Futuristic 3d printer
Best 3D Printers in 2022
Whether you're a hobbyist tinkering with small prints or a pro designing large-scale models, the things you can create with a 3D printer are virtually limitless. 3D printing is becoming increasingly popular, as the innovative technology is a fantastic alternative to traditional molding, forging and sculpting techniques.
Though the technology has been around for decades, these machines have become available for retail sale only recently. So, if you’ve been intrigued by 3D printing, you’ll want to check out our top picks for the best 3D printers, with a range of budgets and features to get you started.
— Best Overall: Dremel DigiLab 3D45 3D Printer
— Best for Beginners: Creality Ender 3 V2 3D Printer
— Best for Miniatures: ELEGOO Mars 2 Pro Mono MSLA 3D Printer
— Best Resin: ANYCUBIC Photon Mono X 3D Printer
— Best for Kids: WEEDO Mini 3D Printer for Kids and Beginners
— Best for Home: Robo E3 3D Printer
— Most Versatile: ANYCUBIC Vyper 3D Printer
— Best for Quiet Printing: Voxelab Aquila 3D Printer
Let’s face it, with prices that can quickly exceed hundreds or even thousands of dollars, a 3D printer is not a purchase you should take lightly. As with many relatively new consumer products that have suddenly become the rage, looking for a 3D printer that will deliver precision models time and time again can seem like an exhausting endeavor—especially when you consider the hundreds of products on the market. So we scrutinized dozens of the top-rated models for this guide before deciding on the handful that made the cut.
For example, 3D printers essentially operate by extruding molten plastic through a tiny nozzle that moves around under precision control to print each layer, wait for it to dry, and then print the next layer on top. So depending on the printer quality, your finished piece may resemble a stunning 3D model or simply a bunch of plastic 2D lines sitting awkwardly on top of one another, resembling a slightly askew deck of cards.
Customer service was another critical factor to consider because of the delicacy of operation and that even the best models tend to occasionally malfunction. However, all of the products we ultimately selected had positive customer reviews regarding customer service, specifically, so if purchasing any of these products, you can rest assured that any malfunctioning parts or issues will be swiftly replaced or troubleshot. Get started with the best 3D printing software.
Get started with the best 3D printing software.
Why It Made The Cut: Go from unboxing to your first print in under 15 minutes using the printer’s large full-color touch screen with intuitive icons for easy setup and operation.
Specs:
— Build Volume: 7 inches L x 10 inches W x 6 inches H
— Weight: 42.8 pounds
— Compatible Materials: ECO ABS, Nylon, PETG, and PLA filament
— Price: $1,999
Pros:
— Extra-large build volume
— Built-in HD camera for remote monitoring
— Five-inch full-color touch screen
Cons:
— Doesn’t work well with aftermarket filament
— Pause button causes the entire printing process to stop
For perfect 3D printed models every time, there’s a reason the Dremel DigiLab 3D45 3D Printer regularly tops editor’s pick lists as best 3D printer overall.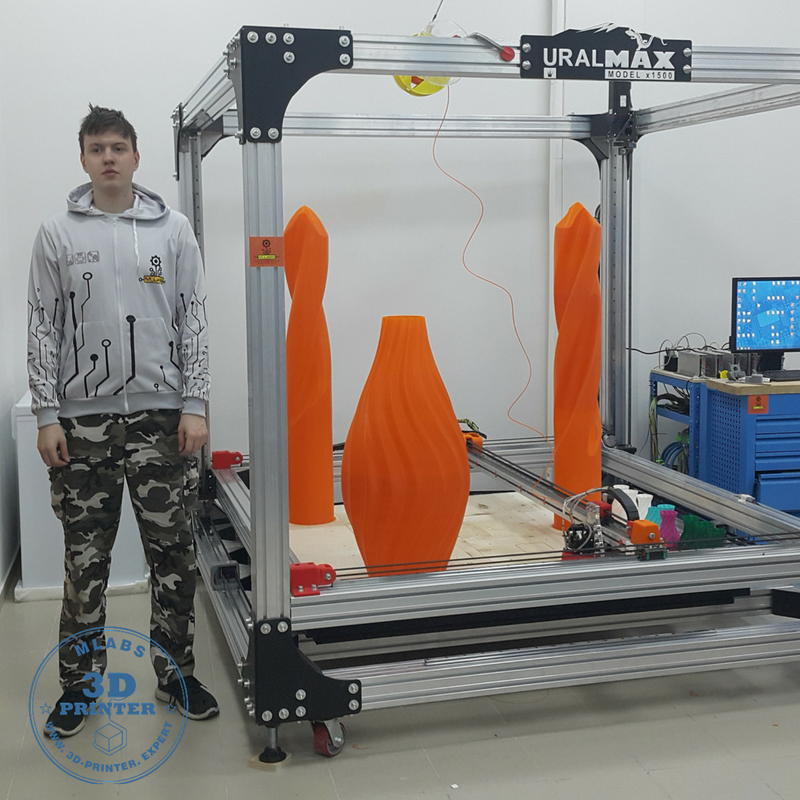 The five-inch, full-color touch screen makes for simple setup and operation—within 15 minutes, even right out of the box! And not only does the fully enclosed sturdy plastic design and large build volume provide better prints and optimal safety, but it also ensures a quiet operation. You could even have this 3D printer running while teaching a lab class because it runs so silently and smoothly.
The five-inch, full-color touch screen makes for simple setup and operation—within 15 minutes, even right out of the box! And not only does the fully enclosed sturdy plastic design and large build volume provide better prints and optimal safety, but it also ensures a quiet operation. You could even have this 3D printer running while teaching a lab class because it runs so silently and smoothly.
Other features include WiFi connectivity with a built-in HD camera and included remote printing software so that you can print and monitor the progress from anywhere. In addition, the removable glass heated build plate heats up to 212 degrees Fahrenheit so you can print with a variety of plastic materials, including PLA, PETG, ECO-ABS, and nylon—as well as ensuring easy removal and cleaning. This device also features an automated nine-point leveling sensor that detects any variation in the print bed and automatically accounts for it.
One of the few gripes some users have is that the printer was designed primarily to use proprietary Dremel filaments, which come in a limited selection of colors and tend to be pricier than aftermarket filaments. To use off-brand filaments, you may have to buy a spool stand or make adapters to pipe through larger rolls. A handful of users also noted a Firmware bug which renders the pause button kind of useless, as you can’t simply pause and resume without the machine coming to a complete stop.
To use off-brand filaments, you may have to buy a spool stand or make adapters to pipe through larger rolls. A handful of users also noted a Firmware bug which renders the pause button kind of useless, as you can’t simply pause and resume without the machine coming to a complete stop.
Why It Made the Cut: Featuring a super-simple setup and operation, this budget-friendly option is the perfect starting point for anyone interested in learning the art of 3D printing.
Specs:
— Build volume: 8.7 inches L x 8.7 inches W x 9.8 inches H
— Weight: 21.1 pounds
— Compatible Materials: ABS plastic, metal
— Price: $279
Pros:
- Semi-assembled kit for simple setup
- Heats within five minutes and maintains its temperature
- Quiet printing
Cons:
- No auto-leveling
- Instructions may be difficult to follow
For those looking to dip their toe into the world of 3D printing, Creality's Ender 3 V2 3D Printer makes the best 3D printer for beginners. Creality recently updated its popular Ender 3 with an updated user interface that makes this printer easier to use, a toolbox to hold all of its accessories, and a custom-built motherboard that ensures its motor doesn't make too much noise when printing.
Creality recently updated its popular Ender 3 with an updated user interface that makes this printer easier to use, a toolbox to hold all of its accessories, and a custom-built motherboard that ensures its motor doesn't make too much noise when printing.
The Ender 3 V2 is compatible with the most common filaments, but won't work with more delicate ones, like glass. It also lacks an auto-leveling function, which means your prints may come out a little lopsided if you don't make sure its glass platform is perfectly flat. Still, this isn't a dealbreaker given the Ender 3 V2's entry-level price point, and it's easy to avoid problems if you take a couple of extra minutes to inspect the printer before making a print.
