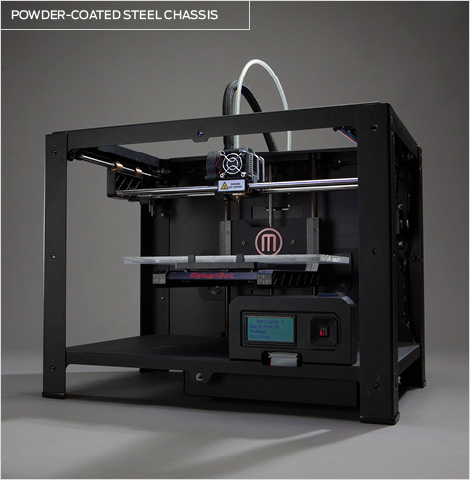
Heated bed for 3d printer
Heat Beds in 3D Printing – Advantages and Equipment – Boots Industries
Why use a heat bed?Heat beds are used because they dramatically improve print quality by keeping the extruded plastic warm and thus preventing warping. Warping is a common condition caused by plastic on the edges of the part cooling down at an uneven rate when compared to the plastic inside of the part. The result is that corners warp up and deform your model.
Rafts are an effective ”no-heat bed” strategy to deal with warping when a heat bed is not available.In the past, techniques such as the raft (building parts on top of a ‘raft’ of material which is larger than the final part onto the build surface) were used to prevent warping by increasing the surface area of the part (and increasing it’s adhesion – thus fighting warping).
Derived from the raft, mouse ears are a clever and effective technique to make sure that the corners of your prints are well secured to the platform and won’t lift. Although they offer greater adhesion by increasing the surface area for your part to grip onto the bed, they are not 100% effective without a heat bed. Sometimes the warping forces are simply too great and can overcome the mouse ears.
Heat beds work to prevent this warping effect by keeping your part warm during the whole printing process which keeps the material at or above heat-deflection temperature (the temperature at which it is malleable). Keeping the parts in the heat-deflection range ensures that the part remains flat on the print bed. Heat beds, in combination with other tools to increase adhesion, will be covered in this article to bolster your ability to fight unwanted effects and improve your printing quality.
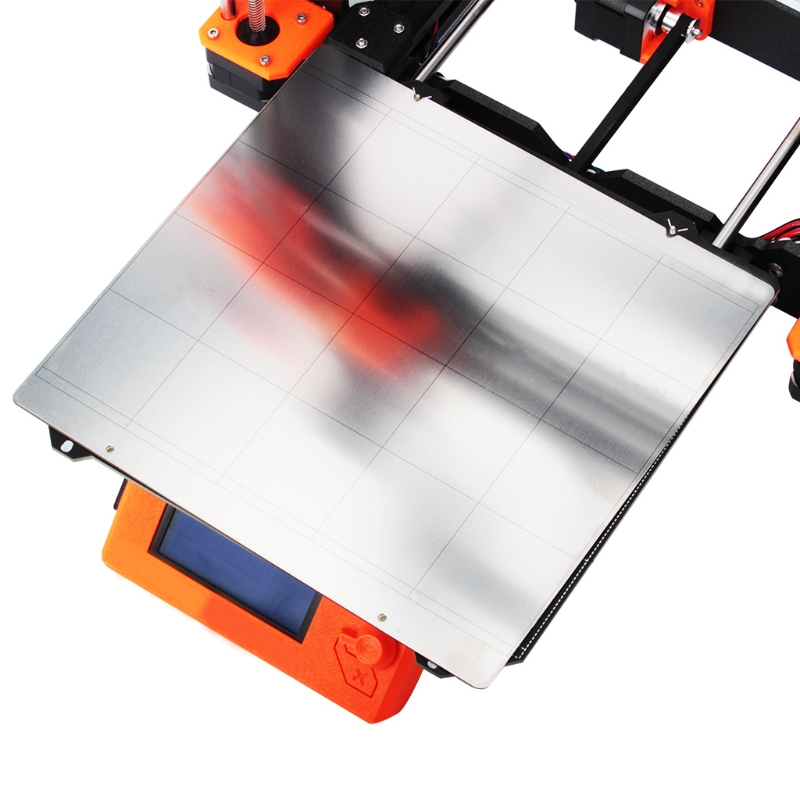
The following video shows what happens with no heat bed and no adhesive added to the glass. It depicts what can typically happen when printing on a non-sticky platform with no heat bed – Disaster!
No heat bed, print stuck to the extruder.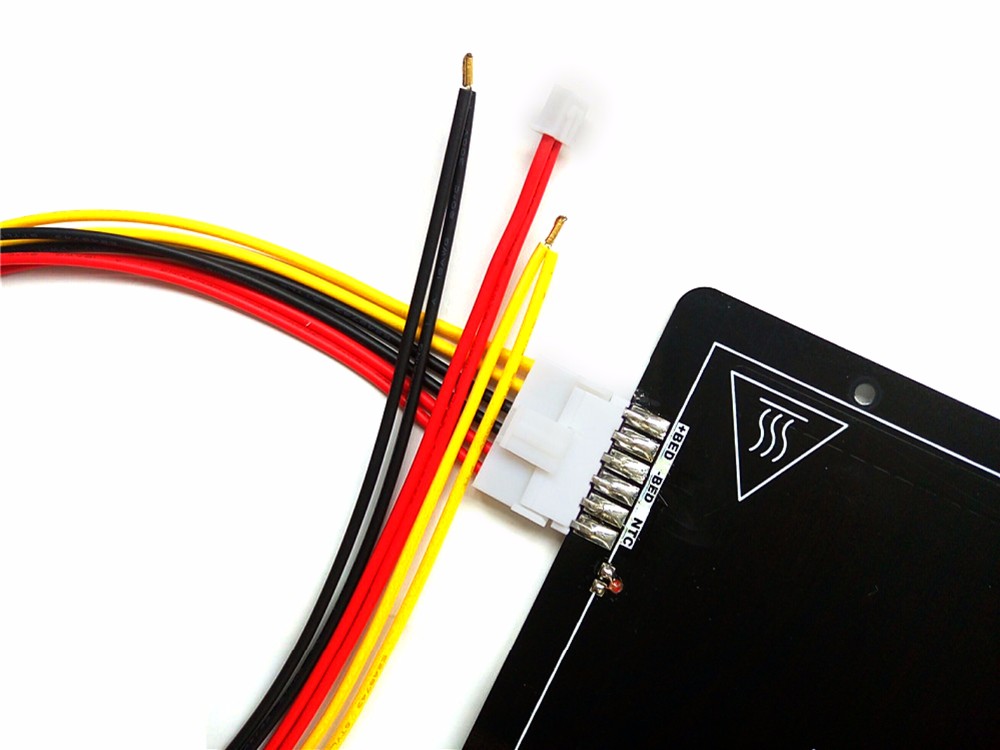 Disaster!No adhesive used; a dramatic result and wasted PLA!
