3D printers pdf
3D printing for dental - Stratasys - PDF Catalogs | Technical Documentation
Add to favorites
{{requestButtons}}
Catalog excerpts
Multi-Color, Multi-Texture, One Print Stratasys dental solutions help laboratories digitize the entire workflow in-house. Only Stratasys 3D Printers give you the versatility to print multiple parts using multiple materials for different applications at the same time. Our solutions increase your productivity by eliminating many production steps. Our multi-material, multi-color 3D printers create unrivaled dental models and appliances leading to faster turnaround times and fewer remakes. PolyJet™ technology’s mixed-tray capability allows simultaneous printing of parts with different...
SCALABLE SOLUTIONS Stratasys offers scalable solutions that easily fit into the workflow of your laboratory, from entry-level 3D printers to multi-color, multi-material 3D production systems. Our dental printers deliver consistent, accurate models and appliances in specialized dental materials, ensuring a rapid return on investment. Each of our plug-and-play solutions offers ease-of-use, no digital design knowledge requirements and a clean, quiet, predictable process. DESIGNED FOR VERSATILITY AND PRODUCTIVITY Stratasys dental printers use PolyJet technology, capable of ultra-fine resolution...
APPLICATIONS KEY BENEFIT STRATASYS SOLUTION DELIVERING VALUE For more information on how Stratasys 3D Printing solutions create opportunities for growth for dental labs, contact: e [email protected] / stratasys.com THE 3D PRINTING SOLUTIONS COMPANY stratasys ISO 9001:2008 Certified ©2017 Stratasys Inc. All rights reserved. Stratasys, Stratasys signet, FDM and PolyJet are trademarks or registered trademarks of Stratasys Ltd. and/or its subsidiaries or affiliates and may be registered in certain jurisdictions. BR_PJD_DentalSolutions_A4_0217a
All Stratasys catalogs and technical brochures
-
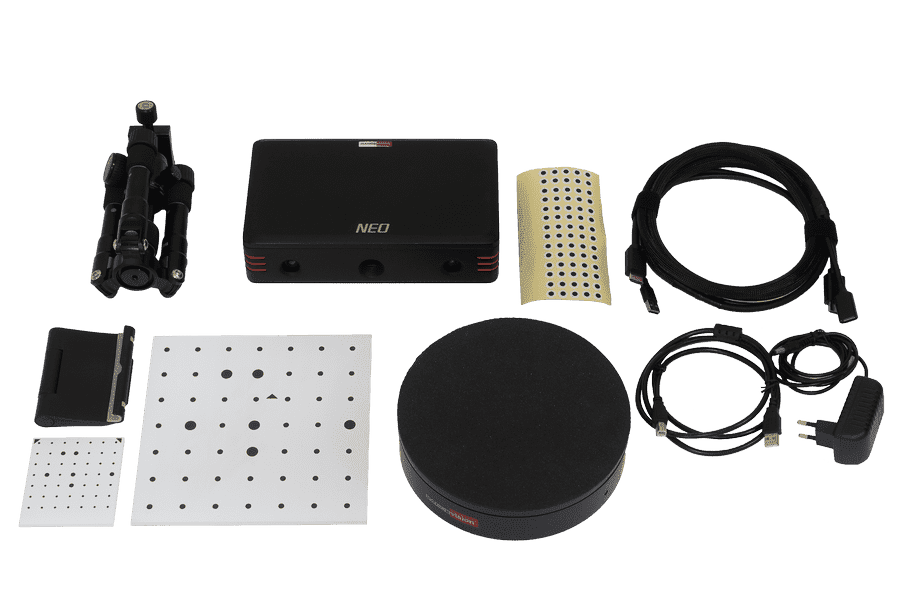
Neo800
2 Pages
-
TECHSTYLE
8 Pages
-
J5 MediJet™
8 Pages
-
F123 Composite-Ready
6 Pages
-
Origin One Dental
8 Pages
-
F900
8 Pages
-
Stratasys J55-Prime
8 Pages
-
FDM Materials and Systems
12 Pages
-
F123 Series Brochure
4 Pages
-
Fortus 450mc
8 Pages
-
Objet 30 V.
 5.
