3D print a human
3D Bioprinting of Living Tissues
Progress in drug testing and regenerative medicine could greatly benefit from laboratory-engineered human tissues built of a variety of cell types with precise 3D architecture. But production of greater than millimeter sized human tissues has been limited by a lack of methods for building tissues with embedded life-sustaining vascular networks.
Play
In this video, the Wyss Institute and Harvard SEAS team uses a customizable 3D bioprinting method to build a thick vascularized tissue structure comprising human stem cells, collective matrix, and blood vessel endothelial cells. Their work sets the stage for advancement of tissue replacement and tissue engineering techniques.Multidisciplinary research at the Wyss Institute has led to the development of a multi-material 3D bioprinting method that generates vascularized tissues composed of living human cells that are nearly ten-fold thicker than previously engineered tissues and that can sustain their architecture and function for upwards of six weeks. The method uses a customizable, printed silicone mold to house and plumb the printed tissue on a chip. Inside this mold, a grid of larger vascular channels containing living endothelial cells in silicone ink is printed, into which a self-supporting ink containing living mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is layered in a separate print job. After printing, a liquid composed of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix is used to fill open regions within the construct, adding a connective tissue component that cross-links and further stabilizes the entire structure.
Confocal microscopy image showing a cross-section of a 3D-printed, 1-centimeter-thick vascularized tissue construct showing stem cell differentiation towards development of bone cells, following one month of active perfusion of fluids, nutrients, and cell growth factors.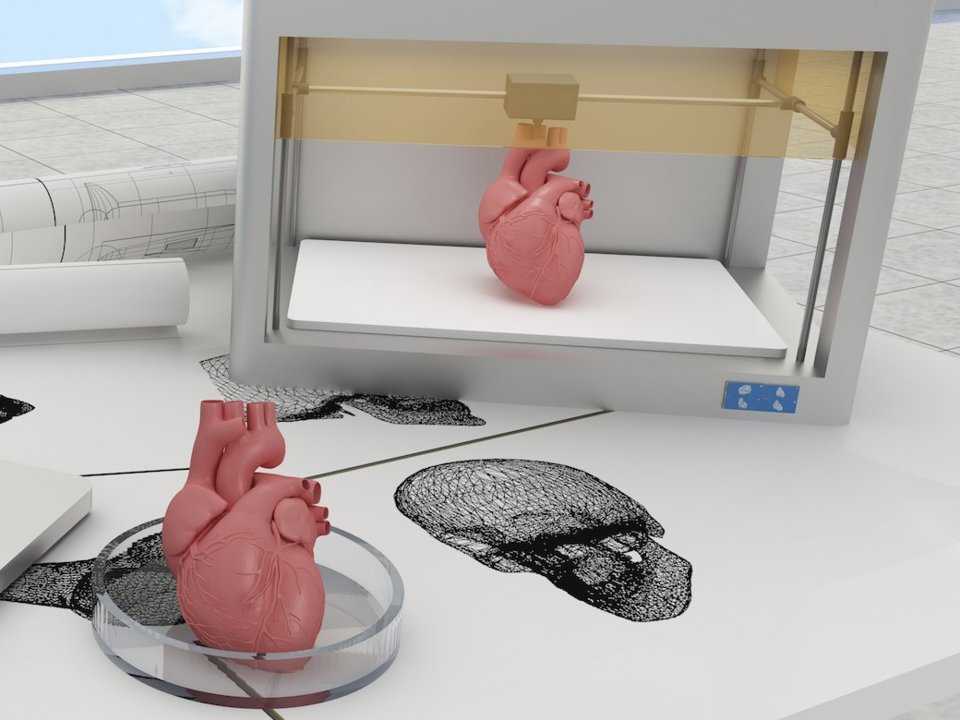 The structure was fabricated using a novel 3D bioprinting strategy invented by Jennifer Lewis and her team at the Wyss Institute and Harvard SEAS. Credit: Lewis Lab, Wyss Institute at Harvard University
The structure was fabricated using a novel 3D bioprinting strategy invented by Jennifer Lewis and her team at the Wyss Institute and Harvard SEAS. Credit: Lewis Lab, Wyss Institute at Harvard UniversityThe resulting soft tissue structure can be immediately perfused with nutrients as well as growth and differentiation factors via a single inlet and outlet on opposite ends of the chip that connect to the vascular channel to ensure survival and maturation of the cells. In a proof-of-principle study, one centimeter thick bioprinted tissue constructs containing human bone marrow MSCs surrounded by connective tissue and supported by an artificial endothelium-lined vasculature, allowed the circulation of bone growth factors and, subsequently, the induction of bone development.
