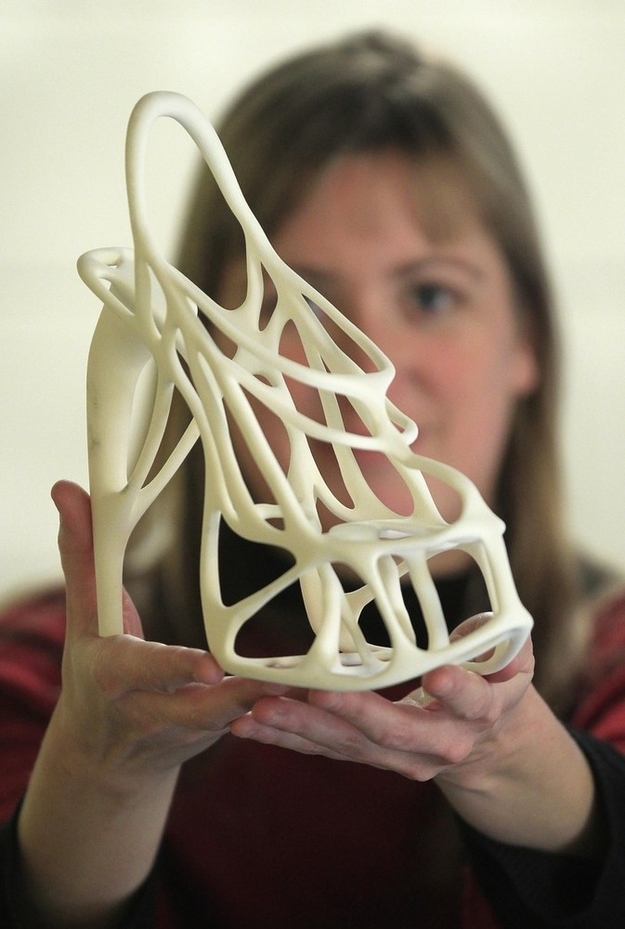
3D printing loughborough
3D Printing Facilities | School of Mechanical, Electrical and Manufacturing Engineering
Within the Wolfson School of Mechanical, Electrical and Manufacturing Engineering, we use various 3D printing facilities to undertake our research. The facilities used within the High Value Manufacturing research theme include:
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
FFF is the most common and accessible form of 3D printing producing parts from many common plastics. This process uses plastic filament (such as ABS or PLA) extruded through a hot nozzle onto a heated bed building the part layer by layer. A great introduction to 3D printing, these are used heavily by our students and researchers. The material costs are low and apart from removal of support material post processing is minimal. Examples include:
Stratasys
Machine: Dimension Elite
Materials: ABS Plastic
Build Volume: 203mm x 203mm x 305mm
Layer Thickness: 0. 178mm or 0.254mm
Ultimaker
Machine: Ultimaker 2+
Materials: PLA, PETG, Nylon
Build Volume: 223mm X 223mm x 305 mm
Layer Thickness: 200 - 800 microns
Raise3D
Machine: Raise3d Pro 2
Materials: ABS. PLA, PETG, Nylon
Build Volume: 305mm x 305mm x300mm
Minimum Layer Thickness: 0.01mm
Nozzle Diameter: 0.4 mm (Default), 0.2/0.6/0.8/1.0 mm (Available)
Max Nozzle temperature: 300 ºC
XYZ Step Size: 0.78125, 0.78125, 0.078125 micron
Markforged
Machine: Markforged Mark Two
Materials: Nylon (Base Material), Carbon Fibre, Glass Fibre, Kevlar (Reinforcement Materials)
Build Volume: 320mm x 132mm x 154mm
Layer Thickness: 100 - 200 microns
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS allows for precision manufacturing through selectively sintering polyamide nylon powder with a CO2 Laser. The EOS P100 SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) machine is where a 70W CO2 laser is used to scan across a bed of fine powder (typically PA12 nylon) sintering/fusing the powder together layer by layer. The un-sintered powder acts as a support meaning when finished the part can be dusted down without further support removal.
The EOS P100 SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) machine is where a 70W CO2 laser is used to scan across a bed of fine powder (typically PA12 nylon) sintering/fusing the powder together layer by layer. The un-sintered powder acts as a support meaning when finished the part can be dusted down without further support removal.
EOS
Machine: EOS P100 Formiga
Materials: Polyamide Nylon Powder (EOS PA2200)
Effective building volume: 200 mm x 250 mm x 330 mm
Building speed (material-dependent): up to 24 mm height/h
Layer thickness (material-dependent): typically 0.1 mm
Laser type: CO2, 30W
Precision optics: F-theta lens
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
The Trumpf Truprint 1000 uses a 200W Fibre Laser to scan across a bed of fine metal powder to selectively melt each build pattern layer by layer producing intricate components which would be difficult or impossible to manufacture using conventional methods.
Trumpf
Machine: Trumpf Truprint 1000
Materials: Aluminium, nickel-based, cobalt-chromium, copper, titanium
Build Volume: Diameter 58 mm x 100 mm Height (normal Builld Volume diameter 100mm x 100mm height)
Laser beam diameter: 55 μm
Layer thickness: 10 - 50 μm
Building rate: 2 - 18 cm³/h
Gas: Nitrogen, Argon
VAT Polymerisation
VAT polymerisation allows for precision manufacturing using UV curing photopolymer resin. The Wolson School has a 3D Systems Viper SLA 3D printer, Formlabs 2 and a Photocentric Precision. This process utilises either a UV laser or digital light projection (DLP) to precisely cure UV curable resin producing highly accurate detailed components.
3D Systems
Machine: 3D Systems Viper Si2
Materials: Accura 60 Resin
Build Volume: 250mm x 250mm x 250mm
Vertical Resolution: 0. 0025mm
0025mm
Beam diameter: 0.075mm (Hi Res), 0.25mm (Standard)
Formlabs
Machine: 3Formlabs Form 2
Materials: Formlabs Clear Resin, Formlabs Flexible Resin
Laser Spot Size: 140 microns
Laser Power: 250mW Laser
Build Volume: 145mm X 145mm x 175mm
Layer Height: 25-300 microns
Photocentric
Machine: Photocentric LC Precision 1.5
Materials: Photocentric Daylight Precision Resins
Build Volume: 121mm x 68mm x 160mm
Layer Thickness: 25, 50, 100 microns
XY Resolution: 47 micron
Loughborough 3D Printing Service - Fast Turnaround
WITH OVER 80+ 5 STAR REVIEWS ON GOOGLE, WE’RE THE BEST LOUGHBOROUGH 3D PRINTING SERVICE.
- FREE TRACKED SHIPPING
- FAST TURNAROUND
- NO HIDDEN COSTS
START PRINTING
OUR CAPABILITIES
3D PRINTING SERVICE, 3D PRINTING UK
We pride ourselves on the quality of our carefully selected materials and accurately manufactured parts at our Loughborough 3D printing service. Our nationwide rapid prototyping service offers unparalleled customer support, assisting customers throughout every stage of the 3D printing process.
Our nationwide rapid prototyping service offers unparalleled customer support, assisting customers throughout every stage of the 3D printing process.
Serving the Loughborough area, we offer fast turnarounds and free shipping on all orders from our Loughborough 3D printing service.
Our engineers have over 10 years of experience in the plastics industry. Working in tandem with suppliers and manufacturers, we utilise the latest in materials and technologies to produce advanced, functioning parts.
