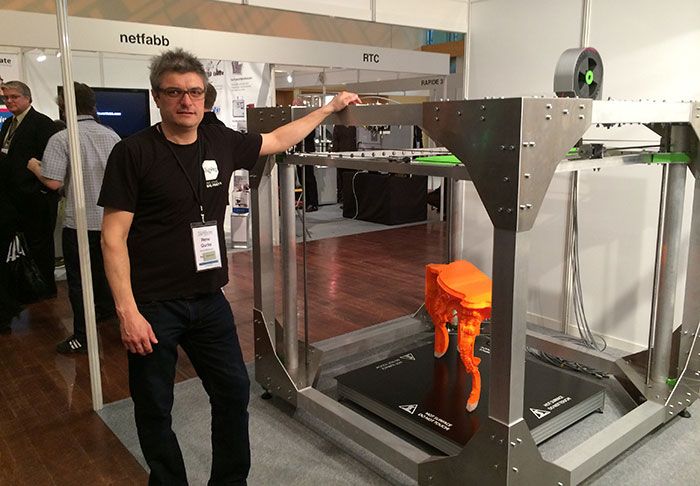
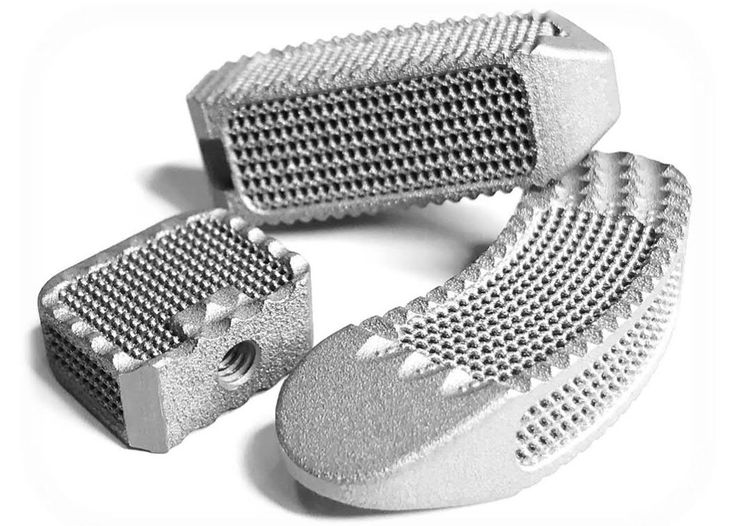
Commercial metal 3d printer
ProJet 6000 HD - 3D Printer
Integrated, Reliable and Proven
The ProJet® 6000 HD from 3D Systems gives you one point of contact to support your applications and daily use of our gold standard technology for additive manufacturing. Customized to our specific 3D print engine, the broad spectrum of Accura® SLA resins generate the consistency and mechanical properties required of each material.
Our SLA printers have high uptime numbers, while 3D Connect™ Service provides a new level of management in 3D production. This secure cloud-based connection to 3D Systems service teams for proactive and preventative support enables better service, improves uptime and delivers production assurance for your system.
Industry-Leading 3D Print Preparation Software
3D Systems' exclusive software for plastic printers to prepare, optimize and print 3D CAD data, 3D Sprint® software delivers all the tools you need to quickly and efficiently go from design to high quality true to CAD printed parts without needing additional third party software.
With 3D Sprint PRO for SLA (optional), facilitate file preparation with native CAD import and advanced mesh repair tools, increase productivity with auto placement, enhance manufacturing efficiency with finely tuned supports, and reduce the need for additional software with embedded Geomagic trusted technology.
Consistently Accurate Parts with the Finest Features
Parts are accurate throughout the entire build platform, print after print, machine after machine. Features are reproducible down to 0.050mm or 0.002 in – depending on geometry, orientation and build mode.
About this printer
-
Applications
-
Benefits
-
Tech Specs
Applications
- Master patterns for vacuum casting
- Sacrificial patterns for metal casting
- Tools, molds and dies
- Functional prototypes and models
- High clarity, transparent products and components
- Complex assemblies
- Wind tunnel models
- Under the hood components
- Rapid production of flow test rigs
- Mass customization (orthodontic, dental)
- Custom assembly jigs and fixtures
Read more about SLA 3D printing technology
Benefits
- Fast, robust and accurate 3D printing
- Finest feature detail on parts of any size
- Smooth surface finish
- Ease of use – intuitive workflow
- Multiple printers in one – quick and easy material changeover
- Single source solution (for printers, materials and software)
- Low material waste
- Broad application flexibility
Tech Specs
- Stereolithography technology (SLA)
- Max build envelope capacity (W x D x H): 250 x 250 x 250 mm (10 x 10 x 10 in)
- Highest precision and accuracy
- Exchangeable Material Delivery Modules (MDMs)
- Utilizing two laser spot sizes per layer – no compromise between speed or feature detail
- True line drawing in X and Y to accurately define curves
- Industry-leading 3D Sprint software for file preparation and production
- Cloud connectivity for predictive and prompt service with 3D Connect
-
3D printing with plastics offers many choices for engineering grade materials, elastomers and composites.
 Do you need flexibility? Strength? Bio-compatibility? More?
Do you need flexibility? Strength? Bio-compatibility? More? -
3D print with plastics to build almost anything - used for prototyping, manufacturing, anatomical models and more. Select a plastic material and 3D technology to deliver the characteristics you need.
Interested in purchasing this printer?
You must have JavaScript enabled to use this form.
First Name
Last Name
Business Email
Company
Country -- Select Country --AfghanistanAlbaniaAlgeriaAmerican SamoaAndorraAngolaAnguillaAntarcticaAntigua & BarbudaArgentinaArmeniaArubaAscension IslandAustraliaAustriaAzerbaijanBahamasBahrainBangladeshBarbadosBelarusBelgiumBelizeBeninBermudaBhutanBoliviaBosnia & HerzegovinaBotswanaBouvet IslandBrazilBritish Indian Ocean TerritoryBritish Virgin IslandsBruneiBulgariaBurkina FasoBurundiCambodiaCameroonCanadaCanary IslandsCape VerdeCaribbean NetherlandsCayman IslandsCentral African RepublicCeuta & MelillaChadChileChinaChristmas IslandClipperton IslandCocos (Keeling) IslandsColombiaComorosCongo - BrazzavilleCongo - KinshasaCook IslandsCosta RicaCroatiaCuraçaoCyprusCzechiaCôte d’IvoireDenmarkDiego GarciaDjiboutiDominicaDominican RepublicEcuadorEgyptEl SalvadorEquatorial GuineaEritreaEstoniaEswatiniEthiopiaFalkland IslandsFaroe IslandsFijiFinlandFranceFrench GuianaFrench PolynesiaFrench Southern TerritoriesGabonGambiaGeorgiaGermanyGhanaGibraltarGreeceGreenlandGrenadaGuadeloupeGuamGuatemalaGuernseyGuineaGuinea-BissauGuyanaHaitiHeard & McDonald IslandsHondurasHong Kong SAR ChinaHungaryIcelandIndiaIndonesiaIraqIrelandIsle of ManIsraelItalyJamaicaJapanJerseyJordanKazakhstanKenyaKiribatiKosovoKuwaitKyrgyzstanLaosLatviaLebanonLesothoLiberiaLibyaLiechtensteinLithuaniaLuxembourgMacao SAR ChinaMadagascarMalawiMalaysiaMaldivesMaliMaltaMarshall IslandsMartiniqueMauritaniaMauritiusMayotteMexicoMicronesiaMoldovaMonacoMongoliaMontenegroMontserratMoroccoMozambiqueMyanmar (Burma)NamibiaNauruNepalNetherlandsNetherlands AntillesNew CaledoniaNew ZealandNicaraguaNigerNigeriaNiueNorfolk IslandNorthern Mariana IslandsNorth MacedoniaNorwayOmanOutlying OceaniaPakistanPalauPalestinian TerritoriesPanamaPapua New GuineaParaguayPeruPhilippinesPitcairn IslandsPolandPortugalPuerto RicoQatarRomaniaRussiaRwandaRéunionSamoaSan MarinoSaudi ArabiaSenegalSerbiaSeychellesSierra LeoneSingaporeSint MaartenSlovakiaSloveniaSolomon IslandsSomaliaSouth AfricaSouth Georgia & South Sandwich IslandsSouth KoreaSouth SudanSpainSri LankaRepublic of Sudan (North Sudan)St. BarthélemySt. HelenaSt. Kitts & NevisSt. LuciaSt. MartinSt. Pierre & MiquelonSt. Vincent & GrenadinesSurinameSvalbard & Jan MayenSwedenSwitzerlandSão Tomé & PríncipeTaiwanTajikistanTanzaniaThailandTimor-LesteTogoTokelauTongaTrinidad & TobagoTristan da CunhaTunisiaTurkeyTurkmenistanTurks & Caicos IslandsTuvaluU.S. Outlying IslandsU.S. Virgin IslandsUgandaUkraineUnited Arab EmiratesUnited KingdomUnited StatesUruguayUzbekistanVanuatuVatican CityVenezuelaVietnamWallis & FutunaWestern SaharaYemenZambiaZimbabweÅland Islands
BarthélemySt. HelenaSt. Kitts & NevisSt. LuciaSt. MartinSt. Pierre & MiquelonSt. Vincent & GrenadinesSurinameSvalbard & Jan MayenSwedenSwitzerlandSão Tomé & PríncipeTaiwanTajikistanTanzaniaThailandTimor-LesteTogoTokelauTongaTrinidad & TobagoTristan da CunhaTunisiaTurkeyTurkmenistanTurks & Caicos IslandsTuvaluU.S. Outlying IslandsU.S. Virgin IslandsUgandaUkraineUnited Arab EmiratesUnited KingdomUnited StatesUruguayUzbekistanVanuatuVatican CityVenezuelaVietnamWallis & FutunaWestern SaharaYemenZambiaZimbabweÅland Islands
State -- Select State --Buenos AiresCatamarcaChacoChubutCiudad Autónoma de Buenos AiresCórdobaCorrientesEntre RíosFormosaJujuyLa PampaLa RiojaMendozaMisionesNeuquénRío NegroSaltaSan JuanSan LuisSanta CruzSanta FeSantiago del EsteroTierra del FuegoTucumánAustralian Capital TerritoryNew South WalesNorthern TerritoryQueenslandSouth AustraliaTasmaniaVictoriaWestern AustraliaBurgenlandKärntenNiederösterreichOberösterreichSalzburgSteiermarkTirolVorarlbergWienAcreAlagoasAmapáAmazonasBahiaCearáDistrito FederalEspírito SantoGoiásMaranhãoMato GrossoMato Grosso do SulMinas GeraisParáParaíbaParanáPernambucoPiauíRio de JaneiroRio Grande do NorteRio Grande do SulRondôniaRoraimaSanta CatarinaSão PauloSergipeTocantinsAlbertaBritish ColumbiaManitobaNew BrunswickNewfoundland and LabradorNorthwest TerritoriesNova ScotiaNunavutOntarioPrince Edward IslandQuebecSaskatchewanYukon TerritoriesAisén del General Carlos Ibañez del CampoAntofagastaAraucaníaArica y ParinacotaAtacamaBío-BíoCoquimboLibertador General Bernardo O'HigginsLos LagosLos RíosMagallanesMauleRegión Metropolitana de SantiagoTarapacáValparaísoAnhuiBeijingChinese TaipeiChongqingFujianGansuGuangdongGuangxiGuizhouHainanHebeiHeilongjiangHenanHong KongHubeiHunanJiangsuJiangxiJilinLiaoningMacaoNei MongolNingxiaQinghaiShaanxiShandongShanghaiShanxiSichuanTianjinXinjiangXizangYunnanZhejiangÎle-de-FranceOccitanieAuvergne-Rhône-AlpesBourgogne-Franche-ComtéBretagneCentre-Val de LoireCorseGrand EstHauts-de-FranceJuraNormandieNouvelle-AquitainePays de la LoireProvence-Alpes-Côte d'AzurBaden-WürttembergBayernBerlinBrandenburgBremenHamburgHessenMecklenburg-VorpommernNiedersachsenNordrhein-WestfalenRheinland-PfalzSaarlandSachsenSachsen-AnhaltSchleswig-HolsteinThüringenAndaman and Nicobar IslandsAndhra PradeshArunachal PradeshAssamBiharChandigarhChhattisgarhDadra and Nagar HaveliDaman and DiuDelhiGoaGujaratHaryanaHimachal PradeshJammu and KashmirJharkhandKarnatakaKeralaLakshadweepMadhya PradeshMaharashtraManipurMeghalayaMizoramNagalandOdishaPuducherryPunjabRajasthanSikkimTamil NaduTripuraUttar PradeshUttarakhandWest BengalCarlowCavanClareCorkDonegalDublinGalwayKerryKildareKilkennyLaoisLeitrimLimerickLongfordLouthMayoMeathMonaghanOffalyRoscommonSligoTipperaryWaterfordWestmeathWexfordWicklowAgrigentoAlessandriaAnconaAostaArezzoAscoli PicenoAstiAvellinoBariBarletta-Andria-TraniBellunoBeneventoBergamoBiellaBolognaBolzanoBresciaBrindisiCagliariCaltanissettaCampobassoCarbonia-IglesiasCasertaCataniaCatanzaroChietiComoCosenzaCremonaCrotoneCuneoEnnaFermoFerraraFirenzeFoggiaForlì-CesenaFrosinoneGenovaGoriziaGrossetoImperiaIserniaLa SpeziaL'AquilaLatinaLecceLeccoLivornoLodiLuccaMacerataMantovaMassa - CarraraMateraMedio CampidanoMessinaMilanoModenaMonza e BrianzaNapoliNovaraNuoroOgliastraOlbia-TempioOristanoPadovaPalermoParmaPaviaPerugiaPesaro e UrbinoPescaraPiacenzaPisaPistoiaPordenonePotenzaPratoRagusaRavennaReggio CalabriaReggio