This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3D tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. The Wyss team is also investigating the use of 3D bioprinting to fabricate new versions of the Institute’s organs on chips devices, which makes their manufacturing process more automated and enables development of increasingly complex microphysiological devices. This effort has resulted in the first entirely 3D-printed organ on a chip – a heart on a chip – with integrated soft strain sensors.
This effort has resulted in the first entirely 3D-printed organ on a chip – a heart on a chip – with integrated soft strain sensors.
- 1/7 Cross section of long-term perfusion of HUVEC-lined (red) vascular network supporting HNDFladen (green) matrix.
- 2/7 Top-down view of long-term perfusion of HUVEC-lined (red) vascular network supporting HNDFladen (green) matrix.
- 3/7 Photograph cross section of printed tissue construct housed within a perfusion chamber.
- 4/7 Photograph cross section of printed tissue construct housed within a perfusion chamber.
- 5/7 Photograph of a printed tissue construct housed within a perfusion chamber.
- 6/7 Photograph of vasculature network and cell inks.
- 7/7 Photograph of 3D printed vasculature network (red) within Red is the
- Next
- Prev
3D Printers Can Already Create Human Body Parts
Do you feel like you are living in a sci-fi version of the future? Because you probably should.
A close up view of the skin bioprinter nozzle.WFIRM
In recent years, updates in 3D printing technologies have allowed medical researchers to print things that were not possible to make using the previous version of this technology, including food, medicine, and even body parts.
In 2018, doctors from the Ontario Veterinary College 3D printed a custom titanium plate for a dog that had lost part of its skull after cancer surgery.
Source: University of Guelph“By performing these procedures in our animal patients, we can provide valuable information that can be used to show the value and safety of these implants for humans”, said veterinary surgical oncologist Michelle Oblak at the time. “These implants are the next big leap in personalized medicine that allows for every element of an individual’s medical care to be specifically tailored to their particular needs.”
And not just for animal patients.
What is 3D bioprinting?
3D bioprinting is the utilization of 3D printing technologies to fabricate body parts.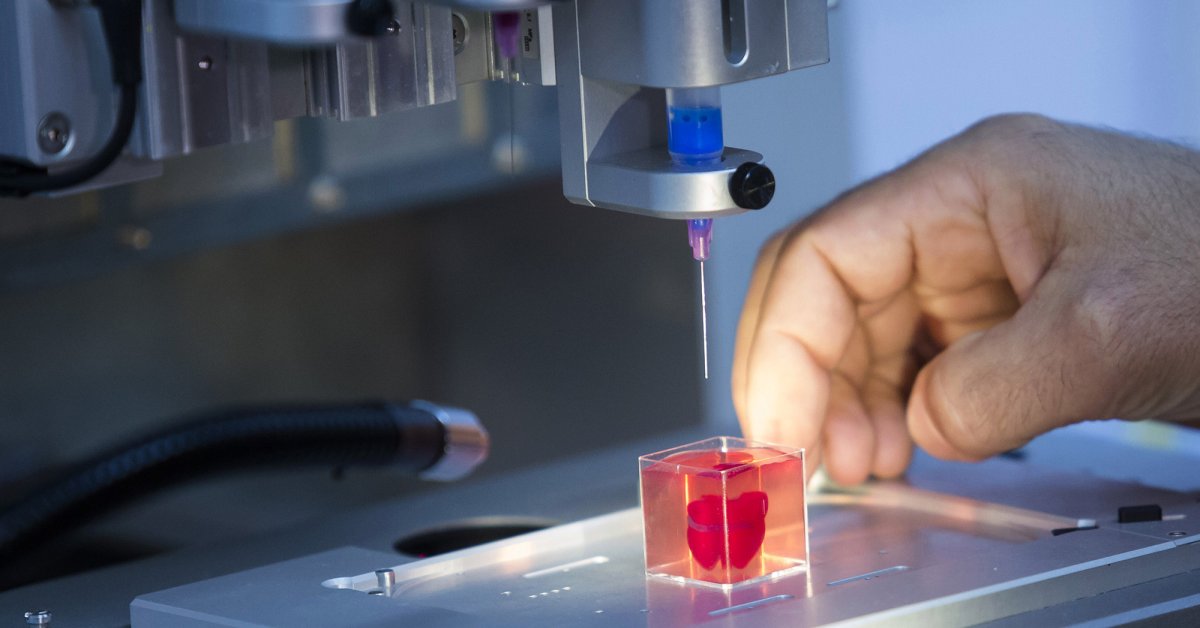 Bioprinters work in a similar way to 3D printers. However, instead of depositing materials such as plastic or ceramic, they deposit layers of biomaterial, including living cells, to build complex structures like blood vessels or skin tissue.