Disaster!No adhesive used; a dramatic result and wasted PLA!There are several types of heat beds & heating elements. We specifically discuss the PCB heat bed, the polyamide film heater (kapton film heater) and the aluminium clad heater. You can find a more exhaustive list of heater types here.
Types of heat bed
Regardless of the heat bed you are using, you should generally use these temperatures (heat deflection points) for PLA and ABS:
| PLA | 50-60°C |
| ABS | 100-110°C |
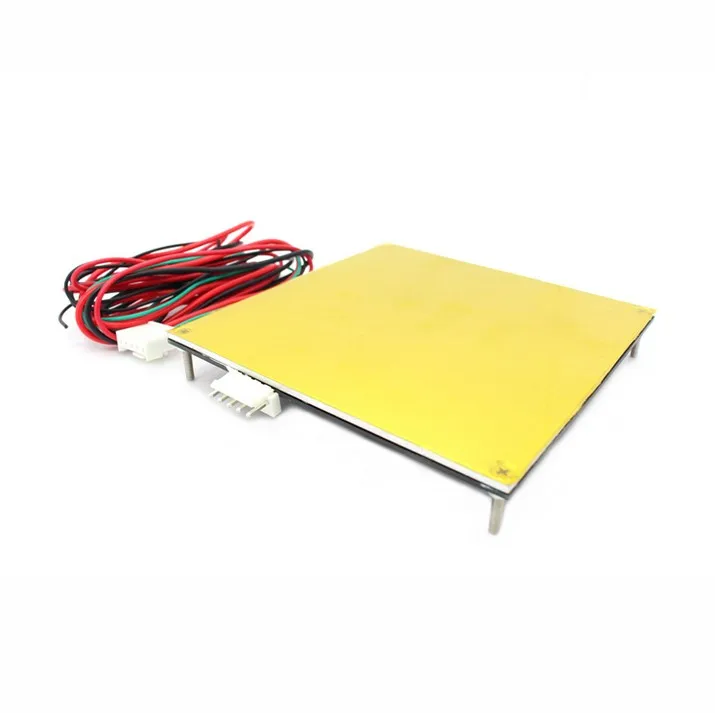
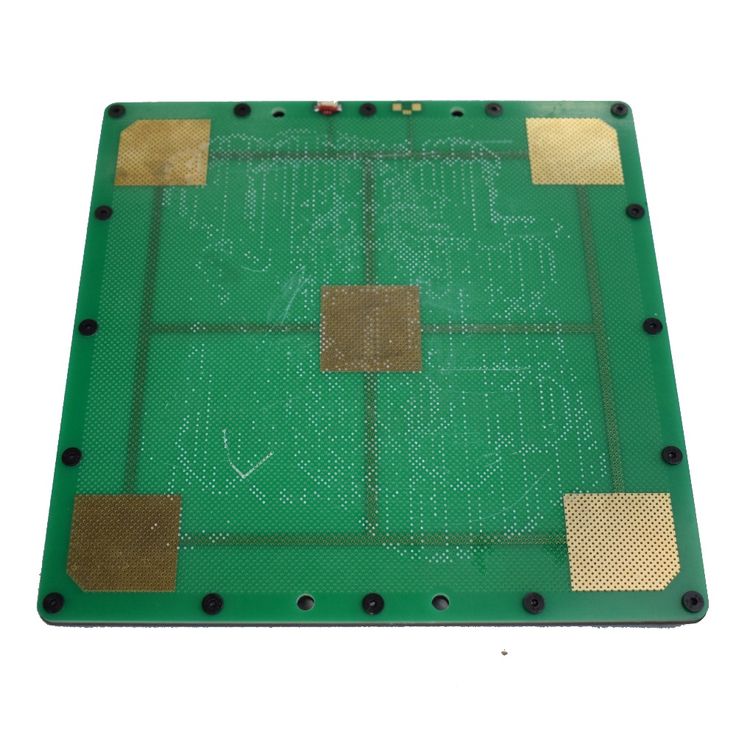
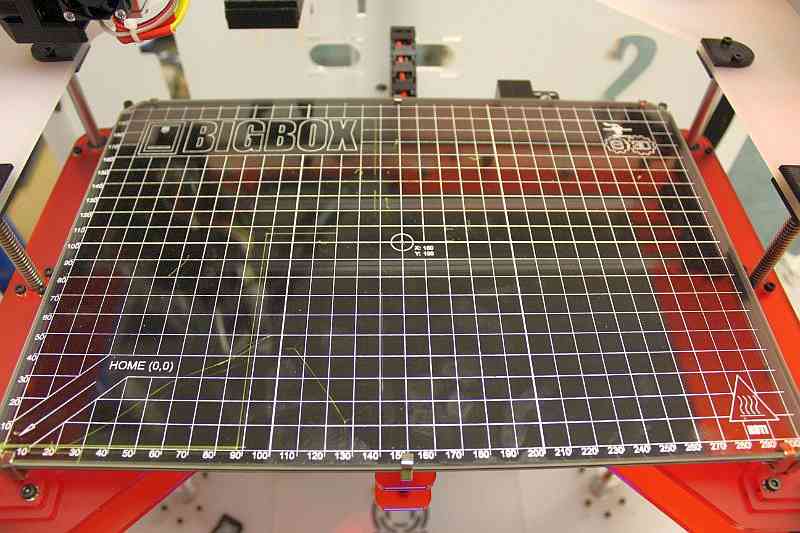
The MK2A heat bed (200mm x 200mm) is a good example of a PCB heat bed. These heat beds are used by many 3D printers and our own (Rostock V1.0) due to their great performance and affordability. This particular heat bed has 2 integrated LEDs and an integrated resistor which makes it rather ‘plug and play’ when compared to other solutions.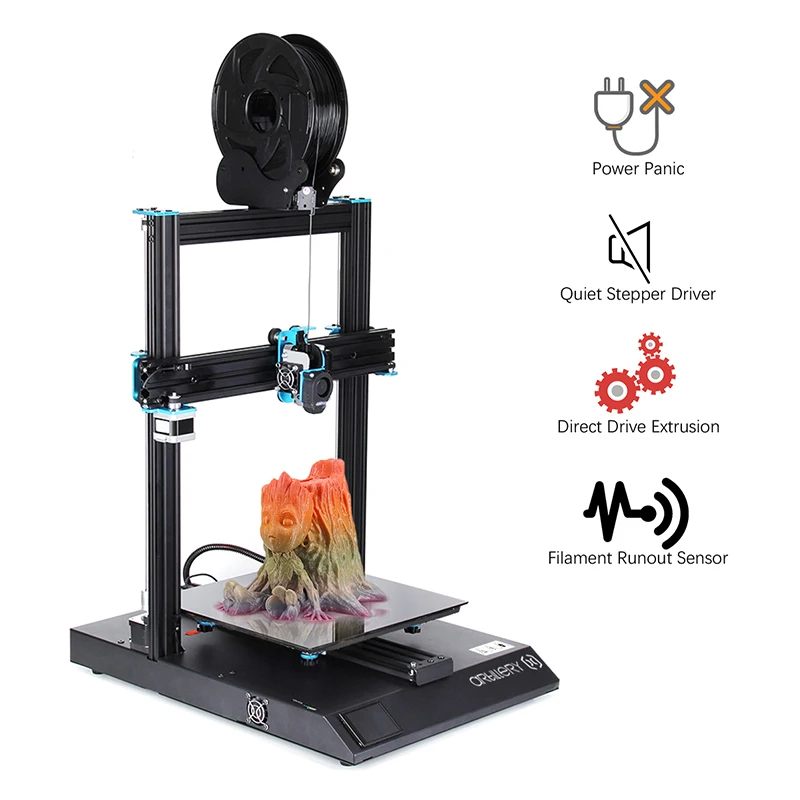
You can generally expect a simple & clean implementation with these heat beds thanks to the 5 holes available for leveling and installation purposes. They require little vertical clearance when compared to a stainless steel sheet mounted with aluminium clad resistors and offer an even heat distribution. The cons is that they can be slow to heat up especially when used with another surface such as a glass pane.
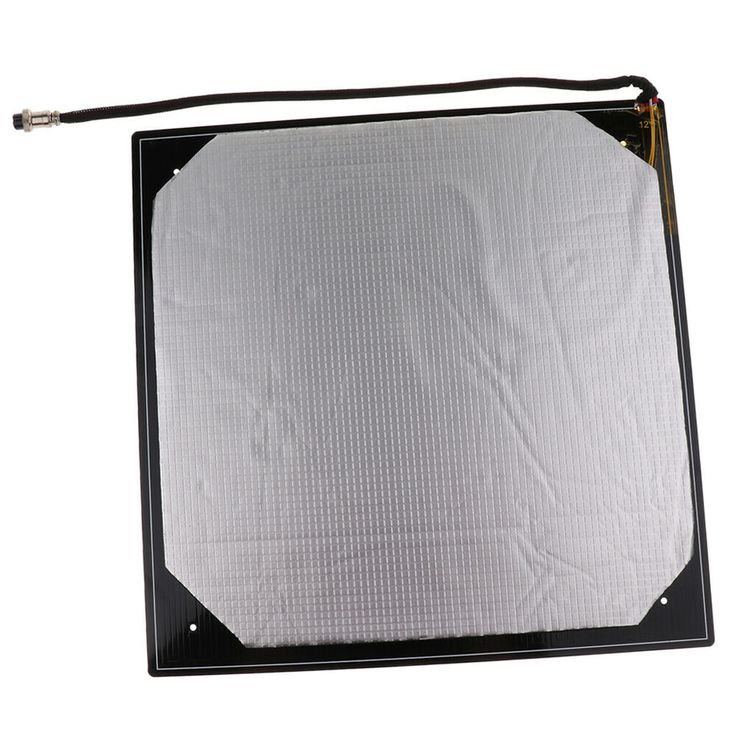
