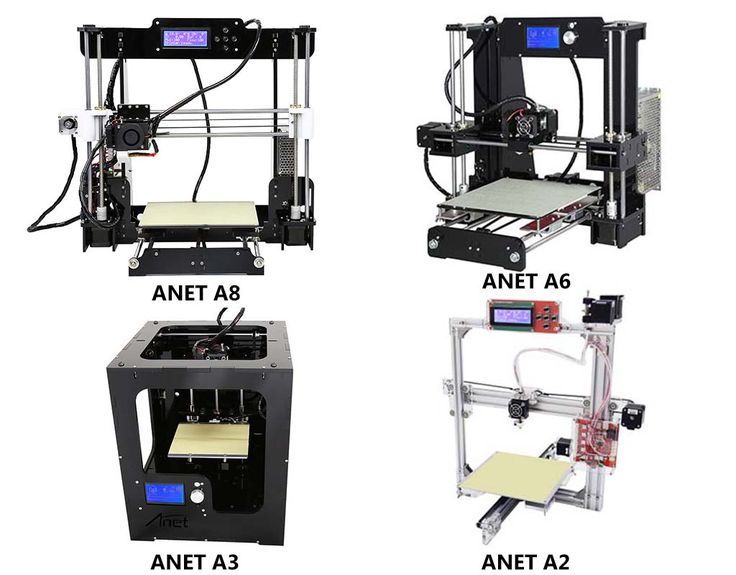
3D printing parts list
3D Printer Parts: Complete List of 3D Printing Components
ADVERTISEMENT
3D printers are becoming popular with time. Some prefer to buy the fully assembled machines while few like to explore a little more with DIY 3D printers.
While working with DIY machines, the most exciting part is exploring the different 3D printer parts that make it such a powerful technology. Though it is difficult at times to complete the assembly in few hours, the experience does provide a lot of know-how about the 3D printer anatomy.
By learning about the parts, one gets better understanding of the working of 3D printers. Hence, can utilize the knowledge later when actually printing with the machine.
One can even solve minor to major problems such a nozzle jam and many others, when familiar with the inside out of these 3D printers.
In short, if users are looking forward to a strong career in 3D printing, the right way would be start with the different parts that make up for the most revolutionary technology.
List of Major 3D Printer Parts
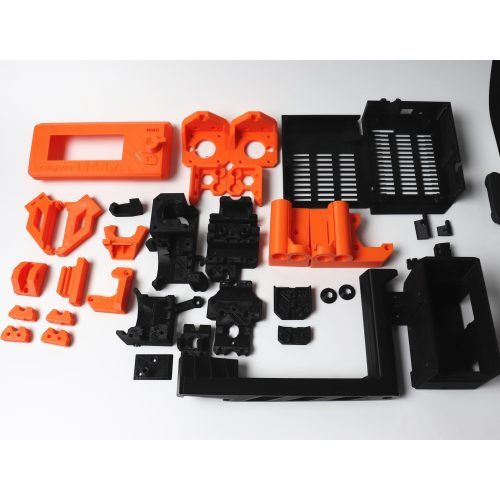
3D printers are complex, however, when examined closely, they can be made super easy to understand and work with. The first step must be to check out the 3D printer parts list.
These components of 3D printers help accomplish tasks from printing smaller to larger parts with ease. The list here contains the component of cartesian printers which are recommended for beginners.
ADVERTISEMENT
MotherBoard or Controller Board
The motherboard which is also known as mainboard or control board. As the name suggests, this component is responsible for maintaining the smooth processing of the machine.
Being responsible for all the fundamental operations, motherboard works as the brain of the 3D printers. It directs the motion components as per the instructions sent from a computer and at the same time, interprets signals from the sensors.
It directs the motion components as per the instructions sent from a computer and at the same time, interprets signals from the sensors.
You must have guessed how crucial it is to have a great quality controller board for achieving high performance from a 3D printer. Even if you put every best part in your machine, while ignoring the controller board, your 3D printer would be worthless.
Frame
Frame helps keep all the other components of your 3D printer together at one place. It also maintains the stability of the entire machine. If your frame is robust, you will have a more durable 3D printer.
Companies use different materials and the most common ones are the metal and acrylic. In old days, wood was used for the frame of the consumer 3D printers.
However, to maintain the highest stability, one must choose the metal body. These printers aren’t always expensive as well.
For example, Monoprice offers budget 3D printers under $300 with aluminium frame.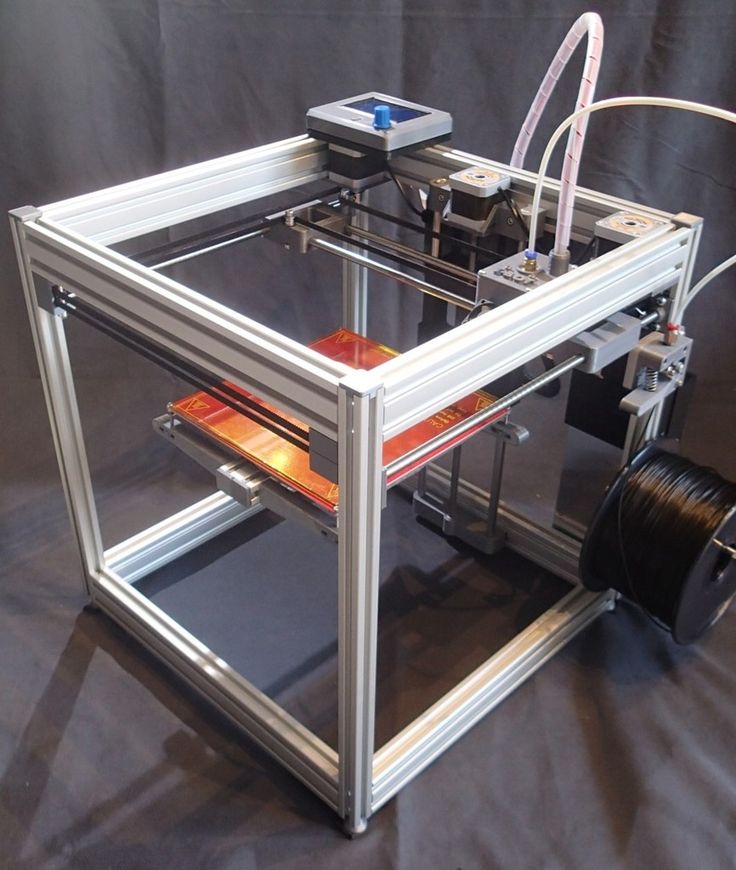 Yes, you heard it right. With limited budget, you can still own a metal frame 3D printer.
Yes, you heard it right. With limited budget, you can still own a metal frame 3D printer.
When talking about frames, the open and closed frame designs also make a difference. A closed frame offers better results by maintaining consistent temperature around the print space. There are few printers that also offer semi-enclosed frames.
ADVERTISEMENT
Print Material
Filament is used for the FDM 3D printers. Filaments are available in spools. These are heated to certain temperature and are liquified to be deposited on the print bed.
This happens in layers. The objects created by 3D printers are made of these filaments. There are many types of filaments used for 3D printing. And, each one of them have different properties. They have their own advantages and limitations.
When getting a printer, one must take care of the compatibility with different filaments. Not all printers allow multiple filament compatibility.
