3D printer with heated bed
Enclosed 3D Printers With Large Heated Bed: Fusion3
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) is a fantastic technology but is also slow. An FDM 3D printer puts plastic down in a small bead, one layer at a time. This speed issue becomes magnified as part size increases.
During sales calls with customers, we often remark:
Plenty of slow 3D printers on the market can print small items with decent to very good quality using low-temperature plastics such as PLA and PETG.
What is difficult is to print large or many parts using high-temperature/engineering-grade plastics at good to excellent quality on a repeatable basis. A company gets even higher marks if their 3D printer can do these at faster speeds at quality (the prints do not take weeks at a time).
Let’s describe some of Fusion3’s advantages in 3d printing large parts or many parts at one time.
Fusion3 EDGE: Enclosed 14.5″ x 14.5″ x 13.5″ Large 3D printer
Very Large 3D Print Build VolumeFusion3 has always been known for fast 3D printers with large build volumes.
Our first 3D printer, the F306, had a 12 “x 12″ x 12″ build area. This grew to 14″ x 14″ x 12.5” with our F400 and F410.
Our latest 3D printer, EDGE (shown) has the largest heated, enclosed build area we’ve ever produced. EDGE has a total size of 14.5″ x 14.5″ x 13.5″ (2842 cu in or almost 48,000 cu cm).
You may not make an item that uses the full height of EDGE.
Still, for producing many parts or student assignments, the entire 14.5″ x 14.5″ aluminum tool plate allows for many items to be placed on the bed and printed using the same settings.
Interchangeable Print Heads / Print TubesEvery Fusion3 EDGE 3D printer ships with a print head with our standard .4MM nozzle. This is the perfect balance of print speed and print quality.
EDGE and its ANVIL print head uses removable/replaceable surgical steel print tubes which resist wear from abrasive, infused materials (such as carbon fiber or metals). Both types, unlike brass nozzles, are the perfect choice for large format 3D printing.
Both types, unlike brass nozzles, are the perfect choice for large format 3D printing.
You might see a smaller nozzle available, especially by hobby component providers. However, our testing has shown that a nozzle any lower than .4MM will have too slow a flow rate to be productive and have too high a probability for print jams.
Depending on your print speed and print quality requirements, we offer larger print heads/print tubes for our 3D printers, which allow you to increase the flow rate and decrease print time for large 3D prints that would otherwise take much longer with a smaller print nozzle.
.6MM
32-40% Reduction in Print Time
.8MM
44-58% Reduction in Print Time
Large, Passively Heated EnclosureFusion3’s enclosed 3D Printers provide a stable, high-temperature environment for printing high-strength, engineering-grade 3D printing materials.
Our EDGE 3D printer features a large multi-zone heated bed which offers the right consistent temperature for proper bed and layer adhesion for all 3D printing materials.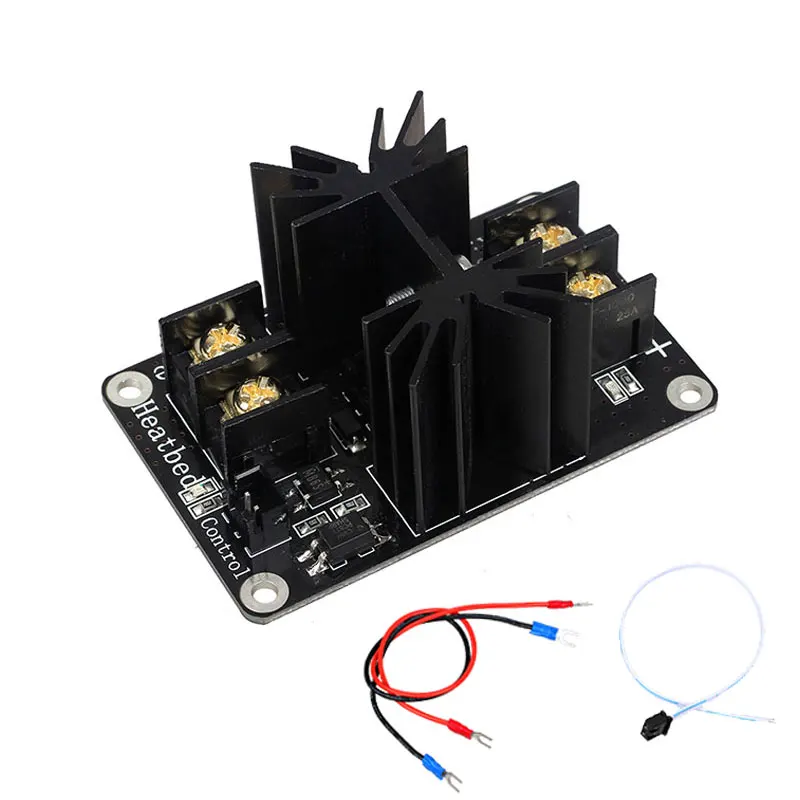
Depending on the material you are printing, the interior temperature will vary between 30*C and up to an astounding 70*C.
