Buy carbon fiber 3d printer
The Carbon Fiber 3D Printer Buyer's Guide 2022
Carbon fiber is strong, stiff, light and increasingly affordable to 3D print for companies, engineers and designers. Carbon fiber is an effective replacement for many metal parts in industry, with 3D printing offering faster prototyping, functional testing, and end user part carbon fiber production.
So, for any decision makers looking to implement carbon fiber 3D printing into their workflow, we’ve summarized all your carbon fiber 3D printer options under $10,000.
Types of carbon fiber 3D printerChopped Carbon Fiber 3D printersChopped carbon fiber filaments are the main filaments used for standard FDM 3D printing.
Most of the lower cost options on this list print chopped carbon fiber filaments, which are tiny sub-millimeter carbon fibers mixed with a standard thermoplastic filament, such as Nylon, ABS, or PLA.
They make the filaments stronger, stiffer and more heat resistant, and print in mostly the same way as the standard filaments, just at higher temperatures and requiring an abrasive-resistant nozzle.
Continuous carbon fibers are long (unchopped and continuous) strands that are laid on top of the original chopped carbon fiber “shell” or “matrix”.
These continuous lengths of carbon fiber are deposited by a second extruder, creating even tougher parts than can absorb tough impacts and distribute heavy loads.
Tips for 3D printing carbon fiber:
- Hardened steel or ruby nozzle: these nozzles better resist the abrasiveness of carbon fiber filaments.
- Print at a higher temperature, as hardened nozzles are less thermally conductive: generally 260°C+.
- Larger nozzle size: se a slightly larger 0.5-0.6mm nozzle rather than a 0.4mm.
- Print slower than you would print standard filaments.
Pulse XE — low cost carbon fiber 3D printer option
- Price: $999 — Available on Matterhackers here
- Build volume: 250 x 210 x 215 mm
Made by trusted 3D printer retailer Matterhackers and inspired from the original Prusa design, the Pulse XE is a low cost carbon fiber 3D printer especially designed to print Matterhackers’ NylonX filament.
NylonX is a mix of nylon with carbon fibers, with the Pulse XE able to print a range of other carbon fiber filaments thanks to its fitted Bondtech BMG extruder and E3D V6 hot end, along with your choice of either a hardened steel nozzle or ruby-tipped nozzle if you choose to upgrade. It’s marketed as a general advanced materials 3D printer capable of printing a variety of other tougher composite and abrasive filaments.
The Pulse XE offers a far cheaper way of 3D printing carbon fiber, but you’ll likely need the enclosure kit (another $300) to avoid warping as maintaining temperature is more difficult in an open air 3D printer than an enclosed 3D printer.
- We also have a ranking of the best enclosed 3D printers.
Taking after the Prusa, it’s a reliable workhorse 3D printer that can also print standard filaments like metal filled filaments, PETG, and many advanced and abrasive filaments and composites. It prints up to 60mm/s (but be wary with tougher materials and slow down if you face issues), with resolutions of up to 20 microns possible.
You can mix and match and upgrade as you see fit based on your needs and preferences, including a hi-res LCD screen, upgrading to a 32-bit board, ruby nozzle, and a host of other improvements — it’s a very versatile carbon 3D printer that’ll save you some money compared to other 3D printers for carbon fiber if you’re on a tight budget.
Raise3D E2
- Price: $3,499 — Available on Matterhackers here / Available on Dynamism here
- Build volume: 330 x 240 x 240 mm
Raise3D make excellent professional 3D printers capable of large-scale 3D printing and high quality prototyping, and we could have also picked the Raise3D Pro2 Plus as an excellent carbon fiber 3D printer option for larger carbon fiber prototypes.
The Raise3D E2 is an enclosed 3D printer featuring IDEX technologies with Mirror and Duplication modes for efficient and effective dual extrusion 3D printing that still offers good print volumes. It’s fully enclosed, with a controlled heated chamber ideal for printing small to medium-sized carbon fiber prototypes.
- And if you’re looking to print larger (up to 600mm tall) prototypes instead, go for the Raise3D Pro2 Plus.