Some can process only one kind of filaments, mostly PLA.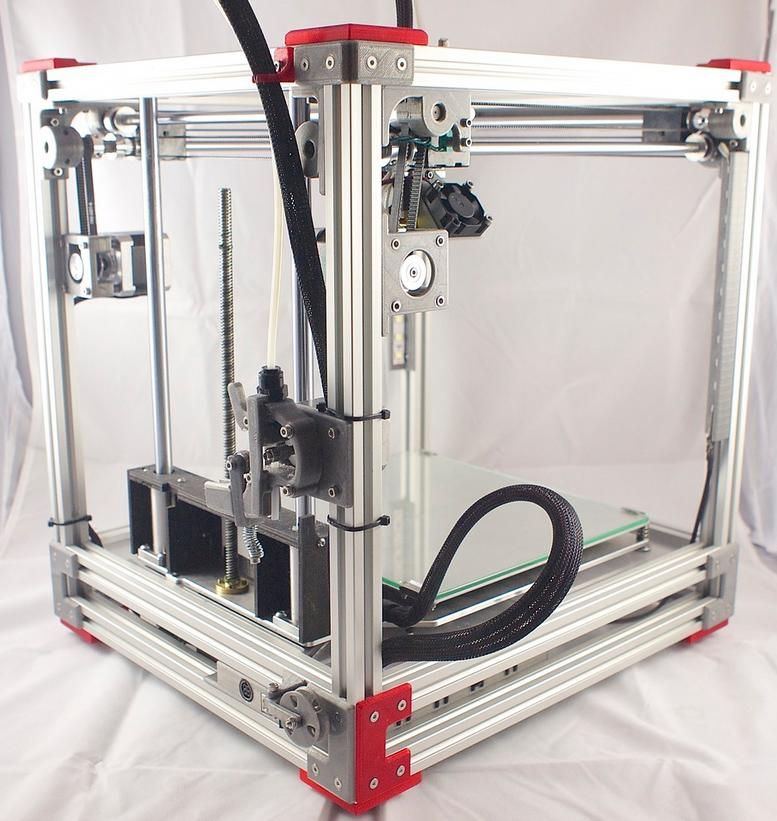 And, others can work with multiple choices of filaments including PLA, ABS and many others.
And, others can work with multiple choices of filaments including PLA, ABS and many others.
There are other 3D printers that only accept the proprietary filaments. Hence, you must be aware of your 3D printing needs before opting for a 3D Printer and the filaments it supports.
Motion Controllers
You must know that the 3D printers, as the name suggests works along the three axes. Motion controllers receive instructions from the mother board about the movement they must make, while they are the ones who perform the actual movements.
- Belts: The belts connected to motors are responsible for moving X-axis and Y-axis. The movement happens from side to side. This movement does affect the print speed and precision, hence are very crucial for the attaining best results. One must ensure that the belts aren’t loose or the print may ruin. For this, one can use tensioners.
- Stepper Motors: These are responsible for the mechanical movement of the device and are controlled by Stepper driver.
 These motors connect with X, Y as well as Z axis. These motors help in driving the print head, print bed, along with the leadscrews. Because the rotations are made in steps, they are called Stepper motors.
These motors connect with X, Y as well as Z axis. These motors help in driving the print head, print bed, along with the leadscrews. Because the rotations are made in steps, they are called Stepper motors. - Threaded rods: Threaded rods are connected to the stepper motors. With the movement of threaded rods, the print head moves in upward and downward directions. In few 3D printers, the print bed movement also relies on threaded rods. So, the Z axis movement is dependent on Threaded rods. Although these could be used for the movement along the X and Y axis, being expensive, majority of the printers use belts. Belts are faster and lighter alongside being cheap.
- End Stops: End stops ensure that the end points are marked along the three axes when the movement of components take place. It identifies the range of movement of each component.
ADVERTISEMENT
PSU
PSU, abbreviated as Power Supply Unit helps in supplying power for a smooth operation of 3D printer.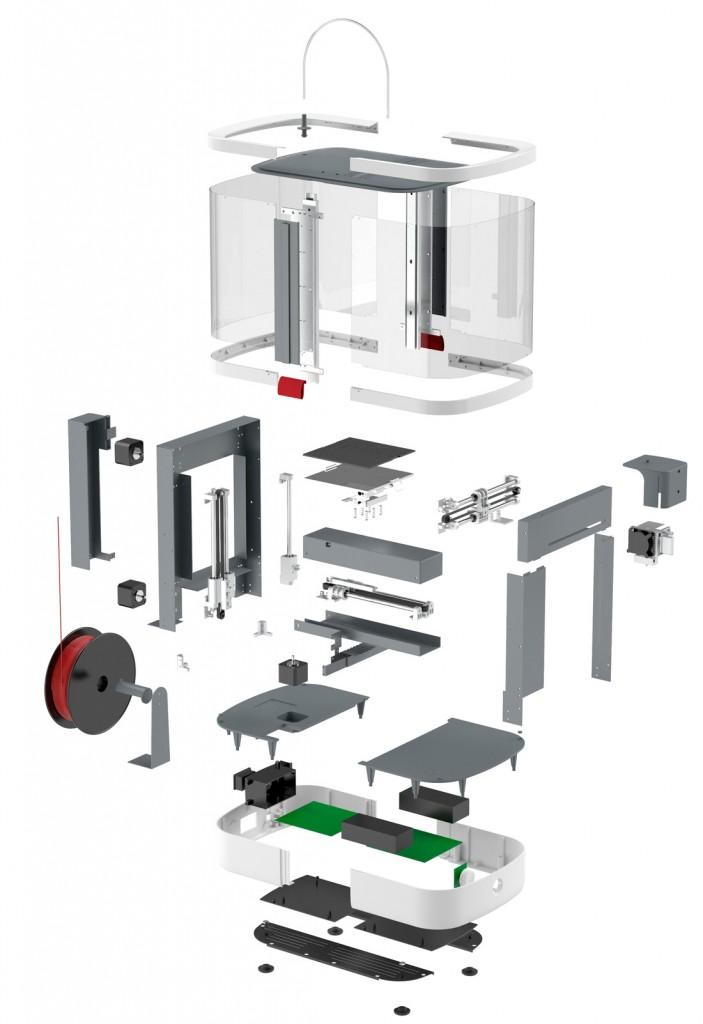 You can find the PSU mounted on the frame. Or, it can also be available separately along with another controller box. However, mounted one provides compact look and occupies less space.
You can find the PSU mounted on the frame. Or, it can also be available separately along with another controller box. However, mounted one provides compact look and occupies less space.
PSU strength would decide what temperature your 3D printer is capable of working with. For advanced materials, one must choose the one with higher temperature range allowance.
Print Bed
Mostly, anyone who has worked with 3D printer would know what a print bed is. This is the component where the models are created.
The filaments are deposited on the print bed, one layer at a time for building the entire object. One of the major 3D printer parts that does decide the quality and surface finish of the printed object.
Different 3D Printers boasts different kinds of print bed. You can find heated as well as non-heated print beds. A non heated print bed may be enough for PLA, however, for advanced filaments, heated beds are recommended. These helps in enhancing adhesion and stability for first layer of the print.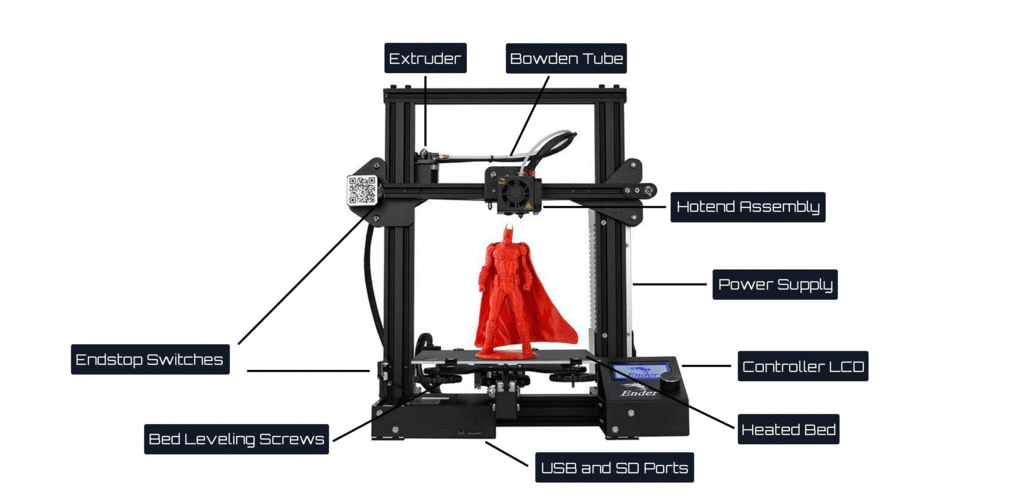
Also, the print beds are designed using different materials. For example, aluminium and glass print beds. Both have its own benefits and limitations. Aluminium print beds heat up faster and glass print beds, being flatter, provides better finish and are easy to maintain as well.
