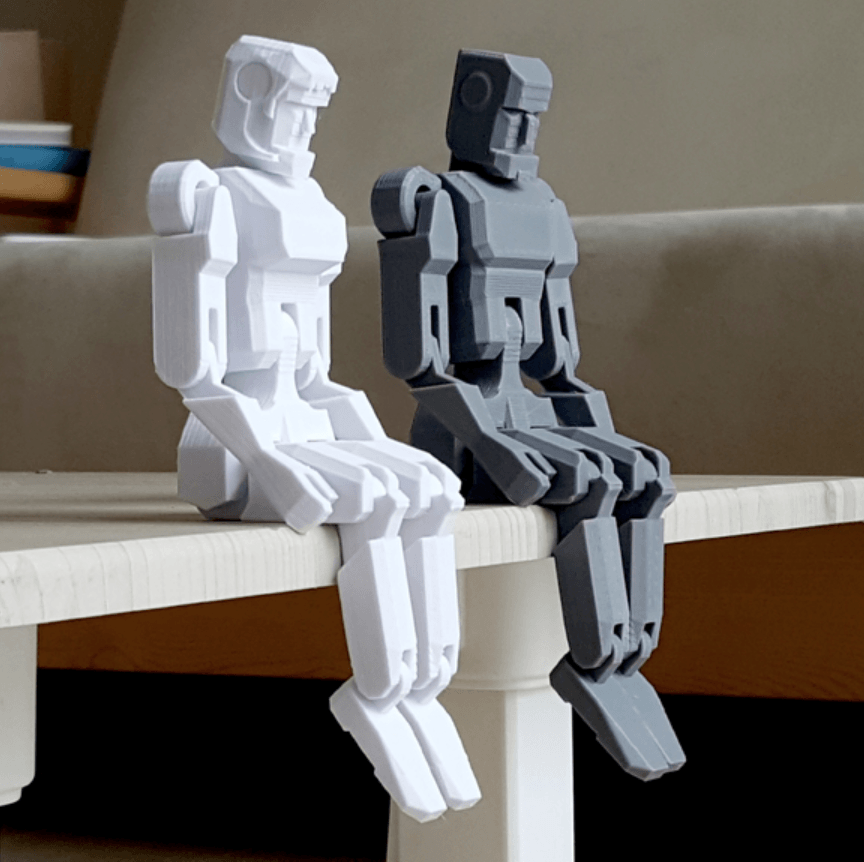
Best flexible 3d printer filament
Best Flexible (TPU/TPE) 3D Printing Filaments in 2023 – Clever Creations
3D printing with flexible filaments opens up a world of possibilities for your projects. From soft washers to shoe insoles to phone cases, you can make all sorts of strong elastic parts from flexible materials. However, with so many different types of flexible filaments available for 3D printing, it can be difficult to know which type, brand, and hardness to choose for your projects.
That’s where we come in! We’ll cover which brands have the best flexible filament, the recommended printing temperatures and other print settings for each brand, the differences between each flexible material, and what to look for when buying so you can always find the best TPU filament possible.
| Best Flexible Filament | Shore | Diameters | Colors | Price | Best Offer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SainSmart Flexible TPU | 95A | 1.75mm | 18 | $25 per 800g | Amazon |
| Ninjatek TPU | 85A | 1. | 11 | $85 per 1kg | Amazon |
| Overture TPU | 95A | 1.75mm | 17 | $24 per 1kg | Amazon |
| FormFutura FlexiFil | 45D | 1.75mm, 2.85mm | 5 | $43 per 500g | Amazon |
| Duramic TPU | 95A | 1.75mm | 5 | $27 per 1kg | Amazon |
| Fillamentum Flexfill TPU | 92A, 98A | 1.75mm, 2.85mm | 20 | $41 per 500g | 3DJake |
| Fillamentum TPE | 92A, 96A | 1.75mm | 5 | $41 per 500g | 3DJake |
| Recreus Filaflex TPU | 60A - 98A | 1.75mm, 2.85mm | 18 | $47 per 500g | 3DJake |
| Polymaker TPU | 95A | 1.75mm, 2.85mm | 6 | $30 per 750g | Polymaker |
| ColorFabb Ngen Flex | 95A | 1. 75mm, 2.85mm 75mm, 2.85mm | 3 | $40 per 650g | MatterHackers |
| MatterHackers Pro Series TPU | 95A | 1.75mm, 2.85mm | 7 | $44 per lb | MatterHackers |
The Best Flexible Filaments in 2023
SainSmart Flexible TPU
Best overall
Check Price
AmazonSainSmart
If you’re looking for a strong and versatile flexible 3D printer filament at a good price point, SainSmart TPU is an excellent choice. With a shore hardness of 95A, it produces durable and rigid 3D prints that are still flexible enough to retain their shape even when significantly bent and deformed.
SainSmart TPU is known for having excellent bed adhesion and virtually no warping when printed with the proper settings. They even provide printer profiles for a wide variety of popular 3D printer models that you can download and load into your slicer for their best-recommended settings for your machine.
You have a lot of versatility in terms of color since SainSmart currently offers 18 different shades for this product. It also has the lowest temp range of any of the flexible 3D printer filaments on this list. If you are worried about your 3D printer’s hot end performance, this should be the easiest to get good results with.
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Material | TPU |
| Diameters | 1.75mm |
| Spool Sizes | 800g |
| Shore Hardness | 95A |
| Elongation at Break | Not specified |
| Colors | 18 |
| Extrusion Temperature | 195°C - 230°C |
| Bed Temperature | 40°C - 60°C |
Ninjatek TPU
Best high-end
Check Price
AmazonMatterHackers
As one of the more expensive options on the list, Ninjatek TPU filament earns its higher price point for its great print quality, ease of use, and optimal performance. Suggested for use with sports equipment, medical devices, and industrial manufacturing, it is an excellent option for commercial applications.
Suggested for use with sports equipment, medical devices, and industrial manufacturing, it is an excellent option for commercial applications.
Ninjatek TPU is known for its vibration dampening, chemical resistance, and abrasion-resistant properties. Its shore hardness of 85A gives the material enough rigidity to withstand repeated high-impact force without failing.
Optimized for easy 3D printing, Ninjatek is textured for better feeding through the extruder. It also boasts a high degree of dimensional accuracy for easy and consistent extrusion in most 3D printers.
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Material | TPU |
| Diameters | 1.75mm, 2.85mm |
| Spool Sizes | 500g, 1kg, 2kg |
| Shore Hardness | 85A |
| Elongation at Break | 660% |
| Colors | 11 |
| Extrusion Temperature | 225°C - 250°C |
| Bed Temperature | Up to 40°C |
Overture TPU
Best on a budget
Check Price
Amazon
Another affordable flexible TPU filament option, Overture, boasts a wide variety of colors, multipacks, and additional discounts for bulk buying.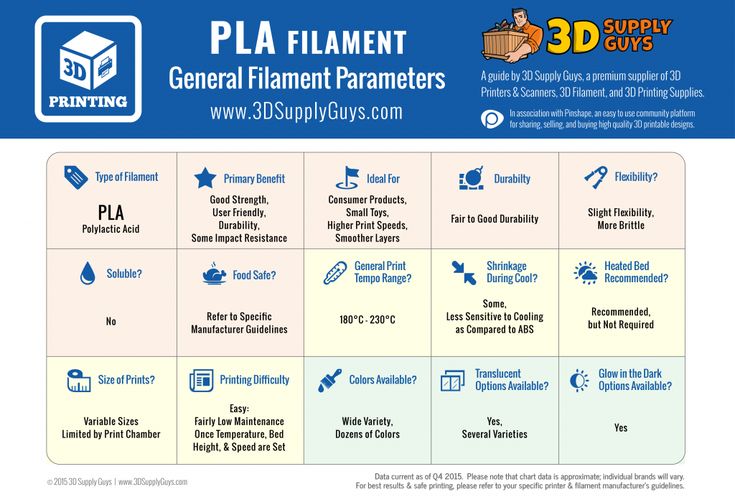 If you have a large project to do and need a lot of filament, this is one of the most cost-efficient brands on the list.