The Raise3D E2 comes with a host of features that make your workflow easier and more efficient, including filament run out sensors, print resume features in the event of a power loss, and a full-color touchscreen with all analytics viewable during printing. The printer also comes with a flexible build plate that makes removing parts easier without damaging them — ideal for quickly removing carbon fiber prototypes to test them and iterate.
The Raise3D E2 CF is also set for release soon, further adding to the carbon fiber printing potential the E2 offers.
It’s not a specialized carbon fiber 3D printer, but it can handle carbon fiber filaments without issue. Beyond just carbon fiber 3D printing, the E2 also comfortably prints glass fiber infused filaments, PP, PC, Nylon, metal filled filaments, ABS, and more.
Fusion3 F410 — large carbon fiber 3D printer
- Carbon fiber 3D printer price: $4,999
- Build volume: 355 x 355 x 315 mm
Offering professional quality and industrial volume at desktop prices, the Fusion3 F410 is one of the top options around if you’re looking for a 3D printer for carbon fiber.
It’s fast — 250mm/s print speed — offers up to 20-micron layer resolution, and is ideal for both businesses and classrooms for 3D printing either larger prototypes or many smaller parts simultaneously for a class. You can add HEPA air filters to keep your print environment more pleasant and prevent any harmful gases being inhaled during the print process.
For 3D carbon fiber printing, the F410’s excellent build volume, large heated bed and enclosed print area make it ideal for high temperature filament printing. It’s been tried and tested with a number of different carbon fiber reinforced filaments, including 3DXTech and various other brands and composites, proving every time to work well. Almost all carbon fiber filaments should be compatible with it, owing to its 300°C maximum nozzle temperature — but you can read the full list of compatible filaments here.
The F410 comes with a hardened steel nozzle that can handle the abrasiveness of carbon fiber and other trickier filaments, and is an ideal carbon fiber 3D printer for under $5,000.
Makerbot Method and Method X Carbon Fiber Edition
- Price: $5,499 — Available on Matterhackers here / Available on Dynamism here
- Build volume: 190 x 190 x 196 mm
Makerbot’s specialized carbon fiber printer, the Method (and Method X) Carbon Fiber Edition, is designed to save businesses costs prototyping and creating, improve productivity, and encourage faster innovation.
The Method Carbon Fiber prints carbon fiber-reinforced Nylon as well as a host of other engineering-grade composite filaments. Makerbot themselves offer two carbon fiber Nylon blends:
- Nylon 6/66: offering fantastic strength to weight ratio and good heat resistance.
- Nylon 12: offering better moisture resistance, as well as a simpler and more reliable 3D printing experience overall.
Both Nylon carbon fiber 3D printer materials work well in structural applications and in general tough part production, with Makerbot championing the materials for replacing metal parts.
In addition to these carbon fiber nylon filaments, Makerbot offer SR-30 soluble filaments that can be dissolved for flawless surface finishes on parts, and a range of other high-quality materials. You can also use other materials as the Method is an open platform for other advanced filaments.
The Method features a 60°C heated chamber, and if you want to go higher, you can instead buy the Makerbot Method X which can reach 110°C to print a wider range of composite materials. You get a dual extruder for multi-material or multi-color 3D printing, and up to 20-micron resolution and 0.2mm dimensional accuracy.
Some may find the smaller than average build volume an issue, especially as if you are planning on using the dual extruder the X-axis maxes out at 152mm rather than 190mm. However, for small and medium part production the Method Carbon Fiber 3D printer is a great overall option, packed with features to maximize prototyping efficiency including a flexible steel build plate for adhesion and quick part removal, a 5-inch full color touchscreen for efficient printer interaction, and a camera for remote print monitoring.
Ultimaker S5
- Price: $5,995 — Available on Matterhackers here / Available on Dynamism here
- Build volume: 330 x 240 x 300 mm
A favorite among designers, prototypers and companies worldwide, the Ultimaker S5 marries fantastic precision and part quality, with the robustness and reliability of a top FDM 3D printer.Switching to the CC print core for 3D printing carbon fiber on the Ultimaker S5.