Professional Printing For Businesses
Get in touch with our Loughborough 3D printing service sales representatives to set up an account today and benefit from our 3D printing services:
- Free UK shipping available
- Dedicated account manager
- 30 day payment terms
- Non-disclosure agreements available
CONTACT US
or call us on:
(+44) 0115 794 0445
UPLOAD YOUR DESIGNS TO GET A FREE INSTANT QUOTE
GET INSTANT QUOTE
How it Works
UPLOAD
Using our simple to use interface, upload your 3D files using our secure system.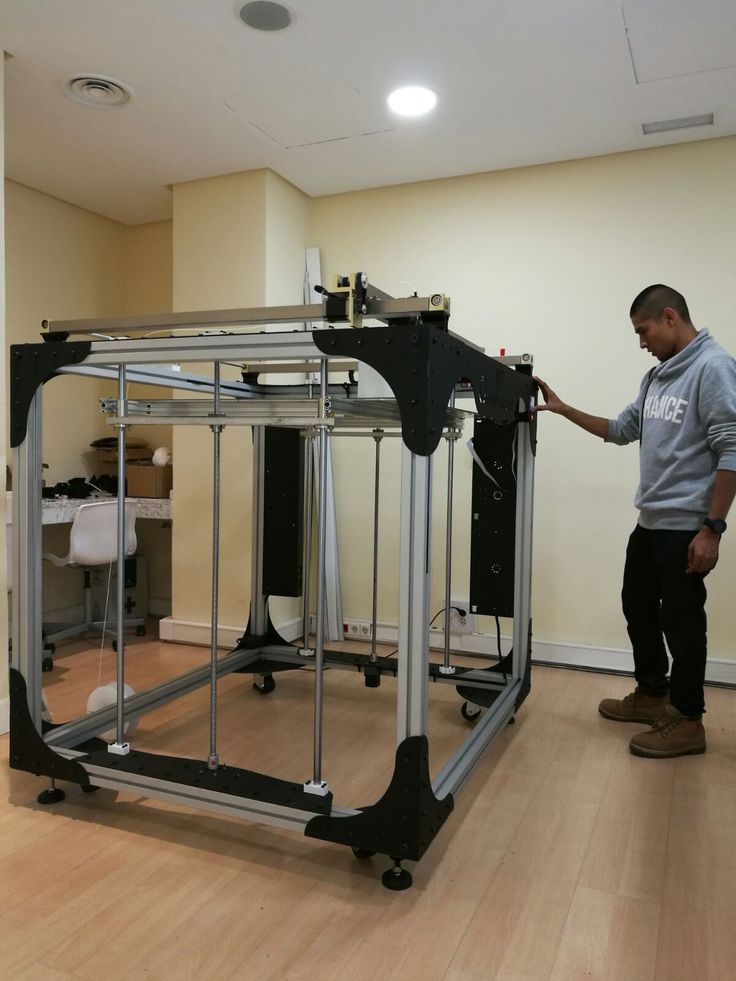 Don’t have the 3D files? Get in touch
Don’t have the 3D files? Get in touch
CONTACT US
INSTANT QUOTE
Browse our different materials, qualities and finishes to get an instant price. What you see is what you pay, no hidden costs!
INSTANT QUOTE
Start Printing
Parts are produced to a high accuracy, using state-of-the-art industrial-grade equipment and the latest materials at our Loughborough 3D printing service
Delivery
Once your parts are finished and checked by our quality engineers, we’ll dispatch your order and email your tracking information – We offer free shipping on all orders!
TRUSTED BY:
SGD is the number one Loughborough 3D printing service, with over 60 Google reviews 1000+ customers trust us. 3D printing technology has advanced considerably over the last decade, and we’re proud to offer the latest material developments and technologies. It’s now even more possible to create the most complex 3D (three dimensional) objects. Almost anything you can imagine can now be designed and produced using a 3D printer, from small plastics moulds & master parts to vast and complex assemblies. We can provide a comprehensive service, offering professional design services to help get your project off the ground. If you’re looking for local 3D printing services in Loughborough, why not use our trusted service!
Almost anything you can imagine can now be designed and produced using a 3D printer, from small plastics moulds & master parts to vast and complex assemblies. We can provide a comprehensive service, offering professional design services to help get your project off the ground. If you’re looking for local 3D printing services in Loughborough, why not use our trusted service!
Whilst we’ve been operating in the East Midlands and the city of Loughborough, we’ve also been providing professional printing services outside of the area too. We operate on a national scale and provide cost-effective, on-demand services for individuals and businesses. We have established an excellent reputation for delivering challenging and complex rapid prototyping and 3D printing services across the UK.
Location isn’t a barrier if you’re looking for 3D printing in the UK, as we offer free tracked delivery nationwide. Our team of expert engineers are happy to provide a free 15-minute consultation and can provide you with a free and no obligation for your next project. This is swift and easy and can be done via our instant quote system from a 3D file (STEP, IGES, STL, OBJ, etc.). Our 3D printing costs are highly competitive, and we aim to price match any prices you’ve seen cheaper elsewhere.
This is swift and easy and can be done via our instant quote system from a 3D file (STEP, IGES, STL, OBJ, etc.). Our 3D printing costs are highly competitive, and we aim to price match any prices you’ve seen cheaper elsewhere.
When it comes to 3D printing, there are many misconceptions about what is involved and the limitations of the process. These issues are clearly explained in our expert 3D printing guide we’ve published. We only use industrial-grade 3D printers, producing high-tolerance parts to standards meeting the requirements of our professional customers. Our knowledgeable engineering team can offer free expert advice on replacement parts, materials, and processes to help get your project off the ground.
3D PRINTING & DESIGN SERVICE
We offer a full range of 3D printing services, often referred to as additive manufacturing. Each service we offer comes with its limitations, and with our expert design service, we can help optimise your design for additive manufacture. With over ten years of experience in the plastics industry, our team of qualified SolidWorks professionals will ensure your parts meet the highest standards using the latest software CAD suites.
With over ten years of experience in the plastics industry, our team of qualified SolidWorks professionals will ensure your parts meet the highest standards using the latest software CAD suites.
We are the premium supplier of 3D printing services to the residents and businesses of Loughborough. We are delighted to be based in East Midlands and are proud to be your local 3D printing service. All our staff regularly update their knowledge with all the latest developments in the 3D printing world. Our expert team is regularly asked to give lectures and talks to industry bodies and professionals.
3D PRINTING - FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
How much does it cost to 3D print?
Many factors can affect the total cost of a 3D print. How many parts you need, the material you require and any post-processing can all add to the total cost. There are ways to make 3D printing cheaper such as nesting your parts together. Use our online 3D printing calculator to see how much it can cost.
Where are you based?
We're based in Nottingham, all parts are produced in our Additive Manufacturing facility. No parts are sub-contracted or outsourced. With over 60 five star reviews on Google, we're Loughborough's number one 3D printing service and are trusted by 1000+ customers.
What is 3D printing and how does it work?
We offer three types of 3D printing, and they all work in different ways. SLS fuses nylon powder using a high powered laser, FDM lays down a molten layer of plastic from a heated nozzle, and SLA creates your model using resin cured with UV light. All these processes eventually create a 3D model with different characteristics.
OTHER AREAS WE SERVE
Once again about the use of 3D technologies
3D Printer in the Construction Industry
A group of engineers from the British University of Loughborough, working under the direction of Dr. Sungwu Lim, managed to create a unique cement composition that allows printing products of any shape: convex, cornerstone, curved, cubic.
