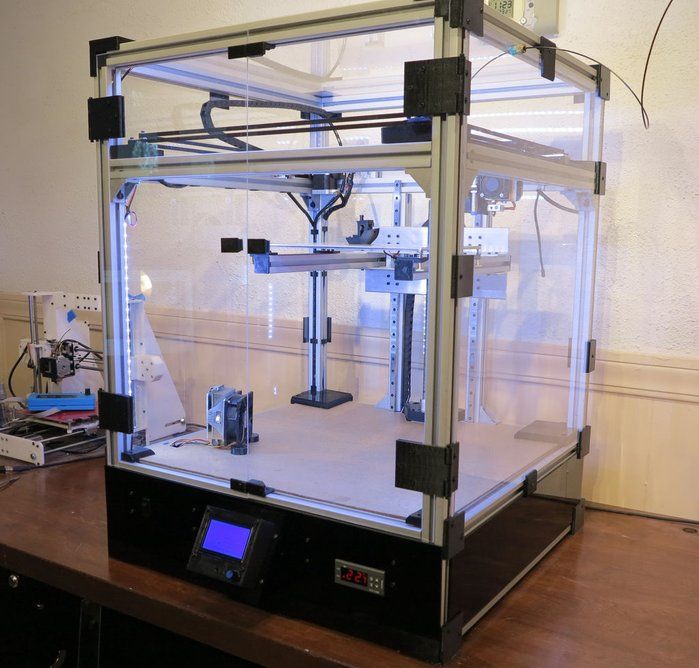
3D printing board
The 6 Best 3D Printer Controller Boards in 2022 – Clever Creations
Our site is reader-supported. When you buy via the affiliate links on this site, we will receive a commission at no cost to you. All opinions remain our own. Learn more
From using Arduinos with CNC shields to now having a full-fledged WiFi-equipped circuit, 3D printer controller boards have come a long way. They’re the brains of any 3D printing setup and are responsible for controlling, coordinating, and executing all of a printer’s functions.
If you’ve bought a fully assembled 3D printer that you are happy with, it’s doubtful that you ever had to think about the controller board. But if you’re someone who wants to upgrade his 3D printer or build a DIY printer from scratch, you probably understand how important it is to select the best 3D printer controller board for your needs.
To help you with getting the best control board for your 3D printer, we’ve compiled a list of the six best motherboard options that you can buy right now.
| 3D Printer Controller | Summary | Input | Processor | Price | Best Offer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duet 2 WiFi | Best overall | 11-25V | 32-bit | $170 | MatterHackers |
| Duet 3 6HC | Best high-end | 11-32V | 32-bit | $255 | MatterHackers |
| BTT SKR Mini E3 V2.0 | Best on a budget | 12/24V | 32-bit | $65 | Amazon |
| Creality 3D 4.2.7 | Best for Ender 3 | 24V | 32-bit | $50 | Creality3D |
| BIGTREETECH Octopus | Most stepper drivers | 4.75-36V | 32-bit | $52 | Amazon |
| BIGTREETECH TFT35 V3.0 | Best LCD add-on | 5V | 32-bit | $45 | Amazon |
Best 3D Printer Motherboards in 2022
Duet 2 WiFi
Best overall
Check Price
AmazonMatterHackersE3D
The Duet 2 Wi-Fi features a 32-bit ARM-based processor specifically designed for industrial automation projects.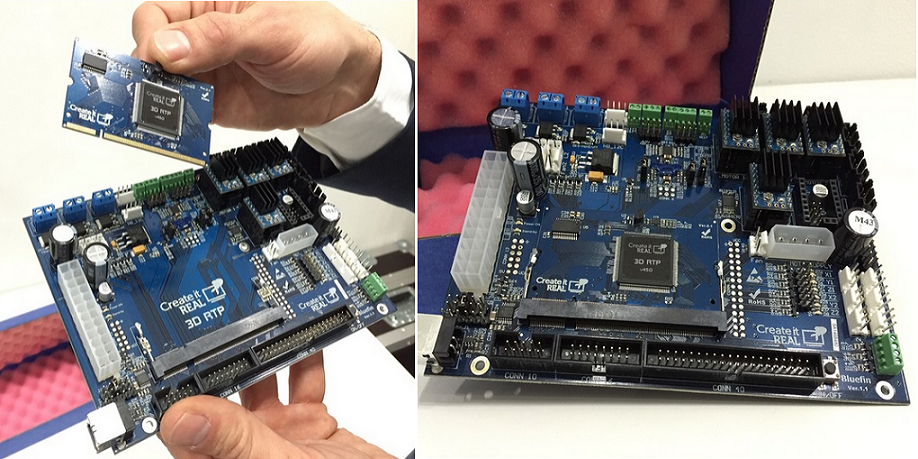 As-is, the Duet 2 Wi-Fi can support up to five unique stepper motors. This, however, can be extended to support up to five extra stepper motors and extruders with the Duex 5 expansion board.
As-is, the Duet 2 Wi-Fi can support up to five unique stepper motors. This, however, can be extended to support up to five extra stepper motors and extruders with the Duex 5 expansion board.
All stepper drivers used on the Duet 2 Wi-Fi are TMC2660s, which have a high current rating of 2.4A and are able to run the stepper motors quietly in up to 1/256 micro-stepping. The board runs on the well-documented and feature-rich RepRap firmware.
The great thing about the Duet 2 Wi-Fi is its compatibility with different Duet expansion boards and accessories. You can connect a PanelDue board to get a full-color graphic touch screen, temperature sensing daughterboards, the Duex 5 for additional steppers, servos, fans, and heaters. It even has the option to use a smart effector for delta 3D printers for bed leveling.
The many features and ability to use it with practically any 3D printer make the Duet 2 Wifi the overall best 3D printer controller board that you can get right now. It definitely costs more than your typical board, but you get what you pay for.
Standout Features
- Wi-Fi connectivity
- External stepper driver support
- Quiet 1/256 microstepping
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Input voltage | 11V - 25V |
| Stepper drivers | 5x TMC 2660 |
| Microstepping | Up to 256 |
| Microprocessor | ARM Cortex M4F, 32-bit |
| Connections | 2.4GHz WiFi, USB serial port |
| SD card slot | Yes |
What We Like
- Powerful
- Many I/O ports
- Built-in Wi-Fi
Could Be Better
- High price
Find Duet 2 WiFi at
AmazonMatterHackersE3D
Duet 3 6HC
Best high-end
Check Price
AmazonMatterHackersE3D
The Duet 3 6HC is the latest release from Duet 3D. The 6HC in the name stands for 6 High Current stepper motors. The board uses a faster 300 MHz 32-bit ARM processor, allowing for high-speed calculations. The Duet 3 features six Trinamic 5160 stepper motor drivers rated at a 6.3 A peak current.
The 6HC in the name stands for 6 High Current stepper motors. The board uses a faster 300 MHz 32-bit ARM processor, allowing for high-speed calculations. The Duet 3 features six Trinamic 5160 stepper motor drivers rated at a 6.3 A peak current.
Other than this, you get 10 PWM outputs for the heated beds, extruders, and fans. It has 9 I/O ports for end-stops, Z probes, filament sensors, and other peripherals. These allow you to decorate your 3D printer with many sensors, fans, and accessories and still have room left for more.
The CAN-FD buses will let you connect other Duet boards, smart tools, and custom add-ons, thus ensuring upgradability. There’s a dedicated high-speed SPI bus to a single board computer (SBC) to let you connect SBCs like Raspberry Pi’s.
The Duet 3 6HC is expensive and aimed at professionals that require a versatile high-end 3D printer controller. However, the RepRap community’s ample amount of documentation and support means that if you want one, you can easily configure it to work with any off-the-shelf 3D printer as well.
Aside from being more than powerful enough to drive nearly any 3D printer, the Duet 3 is an equally attractive option for a home CNC machine or laser engraver.
Standout Features
- High-speed ARM processor
- High current stepper drivers
- Numerous i/o options
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Input voltage | 11V to 32V |
| Stepper drivers | 6x TMC2160 or TMC5160 |
| Microstepping | Up to 256 |
| Microprocessor | ARM Cortex M7, 32-bit |
| Connections | Ethernet and USB Serial port |
| SD card slot | Yes |
What We Like
- Wide stepper motor compatibility
- Suitable for high-end 3D printers
- Lots of expansion options
Could Be Better
- High price
- Requires technical expertise
Find Duet 3 6HC at
AmazonMatterHackersE3D
BIGTREETECH SKR Mini E3 V2.
 0
0 Best on a budget
Check Price
AmazonBigtreetechGeekbuying
The SKR Mini E3 V2.0 is the successor to the original E3, designed explicitly for the Ender 3 3D printers. With the SKR Mini E3 V2.0, Bigtreetech offers support for more Creality machines like the CR-10, CR-10S5, and Ender 3 3D printers.
The V2.0 is a 32-bit 3D printer controller board that features ultra-silent, TMC 2209 stepper motor drivers and can handle 2A RMS current. It also comes with two Z-axis ports, so that you can drive dual Z-axis stepper motors.