Each ensures excellent print results for high-temperature, engineering-grade materials, including polycarbonate, ABS, and nylon.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:LARGE 3D PRINTERS
;">What is a good standard for a large 3D printing area?
A good standard for a large format 3D printer is 300mm x 300mm x 300mm and upward. The F410 has a max build size of 355 x 355 x 315mm.
;">Do I need a large format 3D printer?
If you’re planning on manufacturing larger prints or looking to print a number of smaller prints in one session, a large format printer could be a good choice for you.
;">Do I need to assemble a large format 3D printer?
In the majority of cases, most large format 3D printers require assembly. Some printers require a lengthy, full assembly process, while some come with a simple set up process. Unlike others, Fusion3’s 3D printers are fully assembled at the factory and calibrated to exacting tolerances. Within minutes of removing from the box, you should be printing your first items at high quality and fast speeds.
Unlike others, Fusion3’s 3D printers are fully assembled at the factory and calibrated to exacting tolerances. Within minutes of removing from the box, you should be printing your first items at high quality and fast speeds.
;">Can a beginner use a large 3D printer?
The answer depends on the 3D printer rather than the user. Some large-format 3D printers require complicated assembly, making them harder to use. The Fusion3 F410 comes fully assembled and calibrated making it easier to use than other 3D printers, even for beginners.
Want to find out how quickly your parts will print on a Fusion3 3D Printer?
CLICK HERE TO SPEAK WITH A SALES TEAM MEMBER
3D Printer Heated Bed - Everything About Heated Beds
ADVERTISEMENT
Table of Contents
With the advancement in 3D printing, a lot of new research and experiments have surfaced. Many of them are tailored towards finding the best way to increase the first layer adhesion.
Many of them are tailored towards finding the best way to increase the first layer adhesion.
And, we all know why it is so important. A 3D printer heated bed can handle that part pretty well. Although there are other alternatives to work with the first layer, nothing beats this one.
Most importantly, print beds are a very crucial part of the overall design of the machine. This is because, without a print bed, you won’t be able to create your models.
Hence, realizing how you can make the best use of it must be your first priority to know. Understanding the different types of heated beds and their usefulness would help you select the right device.
So, before we progress to explore everything about the heated bed, let us get an idea about what 3D printing is. Most of us already know about it, but a quick recap will only ensure that all our readers are on the same page.
ADVERTISEMENT
What is 3D Printing?