Some 3D printers offer automatic calibration of print beds. However, users need to level the bed manually in some.
ADVERTISEMENT
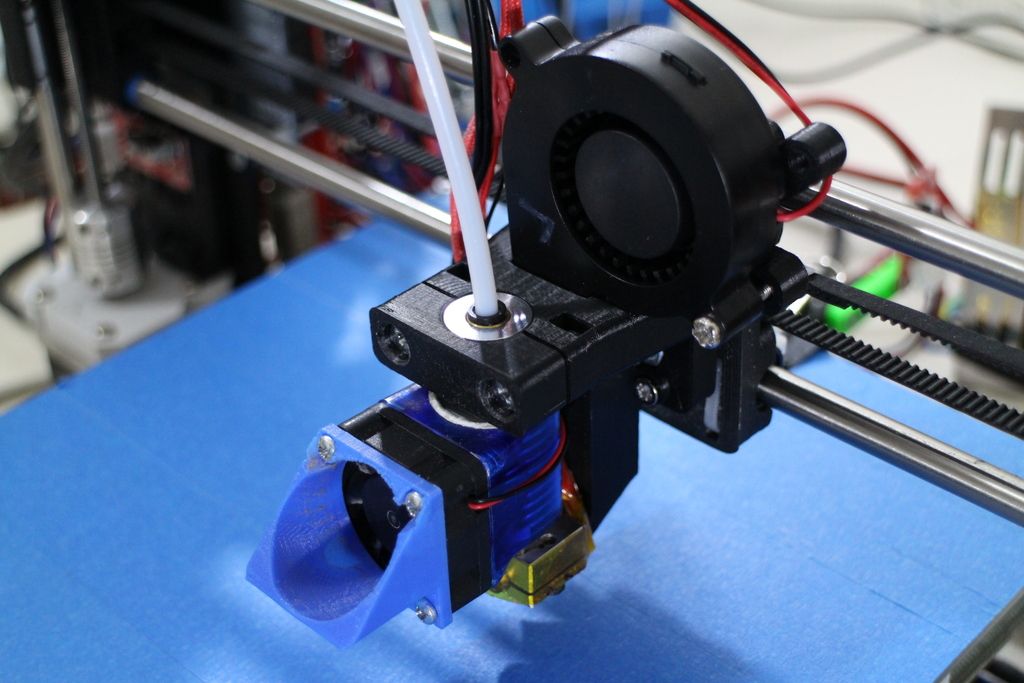
Extruder
The extruder, also known as print head extrudes the filament and deposit it on the print bed. The extruder can be categorized in two sections. One is called the cold end while the other is known as the hot end.
The job of the cold end is to lock the filament while pushing it gradually downwards to the hot end.
The hot end that has a nozzle attached to it at the end, maintains a high temperature greater than the melting point of the filament. The hot end melts the filament which is further deposited on the print bed.
The extruder itself is made of different parts.
- The Filament Drive Gear: Also known as extruder drive gear is responsible for pushing the filament into the hot end.
- The Heat Sink: The heat sink along with the heat Sink Fan ensures that the material is still in solid state until it reaches the nozzle.
- The Heater Cartridge: This is the component that works to heat up the filament.
- The Thermocouple: To maintain the right temperature, the extruder uses a temperature sensor. This is used for the hot end.
- The Cooling Fan: Once the melted filament is deposited, it must be cooled down for setting before the next layer gets deposited. The job of the cooling fan is to ensure the same.
- Nozzle: This forms the tip of the extruder. The filament is melted and it comes out of the nozzle for deposition. There are different sizes of nozzles that the printers use. 0.4 mm is the most common one. By keeping the smaller diameter of nozzle, one can achieve finer details with greater accuracy.
 And, larger nozzle helps in printing at a higher speed.
And, larger nozzle helps in printing at a higher speed.
Some 3D printers are equipped with dual extruders as well. With a dual extruder, one can print simultaneously with two different filaments. Dual extruders have two kinds of setup. Either both the nozzles are included in one print head or connected with two different print heads.
ADVERTISEMENT
Feeder System
There are two most common feeder system used in 3D printers: Bowden feeder system and Direct feeder system. In a Bowden setup, there are different locations for cold and hot ends.
While a filament tube is used to direct the filament towards the hot end. This setup can dramatically increase the print speed as the extruder becomes lighter.
When talking about the direct setup, the cold end and the hot end are directly connected. The direct feeder system is most common among the users who work with flexible filaments.
Connectivity
When it comes to connectivity with other device, 3D printers differ a lot. Some provide only the ethernet or USB port for connection. However, many new 3D printers are now available with Wi-Fi setup as well.
The interface can also help connect the mobile phone or laptop through Wi-Fi connection to your 3D printer. The file transfer can also be done using any of the three options.
For a standalone experience, many 3D printers also come with SD card slots. These slots are used for file transfer while the printer works without a need for any other device.
User Interface
These days, most of the 3D printers, even the budget ones, comes with an LCD user interface. With the help of this interface, one can control the printer settings without a need for computer.
Hence, these machines can work as standalone machines. The majority of the 3D printer has a mounted interface. However, you may find some models with separate controller box including the LCD interface.
This interface can help check and set the machine parameters. You can also use this interface to initiate the loading or unloading of filament. Moreover, an auto-leveling system can be initialized with the help of this small screen on the 3D printer.
The Conclusion
The 3D printing technology is growing with leaps and bounds. Doesn’t matter if are from a technical background or a non-technical one. Users can definitely learn to operate 3D printers because of all the help available online.
And, to know a little more than what others know, would certainly put you in a better place. So, why not start with the components of 3D printers?
3D printers are housed with many smaller and larger parts. Every part has their own role to play. Some tackles the movement while some work for accuracy various other important jobs.
These parts work in conjugation to provide a stable and uniform precision. The objects printed with a 3D printer bear varying properties and quality, depending on the difference in these parts and components.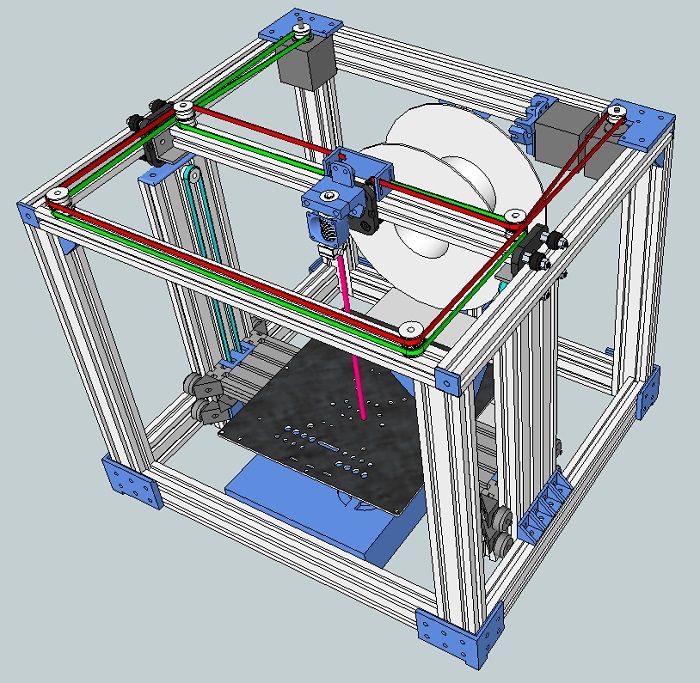
However, all of these components have equal share when it comes to the operation of the 3D printers. Knowing about these 3D printer parts is a great way to start the journey towards 3D printing.
Who knows, you can someday, be able to create your own 3D printer. Possibilities are endless and when basics are strong, one can dream for higher goals.
Every 3D Printer Part Explained
3D printers can be daunting to those untrained in the engineering of complex machines. The calibration and leveling, extruder, and many different parts of a 3D printer can intimidate beginners. We wrote this guide to explain the different 3D printer parts, their uses, and unmask the myth that 3D printers are overly complicated.
Product Review Unboxing March 2 201...