Aside from the excellent stepper drivers, the SKR Mini E3 V2.0 also comes with support for BLTouch and filament detection sensors. This gives you the option to install additional Ender 3 upgrades and Ender 5 upgrades that reduce the chance of failed 3D prints.
The Mini E3 V2.0 supports the open-source Marlin firmware. It offers a variety of additional features like the power resume function, automatic shutdown, and onboard sensorless homing functions.
If you’re on a budget and want to upgrade your Creality 3D printer, the SKR Mini E3 V2.0 is likely the best 3D printer controller for you.
Standout Features
- Parallel Z-axis interface
- BLTouch and filament detection ports
- Improved thermal performance
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Input voltage | 12/24V |
| Stepper drivers | 4x TMC2209 |
| Microstepping | 256 |
| Microprocessor | ARM Cortex-M3, 32-bit |
| Connections | Mini-USB-B type |
| SD card slot | Yes |
What We Like
- Low price
- Easy to use
- Silent stepper drivers
Could Be Better
- Limited upgradability
Find BIGTREETECH SKR Mini E3 V2. 0 at
0 at
AmazonBigtreetechGeekbuying
Creality 3D 4.2.7
Best for Ender 3
Check Price
AmazonCreality3D
The Ender 3 is still one of the best budget Creality 3D printers. But it has aged in terms of its features and capabilities. The latest version of the 3D printer controller board from Creality – 4.2.7 aims to bring the Ender 3 to the current 3D printing trends.
The Creality 3D 4.2.7 controller board features a 32-bit ARM processor with increased flash storage that lets you run more firmware features faster, and with this supporting the latest Marlin 2.0 firmware. Creality calls this controller board the “silent mainboard” due to the TMC 2225 stepper motor drivers that keep your 3D printer’s motors silent.
This 4.2.7 now comes with a pre-installed bootloader, which means that you can update the firmware by merely inserting the SD card with the firmware BIN file. It also has ports for the BLTouch auto leveling sensor and filament sensors that remove the need for any previously needed extenders.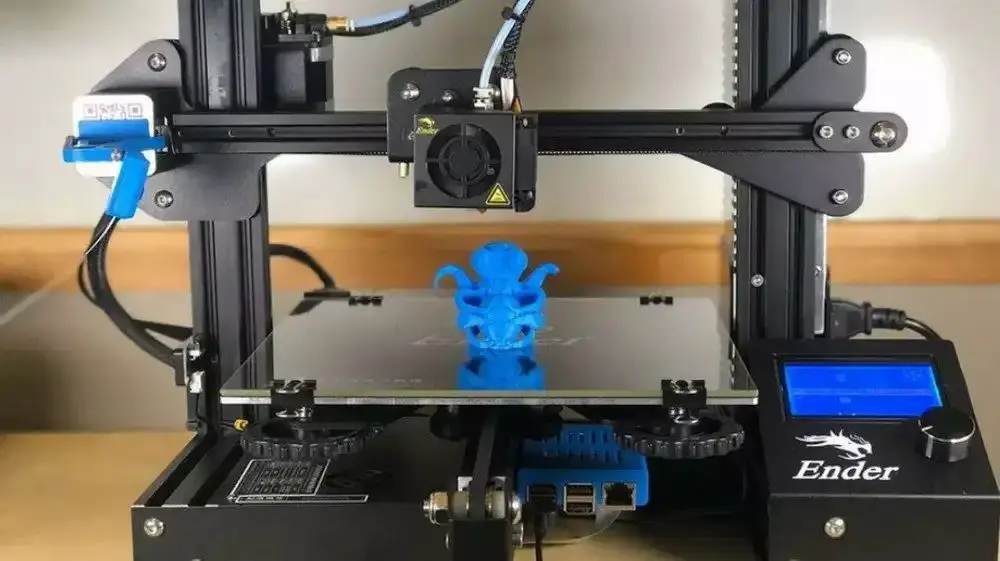
The Marlin 2.0 comes pre-installed with the board, and with a little bit of configuration, you can directly use it with your Ender 3. It is an excellent upgrade for the Ender 3 3D printers, considering that you get an officially supported board with the latest features.
Standout Features
- 32-bit processor
- Pre-installed bootloader
- Silent TMC 2225 stepper drivers
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Input voltage | 24V |
| Stepper drivers | 4x TMC2225 |
| Microstepping | Up to 256 |
| Microprocessor | ARM Cortex-M3, 32-Bit |
| Connections | Micro-USB port |
| SD card slot | Yes |
What We Like
- Easy to install and use
- Official company support
- Affordable
Could Be Better
- No UART control
- Poor quality control
Find Creality 3D 4.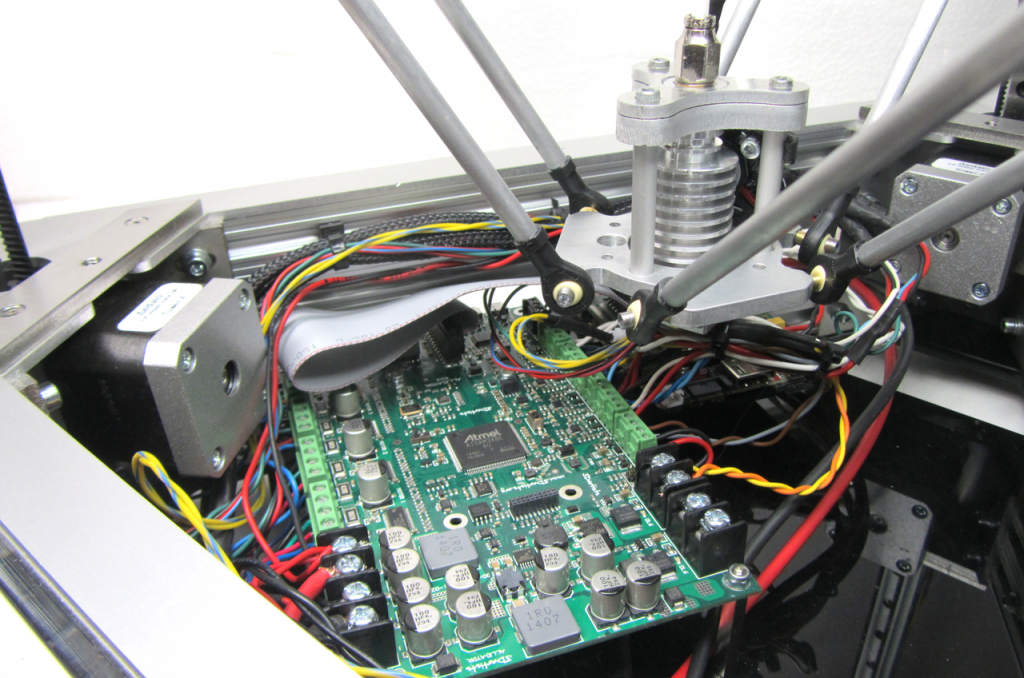 2.7 at
2.7 at
AmazonCreality3D
BIGTREETECH Octopus
Most stepper drivers
Check Price
AmazonBigtreetechGeekbuyingBanggood
The BIGTREETECH Octopus controller board natively supports eight stepper motors. You can choose your stepper motor drivers and the mode in which you want to run them, and this makes the board a beast in terms of sheer stepper motor support.
This 3D printer controller board supports up to four hot-end heaters. Then there are six PWM controllable fan interfaces, six end-stop switches, and two inputs for filament detection sensors. You even get a CAN bus interface if you decide to upgrade further and a USB-A port that can interface with a Raspberry Pi using emulated serial over USB.
Another expansive feature of the Octopus board is the support for a dual Z-axis drive. This can come in handy if you’re building a large cartesian or even a Core XY-type 3D printer. There are many other features too, and the sheer number of connectivity options make it one of the best 3d printer controllers if you’re planning to build something like a Voron 3D printer that needs many stepper motors.
Standout Features
- Supports up to 8 stepper motors
- Interfaces with Raspberry Pi
- Marlin and Klipper firmware support
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Input voltage | 4.75V - 36V |
| Stepper drivers | 8 pluggable stepper driver support |
| Microstepping | Up to 256 |
| Microprocessor | ARM Cortex-M4, 32-bit |
| Connections | USB type C port |
| SD card slot | Yes |
What We Like
- Suitable for large 3D printers
- Lots of expansions ports
- USB-C interface for easy compatibility
Could Be Better
- Complex wiring
- Limited community support
Find BIGTREETECH Octopus at
AmazonBigtreetechGeekbuyingBanggood
BIGTREETECH TFT35 V3.
 0
0 Best LCD add-on
Check Price
AmazonBigtreetechBanggood
The BIGTREETECH TFT35 V3.0 is an LCD touch screen upgrade designed for the Ender 3 and CR-10 3D printers. The V3.0 stands out because of its dual nature. You can use it as a regular LCD screen with the knob or use the touch screen to navigate the menu quickly.