Kapton (Polyamide) film heaterKapton or polyamide is well know as a tape of choice for print surfaces, because of its heat resistance, smooth finish and high adhesion for PLA. Now think about two films of polyamide with a heating element sandwiched in between, now you have a polyamide film heater. Obviously, these are very thin, easy to install with an adhesive back, reliable and heat really fast. They have an integrated thermistor and are provided, unlike the PCB heat bed, in an unlimited variety of shapes. For these reasons, this is the type of heater foil we use on our latest 3D printer (BI V2. 0).
0).
This type of heaters is both very efficient and inexpensive, but they require more installation steps than the last two heat source we’ve discussed. As a matter of fact, they need to be screwed onto a surface, normally a stainless steel or aluminium plate. Then, the electrical circuit needs to be completed with a thermistor and an insulator if you have any temperature sensible elements under the print bed. Finally, it’s also a good idea to use thermal paste between the clad heater and the surface to be heated.
Surface to use with heat bedsAll the heat sources mentioned in this article will typically need an added surface to preserve the quality & integrity of the heating element over time or to provide protection in the event of a hotend collision. Obviously, the aluminium clad heaters are always used in conjunction with a surface.
The recommended print surface to be used with a PCB or Polymide film heater is a borosilicate glass, or when unavailable, a tempered glass. For the PCB heat bed, we recommend layering Kapton tape or using a thin glass (2 mm) over-top.