If you have a large project to do and need a lot of filament, this is one of the most cost-efficient brands on the list.
Like other TPU brands, Overture has great bed adhesion and very little warping, so it is easy to get good base layers on your prints. It also has very little odor while printing, so it does not overpower your home if you have to print inside (though a ventilated 3D printer enclosure is a good practice for anyone printing within their home).
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Material | TPU |
| Diameters | 1.75mm |
| Spool Sizes | 1kg |
| Shore Hardness | 95A |
| Elongation at Break | 300% |
| Colors | 17 |
| Extrusion Temperature | 210°C - 230°C |
| Bed Temperature | 25°C - 60°C |
FormFutura FlexiFil
Highest temperature resistance
Check Price
Amazon3DJake
When you need a flexible material with higher heat resistance than typical flexible TPU filaments offer, using a TPC product like FormFutura FlexiFil should do the trick. With higher heat resistance comes higher print temperatures and a bigger learning curve. However, TPC filaments usually have little to no warping, so while the temperatures are closer to ABS filament, they won’t have the same adhesion problems.
With higher heat resistance comes higher print temperatures and a bigger learning curve. However, TPC filaments usually have little to no warping, so while the temperatures are closer to ABS filament, they won’t have the same adhesion problems.
In addition to heat resistance, FlexiFil is also resistant to chemicals and UV exposure. With a shore hardness of 45A, it is much softer than the other products we have looked at so far. However, with that added elasticity, it also has something called flexural memory, which means it will return to its original shape with no deformation when stretched.
Even with its softer composition, FlexiFil is strong and durable with high impact resistance. It is also a more eco-friendly option since it is made from 43% bio-materials.
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Material | TPC |
| Diameters | 1.75mm, 2.85mm |
| Spool Sizes | 250g, 500g |
| Shore Hardness | 45A |
| Elongation at Break | Not Specified |
| Colors | 5 |
| Extrusion Temperature | 220°C - 260°C |
| Bed Temperature | 90°C - 110°C |
Duramic TPU
Best for Bowden extruders
Check Price
Amazon
Duramic’s TPU filament is notable not only for its affordable price point but also because it is specially formulated to work just as well with Bowden extruders as it does with direct-drive extruders. It’s also designed to be jam-free in general for an easier and more consistent printing experience.
It’s also designed to be jam-free in general for an easier and more consistent printing experience.
It has a shore hardness of 95A and an elasticity of 300% more than its starting length, making it a rigid but impact-resistant option that is perfect for manufacturing parts and tools. Duramic TPU filament has a +/-0.05mm tolerance for good dimensional accuracy. This also helps keep clogging, jamming, and other extrusion issues to a minimum in your 3D printer.
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Material | TPU |
| Diameters | 1.75mm |
| Spool Sizes | 1kg |
| Shore Hardness | 95A |
| Elongation at Break | 300% |
| Colors | 5 |
| Extrusion Temperature | 220°C - 230°C |
| Bed Temperature | 25°C - 60°C |
Fillamentum Flexfill TPU
Best UV resistance
Check Price
3DJakeMatterHackers
Fillamentum offers two different versions of their FlexFill TPU filaments: 92A and 98A. These numbers refer to their respective shore hardnesses and overall rigidity. While both have fairly high levels of rigidity, the 92A line of TPU filament has higher elastic and reversible deformation properties. The 98A line of TPU filament is semi-flexible material with improved UV resistance.
These numbers refer to their respective shore hardnesses and overall rigidity. While both have fairly high levels of rigidity, the 92A line of TPU filament has higher elastic and reversible deformation properties. The 98A line of TPU filament is semi-flexible material with improved UV resistance.
Both products have high tear and tensile strength, good rebound resilience, little to no warping, and high abrasion resistance. They are both resistant to oils, greases, ozone, and aliphatic alcohols. They are also both safe to use in and around electrical and electronic equipment.
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Material | TPU |
| Diameters | 1.75mm, 2.85mm |
| Spool Sizes | 230g, 500g |
| Shore Hardness | 92A, 98A |
| Elongation at Break | |
| Colors | 20 |
| Extrusion Temperature | 220°C - 240°C |
| Bed Temperature | 50°C - 60°C |
Fillamentum TPE
Best food-safe flexible filament
Check Price
3DJake
Like their TPU products, Filamentum’s TPE filament has two different products named based on their shore hardness: 90A and 96A. The 90A products are flexible while the 96A products are semi-flexible.
The 90A products are flexible while the 96A products are semi-flexible.
These products are both certified as safe for food contact and skin contact and have a soft, pleasant surface texture. They both have high degrees of tear strength and abrasion resistance. They are chemically resistant to alkalis, water, alcohol, and acids. They also have very low moisture absorption, making them ideal for outdoor use.
Their tensile strength and elasticity are much lower than the TPU lines, so consider whether you need greater strength against mechanical stress or weather conditions when choosing between the two options.
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Material | TPE (polyolefin + SEBS) |
| Diameters | 1.75mm |
| Spool Sizes | 230g, 500g |
| Shore Hardness | 92A, 96A |
| Elongation at Break | 250% (92A), 150% (96A) |
| Colors | 5 |
| Extrusion Temperature | 224°C - 245°C |
| Bed Temperature | 50°C - 60°C |
Recreus Filaflex TPU
Most eco-friendly
Check Price
3DJake
Recreus Filaflex TPU filament has several different product offerings. They have separate lines based on the product’s shore hardness and include the following measurements: 60A, 70A, 82A, and 95A. They also have specialty flexible filaments, like conductive filament and their Reciflex and Purifier lines.
They have separate lines based on the product’s shore hardness and include the following measurements: 60A, 70A, 82A, and 95A. They also have specialty flexible filaments, like conductive filament and their Reciflex and Purifier lines.
The regular Filaflex options are resistant to solvents, acetone, and fuel. They are also rated safe for skin contact but have not been officially approved for food or medical use. They have good bed adhesion and don’t need adhesives or surface covers to avoid warping. They also are formulated to work well with a wide variety of 3D printers, including those with a Bowden setup.
Their specialty TPU filament options each have their own intended use. Conductive TPU is named as such because it is electrically conductive. This is useful for fabricating conductive prints for devices. Reciflex is a 100% fully recycled TPU filament using waste left over from Recreus’s own production and from waste from the footwear industry.
Filaflex Purifier is especially interesting. It is designed to be a sustainable environmentally-friendly 3D printer filament option. It absorbs pollutants and greenhouse gasses and turns them to mineral waste using a process known as gas mineralization.
It is designed to be a sustainable environmentally-friendly 3D printer filament option. It absorbs pollutants and greenhouse gasses and turns them to mineral waste using a process known as gas mineralization.
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Material | TPU |
| Diameters | 1.75mm, 2.85mm |
| Spool Sizes | 500g, 3kg |
| Shore Hardness | 60A, 70A, 82A, 95A, 82A (Purifier), 92A (Conductive), 96A-98A (Reciflex) |
| Elongation at Break | 500% - 900% |
| Colors | 18 |
| Extrusion Temperature | 215°C - 250°C |
| Bed Temperature | 50°C - 60°C |
Polymaker TPU
Check Price
AmazonPolymakerMatterHackers
PolyFlex TPU filament is another excellent option for flexible filaments. It is a rigid material with a shore hardness of 95A, with enough elasticity to keep its impact resistance high. It is designed to be compatible with a wide variety of machines, though it does still suggest the use of a direct drive extruder in your 3D printer.
