3D printing food packaging
How 3D Printing Transforms the Food and Beverage Industry
17 August 2020
With ever-changing consumer demands, supply chain instability and increasing costs, the food and beverage industry is undergoing a spate of changes.
Both small suppliers, looking to lower production costs, and major producers, targeting even higher production volumes, are in search of solutions that can help them overcome the looming challenges.
3D printing is one of the technologies food and beverage companies integrate into their product development departments and production lines to optimise processes and decrease costs.
To help you better understand the state of 3D printing in the food and beverage industry, we explore application areas that can benefit the most from the technology and highlight some of the examples of 3D printing in action.
Faster packaging development
In the food and beverage industry, packaging serves as the interface between a brand and the consumer. Fundamentally, a good package design attracts the consumer’s attention and impacts the buying decision.
However, developing packaging designs typically involves multiple design iterations that can be costly and time-consuming. Food and beverage brands turn to 3D printing to speed up the packaging development process through faster and more economical production of design variations.
This is possible because 3D printing doesn’t require moulds or other tools for production, only a design file that is sent to a 3D printer and manufactured within several hours.
Furthermore, compared with conventional methods, 3D printing can create prototypes with the finished product’s features and in a variety of colours and materials.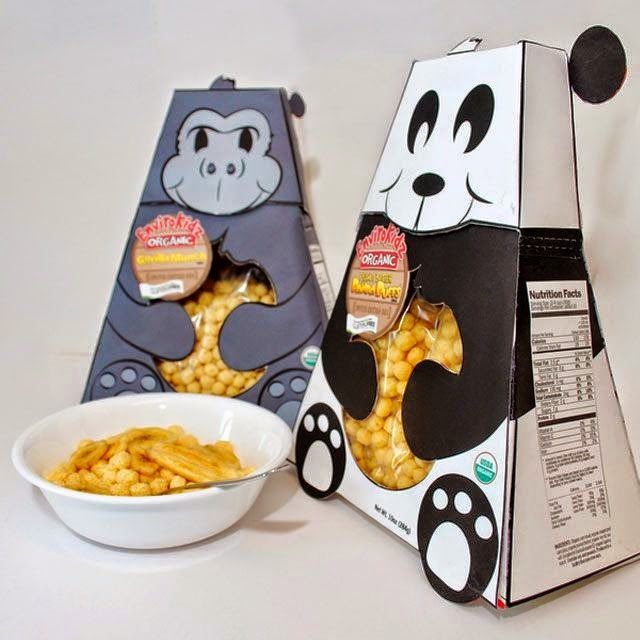 This enables food and beverage companies to test the final product look and feel, further enhancing design reviews.
This enables food and beverage companies to test the final product look and feel, further enhancing design reviews.
For example, Thermos, a manufacturer of insulated food and beverage containers, has been using 3D printing for packaging prototypes since 2006. Switching from outsourcing prototyping jobs to in-house 3D printing reduced the lead time for a prototype from five days to several hours.
The company states that 3D printing allowed them to optimise the fit of the cap stopper and pouring performance of their best-selling Thermos mugs.
Food and beverage companies can increase line uptime by using 3D printing for spare parts production.
The technology helps to ensure that certain spare parts are made available faster, helping to avoid unplanned downtime.
Let’s take beverage filling plants for example. Such plants thrive on speed, with production rates ranging between 40,000 and 80,000 bottles or cans per hour.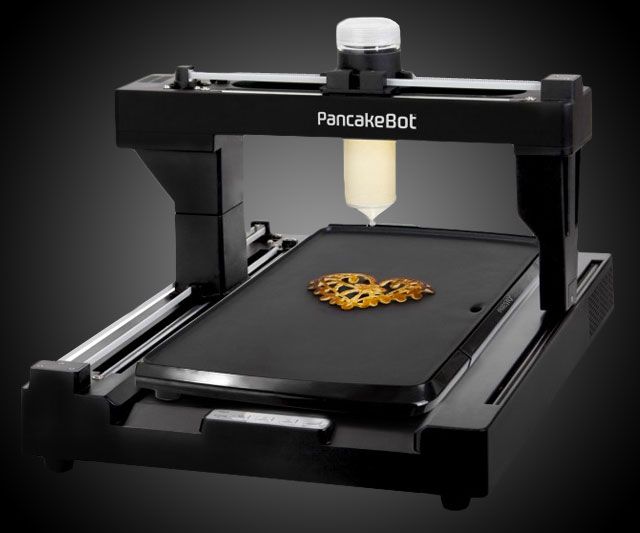 So, if a plant is shut down, its profitability quickly decreases.
So, if a plant is shut down, its profitability quickly decreases.
In the worst-case scenario, finding the issue, requesting a spare part, shipping and installing it, can take a few days. Depending on the size and output of the entire filling line, an hour of lost production may cost anywhere from $4,000 to $30,000.
3D printing enables on-demand spare parts manufacturing that helps to reduce costly downtime. Reducing unplanned downtime, in turn, helps manufacturers to defer costly investment in new assets and increase productivity.