For the PCB heat bed, we recommend layering Kapton tape or using a thin glass (2 mm) over-top.
In addition to a heat bed surface, most users will experience that some form of adhesive or method is required to make PLA or ABS stick properly. This is where Kapton tape, painter’s tape, glue or hairspray comes into play.
Painter’s tape is an ideal product for printing ABS with a heat bed because of it’s textured surface increasing adhesion. We’ve used it with varying degrees of success and others report great results as well.
As far as PLA is concerned, our experience is that it doesn’t stick well to heated painter’s tape and that painter’s tape itself doesn’t stick well to the glass when heated. However, we found that PLA sticks very well to Kapton tape which is typically layered to cover the entire print area. The Kapton tape needs to be periodically replaced and this process can be tedious. To remove this obstacle, you can buy Kapton tape in wider rolls which means you need to layer a lesser amount of strips onto the print area to fully cover it.
Glues are frequently used to make sure your print “sticks” to the print surface. The most common glue we have seen is the typical arts and craft glue stick (Elmers). This technique works well with ABS in conjunction with painter’s tape.
In the PLA department, we prefer to use hairspray on a glass surface. The glass surface is really flat and produces a really smooth finish for our parts. Another advantage of hairspray is that it can be applied in a few seconds and will typically create a thin film that strips away with the printed part or is easily scraped with a wood chisel or similar tool. Sometimes we use a wet rag to remove hairspray residue from the underside of parts when it’s not desired for aesthetic reasons.
What we recommendWe recommend the PCB heat bed or Polyamide film heater in conjunction with a glass surface. For PLA we always apply a thin coating of hairspray and so far this simple combination has been producing great results.
3D Printer Heated Beds - How Important Are They?
Like most tech, 3D printers have a host of accessories and add-ons that improve the quality of prints, decrease the chance of a failed print, and make general use easier.
One such add-on is the 3D printer heated bed, an accessory key to printing more complex projects and tougher filaments, such as ABS, Nylon and PETG.
Without enough heat underneath the model, you run the risk of the filament cooling too quickly, leading to warped edges and corners, and sometimes even cracking in the model’s midsection.
The decision to get a heated bed can be a tough one, especially if you’re new to 3D printing and want to try adding a heated bed.
We’re going to cover some of the most important and frequently sought information regarding these add-ons here, as well as what the best 3D printer bed surfaces are depending on how they’re used.
What Does a Heated Bed Do on a 3D Printer?
Heated beds are a 3D printer bed that heat up to various temperatures in order to regulate the cooling temperature of a print.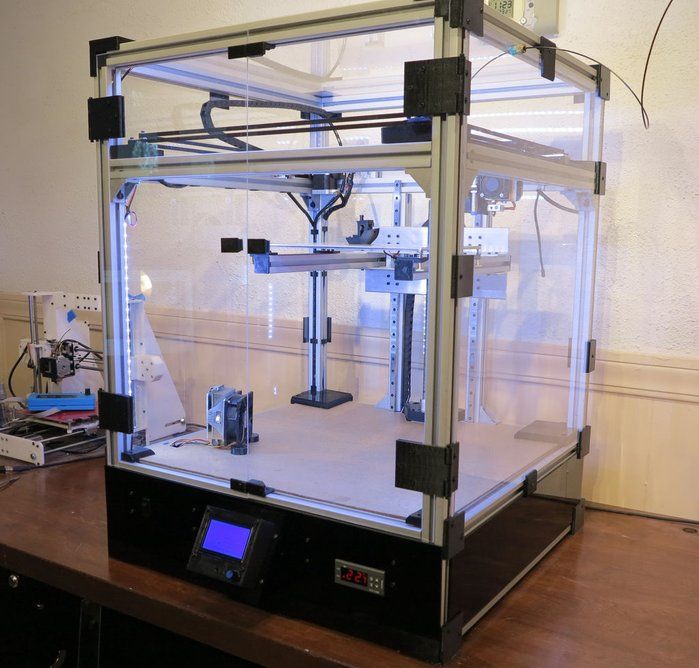
Heated beds are a good choice for filaments and projects that are prone to warping, as the temperature stops a print from cooling too quickly and losing its shape mid-print.
While many commercial 3D printers come with a heated bed as standard (a few years ago this was much rarer), many printers have heated bed add-ons for better ABS printing.
As 3D printers have evolved, so too have the features that come with them as standard, and more and more 3D printers on the market today do come with heated beds.
What are the Benefits of a Heated Bed?
As mentioned before, 3D printer heated beds reduce the chances of warping or mishappen prints for a variety of reasons.
As well as regulating the cooldown, a heated bed will also ensure first layer adhesion. In other words, the first layer of the print will stick more securely to the 3D printer bed. This provides a more solid foundation for the rest of the print, making warping far less likely. This is similar to how a pottery wheel holds the clay steady as it’s reshaped.
A 3D printer’s heated bed also makes post-print removal easier and less likely to damage your project. While the printing material is normally set as one type per project, a heated build surface will ensure any filaments don’t shrink or harden too quickly and become difficult to remove without damaging the print. This is like to how steam makes a letter easier to open by warming the glue on the envelope.
Are Heated Beds Necessary?
Like oiling a squeaky door, 3D printer heated beds are not necessary for most purposes, but they can make things run much smoother. How important they are depends on how you use your 3D printer.
If you prefer to use PLA filaments, then you may be comfortable without a heated bed. PLA barely warps even without a heated bed, and tend to do well as prints. While a 3D printer bed will always do better if heated, PLA users may find the expense and effort of installing a heated bed to simply not be worth it
However, if you use more fragile filaments like ABS and PETG, then a 3D printer heated bed is considered absolutely necessary. A heated bed is even more important if your 3D printer has an open build area, as cooler temperatures and even light breezes can warp these materials which are prone to becoming misshapen while printing.
A heated bed is even more important if your 3D printer has an open build area, as cooler temperatures and even light breezes can warp these materials which are prone to becoming misshapen while printing.
It’s worth noting that there’s no such thing as the perfect filament, no matter the project you have in mind. All 3D printer filaments have the potential to warp, and a heated 3D printer build surface is one of the best ways to minimize the chance of a failed print.