It is a rigid material with a shore hardness of 95A, with enough elasticity to keep its impact resistance high. It is designed to be compatible with a wide variety of machines, though it does still suggest the use of a direct drive extruder in your 3D printer.
It comes in a resealable aluminum package and has a filament gauge and print settings printed directly onto the spool. It has limited color options, but each color available is vibrant and available in both common diameters (1.75 mmand 2.85 mm).
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Material | TPU |
| Diameters | 1.75mm, 2.85mm |
| Spool Sizes | 750g |
| Shore Hardness | 95A |
| Elongation at Break | 300% |
| Colors | 6 |
| Extrusion Temperature | 210°C - 230°C |
| Bed Temperature | 25°C - 60°C |
ColorFabb Ngen Flex
Check Price
MatterHackers
If you want a multipurpose flexible filament for your 3D printing projects, ColorFabb’s Ngen Flex TPU filament is an excellent choice. Designed to work across multiple 3D printer models, you can use it with a Bowden extruder at a normal print speed with little to no issues. This product is as close to using a traditional 3D printer filament as a flexible filament can get.
Designed to work across multiple 3D printer models, you can use it with a Bowden extruder at a normal print speed with little to no issues. This product is as close to using a traditional 3D printer filament as a flexible filament can get.
Because it is temperature resistant up to 125°C, your 3D prints can be steam-sterilized. This trade-off comes at needing a slightly higher printing temperature than the other TPU filaments on this list. It also moves a heated bed from an optional feature to a requirement.
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Material | TPU |
| Diameters | 1.75mm, 2.85mm |
| Spool Sizes | 650g |
| Shore Hardness | 95A |
| Elongation at Break | Not Specified |
| Colors | 3 |
| Extrusion Temperature | 240°C - 260°C |
| Bed Temperature | 80°C (BuildTak) |
MatterHackers Pro Series TPU
Most consistent diameter
Check Price
MatterHackers
The Pro Series TPU filament by MatterHackers is another excellent choice for when you need a reliable and strong flexible 3D printer filament. With a +/-0.02mm tolerance, they have some of the most refined dimensional accuracy allowances in the flexible filament market. Most of the other TPU filaments have a tolerance range of +/- 0.05-0.10mm.
With a +/-0.02mm tolerance, they have some of the most refined dimensional accuracy allowances in the flexible filament market. Most of the other TPU filaments have a tolerance range of +/- 0.05-0.10mm.
Dimensional accuracy is especially important when dealing with flexible filaments since jams and clogs are already an issue due to their elasticity, so if you want a brand with excellent quality control and fewer mechanical failures on your 3D printer, MatterHackers Pro Series is an excellent choice.
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Material | TPU |
| Diameters | 1.75mm, 2.85mm |
| Spool Sizes | 1lb |
| Shore Hardness | 95A |
| Elongation at Break | 508% |
| Colors | 7 |
| Extrusion Temperature | 220°C - 240°C |
| Bed Temperature | Up to 40°C |
Buying Flexible Filament: Things to Pay Attention To
Material
TPE
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) is a term for a broad range of flexible filaments and elastic thermoplastics, including TPU filament. TPE typically refers to polymers with a lower shore hardness, density, and surface smoothness than TPU, but since it covers such a broad range of flexible materials, its properties can vary significantly.
TPE typically refers to polymers with a lower shore hardness, density, and surface smoothness than TPU, but since it covers such a broad range of flexible materials, its properties can vary significantly.
TPU
One of the most common flexible filaments made for 3D printing, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a transparent elastic material that is known for having a high level of shear strength and abrasion resistance. It also has good chemical and impact resistance, as well as resistance to oils and grease. TPU has little tolerance for heat and absorbs moisture much like PLA does. For that reason, it can be useful to use a proper filament storage solution while the filament is not in use.
Recommended:
The 10 Best Filament Storage Containers and Dry Boxes
PEBA
Polyether block amide (PEBA) is a special TPE that was first introduced into the 3D printing industry as a powder for SLS 3D laser sintering. Several companies have now adapted the material into a flexible filament for use in 3D printing.
PEBA is a popular flexible filament material because it has some of the best elasticity with a typical elongation at break range of >500%. It also has excellent chemical, impact, and temperature resistance.
TPS
Thermoplastic polystyrene (TPS) is a softer more rubber-like flexible filament material that is characterized by good elasticity (>500%), higher moisture resistance, and smooth surfaces in 3D printing.
Elongation at Break
Elongation at break is a measurement of how far flexible materials can stretch before they break. Usually represented as a percentage, it shows how much a flexible material can elongate past its original length. A filament with an elongation at break of 500% can stretch five times its original length before breaking.
3D Printer Compatibility
Extruder Type
TPU filament and other flexible materials work best with a direct drive extruder. Bowden-style extruders (one of the more popular setups for 3D printers and the factory configuration for several models like the Ender 3) push the filament toward the nozzle through PTFE tubes.
Usually, the Bowden extruder is mounted to one of the body rails of the 3D printer, so the filament has to travel about a foot and a half to the hot end, but that distance can be more or less depending on the printer.
Direct drive extruders are mounted directly to the print head and located right above the nozzle. Since they are so close to the hot end, direct-drive extruders don’t have as many issues with filament bunching, extruder jams, and clogs as Bowden extruders do.
Maximum Nozzle Temperature
To successfully print with TPU filament, 3D printers should have a maximum extruder temperature of at least 250°C. That is the high end of what the majority of flexible filament brands call for. However, there are some exceptions, so if you want more options, a maximum extrusion temperature of 260°C or 275°C is more reasonable.
Maximum Bed Temperature
Most TPU brands don’t require a heated bed to print and don’t recommend a print bed temperature over 60°C if you plan to use one.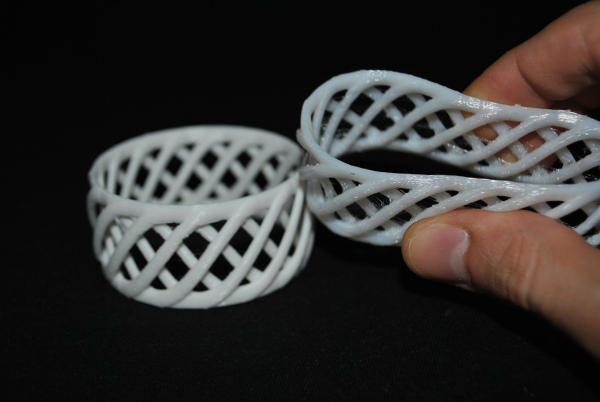 If you do have a heated bed, you should be fine as long as it reaches 40-60°C. If you don’t have a heated bed, you should still be just fine with several different brands. Ninjatek, MatterHackers, and SainSmart are some of the best brands of TPU to use without a heated platform.
If you do have a heated bed, you should be fine as long as it reaches 40-60°C. If you don’t have a heated bed, you should still be just fine with several different brands. Ninjatek, MatterHackers, and SainSmart are some of the best brands of TPU to use without a heated platform.
There are a few specialty filaments on our list that need a higher bed temperature. ColorFabb Ngen Flex, for example, suggests an 80°C heated bed for their product since it is formulated to have higher heat resistance than a typical TPU filament. Always be sure to double-check the manufacturer’s recommended settings before buying to ensure you aren’t getting an outlier when your 3D printer doesn’t have the necessary hardware for it.