We have been hearing about additive manufacturing or 3D printing for a long time now.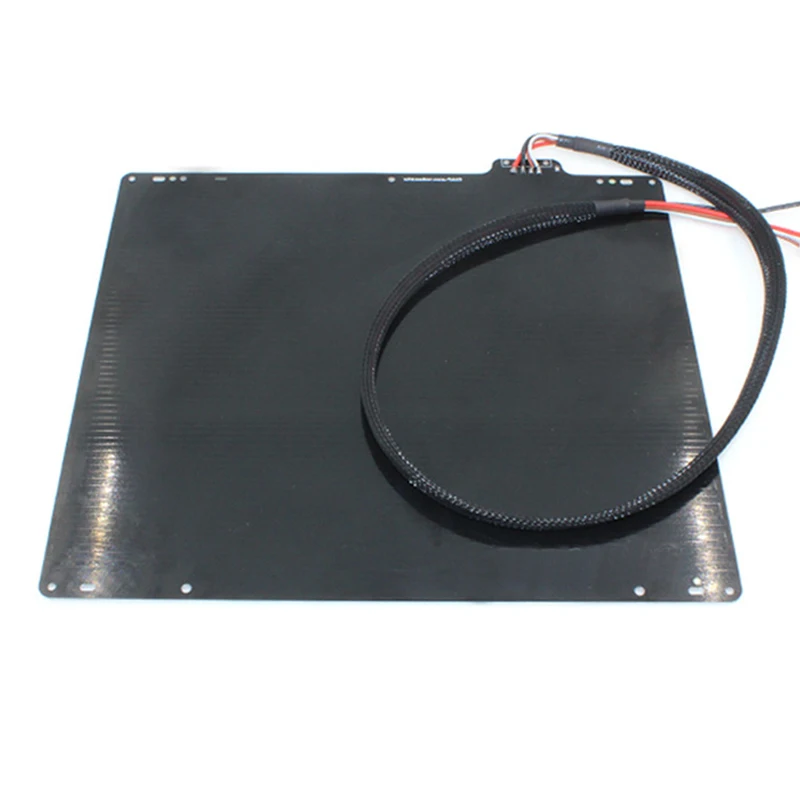 There are few lucky ones who even had the chance to work with this technology. But it’s never late whenever you decide to do something.
There are few lucky ones who even had the chance to work with this technology. But it’s never late whenever you decide to do something.
3D printing has emerged as one of the most revolutionary technologies and is propagating to impact the entire ecosystem of manufacturing units.
But what the technology really entails or means? This is a process where the 3D printers create layers of 3D models, one over the other, to create a complete item.
There are various 3D Printing processes available. For instance, FDM, SLS, SLA, and many others. These differ in the way the layers are created and connected. However, the basics remain the same. The layers forms over each other to build the entire 3D model.
3D printing has made the creation of extremely detailed models and structures possible at much faster and affordable rates. But certain precautions need to be taken while using the printer to ensure the part being printed adheres closely to the desired specifications.
However, 3D printing comes with its own challenges. And, the biggest setback is when the layers rapidly heat and cool down.
One of the serious problems that occur because of such a process is wrapping. It changes the shape of the 3D model and deforms it. Hence, running the entire 3D printing project.
To cater to the problem, the 3D printer heated bed surfaced. These print beds are very successful in allowing the proper cooling of the layers.
At the same time, these help in controlling the temperature while the 3D Printing is in process. Hence, further resulting in proper bed adhesion.
ADVERTISEMENT
What is a 3D Printer Heated Bed?
Coming back to the topic in the light, we must answer the question: What is a 3D printer heated bed? While we have already discussed in brief about the way heated beds are useful, let us find out more about them.
Heated Beds Using PCBs as Heating Element
A 3D printer heated bed design can differ. Among the most common types, the heated bed makes use of circuity boards or PCBs as the heating elements.
Among the most common types, the heated bed makes use of circuity boards or PCBs as the heating elements.
These are available with the budget 3D printers. However, these won’t last long if your 3D printing projects are complex and require frequent jobs with 3D printers. In short, they are meant for smaller projects that do not take much longer to complete.
The reason why these are not suitable for complex 3D printing is that the PCBs are made of copper s and aluminum strips.
And, these are susceptible to deformation when subjected to heat for longer periods. Over time, the heated beds will fail to do the task for which it was chosen in the first place.
There is one more problem that won’t be acceptable to many. These take a longer time for heating up. You can actually get rid of that problem. But you may have to spare some more bucks to get the larger power supply source connecting the bed.
ADVERTISEMENT
Heated Beds Using AC Silicone Encapsulating Heated Element
One more type of heated bed is the one that uses AC silicone encapsulating heated elements. To design the arrangement, the heated element is stuffed between glass pieces and a thermal insulator.
To design the arrangement, the heated element is stuffed between glass pieces and a thermal insulator.
This is to minimize the excess leakage of heat and to deliver the maximum amount of heat to the printing surface. Hence, realizing the efficient design for the creation of 3D printer heated bed.
Moreover, the electricity consumption is also less. And, they can work for longer without giving any trouble to the users.
You can 3D print without much hassle when using the heated bed with AC silicon encapsulating heated element. In addition, these are highly portable too. With all the right perks, it is worth spending a little more if your goal is to 3D print for long.