Like with most things, the bigger the project, the higher the likelihood of failure. Smaller 3D printer projects like statuettes, bookmarks, and keychains will normally print and remove just fine. But larger projects, regardless of your chosen material, will always benefit from a heated build surface.
What’s the Best 3D Printer Bed Surface?
If your 3D printer didn’t come with a heated bed as standard, you may want to look into installing one yourself. Not all heated beds are created equal, and the best 3D printer bed surface – heated or not – also depends entirely on what you want to do with your printer.
3D printer bed surfaces, or build plates, come in many forms, each with their own benefits and drawbacks. We’ll look at a few of the more common ones here so you can decide which is the best 3D printer bed surface is right for you.
Glass
Glass is widely considered to be one of the best 3D printer bed surfaces. It’s solid, flat, and has a longer shelf life compared to most materials even when exposed to heat.
As a heated build surface, glass takes a longer time to heat up compared to others due to its low conductivity at room temperature. However, it’s one of the best 3D printer heated beds as it spreads the heat around more evenly than its metal and polypropylene counterparts.
However, in the event that heat is not spread evenly, glass can crack and even break, meaning it can provide a very dangerous environment if not used with cautious attention. While easily and cheaply replaceable, using glass as a 3D printer heated bed can go very wrong.
If you choose glass as your build plate, be sure to reduce this risk by going with good quality, even sheets at least 3mm thick.
It’s important to note that glass is not naturally adhesive, and so will require the use of glue or similar before printing.
Polypropylene
Polypropylene is similar to glass in that it can provide a smooth finish on the first layer of a print due to its flat, even surface.
While it doesn’t have as long a shelf life as glass, polypropylene sheets are fairly cheap to replace, and are durable enough to handle larger prints and high temperatures.
Polypropylene is also considered to be one of the best 3D printer bed surfaces due to its high adhesion while hot, and low adhesion when cool. This means that when used as a heated bed, it will have solid first layer adhesion to reduce the chance of warping, and is also easy to remove from the project after its cooled, further reducing the chance of breakage.
Ceramic
Ceramic is used as a heating bed due to its even spreading of heat, much like glass. But unlike glass, ceramic build plates are not as prone to fracturing and breakage if heated unevenly.
Ceramic may be one of the best 3D printer bed surfaces due to this reduced risk, though its conductivity is even lower than that of glass, and so fast heating can result in cracks.
Ceramic is also considerably heavier and more expensive than glass, making it somewhat more pricey and unwieldy should it need to be replaced.
As long as precaution is taken when used as a heated bed to ensure a slow increase of heat, ceramic makes an ideal 3D printer build surface.
Metal
Metal materials are commonly used as 3D printer build surfaces due to their high conductivity. Most machines that use metal build plates come with them as standard, as the differences between various metallic materials make it difficult for non-experts to install as 3D printer heated beds.
The magnetic properties of most medals make them easily connectible and removeable to the right devices, especially if they come as thin sheets such as the East-Peelzy or BuildTak FlexPlate.
While metal conducts heat very well and can spread it around evenly, most varieties will expand when used as 3D printer heated beds, which can increase the chances of warping projects and even damage your 3D printer if it has an enclosed build area.
3D Printer Heated Beds Frequently Asked Questions
Are heated beds safe?
Like an iron or oven, the safety of a 3D printer heated bed relies on the caution of the user. Heated beds can reach temperatures of over 110℃, and can be very dangerous if not used with care.
If you are careful not to touch a build plate until it has properly cooled down, and ensure young children and pets are kept away from your printer while it’s in use, a 3D printer heated plate should be as safe as any heated device in your home.
Do I really need a heated bed?
You don’t need to have a heated bed if you’re printing PLA (though it helps), but it’s key to keep a heated bed on for ABS, Nylon and other filaments to prevent warping – ideally within a heated chamber.
Can I use blue tape on a 3D printer heat bed?
Tape is commonly added to 3D printer build surfaces to increase bed adhesion, and the same is true for heated beds. Just be sure to use blue (or painters’) tape, as it is highly heat resistant and can withstand the temperatures of even the hottest and best 3D printer heated beds.
Just be sure to use blue (or painters’) tape, as it is highly heat resistant and can withstand the temperatures of even the hottest and best 3D printer heated beds.
Related articles:
- Ender 3 glass bed – best options and guide
4pcs 18mm Silicone Cushioning Bed Heated Hot Bed Leveling Column Kit for 3D Printer Reviews
4pcs 18mm Silicone Cushioning Bed Heated Hot Bed Leveling Column Kit for 3D Printer Reviews - Banggood UK Online ShoppingCustomer reviews
- 5 star10 (100.0%)
- 4 star0 (0%)
- 3 star0 (0%)
- 2 star0 (0%)
- 1 star0 (0%)
Write a review You'll get double Banggood points for a review if you're one of the first 3 to leave it!
- All reviews (10)
- Image (0)
- Video (0)
- All Stars
- All sprockets (10)
- 5 Star (10)
- 4 Star (0)
- 3 Star (0)
- 2 Star (0)
- 1 Star (0)
Sort by:
evaluation
- estimate
- utility
- date
Reviews only from your country (Russian Federation)
|
Show original
Part of the review is translated automatically.
General 0 page
Go to page
Go
Recommended
-
91.72€
TWO TREES® UNO CNC Set with controller + shield + Nema 23 stepper motors + TB6600 + limited switches
(295)
-
87.65€
Machifit ER11 Chuck CNC 500W Spindle Motor with 52mm Clamps and 110-220VAC Power Speed Controller for CNC Machine
(1999)
-
30.
 57€
57€ Geekcreit® AC 110-240V Input for DC 24V 17A 400W Switching Power Supply Driver Board
(527)
-
€47.90
SUNLU FilaDryer S1 Box PLA 3D Printing Filament Dryer Storage Box-fit Arid Material Machine Box-fit Arid Best 3d Print Partner
(192)
-
63.