EmiliaRietiRiminiRomaRovigoSalernoSassariSavonaSienaSondrioSiracusaTarantoTeramoTerniTrapaniTrentoTrevisoTriesteTorinoUdineVareseVeneziaVerbano-Cusio-OssolaVercelliVeronaVibo ValentiaVicenzaViterboAichiAkitaAomoriChibaEhimeFukuiFukuokaFukushimaGifuGunmaHiroshimaHokkaidoHyogoIbarakiIshikawaIwateKagawaKagoshimaKanagawaKochiKumamotoKyotoMieMiyagiMiyazakiNaganoNagasakiNaraNiigataOitaOkayamaOkinawaOsakaSagaSaitamaShigaShimaneShizuokaTochigiTokushimaTokyoTottoriToyamaWakayamaYamagataYamaguchiYamanashiBusanDaeguDaejeonGangwonGwangjuGyeonggiIncheonJejuNorth ChungcheongNorth GyeongsangNorth JeollaSeoulSouth ChungcheongSouth GyeongsangSouth JeollaUlsanJohorKedahKelantanMelakaNegeri SembilanPahangPerakPerlisPulau PinangSabahSarawakSelangorTerengganuWilayah Persekutuan Kuala LumpurWilayah Persekutuan LabuanWilayah Persekutuan PutrajayaAguascalientesBaja CaliforniaBaja California SurCampecheChiapasChihuahuaCoahuilaColimaDurangoFederal DistrictGuanajuatoGuerreroHidalgoJaliscoMexico StateMichoacánMorelosNayaritNuevo LeónOaxacaPueblaQuerétaroQuintana RooSan Luis PotosíSinaloaSonoraTabascoTamaulipasTlaxcalaVeracruzYucatánZacatecasŚląskieŁódzkieŚwiętokrzyskieDolnośląskieKujawsko-pomorskieLubelskieLubuskieMałopolskieMazowieckieOpolskiePodkarpackiePodlaskiePomorskieWarmińsko-mazurskieWielkopolskieZachodniopomorskieAdygeya, RespublikaAltay, RespublikaAltayskiy krayAmurskaya oblast'Arkhangel'skaya oblast'Astrakhanskaya oblast'Bashkortostan, RespublikaBelgorodskaya oblast'Bryanskaya oblast'Buryatiya, RespublikaChechenskaya RespublikaChelyabinskaya oblast'Chukotskiy avtonomnyy okrugChuvashskaya RespublikaDagestan, RespublikaIngushetiya, RespublikaIrkutskaya oblast'Ivanovskaya oblast'Kabardino-Balkarskaya RespublikaKaliningradskaya oblast'Kalmykiya, RespublikaKaluzhskaya oblast'Kamchatskiy krayKarachayevo-Cherkesskaya RespublikaKareliya, RespublikaKemerovskaya oblast'Khabarovskiy krayKhakasiya, RespublikaKhanty-Mansiyskiy avtonomnyy okrug-YugraKirovskaya oblast'Komi, RespublikaKostromskaya oblast'Krasnodarskiy krayKrasnoyarskiy krayKurganskaya oblast'Kurskaya oblast'Leningradskaya oblast'Lipetskaya oblast'Magadanskaya oblast'Mariy El, RespublikaMordoviya, RespublikaMoskovskaya oblast'MoskvaMurmanskaya oblast'Nenetskiy avtonomnyy okrugNizhegorodskaya oblast'Novgorodskaya oblast'Novosibirskaya oblast'Omskaya oblast'Orenburgskaya oblast'Orlovskaya oblast'Penzenskaya oblast'Permskiy krayPrimorskiy krayPskovskaya oblast'Rostovskaya oblast'Ryazanskaya oblast'Sakha, RespublikaSakhalinskaya oblast'Samarskaya oblast'Sankt-PeterburgSaratovskaya oblast'Severnaya Osetiya-Alaniya, RespublikaSmolenskaya oblast'Stavropol'skiy kraySverdlovskaya oblast'Tambovskaya oblast'Tatarstan, RespublikaTomskaya oblast'Tul'skaya oblast'Tverskaya oblast'Tyumenskaya oblast'Tyva, RespublikaUdmurtskaya RespublikaUl'yanovskaya oblast'Vladimirskaya oblast'Volgogradskaya oblast'Vologodskaya oblast'Voronezhskaya oblast'Yamalo-Nenetskiy avtonomnyy okrugYaroslavskaya oblast'Yevreyskaya avtonomnaya oblast'Zabaykal'skiy krayCentral SingaporeNorth EastNorth WestSouth EastSouth WestA CoruñaÁlava / ArabaAlbaceteAlicante / AlacantAlmeríaAsturiasÁvilaBadajozBalearsBarcelonaBurgosCáceresCádizCantabriaCastellón / CastellóCiudad RealCórdobaCuencaGironaGranadaGuadalajaraGuipúzcoa / GipuzkoaHuelvaHuescaJaénLa RiojaLas PalmasLeónLleidaLugoMadridMálagaMurciaNavarra / NafarroaOurensePalenciaPontevedraSalamancaSanta Cruz de TenerifeSegoviaSevillaSoriaTarragonaTeruelToledoValencia / ValènciaValladolidVizcaya / BizkaiaZamoraZaragozaAargauAppenzell AusserrhodenAppenzell InnerrhodenBasel-LandschaftBasel-StadtBernFribourgGenèveGlarusGraubündenJuraLuzernNeuchâtelNidwaldenObwaldenSankt GallenSchaffhausenSchwyzSolothurnThurgauTicinoUriValaisVaudZugZürichChanghua CountyChiayi CityChiayi CountyHsinchu CityHsinchu CountyHualien CountyKaohsiung CityKaohsiung CountyKeelung CityMiaoli CountyNantou CountyPenghu CountyPingtung CountyTaichung CityTaichung CountyTainan CityTainan CountyTaipei CityTaipei CountyTaitung CountyTaoyuan CountyYilan CountyYunlin CountyŞırnakŞanlıurfaİstanbulİzmirAğrıAd?yamanAdanaAfyonkarahisarAksarayAmasyaAnkaraAntalyaArdahanArtvinAydınBalıkesirBartınBatmanBayburtBilecikBingölBitlisBoluBurdurBursaÇanakkaleÇankırıÇorumDenizliDiyarbakırDüzceEdirneElazığErzincanErzurumEskişehirGaziantepGiresunGümüşhaneHakkâriHatayIğdırIspartaKırşehirKırıkkaleKırklareliKahramanmaraşKarabükKaramanKarsKastamonuKayseriKilisKocaeliKonyaKütahyaMalatyaManisaMardinMersinMuşMuğlaNevşehirNiğdeOrduOsmaniyeRizeSakaryaSamsunSiirtSinopSivasTekirdağTokatTrabzonTunceliUşakVanYalovaYozgatZonguldakCrimeaCherkasyChernihivChernivtsiDnipropetrovskDonetskIvano-FrankivskKharkivKhersonKhmelnytskyiKirovohradKyivLuhanskLvivMykolaivOdesaPoltavaRivneSumyTernopilVinnytsiaVolynZakarpattiaZaporzhzhiaZhytomyrAberdeen CityAberdeenshireAngusAntrimArgyll and ButeArmaghAvonBanffshireBedfordshireBerkshireBlaenau GwentBordersBridgendBristolBuckinghamshireCaerphillyCambridgeshireCardiffCarmarthenshireCeredigionChannel IslandsCheshireClackmannanshireClevelandConwyCornwallCumbriaDenbighshireDerbyshireDevonDorsetDownDumfries and GallowayDurhamEast AyrshireEast DunbartonshireEast LothianEast RenfrewshireEast Riding of YorkshireEast SussexEdinburghEssexFalkirkFermanaghFifeFlintshireGlasgowGloucestershireGreater ManchesterGwyneddHampshireHerefordshireHertfordshireHighlandHumbersideInverclydeIsle of AngleseyIsle of ManIsle of WightIsles of ScillyKentLancashireLeicestershireLincolnshireLondonLondonderryMerseysideMerthyr TydfilMiddlesexMidlothianMonmouthshireMorayNeath Port TalbotNewportNorfolkNorth AyrshireNorth East LincolnshireNorth LanarkshireNorth YorkshireNorthamptonshireNorthumberlandNottinghamshireOrkneyOuter HebridesOxfordshirePembrokeshirePerthshire and KinrossPowysRenfrewshireRhondda, Cynon, TaffRoxburghshireRutlandShetlandShropshireSomersetSouth AyrshireSouth LanarkshireSouth YorkshireStaffordshireStirlingSuffolkSurreySwanseaTorfaenTyne and WearTyroneVale of GlamorganWarwickshireWest DunbartonshireWest LothianWest MidlandsWest SussexWest YorkshireWiltshireWorcestershireWrexhamAlabamaAlaskaAmerican SamoaArizonaArkansasCaliforniaColoradoConnecticutDelawareDistrict of ColumbiaFederated MicronesiaFloridaGeorgiaGuamHawaiiIdahoIllinoisIndianaIowaKansasKentuckyLouisianaMaineMarshall IslandsMarylandMassachusettsMichiganMinnesotaMississippiMissouriMontanaNebraskaNevadaNew HampshireNew JerseyNew MexicoNew YorkNorth CarolinaNorth DakotaNorthern Mariana IslandsOhioOklahomaOregonPalauPennsylvaniaPuerto RicoRhode IslandSouth CarolinaSouth DakotaTennesseeTexasUnited States Minor Outlying IslandsUS Virgin IslandsUtahVermontVirginiaWashingtonWest VirginiaWisconsinWyoming
Industry - None -Academic & ResearchAerospace & DefenseDentalHealthcareManufacturing & PrototypingTransportation & Motorsports
Sub-Industry - Select -Medical Device ManufacturersMedical Contract ManufacturersHospital or Medical ClinicMedical SchoolsOther HealthcareDental ClinicsDental Equipment ManufacturersDental LabsDental SchoolsOther DentalMilitary AviationCommercial AviationDefenseSpace & UAVOther Aerospace & DefenseAutomotiveTruck, Bus & RailMotorsportsAftermarket & ServiceRecreation & MarineOther Transportation3D Printing Service BureausFoundriesElectronics & ConnectorsSemiconductorTurbomachineryJewelryConsumer & Durable GoodsOther Manufacturing
Address
Postal Code
Job Level -- Select Job Level --C-LevelPresident or VPDirectorManagerProfessional StaffConsultant or ContractorIntern or StudentHobbyist
Job Function -- Select Job Function --Engineering - SoftwareEngineering - HardwareManufacturingFinanceITLegalMarketingPurchasingSalesService Technician - HardwareService Technician - SoftwareOther
Level of Interest -- Select Your Level of Interest --Beginning ResearchEvaluating Solutions and CompetitorsInterested in Buying in 1-3 MonthsInterested in Buying in 3-6 MonthsInterested in Buying in 6-12 MonthsI would like to speak with a Solutions SpecialistI have a Support Issue or Question
Area of Interest - Select -Printers• Professional Printer (ColorJet, MultiJet)• Production Printer (SLA, SLS, Metal/DMP)• Figure 4• Titan Additive• OtherSoftwareHaptics• HapticsHealthcare• Virtual Surgical Planning• Anatomical Modeling• Kumovis Additive
3D Printer - Select -MJP• ProJet 2500• ProJet 2500 Plus• ProJet 2500W• ProJet 2500 IC• ProJet 3600• ProJet 5600CJP• ProJet 260 Plus• Projet 360• ProJet 460 Plus• ProJet 660Pro• ProJet 860ProDMP• DMP Flex 100• ProX 200• DMP Flex 200• DMP Flex 350• DMP Factory 350• DMP Factory 500• ProX 100• ProX 300SLS• SLS 6100• SLS 380• sPro 140• sPro 230SLA• SLA 750• ProJet 6000• ProJet 7000• ProX 800• ProX 950Figure 4• Figure 4 Standalone• Figure 4 Modular• Figure 4 Production• Figure 4 JewelryNextDent• NextDent 5100Kumovis• Kumovis R1Atlas• Atlas H• Atlas HSMaterialsBioprinter
Software product - Select -3D Connect Manage3D Connect Service3D Modeling Services3D Sprint3D Sprint Pro for SLA3DXpertGeomagic Control XGeomagic Design XGeomagic for SOLIDWORKSGeomagic FreeformGeomagic SculptGeomagic TouchGeomagic Touch XGeomagic WrapOpenHapticsPhantom Premium
Area of Interest - Select -Medical Device Design and ManufacturingMedical SimulatorsAnatomical ModelsD2P SoftwareDental Manufacturing and Design Services
I consent to receive 3D Systems CommunicationsWould you like to receive special offers, product updates, and event news from 3D Systems? By clicking "Yes", you agree to receive follow-up communications from 3D Systems or our partners. You can also choose to opt out of communications at any time. Please click here to view our Privacy Policy or click here to manage your Preferences.
