3D printing motor
3D Printer Stepper Motors & Stepper Drivers
Sort byRelevanceBestsellersCustomer ReviewsPrice, Low to HighPrice, High to LowNew arrivalsHighest Discount
-
BondTech NEMA17 Pancake Stepper 25mm- Removable cable
- High torque
- Original Bond Tech
-
BondTech Heatsink- Better heat dissipation
- Self-adhesive backing
-
Creality Stepper Motor 8 Model types- Original spare part
- From Creality 3D
-
Anycubic Stepper Motor 5 Model types- Original spare part
- By Anycubic
-
BIGTREETECH Stepper Motor Driver 9 Model types- High-quality
- Different versions available
- Upgrade option
-
FLSUN Stepper Motor 3 Model types- Original spare part
-
BondTech NEMA17 Pancake Stepper 22mm- Fixed cable
- High torque
- Original Bond Tech
-
BondTech NEMA17 Geared Stepper- Planetary gear
- High torque
- Original Bond Tech
-
BIGTREETECH EZ Stepper Driver 2 Model types- 2-in-1 driver and heatsink
- Quiet movements
- Very durable
-
E3D Hemera XS Motor- Original spare part
- For E3D Hemera XS
- Including drive gear
-
BIQU Stepper Driver- Original spare part
-
BIGTREETECH EZ Driver Connector- Adapter for increased compatibility
-
E3D Hemera Motor- Original spare part
- For E3D Hemera
- Including drive gear
-
Zortrax Extruder Motor Set- Original spare parts
-
Artillery Stepper Driver- Original spare part
- From Artillery
-
Artillery Stepper Motor- Original spare part
- From Artillery
All prices incl. VAT.
Has An English Research Center Found a Way to Commercialize a 3D-Printed Electric Motor?
3D printing news Transport Has An English Research Center Found a Way to Commercialize a 3D-Printed Electric Motor?
Published on September 8, 2021 by Mikahila L.
In England, the National Center for Additive Manufacturing (NCAM) has designed a 3D-printed electric motor, which they proclaim is the first of its kind. The motor consists of multiple 3D-printed parts. Furthermore, the motor has comparably more power, requires less assembly time, and reduced mass and size of key components as compared to traditionally build motors. According to the team, this project could go beyond the theoretical stage and pave the way for the commercialization of 3D-printed electric motors.
NCAM is part of the Manufacturing Technique Center (MTC) located in Coventry, England. Its primary mission is to accelerate the adoption of additive manufacturing. The center is now equipped with about twenty machines, from polymer to metal to ceramics.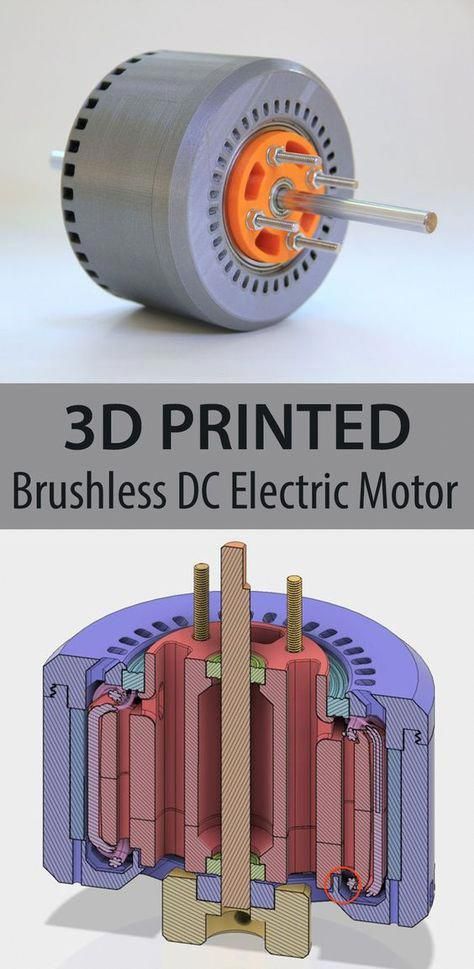 For example, the center has invested in Renishaw, Trumpf, AddUp, HP, XJet, and Photocentric machines. Several post-processing solutions complete the center’s range, which can thus control the entire additive manufacturing value chain. For some time, the team at NCAM has been interested in designing an electric motor.