Researchers abandoned the use of laser sintering technology and digital light processing. Instead, they returned to the origins of 3D printing with a slightly modified fusing technology.
Advanced cement formula is extruded, which greatly simplifies construction work, as it eliminates the need for formwork. Ready-made concrete figures are easy to adjust and finish.
The experiments of British engineers did not go unnoticed. Their idea aroused the keen interest of scientists from the University of Southern California. They suggested using huge 3D printing machines directly on construction sites.
At the moment, a project called Contour Crafting has been sent to the US Patent Office, on the basis of which it is planned to assemble a huge printer that can print complete houses: not only load-bearing walls, but also wiring along with plumbing.
Jewelry Sphere
The main advantages of jewelry 3D printers are ultra-high printing precision and excellent surface quality.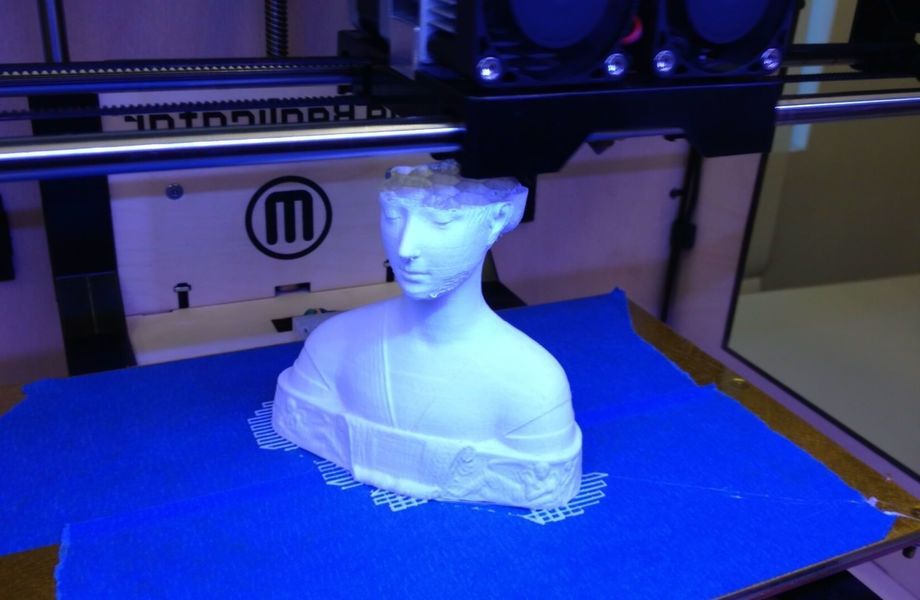 We emphasize once again that thanks to the technologies used, the printed three-dimensional models are exceptionally smooth and do not require additional processing or adjustment.
We emphasize once again that thanks to the technologies used, the printed three-dimensional models are exceptionally smooth and do not require additional processing or adjustment.
Now about a dozen specialized (CAD) programs have come to your aid, allowing you to virtually work out all the smallest details of a future gold or silver jewelry on a computer screen. And if we add the capabilities of modern 3D scanners, which are also available in our company, to the capabilities of CAD programs, then the work of a jeweler will be even more simplified.
Photo - a few examples of 3D printing models of future jewelry, pay attention to the complexity and detail of the elaboration of the smallest elements.
Automotive
Local Motors uses 3D printing to produce their Strati cars.
Local Motors hopes to start selling their car, called the Strati, next year. The car, which will be produced in small series, still has to pass crash tests and overcome a number of other obstacles before this happens. They report that the finished car, which receives the powertrain, suspension and other parts from Renault, will cost in the region of $18,000 - $30,000, including the production of printed parts, which cost more than $5,000.
They report that the finished car, which receives the powertrain, suspension and other parts from Renault, will cost in the region of $18,000 - $30,000, including the production of printed parts, which cost more than $5,000.
But the use of 3D printers is not limited to designs or extravagant cars. Supercar Koenigsegg One:1 with 1,341 hp uses some 3-D printed parts, including a turbo assembly and a titanium exhaust tip, which take only three days to produce, but this reduces their weight by half a kilo. Race car designers Nissan Motor Corp. Delta-Wing uses 3-D printing to create brake radiators, air intakes and transmission side covers.
Among more mainstream production vehicles, the next generation of the Mercedes-Benz S-Class due in 2018 will feature 3-D printed interiors, including air vents and speaker grilles, British website AutoExpress told in August. chief designer of Mercedes.
Medicine
Prostheses - recently in medicine, prostheses made on 3d printers have become widespread, which take into account the individual characteristics of a person as much as possible and can be quite complex in design and withstand heavy loads;
Skull copy – using special scanners, it became possible to reproduce an exact copy of a human skull and use part of this copy as an implant;
Intervertebral discs - thanks to a 3D printer that works with materials containing stem cells, it is possible to restore damaged areas of the spine or even create new, artificial discs;
3D models and crowns - using 3D printing technologies, special 3D models are produced that help in surgery, and dental crowns are also made;
An operation has now been performed to implant a piece of the skull into the patient. This implant was made using a 3d printer, but before that, a model of the patient's skull was created thanks to a 3d scanner, which is also widely used. The advantage of this model is that it takes into account all the uniqueness of the structure and shape of the patient's skull, which means it fits him better. Such a model was made for two weeks after scanning, it was made up of 23 bones, which are part of the human skull. All even the smallest details are taken into account. Such implants are currently helping a large number of people who have suffered from traumatic brain injuries.
This implant was made using a 3d printer, but before that, a model of the patient's skull was created thanks to a 3d scanner, which is also widely used. The advantage of this model is that it takes into account all the uniqueness of the structure and shape of the patient's skull, which means it fits him better. Such a model was made for two weeks after scanning, it was made up of 23 bones, which are part of the human skull. All even the smallest details are taken into account. Such implants are currently helping a large number of people who have suffered from traumatic brain injuries.
In addition to implants, 3D printing is also used to make prostheses for various parts of the human body. These prostheses take into account the individuality of the structure and the uniqueness of human needs, and therefore are very comfortable. In these prosthetic systems, microcavities are specially left, thanks to which the patient's own healthy tissue cells are able to move in them. Thus, faster adaptation to the prosthesis is carried out.
Thus, faster adaptation to the prosthesis is carried out.
Aircraft industry
In 1995, the Northwest Polytechnic Institute of China (NPU) launched the Laser Additive Manufacturing (LAM) research program to develop metal 3D printing devices using titanium alloys, superalloys, and stainless steel.
At present, LAM developments are widely used in the design and manufacture of Chinese military aircraft, in particular, the J-15 carrier-based fighter, the J-16 fighter-bomber, the J-20 stealth fighter and the latest fifth-generation fighter J-31.
In addition to the military, 3D printers are also being used in China's civil aviation.
In 2013, in the laboratory of the already mentioned NPU institute, a 5-meter central wing spar was printed for the promising Comac C-919 passenger aircraft, which was supposed to enter commercial operation in 2016.
Thanks to the use of 3D technologies, it was possible to significantly reduce the weight of the spar - it weighs only 136 kg (a similar part obtained by forging - 1607 kg). At the same time, material savings amounted to 91.5%, and tests have shown that 3D printed parts behave at least as well as those obtained by traditional methods.
At the same time, material savings amounted to 91.5%, and tests have shown that 3D printed parts behave at least as well as those obtained by traditional methods.