Bioprinters work in a similar way to 3D printers. However, instead of depositing materials such as plastic or ceramic, they deposit layers of biomaterial, including living cells, to build complex structures like blood vessels or skin tissue.
The required cells are taken from a patient and then cultivated. These cells are usually combined with a carrier material or scaffold. This carrier is usually a type of biopolymer gel, which acts as a 3D molecular scaffold and provides protection for the cells during the printing process. Cells attach to the gel, which is sturdy enough to allow printing and flexible enough to allow the flow and diffusion of nutrients and the movement of cells. This combination of encapsulated cells and biopolymer gels is the bio-ink used by biomedical engineers to create 3D-printed, tissue-like structures.
Detailed computer designs and models are first made, often based on scans such as magnetic resonance imaging or computerized tomography taken directly from a patient. Precision printer heads then deposit cells and bio-inks exactly where they are needed and, over the course of several hours, an organic object is built up using a large number of very thin layers.
Precision printer heads then deposit cells and bio-inks exactly where they are needed and, over the course of several hours, an organic object is built up using a large number of very thin layers.
The cells are kept alive using liquefied nutrients and oxygen during the whole process.
In the post-printing stage, the structures may be crosslinked with UV light or ionic solutions to make them more stable. Cells are chemically and mechanically stimulated to control the remodeling and growth of tissues. Then, the 3D printed product is put into an incubator to allow the cells to grow.
When it’s ready, the structure must be used as soon as possible, unless the 3D bioprinting is combined with cryopreservative techniques — something that researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School achieved last year.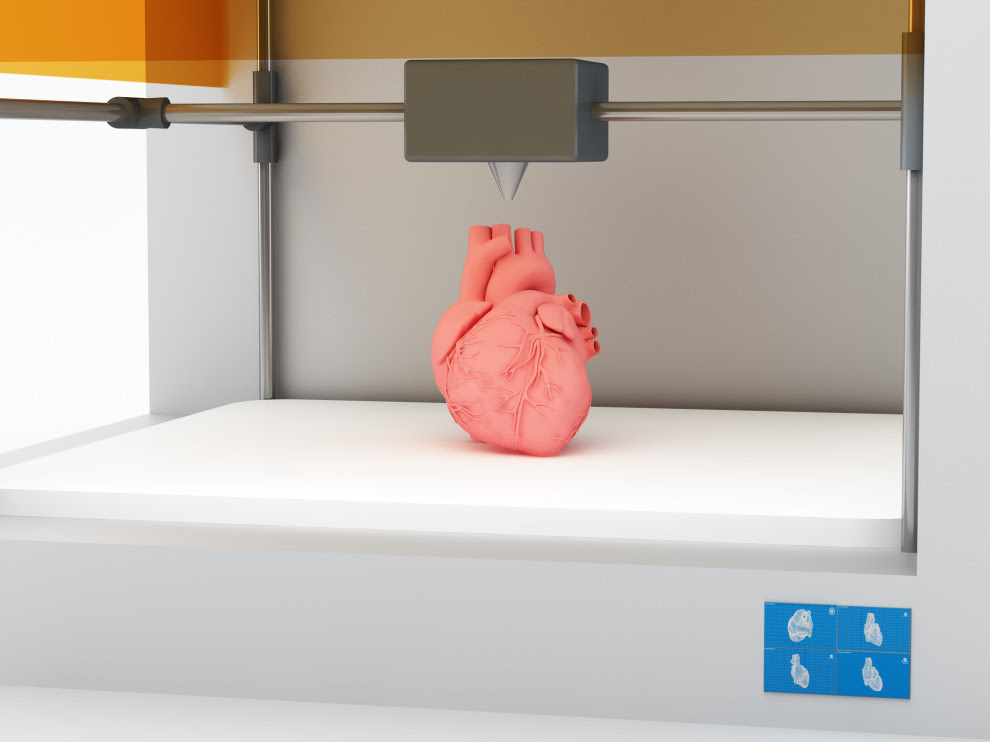
Most Popular
The work, published on December 21st, showed how the team was able to 3D print tissues onto a cold plate at -4°F (-20ºC), after which they were preserved in a freezer at -320.8°F (-196ºC). The tissues, researchers said, can then be thawed within minutes for immediate use.