Shore Hardness
Shore hardness is a measurement of how hard rubber and rubber-like objects are. There are technically three different shore hardness scales, but the one most relevant to flexible filaments and 3D printing is the ‘Shore A’ scale. For reference, a rubber band is a 20A, a pencil eraser is a 40A, a car tire is about 70A, and a shopping cart wheel is about 95A.
Shore hardness measures rigidity, but it does not measure flexibility, so keep that in mind. Just because a filament has the same shore hardness as, say, a shopping cart wheel, does not mean it will be as inflexible as the cart tire. Only that it can be. Flexibility is measured by the elongation at break, which we already discussed above.
What Can You Use Flexible Filament For?
Flexible filament has a myriad of uses, including industrial, medical, automotive, sports, hobby, and fashion.
Parts and Industrial Manufacturing
Certain parts can benefit from the elasticity and durability of flexible filament. Industrial parts that need to withstand mechanical stress while retaining their shape and structure are a perfect use for TPU thanks to its high shear strength.
Even replacement washers, sealant rings, hose adapters, cable ties, elastic bands, straps, furniture bumpers, and other household items are good candidates for flexible filament.
Medical
The use of TPEs in the medical field has long been established. With the introduction of TPU filament, greater emphasis has been placed on flexible 3D printing in the medical community to fabricate things like prosthetics, parts for medical devices, models for education, and prototypes for artificial organs.
Sports
Flexible filaments are being widely utilized in the manufacturing of sports equipment. Padding and bracers in helmets, shoe insoles, chin straps, mouth guards, and other parts are easy to fabricate using TPE and TPU filament in 3D printing.
Hobby
Hobby applications for 3D printing with flexible filament include fabricating parts and upgrades for devices. Drone parts, RC tires, bicycle/motorcycle/etc. handle grips, and more are just a few of the ways TPU filaments can be utilized by hobbyists and prosumers.
Bumper cases for phones, GoPros, and other electronics are good projects for flexible filaments. Laptop sleeves, keyboard covers, and other protective objects have long been manufactured by TPEs.
Fashion
Flexible filament can also work well for applications in the fashion industry. Accessories like watchbands, jewelry, wallets, and belts are easily made with 3D printing TPU flexible filaments.
Some users have also tested the efficacy of TPU filament and other TPE materials for printing footwear with a fair bit of success. Sneakers, sandals, and shoe insoles have all been made from flexible TPU filaments with interesting results.
Tips for Printing With Flexible Filament
Flexible filament can be difficult to use in 3D printing because its elastic properties allow it to bend and elongate in areas where it ideally shouldn’t. Using the proper settings and temperatures for TPU while 3D printing with TPU filament negates some of these issues.
When 3D printing with TPU filament or other flexible materials, be sure to:
- Print slowly. An ideal printing speed for TPU filament is well below the normal printing speed for other filament materials.

- Turn off retraction. Using retraction while 3D printing TPU filament can cause jams, clogs, and mechanical failures in your 3D printers. Turn it off completely or use the lowest retraction settings possible.
- Reduce tension on your filament spool. Place your spool somewhere that will reduce tension while the filament is feeding into the extruder to avoid print quality issues and mechanical failures like jams and clogs.
- Change your infill settings to make your flexible part more or less elastic. More infill makes your prints stiffer and less flexible, while less does the opposite. Different infill patterns also offer different elasticity results. You might not want to use the strongest infill pattern when looking for flexibility.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to use flexible filaments in a Bowden extruder?
Yes, you just have to make sure your temperature settings are dialed in, that none of the tubing makes the filament “stick”, and that you adjust the feed rates to a much slower pace. Or you can simply choose one of the brands like ColorFabb Ngen Flex that is designed to work well with a Bowden extruder.
Or you can simply choose one of the brands like ColorFabb Ngen Flex that is designed to work well with a Bowden extruder.
My TPU filament absorbed moisture. Can I salvage the spool or should I toss it?
It’s important to note that TPU filaments are extremely susceptible to moisture. Just as much—if not more—than PLA. It has to be kept vacuum sealed when not in use and placed in an air-tight container with a desiccant pack after it is open to keep it from taking on moisture from the air.
If it does get affected by moisture, a few hours in a food dehydrator or filament dryer should remove enough of the moisture to make the filament usable again.
Which is better: TPU or TPE?
What qualifies as “better” greatly depends on what your specific needs are. TPE is just a category for flexible thermoplastics anyway. Many brands don’t differentiate between the other non-TPU thermoplastic elastomers and just label them TPE. Therefore, TPE filaments can have a broad range of attributes from moisture resistance to heat tolerance to acid resistance. You just need to determine which attributes your project needs the most.
You just need to determine which attributes your project needs the most.
What is the difference between TPU and PLA?
One of the biggest differences between TPU and PLA is that TPU is a thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), while PLA is a thermoplastic polymer (TP). This means that TPU can be both elastic and plastic, while PLA can only be plastic.
TPU is also much more flexible than PLA, absorbs moisture more easily, and has a higher resistance to wear and tear. On the other hand, PLA is biodegradable, easier to print with, and has a lower melting point.
Which is more flexible, TPE or TPU?
TPU is generally more flexible than TPE. However, there are many different types of TPE filament with different levels of flexibility, so it really depends on the specific filament you are using.
Does TPU have toxic fumes?
No, TPU does not have toxic 3D printing fumes. However, just like all 3D printing filaments, it is best used in a well-ventilated area or with an enclosed 3D printer.
Is TPU filament expensive?
Compared to other filament materials, such as ABS and PLA, TPU is significantly more expensive. Typical prices for TPU are 2 to 3 times higher per kg, even though the best TPU filament can increase your 3D printing costs even more. You can, however, find good budget TPU from brands like SainSmart and Overture.
Can the Ender 3 use TPU?
The Ender 3 3D printer is not specifically designed to use TPU filament, but it is possible to use it with some modifications. We have a list of Ender 3 hardware upgrades you can check out to make printing TPU material easier.
Aside from that, you may need to adjust the print settings and increase the extruder temperature to get optimal results.
What is the softest TPU filament?
The softest TPU filament that we could find is Recreus Filaflex TPU, which has a Shore hardness of only 60A.
Can you print TPU without a heated bed?
Yes, it is possible to print TPU without a heated bed. However, you may need to increase the print temperature and/or use a build plate adhesion method like hairspray or glue stick.
However, you may need to increase the print temperature and/or use a build plate adhesion method like hairspray or glue stick.
At what temp does TPU soften?
Because TPU is already flexible at room temperatures, its glass transition temperature is a bit different from that of other filament materials. It transitions from rigid to flexible at temperatures far below 0°C. The exact temperature depends on the specific type and brand of TPU filament you are using.
Final Thoughts
There are countless flexible filaments available on the 3D printing market. Choosing the best one can be difficult, especially since there are so many varieties of flexible thermoplastics as well.
Recreus Filaflex filaments are a top choice for the best TPU filament because they have so many options. Beyond having 5 different shore hardness options to choose from, they also offer a varied color selection for each hardness. Their specialty TPUs add even more options and possibilities for your projects.
ColorFabb Ngen Flex is a great choice for the best TPU filament as well, for its ease of use, ability to run through a Bowden at a normal printing speed, and because the finished prints can be sterilized. However, Filamentum’s TPE filaments also shouldn’t be overlooked for their safe food and skin contact certification, chemical and water resistance, and multiple shore hardness options.
Are you still struggling with using TPU and other flexible filaments for 3D printing? Let us know what questions you still have in the comments below!