Please enable JavaScript
Product Review Unboxing March 2 2015 - ExperimentalHomesteader.com Sheri Ann Richerson
Each 3D printer component is briefly described, as well as any brief advice we have regarding best use of the 3D printer, for quality, reliability or any other advantage.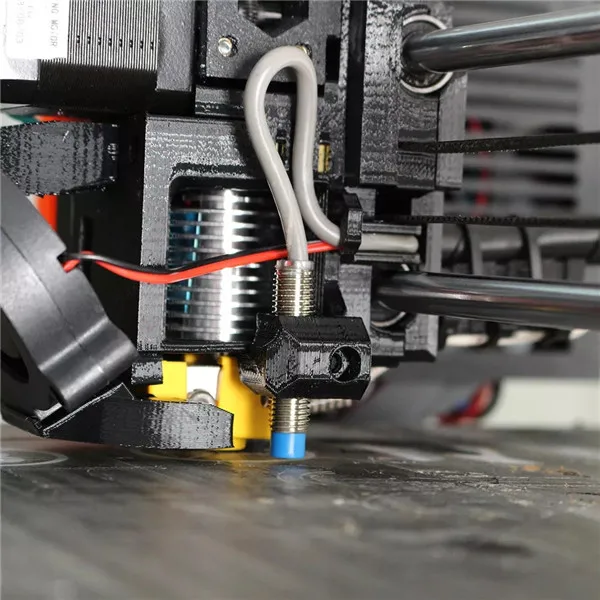 We have also included components of 3D printers that we recommend as high quality and durable.
We have also included components of 3D printers that we recommend as high quality and durable.
Most of this guide focuses on standard FDM 3D printers, but we have also included summaries of the differences in delta 3D printers and in resin 3D printers.
3D Printer Parts Section 1: Parts directly involved in printing
Extruder
The 3D printer extruder is where all the inner workings of the printing process happen. The extruder consists of many smaller pieces, encompassing the cold end and the hot end. We describe the hot end separately as in some cases the cold and hot end are placed in separate parts of the 3D printer.
Some extruder 3D printer parts we recommend:
| Name | Price | Best place to buy: |
|---|---|---|
| E3D V6 | $61 | Amazon here |
| E3D Lite6 | $37 | Amazon here |
| Micro Swiss MK10 All Metal Hot End | $63 | Amazon here |
| Diabase Flexion Single Extruder | $150 | Amazon here |
| Diabase Flexion Dual Extruder | $250 | Amazon here |
| E3D Titan Aero | $140 | Amazon here |
The extruder cold end guides filament towards the hot end, clamping and feeding it through to be melted and deposited on the print bed. It is made up of parts including:
It is made up of parts including:
- Filament drive gear: also known as a hobbed gear, the filament drive gear grips the filament and pushes it through to the hot end. It is an important part as low-quality gears can cause errors and clogs, which are a hassle to deal with.
- Idler gear: a wheel that pushes the filament up against the filament drive gear. It looks similar to the drive gear, and ensures that filament is tightly held in placed as it is pushed through the cold end so that there are no clogs. Most printers have a way to adjust the idler gear’s tension so it doesn’t squeeze filament too hard or too little.
- Feeder system: either a Bowden or a Direct Drive Extruder system:
Bowden extruders: Bowden extruders are set up so that the cold and hot ends are separate, with the cold end usually bolted to the side of the frame. This has advantages with the hot end being lighter and therefore able to travel faster with less mass and less chance of overshooting — so you can print faster. A PTFE tube is usually used to guide filament from the cold end to the hot end to be melted. Delta 3D printers are always set up with Bowden extruders.
A PTFE tube is usually used to guide filament from the cold end to the hot end to be melted. Delta 3D printers are always set up with Bowden extruders.
Direct extruder: direct extruders have the cold end directly on top of the hot end, with filament traveling a shorter distance. Direct extruders are thought to be better for flexible filaments, though this isn’t always the case. There is also less traveling for the filament for any errors to occur during.
Dual extruders: some 3D printers have two extruders rather than one, known as a dual extruder system. This enables the printing of supports in water soluble materials like PLA that are far easier to remove, or printing with two different colors. Some dual extruder 3D printers, such as those by BCN3D, are independent dual extruder systems that can print two different objects simultaneously.
- We also have a separate, in-depth guide to 3D printer extruders.
- We also have a buyer’s guide for the best dual extruder 3D printers.
Hot end
The 3D printer hot end is where filament is melted to be deposited. For such a small part it has a huge impact on print quality, and investing in a good quality hot end always pays dividends.
- We also have a separate, in-depth article focused on 3D printer hot ends.
Depending on the material you want to print, you may need a stronger hot end made from metal, rather than a standard PEEK hot end. PEEK hot ends are typically useful up to around 230C, enough to print ABS and PLA, but not robust enough for tougher materials like PETG and Nylon. Metal hot ends however can handle much higher temperatures and are known for their reliability. They can also create prints with less oozing and a slightly crisper surface finish, and they are usually easier to clean.Parts printed with and without any cooling. Credit: Tech3C on YouTube.
Parts of the hot end include:
- Heat sink: makes sure the filament doesn’t get melted before it reaches the nozzle, as this can cause jams, especially with PLA filament.

- Cooling fan: cools filament down once it is deposited onto the print bed so that the molten plastic solidifies quicker and keeps its shape better, avoiding the deformed, sloppy look. A fan is especially important for delicate overhangs and bridge structures, and makes edges more crisp. Parts printed without a fan start to look increasingly like the Pokémon Muk as gravity pulls the plastic out of its natural shape before it can harden.
- Heater block and cartridge: the parts responsible for heating up and melting filament.
- Thermistor: the sensor that monitors the heater block temperature.
- Nozzle: explained in more detail below.
Nozzle
The 3D printer nozzle fits onto the end of the hot end, and is where filament is extruded from to reach the print bed and form the model. There are decisions to be made about which nozzle to use on your 3D printer, as print quality can vary dramatically based on your nozzle size.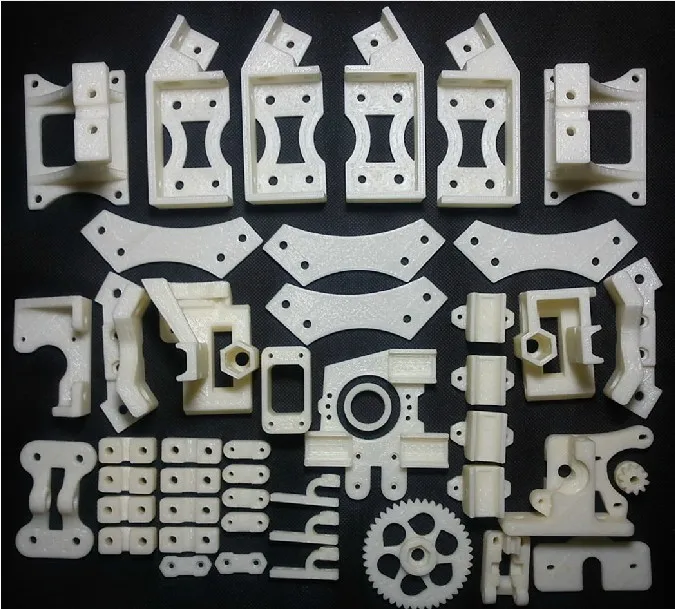
Some nozzle 3D printer parts we recommend:
| 3D printer nozzle material | Where to buy | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Brass | Amazon here | $9 (for 24 nozzles) |
| Stainless Steel | Amazon here | $7 (for 5 nozzles) |
| Hardened Steel (by E3D) | Amazon here | $19 |
| Ruby-tipped (by Olsson Ruby) | Amazon here | $93 |
Smaller nozzles, such as those between 0.15mm and 0.4mm, are more precise and can print details with better accuracy than large nozzles. Larger 3D printer nozzles print much faster and more reliably, clogging far less often. If you are looking to print fine details, go small; but if you want speedy prints, go large.
Additionally, some metals make more durable nozzles than others. Standard nozzles are made from brass, and work with most normal filaments, but wear down quickly and need replacing fairly often. Stainless steel nozzles last longer, and hardened steel nozzles last even longer still. Some hardcore makers even go for ruby-tipped nozzles for printing abrasive materials.