For example, the center has invested in Renishaw, Trumpf, AddUp, HP, XJet, and Photocentric machines. Several post-processing solutions complete the center’s range, which can thus control the entire additive manufacturing value chain. For some time, the team at NCAM has been interested in designing an electric motor.
Photo Credit: MTC
The NCAM team, therefore, 3D-printed several parts of an electric motor. Although the team remains discreet about the processes and materials used, they have shared that the end result is lighter, smaller, and would offer more power. The use of additive manufacturing has allowed NCAM to simplify the entire supply chain and reduce production and assembly times and costs. Steve Nesbitt, Chief Technologist at MTC, explains: “Additive manufacturing is a key tool for developing the complex features and shapes essential to improving the performance and functionality of electric motors. The manufacturing process of these presents a number of challenges, including complex or manual assembly, difficulty to process and sometimes expensive materials, thermal management, and the need to lighten the assembly.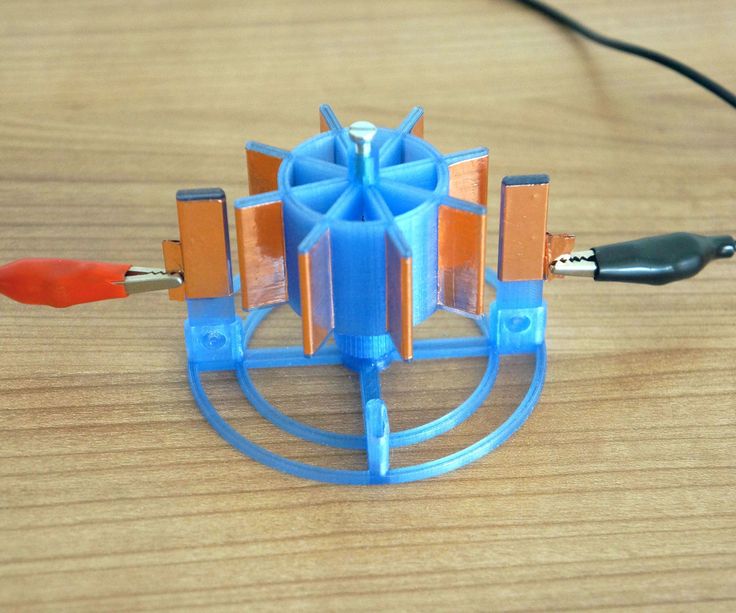 By harnessing the capabilities of additive manufacturing through product redesign, major benefits can be achieved in terms of cost, reduced waste, performance, and ease of manufacture.”
By harnessing the capabilities of additive manufacturing through product redesign, major benefits can be achieved in terms of cost, reduced waste, performance, and ease of manufacture.”
The team had previously designed a 3D-printed electric motor housing: the part in question incorporates cooling channels, a design that could not have been achieved other than through additive manufacturing. Now his goal is to print the entire engine. Dan Walton, Senior Research Engineer at MTC concludes: “Additive manufacturing is complex, but the possibilities for companies to improve their productivity, efficiency and cost savings—and therefore their competitiveness—are great. This project allowed us to identify a roadmap to help manufacturers implement additive manufacturing technologies for electric motors, which have the potential to transform the industry as we know it.” You can learn more about the electric motor project HERE.
What do you think of this 3D-printed electric motor? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages. Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly newsletter, with all the latest news in 3D printing delivered straight to your inbox!
Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly newsletter, with all the latest news in 3D printing delivered straight to your inbox!
3D printing engine (5 best models for 3D printing)
3DPrintStory 3D printing process How to 3D Print an Engine (Top 5 Models for 3D Printing)
3D printing at home has come a long way. To date, there are a huge number of 3D printers in various price ranges, there are plenty to choose from. And as there are more and more happy owners of 3D printers, the community is growing, there is a huge number of 3D models that people share. But the static figures downloaded from Thingiverse are gradually getting bored and I want new challenges and experiments. Well, you've come to the right place. How about printing a running electric motor?