A 3D-printed tool for a Heineken plant in Spain [Image credit: Ultimaker]
In-house 3D printing makes it possible to produce tools for food and beverage plants faster than with conventional processes.
Some of the tools suitable for 3D printing are:
- Maintenance tools
- Safety tools
- (Dis)assembly tools
- Ergonomic tools
- Quality assurance tools
- Spacer and alignment tools
Furthermore, as 3D printing offers design flexibility, tools can be designed ergonomically, providing greater ease-of-use for workers and improving accuracy when performing tasks.
1. 3D printing helps Pepsi to advance packaging design
[Image credit: Pepsi]
Global food and beverage brand, Pepsi, has used 3D printing to create a replica Black Panther mask for soda cans as a part of the promotional campaign for the movie.
Aiming to develop and produce 250 intricate masks as quickly as possible, Pepsi decided that creating moulds would be too expensive. Given its design flexibility and economic low-volume production benefits, 3D printing provided an ideal solution.
Through the partnership with the contract manufacturer, Protolabs, the team used material extrusion technology to create the initial prototypes of the masks. They added some modifications to ensure that the design worked with the picture on the can and that it would remain secure during shipping.
To create the final parts, the team opted for HP’s Multi Jet Fusion technology because of a high-quality surface finish and lower production costs.
In total, it took under six months to go from conceptualisation to a final product, all thanks to 3D printing technology. Both the Pepsi cans and their sleek 3D-printed masks helped gain a lot of attention for the movie, showcasing the power of 3D printing to help develop innovative packaging designs.
Kaspar Schulz, one of the oldest brewing equipment manufacturers in the world, turned to 3D printing to test its design flexibility.
Kaspar Schulz’s new 3D-printed lautering blade cuts the early brewing stages in half, meaning more beer in less time. [Image credit: GE Additive]
In partnership with GE Additive, Kaspar Schulz identified a couple of parts that could benefit from a redesign. One of them is a component inside a Lauter Tun vessel which separates wort – the liquid extracted from the mashing of beer – from solids.
This part is called the racking arm and the team wanted to improve the filtration effect of the spent grain bed inside the vessel.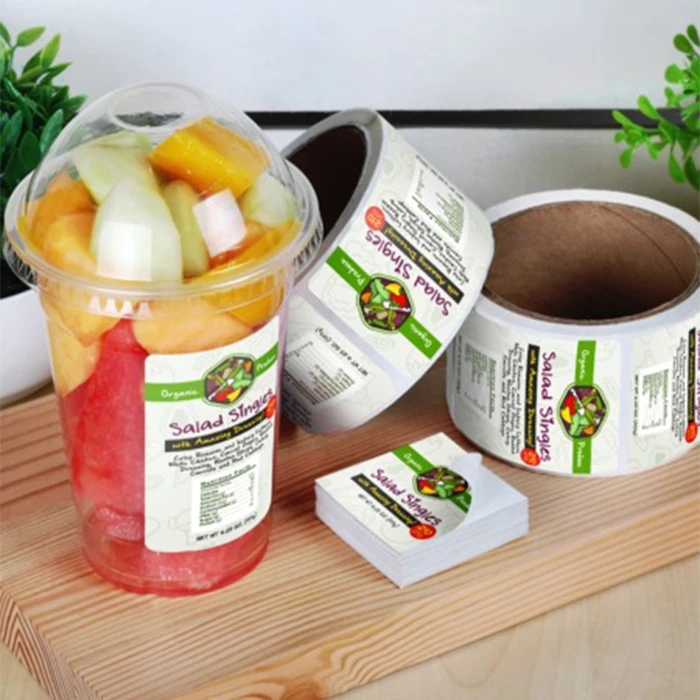
To achieve this goal, GE and Kaspar Schulz designed a thinner blade with internal channels, which loosens the spent grains and distributes water evenly throughout the bed during rotation. Kaspar Schulz’s Head of Research and Development, Jörg Binkert, believes this feature will improve both processing time and yield.
In general, the company sees the key benefits of using AM in the functional integration of parts, which helps to reduce the number of joints and seals. These opportunities, unlocked by the design flexibility of AM, will pave the way for incremental improvements in the brewing process.
Another application for 3D printing in the food and beverage industry is robotic grippers used on food processing lines.