Tendons and ligaments
In 2018, biomedical engineers from the University of Utah developed a method for 3D printing ligaments and tendons. The method involves first taking stem cells from the patient and printing them on a layer of hydrogel to form a tendon or ligament. This is allowed to grow in vitro in a culture before being implanted. However, the process was very complex, because connective tissue is made up of different cells in complex patterns. The team first needed to develop a special printer head that could lay down human cells in the highly controlled manner they require.
To do this, the team partnered with Utah-based company Carterra, Inc., to develop a specialized printhead that would let them lay down cells in complex patterns. The printhead was then attached to a 3D printer normally used to print antibodies for cancer treatment.
The printhead was then attached to a 3D printer normally used to print antibodies for cancer treatment.
With this technique, the scientists managed to 3D print stem cells taken from a patient’s body fat onto a layer of hydrogel. This hydrogel facilitates cell growth in vitro in a culture, forming either a ligament or tendon in the process.
The new tissue is then implanted in the damaged area of the patient’s body, eliminating the need for additional tissue replacement procedures.
Replacement tissues for those needing it are often harvested from elsewhere on a patient's body or from a cadaver. However, tissue from cadavers runs a high risk of being rejected by the surrounding tissues or of being of poor quality and ineffective.
Instead, tissues created from the patient’s own cells can reduce the complications involved with a transplant and speed up the healing process.
Skin bioprinting and wound healing
3D bioprinting could also help us say goodbye to skin grafts in the near future, as doctors could be able to 3D print new skin for each patient.
Skin grafting is the transplantation of healthy skin from an animal, a human donor, or the patient’s own body to another part of his or her body where the skin is badly damaged. The procedure is commonly used to treat severe wounds, burns, ulcers, and infections, or after the removal of skin cancers.
Source: Scientific Animations/Wikimedia CommonsBut the technique involves several risks, from hemorrhages and loss of sensitivity to infections, scarring, and rejection.
This is why scientists from Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) are working on a mobile bedside skin bioprinting system that could let doctors print bi-layered skin directly on the patient’s wound.
“The unique aspect of this technology is the mobility of the system and the ability to provide on-site management of extensive wounds by scanning and measuring them in order to deposit the cells directly where they are needed to create skin,” said Sean Murphy, Ph. D., a WFIRM assistant professor who was the lead author of the paper.
D., a WFIRM assistant professor who was the lead author of the paper.
To do this, the scientists isolated certain skin cells from a biopsy of healthy tissue and grew them in culture. After that, they combined the cells with a hydrogel and put them into the bioprinter. The device printed the cells onto the damaged area following the data extracted from the wound’s scan through a software.
Again, because the cells are taken from the patient’s own body, there is a much lower risk of rejection.
Meanwhile, in Dublin, scientists from the RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences developed a hydrogel scaffold with natural platelet-rich plasma (PRP) that has promising regenerative properties. The compound can be used as a bio-ink to accelerate the wound healing process in 3D printed tissues.
“Existing literature suggests that while the PRP already present in our blood helps to heal wounds, scarring can still occur,” said RCSI Professor Fergal O’Brien. “By 3D printing PRP into a biomaterial scaffold, we can increase the formation of blood vessels while also avoiding the formation of scars, leading to more successful wound healing.”
“By 3D printing PRP into a biomaterial scaffold, we can increase the formation of blood vessels while also avoiding the formation of scars, leading to more successful wound healing.”