5.1 Pages
-
F770
8 Pages
-
Origin One
8 Pages
-
Stratasys h450
8 Pages
-
Fortus 450mc
2 Pages
-
Objet 500 Connex 1
2 Pages
-
Objet 30 Prime
2 Pages
-
Objet 260 Connex 3
2 Pages
-
PolyJet Materials and Systems
16 Pages
-
Stratasys J4100
2 Pages
-
J700 Dental
4 Pages
-
J8 Series Brochure
8 Pages
-
J35 Pro
4 Pages
-
J720 Dental
4 Pages
-
J5 DentaJet
8 Pages
-
ABOUT 3D PRINTING
6 Pages
-
Stratasys Continuous Build 3D Demonstrator
4 Pages
-
Surgical Planning
8 Pages
-
Ebook: 3D printing for medical innovation
22 Pages
-
Solutions: Additive Manufacturing for automotive accelerating vehicle development
4 Pages
-
FDM Material: Nylon 12CF
2 Pages
-
Solutions: Additive manufacturing for Aerospace
4 Pages
Compare
Remove all
Compare up to 10 products
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is becoming popular with manufacturers. The demand is growing due to some of the revolutionary benefits that it can provide. Like almost all technologies it has its own drawbacks that need considering.
The demand is growing due to some of the revolutionary benefits that it can provide. Like almost all technologies it has its own drawbacks that need considering.
This page aims to help with the selection process. We will cover each of the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing.
This production process offers a range of advantages compared to traditional manufacturing methods. These advantages include those related to design, time and cost, amongst others.
1. Flexible Design
3D printing allows for the design and print of more complex designs than traditional manufacturing processes. More traditional processes have design restrictions which no longer apply with the use of 3D printing.
2. Rapid Prototyping
3D printing can manufacture parts within hours, which speeds up the prototyping process. This allows for each stage to complete faster. When compared to machining prototypes, 3D printing is inexpensive and quicker at creating parts as the part can be finished in hours, allowing for each design modification to be completed at a much more efficient rate.
When compared to machining prototypes, 3D printing is inexpensive and quicker at creating parts as the part can be finished in hours, allowing for each design modification to be completed at a much more efficient rate.
3. Print on Demand
Print on demand is another advantage as it doesn’t need a lot of space to stock inventory, unlike traditional manufacturing processes. This saves space and costs as there is no need to print in bulk unless required.
The 3D design files are all stored in a virtual library as they are printed using a 3D model as either a CAD or STL file, this means they can be located and printed when needed. Edits to designs can be made at very low costs by editing individual files without wastage of out of date inventory and investing in tools.
4. Strong and Lightweight Parts
The main 3D printing material used is plastic, although some metals can also be used for 3D printing. However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
Also, parts can be created from tailored materials to provide specific properties such as heat resistance, higher strength or water repellency.
5. Fast Design and Production
Depending on a part’s design and complexity, 3D printing can print objects within hours, which is much faster than moulded or machined parts. It is not only the manufacture of the part that can offer time savings through 3D printing but also the design process can be very quick by creating STL or CAD files ready to be printed.
6. Minimising Waste
The production of parts only requires the materials needed for the part itself, with little or no wastage as compared to alternative methods which are cut from large chunks of non-recyclable materials. Not only does the process save on resources but it also reduces the cost of the materials being used.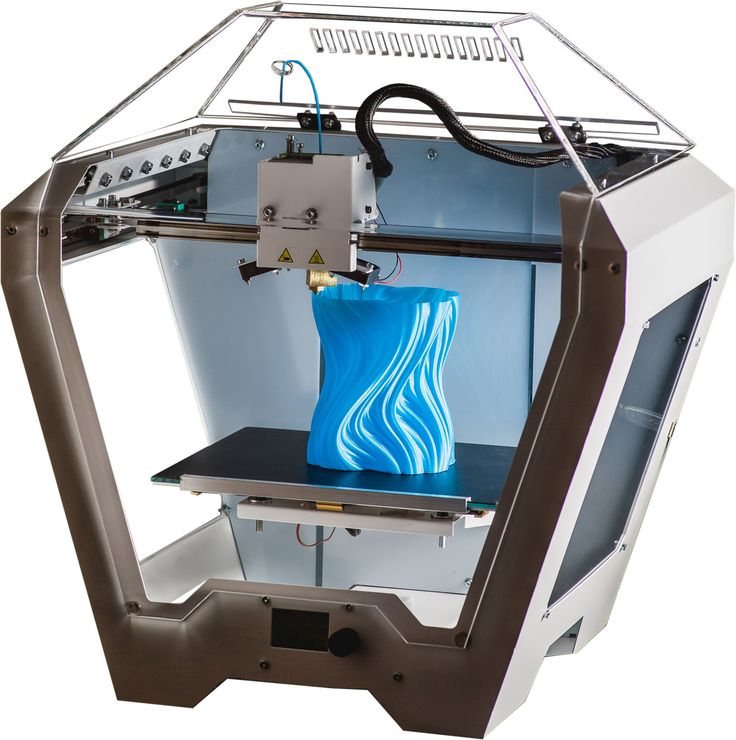
7. Cost Effective
As a single step manufacturing process, 3D printing saves time and therefore costs associated with using different machines for manufacture. 3D printers can also be set up and left to get on with the job, meaning that there is no need for operators to be present the entire time. As mentioned above, this manufacturing process can also reduce costs on materials as it only uses the amount of material required for the part itself, with little or no wastage. While 3D printing equipment can be expensive to buy, you can even avoid this cost by outsourcing your project to a 3D printing service company.