You can also choose to opt out of communications at any time. Please click here to view our Privacy Policy or click here to manage your Preferences.
Area of Interest - None -Appearance ModelsCast UrethaneCJPCNCCNC MetalCNC PlasticDie CastingDigitalization/ScanningDMPEngineering ProjectsFDMInjection MoldingInjection ToolingInvestment CastingInvestment Casting PatternJigs and FixturesMetal CastingMJPMJP-ElastomersQuick Cast PatternsRIMSheet MetalSLASLSToolingVacuum castingVacuum forming
Custom Area of Interest
PPP
PST
Software
Healthcare
ODM
Area of interest Required
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA. The Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
You Might Also Be Interested In
ProJet 7000 HD
Mid-range integrated solution for SLA quality and accuracy
ProX 800
SLA quality at high throughput to address the broadest range of applications
ProX 950
All the benefits of SLA 3D printing in extra-large format
Best metal 3D printers in 2022: comprehensive overview
What is the best metal 3D printer in 2022?
Over the past few years, there has been a surge in both supply and demand for metal 3D printers.
Manufacturers are launching metal additive manufacturing machines that are faster, easier to use, and more powerful with an increasing number of compatible metals.
Many businesses are adopting these 3D metal printing technologies to produce cost-effective metal parts and prototypes, benefiting as well from increased freedom of design linked to additive manufacturing. They are suitable for a variety of industries such as aerospace, automotive, health, engineering, and more.
Although metal 3D printer prices have been slowly and slightly decreasing, these machines are still relatively expensive acquisitions, mostly ranging from $80K to almost $1M.
With our metal 3D printer selection, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of what’s available from well-established and distributed brands, at various price points, and with different metal 3D printing technologies.
The best metal 3D printers in 2022
| Brand | Product | Build size | Country | Price Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Markforged | Metal X (Gen 2) | 300 × 220 × 180 mm11.81 × 8.66 × 7.09 in | United States | $ 99,500125 000 €88,260 £14,831,072 ¥ | Quote |
| Xact Metal | XM200C | 127 × 127 × 127 mm5 × 5 × 5 in | United States | $ 110,000100 000 €97,574 £16,396,160 ¥ | Quote |
| Pollen AM | Pam Series MC | ⌀ 300 x 300 mm | – | $ 140,000135 000 €124,186 £20,867,840 ¥ | Quote |
| TRUMPF | TruPrint 1000 | 100 × 100 × 100 mm3.94 × 3.94 × 3.94 in | – | $ 170,000170 000 €150,797 £25,339,520 ¥ | Quote |
| 3D Systems This brand is a certified partner from our network. | DMP Flex 100 | 100 × 100 × 80 mm3.94 × 3.94 × 3. 15 in 15 in | – | $ 245,000245 000 €217,325 £36,518,720 ¥ | Quote |
| EOS | EOS M 100 | 100 × 100 × 95 mm3.94 × 3.94 × 3.74 in | Germany | $ 350,000350 000 €310,464 £52,169,600 ¥ | Quote |
| XJet | Carmel 700M | 501 × 140 × 200 mm19.72 × 5.51 × 7.87 in | – | $ 599,000599 000 €531,337 £89,284,544 ¥ | Quote |
| Desktop Metal | Production System P-1 | 200 × 100 × 40 mm7.87 × 3.94 × 1.57 in | United States | upon request | Quote |
| Desktop Metal | Studio 2 | 300 × 200 × 200 mm11.81 × 7.87 × 7.87 in | United States | upon request | Quote |
| Digital Metal | DM P2500 | 203 × 180 × 69 mm7.99 × 7.09 × 2.72 in | – | upon request | Quote |
| Formalloy | L-Series | 1000 × 1000 × 1000 mm39.37 × 39.37 × 39.37 in | United States | upon request | Quote |
| GE Additive | Arcam EBM Spectra L | ⌀ 350 x 430 mm | United States | upon request | Quote |
| GE Additive | M2 Series 5 | 250 × 250 × 350 mm9. 84 × 9.84 × 13.78 in 84 × 9.84 × 13.78 in | – | upon request | Quote |
| Renishaw | RenAM 500E | 245 × 245 × 335 mm9.65 × 9.65 × 13.19 in | – | upon request | Quote |
| SLM Solutions | SLM 125 | 125 × 125 × 75 mm4.92 × 4.92 × 2.95 in | Germany | upon request | Quote |
| SPEE3D | LIGHTSPEE3D | 300 × 300 × 300 mm11.81 × 11.81 × 11.81 in | – | upon request | Quote |
| TRIDITIVE | AMCELL | ⌀ 300 x 350 mm | Spain | upon request | Quote |
| Velo3D | Sapphire | ⌀ 315 x 1000 mm | – | upon request | Quote |
Expand to see more specs
Technology: The technologies listed above are main categories of metal 3D printing technologies. Most manufacturers have their own branded technologies, which fall into the main categories that are listed in the table.
The products in the table are ranked by price (low to high).
| Brand | Product | Technology | Build size | Country | Price Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …). | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Markforged | Metal X (Gen 2) | Extrusion | 300 × 220 × 180 mm11.81 × 8.66 × 7.09 in | United States | $ 99,500125 000 €88,260 £14,831,072 ¥ | Get a quote |
| Xact Metal | XM200C | SLM/DMLS | 127 × 127 × 127 mm5 × 5 × 5 in | United States | $ 110,000100 000 €97,574 £16,396,160 ¥ | Get a quote |
| Pollen AM | Pam Series MC | Extrusion | ⌀ 300 x 300 mm | – | $ 140,000135 000 €124,186 £20,867,840 ¥ | Get a quote |
| TRUMPF | TruPrint 1000 | SLM/DMLS | 100 × 100 × 100 mm3. 94 × 3.94 × 3.94 in 94 × 3.94 × 3.94 in | – | $ 170,000170 000 €150,797 £25,339,520 ¥ | Get a quote |
| 3D Systems This brand is a certified partner from our network. | DMP Flex 100 | SLM/DMLS | 100 × 100 × 80 mm3.94 × 3.94 × 3.15 in | – | $ 245,000245 000 €217,325 £36,518,720 ¥ | Get a quote |
| EOS | EOS M 100 | SLM/DMLS | 100 × 100 × 95 mm3.94 × 3.94 × 3.74 in | Germany | $ 350,000350 000 €310,464 £52,169,600 ¥ | Get a quote |
| XJet | Carmel 700M | Material Jetting | 501 × 140 × 200 mm19.72 × 5.51 × 7.87 in | – | $ 599,000599 000 €531,337 £89,284,544 ¥ | Get a quote |
| Desktop Metal | Production System P-1 | Binder Jetting | 200 × 100 × 40 mm7.87 × 3.94 × 1.57 in | United States | upon request | Get a quote |
| Desktop Metal | Studio 2 | Extrusion | 300 × 200 × 200 mm11. 81 × 7.87 × 7.87 in 81 × 7.87 × 7.87 in | United States | upon request | Get a quote |
| Digital Metal | DM P2500 | Material Jetting | 203 × 180 × 69 mm7.99 × 7.09 × 2.72 in | – | upon request | Get a quote |
| Formalloy | L-Series | Directed Energy Deposition | 1000 × 1000 × 1000 mm39.37 × 39.37 × 39.37 in | United States | upon request | Get a quote |
| GE Additive | Arcam EBM Spectra L | EBM | ⌀ 350 x 430 mm | United States | upon request | Get a quote |
| GE Additive | M2 Series 5 | SLM/DMLS | 250 × 250 × 350 mm9.84 × 9.84 × 13.78 in | – | upon request | Get a quote |
| Renishaw | RenAM 500E | SLM/DMLS | 245 × 245 × 335 mm9.65 × 9.65 × 13.19 in | – | upon request | Get a quote |
| SLM Solutions | SLM 125 | SLM/DMLS | 125 × 125 × 75 mm4. 92 × 4.92 × 2.95 in 92 × 4.92 × 2.95 in | Germany | upon request | Get a quote |
| SPEE3D | LIGHTSPEE3D | Material Jetting | 300 × 300 × 300 mm11.81 × 11.81 × 11.81 in | – | upon request | Get a quote |
| TRIDITIVE | AMCELL | Extrusion | ⌀ 300 x 350 mm | Spain | upon request | Get a quote |
| Velo3D | Sapphire | SLM/DMLS | ⌀ 315 x 1000 mm | – | upon request | Get a quote |
Main types of metal 3D printing technologies
The four main types of 3D metal printing technologies are:
- Metal Powder Bed Fusion 3D printing (SLS, SLM, DMP)
- Directed Energy Deposition (DED)
- Metal filament extrusion (FFF, FDM)
- Material Jetting and Binder Jetting
There are also some resin-based metal 3D printers, and metal sheet lamination 3D printers, but they are harder to come by.
It is not uncommon to see different acronyms and names for similar technologies. Each brand markets their own, proprietary methods. Some metal 3D printer companies even use a mix of different technologies.