Well, you've come to the right place. How about printing a running electric motor?
If you're interested, then wellcome to the rest of the article, because here we have collected for you the best options for engine designs that you can print on your 3D printer.
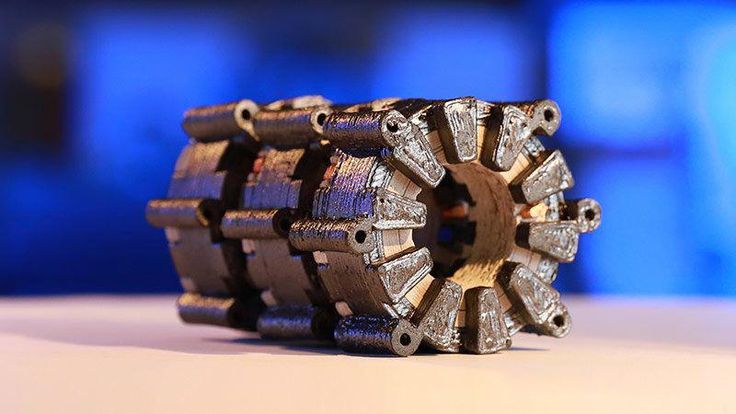
Brushless motor
This motor, designed and manufactured by Christophe Laimar, has impressive power. The 3D printed motor uses a 3D printed rotor and stator and delivers 600W of power with an efficiency of 80%. The complexity of 3D printing rightly allows it to be used as a demonstration of technical prowess as well as knowledge of 3D printing.
Where to find : You can download the part files from the developer's website for a fairly small $10 license fee. Also included is an approved list of 3D printing hardware and engine components.
How to make : Christophe provides very detailed information on how to print and assemble this impressive brushless motor project. You can find the full instructions for 3D printing and assembling this model on Instructables.
You can find the full instructions for 3D printing and assembling this model on Instructables.
In the video below you can see how this engine works.
Simple DC Motor
This motor is amazing in its simplicity: it was designed for training purposes by user Thingiverse for MakerEd Challenge 2.0.
Where to find : Thingiverse has all the parts you need to 3D print this DC motor. In addition, there are detailed instructions for assembling the model, as well as materials with examples of its use.
How to make : Follow instructions on Thingiverse where the author recommends printing at a high resolution of 0.1mm. In addition, it provides a complete list of required parts for a complete build so that even before starting this project, you can be fully prepared and armed with everything you need.
A short video demonstrating the operation of this 3D printed motor is shown below.
Mendocino small solar motor
As stated by the creator, "The Mendocino engine is a solar-powered electric motor with magnetic levitation." Watching a video of his work will definitely make you wonder and realize how interesting this design really is. The assembled model is practically a work of art, with a stylish floating design.
Where to find : This unusual engine model can be found on Thingiverse.
How to make : The author used a 0.5 mm nozzle with a layer height of 0.2 mm for the stator components. Detailed instructions are also provided on the Thingiverse page.
Tesla Turbine
The model was originally designed and manufactured by the Portuguese manufacturer and engineer Integza. This 3D printed engine is based on a Tesla turbine. It is propelled by the use of high-pressure air, acting in a vortex through thin, 3D printed plates. The original design used a few 3D printed components, but the current second iteration is almost entirely 3D printed.0005
It is propelled by the use of high-pressure air, acting in a vortex through thin, 3D printed plates. The original design used a few 3D printed components, but the current second iteration is almost entirely 3D printed.0005
Where to find : The author has posted 3D printing files and instructions on her Thingiverse page.
How to make : unfortunately the author does not offer any technical documentation. But the author has a video where he reveals some background of this project, and also describes the build process.
Spring Motor
Designed and printed by Greg Zumwalt, this powerful 3D printed spring motor demonstrates the unique properties of PLA plastic. And it's especially impressive that Greg has created many other models based on the lessons learned in this project.