Working of 3D Printer Heated Bed
The 3D printer works by extruding the plastic filament over the printed bed. Right after coming out of the extruder, the filament starts cooling.
As we all know, with cooling shrinkage comes hand in hand. The problem arises when the layer does not cool consistently at all points. This leads to uneven shrinking and ultimately, warping of the entire 3D model.
This leads to uneven shrinking and ultimately, warping of the entire 3D model.
To avoid plastic from cooling at different rates at varied points, heated beds were introduced. The job of the 3D printer heated bed is to make sure that the parts do not cool completely unless the printing is still in process. This allows for a more even shrinking process.
In short, the heated beds mainly take care of two things. First of all, by increasing the surface energy of the print bed, the heated bed strengthens the bonding of the top layer.
Plus, it ensures that the bottom layer stays hot enough for avoiding the warping issue in any stage of the 3D Printing process. Hence, the heated bed maximizes the efficiency and avoid excessive cooling of the layers.
When the filament is deposited on the print bed through the extruder, it carries with itself a certain degree of heat. For the best results, the heated bed temperature must be below the glass point.
This is to turn the liquid filament in solid form.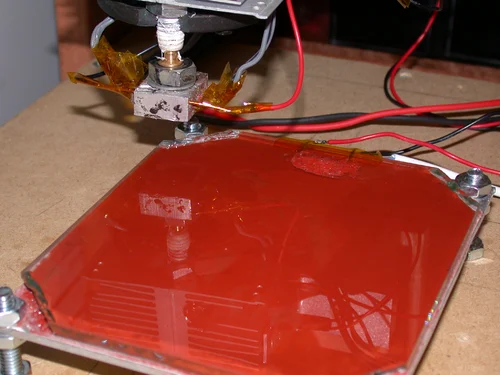 The temperature sensor is responsible for maintaining the required heat of the print bed.
The temperature sensor is responsible for maintaining the required heat of the print bed.
You may have to go through a few trial and error to understand the correct calibration of your machine based on the filament you use. This is because the melting point of filament differs widely.
ADVERTISEMENT
Few 3D Printer Heated Bed DIY Designs
We have already discussed the most basic one before. Let’s elaborate on the topic a little bit.
Apart from the PCB and AC Silicon encapsulating heating element, there are other DIY designs to replace your non-heated bed with a heated one.
Polyamide Film Heater
Polyamide which we also call Kapton is already providing huge benefit as a tape for print surfaces. These are best when used with PLA filament.
By providing efficient heat resistance, and high adhesion for printing with PLA, these are already very popular. These also help in increasing the surface finish of the 3D models.
However, you may not know that when coupled with a heating element which when sandwiched between two films of Polyamide you can come up with a Polyamide film heater.
Plus, they are simple to install as well by adding an adhesive to the back. These heat up really fast.
Moreover, these can be prepared in different shapes and sizes. And, are easily portable. Hence, a great choice for many 3D printing experts as well as beginners.
3D Printer Aluminium Clad Heater
If you are looking for the most effective as well as the inexpensive solution, this is what you must look for. However, do not forget, you may have to go through more steps for installing these heaters to your 3D Printer.
Not to forget, you must also require to screw these onto a surface. Usually, users suffice the arrangement with a stainless steel or 3D printer aluminum heated bed.
Later, you must complete the electric circuit arrangement using a thermistor and an insulator. It is the best way to go about it even if you do have any temperature sensible elements stuffed under the print bed.
Last but not the least, a thermal paste must stay between the clad heater and the build surface. This further enhances the healing process and brings more perks for the users.
This further enhances the healing process and brings more perks for the users.
ADVERTISEMENT
Do I Need A Heated Bed?
Because a lot of 3D printers do not have a heated bed, the question is: Is heated bed required? It is okay to be attentive to the details.
You may have heard that PLA does not need a heated bed to work with. Or, you may also have listened about printing ABS only with a printed bed. But what is the actual story?
You do need a heated bed when 3D printing with ABS material. But why is that so? ABS has the characteristic to contract more than other filaments.
Hence, the chances of warping become higher when printing with ABS. However, with the inclusion of a heated bed, the material finds it easy to attach to the bed surface, while reducing the chances for contraction.