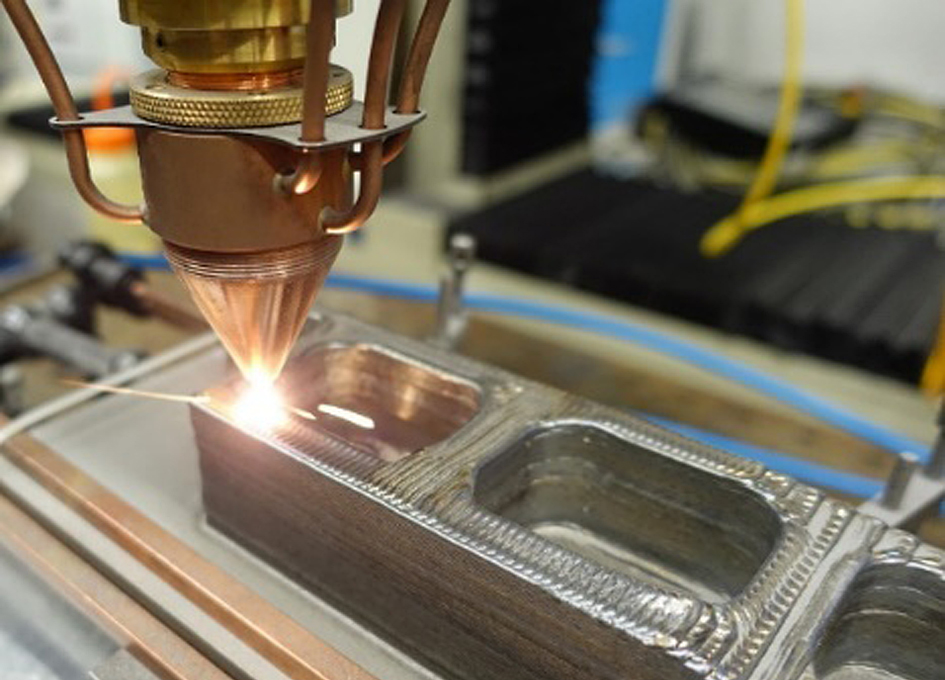
A breakdown of the metal 3D printer market by technology types. Source: Aniwaa database (2019)Here we provide a deeper look into each 3D metal printer from our list. They are grouped together according to their main 3D printing technology type (powder bed fusion, material/binder jetting, extrusion, and DED).
Extrusion-based metal 3D printer selection (FFF, FDM)
Extrusion consists of heating the material (filament) and pushing it through a nozzle. In the metal 3D printing case, the filament is generally made up of metal particles mixed into a binding agent.
After the part is 3D printed, the result is a raw object or part; it must go through several post-processing steps– such as debinding and sintering– to attain its final form.
Most extrusion-based metal 3D printing processes include these steps. The above illustration is sourced from Desktop Metal (Bound Metal Deposition™ process).
The above illustration is sourced from Desktop Metal (Bound Metal Deposition™ process).Desktop Metal’s Studio is an office-friendly, end-to-end metal 3D printing system. Aside from the printer, the Studio line also includes a debinding machine and a furnace for sintering. Indeed, parts 3D printed with this Desktop Metal 3D printer are “green”.
The Studio printer, with its proprietary Bound Metal Deposition technology, uses filament that is filled with small, metal rods. During debinding, the binding material (wax and polymer binders) is dissolved thanks to a proprietary liquid substance. The part is left porous, and must go in the furnace for its particles to fuse and densify the part.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
MarkForged is specialized in continuous fiber 3D printing, but also offers metal 3D printing with their Metal X system, featuring Atomic Diffusion Additive Manufacturing (ADAM) technology.
This MarkForged 3D printer extrudes metal-filled plastic filament to form the part, which must then be washed with a special debinding fluid (Wash-1 Station) and then sintered in a furnace (Sinter-1 or Sinter-2 MarkForged machines).
Available metal 3D printer filament includes various Steels (h23, A2, D2 tool steels, 316L stainless steel) as well as Inconel, Copper, and Titanium.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Canada-based Rapidia offers an interesting and unique way to 3D print metal. They use a water-based metal paste, which eliminates the need for chemical debinding. The water evaporates during the 3D printing process, so the part only needs to go through the furnace in order to completely solidify and attain its final form.
Confirmed, available paste types include several Stainless Steels, Inconel, and a few ceramics. Copper, Tungsten Chrome Carbide, Titanium, and various other metals are in development.
The ExOne Metal Designlab, designed in collaboration with Rapidia, works on the same basis.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Pollen AM is a French manufacturer that has been producing pellet 3D printers since 2013. Their Pam Series MC is a delta-style 3D printer (cylindrical build volume) that can print metals, ceramics, and thermoplastics.
It extrudes injection-molding-grade pellets instead of metal 3D printer filament, driving material costs down significantly. Pollen AM names their technology “Pellet Additive Manufacturing”.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
This machine was built with one goal: enable mass production 3D printing of metal parts 24/7. The AMCELL is fully automated, with auto feedstock control, environment control (temperatures, humidity, air filtering), and an ejection system fitted with a conveyor belt.
Rather than providing one, big build volume, the TRIDITIVE AMCELL boasts eight delta-style ø 220 x 330 mm build areas. Its eight “robots” deposit metal-infused filament to create 3D metal parts. TRIDITIVE states that resulting parts are similar to ones produced with traditional MIM (Metal Injection Molding) methods.
TRIDITIVE’s technology is called Automated Multimaterial Deposition®.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Metal powder bed fusion 3D printer selection (SLS, SLM, DMP, and more)
At the moment, the most commonly used metal additive manufacturing technology is powder bed fusion 3D printing. Simply put, the 3D printer creates objects out of a bed of powdered metal by using a powerful laser.
Simply put, the 3D printer creates objects out of a bed of powdered metal by using a powerful laser.
3D Systems, a historical actor on many 3D printing fronts, presents the DMP FLEX 100 as a fast, precise, and affordable metal 3D printer. It offers impressive part repeatability and surface finishes, of around 20 μm and 5 Ra μm respectively. DMP stands for Direct Metal Printing.
The printer comes with 3D Systems’ software 3DXpert All-in-One Software Solution for Metal Additive manufacturing. Their LaserForm metal 3D powders are certified.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
This compact metal 3D printer is destined for the production of small parts in small quantities. Its material portfolio is especially interesting for medical use cases, namely dental crowns and bridges. EOS certified metal powders include Cobalt-Chrome, Stainless Steel, and Titanium.
The EOS M100’s laser spot is precise enough to provide a great level of detail, backed by 200 W of powder.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Originally a Swedish company, Arcam was acquired by GE Additive a few years ago. The Arcam EBM Spectra L is up to 20% faster than its predecessors and is able to reduce part costs by around 10%.
This metal 3D printer is dedicated to Titanium 3D printing, but Copper is in the pipeline as well. Its laser beam power is equal to 4.5 kW, partly explaining the printer’s high melting capacity and productivity. Common applications for this printer include orthopedic implants and parts for the aerospace industry.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Concept Laser is the company behind GE Additive’s M2 Series 5. It offers an easy, optimized workflow, with a separate processing chamber and handling area that is integrated into the system. This closed-loop material system ensures a safe environment that is free of powder for the operator.
The M2 metal additive manufacturing solution is compatible with a range of metals, from Stainless Steels to Aluminum, Nickel, Titanium, and Cobalt-Chrome.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The RenAM 500E is Renishaw’s entry-level metal additive manufacturing solution. It offers a relatively large build volume and powder can be handled via a dedicated glove box to avoid powder from getting free.
This system is also equipped with an oxygen sensor and a proprietary emission-filtering system branded SafeChange™.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Officially established in 2006, SLM Solutions has been a historical player in the powder bed fusion industry for many years. The SLM 125 boasts an open software architecture that allows users to tweak the system’s parameters according to specific use cases, materials, and general needs.
Options such as laser monitoring and melt pool monitoring are available for businesses that require full transparency and control over their production series.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The TruPrint 1000 is TRUMPF’s most compact metal 3D printing system, with a 100mm-tall cylindrical build volume. It is suitable for the production of small parts and prototypes, and even small production series when equipped with the multilaser option that increases the printer’s speed.
It is suitable for the production of small parts and prototypes, and even small production series when equipped with the multilaser option that increases the printer’s speed.
This metal 3D printer can be operated remotely via a tablet application, which also gives access to its onboard camera stream.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Velo3D Sapphire is a high-volume metal 3D printer from the US designed for production series. This metal 3D printer features Velo3D’s Intelligent Fusion technology to allow for complex geometries and 0° overhangs.
The system is also equipped with a range of metrology sensors that measure each and every layer that is 3D printed.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The XM200C is Xact Metal’s entry-level metal 3D printing solution. It is suitable for both research purposes and small production series. The XM200C benefits from a proprietary Xact Core gantry system for precise movements with a fusing speed of up to 500 mm/s.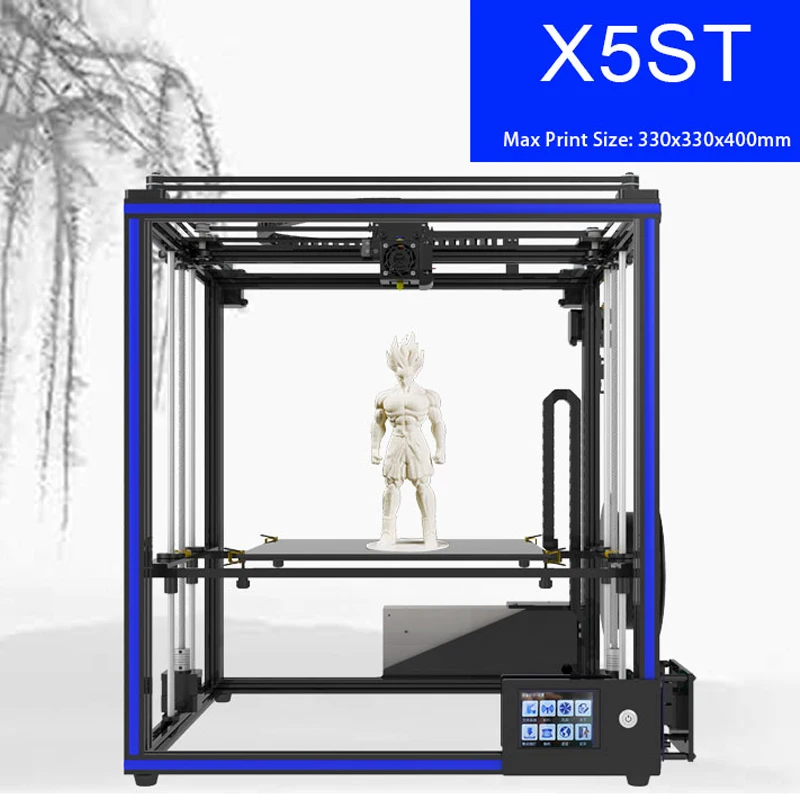
Xact Metal offers their own materials, branded Xact Powder, including various Stainless Steels, Super Alloys, Tooling Steels, Aluminum, Titanium, Bronze, and Copper. Advanced users are able to use their own metal powders if needed.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Metal material jetting and binder jetting 3D printers
Material jetting 3D printers are equipped with various inkjet printheads (somewhat similar to 2D printing) that jet material onto a surface. The material then hardens, and another layer of “metal ink” is jetted on top.
Binder jetting is a similar process, but it is a binding agent that is jetted atop a layer of powder.
The Production System by Desktop Metal was designed for mass production. It is advertised by Desktop Metal as being a fast, cost-effective metal additive manufacturing solution, with a cost per part up to 20 times lower than with other metal 3D printing systems.
This Desktop Metal 3D printer is equipped with over 16,000 nozzles that are mounted onto a “print bar” that recoats the build plate with powder at the same time, hence explaining the technology’s name: Single Pass Jetting™.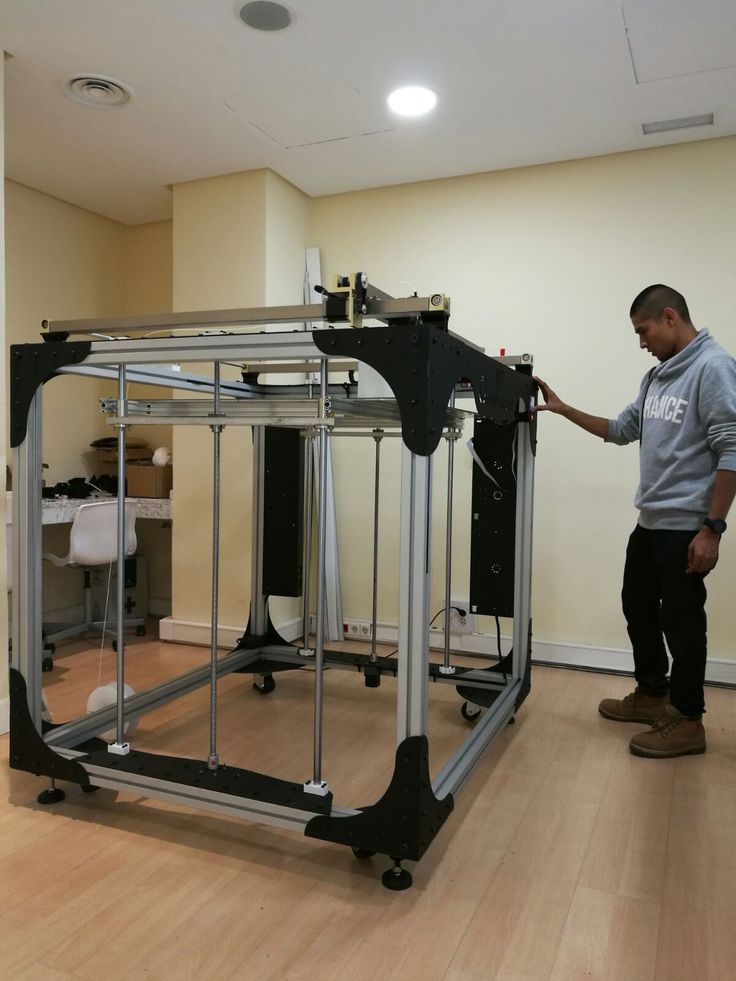
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Digital Metal, a Höganäs Group company, creates incredibly detailed metal parts with their DM P2500 system. It is able to print 3D metal parts with an accuracy as high as 0.001mm (1µ), and with a medical-grade surface quality of around 0.006mm (6µ).
