3D printing effect on economy
Despite fears, 3D printing has positive effects on global trade, study finds -- ScienceDaily
Science News
from research organizations
- Date:
- August 16, 2022
- Source:
- University of California - San Diego
- Summary:
- Research finds the technology is a boon to trade, allowing participating countries to provide higher income and more opportunities to their people.
- Share:
FULL STORY
3D printing technology enables economies to produce goods locally, so conventional wisdom has been that it would dramatically reduce international trade; however, new University of California San Diego and World Bank research presents robust evidence that 3D printing expanded trade.
advertisement
The paper coauthored by Caroline Freund, economist and dean of the School of Global Policy and Strategy, finds that 3D printing changed production processes, but supply chains remained intact. The study is the first to examine the impact 3D printing has on trade.
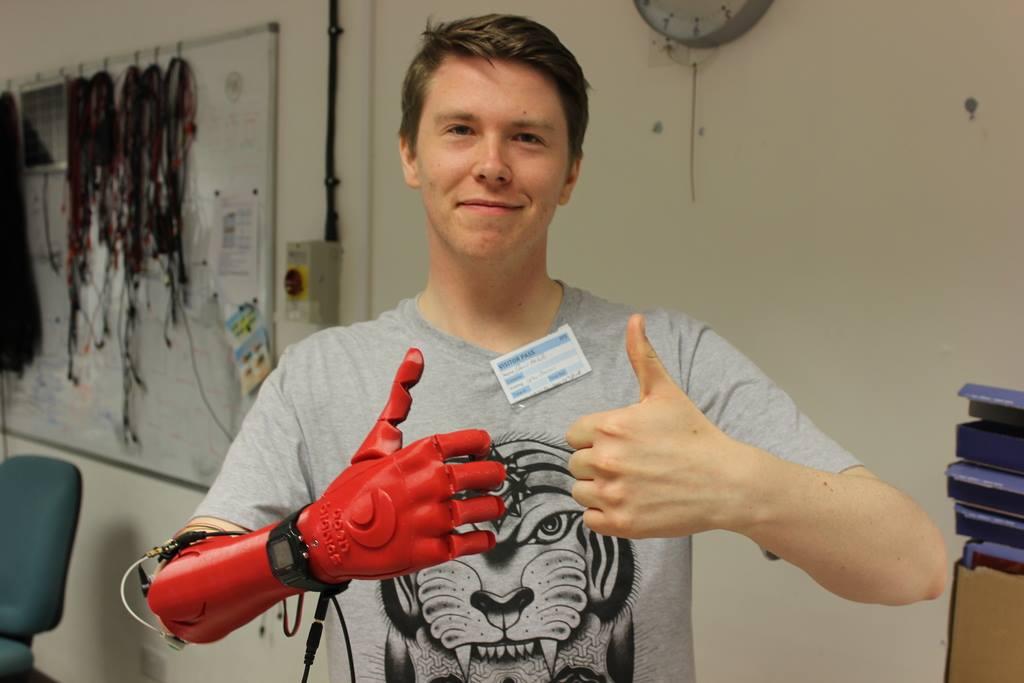
Published in the Journal of International Economics, the paper looks at the production of hearing aids -- a good most commonly produced by 3D printing.
The results reveal that the shift to 3D printing led to a doubling or near doubling in producers' exports after five years and the technology was the main cause for the rise in exports.
Freund and co-coauthors also examined 35 other products, such as running shoes, aircraft parts and prosthetic limbs that are increasingly being 3D printed and they found similar patterns.
"The technology is a boon, not a curse to trade," Freund said. "A country's exports of hearing aids increased more than trade in other similar goods following the adoption of 3D printing by manufacturers there. The new production technology in combination with trade means that consumers around the world suffering hearing loss are benefitting from better and often cheaper hearing aids. "
"
One reason behind the expansion is that printing hearing aids in high volumes requires a large investment in technology and machinery. The countries that were early innovators -- Denmark, Switzerland and Singapore -- dominate exports of the good, while middle-income economies such as China, Mexico and Vietnam also have been able to substantially increase their market shares.
In addition, hearing aids are lightweight products, which makes them fairly cheap to ship internationally. The same is true for the other products the authors examined -- lighter products are associated with more trade growth.
These results are based on comparisons of the growth of the 3D printed products to other similar goods. The authors also accounted for trends and other factors that could skew the data.
"Policymakers often view 3D printing as a means to shorten supply chains when in fact it is more likely to enhance trade and reshape supply chains," said Freund, former global director of Trade, Investment and Competitiveness at the World Bank.