Food processing lines often require custom solutions, and 3D printing offers a viable means of producing grippers customised for specific requirements of these lines.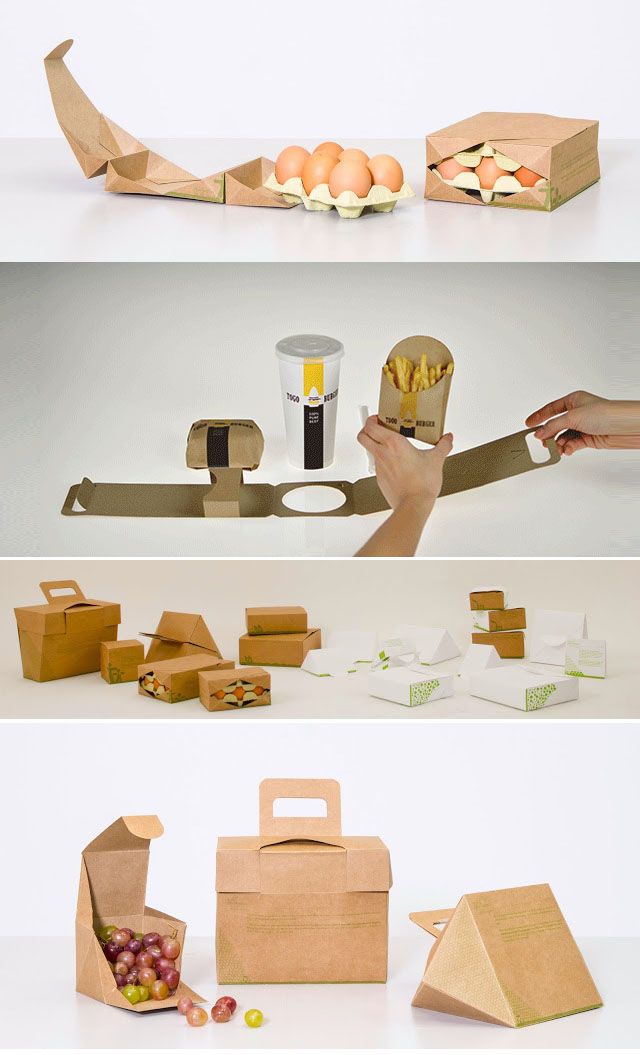
Furthermore, 3D printing makes it possible to reduce the weight of a gripper, unlocking a range of benefits. For example, a lightweight gripper, with the same load capacity, supports faster movements and enables shorter cycle times – a key objective in the manufacturing world.
One company taking advantage of 3D-printed grippers is Icelandic food processing company, Marel. The organisation collaborated with the Danish Technological Institute on the development of nylon grippers integrated into robotic arms that grab meat, such as fillets, to lift it on and off the conveyor belt.
Marel uses 3D printing to create robotic grippers for food processing lines [Image credit: Marel]
Marel sees the critical benefit of 3D printing in its flexibility: the company can customise grippers for different customers without the added cost of milling tools. Additionally, Marel can order grippers to be 3D printed on demand, with a delivery time of just three days – which also helps the company to reduce storage costs and increase agility.
In another example, Langen Group, an equipment supplier to a major U.S. food producer, partnered with the 3D printing service provider, Anubis 3D, to develop lightweight end-of-arm tooling.
This tooling, designed to enable the robots to pick up wrapped, stacked crackers and place them into cardboard boxes, had to weigh less than a kilogram and be able to handle multiple package shapes and sizes.
[Image credit: Anubis 3D]
The Anubis 3D team applied topology optimisation software to create a design that both meets the requirements and is suitable for 3D printing. In the optimisation process, the software algorithms analysed stresses and strains on the structure and adjusted the geometry of a part for strength and lighter weight.
Then, to further increase the grip of the tool, the team created a new design, with profiled holes and channels, that could not have been manufactured conventionally.
3D-printed in nylon, using powder-based 3D printing technology from EOS, the resulting part turned out better than expected. The new gripper provides four times the gripping force of legacy vacuum grippers, uses less air and has greater picking power.
German packaging and bottling machine manufacturer Krones has also showcased how 3D printed parts can be integrated into customised machines in the beverage industry.
[Image credit: Krones]
One such project involved a can twister, 3D printed using a thermoplastic material. In a brewery, for instance, a can twister vertically inverts beer cans by 180 degrees after these have been filled and seamed so that these can then be pasteurised standing upside down.
During the development of the 3D-printed component, many different factors need to be analysed, including the optimal motion sequence of the cans as they are inverted.
The development team needed several attempts to create a design that met all the requirements. But thanks to the advantages offered by AM, the path from design to actual implementation was short.
In addition to faster development, 3D printing creates can twisters with a high level of repeatability – which was a challenge with a manual machining process that would result in deviations in part geometry.
Krones has already successfully tested the can twister in-house, with up to 150,000 cans per hour, and now expects to integrate the component into each of its new canning lines.
After around two years of using 3D printing, Heineken identified multiple applications that helped improve the safety and productivity of its operations.
With the help of Ultimaker’s extrusion 3D printing technology, engineers at the Heineken brewery plant in Spain quickly learned that they could save a lot of time and money by 3D printing custom optimised parts and tools for its production line.
For example, a metal can pusher, used to reject and direct bottles, would cost substantially more and have a longer lead time than a redesigned plastic 3D-printed alternative.
Similarly, the company started 3D printing a stopper tool, which loosens and tightens the columns of guiding wheels that apply bottle labels.
3D printing the tool resulted in dramatic cost savings of 70 per cent and faster delivery time (from three days to one) compared to the previous method of CNC machining. Other simpler tools, such as a toroidal rubber cutter, can be 3D printed in less than an hour.
Overall, the brewery saw several improvements to its production after the adoption of AM in-house. On average, Heineken said it experienced 80 per cent faster delivery times and 80 per cent lower costs for parts.