Stainless steel nozzles last longer, and hardened steel nozzles last even longer still. Some hardcore makers even go for ruby-tipped nozzles for printing abrasive materials.
- We also have a separate, in-depth article focused on 3D printer nozzles.
- For nozzle size: 3D printer nozzle size comparison
Print Bed
The print bed is the surface that filament is deposited on to create the finished part. Most print beds nowadays are heated, allowing for the printing of tougher filaments such as ABS, PETG and PC. A non-heated print bed, such as those found on the Dremel 3D20 and some other affordable 3D printers, limit you to just PLA and TPU printing.
Heated print beds are important to prevent warping during printing, as the heat on the bed stops the plastic cooling too quickly, which can lead to warping.
Print beds are most commonly made from sheets of glass, though aluminium is also used. Some build plates are built to be flexible, making it easier to remove prints.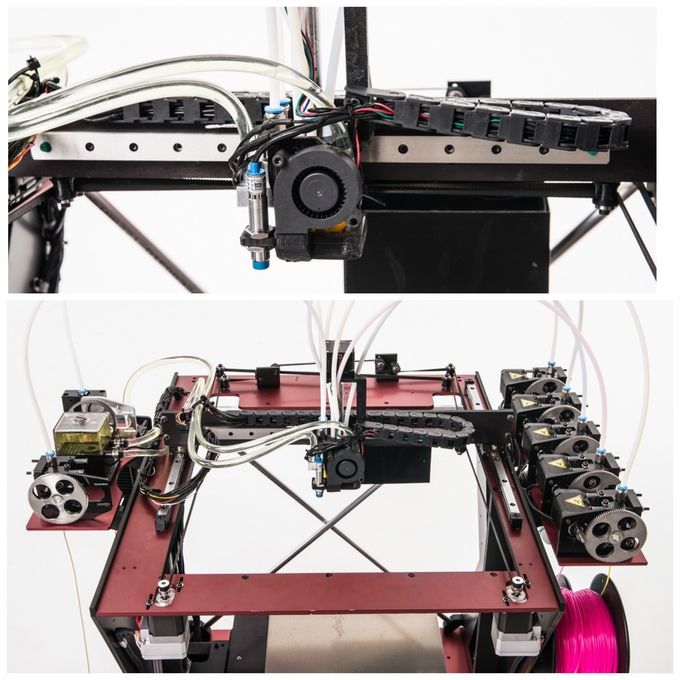 Overall, glass print bed are considered easier to maintain and flatter.
Overall, glass print bed are considered easier to maintain and flatter.
Increasingly, 3D printer print beds can auto-level without much manual interference. This is important, as if the print bed is incorrectly positioned, print quality can be greatly affected. Some 3D printers use compensating leveling, whereas some require manual leveling by adjusting the bed by manually turning the screws in the bed.
The print bed, with a plastic cube being printed on it.Print beds on Cartesian 3D printers are either square or rectangular, depending on the printer’s build volume. Build volume is simply the maximum size that the 3D printer can print, and is specified in terms of the XYZ axes. For example, a Creality CR-10 can print 300 x 300 x 400 mm, meaning it can print up to 300 mm sizes on the X- and Y-axes, and 400 mm height. Delta 3D printers have circular print beds instead.
Print bed surface: surfaces are put on the print bed to help prints stick better and to make them easier to remove. They are key as the first layer of any print is deposited on this surface, before subsequent layers are deposited onto the first filament layer. An uneven first layer will affect every other layer, and the resulting part will not be as crisp and precise.
They are key as the first layer of any print is deposited on this surface, before subsequent layers are deposited onto the first filament layer. An uneven first layer will affect every other layer, and the resulting part will not be as crisp and precise.
Different filaments work best with different solutions, and writing recommendations for every filament type would bloat this section. Some commonly used surfaces include builder’s tape, BuildTak surfaces, and PEI film.
3D Printer Parts Section 2: Parts involved in the backend / movement
Motion Systems
- Stepper Motor – usually a NEMA17 motor (though NEMA14, NEMA23 and NEMA24 motors are common), the stepper motor moves the extruder across coordinates in exact steps to accurately print. They are key to the printer’s mechanical movements as commanded by the controller board.
- Belts – the belts are responsible for accurate extruder movement across the X- and Y-axes. A 3D printer’s belts have a large impact on precision and the 3D printer’s speed.
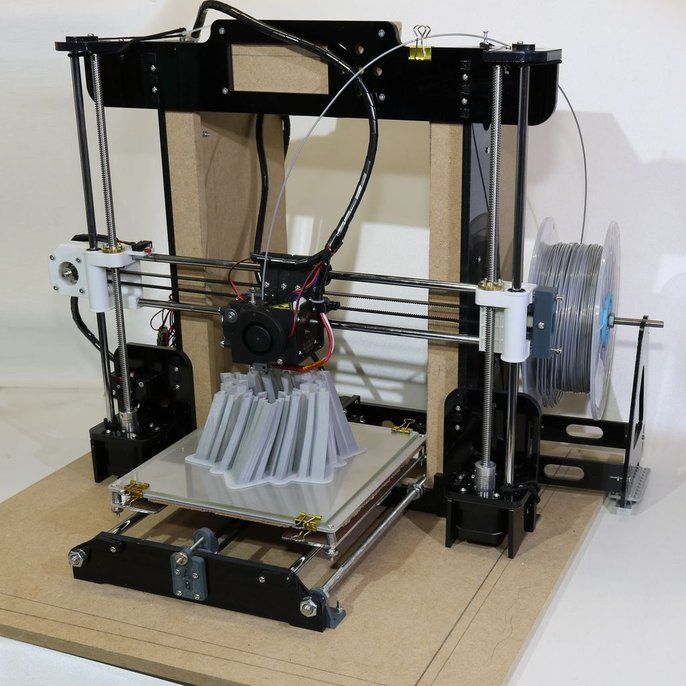 On delta 3D printers they work differently, controlling the Z-axis instead. Belts need to be kept at the right tightness – not too tight, but not too loose either – or printing quality can suffer.
On delta 3D printers they work differently, controlling the Z-axis instead. Belts need to be kept at the right tightness – not too tight, but not too loose either – or printing quality can suffer. - Threaded rods / leadscrew – Threaded rods control the Z-axis, whereas the belts control the X- and Y-axes. Threaded rods connect to the stepper motor, rotating to move the print head either up or down – though a few printers instead move the print bed. Some upgrade to leadscrews, which are better for smoother movement but cost extra.
- End stops – Ends stops function as a sensor so the 3D printer can identify where it is in relation to each axis, informing it when the end of the axis has been reached.
Controller board
Sometimes called a mainboard or motherboard, the controller board is the computer part of the 3D printer, sending commands to the parts of the 3D printer responsible for direction and movement, guiding them with coordinates based on the STL file to print.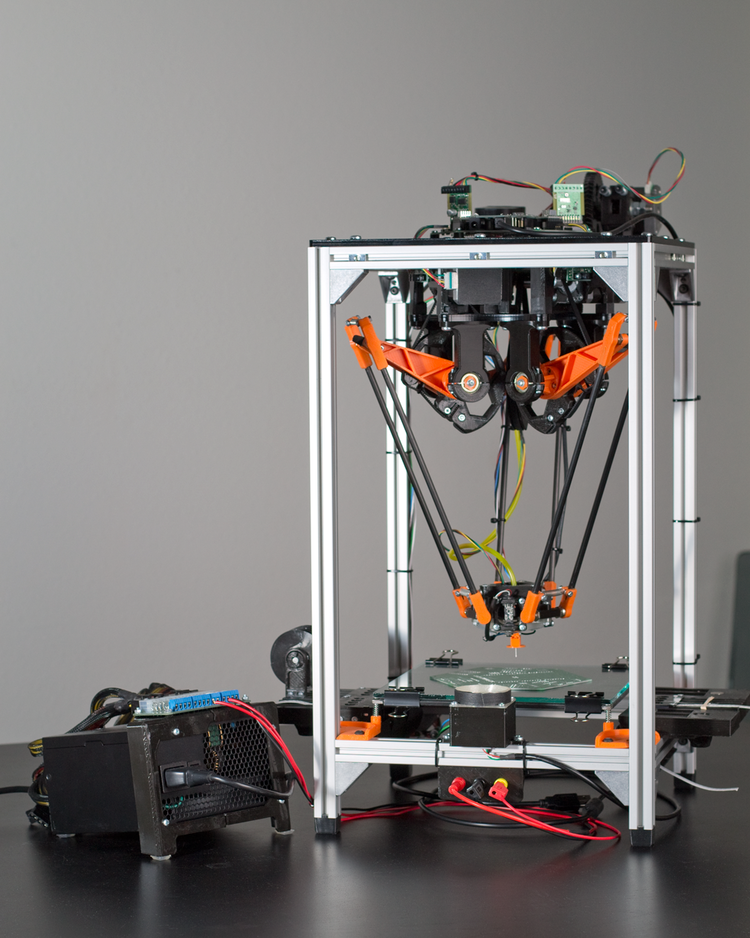
The controller board is key to high quality printing, as inaccurate movement commands, no matter how precise the actual printing parts of the printer are, will lead to sloppy prints. A high quality mainboard sends pinpoint accurate commands to create parts with crisp surface finishes.