Now, what about PLA. Do we require a heated bed or not? In the case of PLA, we do not always need a Heated Bed. However, if you wish to 3D print is longer, or the bottom surface is larger, it is better to use a heated bed to eliminate the chances of probable problems.
However, if you wish to 3D print is longer, or the bottom surface is larger, it is better to use a heated bed to eliminate the chances of probable problems.
Not just that, you must also understand the optimal temperature that you must maintain when working with different materials.
For instance, when working with ABS, you must heat your print bed to 110°C. On the other hand, PLA can be settled for a lesser temperature of around 60°C.
It is very easy to set the temperature of the heated bed with the help of the 3D Slicer. So, you can make the changes as and when required.
ADVERTISEMENT
Caution to Take When Working with Heated Beds?
Heated beds are maintained at a very high temperature. Though we cannot get rid of them because of the many benefits they add to the printing process, we must take the necessary precautions to work around them.
Users must carefully avoid injuries by staying alert and following preventive measures.
These heated beds, when it comes in contact with the skin can end up leaving scars for life. These are very hot and you must avoid any direct contact with the print surface.
These are very hot and you must avoid any direct contact with the print surface.
If you have kids around, you must take the necessary precautions when working with the 3D printers. If possible, you can go to the closed chamber.
This would anyway help to enhance the 3D print results by letting you maintain a consistent temperature around the build surface.
You may get yourself in other problems when the heated bed is not installed properly. In case, the legs of the bed aren’t positioned evenly, or the bed isn’t placed on a uniform surface, it would lead to imperfection in the 3D models.
It is a good idea to purchase the 3D printer with its own heated bed that comes with the package. This is to ensure that the two combos work together in harmony.
Or else, you may find it difficult to fit the parts from different vendors together because of the difference in the temperature gradient.
The Conclusion
It is a very common mistake that we make when avoiding to look for more details about the crucial components of the 3D printer. But we must not do that.
But we must not do that.
3D printers are expensive and before buying one, we must understand what we should look for, depending on our needs.
And, even if a 3D printer heated bed seems to be something not needed at the moment, it may help you stretch your goals later.
So, understand the benefits of the same and look for 3D printers that offer a heated bed already.
Why do I need a heated table for a 3D printer?
3DPrintStory 3D printing process Why do you need a heated table for a 3D printer?
With the development of 3D printing, a lot of new research and experiments have appeared. Many of them are aimed at finding the best way to increase the adhesion of the first layer.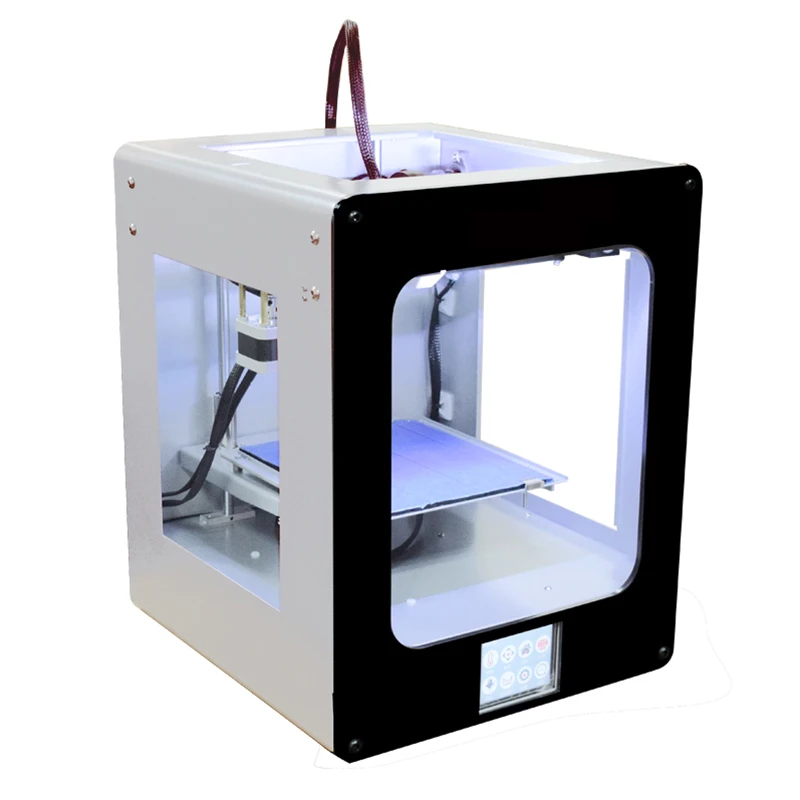
And we all know why this is so important. A standard heated 3D printer table will do the job. Although there are other alternatives when working with the first layer, nothing compares to this one.