The food and beverage industry is grappling with many challenges, and 3D printing provides an efficient solution to some of them. It helps food and beverage companies develop better packaging, stay agile with on-demand 3D printing of spare parts and tooling, and improve operations with advanced components.
It helps food and beverage companies develop better packaging, stay agile with on-demand 3D printing of spare parts and tooling, and improve operations with advanced components.
Going forward, we’ll see more food and beverage companies investigating the technology to drive efficiency and meet the challenges of an uncertain future head-on.
3D Printing and Food Packaging Design: What the Future Holds
Written by Kevin Keating at PKG on Jan 29, 2018 8:00:00 AM
While 3D printing may not have been in the news in 2017 as much as it was in prior years, that does not mean that the technology has stalled.
Individuals may have cooled somewhat toward 3D printing, but industry’s enthusiasm has not waned.
On the contrary, while individual interest in 3D printing seems to have leveled off, industry attention to the technology has risen significantly. Huge, emerging markets in India and China are putting the technology to use bridging infrastructure gaps and leap-frogging older technologies with brand new ones thanks to 3D printing.
Food packaging design is increasingly dependent upon 3D printing because of the many advantages the technology offers. The main uses of 3D printing in industry, in general, are prototyping, the creation of replacement parts, model creation, the creation of jigs and fixtures, and A/B testing of products and their package designs.
3D Printing Is Revolutionizing Food Packaging Design Prototyping
Rather than taking months, as prototyping can do with older technologies, it can be done in weeks using 3D printing technology. Yet, the packaging industry has not embraced 3D printing with the fervor of other industries. Prototypes made with 3D printing can include full-color text and graphics. Additionally, necessary design changes (to shape, or label content, for example) can be incorporated into improved prototypes within a matter of days. Ultimately, this accelerates time to market.
Advances in Product Development and Sustainability
The use of 3D printing to combine both product and packaging into a single entity is another exciting development. A California company has created 3D-printed biodegradable cups with energy drink ingredients encapsulated within the cup itself. Users only need to add water to produce an energy drink.
A California company has created 3D-printed biodegradable cups with energy drink ingredients encapsulated within the cup itself. Users only need to add water to produce an energy drink.
3D printing may actually improve plastic recycling practices considerably.
Current designs of the “smart cups” are lidless, which reduces required storage space and transport weight. Since the cups are biodegradable once they are used, consumers can assuage the guilt they might ordinarily feel buying individually packaged drinks.
Customization and Personalization with 3D Printing
Customization and personalization of food packaging design also lend themselves well to 3D printing. Suppose, for example, a gourmet candy brand could 3D print custom packaging for weddings and other occasions. While this can be done now with older technologies, 3D printing could greatly expand access to custom food packaging design and allow products to reach into new markets. Furthermore, apps could be developed that allow customers to create their own customized food packaging design on demand.
Furthermore, apps could be developed that allow customers to create their own customized food packaging design on demand.
Easier Market Testing of Food Packaging Designs
Imagine how much easier A/B testing of food packaging designs could be with 3D printing. Not only can brands be more creative and novel with their designs, they can test them against each other and against more traditional designs to gauge customer sentiment and readiness for novelty. Brands can do this without big investments in time and infrastructure. Moreover, should testing prove inaccurate, 3D printing allows for much faster design modification than older manufacturing technologies.
Food packaging design may not have shown the level of ardor toward 3D printing that other industries have, but 2018 may be the year the industry catches up. The benefits of 3D printing technology to the food packaging design industry are clear, and innovations like Smart Cups are sure to inspire more ways that 3D printing can be used in the food industry. There is really no time like the present for food packaging designers to embrace the promise that 3D printing technology offers.
There is really no time like the present for food packaging designers to embrace the promise that 3D printing technology offers.
PKG Brand Design is always on the forefront of new CPG branding and packaging initiatives - to read more, please subscribe to our blog to always be current on the latest package design industry news.
Related Posts
How to Appeal to Younger Audiences with Your Packaging 06/29 Kevin Keating at PKG 6 Brands That Have Limited Their Use of Plastics to Create Environmentally Friendly Packaging 06/22 Kevin Keating at PKG 5 Brands That Have Utilized the Most Effective Packaging Designs 06/15 Kevin Keating at PKGWHAT ROLE DOES 3D PRINTING PLAY IN PACKAGING PRODUCTION?
Although 3D printing has been around for quite some time, it has only been in the last few years that it has begun to penetrate more and more into our daily lives. This happens because this technology is becoming less expensive, more mature and more accessible from year to year and can become a real solution to problems for many creators and manufacturers, including packaging manufacturers.
This happens because this technology is becoming less expensive, more mature and more accessible from year to year and can become a real solution to problems for many creators and manufacturers, including packaging manufacturers.
3D printing is still underestimated by many manufacturers. While various media tell us about the benefits, many ordinary people and professionals are rather skeptical and do not notice the huge potential of this technology and its multifaceted possibilities, which seriously question the traditional methods of production and consumption.