It gives you the best of both worlds without the hassles of either. Additionally, you get a port for an external Wi-Fi module, a full-sized SD card slot, and a USB 2.0 port, giving you plenty of options in terms of connectivity.
However, the touch screen is not plug-n-play, and you need to tweak some firmware settings to get it working with your 3D printer. Teaching Tech on YouTube has a comprehensive guide covering everything you need to get the TFT35 working.
The BIGTREETECH TFT35 V3.0 is not meant as a completely new overhaul for your 3D printer but rather is aimed to improve the functionality of interfacing with it. The touch screen combined with the knob is suitable for many users. And considering the price, it is a worthwhile upgrade to make.
And considering the price, it is a worthwhile upgrade to make.
Standout Features
- Dual-mode use
- Pre-installed bootloader
- Wi-Fi module and filament detection ports
Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Input voltage | 5V |
| Microprocessor | ARM Cortex-M3 series 32-bit |
| Connections | USB A port and external Wi-Fi module support |
| SD card slot | Yes |
What We Like
- Easy to use
- Compatible with many 3D printers
- Lots of configuration options
Could Be Better
- Firmware can be buggy
- Technical expertise required
Find BIGTREETECH TFT35 V3.0 at
AmazonBigtreetechBanggood
Buyer’s Guide
Above we have listed some of the best 3D printer controller boards available.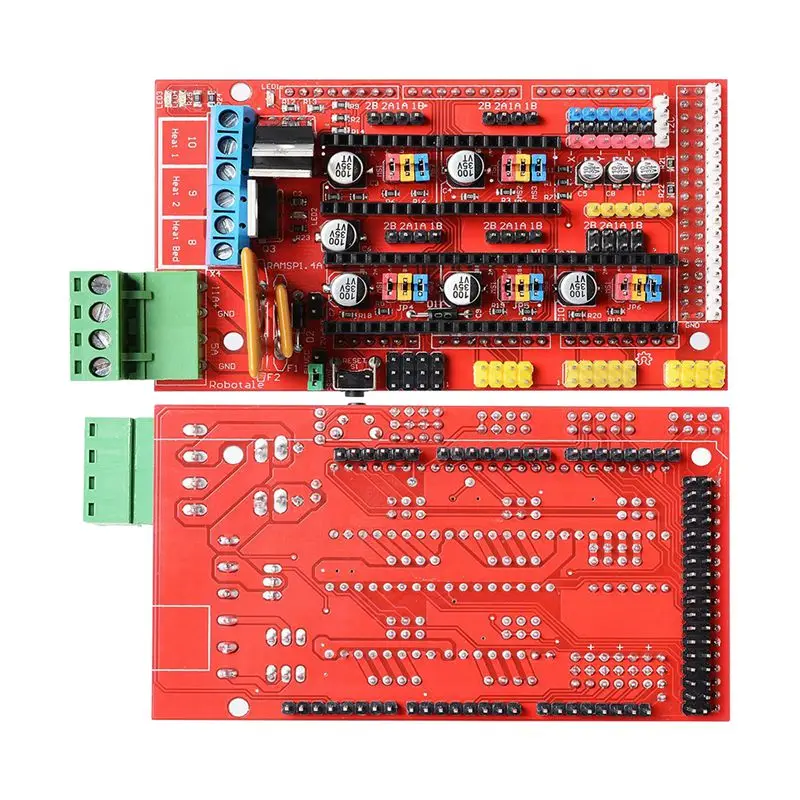 But what if you want to look for more boards? What exactly do you look for in a 3D printer motherboard, and how do you select one for yourself? Here are a few pointers that you need to keep in mind.
But what if you want to look for more boards? What exactly do you look for in a 3D printer motherboard, and how do you select one for yourself? Here are a few pointers that you need to keep in mind.
Firmware Compatibility
Firmware is the software on the 3D printer controller board that is responsible for all calculations and commands to the printer hardware. There are many different types available, for example, Repetier, Prusa, Klipper, and Smoothieware.
Recommended:
Creality Sonic Pad Review: A Klipper Solution That Needs More Work
Each one is designed for a slightly different purpose, and you need to keep in mind your goals with the machine. For example, if you want a high-speed 3D printer, Klipper is the best choice for you. Marlin and RepRap are the go-to options if you want well-documented and widely used firmware.
You need to consider the choice of your firmware beforehand to select the best suitable controller board for yourself. Make sure there’s enough documentation and support available with your combo so that if you run into any issues, you can quickly sort it out.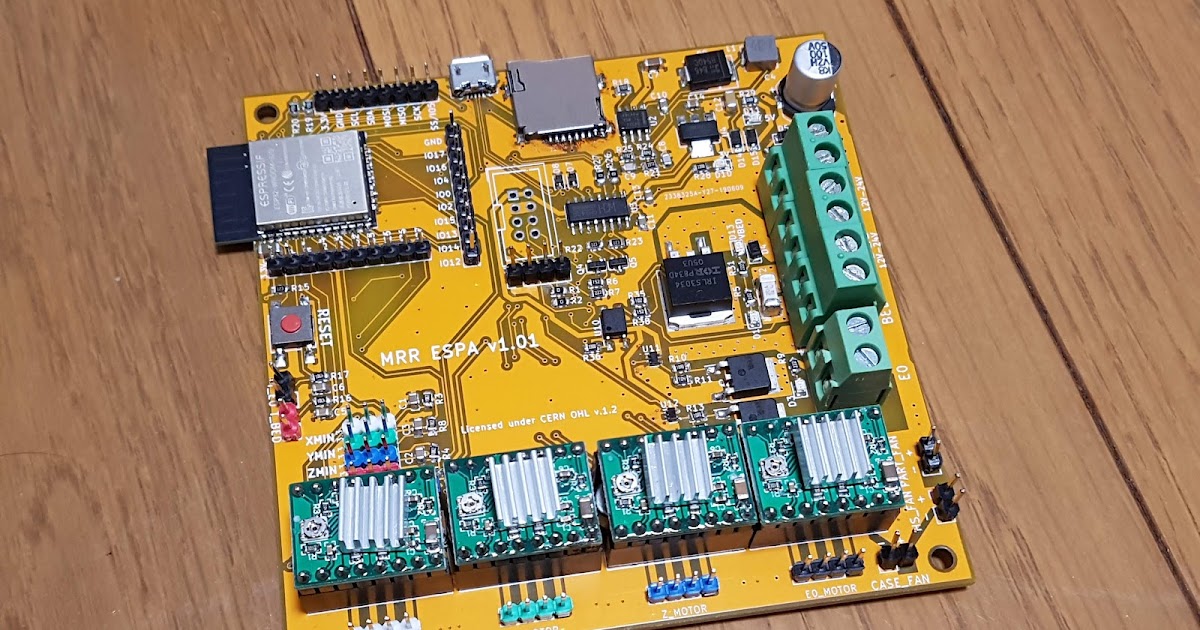
Processor
3D printers either have an 8-bit controller board or a 32-bit board. An 8-bit board is cheap to manufacture and provides all the basic functionalities you would expect from a 3D printer. However, it comes with low onboard memory, and the lower number of bits means that it can process fewer calculations at a time, thus significantly affecting its speed.
32-bit motherboards operate at a higher clock speed, have a slightly greater onboard memory, and execute calculations at a much higher rate. They’re compatible with more I/O ports and communication interfaces, and all of these translate to a more feature-rich 3D printer motherboard.
If you want a basic 3D printer with limited functionalities, 8-bit boards are an option. They’ll save a bit of money, and you won’t have to pay for things you won’t use. However, if you want your 3D printer to be future-proof, have advanced functions, and print faster, a controller board with a 32-bit processor is vastly superior.
In our list with the best 3D printer controller boards above, we have only added 32-bit controllers. We believe that an 8-bit board is not worth buying and a 32-bit board is always the better option.
Communication methods
The most basic method of communication on a 3D printer motherboard is a USB port. A USB serial port allows you to control your 3D printer via a USB connection with a computer.
Wi-Fi and Ethernet ports are other methods of communicating with your 3D printer. An ethernet port would allow you to control your 3D printer over a local wired network.
Wi-Fi connectivity would allow you to control your printer wirelessly. One benefit of Wi-Fi is that you don’t even have to be present in the same room as your 3D printer, and you can control it remotely from anywhere.
Low-end controller boards don’t come with Wi-Fi and Ethernet ports; some might have pins for attaching external Wi-Fi modules, though. A USB serial port is enough if you want a basic 3D printer. If you want wireless 3D printing or operate many 3D printers simultaneously, you should consider getting a Wi-Fi-equipped controller board.
If you want wireless 3D printing or operate many 3D printers simultaneously, you should consider getting a Wi-Fi-equipped controller board.
Connectors
Aside from a USB port, there are many other connectors (or headers) on the controller board. These are used for a wide variety of purposes. Endstop connectors, hot end heaters, stepper motor connectors, bed leveling, and filament runout detection sensors are some of the few.
A well-specced-out controller board like the Duet 2 Wi-Fi or the Duet 3 6HC will have almost all of these connectors and then some more. Connectors allow you to interface various devices with your 3D printer, providing additional functionality.