Another interesting feat to point out is that almost 100% of leftover powder can be recycled for future prints. This metal AM machine is able to churn out serial production series efficiently and reliably; one of the company’s first DM P2500 printers has been running 24/7 since 2013, according to Digital Metal.
The Digital Metal DM P2500 is a certified metal 3D printer (CE and UL) that is compatible with certified metal materials (ISO 22068).
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Australian manufacturer SPEE3D has developed an impressively fast metal 3D printing technology called Supersonic Deposition. The technology is based on metal cold spray, using compressed air to “jet” metal powder through a nozzle at high speeds.
This enables the LightSPEE3D to 3D print at up to 100 grams per minute and with a range of metals including copper.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
XJet developed an impressive, proprietary jetting technology they call NanoParticle Jetting™. This inkjet method disperses millions of tiny droplets that contain nanoparticles of solid metal. The liquid material comes in cartridges that are easy to insert into the printer.
After being printed, the metal parts must go through support removal and sintering processes to attain their final form.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
DED: Directed Energy Deposition metal additive manufacturing systems
Directed Energy Deposition (DED) is comparable to filament extrusion. The metal material is pushed through a special nozzle, like with FFF/FDM, but a powerful laser beam solidifies the material at its deposition point.
Formalloy produces a range of metal DED 3D printers with up to 5 axes of motion.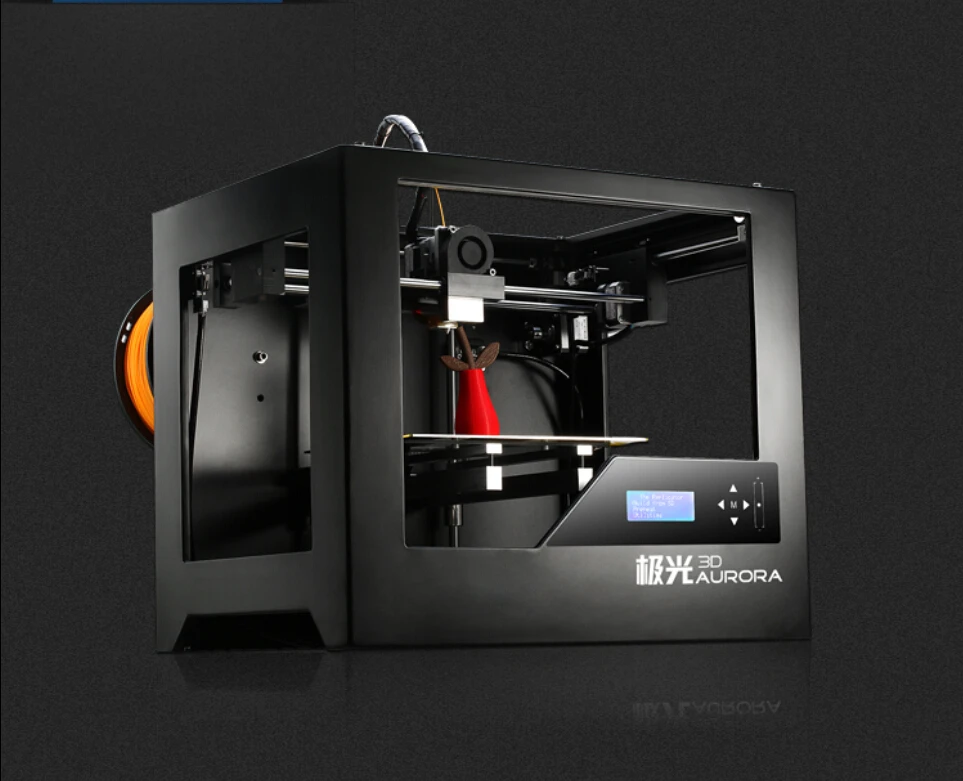 They can be used to produce metal parts but also to repair or clad existing parts.
They can be used to produce metal parts but also to repair or clad existing parts.
Different laser wavelengths are available, as well as different build volumes: 200 x 200 x 200 mm, 500 x 500 x 500 mm, and 1000 x 1000 x 1000 mm. Metal 3D printers from Formalloy can be customized depending on company requirements.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Alternative metal 3D printers and special mentions
Hybrid metal manufacturing systems
Some manufacturers are specialized in hybrid metal manufacturing systems. They combine both subtractive and additive manufacturing methods, often with robotic arms that are able to move on more than three axes.
Some of the biggest actors on the hybrid metal AM system market are:
- Gefertec (Germany)
- DMG Mori (Germany)
- Matsuura (Japan)
- Sodick (United States)
XXL-sized metal 3D printers for industrial production
For those that require very large metal parts, there are several huge, industrial machines that offer gigantic build volumes for industrial production. To name a few:
To name a few:
- Sciaky EBAM 300
- Titomic TKF1000
- ADC Aeroswift
- ADIRA AddCreator
- Fabrisonic SonicLayer 4000
- ExOne X1 160PRO
- InssTek MX-600
- BeAM Modulo 400
- Optomec Lens CS 600
- Additive Industries MetalFAB1
Metal 3D printers from China
There has recently been a lot of growth in the metal 3D printer market in Asia, and more specifically in China. Some Chinese brands have been upping their game in that respect, providing industrial-grade metal 3D printing options:
- Farsoon
- ZRapid Tech
- Shining 3D
- Wiiboox
However, we feel that they are not yet playing in the same league as the 3D printers from our main selection, mostly due to a lack of distribution networks, after-sales service and training, and other factors which tend to matter when considering them together as a whole.
R&D metal 3D printers for labs
In certain cases, metal 3D printers are used for research purposes to develop and test new materials. There are a few machines that are specifically designed for this:
There are a few machines that are specifically designed for this:
- Open Additive PANDA-6”
- Freemelt ONE
- Sharebot metalONE
Pros and cons of metal 3D additive manufacturing
Benefits of 3D printing metal parts
- On-demand production: Metal additive manufacturing offers more flexibility and control over the production line.
- Complex designs made possible: With 3D printing technology, it is possible to create highly detailed and intricate parts that would have to be broken down into several pieces with traditional methods.
- Waste reduction: Compared to CNC milling, for example, metal AM produces much less waste as it only consumes the material needed for a certain part. This is more true for extrusion-based methods than it is for powder-based methods, where it isn’t always possible to re-use 100% of unsintered or unbinded material.

- Lighter parts: Whereas metal parts are usually completely solid infill-wise with other methods, 3D printing allows parts to be more or less hollow without undermining their strength and resistance.
- Cost-effectiveness: All the above benefits of metal 3D printing can inherently reduce costs per part, although high metal 3D printer prices do represent a significant entry barrier. Reaching a positive return on investment can take a while depending on your throughput.
Limits of metal 3D printing
- Metal 3D printing prices: Metal AM systems are still quite expensive, as are metal powders and metal filaments. There are hidden costs, too (e.g. energy consumption, learning curve, etc.).
- Environmental constraints and safety precautions: Most metal 3D printers have a large footprint and require specific operating environments with controlled temperatures, hygrometry, and more.
- Post-processing: In many cases it is necessary for parts to be post-processed, whether it’s debinding and sintering or finishing touches for surface quality.
- Physical properties: It can be difficult to achieve the same physical properties that traditionally manufactured metal parts have. There are a number of factors (e.g. anisotropy) to take into account during the design process and file preparation before even trying to 3D print a certain part.
Metal 3D printing materials
Which metals can you 3D print?
A growing number of metals and metal alloys can be 3D printed. These are the main ones:
- Aluminum
- Titanium
- Nickel, Inconel
- Copper
- Bronze
- Cobalt, Cobalt-Chrome
- Steels (tooling, maraging, stainless)
- Precious metals (gold, silver, platinum)
Which metal 3D printing material formats are available?
Metal 3D printing material can be found in various formats, catering to different metal 3D printing methods. The most common are:
The most common are:
- Powder
- Wire
- Filament
It is also possible to find metal 3D printing resin as well as metal sheets for lamination-based 3D printers.
Metal 3D printer price: how much does a metal 3D printer cost?
Industrial metal 3D printer prices generally range from about $30,000 to over one million dollars for the most premium, industrial-grade metal additive manufacturing systems.
Additional costs to consider are the materials for metal 3D printing, which can cost a few hundred USD/kg, as well as costs linked to post-processing (tools, time, etc.).
Applications for metal AM systems
There are thousands of possibilities and use cases for metal 3D printing in a wide range of industries. A few industries have been incrementally using metal AM:
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Medical
Whether it’s for tooling, replacement parts, or final products, many businesses can benefit from metal 3D printing.
However, metal additive manufacturing isn’t necessarily beneficial for every single metal part. Although some metal 3D printing systems have a relative capacity for serial production, it is generally cheaper to keep using traditional methods for simple parts.
For cases where complex geometries, rapid prototyping, and mass customization are required, metal AM is convenient and efficient.
Metal 3D printing services: order 3D metal parts online
For professionals with limited office space and human resources, low budgets, and/or few needs of custom parts and prototypes, metal 3D printing services can be an ideal solution.
These additive manufacturing service companies own a variety of high-quality 3D printers with different technologies, and their professionals are experts in 3D printing. It is possible to order metal 3D parts on-demand, without acquiring a 3D printer or having to buy a certain material for one-time use.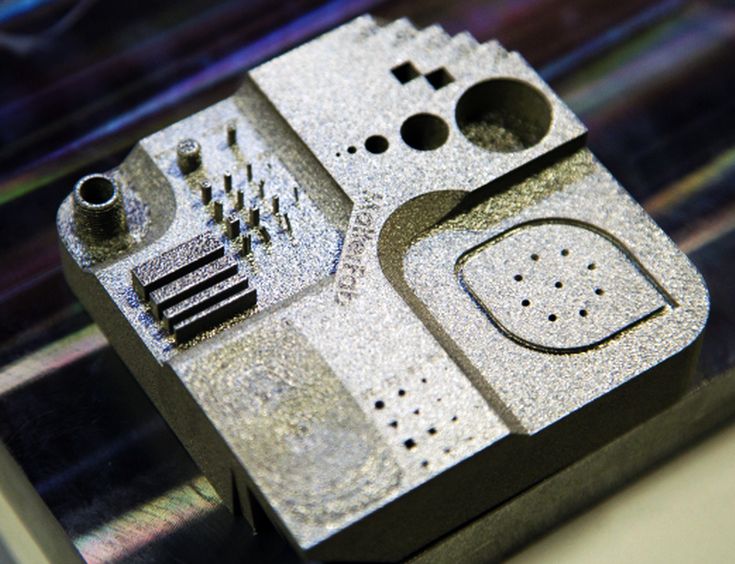
Here are some of the most trusted 3D printing service providers that offer metal printing services:
- Sculpteo
- Shapeways
- Hubs (ex 3D Hubs)
- Stratasys
- i.materialise
- Protolabs
Metal 3D printing technologies and acronyms
Many manufacturers develop proprietary variations of existing technologies and label them their own registered names:
- Powder Bed Fusion (PBF): DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering), DMP (Direct Metal Printing), LaserCUSING, LBM (Laser Beam Melting), LMF (Laser Metal Fusion), SLS (Selective Laser Sintering), SLM (Selective Laser Melting)
- Directed Energy Deposition (DED): DMT (Direct Metal Tooling), EBAM (Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing), EBM (Electron Beam Melting), LENS (Laser Engineered Net Shaping), LMD (Laser Metal Deposition)
- Metal Material Jetting (MJ) or Binder Jetting (BJ): Magnet-o-Jet, Nanoparticle Jetting, SPJ (Single Pass Jetting), Metal Jet
- Metal filament extrusion/Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF): ADAM (Atomic Diffusion Additive Manufacturing), CEM (Composite Extrusion Modeling), FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling), FFD (Fused Feedstock Deposition), FMP (Filament Metal Printing), BMD (Bound Metal Deposition), MIM (Metal Injection Molding)
- Lamination: SL (Sheet Lamination), UAM (Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing)
- Metal resin 3D printing: DLP (Digital Light Processing), FluidFM, SLA (Stereolithography)
Metal 3D printing FAQ
Is 3D printed metal strong?