A wide variety of materials and production methods allows the production of a very wide range of products. To dispel myths and fill gaps in knowledge on this subject, let's see in which areas this technology can be used.
3D printing was only talked about a few years ago, although this technology has been known for quite some time... The first patent application for this technology was filed back in 1984 by three French scientists. At the time, this was referred to in the industry as "additive manufacturing" or "rapid prototype" manufacturing. The latter term was given to this type of manufacturing due to the fact that this technology was the only one at that time that allowed creating prototypes, that is, the first copies of a particular product, in a short time. This is a very important stage in production, as the prototype allows you to test, check the viability of the concept and its manufacturability. 3D printing is very economical compared to traditional manufacturing processes. It omits many of the steps of traditional production methods, such as assembly and many others, which greatly reduces the use of labor and production time. Manufacturers of goods can immediately move from the idea stage to the implementation of a real object, that is, from a 3D model to the first copy and in just a few hours, not weeks! This opportunity to reduce production time and costs is increasingly attractive to industrialists and entrepreneurs in various fields.
At the time, this was referred to in the industry as "additive manufacturing" or "rapid prototype" manufacturing. The latter term was given to this type of manufacturing due to the fact that this technology was the only one at that time that allowed creating prototypes, that is, the first copies of a particular product, in a short time. This is a very important stage in production, as the prototype allows you to test, check the viability of the concept and its manufacturability. 3D printing is very economical compared to traditional manufacturing processes. It omits many of the steps of traditional production methods, such as assembly and many others, which greatly reduces the use of labor and production time. Manufacturers of goods can immediately move from the idea stage to the implementation of a real object, that is, from a 3D model to the first copy and in just a few hours, not weeks! This opportunity to reduce production time and costs is increasingly attractive to industrialists and entrepreneurs in various fields. Well-known companies such as Renault or Adidas are using this technology to create a rapid prototype.
Well-known companies such as Renault or Adidas are using this technology to create a rapid prototype.
As for the topic of immediate interest to us, i.e. packaging, 3D printing can be used to create packaging on demand, according to specific needs. This could significantly reduce both waste and the amount of packaging produced.
In addition, this technology is very good for packaging intended for events limited in time space, such as any special sporting or cultural events, such as the World Cup or the Olympic Games, which require special packaging for souvenirs.
Also, this technology could allow companies to produce personalized packaging for their customers, choosing from a series of pre-existing concepts or making a completely new personalized design. This includes the entire process, from the label to improve or tweak a concept, to a complete redesign of an existing concept for a particular client. This technology is also very important, for example, for gift manufacturers who could add a name, photo or any other element to the package for their client.
At this stage, 2.5D technology can already give excellent results. For example, Casio's Mofrel printer can make textured prints using special paper that is coated with a powder that dissolves under near-infra-red light to create texture. As a result, paper can take on the texture of leather, wood, fabric, and other materials, which can allow manufacturers to create interesting designs for their packaging.
Of course, 3D printers won't be the primary means of packaging production, but they could change the way layouts are designed, allowing packaging makers to make prototypes in a very short time. This would allow the creators to quickly concretize their ideas and resolve emerging technological problems in the shortest possible time. Also, the use of 3D printers would give packaging creators the opportunity to be more creative and interactive, and would allow for faster viability testing.
But not only manufacturers and brand creators are interested in 3D printing, but also logistics companies, big players in the logistics market like UPS or FedEx. Both of these companies have opened 3D printing divisions. Packaging is the main component of logistics, and it is absolutely natural that these transport monsters are developing new technologies. 3D printing technology is also very important, for example, for packaging for small businesses, for companies whose budgets do not allow them to invest in new technologies, including 3D printing technology. In this case, it will be cheaper for them to use the services of their logistics partners.
Both of these companies have opened 3D printing divisions. Packaging is the main component of logistics, and it is absolutely natural that these transport monsters are developing new technologies. 3D printing technology is also very important, for example, for packaging for small businesses, for companies whose budgets do not allow them to invest in new technologies, including 3D printing technology. In this case, it will be cheaper for them to use the services of their logistics partners.
The 3D printing technology used for packaging shows that it is not limited to the creation of new materials or personalization, but it can completely revolutionize the functional properties of packaging! A great example is the company that makes Smart Cups. This is a unique range of energy drinks.
features, pros and cons of each model
0003
Content
-
- What is a food 3D printer
- Scope
- used raw materials
- Types of food 3D printers
- Popular manufacturers
- TOP-10 TOP-10 TOP-10 TOP-10 TOP-20
- 1.
 PancakeBot 2.0
PancakeBot 2.0 - 2. Wiiboox Sweetin
- 3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
- 4. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus 3D Food Printer with Cooling Chamber
What is a 3D food printer
The main feature of a food 3D printer is the raw materials used: instead of printing ink, the device is filled with edible ingredients. The database stores a large number of different recipes, and in order to print a dish, you just need to select one of them and activate the printing process. The final product is layered on a work surface or on a plate: it can be baked in the oven or sent to the freezer.