FOOD
According to most films, our future is scary and wonderful at the same time. What will we see? What do we do? What will we eat? Since microwaves are radiation to many of us, we are constantly inventing new ways of cooking. Now that the world has learned about 3D printing, it is only natural that this technology will be used for cooking and make this process easier, or at least more fancy. If you believe the Star Trek movie, then 3D printing will be the only way to cook food in 2,000 years. So let's go over the list of eleven different food printing machines to get an idea of the near future of food:
1. 3D Systems ChefJet Printer
The ChefJet 3D premiered at CES in January of this year. The 3D printer produces some of the most amazing 3D prints I've ever seen, and they taste just as good as they look. The ChefJet was originally developed by a small firm, Lab Sugar, founded by a married couple of architects, Kyle and Liz von Hasseln.
The ChefJet was originally developed by a small firm, Lab Sugar, founded by a married couple of architects, Kyle and Liz von Hasseln.
To satisfy their sweet tooth, 3D Systems acquired a start-up and rebranded the company, emphasizing that this 3D printer is the ideal tool for restaurateurs, professional chefs. It is also a must for consumers who want to 3D print goodies in beautiful and decorative shapes that are even a pity to eat. ChefJet comes in two versions - standard and professional, which allows you to print in color. What's more, ChefJet prints just about any flavor that a modern food lab can create.
According to 3D Systems, the ChefJet is scheduled to be released in "the second half of 2014" for less than $5,000, the only problem is that the second half of 2014 is almost over and the printer still hasn't hit store shelves. Unfortunately, 3D Systems revealed during its Q3 financial report that many of the printers scheduled for release this year never saw the light of day, so we won't see the ChefJet outside of shows and blogs until next year.
2. Natural Machines Foodini Printer
Although this list is not meant to be rated, Foodini ranks first alongside ChefJet in terms of how they attract public attention. With a marvelous marketing campaign and the ability to prepare savory meals, Natural Machines Foodini 3D Printer is the answer to the age-old question of healthy eating. Foodini users can cook with fresh ingredients, create a variety of pastas, and place them in reusable capsules, which are then printed in any 3D shape. By using freshly made pastas, there is an opportunity to opt for healthy, natural foods, as opposed to processed foods that are crammed with additives.
Natural Machines launched a Kickstarter campaign back in March of this year, but the goal was not met. And it's pretty amazing, as Potato Saladearned got 554928% of its Kickstarter goal. Being confident in their idea, Natural Machines does not give up. Instead, they are completing their funding phase and planning to mass-produce their printers in the second half of 2015 for a retail price of around $1,000. I would like to point out that Foodini does not cook the food it prints, so you need to either print the food that is already edible or cook it. after printing.
I would like to point out that Foodini does not cook the food it prints, so you need to either print the food that is already edible or cook it. after printing.
3. f3d 3d printer designed by smart students from England
is able to use up to five different extruders, and prepares his food prints using a 1400W halogen oven. The students were able to print out three different ingredients—dough, tomato sauce, and cheese—and make one dish: a tiny pizza. The total cost of the components is about $1900.
4. SMRC Food Printer for NASA
What associations do most people have when they hear the word NASA? Food. NASA has been making strides in food science ever since they sent the Tang drink into orbit in 1962 with the Friendship 7 spacecraft.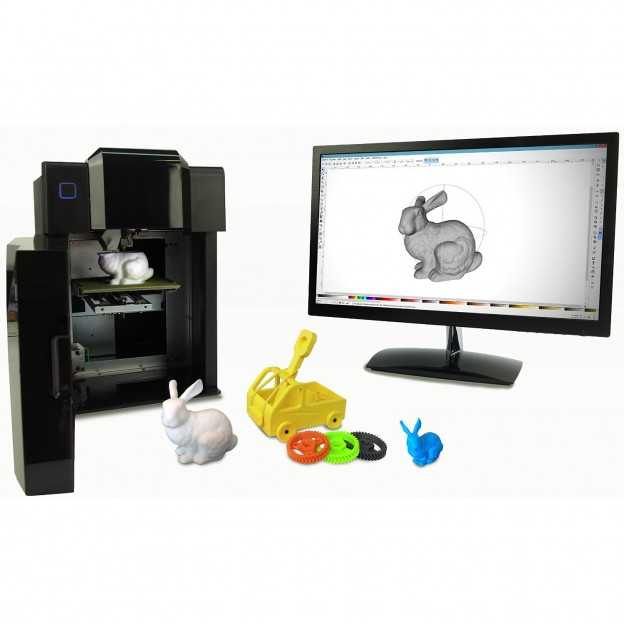 Texas, where Senior Mechanical Engineer Anyan Contractor is working on a food printer for astronauts bound for Mars. Using raw ingredients packaged in capsules, SMRC's food printer can combine different individual ingredients to 3D print a wider variety of food. The firm has already printed proof of its concept, a pizza that was ready in just 70 seconds after printing. The next step for the SMRC is to add nutrients to their meals so that one day, the Mars colonists will be provided with the vitamins and minerals they need to fight the space monsters.
Texas, where Senior Mechanical Engineer Anyan Contractor is working on a food printer for astronauts bound for Mars. Using raw ingredients packaged in capsules, SMRC's food printer can combine different individual ingredients to 3D print a wider variety of food. The firm has already printed proof of its concept, a pizza that was ready in just 70 seconds after printing. The next step for the SMRC is to add nutrients to their meals so that one day, the Mars colonists will be provided with the vitamins and minerals they need to fight the space monsters.
5. Choc Creator Printer by Choc Edge
There are a number of companies on the market that 3D print chocolate. They can either print sweets for you or sell you their own 3D chocolate printers. Choc Creator by Choc Edge is one of the first chocolate 3D printers on the market. Designed by Dr. Liang Hao in 2012, Choc Creator can draw most of the 2D shapes you can think of individually or on cakes and cookies. And with some skill, you can create entire 3D layers. Choc Creator II is currently available for a discounted price of £3200.
And with some skill, you can create entire 3D layers. Choc Creator II is currently available for a discounted price of £3200.
6. Extruder for cakes and chocolate from ZMorph
As you already understood, buying a food 3D printer is not so easy. With the exception of the Choc Creator, commercial food 3D printers really aren't on the shelves yet. Thus, you have to either wait or make them yourself. You can also buy a "regular" desktop 3D printer and make it print with something edible. Some printer makers have already picked up on the idea, like ZMorph, who make a versatile 3D printer with interchangeable tools, including a pasta extruder that can 3D print chocolate and dough.
7. Structur3D's Discov3ry Extruder
If you already have a 3D printer but want to use it for food purposes, you should consider Structur3d's Discov3ry Extruder, which isn't really available online yet. store. Discov3ry is a versatile paste extruder. The campaign to fund it has already been successfully launched on Kickstarter. In no time, you will be able to meet all your printing needs with paste, namely chocolate, icing, or other viscous but less edible materials such as silicone and clay. If you don't feel like waiting, you can build your own versatile grazing extruder, following the example of designer Richard "RichRap" Horne.
store. Discov3ry is a versatile paste extruder. The campaign to fund it has already been successfully launched on Kickstarter. In no time, you will be able to meet all your printing needs with paste, namely chocolate, icing, or other viscous but less edible materials such as silicone and clay. If you don't feel like waiting, you can build your own versatile grazing extruder, following the example of designer Richard "RichRap" Horne.