We consider this printer's resume function to be its best feature, because it gives you some flexibility if something happens in the middle of your print. If you feel uncomfortable leaving the printer running while you're asleep or out of the house, the Ender V2 can accommodate your needs.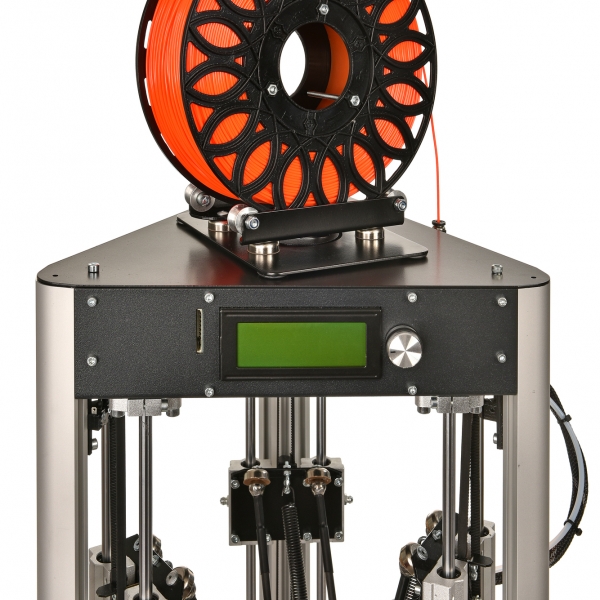 We can confidently recommend Creality's Ender 3 V2 to anyone who's been curious about 3D printing, but hasn't taken the leap because of price. Here are more of the best 3D printers for beginners.
We can confidently recommend Creality's Ender 3 V2 to anyone who's been curious about 3D printing, but hasn't taken the leap because of price. Here are more of the best 3D printers for beginners.
Why It Made The Cut: This 3D printer’s compact yet surprisingly spacious build volume is ideal for printing anything from board game miniatures and jewelry to small industrial parts.
Specs:
— Build Volume: 5.1 inches L x 3.1 inches W x 6.3 inches H
— Weight: 13.67 pounds
— Compatible Materials: Resin, plastic
— Price: $225.99
Pros:
— Machined-aluminum construction
— Monochrome LCD screen with 2K HD resolution
— UV LED light source
Cons:
— LCD screen does not have protective glass
—Resin tray may leak or spill
Significantly enhance your 3D printing efficiency with the best 3D printer for miniatures, the ELEGOO Mars 2 Pro Mono MSLA 3D Printer, which takes just two seconds per layer exposure to cure resin so you can watch your miniature creations come to life even faster. With a lifespan up to four times longer than comparable printers, you can also expect an overall more stable performance and less maintenance. In other words, leveling will be the least of your problems with this model.
With a lifespan up to four times longer than comparable printers, you can also expect an overall more stable performance and less maintenance. In other words, leveling will be the least of your problems with this model.
Constructed of CNC-machined aluminum from the build platform to the resin vat, this printer boasts high durability and solid quality that reliably gets the job done. Likewise, the COB UV LED light source provides optimal heat dissipation with a high luminous maintenance rate and uniform light emission to ensure an even print every time.
As a few customer reviews have noted, however, you have to be really careful with the resin vat to avoid spills or leaks, leading to resin getting into your machine and corroding the parts. In addition, though the monochrome LCD screen is a nice touch, some users felt that it would have been better with a protective glass covering in the event of resin splashes. If you don't want to spend a lot, here are the best budget 3D printers.
Why It Made The Cut: This high-volume 3D printer can crank out flawless resin models at three times the speed, with impressive 3840-by-2400 pixel resolution.
Specs:
— Build Volume: 7.55 inches L x 4.7 inches W x 9.6 inches H
— Weight: 24.25 pounds
— Compatible Materials: Resin
—Price: $379.99
Pros:
— Highly detailed resolution
— Power adjustment function
— Brushed aluminum platform
Cons:
—Touchscreen could have better responsiveness
— Resin can be messy to work with
If you’ve tried filament 3D printers and get frustrated with clogged nozzles and stuck filaments, then ANYCUBIC Photon Mono X 3D Printer, the best resin 3D printer, might be just the trick. With printing that’s three times faster than traditional 3D printers, a single layer only takes one to two seconds for exposure—even when you factor in the large capacity print volume—for an impressively high resolution of 3840 by 2400 pixels.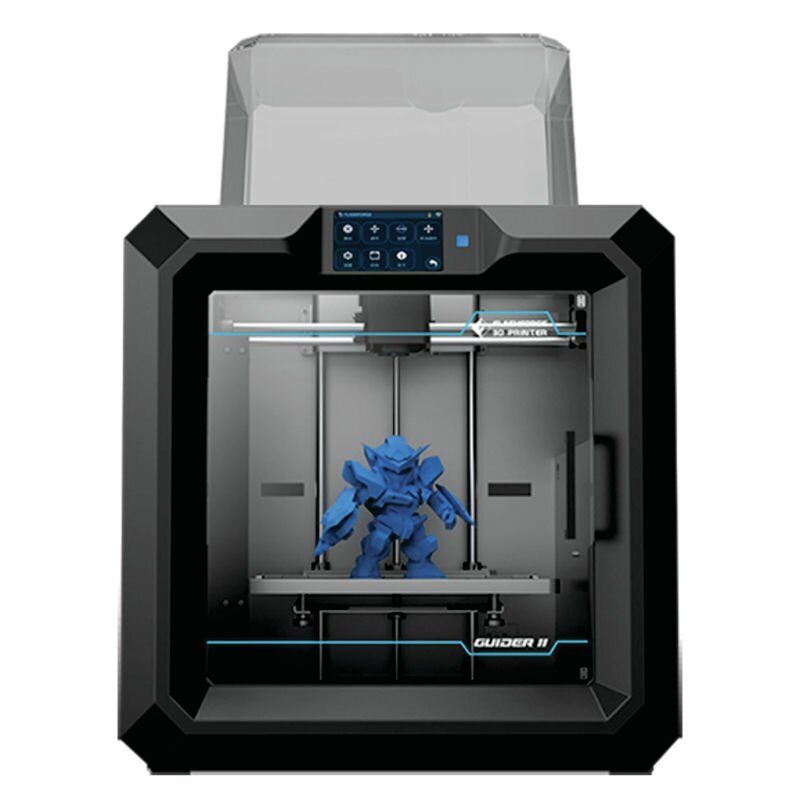
Other valuable features include a power adjustment function, which can adjust between 30 percent and 100 percent exposure, making it compatible with special resins such as dentistry and high temperature. Likewise, the brushed aluminum platform significantly enhances the adhesion between the platform and printers. Finally, the high precision, high transmittance UV light uses quartz lamp beads to ensure a more uniform light source.
However, while avoiding the issues with filament 3D printing, resin can be a challenging material to work with. Everything must be thoroughly cleaned with alcohol, and changing the resin bath can be very expensive, as the brand uses only its proprietary sheets. Another minor gripe among some users is that the touchscreen is outdated and not tremendously responsive, using bubble-style buttons instead of a digital display. Here are more options for the best resin 3D printers.