Application
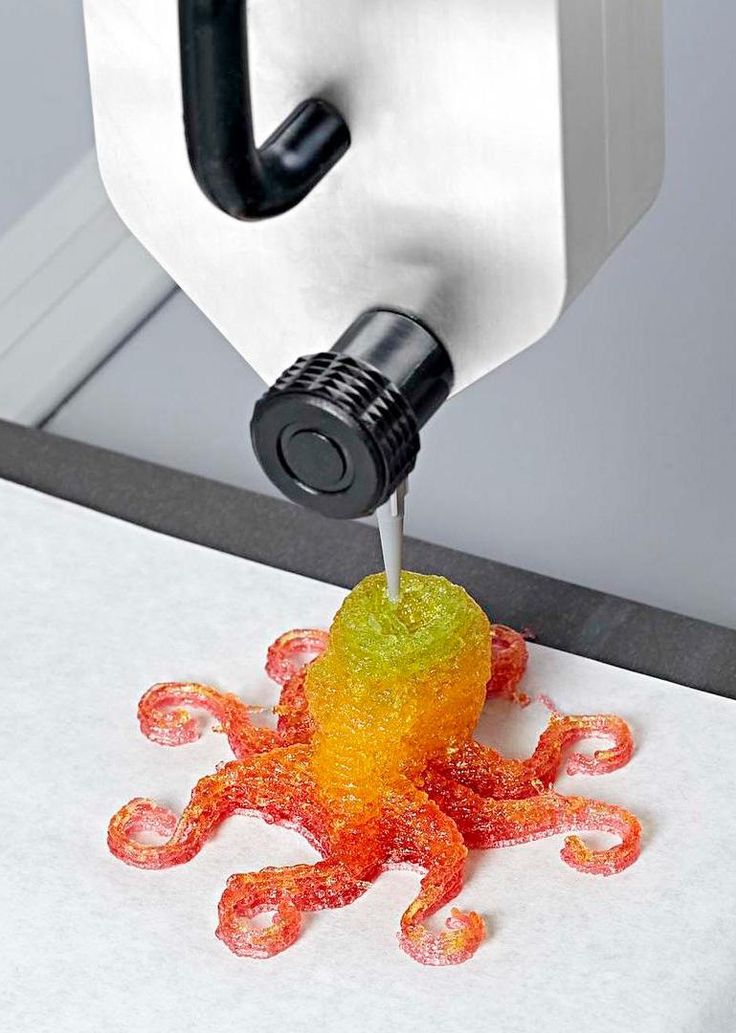
Futuristic 3D Printed Sugar Candy
Cookies printed with icing
Chocolate logos of famous companies
Cream Photo Print
Buying a food 3D printer is worth the owners of coffee houses, author's bakeries and private workshops.
 The finished product has a unique shape and bright appearance. Food printers are often used to create custom wedding cakes, cartoon character cookies, Christmas gingerbread cookies, and so on. The possibilities of a baker who owns such a device are endless: the main thing is to buy quality products.
The finished product has a unique shape and bright appearance. Food printers are often used to create custom wedding cakes, cartoon character cookies, Christmas gingerbread cookies, and so on. The possibilities of a baker who owns such a device are endless: the main thing is to buy quality products. Raw materials used
The following ingredients are used as raw materials:
-
Chocolate without additives and impurities;
-
Mastic;
-
Sugar;
-
Whipped cottage cheese;
-
Vegetable and fruit pastes;
-
Fish and meat pates;
-
Flour;
-
Cheese, etc.
The confectionery pattern is applied to sugar, wafer or shock transfer paper. The first type has a sweetish aftertaste and aroma of vanilla. Due to the snow-white surface, no additional coating is required: the drawings look bright and clear.
 The wafer paper is made from rice flour and does not have a special taste, due to the light shade, the final drawings look less clear. Shock transfer paper is completely transparent and is suitable for transferring a design to a product (for example, a cake). For the packaging of finished products, food-grade plastic for a 3D printer is used.
The wafer paper is made from rice flour and does not have a special taste, due to the light shade, the final drawings look less clear. Shock transfer paper is completely transparent and is suitable for transferring a design to a product (for example, a cake). For the packaging of finished products, food-grade plastic for a 3D printer is used. Interesting! Food printers are involved in waste reduction. Unattractive fruit and confectionery leftovers are used in the preparation of printing mixes. This makes it possible to use the means of production more efficiently.
Types of 3D food printers
Cooking enthusiasts can take advantage of the following food printing devices:
-
3D food printers are devices that print dishes whose recipes are listed in a database. The final product is layer-by-layer superimposed on the work surface, and the raw material comes from filled cartridges;
-
Confectionery printers are used to transfer images onto specialty paper or to design small confectionery products such as candies.
 Such printers print an image on pre-prepared paper: rice, wafer or shock transfer;
Such printers print an image on pre-prepared paper: rice, wafer or shock transfer; -
Food plotters transfer the image not to paper, but directly to the finished product. For example, a plotter is used to transfer an image directly onto a cake.
