems;
- a step-by-step fix wizard to selectively fix certain categories of bugs;
- manual patching tools to restore the most difficult areas.
1. Model editing:
- emptying parts (creating walls) to save material, reduce weight and build speed;
- perforation to extract unused material;
- adding thickness to thin walls or modifying a part using the Offset & Extrude tool;
- converting a thin-walled surface to a solid model using Surface to Solid.
A large-scale SLA-printing project for mammoth bones. Emptying the model reduced material costs by 80%
Since some 3D printers have data upload limits, the following functionality is used to lighten the weight of the file:
- reduction of triangles;
- smoothing sharp edges;
- global rebuilding of the polygonal mesh.
2. Marking:
- Easily add text and images (DXF) to parts as markings.
3. Slicing (to separate the model and print it in parts if it does not fit in the printer chamber):
- notched cuts to reinforce the assembly;
- automatic creation of guide pins for assembly.
Using Magics, Nissan Motor Corporation has reduced the time it takes to process a 3D model and model assembly elements by 85%.
4. Boolean operations:
- just like in any CAD, the software makes it possible to perform Boolean operations, and directly in the STL file.
5. Platform preparation:
- platform visualization;
- automatic placement of objects on the platform;
- comparison of the positions of the model by various parameters;
- placement of the model, taking into account surfaces without supporting structures;
- a large library of 3D printers that you can replenish yourself.
6. Import:
- 3D printing software allows you to import polygonal models in all the most common formats - STL, OBJ, PLY, VRML - and many others.
Import Module
Using this module, you can additionally import CAD formats such as CATIA, NX, SolidWorks, while they are immediately converted to an STL file.
Slice Module
Creating a control program for a 3D printer includes features such as:
- preview of each print layer;
- saving settings for each machine;
- construction of a graph of the distribution of layers, which shows the dependence of the height on the area of a given section.
Structures Module
This 3D printer modeling software allows you to create different structures inside the model for:
- reduction in weight, amount of material used and build time;
- giving greater strength compared to the devastated part;
- Prevent warping and build errors during printing by reducing the area/volume that is exposed to heat.
SL Corporation performs 3D printing of mounting fixtures. Due to the creation of structures inside the part, the weight of the product has decreased by 40%
Sinter Module
Specially designed for SLS printing and provides automatic placement of parts in a given build chamber volume:
- maximum use of the volume of the 3D printer construction chamber when placing parts;
- creation of boxes for fragile or groups of small parts.
SG Module
Performs the function of building supporting structures for printing complex objects using various technologies (FDM, SLA, DLP):
- when changing the orientation, you can see where the supports will be built in real time;
- the serrated shape ensures the generation of strong yet easily removable supporting structures;
- perforated supports help save time and material;
- you can save a support profile with the specified parameters and use it for other products;
- The list of surfaces allows you to analyze and optimize support if necessary.

Tree Support Module
With the help of this software, tree-like supports are built, i.e. structures with a "trunk" and "branches". Tree Support provides the following benefits:
- ability to build supports in semi-automatic mode;
- improved surface quality by minimizing contact points;
- prevention of deformation of the product due to heat removal;
- easy removal of supporting structures by creating break points;
- lack of powder inside the supports;
- determination of the optimal cross-sectional diameter of the tree support depending on the material.
SG+ Module
A special modeling program for a metal 3D printer allows you to:
- to build volumetric supporting structures in order to avoid detachment from the platform and deformation of the product;
- create conical supports in critical places to improve heat dissipation;
- automatically generate angular and tree support.
Read more in the article: Advantages of Materialize Magics when creating supports for 3D printing
Simulation Module
Designed to simulate the printing process with metal and visual display of various mechanical deformations or conduct thermal simulation.
Simulation of risks in 3D printing:
- simulation of mechanical deformations of a part and supports;
- definition of overheating zones;
- compiling the field of internal stresses of the metal on each layer and on the product as a whole;
- definition of zones with high shrinkage;
- visualization of results;
- obtaining a product with compensating dimensions.
The software also evaluates printing risks, such as broken support structures, recoater collisions, shrinkage, overheating, and helps prevent scrap.
Read more in the article: Magics Simulation Review: How to Prevent Risks in Metal 3D Printing
Magics software is also available as a kit for educational institutions.
 The kit contains all the Magics modules and will help schools, universities and educational centers improve the process of teaching additive technologies. A special offer for an educational package includes perpetual licenses for 20 or more seats with annual technical support.
The kit contains all the Magics modules and will help schools, universities and educational centers improve the process of teaching additive technologies. A special offer for an educational package includes perpetual licenses for 20 or more seats with annual technical support. In addition to Magics, Materialize offers 3D printing programs as separate base modules.
-
3-matic is designed for modeling in STL-format (standard triangulation) and makes it possible to perform topological optimization at the microstructure level, including with the help of many CAE programs.
-
e-Stage enables fully automated generation of support structures and reduced post-processing costs. Creates contact points with minimal area support, making it easier to remove. The software is available in two configurations: for photopolymers (SLA) and metals (SLM).
Benefits of Materialize Magics
3D Printing Software-
Speed, optimization and high reliability of all processes.
-
A set of practical and efficient solutions for preparing platforms, building support structures using any 3D printing technology.
-
Wide functionality for editing models (adding logos, textures, images).
-
Ability to perform complex cuts (for example, with built-in connecting pins), Boolean operations, etc.
-
The presence of an extensive library for almost any equipment with prescribed and customizable parameters.
-
Analysis and correction (quick correction, preparation and optimization of the polygon mesh with the best preservation of texture, color and quality, analysis of possible problems).
-
A wide range of tools for conducting additive manufacturing business processes.
-
Intuitive, easily customizable interface with technical support from the developer in Russian.
Do you have questions? Contact iQB Technologies : our experienced experts will advise you on purchasing Magics, 3D modeling and other aspects of 3D technology.