Best for Kids: WEEDO Mini 3D Printer for Kids and BeginnersKid-Friendly Printing.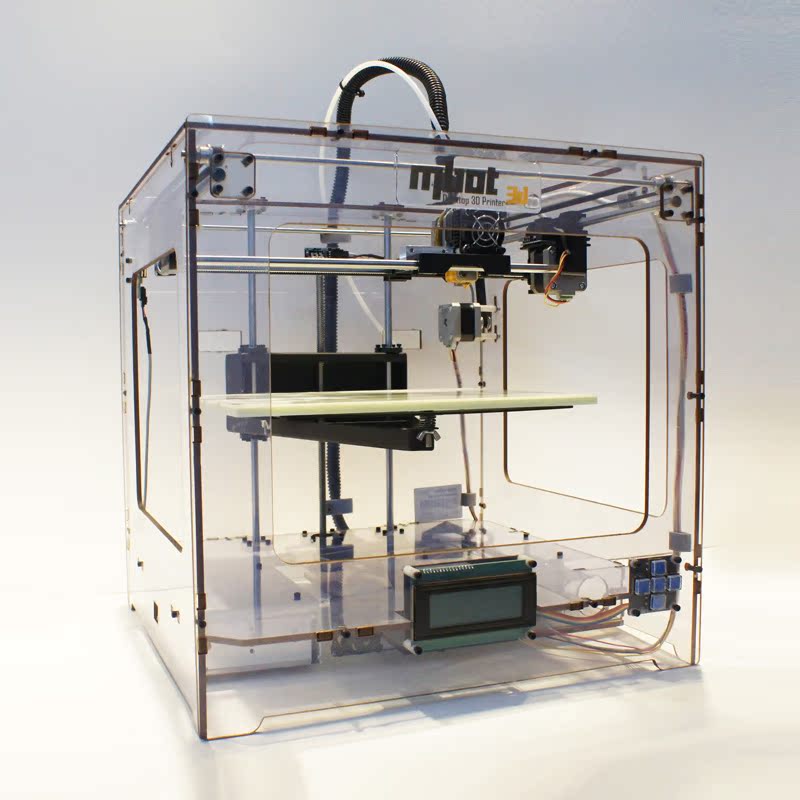 WEEDO
WEEDOWhy It Made The Cut: This little 3D printer uses an unheated print bed, making it a safe choice for kids to try out 3D printing.
Specs:
— Build Volume: 8.07 inches L x 8.07 inches W x 10.63 inches H
— Weight: 6.61 pounds
— Compatible Materials: Plastic
—Price: $149
Pros:
— Lightweight and portable
— Non-heated print bed
— Minimal set up required
— Affordable
Cons:
— Resolution is lower than standard 3D printers
— Auto leveling bed can be finicky
You might have some pretty great ideas to try out and can’t wait to get your hands on a 3D printer, but if you have little ones who want to take a crack at it — or just aren’t ready to invest in a bigger, more expensive piece until you understand the basics — the WEEDO Mini 3D Printer may be your best choice. The printer’s compact design (under 11 inches tall) makes it an easily portable tool that’s ready right out of the box; just plug it in and print.
The Mini printer’s proximity sensor allows for auto bed aligning, which is a win for those who are new to 3D printing as you won’t have to adjust the printing bed, and can simply sit back while the printer does its magic. This is another intuitive printer that incorporates a resume printing function, so if there are any disruptions, you can pick up right where you left off. Finally, the low voltage, unheated print bed makes this a safer, preferred choice for kids (or clumsy adults).
Best for Home: Robo E3All-In-One. RoboWhy It Made The Cut: Robo's E3 is the perfect 3D printer to get if you want to jump into making complex projects right away. It's compatible with over 20 materials, ranging from wood to metal to glass.
Specs:
— Build Volume: 5.9 inches L x 5.9 inches W x 5.9 inches H
— Weight: 19.8 pounds
— Compatible Materials: ABS, PLA, wood fill, copper fill, steel fill, brass fill, carbon fiber fill, magnetic iron, glass fill, bronze fill filaments, and more.
— Price: $999.99
Pros:
— Auto-calibrated print bed
— Can store up to 1,000 models on its internal storage
— WiFi-enabled
— Includes two spools of PLA filament.
Cons:
— Expensive
If you're serious about getting into 3D printing at home, but don't want to make the giant investment required for our top pick, Robo's E3 is the one to get. It's roughly the same size and weight as our other 3D printer recommendations, but it can work with a lot more materials than most.
This gives you the freedom to create 3D prints that wouldn't be possible otherwise, especially if you're making objects that require different elements, like glass and metal. If you plan on printing the same objects over and over again, the E3's built-in storage will come in handy. That's doubly true if you accidentally delete a model on your computer.
While these features add to the E3's cost, it's designed with an auto-calibrating print bed, which improves the odds of you ending up with a satisfying print rather than one that's lopsided. By reducing the number of prints you have to discard due to quality issues, the Robo E3 is great 3D printer for new and experienced users. Plus, it's a lot less wasteful because you won't throw away sub-par prints on your way to perfection. The Robo E3 is so capable relative to most 3D printers it should be the only one you'll ever need unless you start using one for commercial purposes.
By reducing the number of prints you have to discard due to quality issues, the Robo E3 is great 3D printer for new and experienced users. Plus, it's a lot less wasteful because you won't throw away sub-par prints on your way to perfection. The Robo E3 is so capable relative to most 3D printers it should be the only one you'll ever need unless you start using one for commercial purposes.
Specs:
— Build Volume: 9.6 L x 9.6 W x 10.2 H inches
— Weight: 22 pounds
— Compatible Materials: PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU filaments
— Price: $429.99
Pros:
— Operates quickly
— Incredibly versatile
— User-friendly
Cons:
— Difficult to change up filaments
ANYCUBIC Vyper is massive, but it's one of the most user-friendly 3D printers available. Despite not having an enclosure, there are plenty of features here to make this one of the smarter buys for folks new to 3D printing.
There's little to no setup out of the box, and you can start printing everything from miniatures to cookie cutters in as little as one hour. Once it's up and running, expect things to move really quick. It's incredibly versatile and compatible with PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU filaments. However, swapping filament when you've paused a print job is not as intuitive as it could be, and cannot be done with the "unload filament / load filament" commands via the touchscreen. You have to manually release the stepper motor, pull the filament out and then feed the new filament in with force before resuming. That said, once the project is resumed, sailing is more often, very smooth. The build plate is also amazing. When printing, it holds onto objects incredibly well. For a 3D printer in its price range, ANYCUBIC Vyper 3D Printer is unbeatable. Read a full review of the Anycubic Vyper 3D Printer.
Things to Consider Before Buying 3D Printers
There are a few primary considerations you should examine when shopping for a 3D printer. First, ask yourself how you plan to use the printer. Are you a basic hobbyist or a professional looking to do some large-scale modeling? One of the most significant features that differentiate 3D printers is the print volume area, which determines how large your models can be. To create large-scale industrial parts, you’ll probably want a more high-capacity print bed than someone looking only to model small figurines or trinkets.
First, ask yourself how you plan to use the printer. Are you a basic hobbyist or a professional looking to do some large-scale modeling? One of the most significant features that differentiate 3D printers is the print volume area, which determines how large your models can be. To create large-scale industrial parts, you’ll probably want a more high-capacity print bed than someone looking only to model small figurines or trinkets.
Another major consideration is what types of materials you’re planning to print. Although some commercial 3D printers can now even print with metals or foods like chocolate, most home models for purchase print using either plastic filaments or resin—the latter of which tends to be slightly softer than filament and is typically used on a smaller scale.
So, if you plan to make massive 3D-printed models or you want to finish your prints with paint or other coatings, then a filament printer is probably the best choice. On the other hand, if the production quality is your priority or you want to print small models with a high level of detail, then a resin printer is probably the best option.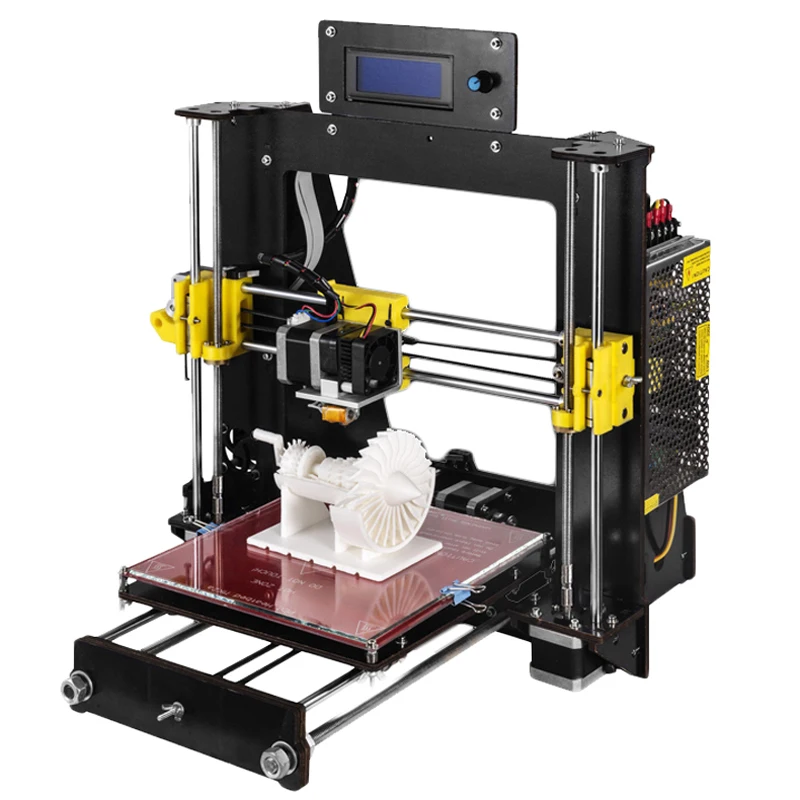 When it comes to printing materials, it’s also a good idea to research which types of materials various 3D printers can accept. Many brands use proprietary filaments or spools, which can quickly add up without a compatible aftermarket or generic option.