Metal 3D printed parts can be as strong (or even stronger) as metal parts created with traditional manufacturing processes such as casting. The part’s strength will, however, depend on the metal AM method used and the conditions in which it is 3D printed.
The part’s strength will, however, depend on the metal AM method used and the conditions in which it is 3D printed.
When was 3D metal printing invented?
Metal 3D printing became possible in the 1990s with the development of Selective Laser Melting technology. However, 3D metal printing only started to gain traction and public interest from around 2010 onwards.
How does metal 3D printing work?
There are several ways to 3D print metal. Layers of metal filament can be deposited one after the other, producing a green part that must later go through debinding and sintering steps. It is also possible to fuse metal powder particles together with a laser, or with an inkjet printhead that deposits drops of binding material onto the powder.
EBM
Metal Industrial 3D Printer Technology of additive 3D printing with metal powder by electron beam melting (EBM - Electron Beam Melting)
Industrial 3D printers for printing metals using electron beam melting (sintering) are designed for the production of ready-to-use metal products (parts). At the same time, the printed parts can have an arbitrary shape, internal cavities, various filling factors (porosity), arched design, parts in parts made in a bionic design to reduce weight and increase the strength of products. nine0005
At the same time, the printed parts can have an arbitrary shape, internal cavities, various filling factors (porosity), arched design, parts in parts made in a bionic design to reduce weight and increase the strength of products. nine0005
In world practice, industrial EBM 3D printers are often used for the production of osteoimplants (artificial bone implants) according to the individual dimensions and geometry of the patient's bones, taken using computed tomography. And there are a number of good reasons for this. Titanium and stainless steel alloys are used to construct osteoimplants. Unlike SLM 3D printers, where the sintering energy is generated using a laser, electron beam printers can use metal powders of a coarser (larger) fraction, for example, 75-120 microns. nine0005
For use inside the human body, the surface roughness of the osteoimplant is not critical and can even provide better fusion with the rest of the body tissues and germination with mesh and arch structures of artificial bones.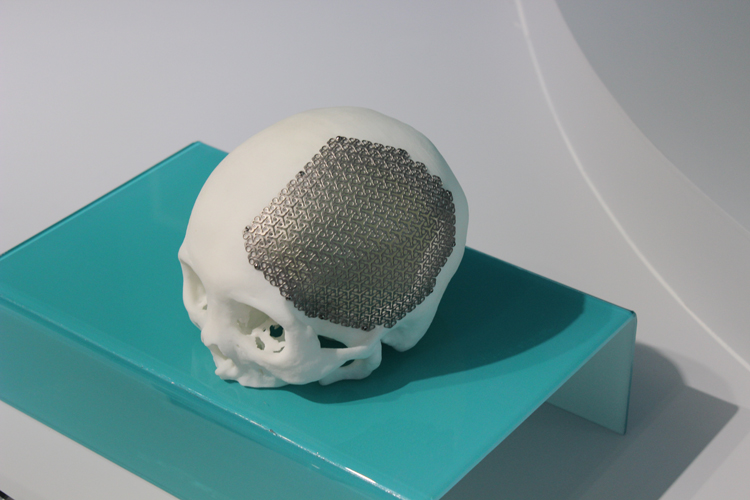 Larger fractions of metal powders have a lower cost, which reduces the cost of the production process.
Larger fractions of metal powders have a lower cost, which reduces the cost of the production process.
Also, 3D printers that print metals using electron beam melting have a higher speed of building a product. The printing itself takes place at a high temperature in the chamber, including metal powder. This makes it possible to obtain finished products with a high degree of sintering (fusion) without the need for additional heat treatment in vacuum furnaces, as in printing using SLM technology. nine0011
In the products themselves, there are no residual thermal stresses that contribute to the formation of cracks and subsequent destruction during the loaded operation of the products.
What is the additive 3D technology of electron beam melting EBM?
A removable build platform is firmly attached to the piston of the elevator system of the 3D printer. A vacuum is created in the sealed chamber of the 3D printer, which is necessary for the free movement of electrons. By the way, the principle of operation of a cathode-beam printer strongly resembles the operation of the kinescopes of the first televisions. nine0011
By the way, the principle of operation of a cathode-beam printer strongly resembles the operation of the kinescopes of the first televisions. nine0011
The scattered electron beam heats up the removable platform and chamber. The moving carriage applies and levels the first layer of metal powder onto the platform. The scattered beam of electrons, if necessary, produces additional heating of the powder layer. Then the beam is focused to a point and at a high scanning speed, in accordance with the program, begins to fuse the metal powder. Electrons are emitted by a tungsten cathode heated to the glow temperature. They are accelerated by a high voltage of 60 kV applied to the anode, which is the build platform and the powder chamber. nine0011
The primary anode serves to improve the focusing of the electron beam. The focusing coil compresses the beam, while the scanning coil deviates it along the X and Y axes. Focused to a point with a diameter of 0.2 mm, an electron beam with a power of up to 3 kW easily fuses even an increased layer of metal powder. Scanning by a magnetic field of a beam of electrons flying at the speed of light is absolutely inertialess, in contrast to a scanning system with mirrors and lasers. It allows you to move the electron beam at a tremendous speed up to 10 km / s and fuse metal powder in a multi-beam way at 100 points simultaneously! nine0011
Scanning by a magnetic field of a beam of electrons flying at the speed of light is absolutely inertialess, in contrast to a scanning system with mirrors and lasers. It allows you to move the electron beam at a tremendous speed up to 10 km / s and fuse metal powder in a multi-beam way at 100 points simultaneously! nine0011
Which accordingly affects the increase in printer productivity, which is at least two to four times higher than the productivity of similar metal laser printers. It should be understood that the energy saturation of electron beam 3D printers of EBM technology is many times higher than the energy of existing models of laser 3D printers using SLM technology. Although inferior to them in the accuracy of the additive construction of products.
After the first layer of metal powder has been melted, the piston moves down by a construction step (about 0.2 mm), the carriage applies and levels the next layer of powder, and the next cycle of zone electron beam melting takes place. nine0005
nine0005
To level the inaccuracy of the platform on which the product is printed, and to level the horizontal surface, at the beginning of the additive printing process, legs - stands are printed. The requirements for their strength and quality are low, so they are printed with a low degree of volume filling. It should be taken into account that during printing, a large amount of heat is released in the product, so heating with a scanning beam is done only when necessary. In general, the preheating temperature of the powder surface can vary in the range of 500 - 1000°C depending on the material of the powder. nine0005
At the end of the production of the finished product, the piston moves up, with the help of a special industrial vacuum cleaner and brush, unused metal powder is collected.
Attention! It is possible to open the vacuum chamber and let oxygenated air into it only after the chamber has cooled down. Metal powders are extremely flammable and ignite instantly in air, especially when heated to high temperatures.
Attention! Work on cleaning unused powder is carried out in a respirator to prevent damage to the respiratory organs by fine metal powder.
After the chamber has cooled down and the unused powder is completely removed, the build platform with the finished product welded to it is unscrewed from the piston. Then, using a tungsten string on an electroerosive machine, the part is cut off from the platform. It is further machined to remove the remnants of the legs. If necessary, sandblasting is performed to reduce the surface roughness of the product. nine0005
Additional heat treatment of parts in most cases is not required. The product is ready for use immediately after printing. And this also affects the cost reduction of additive metal printing on electron beam 3D printers. It should be noted that in the cost of additive 3D printing with metal powder using SLM laser technology, the depreciation of a 3D printer is up to 70% of the cost of the finished product. And the contribution to the cost of a rather expensive, at first glance, metal powder is in second or third place. nine0005
And the contribution to the cost of a rather expensive, at first glance, metal powder is in second or third place. nine0005
Electron beam 3D printers, having higher productivity, make a much smaller contribution from printer depreciation to the cost of the finished product and, accordingly, reduce its cost.
EBM200 industrial cathode beam 3D metal printer technical parameters
| 3D printer settings | Meaning nine0005 |
| Maximum build size | 200x200x240mm |
| Product construction accuracy | (Standard - Ti6Al4V) ± 0.2 mm |
| Maximum electron beam power nine0005 | 3 kW |
| Accelerating anode voltage (on powder) | 60 kV |
| Accelerating anode current | 0-50mA |
| nine0004 Hot cathode type | Tungsten filament |
| Minimum Beam Spot Diameter | 0. |
| Maximum Beam Scanning Speed | > 10 km/s nine0005 |
| Multipath melting | Up to 100 points |
| Ultimate vacuum | <10 -2 Pa |
| Helium partial pressure | nine0051 |
| Powder heating | Scattered Beam Scanning |
| Powder surface temperature | 500-1000℃ |
| 3D printer cooling system nine0005 | Chiller using distilled water |
| Monitoring the build process | Through the glass of the vacuum chamber |
| CAD Interface | STL file format nine0054 |
| Software | Meta Build v1. |
| Printer size | 2100x1000x2300 mm |
| Printer weight | 2000 kg nine0005 |
| Power supply | 3 phase, 380 V, 36 A, 8 kW |
Catalog
Download >>> View >>>
3D printer kit
- Industrial 3D printer of EBM technology.
- Chiller, for the 3D printer cooling system with distilled water. nine0274
- Vacuum drying chamber for metal powder.
- Industrial vacuum cleaner.
Optional:
- Pneumohydraulic machine (sandblaster).
- Machine for electroerosive cutting.
- Air conditioner and dehumidifier.
EBM Metal 3D Printing Room Requirements:
- Maintaining a stable temperature and humidity regime.
 nine0274
nine0274 - Maintaining a stable temperature and humidity regime.
- Temperature 20-26 degrees.
- Humidity less than 40% non-condensing.
- To do this, the room for 3D metal printing should be equipped with an air conditioner and a dehumidifier.
Types of metal powders for additive 3D printing by electron beam method
- Titanium and titanium-based alloys. nine0273 Aluminum alloys.
- Heat resistant steel alloys.
- Cobalt and chromium alloys.
- Stainless steel 316L.
- Copper alloys and many others.
Applications for 3D cathode beam metal printers:
- aerospace,
- medical,
- military,
- industrial area.
Electron Beam Additive 3D Printing (EBM) Benefits:
- High performance EBM 3D printers compared to SLM technology.
- Low cost of products.
- Uses less expensive coarser grade metal powder.
- Possibility of recycling of metal powder after its sieving and vacuum drying.
- The electron beam is controlled by magnetic fields.
- Expensive optical mirrors and germanium or diamond lenses are missing. nine0274
- Inertialess electron beam control gives the highest scanning speed.
- Beam scattering allows heating metal powder without the use of additional heaters and obtaining a high density of products.
- It is successfully used for the production of orthopedic bone implants (osteoimplants) made of titanium, made of porous and arched, promoting osseointegration - fusion of bone tissues with the implant (implant). nine0274
- Allows you to print products from two different materials with a gradual gradient of composition change along the Z axis.
- Allows you to create heat-resistant nozzles and blades for gas turbines, including jet engines. In addition, it is used to create load-bearing titanium elements of an aircraft wing.

- It is used to create elements of rocket engines: combustion chambers and nozzles with resistance to temperatures above 3000°C. Where high pressure and temperature require the use of refractory and durable materials such as titanium. nine0274
- Unlimited by the geometric complexity of the manufactured parts without the need for subsequent assembly or welding.