Where to find : Greg Zumwalt has posted all his part files on MyMiniFactory.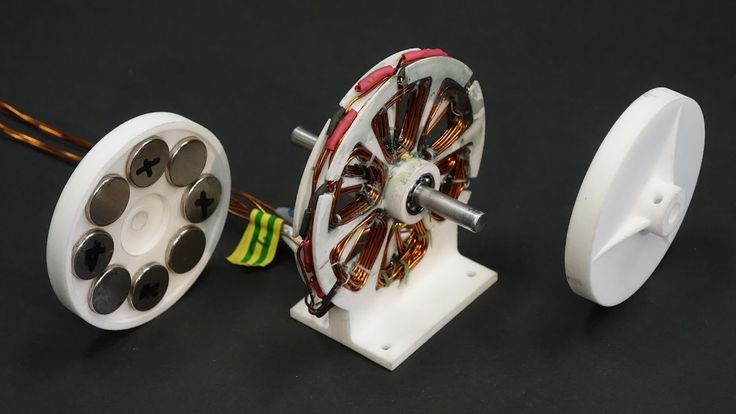
How to make : Greg has posted instructions on MyMiniFactory that explains in detail how to print and assemble each of the parts. The most important tip is to print with 100% coverage. In addition, he recommends using light machine oil for lubrication.
Here are just a few options to make your 3D printed projects even more colorful and impressive. As you can see, 3D printing is about more than just static miniatures. Implement at least a couple of the above projects, and your knowledge in the field of 3D printing (and not only) will expand significantly. Well, if the above electric motor designs are too easy for you, then why not create your own?
stepper motor choice, which is better
With the advent of 3D printers, people's lives have become much easier. Devices are successfully used in many areas - dentistry, industry, jewelry and medicine. Now a 3D printer is not a luxury item, but a design that is quite affordable. But still there are those who decide to independently manufacture printing presses. Next, let's talk about how to choose a stepper motor for a future 3D printer and what features should be taken into account.
Next, let's talk about how to choose a stepper motor for a future 3D printer and what features should be taken into account.
Motor on a 3D printer
In the design of a 3D printer, the main function for the movement of the extruder along the axes is performed by stepper motors. They have low weight and high torque.
A stepper motor is a motor without a commutator, whose rotation is not smooth, but discrete (in steps). By setting the speed and duration of the pulses, you can make the device rotate in a certain direction. In this case, it is possible to adjust the direction of rotation and the number of revolutions of the rotor.
If we talk about the design of such devices, then there are three main types:
- Motors with variable magnetic resistance - have several poles on the stator and a rotor made of soft material, and 3 windings independent of each other. This type is practically not used.
- Permanent Reluctance Motors - Includes stator and magnetized rotor.
 Such motors have 24 to 48 steps per revolution.
Such motors have 24 to 48 steps per revolution. - Devices combining variable and constant magnetic resistance (hybrids) - combination of the best properties of an AC and a constant rotating motor. The number of steps is from 100 to 400.
The hybrid engine is the most common design, which, in turn, is divided into unipolar and bipolar types.
Which stepper motors to choose for a 3D printer: the best options
When buying a rotator for a 3D printer, you should pay attention to the following parameters:
- rotating structure size;
- holding torque - 2.5-4 kg/cm;
- rated current - optimal version for 1.7 A;
- Shaft - Diameter must match the design of the printer.
The most common motors that are installed on the design of the printing device are bipolar with four leads. Such structures in the event of a breakdown are easy to find and replace.
NEMA marked rotary motors are installed in 3D printers.
NEMA is a National Electrical Manufacturers Association that standardizes rotating devices in terms of flange size and fit. This standard allows different manufacturers to produce engines according to certain parameters, depending on the marking.
Most popular models in the NEMA series:
- NEMA 17 with 42*42mm flange;
- NEMA 23 with 57*57mm flange;
- NEMA 34 size 86*86mm.
Stepper motor drivers for 3D printer
To control motors in 3D devices, drivers installed in the board slot have been developed.
There are several types of drivers:
- Constant voltage - such drivers are inefficient and are used in a product with low speeds.
- Two-Level - These controllers support step and half step modes. They reduce engine heat and are efficient in operation.
- PWM drivers are the most popular on the market. They are highly intelligent and have many additional features.

Learn more