3D printing using paper
Paper 3D Printing: The Complete Guide
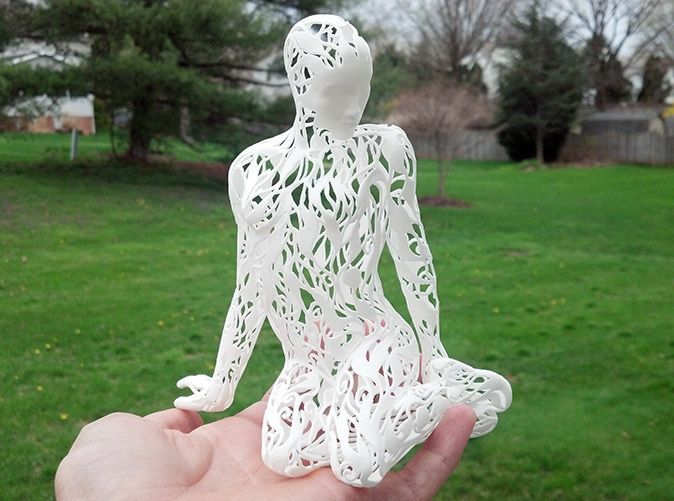
Paper 3D printing might not change the world, but it could be the fun, accessible technology that pushes 3D printing into the mainstream.
Producing customizable, colorful toys and models is one way in which paper 3D printing can enrich our lives, but paper can also be used to create full color prototypes and models for architecture and other uses.
The Science Behind Paper 3D Printing
Paper 3D printing may seem strange in theory. As a material that burns easily, more common methods of 3D printing such as FDM or SLS are an impossibility. What’s more, unless you are skilled with your hands, paper is extremely difficult to manipulate. Forming paper into complex structures is a near impossibility.
That is where we introduce Dutch engineer Beer Holthuis. A graduate of the Design Academy Eindhoven, Beer observed two things: our enormous amount of paper waste, and the lack of recyclable materials used in 3D printing.
Across the world, around 80 kilograms of paper and paperboard is used annually per person. Additionally, 3D printing’s development has not yet reached a stage where environmentally friendly materials are widespread. Bar PLA, most plastic filaments are not biodegradable, and rarely made from recycled sources.
In the earliest stages of paper 3D printing, reusable molds were manufactured with plastic to produce 3D parts using paper pulp. Beer, however, is among the first to pioneer new methods of 3D printing entirely using paper, of which there are a number of similar, yet distinct, techniques.
Paper 3D Printing Technologies
Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)
LOM is the primary technology leading the drive towards mainstream adoption of paper 3D printing, and it is the technique capitalized upon by Beer Holthuis.
LOM was first invented, however, by Cubic Technologies (then called Helisys Inc). The process involves depositing individual layers of adhesive-treated paper material onto the printer’s build plate, which is then laminated with a heat roller. The layers are then all glued together, before a laser or blade cuts out the desired geometry for the shape to produce a finished part.
The layers are then all glued together, before a laser or blade cuts out the desired geometry for the shape to produce a finished part.
While the technique can also be used for plastic and metal, here paper is soaked in adhesive to allow layers to form and make the gluing process easier. Beer has improved the technology by using recycled paper pulp suspended in resin that is deposited to form the layers. Not only does this make paper 3D printing more environmentally friendly, but also makes the process much quicker.
The LOM process for 3D printing paper prototypes.Selective Deposition Lamination
Though SDL also uses a laser to cut shapes into paper, this method differs slightly. Where LOM glues all layers together and cuts shapes from that block, SDL cuts during the production of each layer, then laminates those. It was invented in 2003 by brothers Conor and Fintan MacCormack, and was designed to drastically lower to operating costs of expensive competitors at the time.
A technique used today by companies such as Clean Green 3D, this not only reduces the amount of energy waste by streamlining the lamination stage, but also allows for not just full color, but multicolor production, one of the biggest benefits working in paper 3D printing’s favor.
These intricacies do add to production time; Clean Green 3D say that their CG-1 printers are able to produce 3D models that are recyclable, tactile and biodegradable, making this sector the cleanest in the industry.
If you are looking for a paper 3D printer for rapid prototyping, we may be able to help:
Get a quote*
*One of our trusted partners will be in touch following a quote request.