Most importantly, 3D printer tables are a very important part of the overall design. In fact, without a table, you will not be able to create physical embodiments of your 3D models. Therefore, understanding how you can make the best use of the table should be your top priority for quality 3D printing. Understanding and navigating the different types of heated tables and their features will definitely help you choose the right 3D printer and implement your own ideas.
But before we get into all the 3D printer heated tables, let's get to the bottom of what 3D printing is. Most of us are already aware of this, but a brief overview will ensure that we are on the same wavelength in the context of the current article.
What is 3D printing?
We have been hearing about additive manufacturing or 3D printing for a long time.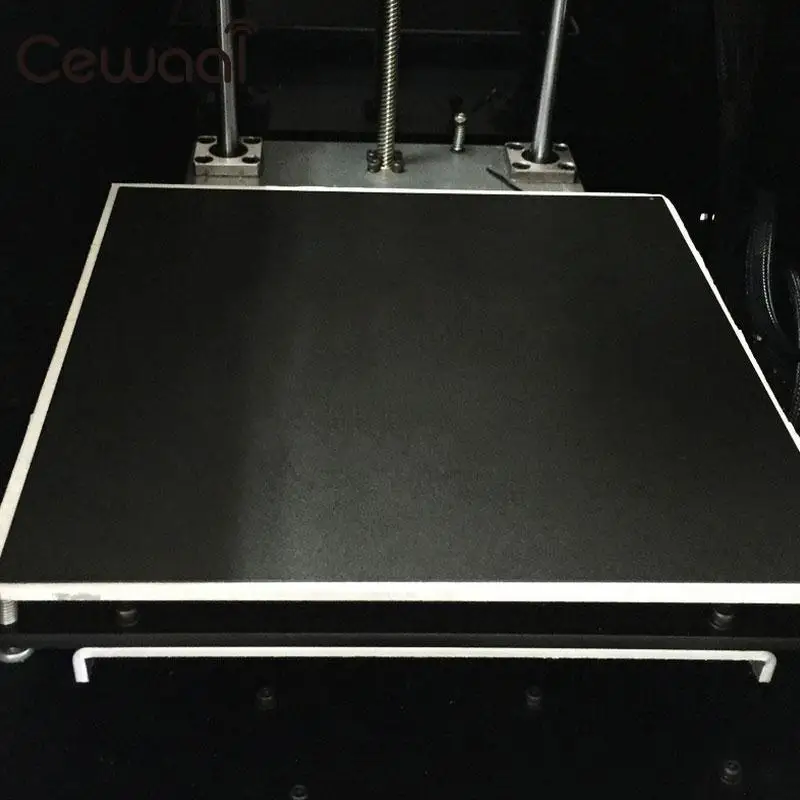 And the lucky ones who had a chance to work with this technology at least once are becoming more and more every day.
And the lucky ones who had a chance to work with this technology at least once are becoming more and more every day.
3D printing has become one of the most revolutionary technologies and is spreading very quickly, influencing the entire ecosystem of production, industry and hobby.
3D printing is a process in which 3D printers create layers one on top of the other to create a finished product of the desired shape and dimensions.
3D printing may differ in the principle of creating 3D models. For example, there are FDM, SLS, SLA and many others. They differ in the way the layers are created and connected. However, the fundamentals remain the same. Layers are stacked on top of each other to build the entire 3D model.
3D printing has made it possible to create extremely detailed models and designs in a short time and in many cases cheaper than classic manufacturing processes. But when using a 3D printer, certain precautions must be taken to ensure that the finished product exactly matches the desired characteristics.
However, 3D printing has its own problems. And the biggest of them is too fast heating and cooling of the layers of the 3D model. One of the major problems that arise from improper heating/cooling is shrinkage. It changes the shape of the 3D model and deforms it. Therefore, in this case, we get low-quality products.