The S5 isn’t as standard a carbon fiber 3D printer, but can be upgraded by buying Ultimaker’s CC Red 0.6 print core, which seamlessly slips into place to start printing abrasive and advanced filaments like carbon fiber. The CC Red works on both the S3 and S5, but not for the Ultimaker 3.
The upgraded print core transforms the Ultimaker S5, giving you all the S5’s precision and reliability in creating fantastic prototypes, as well as the ability to print carbon fiber composites. You can print with dual extruders without issue, and the S5 comes with a 7-inch full color touchscreen for easy operation and print monitoring, and a removable glass print bed for good carbon fiber part adhesion and easy part removal.
XYZprinting PartPro300 XT
- Price: $5,500 — Available on Dynamism here
- Build volume: 295 x 300 x 300 mm
XYZprinting have expanded far beyond their original horizons when they producing some of the best selling cheap 3D printers around — they now sell SLS 3D printers, a handheld 3D scanner, and full color 3D printers.
The PartPro300 XT is XYZprinting’s venture into making a commercial 3D printer capable of consistently printing advanced filaments like carbon fiber. Its dual extruders are fitted with hardened steel nozzles that can handle carbon fiber’s abrasiveness, and prints at a very fast 300mm/s for the rapid prototyping of large parts in record time.
Like most carbon fiber 3D printers the PartPro300 XT has a regulated heated chamber and enclosure for high quality part production, preventing temperature deviations that could cause imperfections in the prototype. The PartPro300’s filament humidity system prevents conditions from affecting filament quality, ensuring parts are as strong and offer the best surface area possible. Overall, it’s a powerful carbon fiber 3D printer that can print a range of other engineering-grade filaments too without issue.
Overall, it’s a powerful carbon fiber 3D printer that can print a range of other engineering-grade filaments too without issue.
Markforged Onyx One — for high quality carbon fiber 3D printing
- Price: $3,499
- Build volume: 320 x 132 x 154 mm
Markforged pioneered composite and high quality carbon fiber 3D printing with their professional FDM printer range, before expanding into metal 3D printers with their Metal X 3D printer.
For designers and engineers looking to print carbon fiber prototypes but without the $10,000+ for the Mark Two, the Onyx One is an ideal continuous carbon fiber 3D printer.
The Onyx One prints with Markforged’s specialized Onyx filament, offering great surface finishes and precision.
Onyx Filament
Specially designed for Markforged’s carbon fiber printers, Onyx is carbon fiber filled Nylon offering high strength, chemical resistance and excellent overall toughness. It can also be reinforced with continuous fibers as a continuous carbon fiber 3D printer filament for even better aluminum-level strength.
It can also be reinforced with continuous fibers as a continuous carbon fiber 3D printer filament for even better aluminum-level strength.
Desktop Metal Fiber HT & LT — Professional Continuous Carbon Fiber 3D Printer
- Price: $3,495 per year — request a quote here
- Build volume: 310 x 240 x 270 mm
Combining the exceptional performance of continuous carbon fiber with FDM 3D printing, Desktop Metal say their Fiber 3D printers produce parts stronger than steel, lighter than aluminum, and capable of operating in up to 250°C temperatures.
Desktop Metal use a process called Micro Automated Fiber Placement to apply continuous carbon fiber (or fiberglass) tape along critical load paths using the second extruder, while printing carbon fiber nylon filaments on the first. This creates denser, reinforced parts with excellent strength and low weight.
The Fiber system uses two print heads: one for either continuous carbon fiber (or fiberglass) tape, and one to deposit the carbon-fiber reinforced filament to make up the “shell” or “matrix” of the part. However, if you’re looking for versatility you can switch the materials and instead print with PEEK, PEKK, or PA6 Nylon.
However, if you’re looking for versatility you can switch the materials and instead print with PEEK, PEKK, or PA6 Nylon.