Paper 3D Printing Applications
Prototypes and Architectural Models
While 3D printing in general is a largely a prototyping technology, LOM and SDL are among the most effective at this. Paper 3D printing allows companies from a range of different industries to quickly, cleanly, cheaply and repeatedly craft product prototypes to visualize a final design in physical form. Traditional manufacturing methods simply cannot compete.
Traditional manufacturing methods simply cannot compete.
Unlike what would be expected, these paper models are surprisingly robust. While paper 3D printing has few practical industrial applications, prototypes can withstand a respectable amount of strain, and paper 3D prints have been used as tools, furniture, or even architectural models.
Paper 3D models are a drastically cheaper alternative than the plastic or metal models used previously, and allow architects to present a more substantial and tactile image to their clients as opposed to the currently widespread use of Virtual Reality. Everything from houses to skyscrapers are possible.
With product development a major cost factor for companies, paper 3D printing is announcing itself as a useful technology in reducing the costly waste that this entails. 3D printed paper prototypes are the cleanest and most cost-efficient choices for the job.
Geological Models
Paper 3D printing has a number of benefits that make geological mapping and wildlife conservation easier than ever before. With these techniques, 3D models of terrain can be accurately produced which are far easier to understand than a 2D map or even a computer model.
With these techniques, 3D models of terrain can be accurately produced which are far easier to understand than a 2D map or even a computer model.
Moreover, with the ability to add color, conservationists are able to plot not only altitude, but species movement, weather, foliage and topography, making route planning and equipment preparation simpler, and reducing transport costs and unnecessary luggage.
Toys and Minifigures
On a more jovial note, paper 3D printing is a perfect way of making a range of toys, figurines and gaming components that can add a touch of personalization to any gaming session.
Whether it be action figures or accessories for children, safe playthings that won’t shatter like plastic can, or even miniatures for use in board games, paper 3D printing can create something unique and vibrant.
This also has the added benefit of increasing customization options for color and design. Making a lookalike Dungeons and Dragons avatar but with rippling muscles and a giant sword is a dream for any gamer, and can add a touch of reality to immerse yourself in.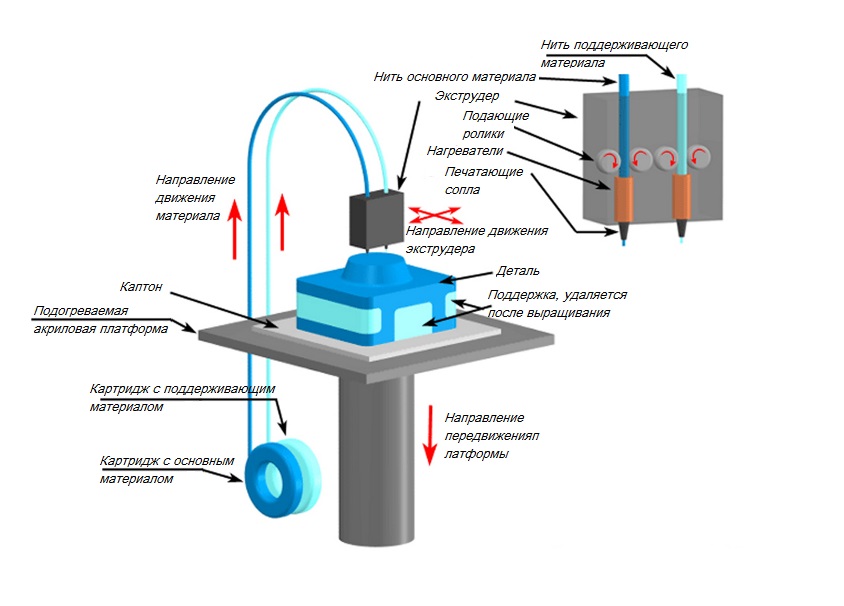
See also: Our list of the best 3D printers for miniatures.
Part 3: The Pros and Cons of Paper 3D Printing
Pros
Cheap
Almost every aspect of paper 3D printing is cheaper than any alternative you’ll find, at about 5% the cost per volume of standard 3D printers. The paper material is cheaper than plastic or metal filaments and the energy costs are lower due to the reduction in heating, using only a heat roller and laser as opposed to melting plastic or metal. This makes it one of the most cost-efficient 3D printing technologies on the market today.
Color Customization
Perhaps the most unique aspect of paper 3D printing is that there is infinite customizability with color. No other 3D printing method has a comparable level of flexibility in design.
Not only can paper be dyed to custom produce parts based on preference, but with SDL, colors can be changed between layers, with full color models that will bring any design to life. Depending on the product, either LOM or SDL will fulfill your needs.