Not only does it send movement information, the controller board also converts 3D printer models into these printing coordinates, and regulates the printer’s temperature. The extruder might physically print the filament, but the controller board is both the 3D printer’s heart and brain.
The ‘brain’ and ‘heart’ of the 3D printer.Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Fairly self-explanatory, the power supply unit supplies power to the printer so it can melt filament and print. More powerful PSUs are needed for higher temperatures and allow for better movement over longer periods of time. Less powerful PSUs usually restrict you to just PLA printing as they are not capable of maintaining the intensity required to precise printing of filaments like ABS, PETG and Nylon at higher temperatures.
Also make sure that you are buying a 3D printer with the correct voltage for your country.
3D Printers Parts Section 3: Parts involved in structure and interaction
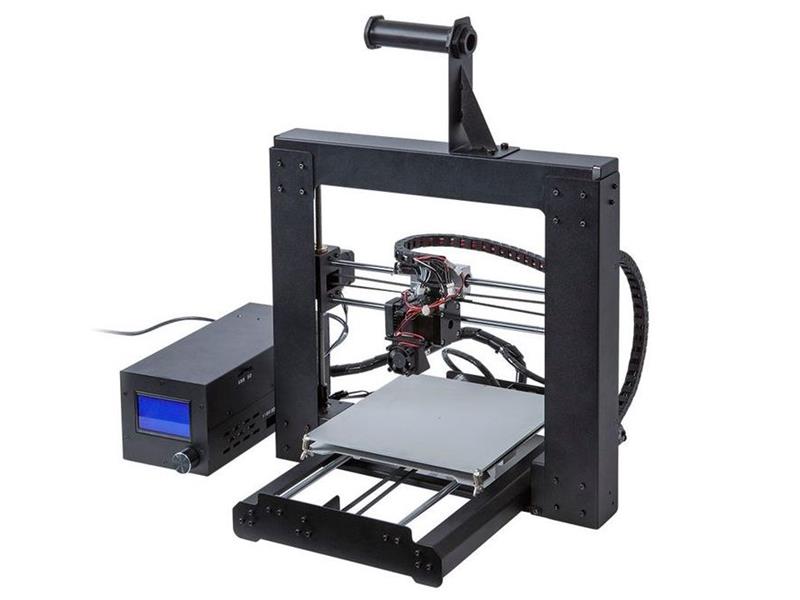
Frame
Seen as an aesthetic, most do not realize how important a 3D printer’s frame is in determine part quality. A high quality frame greatly aids stability, anchoring the printer to the floor and preventing extraneous factors such as vibrations from disrupting print quality.
Nowadays frames are usually made from metals such as aluminium, but some are made from acrylic. The first FDM 3D printer kits, such as early Ultimaker printers, were made from wood. Increasingly, 3D printer kits are made from plastic frames that are actually printed by other 3D printers, especially with RepRap 3D printers.
A robust, durable and heavy frame is key to high quality prints with smooth surface finishes. Some printers come with an enclosed 3D printer frame, which keeps the hot parts such as the print bed and print head away from prying hands, as well as keeping the temperature more consistent during printing to helping reduce warping. They also keep dust out. Enclosed printers become increasingly helpful with tougher filaments.
They also keep dust out. Enclosed printers become increasingly helpful with tougher filaments.
Screen or Interface
Usually a touchscreen LCD screen, but some have rotating knobs such as on the Creality CR-10. These screens make it easier to use and navigate all the printer’s features, options and settings. Some printers can calibrate via this interface, with the colorful screens able to show you extra stats during printing on some printers, such as the estimated time left.
Some printers can also print over WiFi, removing the need for a USB stick or SD card, and allowing you to print remotely. Most desktop 3D printers still usually work by transferring models by USB or SD card, which is still simple and effective.
Filament
3D printer filaments are the materials melted and extruded to create parts on FDM 3D printers. Filaments come on circular spools and are guided through the extruder to the hot end to be melted and deposited in the right place through the nozzle.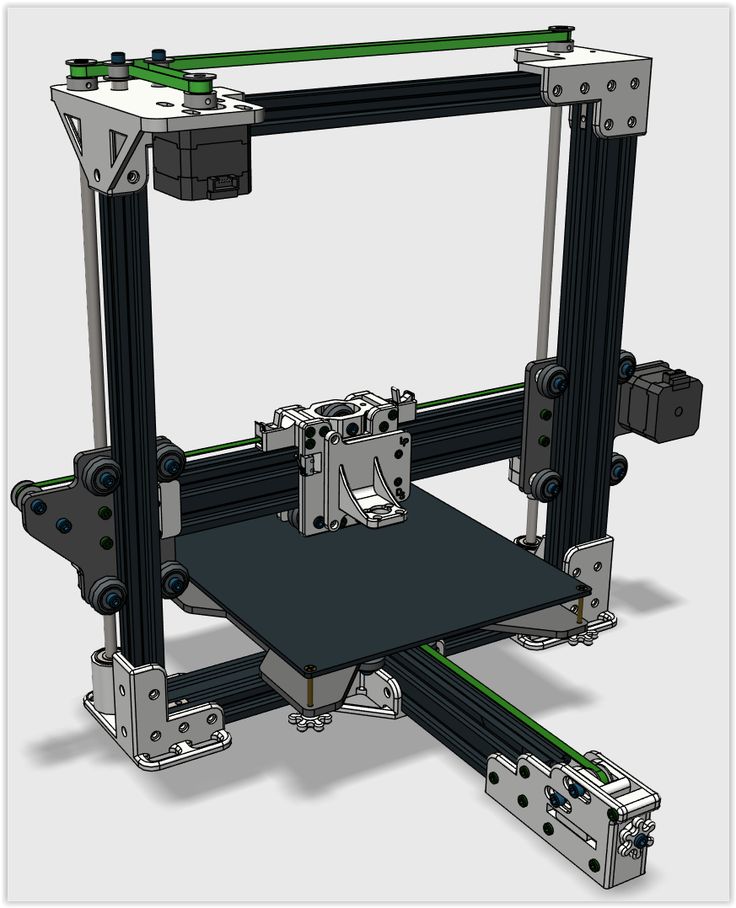
Most 3D printers now use 1.75mm filament, but occasionally you may encounter a printer set up to use larger filament sizes.
Different filaments melt at different temperatures, and most filaments require a heated print bed for effective printing. Additionally, tougher filaments such as PETG and Nylon require higher quality metal hot ends for printing as higher temperatures are needed to melt them which PEEK hot ends cannot handle.
- We explain all the different filament types in our separate 3D printer filament guide.
- For ABS, we have a specialized guide to ABS filament.
- For PLA, we have a specialized guide to PLA filament.
- For PETG, we have a specialized guide to PETG filament.