The Fiber carbon fiber additive manufacturing system comes in two options: the Fiber HT, and Fiber LT, a more basic version. The main difference is the Fiber HT can reach high enough temperatures to 3D print PEEK and PEKK, whereas the LT edition prints with either carbon fiber or Nylon PA6.
- We also have a buyer’s guide for PEEK 3D printers.
Desktop Metal’s innovative business model lets you rent their industrial carbon fiber 3D printers for a yearly fee, rather than shouldering the entire cost upfront. This brings professional 3D printing into range for many more smaller companies looking to prototype or produce parts on-demand, making high-quality continuous carbon fiber 3D printing more accessible than ever.
New EDGE Carbon Fiber 3D Printer
Adding carbon fiber to 3D printing materials makes the materials lighter and can add strength and higher temperature resistance. This makes it very attractive for different industries to implement this material into their 3D printed parts.
This makes it very attractive for different industries to implement this material into their 3D printed parts.
Fusion3 designs its EDGE 3D printer for optimal results with various carbon fiber reinforced 3D printing materials.
This is not an easy feat. Carbon fiber materials are tricky to print and harsh on the 3D printer hardware. Carbon Fiber materials have up to 30-60% of flakes/shards of the additive mixed with plastic and can be quite hard on 3D printer components.
However, as you’ll read below, Fusion3 engineers and supports our 3D printers to ensure our customers get great results when printing carbon fiber. Fusion3 3D printers do not require any modification to print carbon fiber materials, so, out of the box, they withstand the wear and tear subjected to the harsh wear and abrasiveness of the carbon fiber filament as a true carbon fiber 3D printer.
3D Printed Carbon Fiber Bicycle Pedal
FUSION3 EDGE SAMPLE PRINTHelical Bevel Gear 3D printed with Carbon Fiber Nylon
VIEW MORE CARBON FIBER 3D PRINTED SAMPLES
Over 12 Different Carbon Fiber 3D Printer Filaments, Tested & Certified For Fusion3 3D Printers
We have tested and certified a wide variety of Carbon Fiber reinforced materials from leading manufacturers for use in our 3D printers. Materials with various amounts of Carbon Fiber include: Nylon, ABS, PETG, Polycarbonate, Co-Polyesters and PLA.
Materials with various amounts of Carbon Fiber include: Nylon, ABS, PETG, Polycarbonate, Co-Polyesters and PLA.
Fusion3 receives requests from both customers and manufacturers to test new materials as they arrive on the market. Should they pass our rigorous testing process, we provide optimized print settings to all our customers within our REACTOR 3D printing software.
The New EDGE High-Performance 3D Printer Optimized For 3D Printing Carbon Fiber,Kevlar & Fiberglass
Only $6,999 + Shipping
REQUEST DETAILED PRICING NOW
FUSION3’S 3D PRINTERS ARE DESIGNED FROM THE GROUND UP FOR SUPERIOR 3D PRINTING OF CARBON FIBER REINFORCED MATERIALSEvery Fusion3 3D Printer Ships Standard With Wear Resistant Print HeadsCarbon Filled Materials Are Abrasive Live Sandpaper
Carbon fiber printing can quickly destroy a standard brass nozzle or aluminum nozzle. It takes less than 100g of material to erode and deform a common brass nozzle print head to the point of destruction.
It takes less than 100g of material to erode and deform a common brass nozzle print head to the point of destruction.
Fusion3 3D carbon fiber printers do not require different print heads for different materials. Every Fusion3 3D printer since our F400 model come standard with print heads or nozzles that are resistant to wear from abrasive filaments like carbon fiber. hardened steel nozzle as standard equipment. Unlike brass, these components will not erode and print carbon fiber filled filament like a champ.
Fusion3 EDGE Print Head with Surgical Steel, Abrasive Resistant Tube Steel Nozzle
Our Enclosed, Passively Heated Print Chambers Provide Excellent Carbon Fiber 3D PrintsCarbon Fiber Filled Materials Require More Heat To Achieve Full Layer Bond Strength
The Fusion3 EDGE 3D printer uses a high-power, multi-zone heated bed, a high-temperature, high-power print head and an enclosed print chamber. Fusion3’s optimized carbon fiber 3D printers have no issue getting high-performance materials hot enough and keeping your 3D printer warm to achieve high-strength layer bonding.