6 Best TPU Filament & Flexibles: Top Brands 2022
The best flexible filament and the best TPU deliver a tall order. Known for elastic properties similar to rubber, flexible filaments are durable, impact-resistant, and offer an excellent surface finish that’s a pleasure to handle.
Flexible materials have a bad rap among makers for the perceived notion that they are trickier to print than PLA and ABS.
Why? It has higher temperature requirements, surging to 260°C for some brands, and its malleable properties. It’s never been easier to print bendy, quality parts, though, thanks to the rising popularity of 3D printing TPU.
It’s never been easier to print bendy, quality parts, though, thanks to the rising popularity of 3D printing TPU.
In this guide, we’ll share our top recommendations for the best flexible filament brands around, help demystify the different types available, break down the core advantages and disadvantages, and provide some top tips for a smooth printing experience with flexible filaments.
How to 3D Print Flexible Filament (TPU/TPE) – Tips
- Print slowly: 20-40mm/s is a good starting point for most flexible. Direct drive extruders also work better, as Bowden tubes can cause extra friction.
- Check your temperature: TPU and flexible filaments print at anywhere between 210-260°C, depending on the blend. If filament oozes and over extrudes, turn the temperature down; if it’s under extruding, turn the temperature up.
- Retraction settings: flexible can leak more than standard filaments between extruding points.
 Check your slicer settings to optimize for this.
Check your slicer settings to optimize for this. - Use the right bed surface: a thin coating of glue stick gives great results. Some surfaces like PEI can stick too well, so be wary of that.
Different Types of Flexible Filament
TPE – ThermoPlastic Elastomer is an umbrella term for a cross-section of flexibles, including TPU, that regroups the properties of rubber into a plastic polymer.
TPU – ThermoPlastic Polyurethane is the most commonly used flexible for 3D printing. It’s more rigid than straight TPE, which eases the printing processes, hence why makers favor it. TPU also has superb resistance properties, covering chemicals, abrasion, temperature, vibration, and impact.
TPC – Thermoplastic Co-Polyester is an industrial-grade flexible, generally used in fields such as medicine. It’s not as elastic as TPU, but it’s considerably tougher and stronger, along with boosted resistance to chemicals and high temperatures. TPC is usually printed with powder bed fusion printers.
TPC is usually printed with powder bed fusion printers.
PLA Blends – PLA+ and Soft PLA are PLA filaments designed to reduce the natural brittleness of standard PLA to increase their durability and impact resistance. They are also formulated to offer better elasticity. Soft PLA blends PLA with TPU for a best of both worlds material.
For more in-depth details about each of these different types of flexible filament, be sure to check out our complete flexible filaments 3D printing guide.
Best TPU / Best Flexible Filament Brands
3DSourced is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more
Ninjatek
- Price: Check price at Matterhackers here / Amazon here
- Printing Temperature: 210-250°C
- Shore Hardness: 75A, 83A, 85A, 90A, 95A
- Filament Diameter: 1.75 mm and 2.85 mm
- Available Colors: Black, white, gray, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, transparent
NinjaTek’s TPU filament is synonymous with quality in 3D printing circles and the material of choice for discerning makers. It’s premium stuff with an expensive price tag in tow, but worth every penny as it is undoubtedly some the best flexible filament available.
It’s premium stuff with an expensive price tag in tow, but worth every penny as it is undoubtedly some the best flexible filament available.
fNinjaTek offers a range of TPU blends covering most Shore Hardness ratings from ultra-soft Chinchilla 75A to tough Cheetah 95A.
Polymaker PolyFlex TPU
- Price: Check price at Matterhackers here / Amazon here
- Printing Temperature: 200-230°C
- Shore Hardness: 90A, 95A
- Filament Diameter: 1.75 mm and 2.85 mm
- Available Colors: Black, white, gray, teal, orange, red, blue, yellow
PolyMaker’s PolyFlex family regroups some of the best TPU blends available commercially. They shine for demanding applications that require a fine balance between durability and elasticity with solid UV resistance woven in, too. They are also affordably priced and cover 95A and 90A Shore Hardness, both great at making the TPU printing experience a little easier to handle.
Recreus Filaflex
- Price: Check price here
- Printing Temperature: 215-235°C
- Shore Hardness: 60A, 70A, 82A, 95A, 96A
- Filament Diameter: 1.75 mm and 2.85 mm
- Available Colors: Black, white, gray, peach, red, orange, blue, green, yellow, orange, pink, brown
Recreus’ Filaflex is one of the oldest and best TPU filaments on the market, and with years of fine-tuning the formula, you’re certainly buying a quality product.
The straight Filaflex options cover 60A, 70A, 82A, and 95A, while Recreus also has specialist blends, including Conductive Filaflex and Filaflex Purifier, a TPU designed to absorb CO2. All Filaflex is odorless and acetone, solvent, and fuel resistant.
Matterhackers TPU – Build Series & PRO Series
- Price: Build Series around $29 here / PRO series around $50 here
- Printing Temperature: 230-240°C
- Shore Hardness: 95A
- Filament Diameter: 1.
 75 mm and 2.85 mm
75 mm and 2.85 mm - Available Colors: Black, gray, white, transparent, red, green, blue, orange, purple
Matterhackers TPU offering is two pronged. On one side, you have the low-cost MH Build Series TPU, geared to produce quality printed parts without breaking the bank.
On the other, the PRO Series TPU is a premium blend boasting that coveted mix between elasticity and strength. This being MatterHackers, you’ll find an expansive range of available colors, but Shore Hardness is stuck on standard 95A.
Dynamism TPU HS
- Price: $50 – Available at Dynamism here
- Printing Temperature: 200-220°C
- Shore Hardness: 95A
- Filament Diameter: 1.75 mm and 2.85 mm
- Available Colors: Black
If you need a reliable, workhorse TPU capable of producing quality prints that weighs in at just about affordable, Dynamism TPU HS is a winner.
It’s tuned for high flow printing; you can crank up the print speed compared to other best TPU brands. Slim pickings on color and Shore Hardness, black and 95A, respectively.
Sunlu TPU – best cheap TPU filament
- Price: Check price at Amazon here
- Printing Temperature: 200-230°C
- Shore Hardness: 95A
- Filament Diameter: 1.75 mm and 2.85 mm
- Available Colors: Black, white red, blue, green, orange, yellow
Cheap and cheerful, but without sacrificing too much in the way of quality, Sunlu TPU is a solid general-purpose TPU for makers who want to try their hand at TPU but aren’t too fussed about the very best print results.
At $20 a spool, it’s a genuine steal. Add a nice selection of colors and an eco-friendly formula, and Sunlu offers an excellent starter TPU.
Tips For Printing The Best Flexible Filament
What Cura Settings to Print TPU Filament With?
The right settings will largely depend on your printer and the TPU brand. As a general guide, we recommend the following:
As a general guide, we recommend the following:
- Nozzle Temperature – 220°C to 260°C
- Bed Temperature – 0°C to 60°C, depending on manufacturer recommendations
- Print Speed – 5-30 mm/s
- Retraction – 3 mm at 20 mm/s, but don’t hesitate to lower it based on results
- Cooling Fan – Initially set to 0%, then shift to higher as the print progresses, but no higher than 50%
Retraction
If you’re running a new printer, you can tune your retraction settings in line with those of PLA and ABS. For older printers, low retraction settings are vital. The path through the extruder is perfectly designed for flexible filament to clog, wind, and jam around the gears, something exacerbated by high retraction settings. In this case, you’ll want to run very low retraction or turn it off entirely for the best results.