There are several types of food 3D printers:
-
Extrusion - paint is applied to the surface before the dish is created. The process is controlled by the computer with the loaded image. The system has an extruder that heats the food mixture, and the distribution of raw materials depends on the print head. The raw material is loaded into a syringe placed in the head. This means that in order to combine different shades, you have to periodically stop printing and change the syringe;
-
A carousel-type food 3D printer also has an extruder, but its main feature is the method of feeding raw materials: the containers rotate around the working surface, the supply and dosage of the material used depends on the recipe specified in the program.
 The storage can contain countless recipes, and operation does not cause difficulties even for an inexperienced user.
The storage can contain countless recipes, and operation does not cause difficulties even for an inexperienced user.
Popular manufacturers
Eminent manufacturers offer the best value for money food 3D printer. Quality devices provide accurate printing, high speed, durability, simplicity and ease of use.
Wiibox
This company manufactures 3D printers with high build quality and high productivity. These are universal mechanisms that fill both chocolate paste and mashed potatoes. Numerous positive reviews confirm the high quality of Wiibox products.
byFlow
The Dutch company byFlow specializes in food printing technology. The pursuit of excellence helps the company open up new horizons: the technique prints products from spinach, meat emulsion and other materials. High build quality, ease of use and durability - all these characteristics are applicable to the products of this company.
Choc Edge
Choc Edge is committed to revolutionizing the world of chocolate making.
 Numerous experiments and focus on consumer feedback help to create more powerful devices that provide the optimal temperature for preparing and storing chocolate figures.
Numerous experiments and focus on consumer feedback help to create more powerful devices that provide the optimal temperature for preparing and storing chocolate figures. Attention! Printing dishes helps save time on cooking: instead of culinary worries, the user can simply activate the printing process and get on with other things.
Free shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Choc Edge Available on credit. To checkout, add the product to the basket and follow the instructions Go
Manufacturer Wiiboox Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Choc Edge Top 10 Best Food Printers: A List of the Most Current Models
Before you buy a food 3D printer, you need to familiarize yourself with the most popular devices on the world market.
 The top is based on ratings and customer reviews.
The top is based on ratings and customer reviews. 1. PancakeBot 2.0
PancakeBot 2.0 is easy to use, which means it's suitable for inexperienced users too. Users can choose from suggested designs in the software, or create their own. Used to print pancakes.
Pros:
-
Ease of operation;
-
A wide range of proposed projects;
-
High speed.
Cons:
2. Wiiboox Sweetin
Buying a food printer from Wiiboox is worth not only for confectionery lovers, but also for ordinary chefs: the device prints cakes, cookies and even mashed potatoes. The main raw materials can be meat, cheese, chocolate, jam, mashed potatoes, dough and much more. A convenient touch panel helps to set the desired mode of operation, and a stylish appearance complements the interior of any establishment.
Pros:
-
Versatility: the ability to print not only sweet dishes, but also side dishes;
-
Attractive appearance;
-
High build quality;
-
Convenient control by touch panel.

Cons:
-
High price.
3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
When talking about which chocolate 3D printer to buy, it is worth mentioning the numerous advantages of Choc Creator V2.0 Plus. The new model has become more perfect: the developers have worked hard to eliminate the shortcomings of the previous version. The modern model has small dimensions, so it can be used in any kitchen, and the uniform heating of the syringe ensures high-quality and uninterrupted operation. In practice, the chocolate printer has shown tremendous potential: it prints complex figures from chocolate.
Pros of :
-
Attractive appearance;
-
Uninterrupted work;
-
Durability;
-
The ability to create durable and beautiful chocolate figures.
Cons :
4.
 Choc Creator V2.0 Plus 3D food printer with cold chamber
Choc Creator V2.0 Plus 3D food printer with cold chamber
The new version of the Choc Creator V2.0 Plus printer is equipped with cooling chambers by popular demand. Users say that maintaining the optimal temperature in the room to preserve the integrity of chocolate figures is too problematic: therefore, the new device cools the raw materials. The price of a food 3D printer with a cooling system is slightly higher than a classic one, but the high performance of the final product justifies any costs.
Pros of :
-
Availability of a cooling system for finished products;
-
High printing precision;
-
Long service life;
-
Ease of use: You can turn the fans on and off with the side buttons.
Cons :
-
High price.
Attention! Confectionery food 3D printers are often used by artists to create edible masterpieces.
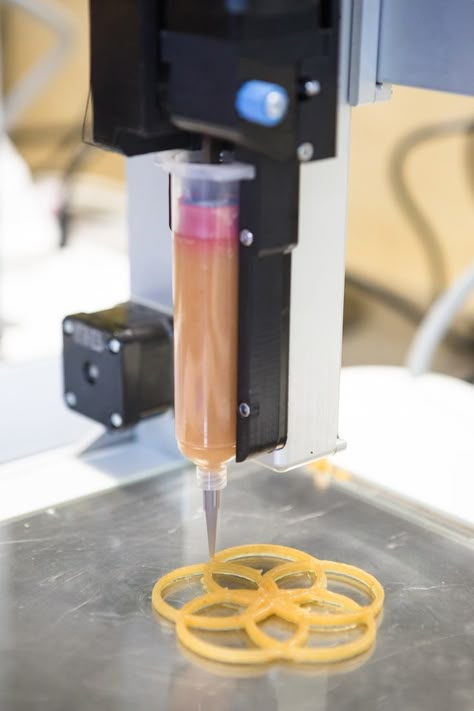 This is a unique technology that helps to unleash the creative potential of the chef.