When it comes to printing materials, it’s also a good idea to research which types of materials various 3D printers can accept. Many brands use proprietary filaments or spools, which can quickly add up without a compatible aftermarket or generic option.
Best for Quiet Printing: Voxelab Aquila 3D Printer
Smooth and Silent. VoxelabSpecs:
— Build Volume: 18.9 L x 20.47 W x 24.41 H inches
— Weight: 21.8 pounds
— Compatible Materials: PLA, ABS, PETG filaments
— Price: $219
Pros:
— Ultra-silent printing
— Fast heating
— Large print volume
Cons:
— Large, bulky model
Don’t let the irritating whir from a 3D printer stop you from creating your masterpiece. Voxelab’s Aquila 3D Printer prides itself on its quiet printing capabilities, maxing out at 50 decibels (which is quieter than your average electric toothbrush). This printer is slightly more upscale than some of the others on the market today, weighing in at just under 22 pounds. The extra weight is put to good use though, with an all-metal body, V-profile, and a user-friendly colored screen with a rotary knob, its sleekness will make you feel like a seasoned printer.
The extra weight is put to good use though, with an all-metal body, V-profile, and a user-friendly colored screen with a rotary knob, its sleekness will make you feel like a seasoned printer.
This is a great option for those who have had some practice and are a little more confident in their 3D printing abilities; the Aquila 3D features an open design, allowing you to modify and upgrade your equipment for a more personalized experience. It also features resume printing functions, fast heating, and its carbon-crystal silicon glass platform prevents your prints from warping. It’s a top-of-the-line model, so the low price is quite a pleasant surprise.
FAQs
Q: Can a 3D printer print anything?The short answer is that yes, a 3D printer can print virtually anything. The only practical limitations are the build volumes, which is essentially the maximum space in which a printer can print. So, in other words, the sky is the limit—as well as your imagination, of course.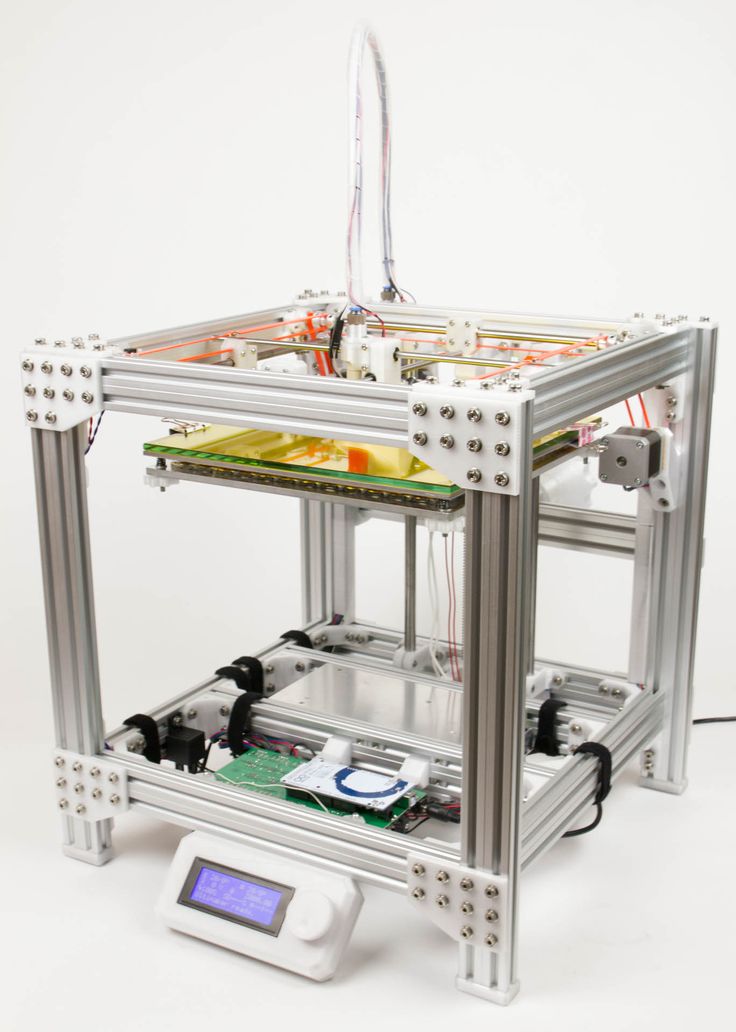
Contrary to popular belief, you do not need any special computer or software, necessarily, to use a 3D printer. These types of printers use data called STL files that tell the machine what to print. Most STL files tend to be smaller and are recommended to be below 15MB, so almost any functioning computer can handle the files. That said, while most models are simple, some high-resolution models can have much larger files.
Q: Can you use a 3D printer with a phone?Depending on what features your 3D printer has, you can likely use it even with your smartphone. There are plenty of 3D-printing apps that are compatible with the best Android and iOS devices. And some of these apps don’t even require a download! You can view files or print progress remotely, design from anywhere, convert images files, and more using these apps.
Final Thoughts on the Best 3D PrintersIf we had to choose our ultimate dream 3D printer, the Dremel DigiLab 3D45 would be our number-one pick. The extra-large print volume, ease of use, and next-level features such as WiFi connectivity and the high definition camera take this printer above and beyond the competition. However, with a hefty price tag, the Dremel DigiLab may not fit into everyone’s budgets, which is why our second pick is the Ender 3 Pro 3D Printer. Not only is the Ender 3 Pro affordable for most households, but it’s also an excellent choice for beginners looking for a 3D printer that’s easy to use with a fantastic output.
The extra-large print volume, ease of use, and next-level features such as WiFi connectivity and the high definition camera take this printer above and beyond the competition. However, with a hefty price tag, the Dremel DigiLab may not fit into everyone’s budgets, which is why our second pick is the Ender 3 Pro 3D Printer. Not only is the Ender 3 Pro affordable for most households, but it’s also an excellent choice for beginners looking for a 3D printer that’s easy to use with a fantastic output.
This post was created by a non-news editorial team at Recurrent Media, Futurism’s owner. Futurism may receive a portion of sales on products linked within this post.
Share This Article
What Does the Future of 3D Printing Look Like?
3D printing has come a long way from the early days of desktop figurines. As technology continues to evolve, the future is brighter than ever.
Once a novelty pipe dream but now an established technology, 3D printing (or additive manufacturing) is positioned for real, important growth. Remember the early days of 3D printing? We shared a collective excitement for model versions of the Brooklyn Bridge and iconic cartoon characters to adorn our desks. Now, 3D printing is tackling much larger issues and solving complex problems across industries of varying scales.
Remember the early days of 3D printing? We shared a collective excitement for model versions of the Brooklyn Bridge and iconic cartoon characters to adorn our desks. Now, 3D printing is tackling much larger issues and solving complex problems across industries of varying scales.
The basis of 3D printing — also called additive manufacturing — is adding layers of materials compounded to make an object. Where cutting and soldering were once required, additive manufacturing gracefully adds layers to build the same type of structures. However, these results are stronger, lighter, more temperature resistant, and require fewer parts.