Direct Drive Extruder
Though flexibles work well enough with Bowden systems, they have an easier time with direct-drive extruders.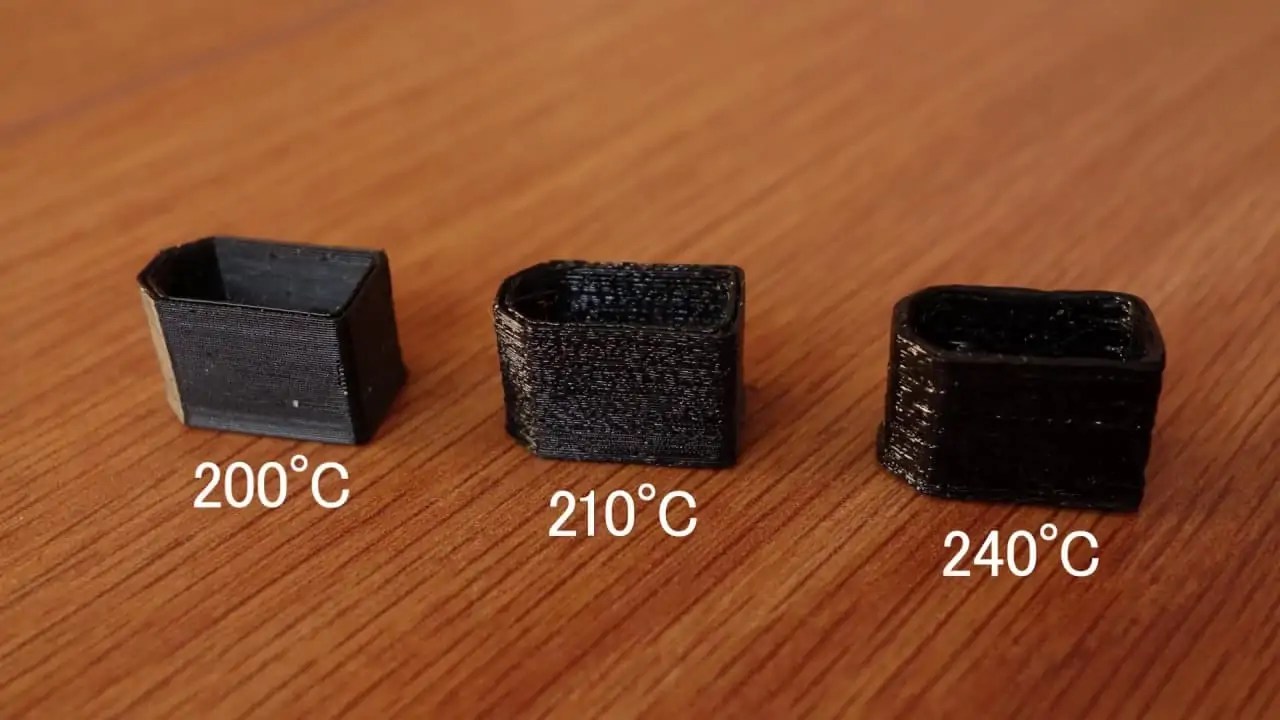 These minimize the potential for the filament to bend, snap, stretch, or otherwise ruin your prints, thanks to a shorter gap between the extruder and hot end. If possible, use a direct drive printer.
These minimize the potential for the filament to bend, snap, stretch, or otherwise ruin your prints, thanks to a shorter gap between the extruder and hot end. If possible, use a direct drive printer.
Print Slow and Hot
Flexibles thrive when print speeds are tuned low. Don’t hesitate to drop down anywhere from 5 mm/s to 30 mm/s for the best results. Similarly, these materials prefer very hot nozzle temperatures. Look to manufacturer recommendations for the latter.
Keep Flexible Filament Dry
An obvious one, but do your very best to ensure flexible filament is kept dry and away from moisture. Proper storage is critical.
How To Pick The Best TPU
Shore Hardness
Flexibles come in different levels of hardness, measured in Shore Hardness, a measurement of a material’s hardness. You’ll find options running from highly flexible to reasonably stiff.
For 3D printer flexibles, the Shore Hardness ranges from around 75A to 100A, with the numerical value ascending in hardness.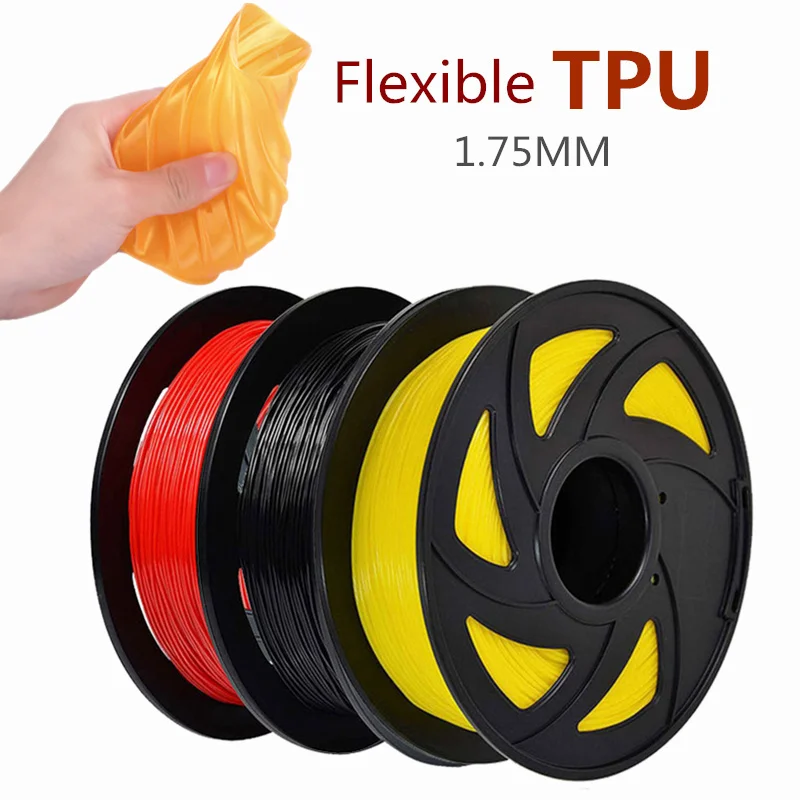 With 100A being much less flexible (think the rubber on a shopping cart wheel) – and 75A being more or less the softest limit you can print using current FDM printers. Stiffer materials tend to be easier to print, while very soft materials can be problematic.
With 100A being much less flexible (think the rubber on a shopping cart wheel) – and 75A being more or less the softest limit you can print using current FDM printers. Stiffer materials tend to be easier to print, while very soft materials can be problematic.
We recommend sticking to no lower than 85A as incredibly soft filament tends to complicate the printing process.
- Interested in seeing filament strength in action? Check out our guide to how strong are 3D printed parts.
Buy From Reputable Brands
Flexibles are difficult enough to print without throwing in a sketchy third-party manufacturer who’s out to cash in on unsuspecting makers rather than provide a solid product.
To avoid mishaps and potentially hours of wasted time, stick to the well-known, best flexible filament brands – MatterHackers, PolyMaker, NinjaTek, Colorfabb, Sainsmart, etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Flexible Filament
Advantages
- Flexible and durable: flexibles resemble rubber in their elasticity, often bending and extending well beyond their normal shape without breaking.

- Resistant: flexible filament is generally impact, abrasion, UV, low-temperatures, chemical, oils, greases, and solvent resistant.
- Smooth finish: Printed flexible generally boasts a smooth surface finish, ideal for soft consumer parts subject to regular handling.
- Warp-free: unlike other 3D printed filaments like ABS, flexible rarely curl, offering superb layer adhesion.