The more connectors your controller board has, the more expensive it will be and take a lot of space. You need to know what features you want in your 3D printer and select the board with the particular connectors to get the maximum benefit.
Stepper Drivers
Stepper motor drivers affect the size of the stepper motors you can drive in your 3D printer and the sound levels you hear in the process. On most 3D printer controller boards, stepper drivers can’t easily be swapped out. Therefore, selecting the right kind of controller board with the right stepper driver is essential.
On most 3D printer controller boards, stepper drivers can’t easily be swapped out. Therefore, selecting the right kind of controller board with the right stepper driver is essential.
Basic stepper drivers like the A4988 are cheap, easily accessible, and provide a relatively good experience for basic 3D printers. They do drive stepper motors loud, are unreliable, and can only provide the steppers with limited current.
TMC drivers, on the other hand, are known for their silent operation and current-carrying capacities. The TMC 2xxx series are rated at 2A peak current, while the TMC 5160 typically offers 3A to 4.4A on 3D printer controller boards.
You need to consider the microstepping capabilities of the stepper motor drivers as well. Microstepping divides a full step into smaller steps. The smaller the step, the higher the resolution and the smoother the vibration. As a minimum, you want 1/16 step microstepping, but the best 3D printer controller options offer up to 1/256 step
Touch screen support
A touch screen enhances the functionality and ease of use of a 3D printer by making navigating the menu and dialing in the various features easier.
Not all controller boards have touch screen support built-in. While choosing a controller board, look at the connectivity options and the compatible touch screens. You need to make sure that the board’s firmware supports it, and there is at least a little bit of documentation on how to interface the controller with the touch screen.
FAQ
What is a 3D printer controller board?
A 3D printer controller board is a piece of hardware that controls all electronic components in a 3D printer. It is responsible for motion, temperature control, and reading all commands from GCode files.
Why upgrade your printer’s stock controller board?
As time passes, the current features in your 3D printer start to seem obsolete. A controller board upgrade will give you access to many advanced features, allow for added functionalities and enhance your overall 3D printing experience.
Is a 3D printer controller board the same as a 3D printer motherboard?
Yes, in the context of 3D printing, the terms ‘controller board’ and ‘motherboard’ are used interchangeably. They mean exactly the same thing.
They mean exactly the same thing.
Conclusion
The best 3D printer controller boards are the ones you’re able to afford and will work with your 3D printer. With so many options on the market, it can be tough to choose just one. The important thing is figuring out which one of these top-rated controllers would be right for you.
In our opinion, the Duet 2 Wi-Fi is the overall best 3D printer controller board that you can get right now. Despite its high price, the Duet 2 Wi-Fi ticks all the boxes in terms of features, connectivity, upgrades, and ports. It is designed to be a universal solution for all types of 3D printers and can serve as an effective replacement for practically any board.
Let us know what you think about it, and if you have anything else to add, feel free to comment below.
Scroll to Top
6 Best 3D Printer Controller Boards In 2022
- Last Updated: October 19, 2022
- Jackson O'Connell
The controller board on a 3D printer is arguably the most important part of a machine. Just like you can’t function without a brain, a 3D printer can’t function without this integral circuit board.
Just like you can’t function without a brain, a 3D printer can’t function without this integral circuit board.
The controller board, sometimes known as a motherboard or mainboard, is responsible for processing and carrying out all of the commands sent to the machine. Without it, your 3D printer is just a bunch of motors, sensors, and probes, sitting on a metal frame, doing absolutely nothing.
The controller board varies from printer to printer (often based on brand), and some are better than others for reasons we’ll explain later. Luckily, you can usually replace the board on your printer to improve printing performance, usability, or other factors.
In the sections below, we’ll explain more about 3D printer motherboards and how they vary. We’ll then dive into our review of some of the best controller boards on the market that you can use on your machine.
Enjoy!
BTT SKR Pro V1.2
Check Latest Price
BTT SKR Mini E3 V2. 0
0
Check Latest Price
Duet 2 Wi-Fi V1.04
Check Latest Price
Table of Contents
- Best 3D Printer Controller Boards At A Glance
- What Is A 3D Printer Controller Board?
- Why Change Your 3D Printer’s Board?
- What To Consider When Buying a Controller Board?
- Processor
- Number of Ports
- Compatibility
- Stepper Drivers
- Quality
- Price
- Best 3D Printer Controller Boards
- 1. BTT SKR Mini E3 V2.0 (Best Overall)
- 2. Duet 2 Wi-Fi V1.04 (Best Premium Choice)
- 3. BTT SKR Pro V1.2 (Best Value)
- 4. Creality V4.2.7
- 5. MKS Robin E3D
- 6. Smoothieboard (V1)
- Conclusion
Best 3D Printer Controller Boards At A Glance
1. BTT SKR Mini E3 V2.0 (Best Overall)
2. Duet 2 Wi-Fi V1.04 (Premium Choice)
3. BTT SKR Pro V1.2 (Best Value)
4. Creality V4.2.7
Creality V4.2.7
5. MKS Robin E3D
6. Smoothieboard (V1)
What Is A 3D Printer Controller Board?
A 3D printer controller board is a type of microcontroller meant for a 3D printer. As a microcontroller, the board’s sole purpose is processing commands, known as G-code for 3D printers, and following them.
Every electronic component – motors, sensors, probes, etc. – is wired to the different ports on the board. When the processing chip on the motherboard reads a G-code command, it gives power to the specific motor ports to carry out the command. And, when data needs to be used, it takes it from the sensor ports, like an automatic bed leveling sensor if your printer has one.
The board is also where the firmware program is running. If you’re unfamiliar with the term, firmware helps bridge the digital and physical realms of 3D printing by giving the controller board a way to decode the G-code commands so it can carry them out. Firmware also contains certain features and capabilities like linear advance and meshes for automatic bed leveling.
Firmware also contains certain features and capabilities like linear advance and meshes for automatic bed leveling.
3D printer controller boards also have something called stepper motor drivers. These components of the board are responsible for the rotation of the motors connected to the board. Stepper motor drivers directly impact the noise level produced by the motors as well as their accuracy and precision.
Some boards have integrated stepper motor drivers, which means they can’t be changed and are built into the board. However, other, more customizable boards, have stepper motor driver ports that allow you to use your own drivers.
But most of this explanation isn’t what you’ll be needing in your day-to-day 3D printing activities. The main thing you need to know about a controller board is that it has different ports to support different hardware, and each controller board is different.
Why Change Your 3D Printer’s Board?
Source: Youtube Design Prototype TestSo, why change your 3D printer’s controller board?
Well, as we said, each board is different, and some are better than others, offering enhanced features. This might mean more ports, a faster processor chip, or support for different firmware programs, which can all directly or indirectly improve the printing and usability of your machine.
This might mean more ports, a faster processor chip, or support for different firmware programs, which can all directly or indirectly improve the printing and usability of your machine.
Perhaps the most common reason to switchboards is to enable a certain upgrade that requires an extra port. This includes adding a second Z-axis stepper motor or an automatic bed leveling sensor.
Another reason is for a better processor chip to get better prints. For example, motherboards that have a 32-bit processor architecture are known to yield smoother prints compared to 8-bit boards.
Yet another example is to get a quieter printing experience by switching to a motherboard with newer stepper motor drivers than your old board. Check out our review of the best quiet 3D printers here.
What To Consider When Buying a Controller Board?
3D printer controlled boards are pretty complex, with many different features onboard. As such, there are quite a few considerations to keep in mind when looking for a controller board for your machine.
In this section, we’ve gone over what we considered when picking out the best controller boards for this list.
Processor
Our first consideration was the processor on the controller boards. In the early days of 3D printing, the typical motherboard had an 8-bit microprocessor, but, now a 32-bit processor is the new standard. All of our selections have a 32-bit architecture as we wanted to make sure they can all handle the latest firmware features, like linear advance.
Number of Ports
The second consideration is the number of ports, including both motor and sensor ports. All of the controller boards on this list feature the necessary four (X, Y, Z, E) motor ports, but some go above and beyond with extra stepper motor ports to allow for more upgrades.
As for the sensor ports, each of the included controller boards has a sensor port for an automatic bed leveling sensor, and many have ports for a filament runout sensor as well.
Compatibility
Our third consideration was the popularity and compatibility of the controller boards. While a board can be unpopular and a good option, typically, the more popular a 3D printer controller board is, the more firmware programs support the board. We made sure at least a few different firmware programs could run on each of the included controller boards.
Stepper Drivers
Fourth, the stepper motor drivers were another thing we kept in mind when looking at the controller boards. If the board had integrated drivers, we made sure they were at least decently quiet. And, if the board had open driver ports, we made sure they supported some of the more recent TMC drivers as these types of drivers are most popular.
Quality
Fifth, the manufacturer of the product also matters, and we didn’t forget about it. A quick search on AliExpress will bring up many 3D printer boards that seem good on paper, but, when they arrive, they perform poorly. We made sure each of the controller boards we’re calling the “best” come from the best and most reputable manufacturers around.