 18€
18€ Creality 3D® Filament Dry Box Dust / Moisture / 3D Printer Protection Kit to Protect Print Materials
(22)
-
15.28€
SIMAX3D® 13/24 pcs. Polycarbonate Pulley Wheel Plastic Pulley Linear Bearing for Creality CR10 Ender 3 3D Printer Part
(90)
-
63.
 18€
18€ Baseus 150PSI Digital Auto Air Compressor Wireless Tire Inflator Motorcycle Bicyle Inflatable Portable Electric Tire
(6)
-
30.57€
SONOFF 4CH R3 & 4CH PRO R3 AC100-240V 50/60Hz 10A 2200W 4 Gang WiFi DIY Smart Switch Inching/Self-Locking/Interlock 3 Work Mode APP Remote Control Switch Workes with Alexa and Google Home
(386)
-
24.
 45€
45€ Foxeer Echo 2 9dBi 5.8G SMA/RPSMA Adapter LHCP/RHCP Direction Patch FPV Antenna for FPV Racing RC Drone
(19)
-
6.11€
KINGROON® Long Type Linear Bearings LM6LUU LM8LUU LM10LUU LM12LUU Engraving Machine 3D Printer Accessories
(0)
-
20.
 38€
38€ Eachine NANO VTX 5.8GHz 48CH 25/100/200 / 400mW Switchable FPV Transmitter Support OSD / Pitmode / IRC Tramp for RC Drone Tiny whoop
(952)
-
8.14€
5 pcs. Creality 3D® 8*25mm Equalization Spring For CR-10S PRO / CR-X 3D Printer 3D Extruder Heated Part Bed
(225)
-
12.
 22€
22€ Creality 3D® Y-Axis 3Pin N/ON/C Limit Switch Control Limit Switch for Makerbot/Reprap 3D Printer
(2)
-
8.65€
Creativity® MK8 Full Metal Hot End Kit with Extruder Unit Heater for CR-10 / CR10 / CR10S / Ender2 / Ender3 / Ender 5 printers
(0)
-
492.
99€
Easythreed® X8 Desktop Mini FDM 3D Printer 2.4" LCD Display Touch Screen for Kids Student Home Education
(0)
-
13.19€
Lerdge® Super Silent TMC2208 Stepper Motor Driver Module with Heat Sink for
3D Printer Parts(0)
-
9.
16€
0.4mm V5/6 M6 Threaded Brass Tip Airbrush Nozzle for Ultimaker 3D Printer Filament 1.75mm
(6)
-
54.01€
0.4mm High Temperature Titanium Alloy V6 Gem Nozzle Compatible PETG/ABS/PEI/Nylonfor Prusa I3 3D Printer
(0)
-
83.
84€
MK52 Steel Plate Platform + 2pcs 253.8*241 PEI sheet + Y Line Support Plate Kit Kit for Prusa i3 MK3 Voron SW
3D Printer(1)
-
10.18€
BIQU® 4PCS New TL-Smoother V1.0 Addon Module for 3D Printer Motor 9 Drivers0017
(877)
-
21.
39€
Creality 3D® 310*310mm Flexible Magnet Build Surface Plate Soft Heated Magnetic Bed Sticker
(161)
-
17.32€
SIMAX3D® 235 x 235 x 4mm Heated Glass Platform Build Surface Tempered Glass Plate for Ender 3 V2/3 Pro/5/5 Pro 3D Printer
(0)
-
4.
 07€
07€ Creativity® 1pc 1M Heating Tube 6*20mm 12V 24V 40W Ceramic Cartridge Heater with 2.54 for CR10SPRO Ender3 HotEnd J-Head 3D Printer
(5)
-
€5.10
MK8 Extruder Nozzle Head Brass FDM Set M6 Thread 1.75/3.0 Nozzle Filament 3D Printer Accessories
(2)
-
8.
 48€
48€ Aluminum Alloy M4 Kossel Fisheye Effector 4mm Hanging Hammock Station for 3D Printer Extruder Part
(2)
-
€10.04
Creality 3D® 320*310mm Matte Heated Bed Heated Bed Platform Sticker with 3M Backing for CR-10S Pro/CR-X 3D Printer
(44)
-
44.
 84€
84€ Tuya RPP06 1080P PTZ Wireless WiFi IP Camera TF Card Tuya Smart Home Voice Intercom Security Night Vision Waterproof Pan Tilt IP Camera
(181)
-
40.76€
Creality 3D® Ender-3 Direct Extrusion Mechanism Extruder Nozzle Kit Stepper Kit Motor
(503)
-
16.
 30€
30€ VEIKO 9.5mm Pocket Hole Drill Locator Woodworking Manual Bolt Angle Positioning Drill
(79)
-
30.57€
Drillpro Aluninum Alloy 2 Pocket Holes Syestem Pocket Holes Drill Guide with Drill Screwdriver Set and Pocket Hole Bolt Plug
(8)
-
€11.
 20
20 SIMAX3D® 5 pcs. 4 to 2mm Throat with Hotend Stainless Steel PTFE Nozzle Throat 1.75mm Filament for 3D Printer
(1)
-
57.07€
2000W 90bar 22000mAh High Pressure Accumulator Car Washer Water Sprayer Pump Portable Car High Pressure Washer Ma
(48)
-
19.
 36€
36€ URUAV GRAPHENE V2.0 14.8V 1100mAh 160C 4S Lipo Battery XT60 Connector for FPV Racing Drone
(0)
-
17.32€
RCInpower Smoox 1404 Plus 2750KV 4-6S/3850KV 3-4S/5000KV 2-3S Brushless Motor for 2.5-4 Inch Toothpick Long Range FPV Racing Drone
(1)
-
10.
 18€
18€ Eachine StingPad 5.8G 16dBi High Gain Flat Panel FPV Antenna SMA/RP-SMA for RC Drone Receiver Receiver
(1567)
-
€160.01
Wltoys 124017 Brushless V2 New Upgraded 4300KV Motor 0.7m 19T RTR 1/12 2.4G 4WD 70km/h RC Car Vehicles Metal Chassis Models YG
(450)
-
42.