Environmentally Friendly
Again, being set apart from other 3D printable filaments, paper 3D printing supports the use of recyclable and biodegradable material. Paper 3D printing also doesn’t involve much heating, saving energy and making it one of the cleanest methods around.
Cons
Lack of Applications
Despite the fact that 3D printed paper products are surprisingly robust and impact resistant, the biggest drawback is that there are few practical applications in which paper is a good choice.
It is biodegradable, which is helpful in being environmentally friendly, but also means that paper parts decay quicker than other materials making it less useful in industries like construction. Its weak parts are easily crushed and are therefore better suited to aesthetic prototypes rather than practical tools.
Lack of Precision
The nature of using blades and lasers to cut layers into shape means that the level of complexity possible with these techniques is drastically lowered. This means that prototypes or models with intricate designs and edges are much more difficult to produce. For producing prototypes with more complexity, using plastics or metals will produce much better results.
This means that prototypes or models with intricate designs and edges are much more difficult to produce. For producing prototypes with more complexity, using plastics or metals will produce much better results.
Conclusion: How Useful Can Paper 3D Printing Be?
Paper 3D printing has already proven useful in certain situations, but paper’s issues have hindered development. If the structural issues can be fixed, paper could be used far more in industry.
If the limitations of the design complexity can be diminished, many internal mechanical components such as cogs and pulleys can be manufactured as replacements much more quickly and cheaply. These parts experience very little stress and therefore a paper alternative would be not be required to withstand any great force. The main prohibiting factor is that these parts can often be small, with intricate edges, something that is not possible with paper at the moment.
Additionally, while paper does degrade at faster rates than plastic or metal, replacement costs will be low enough that this issue does not bear any real consequences.
The lack of strength is also a hinderance, but one that can only be managed rather than eradicated. Paper is not strong, and while post-processing treatments can help, it will never be strong enough to have industrial applications.
One interesting avenue in which paper is finding some use is fashion. Research has been conducted to explore 3D printing technology in general as a means to achieving zero emissions in the fashion and jewelry industry, and other experts have claimed that using paper 3D printing would be a benefit by rapidly and cleanly producing garment prototypes.
See also: our deep dive into the world of 3D printed fashion.
With paper 3D printing continuing to develop, perhaps it won’t be long until we see its fun and colorful potential arrive in our homes.
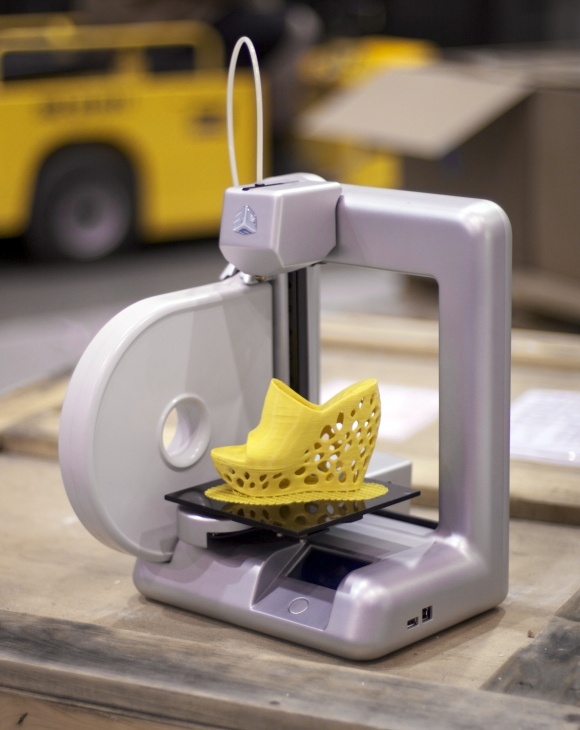
The Paper Pulp Printer replaces plastic with paper waste
Published on November 9, 2018 by Michelle J.
The market for Additive manufacturing is constantly growing in everything from the automotive industry to ceramics. However the biggest part is still in more traditional areas like prototyping using plastics. While 3D printing do bring advantages such as being faster and less wasteful than traditional manufacturing, also making it easier to produce on demand. The problem is that the majority of print material used is still plastic, which is one of the most harmful materials for the environment.
However the biggest part is still in more traditional areas like prototyping using plastics. While 3D printing do bring advantages such as being faster and less wasteful than traditional manufacturing, also making it easier to produce on demand. The problem is that the majority of print material used is still plastic, which is one of the most harmful materials for the environment.