Disadvantages
- Stringing: flexibles are particularly susceptible to stringing during the printing process.
- Tricky to print compared to PLA: the natural elastic properties of flexibles can make the printing process challenging, with clogging and jamming a common issue for printers that aren’t set up, dialed, and calibrated correctly to handle flexible filament.
- Hygroscopic: flexibles absorb moisture, which can affect printing performance.
- Post-Processing: due to its composition and elasticity, flexible filament isn’t suited to heavy post-processing work.

FAQs
How to Dry TPU Filament?
For convenience, the best way to dry TPU is to invest in a dedicated filament drying system such as the Sunlu FilaDryer S1 and PrintDry Pro. These devices automate the drying process for you.
Beyond these, there are multiple DIY options. Using a standard domestic oven or food dehydrator is a popular choice, or you can experiment with more left-field solutions, such as a lamp placed in a bucket perforated with air holes.
What is TPU filament used for?
TPU is used for a broad range of applications requiring strong, durable, impact-resistant, and flexible parts, such as phone cases, shoe soles, straps, bumpers, RC car tires, etc.
How to Store TPU Filament?
TPU is best stored in an airtight container or resealable vacuum bag with desiccant sacs. If TPU does absorb moisture, it’s possible to dry it out using several methods, including an oven, purpose filament dryer, or food dehydrator. Although not as hygroscopic as nylon, TPU still readily absorbs moisture if left out in the open.
How to Dry TPU Filament in an Oven?
Set your oven to 55°C/131°F, place the TPU spool inside, and leave it to dry for around four hours to remove all the accumulated moisture.
How to Improve Supports When Printing TPU Filament?
If you’re set on using supports, the first step is to extend the distance between the print and supports. Next, reduce the support infill density. However, we recommend a dual extruder printer that can print the supports in soluble PVA for the best results.
TPU and supports don’t play nice together because the best TPU boasts incredibly strong layer bonding properties, which means removing supports is a task and a half that often ruins the part’s surface finish.
How Much Does TPU Filament Cost?
A 1 kg spool of TPU filament costs roughly $30 to $50 for entry-level options, but for more premium, high-quality TPU blends, the cost can rise to $100+.
How Susceptible Is TPU Filament to Moisture?
Even the best TPU filament is relatively hygroscopic, which signals that it pulls moisture from the ambient air if left exposed. Prevention is the best way to counteract this. Store your TPU in an airtight container when not in use.
Prevention is the best way to counteract this. Store your TPU in an airtight container when not in use.
What 3D Printer Filament Is Flexible?
TPU, TPE, PCTPE, Soft PLA, TPC, and PLA+ are all considered flexible filaments. But, even standard 3D printer filaments like Nylon are somewhat flexible, which aids their impact resistance.
How to Print Flexible Filament on Ender 3?
Is TPU filament like rubber?
Of all the available 3D printing filaments, TPU is the one that mimics the properties of rubber the most. It’s flexible, durable, and tough, just like rubber. Unfortunately, rubber can’t be 3D printed, which we explain in our rubber 3D printing guide.
What is better, PLA or TPU?
It depends on your needs. The best TPU is flexible but tough to print, while PLA is stiff and brittle but easy to print.
Is TPU Filament Toxic?
Like all 3D printer filament, the TPU printing process does release fumes and particles that can be damaging if inhaled in large doses, so adequate ventilation is required. Printed TPU is no more toxic than PLA and ABS.
Printed TPU is no more toxic than PLA and ABS.
Are TPU and PETG the Same?
No, Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol and Thermoplastic Polyurethane are different types of filament. PETG is best considered as a more flexible form of PLA, while TPU is vastly more elastic and impact resistant.
Best 3D Printer Filaments (Review 2021)
Once you've chosen your 3D printer, you need to choose the type of filament intended for your project. Filament is a raw material used in 3D printers that will be heated to a high temperature to turn it into a semi-solid state. At this point, the printer can easily create the appropriate design layers and print the entire 3D CAD model onto a plate.
However, as you research the various 3D printer filaments, you will hear of numerous materials that can only make it harder to choose the right one for you. This is especially true for people who are just starting to explore the world of the 3D printing process. nine0003
While most of us are not new to PLA and ABS, there are other fiber materials you should be aware of such as HIPS, PET, PETG, TPE, TPU, TPC and a few others. And to get a better idea of them, here are some of the more typical types of 3D printer filaments available on the market.
And to get a better idea of them, here are some of the more typical types of 3D printer filaments available on the market.
3D Printer Filament Types
PLA Filament
Polylactic acid (PLA) reigns supreme in the industrial 3D printing world. 3D printing with PLA is so easy. It has a lower plate temperature, so it doesn't need a heating bed and therefore has fewer warping issues. nine0003
It is widely used in prototyping, such as printing low-wear toys, prototype parts and containers. Please note that it cannot be used for anything that has a temperature rating of 60°C or higher as it warps at 60°C. For all other purposes, PLA is suitable for a general 3D printer.
ABS Filament
ABS (also known as Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is the second most popular 3D printing filament. In general, ABS withstands high loads and high temperatures. Thus, it is suitable for most applications. It is great for items that are frequently handled, dropped or heated. For example, mobile phone cases, high-wear items, automotive trim parts, and electronic houses. nine0003
It is great for items that are frequently handled, dropped or heated. For example, mobile phone cases, high-wear items, automotive trim parts, and electronic houses. nine0003
Nylon filament
Nylon is the preferred family of synthetic polymers for many industries, professional 3D printing being one of them. As for other forms of filament, they have better performance, efficiency, versatility and durability. Given the strength and versatility of nylon, this type of 3D printer filament can be used to make loops, buckles or gears, as well as working prototypes.
PET (G) thread
The most widely used plastic in the world is polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is best known as water bottle thread, but it is also used in clothing fibers as well as food containers. Although PET is commonly used in 3D printing, its modified version PETG is becoming more common.
The G in PET stands for glycol, resulting in a more transparent filament that is less prone to cracking and easier to use.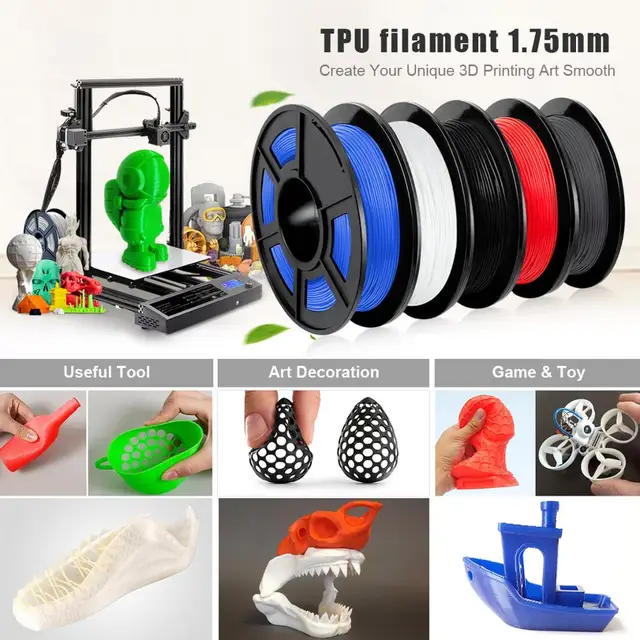 PETG is versatile but surpasses many forms of 3D printer filament in its strength and inability to reach high temperatures or withstand strong impacts. The fulfillment of the following conditions makes it an excellent choice for 3D printing filament for practical parts such as mechanical parts, printer parts, and protective materials. nine0003
PETG is versatile but surpasses many forms of 3D printer filament in its strength and inability to reach high temperatures or withstand strong impacts. The fulfillment of the following conditions makes it an excellent choice for 3D printing filament for practical parts such as mechanical parts, printer parts, and protective materials. nine0003
TPE, TPU, TPC filament
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPE) is a flexible and durable plastic similar to rubber. In addition, TPE is mainly used for the production of auto parts and household appliances.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyester E) is a special form of TPE that is very common among high end 3D printers. Compared to conventional TPE, TPU is significantly more flexible, hence allowing more control during printing.