We made sure each of the controller boards we’re calling the “best” come from the best and most reputable manufacturers around.
Lastly, we reviewed the price of each of the listed products to make sure they all were in reach for the average hobbyist. We can’t be comparing $2,000 boards to $50 boards cuz’ that wouldn’t make sense.
Best 3D Printer Controller Boards
Now that we’ve gone over what a 3D printer controller board is, it’s time to get into the options. We’ve scoured the market and handpicked the best boards for you, reviewing each in the sections below.
1. BTT SKR Mini E3 V2.0 (Best Overall)First up, the BTT SKR Mini E3 V2.0 is a very powerful 3D printer motherboard developed by the experts at BigTreeTech (BTT). Hence its name, the SKR Mini, has a pretty small footprint and can fit in consumer-grade printers like the Ender 3.
What’s most appealing about the board, however, isn’t its size but rather its 32-bit architecture.
Moreover, the board has a powerful processor chip that runs an astounding 72-MHz, which is much faster than almost any stock board on consumer 3D printers. This will allow you to run larger and more feature-heavy firmware programs like Marlin 2.0 for your machine.
If that doesn’t get you excited, the board also provides five stepper motor ports and even a port dedicated to an automatic bed leveling sensor. This will allow you to make upgrades to your printer, like dual Z-axis motors and auto bed leveling, without having to ask, “Can my motherboard handle this?”.
Additionally, the device features onboard TMC2209 stepper motor drivers. While the 2209s aren’t the latest drivers in the game, they will provide a decently-quiet printing experience, not counting for the noise from the fans.
On this note, the Mini E3 also has three fan ports, which certainly isn’t a lot but is standard for today’s boards. A few other features of this board is a micro-USB connector, a micro-SD card slot for printing storage, and support for a touchscreen LCD.
- 5 stepper motor ports, automatic bed leveling sensor port
- 32-bit architecture and 72-MHz processor chip
- Support for touchscreen LCD and large firmware packages
- Micro-USB and micro-SD card connectivity options
- TMC2209 stepper motor drivers built-in
- Only three fan ports
- The stepper motor drivers are somewhat old
Check Latest Price
2.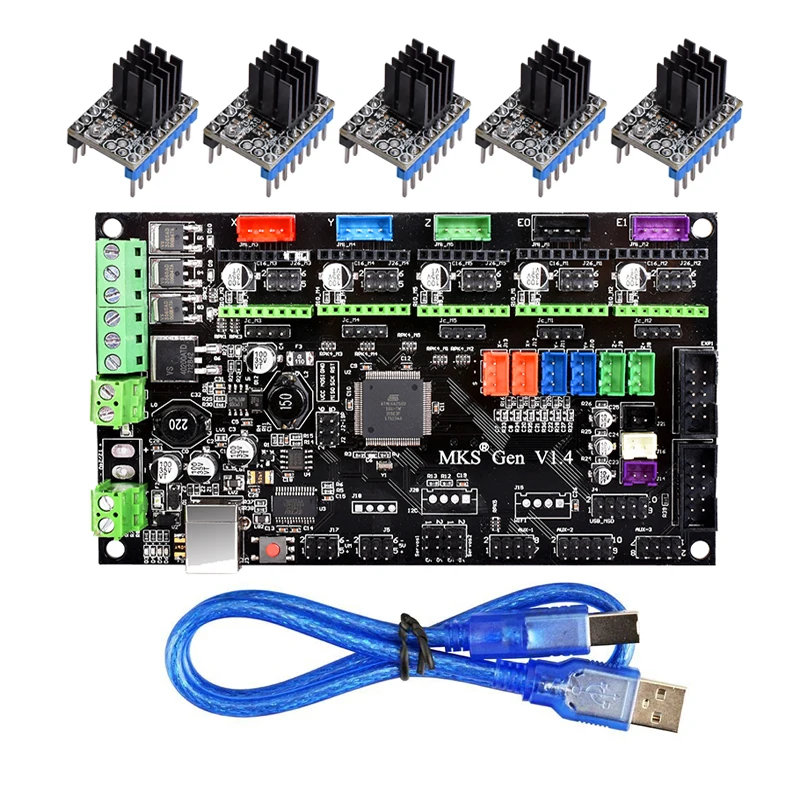 Duet 2 Wi-Fi V1.04 (Best Premium Choice)
Duet 2 Wi-Fi V1.04 (Best Premium Choice) Duet3D is on the pricier side of the consumer 3D printing market but they still make the cut.
Their Duet 2 Wi-Fi V1.04 board is a great option, especially for DIY 3D printers where the hardware isn’t made by just one manufacturer. That’s because the board is completely open-source, so you can use basically any motors, sensors, or other electronic attachments and, with some configuration, get them to work with the board.
As indicated by the name of this product, the Duet 2 Wi-Fi has an onboard Wi-Fi module that allows you to control your printer remotely. This means you can use Duet3D’s default online interface to start/stop prints, send G-code commands, set temperatures, and more.
It’s like an OctoPrint server built into the board!
And, when it comes to ports, the Duet 2 has got you covered with five motor ports to allow for an extra Z-axis motor. There are also plenty of other ports to allow for a Duet3D-developed PanelDue touchscreen LCD, two hot ends, a heated bed, and five endstops. And don’t forget about your automatic bed leveling sensor (e.g. BLTouch) or filament runout sensor because those can also both fit on this board.
And don’t forget about your automatic bed leveling sensor (e.g. BLTouch) or filament runout sensor because those can also both fit on this board.
And, in the unlikely scenario that you are still a few ports short, you can purchase Duet3D’s expansion board, which connects to the Duet 2 Wi-Fi and provides a few more motor and sensor ports.
As for the processor, it just makes sense that Duet3D used a powerful 32-bit chip on this monster of a board.
The drivers on the board are also exceptional and Duet3D opted for TMC2660 stepper drivers, which are some of the latest in the game. On top of keeping your printer quieter than quiet, these high-quality drivers allow for 256 microstepping. This feature ensures a super high level of accuracy and precision in stepper motor movements, improving the quality of prints.
Besides the close to $200 price tag, another major downside of this board is its massive size, which comes with offering the number of ports it does. The Duet 2 Wi-Fi isn’t a board that will fit into your Ender 3, Anycubic Mega, or really any other consumer-grade 3D printer. You’ll have to make a custom fitting (many 3D printable options online) to fit the board on your printer.
The Duet 2 Wi-Fi isn’t a board that will fit into your Ender 3, Anycubic Mega, or really any other consumer-grade 3D printer. You’ll have to make a custom fitting (many 3D printable options online) to fit the board on your printer.
- Built-in WiFi support and an online control interface
- Many motor ports for more upgrades
- Many sensor and attachment ports to support ABL and runout sensors
- TMC2660 stepper drivers and 256 microstepping
- 32-bit processing
- Optional expansion port board
- Very large; hard to fit on a regular 3D printer
- Very expensive
- Duet3D makes it difficult to run certain firmware programs (e.
 g. Marlin)
g. Marlin) - Only a few LCDs are supported by the board
Check Latest Price
3. BTT SKR Pro V1.2 (Best Value)Another board from BigTreeTech is the BTT SKR Pro V1.2. The board is called “Pro” because it has more features and better features than most of BTT’s other boards. Unlike the Duet 2 Wi-Fi, though, this board is a normal size and can fit in most printers like the Ender 3.
But don’t be misled by the pretty regular size of the board as the SKR Pro V1.2 is far from normal. Boasting seven motor ports, the Pro V1.2 is a great option for dual-extrusion printers, where you need two extruder motors and two X-axis stepper motors. Alternatively, you can use the extra motor ports to have dual Z-axis motors to improve the quality of your prints.
Surprisingly, despite having seven motor ports, the Pro V1. 2 only has six driver ports for the stepper motors. That’s because one of the drivers is meant to run both of the motors in the Z-axis motor ports.
2 only has six driver ports for the stepper motors. That’s because one of the drivers is meant to run both of the motors in the Z-axis motor ports.
On this note about the drivers, the Pro V1.2 has open stepper motor driver ports, meaning you can fit whatever compatible stepper drivers you want. While this means the price of the board (which isn’t too much) isn’t the full price because you have to buy drivers, this allows you to choose what drivers you want based on how quiet and accurate you need your stepper motors to be.
Overall, the SKR Pro V1.2 is the board to get if customization is your middle name. Moreover, the board supports a lot of different drivers, firmware programs, and LCDs. The many ports on the board allow for basically whatever upgrade you want.
- Open-ended stepper drivers
- Wide support for firmware programs, LCDs, stepper drivers
- Seven motor ports
- 32-bit processor
- Wi-Fi module
- Small footprint
- Somewhat expensive
- Cable management can be difficult
- You have to buy the drivers separately
Check Latest Price
4. Creality V4.2.7
Creality V4.2.7 Creality is one of the largest names in the consumer 3D printing industry, with tens of the most popular printers on the market under its belt. Creality also makes a fair amount of optional upgrades for their printers, like the Creality V4.2.7 board.