- Ability to print internal cavities and parts in parts.
Disadvantages of electron beam additive 3D technology (EBM):
- Relatively small build chamber.
- Increased roughness, printed products.
- During the operation of a 3D printer, X-ray bremsstrahlung occurs, from which it is necessary to protect both equipment and maintenance personnel. nine0274
- Respiratory protection of service personnel from fine metal powder is required.
- Tendency to ignite metal powders of titanium and steel.
China is the world's first economy and the world's largest manufacturer of 3D printers.

The quality of Chinese 3D printers often exceeds American and German counterparts due to mass production and application. At the request of the customer, American lasers and German scanners, Japanese servomotors, and Taiwanese controllers are used in 3D printers. Industrial 3D printers and software are updated and improved every 2 weeks. Hundreds of prototyping centers operate throughout China to provide quality prototypes and finished products to China's most powerful industry in the world. nine0005
Video
Related products
3D printer SLA-600
Industrial stereolithographic 3D printer SLA on photopolymer resin
Equipment for the production of metal powders for 3D printers using induction vacuum melting and gas atomization
Industrial 3D printers for metal printing SLM nine0005
Industrial 3D Metal Printers LMD
Industrial 3D printers for printing sand in a resin shell for injection molds and polystyrene
Industrial 3D printers for printing with nylon (polyamide) and polypropylene powder
Industrial 3D printers for printing ceramics
Auxiliary equipment for additive 3D manufacturing and prototyping nine0005
The author of the article is the director of the Mosinductor company
© 2017 Kucherov Vyacheslav Vasilyevich
Copyright reserved.
Prosecution Guaranteed
for posting an article or part of it
on any site except www.mosinductor.ru
Metal 3D Printing - A Fundamental Guide
There is no hotter trend in 3D printing today than metal. We will talk about metal printing at home, how it is done on an industrial scale, about technologies, applications, printers, processes, prices and materials. nine0011
Metal 3D printing has grown in popularity over the past few years. And this is quite natural: each material offers a unique combination of practical and aesthetic qualities, can be suitable for a wide range of products, prototypes, miniatures, decorations, functional details and even kitchen utensils.
The reason metal 3D printing has become so popular is because the printed objects can be mass-produced. In fact, some of the printed parts are just as good (if not better) than those made with traditional methods. nine0005
In traditional production, working with plastic and metal can be quite wasteful - there is a lot of waste, a lot of excess material is used. When an aircraft manufacturer makes metal parts, up to 90% of the material is simply cut off. 3D printed metal parts require less energy and waste is reduced to a minimum. It is also important that the final 3D printed product is up to 60% lighter than a traditional part. Billions of dollars could be saved in the aviation industry alone—mainly through weight savings and fuel savings. nine0005
When an aircraft manufacturer makes metal parts, up to 90% of the material is simply cut off. 3D printed metal parts require less energy and waste is reduced to a minimum. It is also important that the final 3D printed product is up to 60% lighter than a traditional part. Billions of dollars could be saved in the aviation industry alone—mainly through weight savings and fuel savings. nine0005
So, what do we need to know about metal 3D printing?
3D metal printing at home
If you want to make objects at home that will look like metal, it is best to pay attention to metalized PLA filaments (Photo: colorFabb)
where to start if you want to print metal objects at home? Given the extreme heat required for true metal 3D printing, a conventional FDM 3D printer will not be able to do this. nine0005
It is unlikely that in this decade it will be possible to print with liquid metal at home. Until 2020, you probably will not have a printer specialized for this purpose at home. But in a few years, as nanotechnology advances, we may see significant developments in new applications. This can be 3D printed with conductive silver, which will emit in much the same way as it does in 2D home printers. It will even be possible to mix different materials like plastic and metal in one object. nine0005
But in a few years, as nanotechnology advances, we may see significant developments in new applications. This can be 3D printed with conductive silver, which will emit in much the same way as it does in 2D home printers. It will even be possible to mix different materials like plastic and metal in one object. nine0005
Materials for metal 3D printing at home
Even though you can't print actual metal objects at home, you can turn to plastic filament that has metal powders added to it. ColorFabb, ProtoPasta and TreeD Filaments all offer interesting metal-PLA composite filaments. These filaments, containing a significant percentage of metal powders, remain pliable enough to be printed at low temperatures (200 to 300 Celsius) on virtually any 3D printer. At the same time, they contain enough metal to make the final object look, feel, and even weigh like metal. Iron-based filaments even rust under certain conditions. nine0005
But you can go further. Typically, up to 50 percent metal powder is added to 3D printing filament. Dutch company Formfutura says they have achieved 85 percent metal powder with 15 percent PLA. These filaments are called MetalFil Ancient Bronze and Metalfil Classic Copper. They can be printed even at "moderate" temperatures from 190 to 200 degrees Celsius.
Dutch company Formfutura says they have achieved 85 percent metal powder with 15 percent PLA. These filaments are called MetalFil Ancient Bronze and Metalfil Classic Copper. They can be printed even at "moderate" temperatures from 190 to 200 degrees Celsius.
Metallic 3D Printing Filament Spools, in this case from SteelFill and CopperFill colorFabb (Steel and Bronze), Ancient Bronze (Ancient Bronze) from Formfutura
Here are the key points about metal printing at home
- Gets a unique metal surface and look
- Ideal for jewelry, figurines, housewares, replicas
- Durability
- Objects are not flexible (structure dependent)
- Objects do not dissolve
- Not considered food safe
- Typical print temperature: 195 - 220°C
- Extremely low shrinkage on cooling
- No table heating required
- Printing complexity is high, requires fine tuning of nozzle temperature, feed rate, post-processing
Preparing your home printer for metal 3D printing
Since getting metal 3D prints is more difficult than usual, you may need to upgrade your 3D printer nozzle, especially if you are an entry-level printer. The metal filament wears it out quickly. There are hard-wearing hot-ends (like the E3D V6) that are themselves made of metal. They can withstand high temperatures and fit most printers. Be prepared for the fact that the nozzles will have to be changed frequently, because the metal filament is very abrasive. nine0005
The metal filament wears it out quickly. There are hard-wearing hot-ends (like the E3D V6) that are themselves made of metal. They can withstand high temperatures and fit most printers. Be prepared for the fact that the nozzles will have to be changed frequently, because the metal filament is very abrasive. nine0005
You will also need to take care of the final finishing of the surface (cleaning, grinding, oiling, waxing or priming) so that the printed metal object shines as it should.
How much does metal filament for 3D printing cost?
And what about metal filament for 3D printing? - you ask. Here are some examples:
- ColorFabb's 750 gram Bronzefill spool is $56.36
- ColorFabb 750g Copperfill Coil $56.36
- Protopasta's Polishable Stainless Steel PLA Composite is $56 for 56 grams of
- Protopasta's Rustable Magnetic Iron PLA Composite is $34.99 for 500 grams of
Industrial metal 3D printing
But what if you want a better result or even full metal 3D printing? Should a real "metal" 3D printer be purchased for business needs? We wouldn't recommend it - unless you're going to be doing it every day. A professional metal 3D printer is expensive: EOS or Stratasys devices will cost you 100-500 thousand dollars. In addition, the costs will be even greater, since you will have to hire an operator, a worker to maintain the machine, as well as to finalize the printouts (polishing, for example). Just a note: In 2016, an affordable metal 3D printer didn't exist. nine0005
A professional metal 3D printer is expensive: EOS or Stratasys devices will cost you 100-500 thousand dollars. In addition, the costs will be even greater, since you will have to hire an operator, a worker to maintain the machine, as well as to finalize the printouts (polishing, for example). Just a note: In 2016, an affordable metal 3D printer didn't exist. nine0005
Lowering Metal 3D Printing Costs
If you are not going to open a metal 3D printing business, but still need a professionally 3D printed metal part, it is better to contact the appropriate company that provides such services. 3D printing services like Shapeways, Sculpteo and iMaterialise offer direct metal printing.
They currently work with the following metal materials in 3D printing:
- aluminum
- steel
- brass
- copper
- bronze
- sterling silver
- gold
- platinum
- titanium
If you are a jeweler, you can also order wax models for casting in precious metals.
If we talk about wax models, then in most cases they (with subsequent melting) are used when printing with metals (including gold and silver). Not all orders are carried out directly by these firms. They usually turn to other metal 3D printing companies to complete the order. However, the number of such services around the world is growing rapidly. In addition, metal 3D printing techniques are becoming more and more common in companies that offer such services. nine0005
The reason big companies love 3D printing so much is that it can be used to build fully automated lines that produce "topologically optimized" parts. This means that it is possible to fine-tune the raw materials and make the components thicker only if they must withstand heavy loads. In general, the mass of parts is significantly reduced, while their structural integrity is preserved. And this is not the only advantage of this technology. In some cases, the product turns out to be significantly cheaper and affordable for almost everyone. nine0005
nine0005
Please note that metal 3D printing requires special CAD software for modeling. It is worth paying attention to the recommendations of Shapeways - 3D printing metal guidelines. To delve further into the topic, check out Statasys’ information on related 3D printers and the nuances of metal 3D printing.
Here are some examples of Benchy test model prices for metal 3D printing:
- Metal plastic: $22.44 (former alumide, PLA with aluminium)
- Stainless steel: $83.75 (plated, polished)
- Bronze: $299.91 (solid, polished)
- Silver: $713.47 (solid, mirror polished)
- Gold: $87.75 (gold plated, polished)
- Gold: $12,540 (solid, 18K gold)
- Platinum: $27,314 (solid, polished)
As you might expect, solid metal 3D printing prices are quite high.
Metal 3D printing. Applications
GE LEAP aircraft engine parts 3D printed at Avio Aero (Photo: GE)
There are several industries already using 3D printers to make everyday objects – you may not even know that these objects are printed. nine0005
- The most common case is surgical and dental implants, which are considered the best option for patients today. Reason: they can be tailored to individual needs.
- Another industry is jewelry. Here, most manufacturers have abandoned resin 3D printing and wax casting, switching directly to metal 3D printing.
- In addition, the aerospace industry is becoming more and more dependent on 3D printed metal objects. The Italian company Ge-AvioAero was the first to do all-metal 3D printing. It manufactures components for LEAP aircraft engines. nine0274
- Another industry targeting metal 3D printing is the automotive industry. BMW, Audi, FCA are seriously considering this technology, not only for prototyping (3D printing has been used for this for quite some time), but also for making real parts.
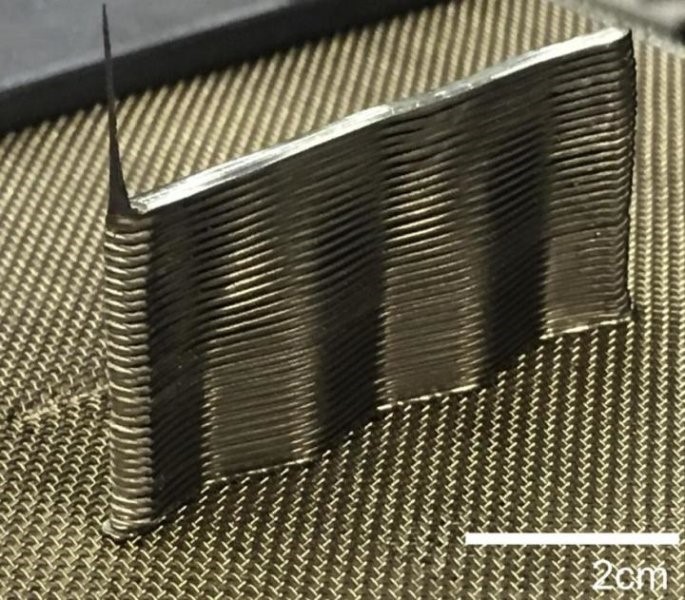
Before metal 3D printing really takes off, however, there are some hurdles to overcome. And first of all, this is a high price, which cannot be made lower than during molding. Another problem is the low production speed. nine0005
Metal 3D printing.