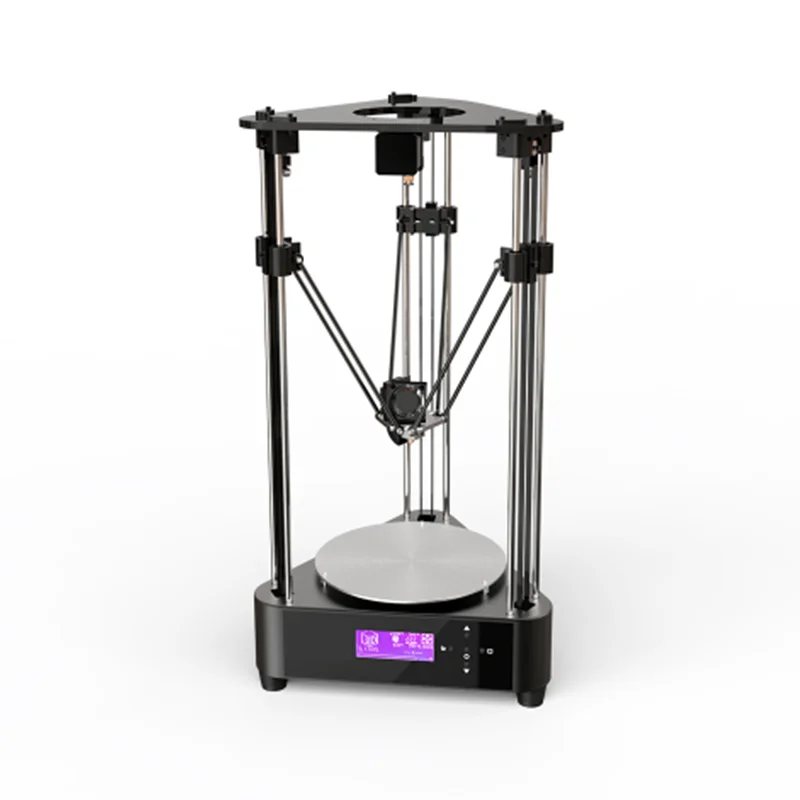
Instead of stepper motors, delta 3D printers use effectors for movement. These effectors control the three arms that move the extruder into the correct place for printing. These three arms meet in the center and conect to the extruder, allowing them to move the extruder in any direction across the three axes to deposit filament.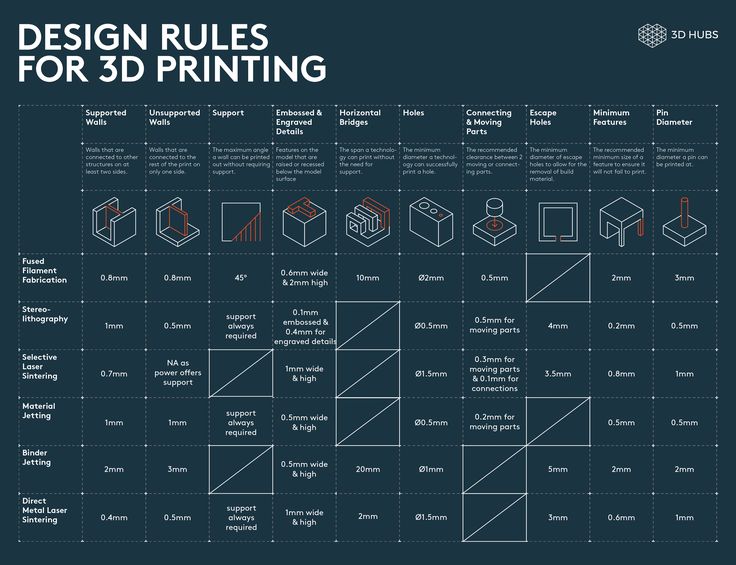
3D Printers Parts Section 5: Resin 3D printer parts
The main parts of a resin 3D printer vary based on the type (LCD vs SLA vs DLP), but include:
- Resin vat: also known as a resin tank, contains the resin to be cured
- Light source: either an LCD, DLP projector or SLA UV light source
- Build platform: where the solid object is formed, and moves up or down when each layer is finished
- Resin: variety of types, such as daylight-sensitive, castable, UV resins
- Roller: some resin printers have a roller that moves across the built platform to make sure resin is sat properly.
3D printer models
Looking for 3D printer models? The Internet is filled with sites that offer them for free. We have collected the TOP 10 catalogs that you can use to search and download free models in STL format. We hope you can find what you are looking for.
- Yeggi
- Yobi 3D
- STLfinder
→ myminifactory. com
com
My Mini Factory is a 3D model depository operated by iMakr, an online store that sells 3D printers and accessories. It also has one of the biggest 3D printer shops in Central London. The site contains 3D models designed by professionals, and all models stored on it are checked for quality. You can also make a request for the desired model, which their designers will create and put in the public domain. Billing itself as a 3D printing social network, MyMiniFactory is a thriving community of makers who love to showcase their creations. Users vote for the best models, which allows popular creations to rise to the top of the list and gain popularity. The site presents models that are stored on its social network, as well as outside it, for example, on the Thingiverse and YouMagine sites.
→ thingiverse.com
The most popular and famous site among 3D printer users, Thingiverse is owned by MakerBot Industries, the creator of the popular Replicator 3D printer series.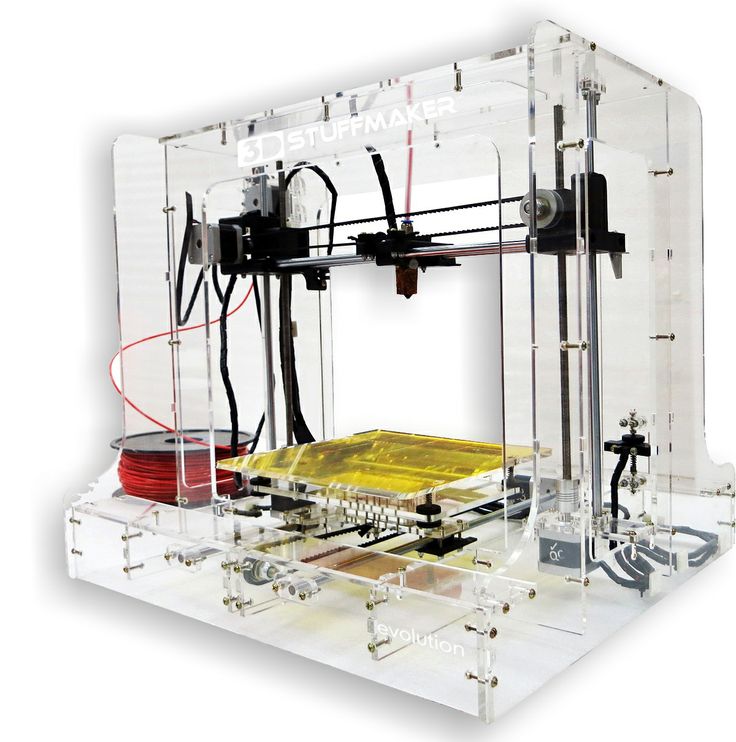 The site allows users to store and share 3D model files that are used with 3D printers. It's a very popular site and has a large community of people hosting various categories of files on it. So if you're looking for "cool" printable stuff, Thingiverse is worth a visit. It is a portal designed to provide its users with ways to share their designs and to help print 3D creations. The site has a system that tries to find out what you like. The more you interact with the site, downloading and evaluating various developments, the better its recommendations will be.
The site allows users to store and share 3D model files that are used with 3D printers. It's a very popular site and has a large community of people hosting various categories of files on it. So if you're looking for "cool" printable stuff, Thingiverse is worth a visit. It is a portal designed to provide its users with ways to share their designs and to help print 3D creations. The site has a system that tries to find out what you like. The more you interact with the site, downloading and evaluating various developments, the better its recommendations will be.
→ 3dshook.com
Another online community for 3D printing hobbyists showcasing interesting 3D printer accessories, electronics and most importantly 3D models. The site contains many very interesting models of cars and buildings, as well as various add-ons and spare parts for your 3D printer. A huge catalog of paid and free models for a 3D printer. There are original unique products. Convenient search, navigation, rubricator. 3DShook has over 40 categories and adds over 100 new models to its collection every month. On 3DShook you can always find something for your home, animals, kids or something special for yourself.