To solve this problem, heated tables for 3D printers have appeared. These tables, among other things, are designed to maintain the required temperature of the first layers of the model and the entire model as a whole. They help control the temperature during the entire 3D printing process. Therefore, this additionally results in proper adhesion of the first layer throughout the entire 3D print time of your model.
What is a heated 3D printer bed?
Returning to the main topic of the article, we must answer the question: what is a heated table for a 3D printer? Although we have already briefly discussed the usefulness of heated tables, let's learn more about them.
Heated tables using printed circuit boards as heating element
Heated tables for 3D printer designs may vary. Among the most common types of heated tables, mounting or printed circuit boards are used as heating elements. They usually come with budget 3D printers. However, this solution is not very suitable if your 3D printing projects are complex and require frequent work with a 3D printer. In short, they are designed for small projects that do not take much time to complete.
The reason why they are not suitable for complex 3D printing is that PCBs are made of copper and aluminum plates, and they are prone to deformation when heated for a long time. Over time, heated plates will no longer perform the task for which they were originally designed.
There is another problem that may arise. They take longer to heat up. You can get rid of this problem, but for this you will need to replace the power supply with a more powerful one.
Heated tables using AC silicone encapsulating heating element
The second type of heated 3D printer table is one that uses silicone to encapsulate the heated elements. To create a structure, a heated element is inserted between pieces of glass and a heat insulator.
To create a structure, a heated element is inserted between pieces of glass and a heat insulator.
This is to minimize excess heat leakage and to deliver maximum heat to the table surface. In addition, electricity consumption also becomes smaller. And they can work longer without causing any problems to users.
This version of the heated table design is much more reliable and can last you much longer. In addition, the bill for the consumed electricity will also be reduced due to the minimization of losses for heating the table.
Heated table 3D printer operation process
The 3D printer works by extruding a plastic filament onto the table. Immediately after exiting the extruder, the material begins to cool. As we all know, shrinkage goes hand in hand with the cooling process. The problem arises when the layer is not cooled uniformly at all points. This leads to uneven shrinkage and, ultimately, to deformation of the entire 3D model.
To avoid cooling the plastic at different rates at different points, heated tables have been developed. The job of a heated 3D printer bed is to ensure that the parts do not cool completely until the 3D print is complete. This allows for a more uniform shrinkage process.
The job of a heated 3D printer bed is to ensure that the parts do not cool completely until the 3D print is complete. This allows for a more uniform shrinkage process.
In short, heated tables basically take care of two things. First of all, by increasing the surface energy of the printing table, the heated layer enhances the adhesion of the first layer. Secondly, a sufficiently high temperature of the lower layer is ensured, which avoids the problem of deformation at any stage of the 3D printing process. Therefore, the heated bed maximizes efficiency and avoids excessive cooling of the layers.
When material hits the 3D printer bed through the extruder, it carries a certain amount of heat with it. For best results, the temperature of the heated bed should be below the glass transition point. This should turn the liquid thread into a solid form. The temperature sensor is responsible for maintaining the required temperature of the table.
You may need to experiment to find the optimum table temperature, as the melting point of different materials and manufacturers is different.
Several DIY Heated Table Designs for 3D Printer
The basics have already been discussed above, now let's look at some interesting DIY solutions.
In addition to the PCB and AC sealed heating element, there are other DIY designs to replace your table with a heated table.
Polyamide Film Heater
Polyamide, which we also call Kapton, offers a huge advantage when used as a tape for printable surfaces. They are best suited for use with PLA plastic. Providing effective heat resistance and high adhesion for PLA printing, this film is very popular. The use of this film helps to improve the surface quality of 3D models.
However, you may not know that in combination with a heating element sandwiched between two polyamide films, you can get a polyamide film heater. In addition, they are easy to install by adding glue to the back. They heat up very quickly. In addition, they can be of different shapes and sizes. So this is a great option to upgrade your 3D printer table.
Aluminum Coated 3D Printer Heater
If you are looking for an efficient and cost effective solution, this is the one for you. However, keep in mind that installing these heaters on your 3D printer may require some work.
After installing the heaters, it is necessary to close the electrical circuit using a thermistor and an insulator. Last but not least, the thermal paste must remain between the lined heater and the build surface.
Do you need a heated table for your 3D printer?
Since many 3D printers do not have a heated bed, the question is, do you need a heated bed?