Blood vessels
Perhaps the ultimate goal of 3D bioprinting is to assemble functional organs and solve the problem of organ transplantation.
Currently, there are more than 100,000 people waiting for an organ on the U.S. national transplant waiting list. Roughly 17 of them die each day because they don’t receive the organ they need. This is largely due to the lack of donors. Although around 60% of Americans are signed up as donors, organ donation is only possible in 3 out of every 1,000 deaths.
3D bioprinting of organs could save a lot of lives, but scientists struggle to create the vascular structures needed to create viable printed organs. All organs, including 3D-printed ones, need an effective, continuous blood supply to prevent the death of the cells and the tissues.
In October 2021, a team of researchers at Israel's Technion Institute of Technology managed to 3D print blood vessel structures to add a blood supply to tissue implants.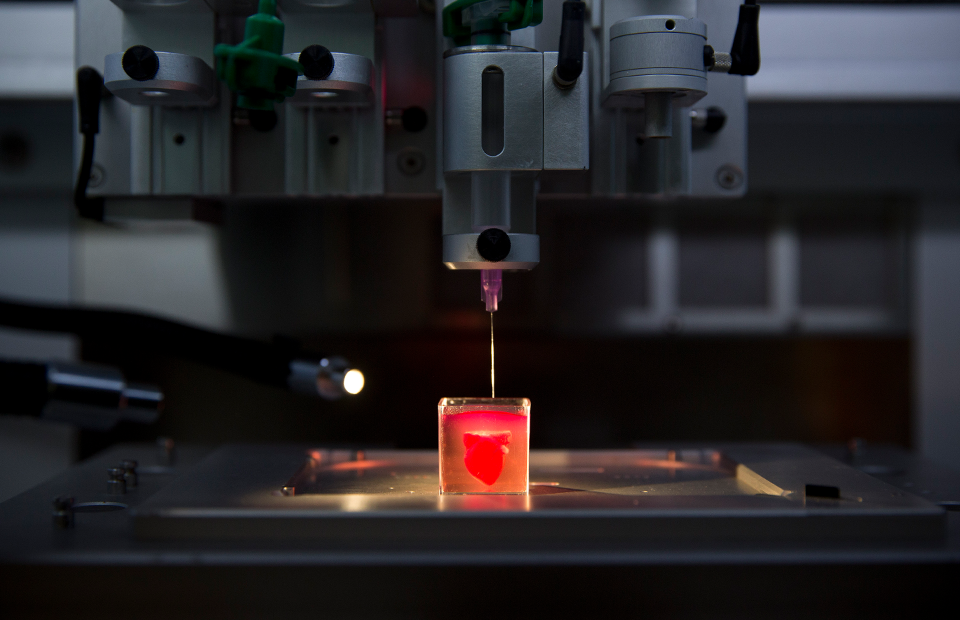
These structures grew spontaneously after the team implanted endothelial cells from the inner layer of blood vessels in the body in a polymeric collagen scaffold.
However, these are only microvessels that can be used to improve in vitro tissue development — they wouldn’t be able to, “feed” a whole organ, and so far, they don’t allow the integration of lab-grown tissues into the patient’s vascular system.
This study shows that there’s still a long way to go until we can actually 3D print organs on demand. But who knows which techniques can scientists develop to solve this issue in the future?
For You
innovation
Thinking Huts rely on additive manufacturing technologies to build sustainable schools. Recently, they built the first 3D-printed school in Madagascar.