This became apparent for designer Beer Holthuis as well, who wondered why there isn’t more sustainable materials for 3D printing. This has led him to develop a method to print with sopping wet paper. The Paper Pulp Printer, is the world’s first 3D printer using paper pulp to replace plastic. Generally the market of materials is growing and there are other alternative materials you can choose from for your prints. However most other are still hybrid materials using PLA as a base.
Beer Holthuis 3D prints with paper waste
Beer Holthuis, from the netherlands, is as a product designer. In this regard, he has crossed path with 3D modeling and additive manufacturing. Through this process, he noticed the worrying amount of plastic being used in the process and started searching for a more sustainable material to replace it.
Through this process, he noticed the worrying amount of plastic being used in the process and started searching for a more sustainable material to replace it.
As the amount of paper waste per person is at around 80 kg yearly, he decided to work with this wasteful and hugely used material. Unlike earlier paper printing techniques such as the 3D printing technology from Mcor, Beer wanted to print directly with the waste material itself. Giving us the world’s first 3D printer to print pulp.
A paper pulp printed speaker
How the Paper Pulp Printer works
The printer itself are currently pretty straight forward and works overall similar to other 3D printers. For the material he takes regular paper pulp in combination with a natural binder to keep it together. That the binder itself is a natural material as well means that the 3D printed products can continuously be recycled. This creates a closed loop system making it very sustainable long term. He then basically extrudes the paper material through a syringe type extruder from a pressure vessel. The main issue lies with when the printer stops and possible problems with how to keep it from gunking up.
The main issue lies with when the printer stops and possible problems with how to keep it from gunking up.
The aesthetics of Paper Pulp Printing
The overall look coming out from the Paper Pulp Printer and texture it produces stands out on it’s own. As Beer Holthuis himself explains, “The design of the printed objects are using the possibilities and beauty of this technique,” And he continues, “The tactile experience, bold lines and print speed results in distinctive shapes. The objects are also durable: Printed paper is surprisingly strong.” The special look of the print gives the designs a bit of personality, bringing something extra to the table.
With everything being low cost in combination with the sustainable aspect there are future potential. This recycling system should be able to take off and work on a high production level.
If you want to see the printer in action, check out the video below:
What to you think of this 3D Paper Pulp Printer? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages! And remember to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter, to get all the latest news in 3D printing send straight to your inbox!
3D paper printing - Creating products by laminating
LOM - 3D paper printing
3D paper printing is not the most accurate name for the LOM technique, which stands for Laminated Object Manufacturing. In fact, plastic, metal foil, and some other raw materials are also available as consumables for this technique. However, sheets or rolls of paper are the most common, and even ordinary A4 paper is used in some devices. nine0005
Even for those who are already somewhat familiar with additive manufacturing techniques, the very idea of using paper as a consumable for 3D printers may seem strange and ridiculous. However, often at first glance, unusual ideas can result in something very promising. This is exactly what 3D paper printing is, and in this article we will tell you all about the unusual technique and its features.
This is exactly what 3D paper printing is, and in this article we will tell you all about the unusual technique and its features.
How is paper 3D printed?