 80€
80€ Guudgo 1080P 10 LED Upgraded 5x Zoom Quad Antenna HD Outdoor PTZ IP Camera Two Way Audio Speech Wifi
(310)
-
45.86€
ESCAM QF218 1080P Pan/Tilt AI Humanoid Detection Cloud Storage Waterproof WiFi IP Camera with Two Way Audio Camera
(534)
-
46.
 88€
88€ Hiseeu 1080P Speed Dome WIFI Camera 2MP Outdoor Wireless PTZ IP Camera Cloud-SD Slot ONVIF Two Way Audio Video Surveillance
(318)
-
4.07€
Creativity® Extruder Rear Plate + X Motor Front and Rear Plate + Z Block 2.5mm and 3.0mm Plate CR-10S PRO CR-10 MAX 3D Printer Kit
(0)
-
7.
 12€
12€ FLSUN® 3PCS M3 Carbon Steel T Type Sliding Nuts for 3D Printer
(3)
-
36.68€
Creality 3D® White/Black/Yellow/Blue/Red 1kg 1.75mm PLA 3D Printer Filament
(1730)
-
€7.12
200*3mm Round Bed Heating Heating Element Insulation Cotton with Cork Glue for 3D Printer Reprap Ultimaker Makerbot
(1)
-
539.
 19€
19€ Creality 3D® Ender-3 S1 Plus 300*300*300mm 3D Printer Larger Build Volume with Dual Gear Solid Metal Direct Extruder/Auto
(2)
-
6.11€
Hot Bed Platform Lattice Glass Mount Clamp Hot Bed Stainless Steel Mount Clamp for 3D Printer
(0)
-
223.
 22€
22€ Creativity 3D® Ender-3 Pro DIY 3D Printer Kit 220x220x250mm Print Size with Magnetic Removable Platform Sticker
(3511)
recommendation for you
Why do I need a heated table for a 3D printer?
3DPrintStory 3D printing process Why do you need a heated table for a 3D printer?
With the development of 3D printing, a lot of new research and experiments have appeared.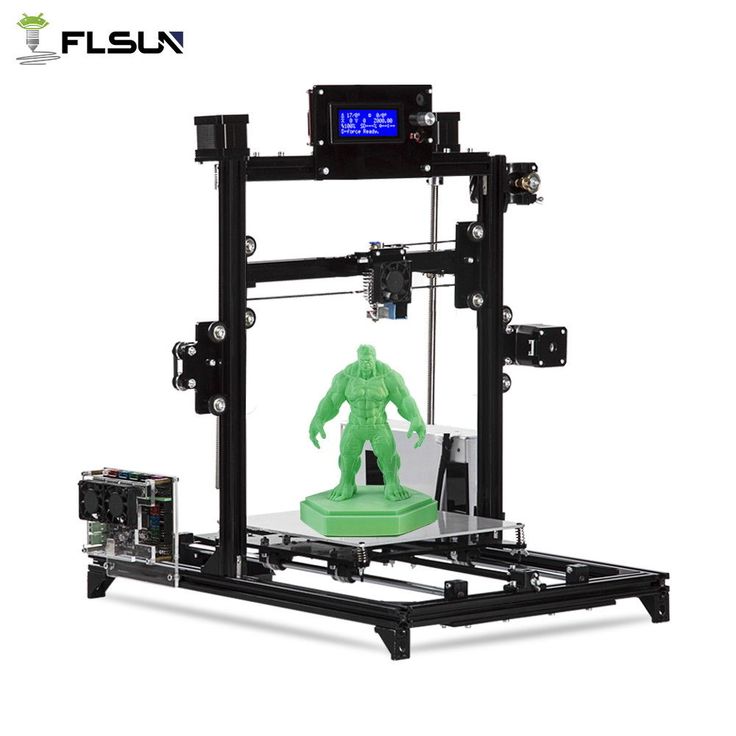 Many of them are aimed at finding the best way to increase the adhesion of the first layer.
Many of them are aimed at finding the best way to increase the adhesion of the first layer.
And we all know why this is so important. A standard heated 3D printer table will do the job. Although there are other alternatives when working with the first layer, nothing compares to this one.
Most importantly, 3D printer tables are a very important part of the overall design. In fact, without a table, you will not be able to create physical embodiments of your 3D models. Therefore, understanding how you can make the best use of the table should be your top priority for quality 3D printing. Understanding and navigating the different types of heated tables and their features will definitely help you choose the right 3D printer and implement your own ideas.
But before we get to the bottom of everything related to heated 3D printer tables, let's understand what 3D printing is. Most of us are already aware of this, but a brief overview will ensure that we are on the same wavelength in the context of the current article.
What is 3D printing?
We have been hearing about additive manufacturing or 3D printing for a long time. And the lucky ones who had a chance to work with this technology at least once are becoming more and more every day.
3D printing has become one of the most revolutionary technologies and is spreading very quickly, influencing the entire ecosystem of production, industry and hobby.
3D printing is a process in which 3D printers create layers one on top of the other to create a finished product of the desired shape and dimensions.
3D printing may differ in the principle of creating 3D models. For example, there are FDM, SLS, SLA and many others. They differ in the way the layers are created and connected. However, the fundamentals remain the same. Layers are stacked on top of each other to build the entire 3D model.
3D printing has made it possible to create extremely detailed models and designs in a short amount of time and in many cases cheaper than classic manufacturing processes. But when using a 3D printer, certain precautions must be taken to ensure that the finished product exactly matches the desired characteristics.
But when using a 3D printer, certain precautions must be taken to ensure that the finished product exactly matches the desired characteristics.
However, 3D printing has its own problems. And the biggest of them is too fast heating and cooling of the layers of the 3D model. One of the major problems that arise from improper heating/cooling is shrinkage. It changes the shape of the 3D model and deforms it. Therefore, in this case, we get low-quality products.
To solve this problem, heated tables for 3D printers have appeared. These tables, among other things, are designed to maintain the required temperature of the first layers of the model and the entire model as a whole. They help control the temperature during the entire 3D printing process. Therefore, this additionally results in proper adhesion of the first layer throughout the entire 3D print time of your model.
What is a 3D printer heated bed?