8. Dovetailed Fruit 3D Printer
If you're picky enough that you don't want to eat pasta, then wait until Fruit 3D Printer comes out. Its creators have come up with a way to fill a sodium gel with flavors that mimic strawberries, after which the entire mixture is placed in a solution of calcium chloride to obtain a product that looks like raspberries. After an initial flurry of media coverage and prints that look more like jelly than real fruit, the firm is never heard from again. However, this is an innovative approach to the art of food printing.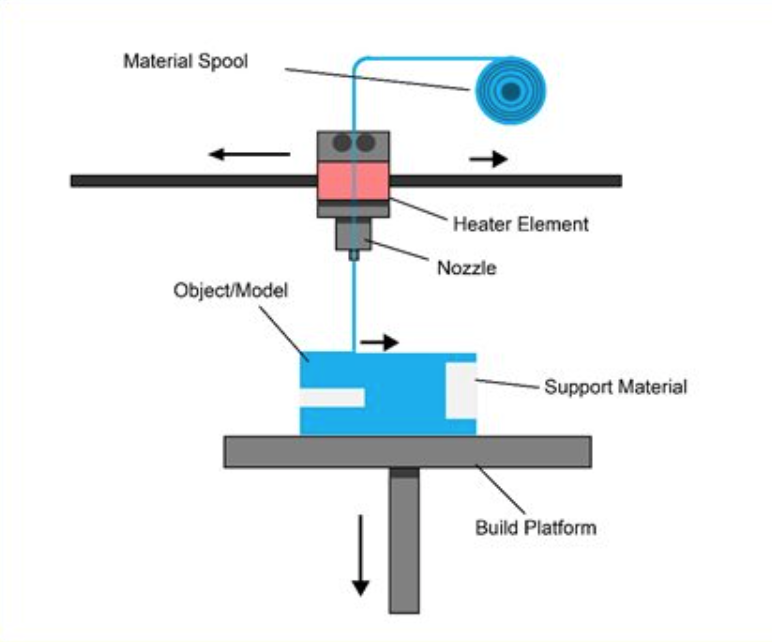
9. TNO's 3D Everything Printer
TNO (or "Nederlandse Organisatie voor Toegepast Natuurwetenschappelijk Onderzoek", I hope you haven't broken your tongue) has come a long way in the field of food printers. This Dutch research group has been working on 3D food printing since 2012 and treats the topic as a major technological breakthrough, not a kitchen fantasy.
TNO believes that these printers can help humanity print food according to the individual needs of each individual. Using historical and physiological data, the printer can prepare food that contains the right amount of nutrients, and at the same time uses flavors according to the user's mood, using alternative sources of nutrients: algae, beet leaves and even insects.
TNO is already partnering with Barilla 3D printing 15-20 pasta every two minutes. They have also teamed up with Chloé Rutzerveld and 3D printed biscuits made from dried fruits, vegetables, nuts and seaweed filled with yeast, bacteria and germinated seeds. Delicious!
Delicious!
10. Goop Printer by Biozoon
If you're under 60, chances are you won't see this printer any time soon. The German company Biozoon is developing mold printing from a nutrient mash specifically for elderly residents of a nursing home. With financial support from the EU, Biozoon plans to complete the 3D food printer by 2015. Using 48 nozzles, liquefied food and a thickening agent, this printer will recreate the shape and taste of something hard to swallow, like a chicken wing, but such a product will simply melt in the mouths of old people. Moreover, such food will be full of nutrients, so necessary to maintain their health.
11. The original food printer from Fab@Home
It is possible that the entire food printer industry began with Fab@Home. The fact is that the creators of this device, Hod Lipson and Evan Malone from Cornell University, just decided to experiment with the introduction of rapid prototyping to the masses at a low price, and the instructions were posted in the public domain. With this, their task was completed. Since 2010, their lab, along with local partners such as the French Culinary Institute, have been among the first to experiment with food extrusion: 3D baked livers with letters baked inside, spaceship-shaped scallops, chocolate, icing, cheese and more. . If it weren't for their creation, we might never have even seen 3D like this - non-printed cakes, chicken wing-shaped porridges, or small pizzas.
With this, their task was completed. Since 2010, their lab, along with local partners such as the French Culinary Institute, have been among the first to experiment with food extrusion: 3D baked livers with letters baked inside, spaceship-shaped scallops, chocolate, icing, cheese and more. . If it weren't for their creation, we might never have even seen 3D like this - non-printed cakes, chicken wing-shaped porridges, or small pizzas.
What associations do most people have when they hear the word NASA? Food. NASA has been making strides in food science ever since they sent the Tang drink into orbit in 1962 with the Friendship 7 spacecraft. Texas, where Senior Mechanical Engineer Anyan Contractor is working on a food printer for astronauts bound for Mars. Using raw ingredients packaged in capsules, SMRC's food printer can combine different individual ingredients to 3D print a wider variety of food. The firm has already printed proof of its concept, a pizza that was ready in just 70 seconds after printing. The next step for the SMRC is to add nutrients to their meals so that one day, the Mars colonists will be provided with the vitamins and minerals they need to fight the space monsters.
The next step for the SMRC is to add nutrients to their meals so that one day, the Mars colonists will be provided with the vitamins and minerals they need to fight the space monsters.
Weapons
For the first time the idea to print military weapons on a 3D printer appeared in the United States of America.
In May 2013, a video appeared on the Internet in which a man shoots from a printed mock-up of a Liberator pistol. It was 25-year-old Cody Wilson, head of Defense Distributed, which promotes the idea of universal availability of 3D weapons.
Using a 3D printer, they printed firearms and uploaded the files of their work to the World Wide Web. Defense Distributed employees have already made magazines that hold more cartridges for the AR-15s rifle and the legendary Kalashnikov assault rifle (AK-47 modification). Also on their account is the manufacture of the lower part of the receiver, in which the bolt of a self-loading rifle AR - 15 is placed.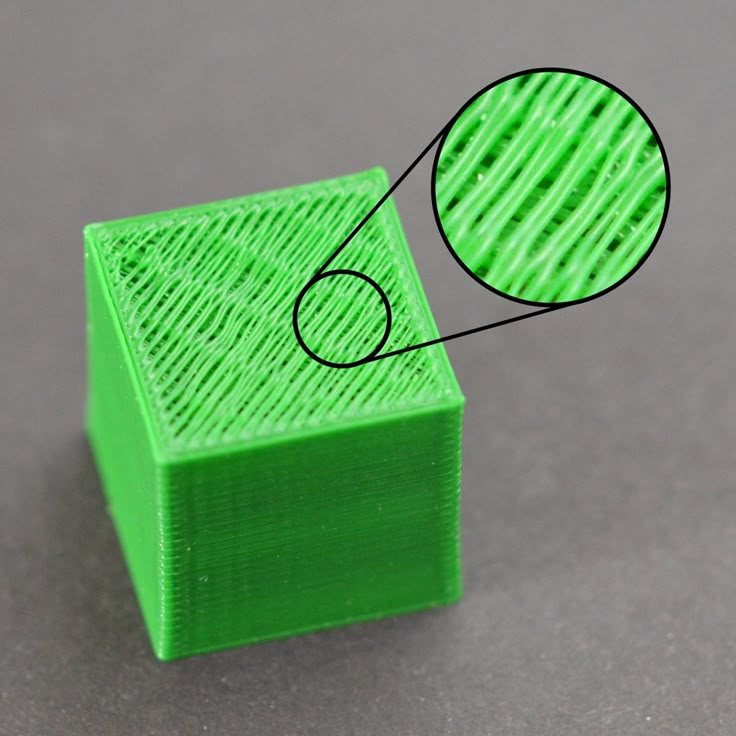 You can attach the barrel and magazine to it, having received a finished weapon without any problems. No authorization is required to purchase parts in the USA. Now work is underway on a 3D printout of the entire rifle. In doing so, Cody and his team dealt a major blow to the American gun control debate. The discussion began in December, after twenty children and six adults were killed by assassins at a junior high school in Connecticut. The vast majority of Americans rallied to support government reform. This is a thorough check that will make it difficult for criminals to obtain weapons. However, this did not prevent Mr. Wilson from obtaining a federal license to manufacture and sell firearms.