Infrared Image of the Fusion3 EDGE’s Multizone Heated Bed
Fusion3 Provides Optimized Settings for a Wide Variety of Carbon Fiber 3D Printer Materials To Ensure Great ResultsCarbon Fiber Filled Materials Are Significantly More Expensive Than Their Unfilled Counterparts.
3D printing with carbon fiber can be expensive. The last thing you want to do is waste material on failed prints while trying to figure out the right print settings.
Fusion3’s material testing lab takes out all of this guesswork for our customers. We have already tested and certified over 12 different Carbon reinforced materials and have more in testing. These optimized profiles are found within our REACTOR 3D printing software ready for you to use.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:CARBON FIBER 3D PRINTERS & FILAMENTS
;">How does carbon fiber 3D printing work?
Carbon fiber 3D printing filament consists of tiny carbon fibers infused into a base material. These blends allow carbon fiber printers, such as the F410, to print lighter and more durable and rigid objects.
These blends allow carbon fiber printers, such as the F410, to print lighter and more durable and rigid objects.
;">Do I need to get a carbon fiber specific printer for carbon fiber printing?
Carbon Fiber is an abrasive, difficult to print material that requires specialized hardware. If you are only experimenting with a carbon fiber PLA, you can likely get away with using an inexpensive hobby 3D printer. However, the minute you require either a higher temperature material like a carbon fiber nylon, ABS, polycarbonate, or similar or need to use in a business / commercial environment, a professional 3D printer like the Fusion3 F410 that has special capabilities becomes an absolute requirement. The F410’s hardened steel nozzle which resists wear, the printer’s heated chamber will ensure great layer adhesion and the multizone heat bed will resist part warping.
;">How is carbon fiber filament made?
Carbon fiber filament is made from short carbon fibers, consisting of segments of less than 1mm in length.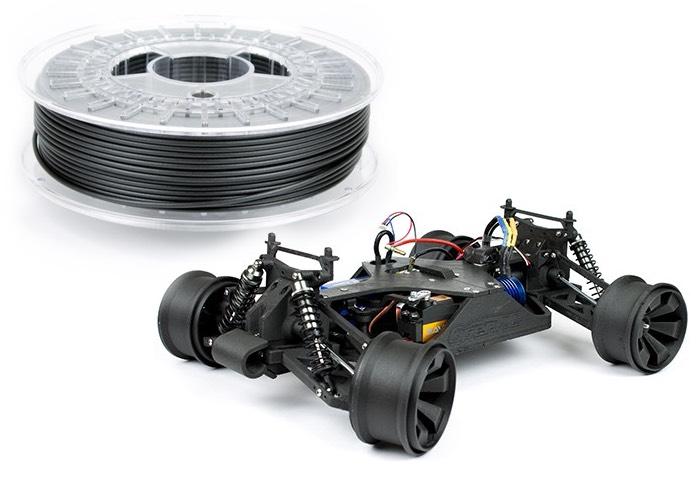 These fibers are mixed with a thermoplastic base material. The most common carbon fiber filament base materials are PLA, PETG, Nylon, ABS, and Polycarbonate.
These fibers are mixed with a thermoplastic base material. The most common carbon fiber filament base materials are PLA, PETG, Nylon, ABS, and Polycarbonate.
EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT 3D PRINTING WITH CARBON FIBER
EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT 3D PRINTING WITH CARBON FIBER
Before you start working with 3D printing with carbon fiber, read the basic information that we have collected specifically for you. Read on and learn about the advantages, disadvantages, history and applications of carbon fiber 3D printing.
CARBON FIBER AS A MATERIAL
Carbon fiber comes in many shapes. Can be used together with resin and molds; it can be combined with polymers in composite form. It has been used for everything from light bulbs to high-performance racing cars - and has even been tested on rockets flying to Mars. Despite its wide range of applications, the most obvious advantage of carbon fiber is its high strength to weight ratio.