Returning to the main topic of the article, we must answer the question: what is a heated table for a 3D printer? Although we have already briefly discussed the usefulness of heated tables, let's learn more about them.
Heated tables using printed circuit boards as a heating element
Heated tables for 3D printer designs may vary. Among the most common types of heated tables, mounting or printed circuit boards are used as heating elements. They usually come with budget 3D printers. However, this solution is not very suitable if your 3D printing projects are complex and require frequent work with a 3D printer. In short, they are designed for small projects that do not take much time to complete.
The reason why they are not suitable for complex 3D printing is that PCBs are made of copper and aluminum plates, and they are prone to deformation when heated for a long time. Over time, heated plates will no longer perform the task for which they were originally designed.
There is another problem that may arise. They take longer to heat up. You can get rid of this problem, but for this you will need to replace the power supply with a more powerful one.
Heated tables using AC silicone sealant for heating element
The second type of heated 3D printer table is one that uses silicone to seal the heated elements. To create a structure, a heated element is inserted between pieces of glass and a heat insulator.
To create a structure, a heated element is inserted between pieces of glass and a heat insulator.
This is to minimize excess heat leakage and to deliver maximum heat to the table surface. In addition, electricity consumption also becomes smaller. And they can work longer without causing any problems to users.
This version of the heated table design is much more reliable and can last you much longer. In addition, the bill for the consumed electricity will also be reduced due to the minimization of losses for heating the table.
3D printer process with heated table
The 3D printer works by extruding a plastic filament onto the table. Immediately after exiting the extruder, the material begins to cool. As we all know, shrinkage goes hand in hand with the cooling process. The problem arises when the layer is not cooled uniformly at all points. This leads to uneven shrinkage and, ultimately, to deformation of the entire 3D model.
To avoid cooling the plastic at different rates at different points, heated tables have been developed. The job of a heated 3D printer bed is to ensure that the parts do not cool completely until the 3D print is complete. This allows for a more uniform shrinkage process.
The job of a heated 3D printer bed is to ensure that the parts do not cool completely until the 3D print is complete. This allows for a more uniform shrinkage process.
In short, heated tables basically take care of two things. First of all, by increasing the surface energy of the printing table, the heated layer enhances the adhesion of the first layer. Secondly, a sufficiently high temperature of the lower layer is ensured, which avoids the problem of deformation at any stage of the 3D printing process. Therefore, the heated bed maximizes efficiency and avoids excessive cooling of the layers.
When material hits the 3D printer bed through the extruder, it carries a certain amount of heat with it. For best results, the temperature of the heated bed should be below the glass transition point. This should turn the liquid thread into a solid form. The temperature sensor is responsible for maintaining the required temperature of the table.
You may need to experiment to find the optimum table temperature, as the melting point of different materials and manufacturers is different.
Several DIY Heated Table Designs for 3D Printer
We have already discussed the basics above, now let's look at some interesting DIY solutions.
In addition to the PCB and the sealed AC heating element, there are other DIY designs to replace your table with a heated table.
Polyamide Film Heater
Polyamide, which we also call Kapton, offers a huge advantage when used as a tape for printable surfaces. They are best suited for use with PLA plastic. Providing effective heat resistance and high adhesion for PLA printing, this film is very popular. The use of this film helps to improve the surface quality of 3D models.
However, you may not know that in combination with a heating element sandwiched between two polyamide films, you can get a polyamide film heater. In addition, they are easy to install by adding glue to the back. They heat up very quickly. In addition, they can be of different shapes and sizes. So this is a great option to upgrade your 3D printer table.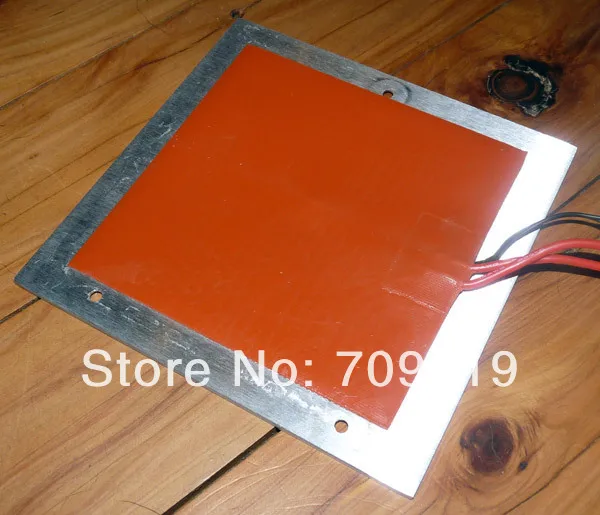
Aluminum Coated 3D Printer Heater
If you are looking for an efficient and cost effective solution, this is the one for you. However, keep in mind that installing these heaters on your 3D printer may require some work.
After installing the heaters, it is necessary to close the electrical circuit using the thermistor and insulator. Last but not least, the thermal paste must remain between the lined heater and the build surface.
Do you need a heated table for your 3D printer?
Since many 3D printers do not have a heated bed, the question is, do you need a heated bed?
You may have heard that working with PLA plastic does not require a heated table. Or perhaps you've only heard of ABS printing on a heated table. But what is the truth?
When 3D printing with ABS you will need a heated table. Why is that? ABS tends to compress more than other materials. Therefore, the likelihood of deformation increases when 3D printed using ABS. With the table heating turned on, the material will better set on the first layer, minimizing potential deformations at the edges of the 3D model.
With the table heating turned on, the material will better set on the first layer, minimizing potential deformations at the edges of the 3D model.
What about PLA? Do we need a heated table or not? In the case of PLA, heating is not always needed. However, if you want to print large models, it is better to use a heated bed to eliminate the possibility of possible problems.
As mentioned above, you also need to know the optimum temperature for your material. Otherwise, there will be no point. For example, when working with ABS, it is recommended to heat the table to 110 ° C. On the other hand, when using PLA, it is worth stopping at 60 ° C. By the way, the temperature of the 3D printer table is set at the stage of processing the model in the 3D slicer.
3D Printer Heated Table Precautions
Heated tables maintain very high temperatures, so you should take the necessary precautions.
Heated tables can leave scars for life if they come into contact with the skin.