The V4.2.7 was originally developed as a “silent” board for Creality’s Ender 3 V2, but it can be used on whatever printer you want as long as the parts are compatible.
As an Ender 3 enthusiast myself, I can honestly tell you that this board has improved my printing experience a lot.
First off, the 32-bit processor and decently-large EEPROM (storage space) on the V4.2.7 allow you to run feature-heavy firmware programs like Marlin 2.0. The board also has a built-in bootloader that allows you to flash new firmware programs through the micro-SD card slot.
But, in my opinion, the most beneficial part of the V4.2.7, is its integrated TMC2225 drivers.
The drivers quiet your printer so much to where you can really only hear the light humming of the fans. While these drivers can only reach 32 microstepping, which isn’t as accurate as some of the later TMC drivers, it’s still good enough to make parts very accurate.
While these drivers can only reach 32 microstepping, which isn’t as accurate as some of the later TMC drivers, it’s still good enough to make parts very accurate.
It’s also worth mentioning that the board is pretty small and can fit in many consumer-grade printers like all Creality printers as well as some non-Creality machines too. Sadly, the board only has four motor ports, so you can’t run two extruders or two Z-axis motors.
However, this 32-bit 3D printer board has specific ports for an automatic bed leveling sensor and a filament runout sensor, making installing those upgrades super easy.
- TMC2225 drivers for very quiet printing
- Small size; fits in most Creality printers
- Firmware flashing is possible through the micro-SD card slot
- Not too expensive
- 32-bit processor
- Ports for an ABL sensor and a filament runout sensor
- Microstepping capabilities aren’t super good
- Only four motor ports
Get Discount (Official Store)
Check Latest Price
5. MKS Robin E3D
MKS Robin E3D Our last board comes from the experts at Makerbase, who make the MKS line of motherboards for 3D printers. The MKS Robin E3D isn’t the most popular board from Makerbase, but I think it’s very underrated and deserves a lot more credit for what it offers.
First off, the board has six motor ports to allow for both dual Z-axis motor and single-headed dual extrusion. Alternatively, you could build an independent dual-extrusion printer with the same number of motor ports.
However, this isn’t the only good part about the Robin E3D, and I think the open-ended stepper motor driver ports are another one of its main benefits. While the market seems to dislike the open-ended driver boards, they allow you to basically control the price of the machine because drivers make up a large part of the cost for most boards.
The E3D supports many different drivers, and you can put some TMC2209s on the board to achieve low noise and also have the option to run linear advance if you’re using Marlin firmware.
On a note about firmware, you should be able to change your board’s firmware through the micro-SD card slot, and most firmware programs are compatible (e.g. Marlin).
The board also supports many sensors, like ABL and filament runout ones. You can also connect a touchscreen LCD to the board and use Makerbase’s default TFT interface to control your printer through the screen.
The board is just a bit bigger than the default boards found on most consumer printers like the Anycubic Mega and Ender 3, so upgrading will require a fitted mount. However, it won’t be too hard as there are some 3D printable models online that work.
- Open-ended stepper drivers
- Small footprint
- Supports many sensors and attachments, like ABL, filament runout, and TFT screens
- Supports many different firmware programs
- Six ports for stepper motors
- Requires modifications to fit in most printers
- You have to buy your own stepper drivers
Check Latest Price
6. Smoothieboard (V1)
Smoothieboard (V1) While not as popular as the mass-manufacturing companies like BTT, MKS, and Creality, Smoothieware sure knows how to make a good motherboard. Smoothieware’s v1 Smoothieboard is the company’s flagship product and it launched on Kickstarter a few years ago, passing its target goal by about $100,000.
Perhaps the main reason this board is so revered is that it’s basically the only one ever made by an organization that develops 3D printer firmware. As such, the Smoothieboard v1 is optimized to run Smoothieware, which is the name of the firmware program that Smoothieware makes.
Yeah, it’s very confusing to talk about!
While the board is usually unavailable due to its lack of popularity, it doesn’t really need to be super popular when it has a native firmware program that it’s optimized for. But still, the board has a decent amount of other features too, like its 32-bit ARM processor which handles the rather-large Smoothieware firmware package.
The board comes in a few variations, like the 3X, 4X, and 5X, which have 3, 4, and 5 motor ports, respectively. While this isn’t too many motors, the 4X and 5X versions should be great for your printer and you might be able to use the 3X for a different type of CNC-style machine.
- Optimized to run Smoothieware
- 6 endstop ports and 6 other ports for fans, heaters, and more
- Ethernet port for internet connection
- Powerful 32-bit ARM processor
- Unavailable on many sites
- Relatively expensive
- Doesn’t have too many motor ports
- Pretty old integrated stepper motor drivers (Allegro A5984, 32 microstepping)
- Doesn’t run other firmware programs
Check Latest Price
Conclusion
Just like you wouldn’t want to have an outdated brain, you don’t want to use an outdated motherboard on your 3D printer. And, while you can’t easily replace your brain, upgrading your controller board isn’t too difficult.
And, while you can’t easily replace your brain, upgrading your controller board isn’t too difficult.
There are many different controller boards on the market today, and each has different stepper drivers, processors, motor ports, sensor ports, attachment ports, and firmware support. As such, the best 3D printer controller board for you depends on what features you plan on using or upgrades you plan on making.
If you just want to make the switch from an 8-bit to a 32-bit microcontroller board, but don’t plan on making too many upgrades, I would suggest going with the Creality V4.2.7. This board has a great 32-bit chip, can handle the latest firmware programs, and has a few extra sensor ports, but is nothing fancy.
Now, if you want to go all out and make as many upgrades as possible, the Duet 2 Wi-Fi is more up your alley. The many ports on the board, combined with the optional expansion board and onboard Wi-Fi module, make it a great option for those looking to explore the upgrade capabilities of their machine.
How are 3D printing standards improving the performance of Olympic athletes?
You are here
Home
Some of the Olympic cycling teams competing in Tokyo made extensive use of 3D scanners and 3D printers to customize equipment and fit bike parts exactly to the requirements of the athletes. The teams used 3D printers to make new bike handlebars and chains, avoiding the use of expensive tooling/moulds.
Use of 3D printing to help athletes outside the Tokyo Olympics
To be fair, 3D printing advances are being applied to other sports disciplines as well. For athletes competing in the upcoming Paralympic Games, for example, 3D printing offers an effective way to create lighter and more aerodynamic prostheses, as well as wheelchairs.
Chevrolet is now actively outfitting its INDYCAR and NASCAR race cars with 3D printed parts including oil tanks, intake manifolds and fuel tank caps. The company uses this technology both at the stage of prototyping and at the stage of final production. London-based Cavendish Imaging is using the technology to produce protective masks that allow athletes with facial injuries (such as a broken nose/cheekbone) to continue playing. Using special software, the company 3D-scans the athlete's face and creates a model, on the basis of which the individual protective mask is printed.
The company uses this technology both at the stage of prototyping and at the stage of final production. London-based Cavendish Imaging is using the technology to produce protective masks that allow athletes with facial injuries (such as a broken nose/cheekbone) to continue playing. Using special software, the company 3D-scans the athlete's face and creates a model, on the basis of which the individual protective mask is printed.
This innovation reduces the athlete's downtime associated with injury and prevents further injury while healing. The company's masks have already been worn by several professional football and rugby players, including former Chelsea Football Club captain John Terry and footballer Sergio Ramos. Most bicycle helmets are made of foam, which is not completely safe when dropped. HEXR has created a new type of helmet in polyamide 11 (PA 11). The product is made by 3D printing to provide maximum personalization through 3D scanning of the shape of the head and thus increase protection.
Another sport supported by the 3D printing industry is surfing. The French startup Wyve is already developing surfboards using this technology, which allows you to create personalized products with an original translucent design. The company produces boards from recycled plastic waste, offering the end user a reliable solution with optimal performance. An original way to combine sustainability and innovation in one project. 3D printing of sports shoes may soon be on the stream. More and more sporting goods manufacturers including Adidas, Nike and Reebok are using the technology in question. A prime example is the Adidas 4D Fusion sneakers. The reason for the growth in the use of 3D printing in this area is again the possibility of personalization. 3D technologies can be used to scan a consumer's foot, develop a 3D model, and print in record time. The result is footwear adapted to the morphology, needs and style of the consumer. When it comes to ski boots, skiers often have to choose between high performance and comfort: boots that are too loose, yet more comfortable, can't provide the level of control they need. Using the latest 3D printing technology, Tailored Fits has developed ski boots that combine comfort and performance. Thanks to 3D scanning technology, Tailored Fits can 3D print the inside of the boot to suit any individual, providing a direct transfer of energy. And the buckle-free design ensures free circulation, helping you feel the slopes and keep your toes cool.
Using the latest 3D printing technology, Tailored Fits has developed ski boots that combine comfort and performance. Thanks to 3D scanning technology, Tailored Fits can 3D print the inside of the boot to suit any individual, providing a direct transfer of energy. And the buckle-free design ensures free circulation, helping you feel the slopes and keep your toes cool.