You can attach the barrel and magazine to it, having received a finished weapon without any problems. No authorization is required to purchase parts in the USA. Now work is underway on a 3D printout of the entire rifle. In doing so, Cody and his team dealt a major blow to the American gun control debate. The discussion began in December, after twenty children and six adults were killed by assassins at a junior high school in Connecticut. The vast majority of Americans rallied to support government reform. This is a thorough check that will make it difficult for criminals to obtain weapons. However, this did not prevent Mr. Wilson from obtaining a federal license to manufacture and sell firearms.
More serious developments in the field of printing firearms on a 3D printer are being carried out in Austin, Texas. The project is led by Eric Macler, coordinator at Solid Concepts, a 3D printing company.
Erik Machler
Ten industrial 3D printers are installed at the Austin plant. Solid Concepts received a federal license to manufacture weapons, and now, using direct metal laser sintering technology, produces the Browning 19 pistol.eleven". Making a pistol takes up to 35 hours. Depending on which printer and materials are used. More than 1,000 shots have already been fired from the first printed pistol, Solid Concepts, while the company has created a second version of the Browning 1911 model.
Solid Concepts received a federal license to manufacture weapons, and now, using direct metal laser sintering technology, produces the Browning 19 pistol.eleven". Making a pistol takes up to 35 hours. Depending on which printer and materials are used. More than 1,000 shots have already been fired from the first printed pistol, Solid Concepts, while the company has created a second version of the Browning 1911 model.
FASHION
Another famous designer has started experimenting with 3D printing technology. And the results are simply amazing. Katherine Wales started her career in the fashion industry over 15 years ago. She has trained and collaborated with some of the most eminent professionals in the profession, including Jasper Conran, Jean Charles de Castelbajac, Oswald Boateng, Emmanuel Ungaro and Saint Laurent. However, she worked independently on her latest collection. The collection was born thanks to the innovative achievements in the field of additive technologies of the London College of Fashion. She combined all the models into a collection called "DNA Project", thanks to which, among other things, the designer touched the world of 3D printing and transferred her ideas to the creation of accessories.
The collection was born thanks to the innovative achievements in the field of additive technologies of the London College of Fashion. She combined all the models into a collection called "DNA Project", thanks to which, among other things, the designer touched the world of 3D printing and transferred her ideas to the creation of accessories.
The DNA Project is not entirely unique. The collection is the result of a synergy of haute couture, technology and science. As a result of this interaction, incredible models were born that embody the features and structure of human chromosomes. The DNA Project is almost entirely made up of separate and identical balls and structural components (through the use of 3D printing technology) that can create a wide variety of shapes.
FURNITURE
A graduate of the Royal Academy of Art in The Hague, Lillian van Daal was one of the first to develop a unique structure ideal for creating 3D printed furniture.
The designer took the cell structure of living organisms as a basis. A mixture of modern technology, creative genius, and the ability to visualize the finished result helped her create a Biomimicry soft chair printed with plastic filament. The finished product consists of a binding of soft and hard elements, thanks to which it provides a comfortable fit and stands out for its high strength and wear resistance compared to other furniture designs.
It is noteworthy that Lillian van Daal continues to work in this direction. The designer plans to replace polyamide with an environmentally friendly material to create truly safe furniture. It is possible that in the near future stands of the new Biomimicry brand will appear in furniture stores.
EDUCATION
The introduction of 3D printers into the school system is a progressive phenomenon. It contributes to the creation of new opportunities in the study and consolidation of many school subjects.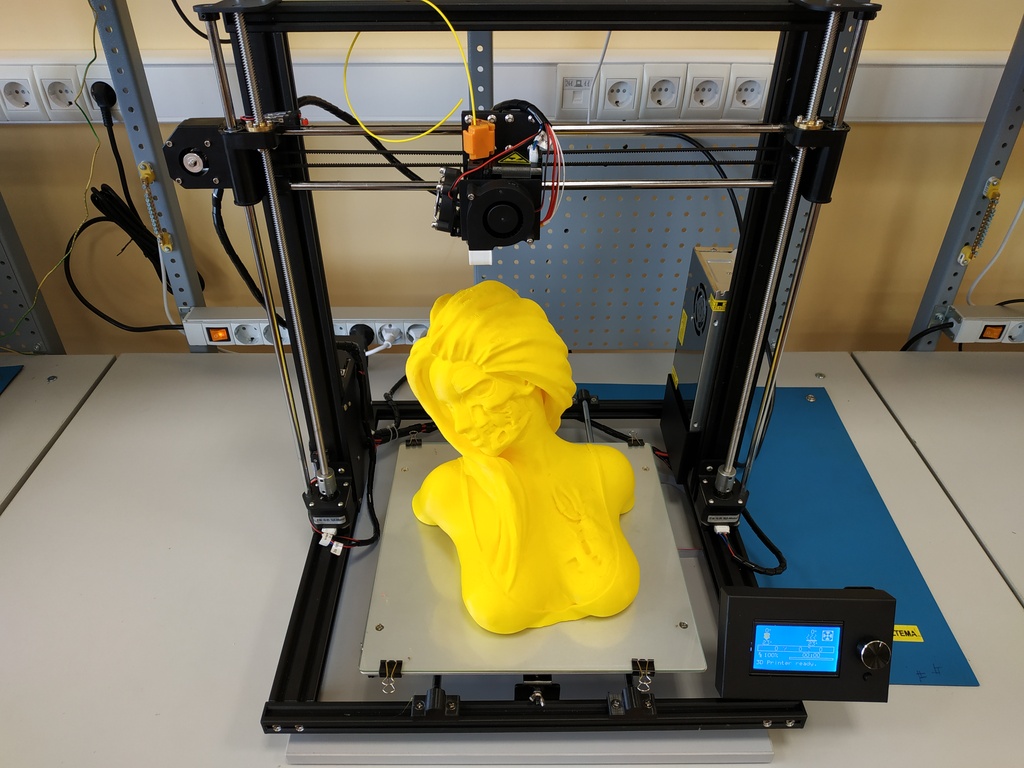 For example, a teacher in a biology class can create a visual aid: some part of an animal skeleton, a human eye, and so on. Or prepare a model of a system of blocks for students for a physics lesson, details of various mechanisms.
For example, a teacher in a biology class can create a visual aid: some part of an animal skeleton, a human eye, and so on. Or prepare a model of a system of blocks for students for a physics lesson, details of various mechanisms.
ARCHITECTURE
Throughout twenty years of work in the field of computer-aided design, R. "Parta" Parthasarati meets a new client with the same question: "What problem can we solve for you?"
The usual answer is: "Accelerate time to market for our product."