While the analysis of 3D printing's impact on trade is positive, it has the possibility of being short-lived. If 3D printers become more accessible to local producers or even consumers in some sectors, production could be more localized, hindering development opportunities through trade.
The study "Is 3D printing a threat to global trade? The trade effects you didn't hear about" is coauthored by Alan Mulabdic, economist for the Equitable Growth, Finance and Institutions' Chief Economist's Office at the World Bank, and Michele Ruta, lead economist at the World Bank.
make a difference: sponsored opportunity
Story Source:
Materials provided by University of California - San Diego. Original written by Christine Clark. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference:
- Caroline Freund, Alen Mulabdic, Michele Ruta. Is 3D printing a threat to global trade? The trade effects you didn't hear about.
 Journal of International Economics, 2022; 138: 103646 DOI: 10.1016/j.jinteco.2022.103646
Journal of International Economics, 2022; 138: 103646 DOI: 10.1016/j.jinteco.2022.103646
Cite This Page:
- MLA
- APA
- Chicago
University of California - San Diego. "Despite fears, 3D printing has positive effects on global trade, study finds." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 16 August 2022. <www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/08/220816175114.htm>.
University of California - San Diego. (2022, August 16). Despite fears, 3D printing has positive effects on global trade, study finds. ScienceDaily. Retrieved October 26, 2022 from www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/08/220816175114.htm
University of California - San Diego. "Despite fears, 3D printing has positive effects on global trade, study finds." ScienceDaily. www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/08/220816175114.htm (accessed October 26, 2022).
advertisement
5 Ways 3D Printing Will Change the Economy [Infographic] [Infographic]
Home Blog 5 Ways 3D Printing Will Change the Economy [Infographic]
Three-dimensional printing, while once innovative and exciting, is, like traditional paper printing, becoming commonplace. As a result, those who use it take it for granted. However, projections that examine 3D printing’s economic impact on society suggest that maybe we should give this new-old technology some credit.
Experts anticipate that 3D printing technology will affect the economy in numerous ways. However, there is a handful that promise to provide direct benefit to business owners and consumers alike.
5 Ways 3D Printing Will Change the Economy
Job Growth
As the use of 3D printing increases across the globe, so too will the need for more skilled laborers in the manufacturing sector. It is anticipated that by 2027, the prevalence of this technology will create 3 million to 5 million new jobs across the aerospace, industrials, consumer products, health care and automotive industries in the U. S. alone. An estimated 2.8 billion of those jobs will involve 3D printing enabled manufacturing, while another several billion may include the design, maintenance and material development for the printers themselves.
S. alone. An estimated 2.8 billion of those jobs will involve 3D printing enabled manufacturing, while another several billion may include the design, maintenance and material development for the printers themselves.
Reduced Production Costs
Because 3D printers can fabricate the various parts and components that are used on multiple machines throughout a factory, they can do the job of numerous pieces of equipment and workers. This type of productivity can lead to reduced production costs, which can help industrial companies remain competitive and profitable. It may also reduce production time, which invariably translates to more profit.
No Need for Shipping
3D printing enables the sharing of physical objects between two people or entities who may be located in different towns, cities, states or even countries. The significance of this is huge for industrial companies and buyers. For one, it means that manufacturers are not limited to whom they can sell, at least not geographically speaking.
With the cost of shipping no longer an obstacle, an overseas buyer can purchase a machine, part or component from a U.S. based manufacturer without fear of incurring thousands of dollar’s worth of shipping charges. Also, because, theoretically speaking, consumers can manufacture their own products, manufacturers may no longer have a need for huge industrial warehouses or factories.
Improved Health Care
The health care industry has already been and will continue to be impacted by 3D printing. Invisalign is an excellent example of how health care professionals can use 3D technology to provide an effective yet affordable form of treatment.
Beyond Invisalign, however, surgeons are using the technology to practice sophisticated and tedious procedures before performing them in real life; medical device companies are creating replicas of organs to customize devices and stints; donor companies are creating models out of actual human cells to transplant into the human body.
The possibilities for 3D printing’s use in the health care industry are endless, and they promise to increase society’s overall quality of life, reduce health care costs and even save lives.
Stock Market Boom
Because of its various applications in a wide range of sectors, three-dimensional printing is bound to infiltrate industry after industry. As it does, it is only reasonable to think that the stock market prices within those sectors will soar as the technology positively impacts each in various ways.