The essence of the technology lies in sequential gluing of sheets of consumable material (paper, foil, etc.) to each other. In order for each layer of the material to correspond to the layer of the given 3D model, it is cut along the required contour with a laser or a knife. Below we will give an image and describe step by step all the stages of 3D printing. But first, a few words should be said about 3D models for 3D printing. They are created according to certain rules, which you can read about here. The finished model is loaded into a slicer program (for example, Cura), where it is divided into layers and the necessary 3D printing settings are set. The resulting file, usually in STL format, is loaded into the 3D printer. nine0005
After the model is launched for printing, the consumable material (a single sheet or from a roll) is fed to the working platform of the 3D printer, heated to the desired temperature and distributed under a certain pressure.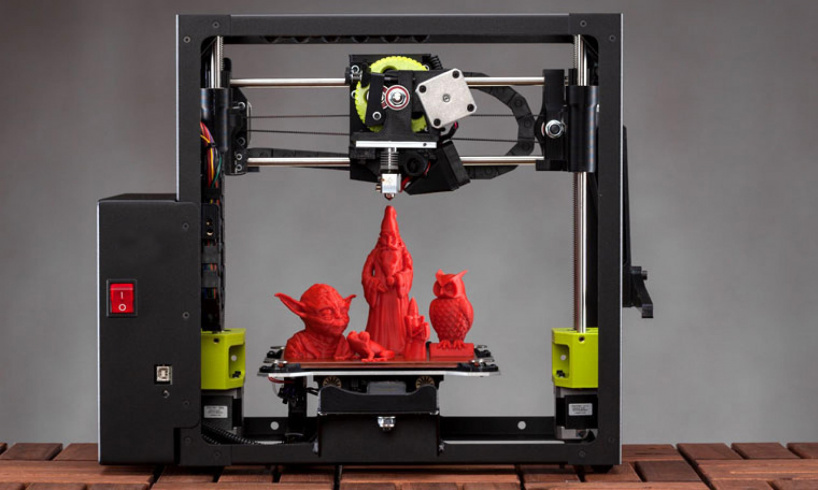 After that, using a special knife or a laser, the contour of the first layer is cut out on the sheet, and the areas that need to be removed upon completion of 3D printing are cut in a certain pattern. The platform is then lowered down to the height of one layer. In the case of roll media, the roll rotates to feed new material and remove residue. If sheets are used, a new sheet is fed with each new layer. nine0005
After that, using a special knife or a laser, the contour of the first layer is cut out on the sheet, and the areas that need to be removed upon completion of 3D printing are cut in a certain pattern. The platform is then lowered down to the height of one layer. In the case of roll media, the roll rotates to feed new material and remove residue. If sheets are used, a new sheet is fed with each new layer. nine0005
In this case, before applying each subsequent layer, the consumable is covered from below with a special adhesive. By heating and laying under pressure, a single piece is formed. The process of cutting layers and applying new sheets of material is repeated until the complete construction of the object, after which 3D printing from paper can be considered complete. The finished product is removed from the 3D printer and, if necessary, post-processed.
Method features
Paper 3D printing is different from other additive manufacturing techniques and has some interesting features. So, the accuracy of this type of 3D printing directly depends on the type of material used, the thickness of which will correspond to the height of the layer of the formed object. Also, products made by this method lend themselves well to post-processing, since they resemble wood in texture. Moreover, finished objects require varnishing.
So, the accuracy of this type of 3D printing directly depends on the type of material used, the thickness of which will correspond to the height of the layer of the formed object. Also, products made by this method lend themselves well to post-processing, since they resemble wood in texture. Moreover, finished objects require varnishing.
Benefits:
- Low production cost. Although paper 3D printing is not the cheapest technique, the cost of reproducing products with it is much lower than other professional techniques (SLS, SLM, etc.). The price of equipment also plays a role in this;
- Use of common consumables. Agree, metal foil or A4 paper can be found at home for most of us. Even plastic and photopolymer resin for budget FDM and SLA techniques will cost more; nine0034
- Ability to create full color products. Some LOM 3D printers are focused on making objects in specified colors, which will speed up and simplify their post-processing.

Disadvantages:
- Printing accuracy is lower than than other industrial methods. Alas, in terms of the quality of the resulting products, 3D paper printing is slightly inferior to other technologies. The average layer height offered by LOM printers is 300 microns; nine0034
- Delamination hazard. Obviously, the resulting models cannot boast of high strength, but in the absence of proper care (and sometimes for no apparent reason), the products diverge along the cross section of the layers;
- Paper absorbs moisture well. To protect printed models, it is recommended to cover them with varnish or special inks. This will extend the life of the products and help avoid delamination.
Where is paper 3D printing used?
Now that we understand the technical aspects of the technique, it's time to talk about the applications of LOM technology. In view of its features, it makes no sense to talk about the industrial use of the technique. Although in some cases 3D paper printing is still used to create prototypes in various areas of production. Otherwise, the technology is in demand in the following industries:
Although in some cases 3D paper printing is still used to create prototypes in various areas of production. Otherwise, the technology is in demand in the following industries:
- Prototyping. This is not only about professional (let's say, architectural) layout, but also about the use of LOM technology to create amateur layouts. Among the equipment for this 3D printing technique there are budget models; nine0034
- Design. As well as all kinds of art. The same budget and availability of materials make this technique attractive to creative people, product and industrial designers. Complementing the picture is ease of post-processing and the ability to create color products;
- Education. In general, this category can be attributed to layout, because it is medical, geographical and other layouts that interest figures in the field of education; nine0034
- Souvenir products.
 Low cost, colorful products, good detail - all this is great for creating lovely souvenirs.