History
Carbon fibers were first discovered by Thomas Edison in the late 19th century for use as the filament in early light bulbs. In the late 1950s, the Union Carbide Corporation first recognized the strength advantages that could be achieved with additional processing methods. Over the next 50 years, manufacturing technology advanced further, and today carbon fiber has become a ubiquitous high performance product, from racing cars to airplanes.
In the late 1950s, the Union Carbide Corporation first recognized the strength advantages that could be achieved with additional processing methods. Over the next 50 years, manufacturing technology advanced further, and today carbon fiber has become a ubiquitous high performance product, from racing cars to airplanes.
Production
Generally, all carbon fiber is produced using a six step process. PAN (polyacrylonitrile) is obtained as a by-product of petroleum and is generally the material of choice for carbon fiber production. PAN is mixed with other ingredients and converted into fibers up to 10% of the thickness of a human hair. The fibers are then oxidized to stabilize the bond before undergoing carbonization, during which the fibers are heated to 1000°C to remove impurities. The surface is then treated to improve adhesion before the final sizing step, in which the fibers are coated and spun into threads of varying thicknesses.
These yarns can then be further processed in a variety of ways, depending on the end use. The yarn can be woven into sheets or, in the case of 3D printing, it can be cut into short fibers, mixed with a base polymer, and then extruded into a filament for a 3D printer.
The yarn can be woven into sheets or, in the case of 3D printing, it can be cut into short fibers, mixed with a base polymer, and then extruded into a filament for a 3D printer.
Pre-cut carbon fiber for 3D printing resin
3D PRINTING WITH CARBON FIBER
3D printing with carbon fiber means choosing the right composites. The base polymer can determine the final properties of the part, as well as considerations that need to be taken into account when 3D printing. Below you will see various carbon fiber 3D printer composites and some of their strengths and weaknesses.
Nylon Carbon Fiber PA CF
Nylon Carbon Fiber is one of the most popular composites when it comes to 3D printer. This is because nylon already has desirable properties for engineering applications. It has a high degree of strength and high temperature resistance. It also has a high degree of strength that balances out the brittleness of the carbon fiber itself.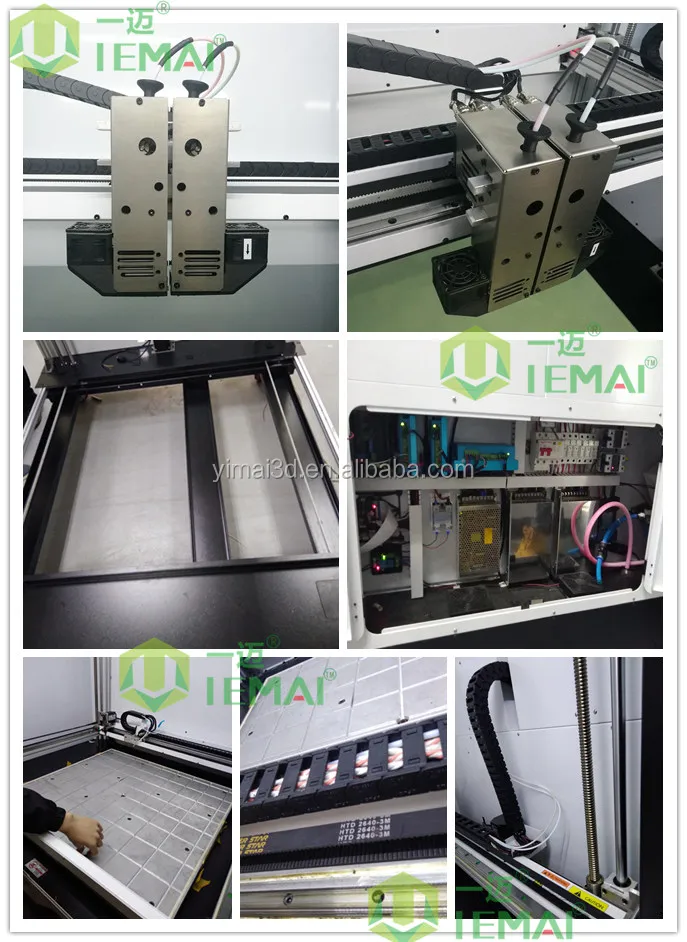 A potential disadvantage of nylon is its hygroscopicity, which makes it even more important to have a protected environment for nylon carbon fiber spools such as a mylar bag and a sealed material compartment.