With regard to architecture, Parthasarathy found that the two main causes of delays came down to a lack of theoretical study of the project and poor communication. Two years ago, he discovered 3D printing, a completely new technology that significantly reduces design time. It allows you to make an accurate three-dimensional physical model of the building and make it an important element in the work of every designer. Partha saw this as a great opportunity to improve understanding among all those involved in the project, increase efficiency and eliminate costly mistakes. Thus was born iKix, India's first architectural 3D printing service bureau.
Thus was born iKix, India's first architectural 3D printing service bureau.
Previously, all construction models were made by hand. Since this process is time consuming and expensive, architects only make the layout at the final stage of the project, just before the public presentation.
“iKix prints a 3D layout in an average of six to ten days, which is much faster than the month it takes to produce a similar layout by hand,” says Parta. “Let's say a 1,000-acre plot layout—including houses, schools, churches, golf courses, and more—we can build in six weeks versus five months of manual work. The time and cost savings become even more noticeable when plans change and the layout has to be adjusted on the fly.”
iKix uses the color Spectrum Z510 from Z Corp. The capabilities of this printer allow the architect and project manager to quickly obtain multiple copies of the layout - one each for the architect, client, general contractor, subcontractor and civil authorities. “A 3D printer is more than just a prototyping machine,” Parta says. – It really became one of the developer's tools. 3D printing is a breakthrough that I believe will determine the future of technical information exchange for the next two hundred years. Each project must be presented in 3D, and soon it will be so. I sincerely believe that all architects will work in 3D. iKix clients come here to implement more and more new projects in three-dimensional layouts. The benefits are undeniable."
– It really became one of the developer's tools. 3D printing is a breakthrough that I believe will determine the future of technical information exchange for the next two hundred years. Each project must be presented in 3D, and soon it will be so. I sincerely believe that all architects will work in 3D. iKix clients come here to implement more and more new projects in three-dimensional layouts. The benefits are undeniable."
Parta believes that infrastructure objects also need physical layouts. For example, when the authorities decided to build a highway interchange, it is necessary to plan traffic in all modes of its operation. The presence of a physical 3D model simplifies the solution of this problem.
MEDICATIONS
The US Food and Drug Administration has approved the use of 3D printed medicines for the first time. Aprecia Pharmaceuticals has received permission to manufacture tablets using 3D printing. The drug is used to prevent seizures in adults and children with epilepsy.
The tablet, called Spritam, contains a large dose of an anti-epileptic drug that dissolves in a small amount of water, which the manufacturer says should help patients with swallowing problems.
However, the big news is that this is the first time a 3D printed drug has been approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration), writes Business Insider.
Researchers are impressed with the potential of 3D drug printing. The technology makes it possible to create individual medicines with an accurate dosage for each patient.
3D printing can also be seen as an inexpensive way to produce drugs for developing countries. The main thing here is to prevent the production of illicit drugs, the recipe and chemical components of which can be obtained using the Internet.
It is worth noting that the FDA has long appreciated the benefits of 3D printing in medicine.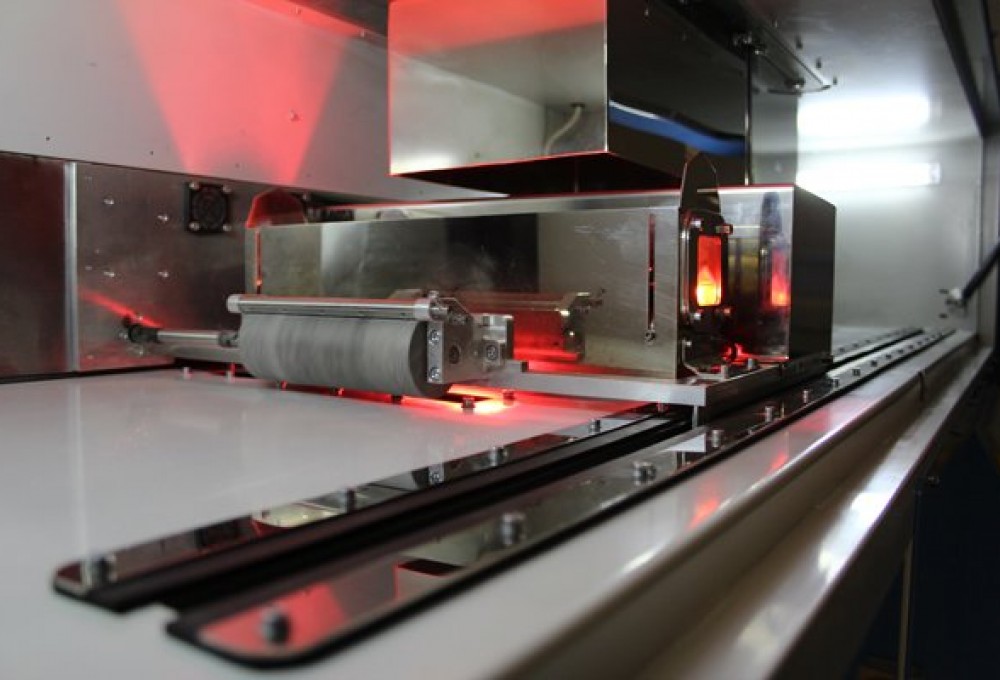 The organization previously approved 3D printing of medical devices.
The organization previously approved 3D printing of medical devices.
MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS
Olaf Diegel, a talented designer who is crazy about 3D printing, presents to your attention his new creation - incredibly beautiful musical instruments. As you may have guessed, many components of the drum kit and synthesizer were recreated using a 3D printer.
“I thought that the consumable that was used in the printing process would greatly affect the sound. Fortunately, this did not happen. Of course, there are some differences, but there is no particular distortion,” says Digel.
Source
Tags:
Printing cement, laser sintering, layer -by -layer, jewelry 3D printing, 3D prosthesis printing, 3D printing titanium, implant, 3D models, 3D models, 3D models, 3D models, 3D models, 3D models, 3D models, 3D models, 3D models, 3D models, 3D models, 3D models. prosthesis printing, house printing, additive manufacturing, food printer,
3D-printed custom splints to relieve arthritis
Archive
Subscribe to author
Subscribe
Don't want
1
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disabling autoimmune disease, a painful condition that can cause severe impairment and ultimately reduce a person's ability to work. Symptoms include swelling and stiffness of the joint, which makes the patient very uncomfortable. But now, thanks to 3D printing technology, a new tire has been developed to help those suffering from this debilitating disease. Even doctors without 3D modeling experience can create such custom splints on the wrist.
Symptoms include swelling and stiffness of the joint, which makes the patient very uncomfortable. But now, thanks to 3D printing technology, a new tire has been developed to help those suffering from this debilitating disease. Even doctors without 3D modeling experience can create such custom splints on the wrist.