What's more, TPC (Thermoplastic Copolyester) is also another form of TPE that is not as widely used as TPU. The key advantage of TPC over TPE is its greater resistance to chemical and UV attack, as well as heat (up to 150°C). nine0003
nine0003
If you need to create items that require a lot of wear, use TPE or TPU because these filaments use 3D printed filaments that are vulnerable to deformation. Products such as toys, mobile phone cases, or wearable items such as wristbands can be some examples of its application. On the other hand, TPC performs well for comparable applications, but outperforms it in harsher environments, including outdoors. nine0003
Wood filament
Technically not wood because it contains wood fiber in enhanced PLA. Generally speaking, wood products are valued for their natural beauty rather than their practical utility. When printing items for tables, tables or shelves, it is recommended to use wood 3D printing media. Any of the application examples include chalices, figurines, and trophies. What's more, it's a truly innovative application for 3D printers, which are often used to model real buildings, structures, or trees. nine0003
Metal thread
Like wood thread, it is not 100% metal. Specifically, it is composed of metal powder, and one of the following materials is PLA or ABS. However, the effects also have a metal-like aesthetic appeal. Metal Infused can be printed for both decorative and practical purposes. Figures, prototypes, toys, including tokens, can be 3D printed from metal and give them a great look. You can also use metallic 3D printer filament to make parts such as tools or finishing components in light applications. nine0003
Specifically, it is composed of metal powder, and one of the following materials is PLA or ABS. However, the effects also have a metal-like aesthetic appeal. Metal Infused can be printed for both decorative and practical purposes. Figures, prototypes, toys, including tokens, can be 3D printed from metal and give them a great look. You can also use metallic 3D printer filament to make parts such as tools or finishing components in light applications. nine0003
Biodegradable (biophila) filament
This biodegradable 3D printer filament aims to reduce the impact of all plastic waste into the atmosphere. Although biodegradable 3D filament was originally environmentally friendly, it can still produce quality printed products. Choose this biophile if you don't have special requirements for strength, versatility or endurance. For projects that require prototyping, you can also benefit from these flawless fiber prints that can be biodegraded responsibly. nine0003
Conductive thread
This is a kind of three-dimensional material with conductive carbon particles in it. It is ideal for Arduino-based open source businesses. You'll want to look into this filament if you want to make circuits, LEDs, sensors, and other low voltage projects.
It is ideal for Arduino-based open source businesses. You'll want to look into this filament if you want to make circuits, LEDs, sensors, and other low voltage projects.
Magnetic filament
PLA magnetic iron filament is as magnetic as the name suggests. This one-of-a-kind filament is made from PLA material impregnated with powdered iron. It is ideal for making fridge magnets and other custom-made decorative items. Also, it can be used to create multiple DIY structures, sensors, educational resources, etc.0003
Top Five 3D Printer Filaments
Access to a 3D printer creates a whole new world of creative printing. There are several purposes and hobbies that 3D printing serves, but they all rely on the same raw material - 3D printer filament.
While unique materials are recommended for durable and impressive models, you need to select the right material for your 3D image. need printer. You also need to consider the quality and attributes of the thread. That being said, finding the right 3D filament is no picnic. nine0003
That being said, finding the right 3D filament is no picnic. nine0003
As such, we sought the advice of tech experts and 3D printer enthusiasts to find the most popular 3D printing filaments on the market. And to give you a clearer idea of their main features and specifications, we have done a detailed analysis to better understand which filament you should pair with your 3D printer. Also, don't forget to click on the buttons below to get the best deals on Amazon!
What is 3D printer filament and how to choose it? nine0001
December 3, 2021
To print objects on a 3D printer, he needs the appropriate material. 3D printers typically use special plastics that have different properties depending on their composition. These plastics are called filaments. And because of their shape, in the form of a thin thread, everyone is used to calling them that way. And you yourself choose which filament for a 3D printer to buy in order to get the desired result.
It is important to understand that during the printing process, the filament is heated, melted and extruded through the 3D printer's extruder nozzle. There are many 3D printing filaments used in printing today, from standard plastic filaments to metallic imitations or wood or flexible filaments. nine0003
There are many 3D printing filaments used in printing today, from standard plastic filaments to metallic imitations or wood or flexible filaments. nine0003
It's important to choose the right filament for your 3D printer. Using filament with the wrong diameter or settings will inevitably result in printing failure or damage to the printer. This can be avoided if you understand which filament is best for your printer and your part. All 3D printers have a unique set of temperatures, speeds, and features that you must also consider in order to buy the right filament.
Each filament has its own set of characteristics both in terms of appearance and physical properties. Each offers its own set of features that you need to know to optimize your printing. You also need to consider what properties are needed for the object you are printing. Will the material be used indoors or outdoors? Should the part move and flex, or should it be absolutely rigid? What forces will be applied to the object? What post-processing methods will be applied to the finished 3D print? It depends on what thread you need to buy.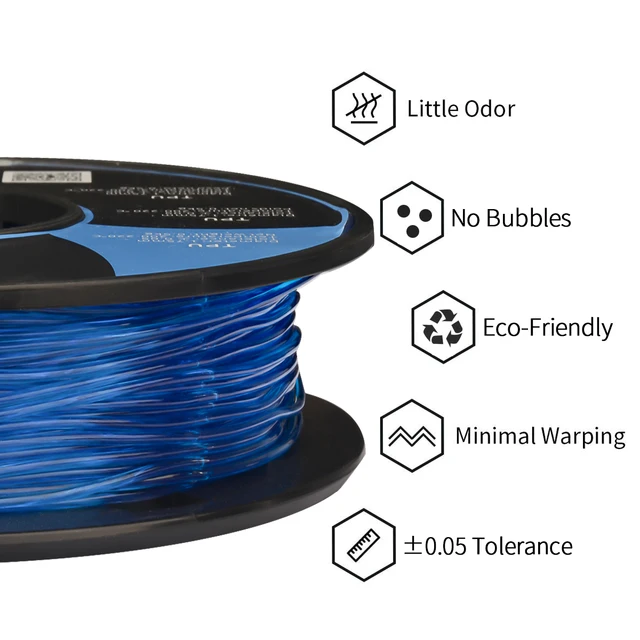 nine0003
nine0003
Of the many threads available, some are more popular than others. These are such filaments as ABS, PLA and PET/PETG.
ABS is popular because it is strong and impact resistant. It's this strength and moderate flexibility that makes it a great choice for 3D printing. In addition, it is easy to extrude from the nozzles of the printer, so it is easy to work with and can be bought anywhere.
PLA (polylactic acid) is a special type of thermoplastic made from organic materials such as corn starch and sugar cane. The main benefits of PLA are that it is safer and easier to use and does not contain toxic fumes to worry about. Compared to ABS, PLA allows you to print more aesthetically pleasing 3D parts, thanks to its unique luster and smooth appearance. nine0003
PET, also known as polyethylene terephthalate, is a stable and harmless plastic, odorless and fully recyclable. In its raw state, the thread has no color and is crystal clear. After exposure to cold or heat, the material quickly becomes opaque.