A potential disadvantage of nylon is its hygroscopicity, which makes it even more important to have a protected environment for nylon carbon fiber spools such as a mylar bag and a sealed material compartment.
Carbon fiber ABS. ABS CF
ABS is a well known material due to its wide application in injection molded consumer products. In carbon fiber 3D printing, ABS works as a solid base polymer due to its properties. ABS carbon fiber also tends to have a very nice surface finish, which is almost always welcome whether the application is a prototype or part of a final product. One disadvantage of this connection is that it requires a heated 3D printer chamber, which is usually only found in higher end 3D printers.
Carbon fiber PETG CF
PETG is a material known for its resistance to chemicals and moisture in general, making it a good composite resin for 3D printers under exposure conditions. Examples of such applications include parts that may come into contact with coolants or simply products that will be used outdoors in rainy climates.
Examples of such applications include parts that may come into contact with coolants or simply products that will be used outdoors in rainy climates.
Carbon fiber PEEK CF
PEEK is one of the most efficient thermoplastics ever invented.
PEEK-CF thread includes carbon fibers for added strength. Chopped carbon fiber gives printed parts high rigidity and dimensional stability. This material provides long term performance up to 240°C including exceptional chemical resistance. These properties make it particularly suitable for metal replacement in critical end-use applications such as oil and gas, aerospace and automotive. The flammability of PEEK-CF is low, as well as the emission of smoke and toxic gases.
Due to its high mechanical properties, PEEK-CF is used for critical applications, in some cases even allowing the replacement of metal parts of the structure.
(Alternative) Fiberglass
Carbon is not the only filler for 3D printer composites. Fiberglass is an alternative to carbon fiber 3D printing when a more flexible end product is required. It can be combined with many materials of the same type and can provide high strength in the same way as carbon fiber.
Fiberglass is an alternative to carbon fiber 3D printing when a more flexible end product is required. It can be combined with many materials of the same type and can provide high strength in the same way as carbon fiber.
BENEFITS
➜ Strong and lightweight: Carbon fiber's most well-known property is its strength to weight ratio, which is why it is often used in high performance products. This is due to the low density.
➜ Heat Resistance: is able to withstand higher temperatures than many polymers and even increase the HDT of these polymers when mixed to form a composite.
➜ Stiffness: While some polymers may have high strength and durability, this often comes at the expense of stiffness. The ability of carbon fiber to retain its shape under high loads is a huge plus for many applications.
DISADVANTAGES
➜ Expensive: Due to the complex manufacturing processes of carbon fiber, this material is known to be quite expensive, making it a luxury item, which is one of the reasons why it appears in high-end products but not on mass market.
➜ Brittleness: One of the disadvantages of high stiffness is that the carbon fiber can crack under high impact force. This means applications with such loads will not be ideal for carbon fiber.
RAise3D RMF500 for 3D printing with materials reinforced with carbon fiber
Autumn of last year, a well-known Chinese manufacturer Raise3D, announced the creation of a new 3D-printer for small-scale production industrial sector - RMF500 . The unique feature of the novelty is combination of the ability to print with carbon fiber reinforced material (colloquially carbon fiber), wide format and affordability of .
We all know that high technology is becoming more accessible every day, and the RMF500 is a prime example of this. There have been systems on the 3D printing market for several years that print carbon fiber composites of similar quality, but, unfortunately, they are not available to all companies due to the very high cost and supply problems. For example, such professional 3D printers are produced by the American company Stratasys - Fortus 450mc, but they are equipped with less technological features and are much more expensive.
Let's take a closer look at what the RMF500 is and how it differs from other 3D printers.