This is a unique technology that helps to unleash the creative potential of the chef. 5.byFlow Focus
Food printer from the Dutch company byFlow, which specializes in 3D printing of food. The compact high-tech device is used for the bakery industry, and the cartridges are suitable for the application of any pasty ingredients.
Pros:
Cons:
6. Chefjet Pro
Buying a ChefJet Pro food printer is a must for people who dream of making bright and stylish sweets. The device is created on the principle of inkjet printing: sugar-containing powder materials are used instead of paints. The final product is made by powder layering. The printer is suitable for combining different shades and creating gradients.
Pros:
-
The ability to create unique flavors;
-
Neat and bright printing;
-
Aesthetic appearance of the device.

Cons:
-
High price.
7. Foodini
The 3D food printer from Foodini works on the principle of a stationary printer, but instead of printing inks, layer-by-layer imposition of edible raw materials is used: dough, cream, chocolate, cream, etc. The device is versatile: the user himself can choose the material, or use ready-made cartridges with products.
Pros:
-
Practicality;
-
High build quality;
-
Attractive appearance;
-
Availability of an online platform with unique recipes.
Cons:
8. Mmuse – Chocolate 3D Printer
The closed MMuse 3D printer is suitable for chocolate printing. Chocolate beans are used as raw materials: they are heated in an extruder and fed to the work surface through the print head.

Pros:
Cons:
9. ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5
ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5 3D Printer
A food printer from Chinese manufacturers is used in the process of making pancakes of various shapes. Ease of operation allows the device to be used by children under adult supervision.
Pros:
-
Ease of operation;
-
High build quality;
-
Affordable cost.
Cons:
10. ZMorph VX
A multifunctional 3D printer capable of printing not only food, but also rubber, ABS plastic, polylactide, PVA, nylon, elastic and metal materials. The product is able to print with chocolate, butter, cookies, icing and other ingredients. In addition, there is a function of engraving and CNC milling.
Pros:
Cons:
-
High price.
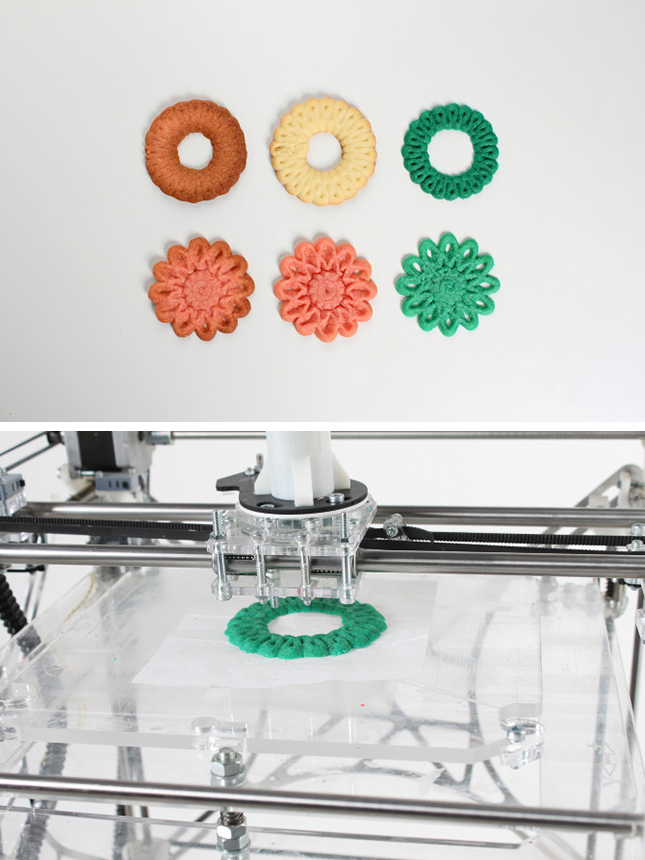

Selection guide
The modern market offers a wide range of food printers. Before making a purchase, you need to carefully study the characteristics of each model and build on your own preferences. Experts have created several recommendations for choosing:
-
In case you want to create realistic images for confectionery 3D printing, pay attention to the diameter of the nozzle: the narrower it is, the more accurate the image will be;
-
It is better for people living in regions with a warm climate to purchase chocolate 3D printers with a cooling system: such devices ensure that the figurines are kept at the optimum temperature;
-
The possibility of self-refilling the cartridge is the most practical and economical way to operate the printer;
-
Print speed is an important consideration for restaurant owners. Large batches of dishes must be produced quickly, and for home use this is not a very strict selection criterion.

Learn more
-
- 1.
- What is a food 3D printer