Applications Showcasing What the Future Holds for 3D Printing
While there are endless examples of 3D printing being used for incredible things, here are a few examples of what the future holds:
- 3D printers have long been able to print rocket-shaped objects, but now companies in the aerospace industry are actually printing rockets.
 Companies like Aerojet Rocketdyne are using additive manufacturing for rocket engine and defense system applications. These companies cite reduced lead times, affordability, and new approaches to design as factors in the decision to use additive manufacturing to deliver hypersonic flight.
Companies like Aerojet Rocketdyne are using additive manufacturing for rocket engine and defense system applications. These companies cite reduced lead times, affordability, and new approaches to design as factors in the decision to use additive manufacturing to deliver hypersonic flight.
- In healthcare, additive manufacturing is also making grand promises. 3D Systems, in partnership with CollPlant, is working on printing artificial tissues and scaffolds, advancing regenerative medicine through the use of rhCollagen as a 3D printing substrate.
- The electric vehicle industry is a similar story. Local Motors Industries, a company with only 130 employees, has already printed a 3D car that has since been discontinued. Now, they’re printing an urban electric shuttle, citing digital design advancements as a contributing factor.
At the Forefront of Evolving Technology
A generatively designed color part from the HP MJF 580 3d printer at the Autodesk Technology Center in Toronto.
Experts predict the largest industry leaps will happen in the technology facilitating additive manufacturing. Printers will likely become even faster, meaning they’ll be able to work on larger, industrial types of projects. Forbes also reports that MELD Manufacturing has designed machines that allow additive manufacturing in uncontrolled environments, which means they can operate in the field. As a result, they’re more useful in remote areas and enable a greater variety of 3D printed structures.
3D printing seeks to address efficiency problems throughout supply chains as well. Nora Toure, Founder of Women in 3D Printing, writes, “I predict there will be a countless number of companies that have adopted additive manufacturing into their supply chain commercially with a vast majority of products to be produced on-demand and locally (not necessarily through additive manufacturing, but more as a combination of manufacturing tools, including additive manufacturing).”
3D printers will also add versatility in other ways — using different materials, including metal and even ceramics, even within the same machine. Printers will be able to print one object containing multiple materials, paving the way for a significantly widened field of use.
Printers will be able to print one object containing multiple materials, paving the way for a significantly widened field of use.
Autodesk Fusion 360 and Additive Manufacturing
Integrated CAD + CAM software like Autodesk Fusion 360 will enable additive manufacturing to soar to entirely new levels. The Fusion 360 team is constantly thinking of ways to improve and enhance the additive manufacturing process. We recently announced a new method for generating additive manufacturing outcomes using generative design. This new method does a better job of meeting minimum thickness requirements, balancing design mass, and minimizing support material — without sacrificing shape quality to be fully self-supporting.
Many leading companies have explored the benefits of using generative design in tandem with additive manufacturing, including Hyundai, Panasonic, and more. Download Fusion 360 today to explore innovative additive manufacturing solutions.
3D printing technology for residential buildings becomes a reality in 24 hours
From space exploration to robotics and medicine, 3D printing has huge potential in all areas, but especially it is starting to make a real impact in the world of affordable housing. The latest example of this is a slightly augmented project for the homeless in Texas, USA, which began with the construction of a stylish new 3D-printed administrative block in just one day.
The latest example of this is a slightly augmented project for the homeless in Texas, USA, which began with the construction of a stylish new 3D-printed administrative block in just one day.
The construction company behind the new 3D printed homes goes by the name ICON. The company presented its first prototype during the Texas media conference SXSW 2018, and after that it set about building an entire village - the world's first 3D-printed neighborhood, in a poor area of South America. Its Vulcan II 3D printer is designed to build simple boxes of houses, while the installation of roofs, doors and window openings is carried out by builders. The company is able to build housing much cheaper and more efficiently, and its concept shown at SXSW took just 48 hours to complete and cost just $10,000.
The Village of 3D Printed Homes aims to instill hope for a secure future for low-income people whose income does not exceed $200 a month, while promoting this concept of affordable housing solutions around the world.
Participation in a new project in Austin, Texas called Community First! Village was the next step for ICON. The project is led by local non-profit organization Mobile Loaves & Fishes for the homeless and will include more than 500 homes on 20 hectares when completed. In this social settlement of more than five hundred houses, additional addresses will appear - six objects made using the 3D construction method. Designed by Texas-based Logan Architecture, Icon will print three houses at once for the first time to showcase their build efficiency and focus on cost reduction. According to the company, all six houses will be rented out before the end of the year, but construction of the 46 sq. m. welcome center building is already completed at this stage. m for the future village, which was printed in just 27 hours. These 3D houses are among the affordable ones and will be ready to move in in just a few weeks.
How does it work?
The façade of the building is erected on the Vulcan printer developed by the company.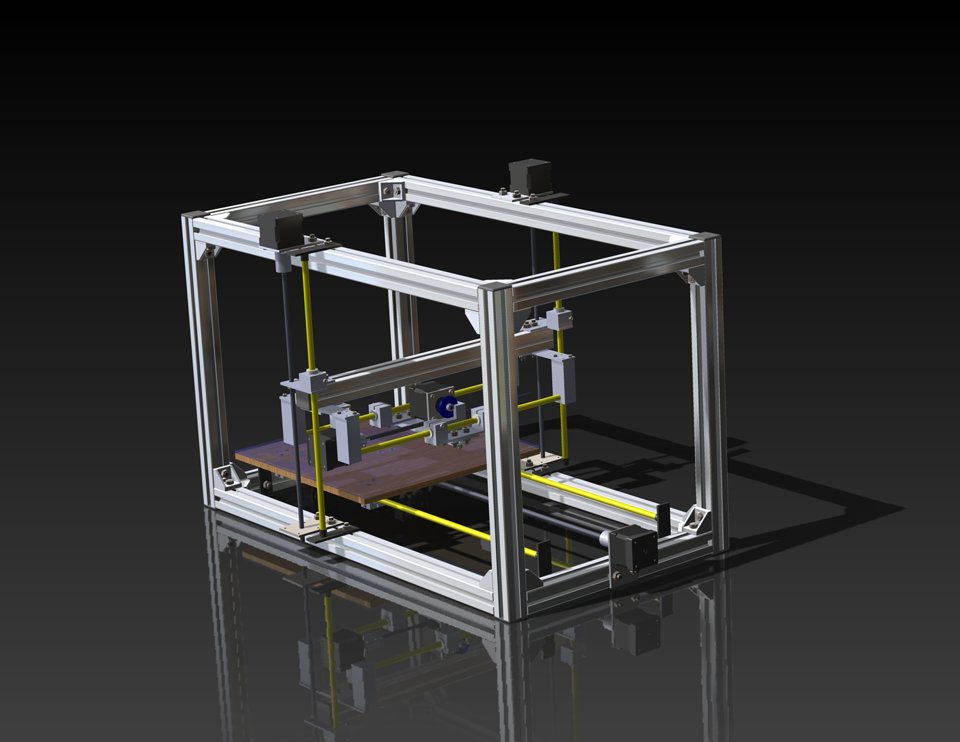 The device prints walls with a mortar of concrete that retains its shape as it cures. Such technology allows them not to collapse. After erecting the facade, the builders install the necessary infrastructure, a wooden roof and windows. It takes a little more than 24 hours to fully build a finished house, depending on the building area, the maximum figures of which are about 75 square meters. The company installed the first such house in the American city of Austin.
The device prints walls with a mortar of concrete that retains its shape as it cures. Such technology allows them not to collapse. After erecting the facade, the builders install the necessary infrastructure, a wooden roof and windows. It takes a little more than 24 hours to fully build a finished house, depending on the building area, the maximum figures of which are about 75 square meters. The company installed the first such house in the American city of Austin.
This development has a number of advantages, such as relative cheapness, construction time, and the ability to build houses in conditions with limited resources and harsh climatic conditions. In addition, the walls of the building have an air gap that retains heat in cold weather. The estimated cost of building a dwelling is $4,000.