The RMF500 is specifically designed for printing complex parts with high durability. It will enable 3D printing companies to expand their product portfolio with carbon fiber and fiberglass end parts. Both materials specially developed by Raise3D, such as PA12 CF, and materials from other manufacturers approved by Raise3D under the Open Filament Program (OFP) will work. Parts made of carbon and fiberglass are more rigid, durable, resistant to heat and shock than parts made of other plastics. For carbon and fiberglass printing, the RMF500 uses silicon carbide nozzles with a hardness of more than 60 HRC.
Parts made of carbon and fiberglass are more rigid, durable, resistant to heat and shock than parts made of other plastics. For carbon and fiberglass printing, the RMF500 uses silicon carbide nozzles with a hardness of more than 60 HRC.
PA12 CF filament is the result of a long-term development by Raise3D engineers. This is a carbon fiber reinforced filament with increased stiffness and reduced shrinkage and does not require a thermostatic print chamber. The parts obtained from it are light and extremely durable, sometimes they can even be used instead of metal. In addition, the company has developed the PPA GF glass-filled filament specifically for the RMF500 and plans to release PET-CF, ASA-GF, PPSU-GF and PP plastics for medical use. Raise3D promises that all fiber reinforced plastics will be competitively priced.
The RMF500 has a huge building area 500x500x500mm. The size of the build area matters in the production of large parts and small-scale production. For comparison, the print area of the Fortus 450mc is 406x355x406mm.
For comparison, the print area of the Fortus 450mc is 406x355x406mm.
In the photo: printing a large model with carbon fiber in the RMF500 3D printer from Raise3D.
Repeatability and print speed are very important for low volume production. The maximum print speed of the RMF500, according to the manufacturer, can reach 300 mm/s. Positioning accuracy along the XY axis - 1 micron, along the Z axis - 0.09765 microns.
Synchronous feedback control with 1 µm accuracy reduces speed fluctuations as motor load changes, further improving accuracy. Stability and repeatability of printing has long been a hallmark of Raise3D printers. The FFF technology on which this 3D printer is based allows the production of parts with a high degree of repeatability, high positioning accuracy and uniform extrusion. The RMF500 can quickly print large batches of identical parts.
Pictured: production of lots from a large number of parts on the RMF500.
The printer has a printing system with two independent IDEX extruders. It allows you to print with one or two extruders at once. The RMF500 can run two jobs at the same time, further increasing productivity and task speed. The extruders are manufactured using high temperature alloys and industrial ceramic composite materials. These characteristics provide stable and high extrusion speed up to 500 g/h.
The RMF500 has a strong design . The one-piece frame is made of hardened steel. Stainless steel linear guides have a design load of approx. 100 kg. The bearing of the linear guides has minimal backlash and does not require frequent maintenance.
An important detail - Raise3D has developed a special support material for printing with reinforced plastic PA12 CF, which can be easily detached.
Pictured: Parts printed on the RMF500 with PA12 CF filament with special proprietary support.
The RMF500 is equipped with four large compartments for plastic spools. Switching between the main and auxiliary compartments occurs automatically. This feature reduces the amount of time spent threading the filament. The humidity control system keeps the relative humidity in the chamber below 5%, preventing humid air from entering from outside.
Switching between the main and auxiliary compartments occurs automatically. This feature reduces the amount of time spent threading the filament. The humidity control system keeps the relative humidity in the chamber below 5%, preventing humid air from entering from outside.
What else is there in the RMF500 from nice additional options. The front of the printer has a large 13.3-inch touch screen. Supports connection, management and printing via Wi-Fi and LAN. There is a reliable auto-calibration system from Raise3D.
Carbon fiber printed parts are strong enough to be used in the automotive and aerospace industries. Of course, they will not replace functional parts that have a special load, but their scope can be very wide. Raise3D has already presented the results of the first RMF500 printing and its application.
Pictured: Functional parts, accessory tools and fixtures, car décor printed on the RMF500.
Pictured: Functional parts, accessories and aerospace prototype printed on the RMF500.
Learn more






-kupit-v-soin-store.ru-3.png)