Destructive effect of rheumatoid arthritis on the joints (front view)
Inscriptions in the figure: bone - bone, erosion into corner of bone - destruction of bone tissue, thinning of cartilage - thinning of articular cartilage, muscle - muscle, capsule (ligaments) - connecting capsule inflamed synovium spreading across joint surface - inflammation of the synovial membrane of the joint , sinovial fluid - synovial fluid, tendon - tendon, inflamed tendon sheath - inflamed tendon sheath
The destructive effect of arthritis on the joints
Rheumatoid arthritis causes inflammation in the synovium. This is comparable to the inflammation of a cut or wound - redness, swelling, excess fluid and pain.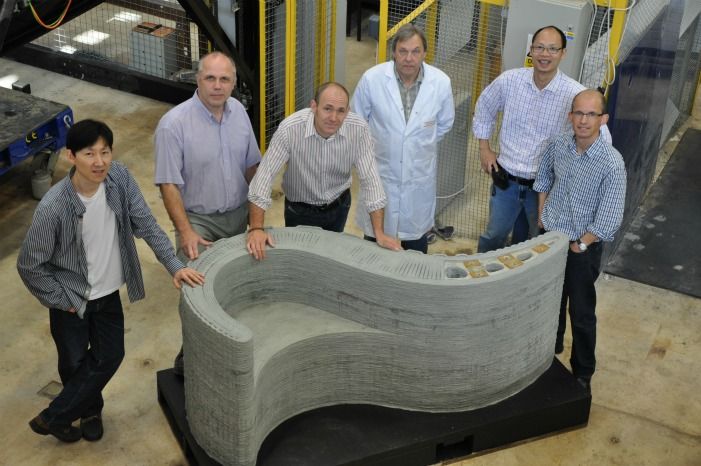 The redness is caused by increased blood flow, which makes the inflamed joint feel warmer than usual. The inflammation is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the synovium. Joints are damaged for two reasons: the nerve endings are irritated by chemicals released during inflammation, or the capsule is stretched due to swelling in the joint.
The redness is caused by increased blood flow, which makes the inflamed joint feel warmer than usual. The inflammation is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the synovium. Joints are damaged for two reasons: the nerve endings are irritated by chemicals released during inflammation, or the capsule is stretched due to swelling in the joint.
Presumably, the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis varies between 0.3% and 1% [1] and is most typical for women and residents of developed countries. However, in many countries it is not possible to estimate the incidence of this disease on the basis of data from public health information systems [2]. The exceptions are Finland and Sweden, where registers have been created for people who are eligible for reimbursement of medical expenses. These logs can be linked to death and cancer data. Another notable exception is the UK, where GPs record the reasons for each consultation. In the UK alone, there are about 690 thousand [3] adults living with the condition.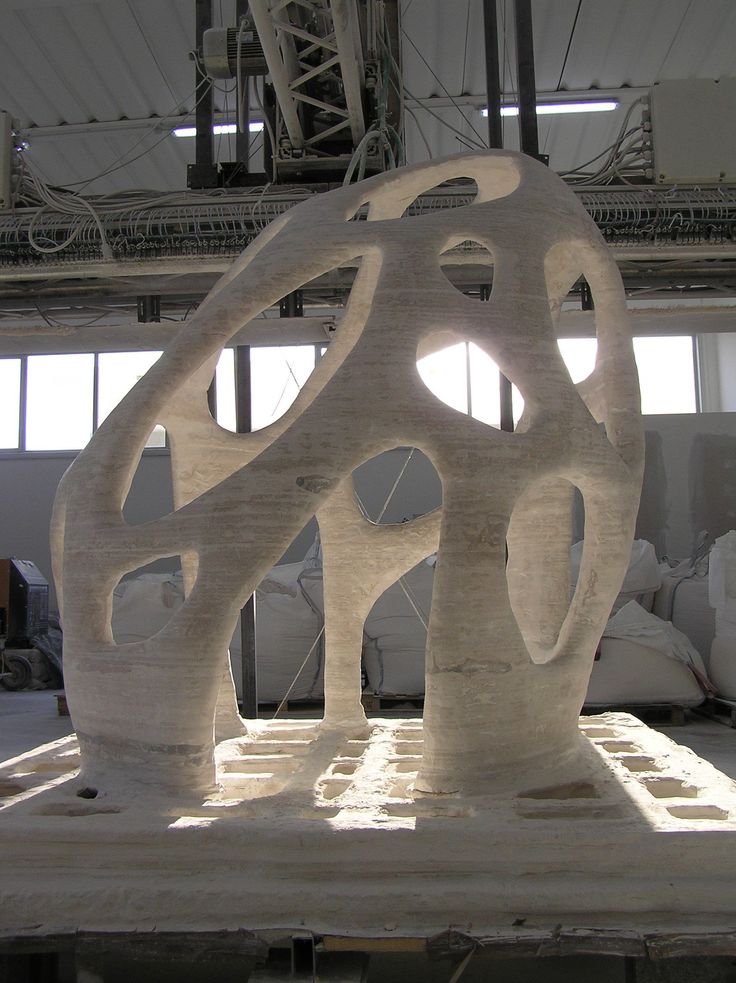 10 years after the discovery of the disease, at least 50% of patients in developed countries are no longer able to work full-time. The economic cost of this disease in the UK as a whole is 3.8-4.75 billion pounds per year. In addition, about 12,000 children under the age of 16 with the juvenile form of the disease have also been recorded in the country.
10 years after the discovery of the disease, at least 50% of patients in developed countries are no longer able to work full-time. The economic cost of this disease in the UK as a whole is 3.8-4.75 billion pounds per year. In addition, about 12,000 children under the age of 16 with the juvenile form of the disease have also been recorded in the country.
And just in the UK, a university teacher has developed a concept for a computer program that will allow doctors without 3D modeling experience to design and print custom-made 3D wrist splints for rheumatoid arthritis sufferers. Dr. Abby Paterson of the School of Design at Loughborough University has developed software for customizing 3D printed tires, which has the potential to be a much more convenient, attractive and potentially less expensive solution than currently available.
Dr. Paterson says: “I wanted to give doctors the ability to create splints that they couldn't do before. They can enhance the look, fit and integrate additional functionality, all the result of our 3D printing device designed here at Loughborough University.With our Objet Connex printer, we can combine multiple materials into a single splint, such as elastic one-piece loops or shock absorbers, but more importantly, the custom software we've prototyped will allow clinicians to design these splints for their patients on their own."
These splints are the result of research that Dr. Paterson started during her Ph.D. at Loughborough University in 2009-2012 under Dr. Ian Campbell and Dr. Richard Bibb, proposing to make custom wrist splints as early as the late 1990s. -X. Dr. Bibb, facilitator of the Medical Applications of 3D Printing course at Loughborough University, said: “We are in the development stage. Studies have proven how much it is in demand and how doctors want it. We know this technology has great potential."
Innovative splints are made by scanning the patient's arm in the appropriate position to determine the exact dimensions and ensure the best possible fit. The 3D digital model can then be printed, producing as many tires as needed. The researchers used Objet Connex 3D printers, which use a variety of colors and materials to achieve the most comfortable tire fit possible. With these devices, complex geometries can be precisely defined when forming the lattice structure of the tire for additional ventilation, and in addition, the patient can choose the type of fastening that is convenient for him.
The researchers used Objet Connex 3D printers, which use a variety of colors and materials to achieve the most comfortable tire fit possible. With these devices, complex geometries can be precisely defined when forming the lattice structure of the tire for additional ventilation, and in addition, the patient can choose the type of fastening that is convenient for him.
Dr. Bibb and Dr. Paterson are currently conducting a thorough cost analysis of custom tires. According to their estimates, the production of tires using 3D printing technologies should be more cost-effective than their traditional production. The developers hope that, having received appropriate financial support, they could prepare a program for use by doctors in 18 months.
[1] Chronic rheumatism - World Health Organization
[2] World prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in 2000 - Deborah Simmons, Colin Mathers, Bruce Fleger
[3] What is rheumatoid arthritis? — Ailsa Bosworth, National Society for the Study of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Image sources: top - Arthritis Research UK; lower — Loughborough University
Article prepared for 3DToday.