Category: Blog
Related Posts
Five factors impacting 3D printing on the global economy
02/25/2014
The rapid development of 3D printing technologies will be accompanied by five trends in the current balance of the global economy, the consulting firm McKinsey & Co. recently concluded.
Last year, the company listed 3D printing as one of the 12 technologies that could impact the global economy and predicted the 3D printing market would grow to $550 billion by 2025. Now, McKinsey is putting 3D printing at the forefront and is advising property managers to prepare for five changes in the global economy that will accompany the development of 3D technologies.
Now, McKinsey is putting 3D printing at the forefront and is advising property managers to prepare for five changes in the global economy that will accompany the development of 3D technologies.
1. Accelerate Product Development Processes
Since 3D printing devices have become widely available, 3D printers have been used for rapid prototyping, reducing the development time for new designs. The declining cost of 3D printers is leading to increased adoption of the technology. 3D printed prototypes enable companies to improve customer experience by quickly providing customers with prototypes for feedback and recommendations. McKinsey predicts that the use of 3D printing - both for prototyping and for creating intermediate products needed to develop final products - will increase, speeding up production cycles.
2. New production facilities
In 2011, only about 25% of the 3D printing market's production capacity was used directly for the production of final products. This segment of the market shows the highest rate of annual growth - about 60%. Lower prices and improvements in 3D printing technology mean that 3D printing can become an efficient method for producing custom products with high component complexity but low production volumes.
This segment of the market shows the highest rate of annual growth - about 60%. Lower prices and improvements in 3D printing technology mean that 3D printing can become an efficient method for producing custom products with high component complexity but low production volumes.
3. Changing demand and revenue streams
The sheer potential of 3D printing, including order customization, modular design and one-to-one production of spare parts, means that companies and customers will have to adapt to new opportunities. New manufacturing processes require re-evaluation of manufacturing models, and in the case of 3D printing, the changes will affect both suppliers and consumers, who can in turn become manufacturers.
4. New features
3D printing offers ever-increasing possibilities that many managers are simply unaware of, and this ultimately leads to their limited use. Companies already considering the market implications of 3D printing will benefit from timely development of technical expertise and efficiency gains ahead of the competition.
5. New Competition
3D printing lowers the cost of small batch production by eliminating the cost of special production equipment. This means that new companies specializing in the creation and rapid delivery of complex designs will enter the small-scale production market. Over time, 3D printing technologies may allow such companies to become serious competitors. In the meantime, the domestic use of 3D printing itself will have an impact on the general principles of competition.
More information on McKinsey's forecasts can be found here.
Source
The global impact of 3D printing and safety of the process itself.
One of the key factors behind this claim is that 3D printing has the potential to bring production closer to the end user and/or consumer, thereby reducing existing constraints in the supply chain. The customization of 3D printing and the ability to produce small batches on demand is a sure way to engage consumers and reduce or eliminate logistics costs.
Shipping parts and products from one part of the world to another may become irrelevant as they can be printed locally. This can have a big impact on how businesses large and small alike operate and interact globally in the future. The end goal for many is for consumers to be able to use their own 3D printer at home or in their community. At the same time, digital designs of any product can be downloaded via the Internet and sent to a printer that will be supplied with the necessary material (materials).
There is currently debate about whether this will ever happen, and even more serious debate about the timing in which it might happen.
The wider adoption of 3D printing is likely to lead to the reinvention of a number of products, and of course even more completely new products.
Today, previously impossible shapes and geometries can be created with a 3D printer, but the journey has only just begun.
For the global economy
The use of 3D printing technology has the potential to impact the global economy if this technology is adopted worldwide. A shift in production and distribution from the current model to localized production on demand, on site, to order, has the potential to reduce the imbalance between exporting and importing countries.
A shift in production and distribution from the current model to localized production on demand, on site, to order, has the potential to reduce the imbalance between exporting and importing countries.
3D printing has the potential to create new industries and completely new professions, such as those associated with the production of 3D printers. There is an opportunity for professional 3D printing related services ranging from product designers, printer operators, material suppliers to legal disputes and intellectual property settlements as piracy is a burning issue.
The impact of 3D printing on developing countries is a double-edged sword. One example of a positive effect is the reduction in production costs through the use of recycled and local materials. But the loss of manufacturing jobs could hit many of them hard, which will take time to overcome this problem.
The developed world is likely to benefit the most from 3D printing, where a maturing society and changing age demographics are raising manufacturing and workforce concerns.