3DShook has over 40 categories and adds over 100 new models to its collection every month. On 3DShook you can always find something for your home, animals, kids or something special for yourself.
→ youmagine.com
YouMagine catalog for 3D Systems Cube series consumer 3D printers. The site mainly offers various ways to buy 3D printer supplies and files, but it also has a number of cool free items available, mostly in the Kids section. Some of these elements can be customized by children using an online application. The company offers 3D modeling and publishing tools on its website for both hobbyists and professionals. The site offers a content warehouse where the community hosts and shares models. Registration is required to download files.
→ 123dapp.com
Autodesk 123D is a suite of computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D modeling tools aimed specifically at hobbyists. Along with the toolkit, Autodesk also has a website where users can record their designs and share them with other users.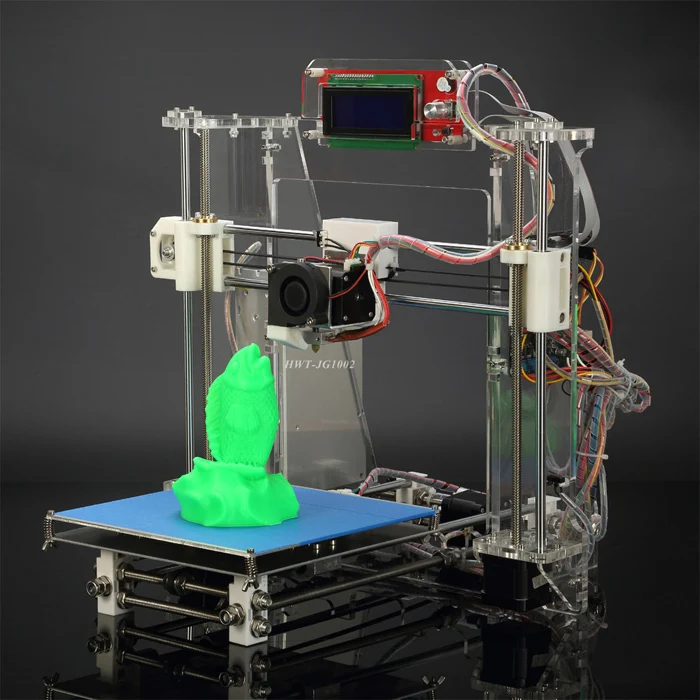 Many of these models can be downloaded and printed using Autodesk as a utility to interface with the MakerBot 3D printer. The goal of the Autodesk website is to "help engineers build products faster." The site offers tools to help them collaborate on their files. For the casual 3D printing enthusiast, the best part of the site is the large library of free files created by a community of over a million engineers. Registration on the site is required, but the number of files that are then available is worth it.
Many of these models can be downloaded and printed using Autodesk as a utility to interface with the MakerBot 3D printer. The goal of the Autodesk website is to "help engineers build products faster." The site offers tools to help them collaborate on their files. For the casual 3D printing enthusiast, the best part of the site is the large library of free files created by a community of over a million engineers. Registration on the site is required, but the number of files that are then available is worth it.
→ cgtrader.com
Being primarily a place to buy and sell a variety of 3D models (not necessarily just those designed for 3D printers), CGTrader does offer a selection of free models that can be used on 3D printers. The site has a system that tries to find out what you like. The more you interact with the site, downloading and evaluating various developments, the body will have better recommendations.
→ cults3d.com
A French community and marketplace where developers can share or sell their creations. The site has a collection of high quality models that you can download. Users can follow the work of the designers they like and get instant updates when a new creation is posted on the site. The site's name, Cults, is a backwards spelling of St. Luc, the patron saint of artists. The site also supports English. This is a relatively new community, so the number of its users is not very large yet.
The site has a collection of high quality models that you can download. Users can follow the work of the designers they like and get instant updates when a new creation is posted on the site. The site's name, Cults, is a backwards spelling of St. Luc, the patron saint of artists. The site also supports English. This is a relatively new community, so the number of its users is not very large yet.
→ instructables.com
The Instructables website is a community where users can share their DIY projects. This also includes products obtained using 3D printers. The site also provides explanations and instructions describing how to build 3D elements, and some designers take the time to answer questions from site members. Instructables allows users to store and organize their 3D printing projects. This is done to help them work together in the future. You can think of this site as a GitHub 3D printing site where users can share their files, discuss projects, and participate in them. The site also offers the ability to make a request, so if you can't find what you're looking for, you can ask the site's community about it.
The site also offers the ability to make a request, so if you can't find what you're looking for, you can ask the site's community about it.
→ pinshape.com
Pinshape, a marketplace for 3D models, is similar in style (layout, look, and ability to capture likes) to the well-known site Pinterest. You can buy models from designers, or download them for printing yourself if they are offered for free. Pinshape allows users to host and share 3D model files on it. Basically, this site acts as an online store where you can buy 3D printed parts, or order your own 3D model to be printed. But if you look closely enough, you can find people who sell their products and also offer the files you need so you can print them yourself.
→ 3dfilemarket.com
A new and growing repository of 3D File Market models. All models are tested for suitability for 3D printing. You can download as many models as you like without registration, although you must provide your email address to access the 3D model files. This is a very simple site aimed at being a repository of model files for 3D printers, and nothing more. The basic design of the site allows users to put files on it for public access, and download files that they would like to use. The site contains many small, simple 3D models ready to be printed, as well as a good selection of everyday items and even spare parts for 3D printers.
This is a very simple site aimed at being a repository of model files for 3D printers, and nothing more. The basic design of the site allows users to put files on it for public access, and download files that they would like to use. The site contains many small, simple 3D models ready to be printed, as well as a good selection of everyday items and even spare parts for 3D printers.
Search engines for 3D models in various formats, including STL for a 3D printer. Use queries in English, these search services collect information about models from all over the Internet.
→ yeggi.com
Yeggi is a search engine that will browse major 3D printing sites to find files compatible with 3D printers. You can also browse some popular searches to get an idea of what the community is currently interested in.
→ yobi3d.com
When in doubt, use yobi3D to search for files that match the desired 3D printer. This tool is useful if you want to search for one thing across all sites at once. A very convenient format filter, fast search, high-quality previews and stl models prepared for 3D printing for printing.
A very convenient format filter, fast search, high-quality previews and stl models prepared for 3D printing for printing.
→ stlfinder.com
This is another STLfinder that surfs the web looking for 3D printing. To select files compatible with 3D printers, he goes through many 3D modeling sites.
50 Cool Things to 3D Print / Sudo Null IT News
No ideas for 3D printing? Tired of worthless trinkets? Here is a list of 50 cool really useful things for 3D printing.
Like us, you're excited about the possibilities of 3D printing. But, unfortunately, the horizon is littered with trinkets, trinkets and other unnecessary things. We are in danger of being buried under a heap of useless rubbish.
Throw off the shackles of mediocrity! Let's create really useful things! Here is a list of cool things that you can make on a 3D printer right now. Prove to your family and loved ones that this wonderful technology can be used daily and in practice.
No access to 3D printer? No problem. Just upload your files to our 3D printing price comparison system and choose the best price, ONLINE!


 You can change the pattern of the inner pallet if you wish.
You can change the pattern of the inner pallet if you wish.  Print it out and give it to your grandmother. She will appreciate this gesture.
Print it out and give it to your grandmother. She will appreciate this gesture.  " Do you have such a business card? Find her a pair in the form of this business card holder, printed in its entirety (yes, already with a hinged lid). Instructions for adding a custom logo are included.
" Do you have such a business card? Find her a pair in the form of this business card holder, printed in its entirety (yes, already with a hinged lid). Instructions for adding a custom logo are included. 
 It is especially suitable for kitchen plants. The next time you buy fresh herbs for cooking, transplant them into this neat device and they'll stay fresh all week long.
It is especially suitable for kitchen plants. The next time you buy fresh herbs for cooking, transplant them into this neat device and they'll stay fresh all week long.  It’s great if you have water limits set in the height of summer.
It’s great if you have water limits set in the height of summer.  28: Protection for disk
28: Protection for disk  39: Holder for a children's bottle MyMiniFactory
39: Holder for a children's bottle MyMiniFactory