The Value of 3D Printing Standards
In short, in the world of sports today, 3D printers are being used to produce a variety of objects that improve the performance of athletes: from sneakers and ski boots to surfboards and racing car parts. This technology additionally comes to the rescue in case of accidents and injuries.
International standards have played a decisive role in ensuring the reliability, efficiency and safety of 3D printers and related device components, as well as consumables used in advanced equipment in this category. A number of technical committees and subcommittees make a significant contribution to standardization work. For example, ISO / IEC STK 1, a joint technical committee of the International Electrical Commission (IEC; IEC) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO; ISO), develops standards on the topic of 3D printing and 3D scanning , including the fundamental standards that form the basis of new documents.
For example, ISO / IEC STK 1, a joint technical committee of the International Electrical Commission (IEC; IEC) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO; ISO), develops standards on the topic of 3D printing and 3D scanning , including the fundamental standards that form the basis of new documents.
In addition, a number of IEC technical committees and subcommittees are working to determine the feasibility of preparation, development and harmonization of international standards on electrical and electronic components installed inside 3D printers. Relevant parts and components include, but are not limited to, switches and relays covered by IEC/TC 17 (Switching and control gear) and TC 121 (Switching and control gear and low voltage assemblies) technical committees. Servo drives and stepper motors used to move the extrusion head of the 3D printer / sintering laser are covered by TC 2 (Rotating Equipment) standards. Power supplies for 3D printers cover papers authored by TC 9 experts6 (Transformers, reactive coils, power supplies and their combinations).
The most important components are the various types of lasers used to sinter metals and polymers. TC 76 (Optical Radiation Safety and Laser Equipment) is the leading body for the standardization of lasers, including high-power laser equipment used in industrial facilities and research centers that serve, among other things, the 3D printing industry.
Source
Tags:
3D scanners, 3D printers, Tokyo Olympics, Application of 3D printing to help athletes, 3D scanning, new type of polyamide 11 (PA 11) helmet, 3D technology, 3D technology print, sneakers Adidas 4D Fusion
Other materials:
- How 3D printing is developing the medical industry
- Additive manufacturing of molding tooling from polymer and composite materials
- Additive technologies in the system of secondary vocational and higher education
- House on a printer: developers talk about 3D printing of new buildings in St. Petersburg
- Quality is the top priority
Attention!
We accept news, articles or press releases
with links and images. [email protected]
[email protected]
Types of materials for 3D printing
Types of materials for 3D printing
3D printing or "additive manufacturing" of objects of almost any geometric shape is now ubiquitous.
3D printing is based on the concept of building an object in successive layers that display the contours of the model.
In fact, 3D printing is the exact opposite of traditional manufacturing and processing methods such as milling or cutting, where the appearance of the product is formed by removing excess material (“subtractive manufacturing”).
Models made using the additive method can be used at any stage of the production process, whether for the production of prototypes (rapid prototyping) or as finished products themselves (rapid manufacturing).
3D printing technologies are used in architecture, construction, industrial design, automotive, aerospace, military-industrial, engineering and medical industries, bioengineering, fashion and footwear, jewelry, education, geographic information systems, food processing and many other areas.
In home use, additive technology is also gaining popularity, and often the capital cost of purchasing a 3D printer is repaid by savings on household production of various items.
There are currently several methods of additive manufacturing. The main differences between them are in the method of applying the layers and the consumables used.
The most common methods are Fused Deposition Method (FDM or FFF), liquid polymerization (stereolithography/SLA) and digital LED projection (DLP)), in addition, less common methods are selective laser sintering (SLS), selective laser melting (SLM), direct metal laser sintering (DMLS).
FDM/FFF method
The advantages of this technology:
- additives, but also based on thermoplastics)
Let's talk more about consumables for 3D printers with technology (FDM/FFF).
Polylactide (PLA, PLA)
The main feature of this material is its environmental friendliness, since polylactide is a polymer of lactic acid, and its raw materials are corn and sugar cane. The result is a completely biodegradable material, but at the same time it is not as durable and it easily absorbs water.
The result is a completely biodegradable material, but at the same time it is not as durable and it easily absorbs water.
Polylactide is suitable for making toys, souvenirs. In the industry, PLA is used for food packaging, drug containers and surgical sutures, as well as use in bearings that do not carry a high mechanical load (for example, in modeling), which is possible due to the material's excellent slip coefficient.
One of the most important factors for 3D printing applications is the low melting temperature of only 170-180°C, which contributes to relatively low power consumption and the use of inexpensive brass and aluminum nozzles. As a rule, extrusion is carried out at 160-170°C. At the same time, PLA solidifies quite slowly (glass transition temperature is about 50°C), which should be taken into account when choosing a 3D printer. The best option is a device with an open case, a heated work platform (to avoid deformation of large models) and, preferably, additional fans to cool the fresh layers of the model.
PLA has low shrinkage, i.e. loss of volume on cooling, which helps prevent warping. However, shrinkage has a cumulative effect as the dimensions of printed models increase. In the latter case, the build platform may need to be heated to evenly cool the printed objects.
The cost of PLA is relatively low, which adds to the popularity of this material.
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
ABS plastic is characterized by excellent mechanical properties, durability and low cost. In industry, ABS plastic is widely used in the production of car parts, housings for various devices, containers, souvenirs, various household accessories, etc. , at the same time, rather high indicators of thermal stability – from 90°C to 110°C. The exception is some types of ABS plastic, which break down when exposed to direct sunlight. At the same time, ABS plastic is easy to paint, which allows you to apply protective coatings on non-mechanical elements.
ABS extrusion temperature 180°C. And the low temperature spread between extrusion and glass transition allows ABS to cure faster than PLA.
ABS is highly soluble in acetone, allowing large models to be produced piece by piece and glued together, greatly expanding the capabilities of inexpensive desktop printers.
The main disadvantage of ABS plastic can be considered a high degree of shrinkage during cooling - the material can lose up to 0.8% of the volume. This effect can lead to significant deformations of the model, twisting of the first layers and cracking.
To combat these unpleasant phenomena, two main solutions are used:
-
heated work platforms that help reduce the temperature gradient between the lower and upper layers of the model;
-
closed housings and adjustment of the oven background temperature.
It should be noted that at room temperature, ABS plastic does not pose a threat to health, but when heated, acrylonitrile vapors are released - a toxic compound that can cause irritation of mucous membranes and poisoning. Although the amount of Acrylonitrate produced in small scale printing is negligible, it is recommended that you print in a well ventilated area or use an exhaust hood.
Although the amount of Acrylonitrate produced in small scale printing is negligible, it is recommended that you print in a well ventilated area or use an exhaust hood.
ABS is not recommended for food containers and utensils (especially for storing hot food or alcoholic beverages) or toys for small children.
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)
Polyvinyl alcohol has the unique property of being water soluble. This material is used in 3D printers equipped with dual extruders, in which case supports for the model are printed from PVA, which are subsequently dissolved in water, and the created model does not require mechanical or chemical processing of irregularities. In addition, PVA can be used to create water-soluble master patterns for molds and molds themselves.
The mechanical properties of PVA are quite interesting. At low humidity, plastic has high tensile strength. With increasing humidity, strength decreases, but elasticity increases. The extrusion temperature is 160-175°C, which allows the use of PVA in printers designed for printing with ABS and PLA plastics.
The extrusion temperature is 160-175°C, which allows the use of PVA in printers designed for printing with ABS and PLA plastics.
Store PVA plastic in dry packaging and, if necessary, dry before use. Drying can be done in a pottery kiln or an ordinary oven. As a rule, drying of standard coils takes 6-8 hours at a temperature of 60-80°C. Exceeding 220°C will cause the plastic to decompose, which should be taken into account when printing.
Nylon
The great advantage of nylon is its wear resistance and low coefficient of friction.
For example, nylon is often used to coat friction parts, which improves their performance and often allows them to function without lubrication.
There are several types of nylon produced by different methods and with slightly different characteristics. Let's talk about them in more detail.
-
Nylon 66 and Nylon 6 are the best known.
 These two options are very similar. In terms of 3D printing, the main difference is the melting point: Nylon-6 melts at 220°C, while Nylon-66 melts at 265°C.
These two options are very similar. In terms of 3D printing, the main difference is the melting point: Nylon-6 melts at 220°C, while Nylon-66 melts at 265°C. -
Many hobbyists prefer to use commercially available nylon threads such as trimmer wire. The diameter of such materials often corresponds to the diameter of standard FFF materials, which makes their use tempting. At the same time, these products are usually not pure nylon. In the case of trimmer rods, the material consists of nylon and fiberglass for an optimal combination of flexibility and rigidity. Fiberglass has a high melting point, and therefore printing with such materials is fraught with high nozzle wear and plugging.
-
Recently, attempts have been made to commercially develop nylon-based printing materials specifically for FDM/FFF applications, including Nylon-PA6 and Taulman 680. These grades are extrudable at 230-260°C.