Low cost, colorful products, good detail - all this is great for creating lovely souvenirs.
But don't think that paper 3D printing is limited to this. Significant improvements in technology are planned for the future. So, already in 2019, the world will see a professional 3D printer for creating serious products, including furniture.
We invite everyone interested in 3D printing to read about other technologies, as well as look at our online store. For questions about ordering 3D printing, 3D modeling, 3D scanning services and purchasing the relevant equipment, please contact us by phone or e-mail listed in the "Our Contacts" section.
Back to main page
Plain paper 3d printing technology.
Business
Subscribe author
Subscribe
Don't want
8
Good afternoon! In our last article 'Economical 3D Printing with Plain Paper' we talked about the Mcor 3D printers.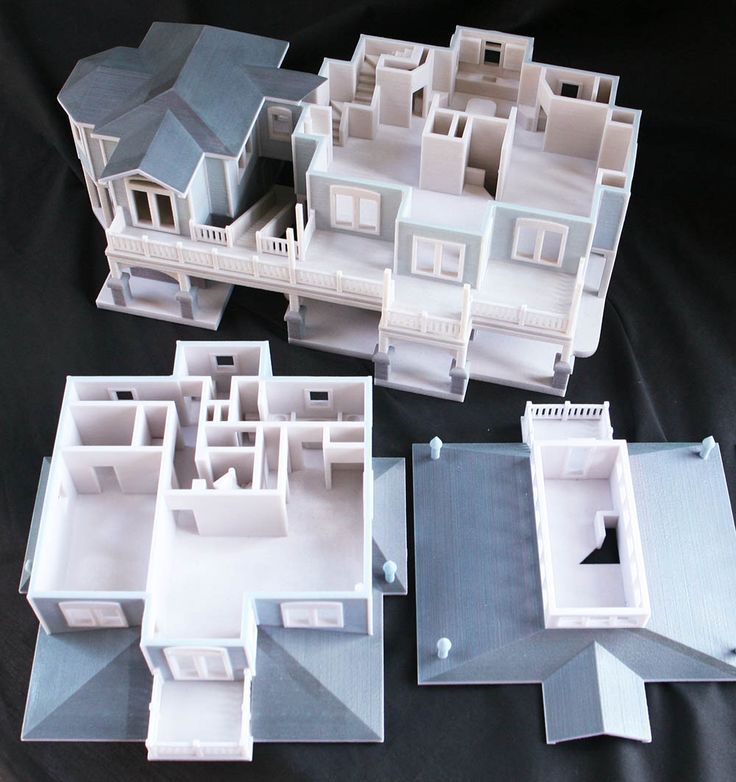
The article received many comments and questions about a more detailed disclosure of the technical part.
So, in more detail to the technical specifications:
Detailing: 0.01 mm x 0.01 mm x 0.1 mm, where the last 0.1 mm is the thickness of the layer of a sheet of paper, A4 format, 80 gr.
How do you get high detail? nine0005
Mcor tungsten carbide blade is so sharp that it can make 0.01 mm pitch in 2 axes. Thanks to this detail, it is possible to convey the wrinkled skin of a turtle
Color rendering: more than 1 million colors, resolution along the x, y, z axes: 5760X1440X508 dpi.
This color transfer technology is more than 20 years old and its main advantage is the high quality of color printing. This is a simple inkjet print on paper. In our case, this is the printer Epson 510DN and A4 office paper, 80 g. provides full color on all surfaces.
Cartridges with pigment ink Mcor - are also developed by the company Mcor Technologies . Their main advantage is that the resulting colors are durable and better retain their properties with external irritants and water. At the same time, the colors do not lose their brightness and do not fade. nine0005
Their main advantage is that the resulting colors are durable and better retain their properties with external irritants and water. At the same time, the colors do not lose their brightness and do not fade. nine0005
Chamber size: 256 mm by 169 mm. In height up to 150 mm. But the grown models can be easily glued together, and due to the fact that we work with paper, the joints between the models are almost invisible. Below is an example:
The model consists of 4 parts, and its total size is: 165 mm x 320 mm x 240 mm (height)
Mcor works on SDL printing technology .
How does this happen?
The Epson B510DN printer prints color on paper. nine0005
Then the stack of paper moves into the Mcor chamber (fig. 1)
Mcor chamber or paper tray (fig. 1)
After that, the printer applies glue and picks up 1 sheet of paper from the chamber (fig.