The second generation of this printer, the Vulcan II, is designed specifically for the production of reliable one-story buildings - quickly, inexpensively and with great variability. The printing area has been increased to 186 square meters. m, the width of the walls is adjustable for different sizes of panels. You can transport the printer in a special trailer; no assembly is required before starting work.
The printing area has been increased to 186 square meters. m, the width of the walls is adjustable for different sizes of panels. You can transport the printer in a special trailer; no assembly is required before starting work.
As ICON assures, anyone who has been instructed will be able to operate this printer. All functions are intuitive and displayed on the tablet screen. The printer itself is 3.5 meters high and 10 meters wide. It prints walls up to 2.5 meters high on a foundation up to 8.5 meters wide. It prints a part 0.3 high and 0.6 m wide at a speed of 1.5 - 2 meters per second.
Especially for the operation of the machine, the company has developed and patented a recipe for concrete-lime material Lavacrete. It has passed all strength tests and is recognized as safe for residential construction.
This is not the first attempt at 3D printing living spaces. Recall that in the spring of 2017, researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology presented a similar construction technology.
Not only American startups are going to solve the problem of affordable housing with printing. A similar project is planned in India. Tvasta promised the first printed houses this year. Indian technology takes more time: the startup plans to print the components of a 30-square-meter house in about three days, and assemble it “under the roof” within a week.
Source: New Atlas
3D printers in construction: prospects for application
At first glance, 3D printing structures seem to be some kind of shell of a half-finished building. But upon closer examination, you will not find even a brick. Layers of material seem to build up one on top of the other - this is how a complex structure is created. It's a futuristic world of 3D printing where robotic arms automatically layer and compress layers of concrete or plastic or any other material into a foundation and build a structure.
This method of construction is quite niche today - only a few prototypes of 3D houses and offices have been printed in the world. However, this technology represents an exciting and potentially powerful solution to building change.
However, this technology represents an exciting and potentially powerful solution to building change.
What is 3D printing in construction, what is the potential, and will we be working on 3D printed projects in the near future?
- What is 3d printing in construction?
- 3D printers in construction: how is it done?
- 5 examples of innovation
- How can 3d printed projects help construction companies?
- 3D printing distribution
- Civil engineering 3D printing
- Wiki House technology - an open source project for 3D printing: what is behind the concept
- Reverse side of the coin
- How 3D printing can be integrated into construction
- About PlanRadar
3D printing in construction - what kind of technology?
3D printing for construction uses both a 3D printer, which has a robotic "crane-arm" that builds structures right on the construction site, and the creation of certain elements by printers at the factory, which are already assembled into a structure on site.
The concept of 3D printing is not new: it first appeared in the 80s. But it's only in the last decade that this technology has been improved enough (and the cost significantly reduced) to become a real mainstream.
3D printers are not much different from conventional inkjet office printers. The software tells the printer about the dimensions of the final product. And then the printer starts to output the material to the platform according to the plan. 3D printers often use liquid metals, plastics, cement, and variations of various materials that, when cooled and dried, form a structure.
In a 3D construction printer, the CAD or BIM programs tell the device what to print, and the machine begins layering the material according to the design plan.
3D printers in construction: how do they work?
3D printing concept - the printer extrudes a certain liquid mixture in layers, level by level, creating a design based on a three-dimensional model. The prepared mix of concrete, filler, plasticizer and other components is loaded into the hopper of the device and fed to the print head. The mixture is applied to the surface of the site or to the previous printed layers. This is how most 3D printers work. Among them, there are three types of devices for 3D printing:
The mixture is applied to the surface of the site or to the previous printed layers. This is how most 3D printers work. Among them, there are three types of devices for 3D printing:
Robotic printer
Read also: New technologies in construction 2021
5 innovative examples of 3D printing
To date, only a few 3D printing projects have been implemented in the construction industry. Here are five of the most impressive and promising projects:
Dubai City Hall Office Building, UAE
1. Dubai City Hall Office Building, UAE
3D printed building. The office block built in the UAE is 9,5 meter high building with an area of 640 m2.
An Apis Cor 3D printer moved around an open-air construction site with a crane and erected different parts of the structure.
2. Office of the Future, UAE
Office of the Future, UAE
Another impressive 3D printed building in the UAE, the Office of the Future is a unique, fairly large structure that currently houses a temporary headquarters organization Dubai Future Foundation.
For this building, the elements were not created on site and were printed in 17 days, while the building itself was assembled in 48 hours.
3. WinSun 3D Printer Homes, China
WinSun 3D Printer Homes, China
WinSun 3D Printing Company of China has also used factory-built 3D printers to build residential buildings. The company has created several house projects, including a small multi-storey building. All construction details can be printed quickly and cheaply and then quickly assembled on the construction site.
The company calculated that it would cost as little as $161,000 to build and print their five-story building.
4. 3D printed license plate at Lewis Grand Hotel, Philippines
3D printed license plate at Lewis Grand Hotel, Philippines
When planning a trip to the Philippines, consider staying at the Lewis Grand Hotel in Angeles City , Pampanga, where visitors will be greeted with the world's first 3D printed hotel suite.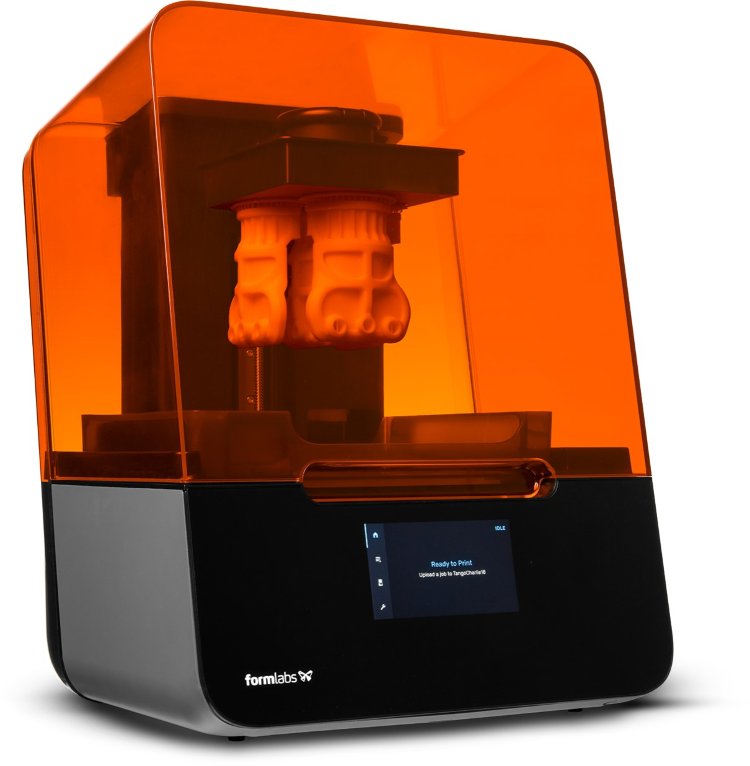 The hotel room was designed by Lewis Jakich, hotel owner and materials engineer, in collaboration with 3D printing specialist Anthony Rudenko. They created a massive 3D printer that prints sand and concrete based on volcanic ash. The room was printed in 100 hours.
The hotel room was designed by Lewis Jakich, hotel owner and materials engineer, in collaboration with 3D printing specialist Anthony Rudenko. They created a massive 3D printer that prints sand and concrete based on volcanic ash. The room was printed in 100 hours.
5. Two-story mansion in Beckum, Germany
Two-story mansion in Beckum, Germany
The first 3D-printed residential building with an area of about 80 square meters - the brainchild of the German construction company PERI GmbH and the architectural design bureau MENSE-KORTE ingenieure + architecture. A BOD2 3D printer was used to print one square meter of double wall cladding in 5 minutes. The building is a structure with three-layer hollow walls filled with insulating mass. Installation of hollow pipes and connections during printing was carried out manually.
3D printing in construction seems really impressive, but what are the real benefits of such technology?