You may have heard that working with PLA plastic does not require a heated table. Or perhaps you've only heard of ABS printing on a heated table. But what is the truth?
When 3D printing with ABS you will need a heated table. Why is that? ABS tends to compress more than other materials. Therefore, the likelihood of deformation increases when 3D printed using ABS. With the table heating turned on, the material will better set on the first layer, minimizing potential deformations at the edges of the 3D model.
With the table heating turned on, the material will better set on the first layer, minimizing potential deformations at the edges of the 3D model.
What about PLA? Do we need a heated table or not? In the case of PLA, heating is not always needed. However, if you want to print large models, it is better to use a heated bed to eliminate the possibility of possible problems.
As mentioned above, you also need to know the optimum temperature for your material. Otherwise, there will be no point. For example, when working with ABS, it is recommended to heat the table to 110 ° C. On the other hand, when using PLA, it is worth stopping at 60 ° C. By the way, the temperature of the 3D printer table is set at the stage of processing the model in the 3D slicer.
3D Printer Heated Table Precautions
Heated tables maintain very high temperatures, so you should take the necessary precautions.
Heated tables can leave scars for life if they come into contact with the skin. They are very hot, so direct contact with their surface should be avoided.
They are very hot, so direct contact with their surface should be avoided.
If you have children, you must take the necessary precautions when working with 3D printers.
If the heated table is not properly installed, you may experience other problems. If the legs of the table are uneven or the table is not placed on a level surface, this can lead to defective 3D models.
Conclusions
Heated table is an almost essential attribute of a 3D printer, which will provide high-quality 3D printing using various types of materials. If possible, it is better to buy a ready-made heated table, and not develop it yourself, since many subtle nuances in the assembly will already be taken into account. Remember to take precautions when working with heating elements and good luck with your 3D printing.
heating connection, from which to make heating from 220 volts
Depending on the type of plastic used during printing, the 3D printer's desktop may need to be heated. In addition, budget devices do not always have such a function. Therefore, many make a heating table with their own hands.
In addition, budget devices do not always have such a function. Therefore, many make a heating table with their own hands.
Heating table for 3D printer
The heating table is a working surface consisting of several layers, one of which has a heating element. On the heating table and prints the printer.
The heater usually has a serpentine pattern.
Why is heating needed?
Using a heated bed during 3D printing is a simple and reliable way to protect finished products from uneven cooling, which often causes deformation of the part. Even on the cheapest printer, you can get good quality models using a heated work surface.
How to make a table for a 3D printer with your own hands?
Types of heating tables:
- Textolite. This is the most affordable option. The textolite table consists of a textolite plate with copper tracks applied to it. Most often, they are powered by 12 or 24 V. Direct printing on a textolite sheet will not work, since it is quite flexible and deforms during heating.
 Glass is attached to it from above to stiffen and level the surface.
Glass is attached to it from above to stiffen and level the surface. - Aluminium. Textolite is also used in aluminum tables, but instead of glass, an aluminum sheet is laid on top.
- Silicone. Can be flexible or rigid, depending on the design. It consists of a heating element, which is filled with heat-resistant silicone.
Step-by-step instructions
The easiest way to make a table is with silicone. To do this, you will need to prepare the following materials:
- nichrome wire with a diameter of 0.2 mm;
- sheets of cardboard;
- mounting tape;
- small-headed nails;
- glass;
- heat resistant silicone sealant.
Manufacturing process:
- Several sheets of cardboard are stacked on top of each other and held together with adhesive tape.
- With the help of studs, a regular checkered sheet is attached.
- Hats are recessed and aligned.
- Tape strips are glued on the sides (next to the hats).
- The studs are carefully removed so that everything stays in place.
- The paper is also carefully removed.
- Glass wiped with alcohol. After that, the resulting design is glued to the glass. First you need to glue one strip, and then the second with a stretch.
- Lubricate everything liberally with heat-resistant sealant (except adhesive tape). The layer must be at least 2 mm.
- After drying, the adhesive tape is removed and the empty spaces are also smeared with silicone.
- A wire is soldered to the end of the wire to connect to the mains.
Mistakes and how to avoid them
It is important to correctly calculate the length and thickness of the wire.