Because nylon readily absorbs moisture, store consumables in vacuum packaging or at least in a container with water-absorbent materials. A sign of excessively damp media will be steam escaping from the nozzle during printing, which is not dangerous, but may degrade the quality of the model.
A sign of excessively damp media will be steam escaping from the nozzle during printing, which is not dangerous, but may degrade the quality of the model.
When printing with nylon, it is not recommended to use a polyimide desktop coating as the two materials fuse together. As a coating, you can use adhesive tape with wax impregnation (masking tape). The use of a heated bed will help reduce the possibility of deformation of the model, similar to printing with ABS plastic. Due to the low coefficient of friction of nylon, extruders with studded feeders should be used.
The nylon layers have excellent adhesion, which minimizes the chance of delamination of models.
Nylon is difficult to bond, making it difficult to print large multi-piece models. Alternatively, fusion of parts is possible.
Since nylon can release toxic fumes when heated, we recommend that you print in a well-ventilated area or use an exhaust fan.
Polycarbonate (PC)
This material is attractive due to its high strength and toughness.
An important consideration is the health risk of printing: the raw material is often the toxic and potentially carcinogenic compound bisphenol A, so it is recommended to print in well-ventilated areas. And also do not use finished products made of polycarbonate at high temperatures.
The extrusion temperature depends on the printing speed to avoid cracking, but the minimum temperature at 30mm/sec can be considered as 265°C. When printing, the use of polyimide film is recommended for better adhesion to the desktop surface. The high susceptibility of polycarbonate to deformation requires the use of a heated platform and, if possible, a closed housing with heating of the working chamber.
Polycarbonate easily absorbs moisture, so it must be stored in a moisture-proof location, and if printing in humid climates, the print spool must be stored in the same way.
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Despite being the most common plastic in the world, polyethylene is extremely rare in 3D printed materials. The reason for this is the difficulty in layer-by-layer manufacturing of models.
Polyethylene has a low melting point (130-145°C) and cures at 100-120°C, so the applied layers do not have time to set. In addition, polyethylene has a high shrinkage, which provokes the twisting of the first layers and the deformation of the models as a whole during uneven solidification. Accordingly, for printing with polyethylene, it is necessary to use heated platforms and heated working chambers, in addition, the printing speed must be sufficiently high.
Difficulties in use are compensated by the low price and general availability of this material. Recently, several devices have been developed for processing plastic waste from HDPE (bottles, food packaging, etc.) into standard filaments for printing on FDM/FFF printers. Examples are FilaBot and RecycleBot. Due to the simplicity of design, RecycleBot devices are often assembled by 3D craftsmen.
Examples are FilaBot and RecycleBot. Due to the simplicity of design, RecycleBot devices are often assembled by 3D craftsmen.
Melting polyethylene releases vapors of harmful substances, therefore it is recommended to print in well ventilated areas.
Polypropylene (PP, PP)
Polypropylene is a widely used plastic used in the manufacture of packaging materials, dishes, syringes, pipes, etc. The material has a low specific gravity, is non-toxic, has good chemical resistance, is resistant to moisture and wear and cheap enough.
Disadvantages of polypropylene are vulnerability to temperatures below -5°C and exposure to direct sunlight.
The main difficulty when printing with polypropylene is the high shrinkage of the material during cooling - up to 2.4%, so it is recommended to print on a heated platform to avoid model deformation. The minimum extrusion temperature is 220°C.
Polypropylene printing filaments are sold by Orbi-Tech, German RepRap, Qingdao TSD Plastic. Stratasys has developed a polypropylene simulant optimized for 3D printing called Endur.
Polycaprolactone (PCL)
Polycaprolactone (Hand Moldable Plastic, Mold-Your-Own Grips, InstaMorph, Shapelock, Friendly Plastic, Polymorph, Polymorphus, Ecoformax) has an ultra-low melting point of 60°C, which radically limits the number of 3D printers with which this material can be used.
Polycaprolactone is non-toxic, biodegradable polyester, which makes it suitable for medical applications and food containers. When ingested, polycaprolactone breaks down.
The material sticks easily to the surface of even a cold working table and is easy to paint.
In addition, polyprolactone is very plastic, so it can be reused many times.
Polycaprolactone is not suitable for creating functional mechanical models due to its viscosity (glass transition temperature is -60°C) and low heat resistance (melting point is 60°C).
Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU)
This thermoplastic has such high strength and fire resistance that it is widely used in the aviation industry. It is resistant to solvents and fuels and lubricants.
Polyphenylsulfone is suitable for the production of tableware and food containers. Operating temperature range is -50°С - 180°С.
For all its merits, polyphenylsulfone is rarely used in 3D printing due to its high melting point, reaching 370°C. Printing at this temperature requires ceramic nozzles. Currently, the only active user of the material is Stratasys, which offers industrial Fortus installations.
Polymethyl methacrylate (Acrylic, plexiglass, acrylic, PMMA)
Polymethyl methacrylate is organic glass.
This material has good characteristics: strength, moisture resistance, environmental friendliness, easy bonding, plasticity and resistance to direct sunlight.
However, acrylic has a number of disadvantages and is not suitable for FDM/FFF printing.
-
First, polymethyl methacrylate does not store well in the form of filament spools, since constant mechanical stress leads to the gradual destruction of the material.
-
To avoid bubbles, the print resolution must be fairly high, and this accuracy is rare among home printers.
-
Fast curing of acrylic requires tight environmental control of the working chamber and high print speed, while the print speed of FDM / FFF printers is inversely proportional to print resolution, which does not allow meeting the previous requirement.
However, attempts to print with acrylic are being made, but at the moment the best results with acrylic are shown by another printing technology ((MJM) from 3D Systems) - multi-jet modeling using photopolymer acrylic. Stratasys has also made significant strides using its proprietary VeroClear photopolymer acrylic simulant on Objet Eden printers.
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET, PET)
The advantages of this material are that it has high chemical resistance to acids, alkalis and organic solvents, has good wear resistance at temperatures from -40°C to 75°C, and also , easy to machine.
There are a number of difficulties when printing PET: the melting point is 260°C, and the shrinkage on cooling reaches 2%. The solution to these issues are heated working platforms and closed working chambers with temperature control.
In order to obtain transparent models, it is necessary to cool them quickly when they pass the glass transition threshold of 70°C - 80°C.
Undoubtedly, the material has become the focus of 3D craftsmen who use used containers as raw materials for the domestic production of 3D printing consumables. Recycling devices such as FilaBot or RecycleBot are used to make threads.
High impact polystyrene (HIPS)
High-impact polystyrene is widely used in industry in the production of various household products, building materials, disposable tableware, toys, medical instruments, etc.
The most attractive feature of polystyrene, unlike ABS, is that it is quite easily amenable to the organic solvent Limonen. Since Limonene has no effect on ABS plastic, it is possible to use polystyrene as a material for constructing soluble support supports. Compared to the convenient, water-soluble polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) plastic, polystyrene compares favorably with relatively low cost and resistance to humid climates that make PVA difficult to work with.
It's worth mentioning that some ABS manufacturers mix slightly cheaper polystyrene into their consumables. Accordingly, models made from such materials can be dissolved in Limonene along with supporting structures.
When polystyrene is heated to extrusion temperature, toxic fumes can be released, so printing in a well-ventilated area is recommended.
Simulators
All of the above plastics do not eliminate the need to use 3D printing technology when working with other materials such as wood, sand, metals. For this, imitators of these materials are created, based on the original material, and thermoplastic is the link. Let's consider them in a little more detail.
For this, imitators of these materials are created, based on the original material, and thermoplastic is the link. Let's consider them in a little more detail.
Wood Simulators (LAYWOO-D3, BambooFill)
LAYWOO-D3 is a revolutionary invention by Kai Party. This material consists of 40% natural wood chips of microscopic size and 60% binder polymer. As a result, products imitate wood in appearance and smell.
LAYWOO-D3 is virtually indestructible and therefore does not require the use of a heated platform.
Another advantage is that these materials are non-toxic and completely safe.
When printing, you can use the unique feature of wood imitators, because depending on the extrusion temperature (180°C-250°C), the shade can change, the higher the temperature, the darker the shade of the wood.
In addition, upon completion of printing, ready-made models are easy to work on, they lend themselves well to any mechanical processing, and are easy to color.
The main disadvantage of such materials is their cost, which is almost four times higher than the prices of PLA and ABS plastics.
Alternative materials are currently being developed and tested, such as BambooFill from the Dutch company ColorFabb.
Sandstone Simulators (Laybrick)
Laybrick is a composite material also invented by Kai Parthi. This time he set out to create an imitation of sandstone, using the proven method of mixing a binder with a filler - in this case a mineral one.
Laybrick allows you to print objects with different surface textures. How it works: at low extrusion temperatures (165°C-190°C) finished products have a smooth surface, with increasing temperature the material becomes rougher, up to a high degree of similarity to natural sandstone at an extrusion temperature above 210°C.
The advantages of wood imitators are preserved here as well.