Technologies
Most metal 3D printing processes start with an “atomized” powder
You can talk a lot about “metal” 3D printers, but their main problems remain the same as any other 3D – printers: software and hardware limitations, material optimization and multimateriality. We won't talk too much about the software, we'll just say that most of the major specialized software companies, such as Autodesk, SolidWorks and solidThinking, try to emphasize as much as possible the fact that as a result of the 3D metal printing process, you can get any shape you want. nine0005
In general, printed metal parts can be as strong as parts made by traditional processes. Parts made using DMLS technology have mechanical properties equivalent to casting. In addition, the porosity of objects made on a good "metal" 3D printer can reach 99.5%. In fact, manufacturer Stratasys claims that 3D printed metal parts perform above industry standards when tested for density. nine0005
Parts made using DMLS technology have mechanical properties equivalent to casting. In addition, the porosity of objects made on a good "metal" 3D printer can reach 99.5%. In fact, manufacturer Stratasys claims that 3D printed metal parts perform above industry standards when tested for density. nine0005
3D printed metal can have different resolutions. At the highest resolution, layer thickness is 0.0008 - 0.0012" and X/Y resolution is 0.012 - 0.016". The minimum hole diameter is 0.035 - 0.045".
However, let's look at what metal 3D printing technologies are. formed layer)
The metal 3D printing process used by most relevant large companies today is called Powder Bed Fusion. This name indicates that some source of energy (a laser or other energy beam) melts an "atomized" powder (i.e., a metal powder that is carefully ground into spherical particles), resulting in layers of a printed object.
There are eight major manufacturers of metal 3D printers in the world that already use this technology; while we are talking here, there are more and more such companies. Most of them are in Germany. Their technologies are called SLM (Selective Laser Melting - selective laser fusion) or DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering - direct metal laser sintering). nine0005
Most of them are in Germany. Their technologies are called SLM (Selective Laser Melting - selective laser fusion) or DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering - direct metal laser sintering). nine0005
Metal 3D-printing process No. 2:
binder Jetting (spraying the binder)
9044 : ExOne)
Another professional approach that also uses a powder base is called Binder Jetting. In this case, the layers are formed by gluing metal particles together and then sintering (or fusing) them in a high-temperature furnace, just like it is done with ceramics. nine0005
Another option, which is similar to working with ceramics, is mixing metal powder into metal paste. A pneumatically extruded 3D printer (similar to a syringe bioprinter or an inexpensive food printer) forms 3D objects. When the required shape is reached, the object is sent to the furnace, i.e. in the mountains
This approach is used in the Mini Metal Maker, apparently the only inexpensive "metal" 3D printer.
Metal 3D printing process #3: 9Metal Deposition This is not entirely true. Of course, on some desktop device, simply fusing metal threads onto the base will not work. However, very large steel companies can do it. And they do. There are two options for working with "metal surfacing". nine0005
One is called DED (Directed Energy Deposition) or Laser Cladding. Here, a laser beam is used to melt the metal powder, which is slowly released and solidifies as a layer, and the powder is fed using a robotic arm.
Normally the whole process takes place in a closed chamber, but the MX3D project used conventional 3D printing techniques to build a full-size bridge. Another option for metal fusion is called EBAM (Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing - additive electron beam technology), which is essentially soldering, in which a very powerful electron beam is used to melt 3 mm titanium wire, and the molten metal forms very large finished structures. As for this technology, its details are known so far only to the military.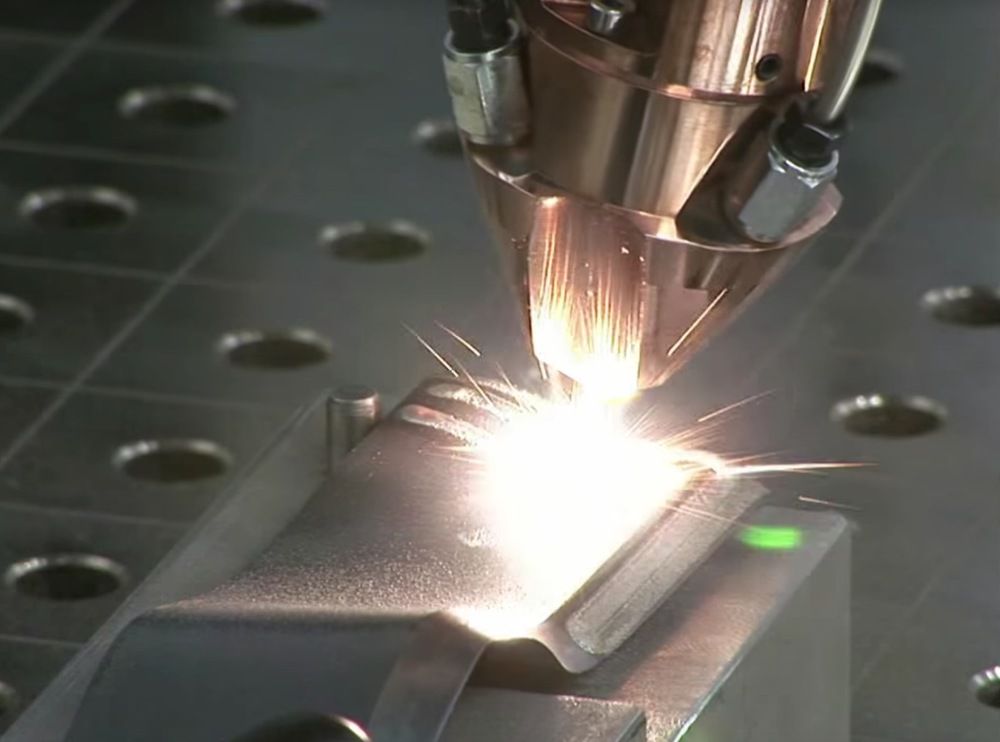 nine0005
nine0005
Metal 3D printing. Metals
3D Printing Metal #1: Titanium
Pure titanium (Ti64 or TiAl4V) is one of the most commonly used metals for 3D printing and is definitely one of the most versatile, strong and lightweight. Titanium is used both in the melting process in a preformed layer and in the process of spraying a binder and is used mainly in the medical industry (for the manufacture of personal prostheses), as well as in the aerospace industry, automotive and machine tools (for the manufacture of parts and prototypes). But there is one problem. Titanium is very reactive and explodes easily in powder form. Therefore, it is necessary that titanium 3D printing takes place in a vacuum or in an argon environment. nine0005
3D printing metal #2: Stainless steel
Stainless steel is one of the cheapest 3D printing metals. At the same time, it is very durable and can be used in a wide range of manufacturing and even artistic and design applications. The type of steel alloy used also contains cobalt and nickel, is very difficult to break, and has a very high elasticity. Stainless steel is used almost exclusively in industry. nine0005
The type of steel alloy used also contains cobalt and nickel, is very difficult to break, and has a very high elasticity. Stainless steel is used almost exclusively in industry. nine0005
3D Printing Metal #3: Inconel
Inconel is a superalloy manufactured by Special Metals Corporation, its registered trademark. The alloy consists mainly of nickel and chromium and is very heat resistant. Therefore, it is used in the oil, chemical and aerospace (for black boxes) industries.
3D Printing Metal #4: Aluminum
Due to its lightness and versatility, aluminum is very popular in 3D printing. Aluminum alloys are commonly used. nine0005
3D Printing Metal #5: Cobalt Chrome
gap). It is most commonly used in the manufacture of turbines, dental and orthopedic implants, where 3D printing has become the dominant technology.
3D printing metal #5. Copper and bronze
With some exceptions, copper and bronze are used in wax melting processes, rarely in layer melting. The fact is that these metals are not very suitable for industry, they are more often used in the manufacture of works of art and crafts. ColorFabb offers both metals as the basis for a special metal filament.
The fact is that these metals are not very suitable for industry, they are more often used in the manufacture of works of art and crafts. ColorFabb offers both metals as the basis for a special metal filament.
3D Printing Metal #6. Iron
Iron, incl. magnetic, also mainly used as an additive to PLA-based filaments, which are produced, for example, by ProtoPasta and TreeD. nine0005
3D printing metal #7. Gold, Silver and Other Precious Metals
Most preformed layer companies can 3D print precious metals such as gold, silver and platinum. Here, along with the preservation of the aesthetic properties of materials, it is important to achieve optimization of work with expensive starting powder. Precious metal 3D printing is required for jewelry, medical applications and electronics. nine0005
Metal 3D printing. Printers
Do not even hesitate - the purchase of a metal 3D printer will not pass without a trace on your budget. It will cost at least 100-250 thousand dollars. Here is a list of a variety of "metal" printers, some of which can be found in firms providing 3D printing services.
It will cost at least 100-250 thousand dollars. Here is a list of a variety of "metal" printers, some of which can be found in firms providing 3D printing services.
Metal 3D Printer #1:
Sciaky EBAM 300 - metal filament printing
If you need to print really large metal structures, Sciaky's EBAM technology is your best bet. By order, the device can be built in almost any size. This technique is used mainly in the aerospace industry and the military.
Sciaky's largest serial printer is the EBAM 300. It prints objects in a volume of 5791 x 1219 x 1219 mm.
The company claims the EBAM 300 is also one of the fastest industrial 3D printers on the market. A three-meter-sized titanium part for an aircraft is printed on it in 48 hours, while the material consumption is about 7 kg per hour. In general, forged parts that usually take 6-12 months to complete can be made in 2 days with this 3D printer. nine0005
nine0005
The metal layers are first cut and then ultrasonically welded. The largest Fabrisonic 7200 printer operates in a volume of 2 x 2 x 1.5 m. The metal powder 3D printer is the Concept Laser XLine 1000. It has a modeling volume of 630 x 400 x 500 mm and is the size of a house. nine0005
Its German company, one of the main suppliers of 3D printers for aerospace giants like Airbus, recently introduced a new machine, the Xline 2000.
This machine uses two lasers and has a working volume of 800 x 400 x 500 mm. Uses LaserCUSING laser technology (a variant of selective laser fusion) from Concept Laser, which allows you to print alloys of steel, aluminum, nickel, titanium, precious metals and even some pure substances (titanium and stainless steel). nine0005
Metallic 3D printing. Services
There are more than 100 companies worldwide offering metal 3D printing services. We list the most popular services for consumer needs.
Metal 3D Printing Service #1: Shapeways
The world's most popular 3D printing service, Shapeways offers two types of services. As a consumer, you can choose from a wide range of professionally designed objects, customize them, and then have them printed to your specifications. Like other 3D printing services, Shapeways offers a platform for designers to sell and print their work. Shapeways is also a good place for rapid prototyping: customers benefit from industrial-grade printers (EOS, 3D Systems) and personal technical support. nine0005
As a consumer, you can choose from a wide range of professionally designed objects, customize them, and then have them printed to your specifications. Like other 3D printing services, Shapeways offers a platform for designers to sell and print their work. Shapeways is also a good place for rapid prototyping: customers benefit from industrial-grade printers (EOS, 3D Systems) and personal technical support. nine0005
3D printing metals: aluminium, brass, bronze, gold, platinum, precious metal plating, silver, steel. There are also wax molds for jewelry purposes.
Metal 3D Printing Service #2: Sculpteo
Like Shapeways and i.materialise, Sculpteo is an online 3D printing service that allows anyone to upload 3D models and send them to fabrication in a wide range of materials . Like its competitors, Sculpteo provides a platform for hobbyists and professionals to showcase and sell their designs. The stable of Sculpteo printers includes highly professional machines from 3D Systems, EOS, Stratasys and ZCorp. Extensive technical documentation will help identify design flaws and select the right material for the project. nine0005
Extensive technical documentation will help identify design flaws and select the right material for the project. nine0005
3D printing metals: alumide (plastic with aluminum particles), brass, silver.
Metal 3D Printing Service #3: iMaterialise
Materialise is a company that works with industrial customers to prototype 3D printed products. For casual users and designers, Materialize offers an online 3D printing service called i.materialise. As with Shapeways, this service allows anyone to upload their 3D designs and print them out. Once an object has been uploaded and successfully printed, a designer can list it for sale either in the gallery of the i.materalise online store or by embedding some code into their website. nine0005
3D printing metals: alumide (plastic with aluminum powder), brass, bronze, copper, gold, silver, steel, titanium.
Metal 3D Printing Service #4: 3D Hubs
Through 3D Hubs, you can search for individuals and firms that offer 3D printing services in your area, upload STL files (which are immediately evaluated for defects ) and contact service providers directly to get the job done.


 Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …).
Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …). 2 mm
2 mm  2, for PC
2, for PC