Deena Theresa | 8/10/2022
scienceJames Webb head explains why the telescope is more advanced than anything ever built
Stephen Vicinanza| 10/12/2022
innovationBrainwaves synchronize during online games when players aren't in the same room
Stephen Vicinanza| 9/25/2022
More Stories
culture
Halloween warning: Kids you may get a candy bar that plays Doom
Stephen Vicinanza| 10/26/2022
innovation
No more Lithium: 4 ways renewable energy could be stored in the future
Ameya Paleja| 10/17/2022
science
Advanced alien civilizations haven't contacted us because of the age of our Sun
Ameya Paleja| 10/26/2022
3d printing of a person - 3d printing of figures of people on a 3d printer in Moscow
Masterpieces of fine art always amaze with filigree and liveliness of human images.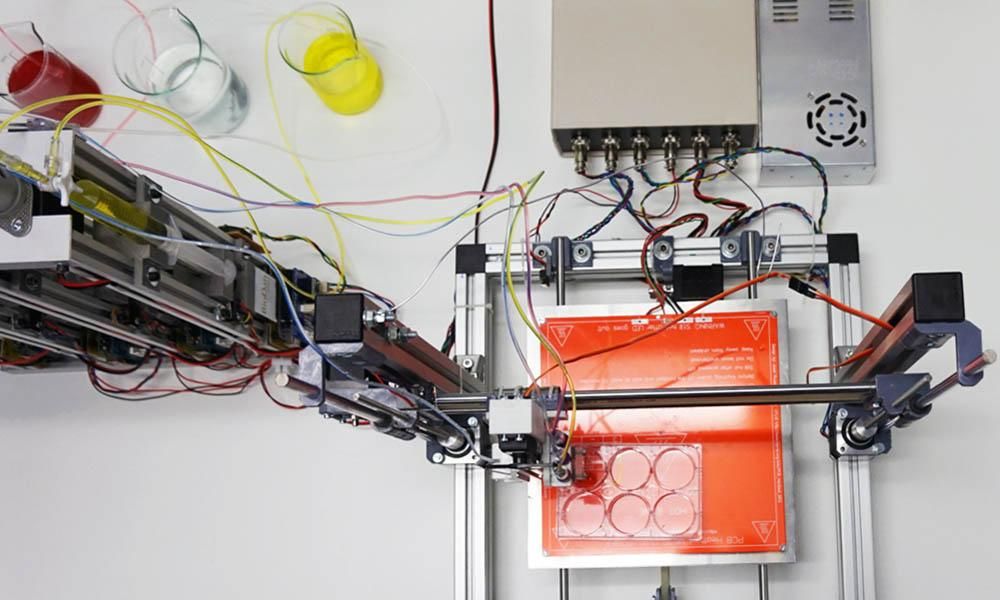 It would seem that copying the human image will forever remain beyond the capabilities of ordinary people. But, nevertheless, time moves inexorably forward, sweeping away restrictions and providing opportunities.
It would seem that copying the human image will forever remain beyond the capabilities of ordinary people. But, nevertheless, time moves inexorably forward, sweeping away restrictions and providing opportunities.
Possibilities and advantages of the masterpiece technology
Every person on the planet is unique, therefore, any copy of a person, whether it be a statuette, a model or a portrait on paper, will also have a uniqueness. 3D printing of people is a technology that allows you to reduce the centuries-old most complex mystery of sculpture, painting, modeling of human images to a few simple manipulations with modern digital equipment.
And, let it sound a little cynical, but 3D printing of a person opens up incredible opportunities in various areas of our lives. Just imagine, the creation of sculptural copies of a person takes months, and sometimes years. The cost of such a sculpture is often simply beyond the reach of an ordinary person. And the chances of becoming a model of a talented sculptor are negligible.
On the other hand, getting your own exact copy a few centimeters in size is now not at all difficult and not expensive. Moreover, a real boom in the popularity of 3D printing is brewing in the world, which will soon create a significant alternative to photo printing and video chronicles. And it's not just about private ambitions and fun!
Spheres of demand for 3D printing technology of people
3D printing of figurines is already widespread today in:
● advertising;
● decoration of wedding celebrations;
● souvenir industry;
● prototyping of industrial and commercial facilities;
● design;
● medicine.
The noble mission of innovative technology
Moreover, the circle of people professionally interested in the service in order to develop their business is constantly growing. In addition to the persistent interest in technology, its profitability and spectacularity, 3D printing of people also serves noble purposes, for example:
● allows blind people to tactilely get acquainted with the external images of their relatives and friends, communication with which is limited to virtual space;
● allows future parents to admire their baby in the womb, not only with the help of ultrasound pictures. 3D printing of a baby figurine built thanks to innovations will allow you to get to know him visually even before he is born;
3D printing of a baby figurine built thanks to innovations will allow you to get to know him visually even before he is born;
● Printing figurines on a 3D printer helps people with mental trauma and disorders to adapt to a certain social environment;
● in psychology and educational disciplines, three-dimensional models of people are involved in methods of working with children.