How can 3D printed designs be useful for construction companies?
Proponents of 3D printing houses and commercial offices point to several advantages of this construction method:
- Zero waste construction
In the UK, almost a third of the waste comes from the construction industry. According to the Transparency Market Research Group, the construction industry worldwide will produce 2.2 billion tons of construction waste by 2025. And although most of the waste is related to the demolition of buildings, the construction sites themselves produce a lot of waste.
According to the Transparency Market Research Group, the construction industry worldwide will produce 2.2 billion tons of construction waste by 2025. And although most of the waste is related to the demolition of buildings, the construction sites themselves produce a lot of waste.
Conversely, 3D printing can reduce waste to almost zero. A 3D printer uses a well-defined amount of material that is required to print a design - no more, no less. This can be a big savings.
- Reduced energy consumption
3D printing in construction encourages the use of locally available materials and natural ingredients. This practice can reduce energy costs in transportation, construction and manufacturing, as most local materials require less energy to process or install. If traditional materials with toxic chemical impurities are replaced with natural ones, then the toxicity of the entire construction can be reduced. In addition, local materials are often better suited to local climates and can reduce the heating or cooling load of a building, which also reduces construction costs.
- Save time and money
As with AI in construction, a 3D printer can run 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. This means construction projects have the potential to be completed much faster and a number of low-skilled labor costs can be avoided. What's more, 3D printing eliminates the need for temporary structures, such as formwork and scaffolding, that are commonly used in traditional construction. Studies of 3D printed concrete structures have shown a significant reduction in formwork requirements, reducing costs by 35-60%.
- Can realize unusual design shapes
One of the most attractive characteristics of 3D printers is their ability to create complex and unusual design designs, including a single, unique one. Since the job of a 3D printer is to layer the material, they can be programmed into absolutely any unusual shape that would be much more difficult to create with traditional techniques.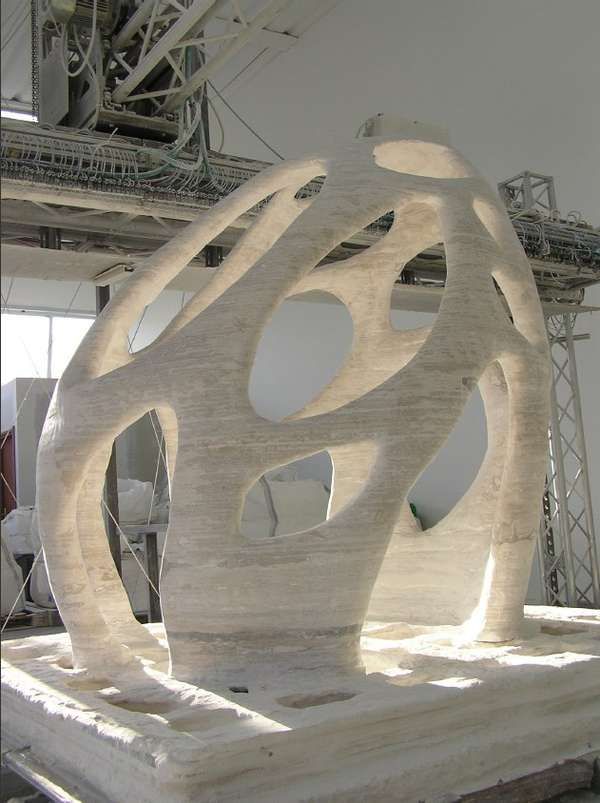
- Minimize human error and improve safety
The published injury statistics at the workplace by the American agency BLS in 2020 indicates that construction is one of the most traumatic areas and a high incidence of diseases. Every day, about 5333 workers die on the construction site. And with the advent of 3D printing, the number of work injuries and fatalities will obviously decrease, as it makes construction more programmable and automated. Robotic construction requires standardized, accurate and complete digital building information, making this technology more accurate and efficient, with minimal rework due to human error or any information inconsistencies. The usual problems with materials and components that need to be stored somewhere, protected from damage are leveled out, problems with installation and work in progress due to damage also disappear - 3D elements are created as they are built, they do not need to be moved and stored.
- Exploring new markets
The use of a 3D printer also allows construction companies to enter new market sectors that were previously inaccessible to them. And for start-up companies, having a 3D printer will be a competitive advantage. What's more, 3D printing is a brilliant way to elevate or improve the reputation of a construction company's brand among those who believe that concrete production has an impact on the planet's environment.
Distribution of structural 3D printing
3D printing for structural reinforcement, small scale components and structural steel could revolutionize design, construction and space exploration. In addition, the European Space Agency (ESA) believes that using 3D printed metals to create high-quality complex shapes can significantly reduce their cost, and they will become very common.
ESA has developed a project with the European Commission to improve the printing of metal components that can be used in space. In total, 28 European partners have united for the joint project AMAZE (Additive Manufacturing Aiming Towards Zero - layer-by-layer 3D printing for zero waste from production and efficient production of high-tech metal products).
In total, 28 European partners have united for the joint project AMAZE (Additive Manufacturing Aiming Towards Zero - layer-by-layer 3D printing for zero waste from production and efficient production of high-tech metal products).
Almost everything can be designed on a computer, so AMAZE plans to install a 3D printer on board the spacecraft, and as soon as an astronaut needs any part, a tool, he can simply print it.
Structural 3D printing
Civil engineering 3D printing
Civil engineering 3D printing has been gaining popularity over the past decade, as has the aerospace and biomedical industries. This revolutionary manufacturing technique is based on its unique ability to create any geometric shape without any formal restrictions, minimizing waste but increasing productivity and results. The construction industry's push towards automation has recently reached important milestones, including the creation of the first structures using robotic "arms" and 3D printing technology.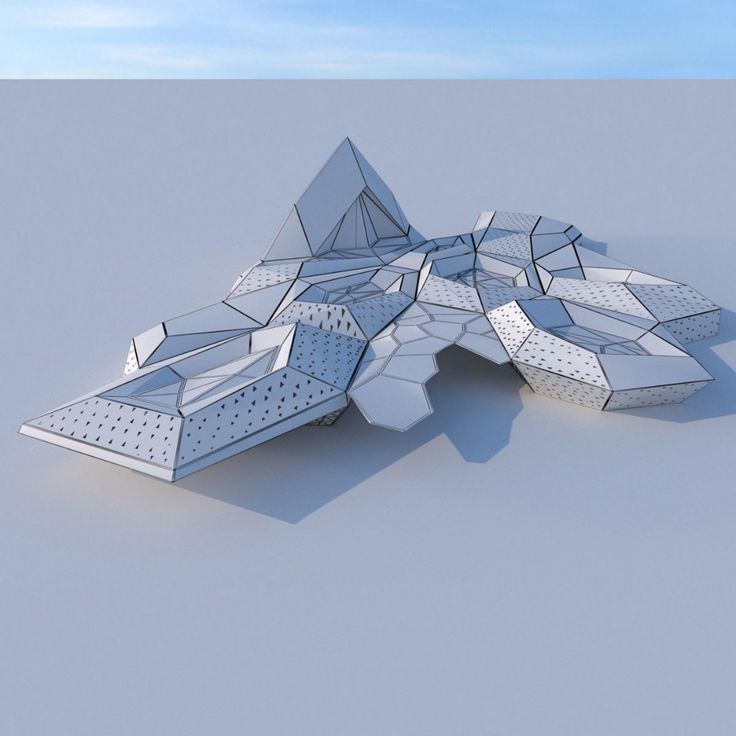
The use of 3D printing in the creation of structural elements from polymer materials, concrete and metals is becoming more common.
These civil engineering technicians can create freeform and innovative architectural designs using CAD-integrated software.
However, despite considerable research in the aerospace and bioengineering industries to evaluate and analyze this mechanism, there is still a lack of understanding of its use, the impact of 3D printed materials in civil structures, both in terms of material properties and structural response.
Imperial College London
Read also: Best Building Apps in 2021
WIKI HOUSE - 3D printing in construction: what is the concept behind
Wiki House is an innovative project created by a small group of architects in London in 2011 . It offers an open source digital house design system that allows users to create, upload and share designs and print their own houses.
The kit does not require any special knowledge and training and can be created in 1 day. Elements are digitally cut from ordinary sheet material, like plywood, using a CNC machine. And it's much faster, less costly, and doesn't require the involvement of experts, as in conventional traditional construction.
Elements are digitally cut from ordinary sheet material, like plywood, using a CNC machine. And it's much faster, less costly, and doesn't require the involvement of experts, as in conventional traditional construction.
A standard two bedroom house can be built for less than £50,000 and additional components such as cladding, insulation, windows and more can be added to the main frame of the structure. The first house that was built on the basis of the open source Wiki House technology was a two-story building. The 3D printed house was presented at the London Design Festival in 2014.
The Wiki House movement was spearheaded by Alastair Parvin, whose TED presentation "Architecture for People, Built by People" talked about the promise of 3D printing in construction. The creator of this project believes that Wiki House can help solve the housing problem, especially in emergency situations such as earthquakes (there is already evidence that 3D-printed houses can withstand shocks up to magnitude 8).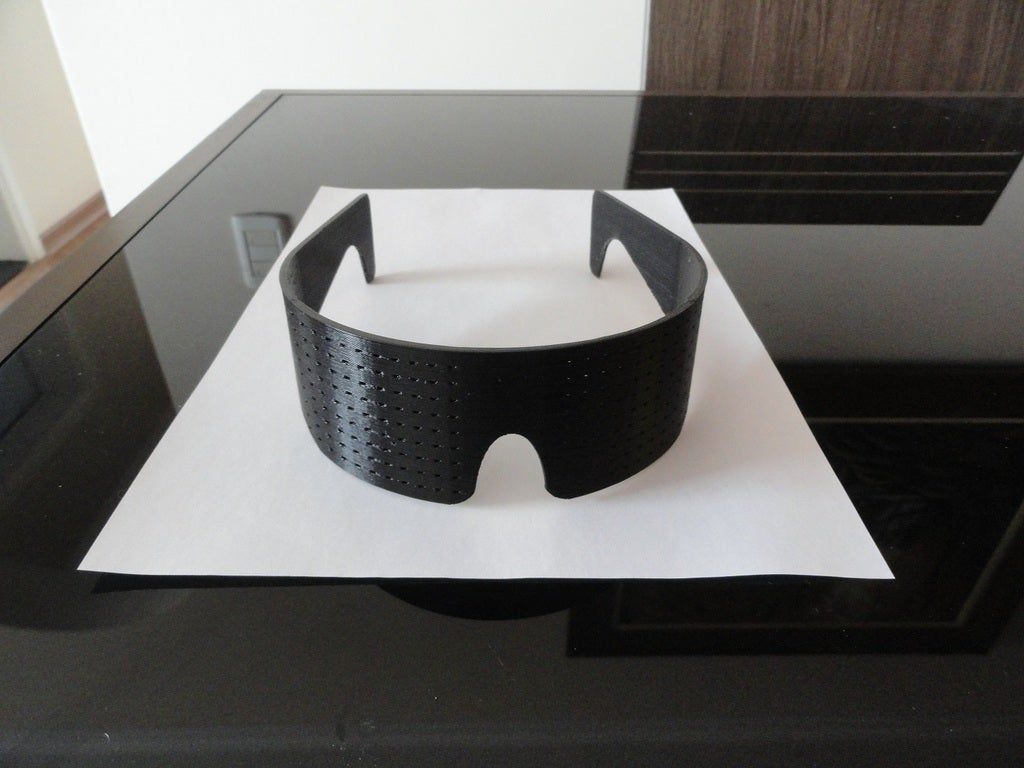
In the future, this could become a real alternative to low-cost houses, while allowing the customer to control the design of the project.
3D building built using Wiki House
Will 3D printing be the sustainable future of building?
3D printing has the potential to revolutionize the supply chain and structure through a new method of design and manufacturing. According to the study, 3D printing can help the construction industry become more economical, more efficient and greener.
Saxon University of Applied Sciences scientists Ivo Kotman and Neils Faber claim that 3D printing technology will be a "game changer". They explored the possibilities of 3D printing concrete, and their conclusions are:
- 3D printing shortens the supply chain and the entire design process. 3D printing right on the job site eliminates time-consuming steps in the design process. The architects, engineers, contractors, clients, and executives who normally have to be actively involved in a project are no longer needed in 3D printing.
 Since all tasks can be combined in one figure of the architect, who uses the modeling method and reproduces the exact holistic designs.
Since all tasks can be combined in one figure of the architect, who uses the modeling method and reproduces the exact holistic designs. - Pipe fitting and electrical wiring become easier and more efficient. Heating systems, insulation, plumbing and electricity all require the laborious on-site installation of conventional construction. However, in 3D printing, some of these features can be incorporated into the 3D printing process. Cavity wall printing is less resource intensive, improves insulation, and allows the use of 3D-printed hot or cold water channels. Moreover, the need for on-site installation is eliminated, which directly affects the reduction of waste.
- The best logistics. 3D printing eliminates 3 logistics and shipping issues. Firstly, many materials and elements often deteriorate upon delivery, and if everything is printed on site, then damage is minimized
Secondly, in order to withstand transportation, the parts must be with increased technical characteristics, which by default increases the cost of them, and therefore the entire project. 3D printing right on the construction site will help to avoid such additional costs.
3D printing right on the construction site will help to avoid such additional costs.
- Creation of individual house designs available to the general market. Usually, building a house with the involvement of an architect is an expensive pleasure for most consumers. But with concrete 3D printing, you don't have to worry about the chosen shape, it won't cost more. In fact, this means that in the future more people will be able to buy houses of their own design according to their individual needs
Reverse side of the coin
While 3D printing is definitely attractive, it's still important to look at it impartially, removing some of the promotional stimulus. Skeptics note several disadvantages of this technology.
- Research and development costs
Most construction companies operate with relatively low profitability. To start using 3D printing everywhere, significant investments will be required.
- Will consumers see this as a marketing ploy?
3D printed houses, offices, shops and other infrastructure are often impressive. But do most people really want to live or work in one? For most people, brick houses are much more familiar and attractive. Other technologies such as prefabricated houses also seemed like an attractive technology of the future for some time, but have not been widely adopted, despite the fact that in many cases they were cheaper than traditional ones.
- Difficulty integrating with other components
3D printers can create unique and interesting designs. However, if you need a building that will use different materials or different elements that will not be suitable for 3D printing, then it will be a challenge to include a 3D printer for the building process.
- Lack of skilled labor
With the current problem of a shortage of skilled labor in the construction sector in general, 3D printing will require an even larger set of specialized knowledge and skills, which will have to be selected from an already small niche of candidates. So finding specialists to work in 3D printing for construction may be another difficult task in the future.
- Construction quality control
Weather conditions can slow down the traditional building process, but things are even worse for 3D printing. The environmental factor for commercial construction may reduce the demand for 3D printing. What's more, quality control can be a much more serious task, requiring constant monitoring of the process by real people at the construction site.
- No standards and regulations
Despite the regular mention of 3D printing in the media, it still has not had a significant impact on the construction sector. There is an obvious liability issue when using these printers, even more so than human liability when doing some construction work. And quite a few other ambiguities regarding this technology. So until norms and standards are established, as well as rules in this area, 3D printing is unlikely to become mainstream in the construction industry.
There is an obvious liability issue when using these printers, even more so than human liability when doing some construction work. And quite a few other ambiguities regarding this technology. So until norms and standards are established, as well as rules in this area, 3D printing is unlikely to become mainstream in the construction industry.
Read also: New technologies in construction 2021
How can 3D printing be integrated with construction?
At the moment there is strong evidence that 3D printing is worthy of attention and can be applied in the construction segment, and it is likely that this technology will be used more in the coming years. True, it is not known how widely these devices will be used on the construction site, or whether they will remain only a tool for the manufacture of block elements for prefabricated structures. But for certain projects, it is reasonable to assume that 3D printers and this technology in construction will be a must-have tool in the arsenal of builders.