Steps for creating 3D copies of a person
High-quality and high-quality 3D printing of people actually requires several preparatory steps.
● In the first, a full-length 3D scan of a person is performed
● In the second, a copy of the 3D model is carefully processed
● In the third, the figure is scaled down and printed.
The technology also includes a number of post-press processing measures. Figures may require surface grinding, painting or tinting, freeing them from auxiliary elements - clamps, additional details, coating with protective varnishes, finishing agents.
Consumables and features of technological processes
Various materials are used for 3D printing of human figures and
even different equipment, technically and technologically different from each other. So, the result can be presented in plastic, gypsum, polymer mixtures. It can be single color or multicolor. Realistic or only in general terms reminiscent of the original.
Human 3D printing technologies are also different. The most popular and frequently used are two:
● layer-by-layer reconstruction of the model on an inkjet 3D printer;
● laser baking, stereolithography on a laser printer.
For the best and most accurate reproduction of the image of a person, it is advisable to use the method of layer-by-layer gluing of a cellulose-starch mixture.
The use of 3D printed human figures in the advertising industry
Of course, the advertising industry has traditionally been at the forefront of bringing innovation to its service. 3D printing of human figures has become the basis of several high-profile advertising campaigns in Spain, Germany, and the UK, during which passers-by on the streets and visitors to shopping centers were asked to quickly create their own miniature on a 3D printer.
3D printing of human figures has become the basis of several high-profile advertising campaigns in Spain, Germany, and the UK, during which passers-by on the streets and visitors to shopping centers were asked to quickly create their own miniature on a 3D printer.
But the scope of advertising use of this technology is much wider:
● Figures of real employees of the company in company uniforms can make up a static installation.
● May be part of a believable animated advertisement.
● Given as a souvenir, they will be a powerful motivation for a common cause and common success.
● 3D printing of human figures in addition to the presentation of 3D models of industrial, construction, social facilities can bring liveliness and dynamics to the presentation of projects.
● Using a 3D printer, you can create not only mini copies of real people, but also transform familiar replicated images of famous sculptures. For example, dress the Venus de Milo in the costume of a stewardess of the advertised airline, and use a mini copy of Rodin's sculpture in an advertisement for ladies' accessories.
The position of 3D copies of a person in souvenir production
A treasure trove of invaluable prospects 3D printer and human printing will bring to souvenir production. With the help of technology, you can make:
● popular interior figurines;
● intricate paperweights;
● gift personalized figurines;
● wedding souvenirs of the bride and groom;
● commemorative figurines of anniversaries and heroes of the occasion.
Variants of representation of the image in a three-dimensional miniature
When creating souvenir miniatures of people, you can most often find three directions for recreating the image:
● realistic or ordinary, the one that can be found in an amateur photo or in life;
● staged, when models are presented in fantasy, stylized images, for example, superheroes or characters from famous fairy tales, movies, literary works, comics;
● wedding, couple real or fictional image.
Bride and groom figurines - this is just the beginning!
The industry of wedding paraphernalia, in addition to commemorative figurines of the newlyweds, can use 3D printing of figurines to create original decorations for invitations, decorating a wedding cake, a festive table, use mini-copies as props for an original wedding photo shoot and video shooting of a romantic love-story.
Online services and their features
It is worth saying a few words about online 3D scanning services. This first step of 3D printing a figurine takes the least time and is the least labor intensive. The presence of many specialized applications on the network that help you scan the image yourself makes the task even easier.
Actually, the results of scanning and allow you to remotely provide services of three-dimensional modeling of a person. The more diligently the scan is made, the more similarity will be between the model and the figurine. By the way, the service of 3D printing of people can be provided not only on the basis of a scan of a real person, but also on the basis of photographs taken from different angles.
Ways to obtain the necessary sources for 3D printing
To recreate the image in a 3D model, try to get pictures from eight angles in a circle, where the angle step will be 45 degrees. This information will be useful to those who are planning to organize a surprise related to the secret production of a mini-copy of a person on a 3D printer. And even if a spontaneous photo session provides less information about the image than a scan, the result will still be recognizable.
Our company is ready to offer all interested people 3D human printing services, as well as business cooperation in this area. Our technical equipment allows us to implement not only our own, but also third-party projects, providing a successful launch pad for your business to take off. We will be glad to assist you in creating a three-dimensional human copy and mutually beneficial cooperation.
3D human figurines • Custom made from photo
3D human figurine • Custom made from photo.
Studio of design and 3D print 3DSOL Creates exclusive
3D figures of people according to the photos sent photos for an unexpected
gift to a person to a person
to order a 3D figure on photo
9000 2 TIN 15040704444080 2 MIRS and 3D printing
3D figures of people from photo
We ran out of ideas and you don't know what to give
to a loved one? Send us a photo, according to them we will make a mini-copy of it, a 3d figurine with a portrait resemblance, which will be an unexpected surprise for a relative, friend.
Telegram Instagram icon-Phot icon-mail WhatsApp
Ask a question
Portfolio
Partettes
9000 3dSolIn several photographs we will make paired statuets of two loving each other, and you will give close emotion to the nearby unpretentious. .
More
Celebrity figurines
3DSOL
Order 3d celebrity figurines for your collection.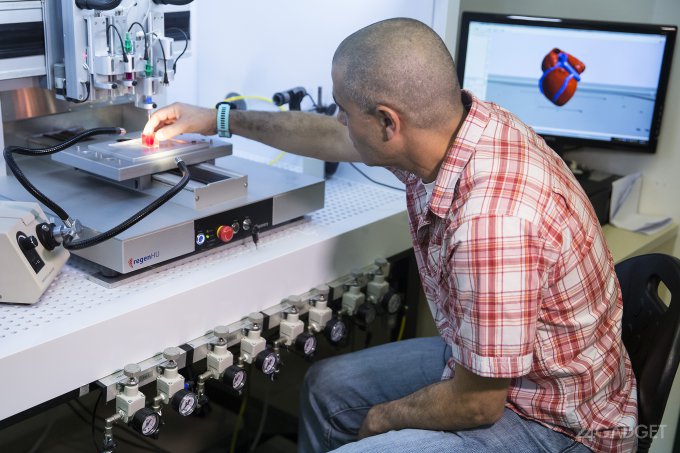 Choose a photo where you like the emotion and pose of your idol.
Choose a photo where you like the emotion and pose of your idol.
More details
Athletes figurines
3DSOL
a gift to someone close to you.
More details
Character figurines
3DSOL
Order a 3D figurine of your favorite character for your collection. Give your loved one a mini-copy of their favorite character.
More
Sculptural compositions
3DSOL
Order exclusive figurines, full-length 3D figures for landscaping parks, recreation areas, decoration of festive events.
More details
Hobby figurines
3DSOL
Give your loved one a 3d figurine — his mini-copy, which will remind him of his favorite pastime.
Read more
Caricature figurines
3DSOL
Caricature 3d figurine is an excellent gift solution for a loved one. This is a gift that will definitely never be forgotten and will delight every time
This is a gift that will definitely never be forgotten and will delight every time
More details
Single figurines Pair figurines Famous people figurines Athletes figurines Character figurines Sculptural compositions Hobby figurines Caricature figurines
Photopolymer figurines
Large selection of photopolymer 3D technologies print 3D growth figures made of foam and plastic have found their application in a variety of areas: outdoor advertising, decorating cafes and restaurants, decorating shopping centers and offices, photo studios and children's entertainment centers, conducting promotions and advertising campaigns, landscape gardening and decor. »
© Sprint3d
Order a 3D growth figure
Materials for 3D printing
Reviews
The best gift is an unexpected surprise. But often the problem arises that the holiday is near, and you have run out of all the ideas and you don’t know what to give.
Design and 3d printing studio 3dSol offers an excellent option: to make exact mini copies - 3d figures of people you love from the photos you sent.
The figurine will remain with a person for life, it will give a good mood, remind you of you and a memorable day.
We will help in its manufacture, surprise you with an acceptable price and good quality. You can order both a figure of one person and a composition of a group of people.
3d figurine from the photo is a good gift for parents on their wedding anniversary, friend, team leader.
It is better to give a single figurine to a loved one for any holiday. It will be done in an original way every year, and fix changes in a person's appearance.
Making a figurine from a photo to order is a team work in which you will also have to participate:
First, you need to decide on the style of the figurine. Will it be a cartoon or a classic 3D figurine? What material will it be from?
How tall will the 3d human figurine be? Then select photos.