8. Ease of Access
3D printers are becoming more and more accessible with more local service providers offering outsourcing services for manufacturing work. This saves time and doesn’t require expensive transport costs compared to more traditional manufacturing processes produced abroad in countries such as China.
9. Environmentally Friendly
As this technology reduces the amount of material wastage used this process is inherently environmentally friendly. However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
10. Advanced Healthcare
3D printing is being used in the medical sector to help save lives by printing organs for the human body such as livers, kidneys and hearts. Further advances and uses are being developed in the healthcare sector providing some of the biggest advances from using the technology.
Like with almost any other process there are also drawbacks of 3D printing technology which should be considered before opting to use this process.
1. Limited Materials
While 3D Printing can create items in a selection of plastics and metals the available selection of raw materials is not exhaustive. This is due to the fact that not all metals or plastics can be temperature controlled enough to allow 3D printing. In addition, many of these printable materials cannot be recycled and very few are food safe.
2. Restricted Build Size
3D printers currently have small print chambers which restrict the size of parts that can be printed. Anything bigger will need to be printed in separate parts and joined together after production. This can increase costs and time for larger parts due to the printer needing to print more parts before manual labour is used to join the parts together.
3. Post Processing
Although large parts require post-processing, as mentioned above, most 3D printed parts need some form of cleaning up to remove support material from the build and to smooth the surface to achieve the required finish. Post processing methods used include waterjetting, sanding, a chemical soak and rinse, air or heat drying, assembly and others. The amount of post processing required depends on factors including the size of the part being produced, the intended application and the type of 3D printing technology used for production. So, while 3D printing allows for the fast production of parts, the speed of manufacture can be slowed by post processing.
4. Large Volumes
3D printing is a static cost unlike more conventional techniques like injection moulding, where large volumes may be more cost effective to produce. While the initial investment for 3D printing may be lower than other manufacturing methods, once scaled up to produce large volumes for mass production, the cost per unit does not reduce as it would with injection moulding.
5. Part Structure
With 3D printing (also known as Additive Manufacturing) parts are produced layer-by-layer. Although these layers adhere together it also means that they can delaminate under certain stresses or orientations. This problem is more significant when producing items using fused deposition modelling (FDM), while polyjet and multijet parts also tend to be more brittle. In certain cases it may be better to use injection moulding as it creates homogenous parts that will not separate and break.
6. Reduction in Manufacturing Jobs
Another of the disadvantages of 3D technology is the potential reduction in human labour, since most of the production is automated and done by printers.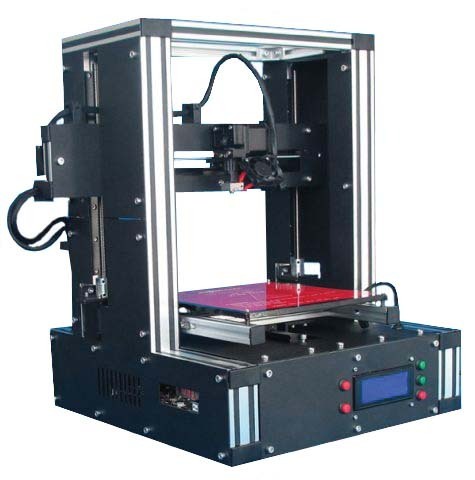 However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
7. Design Inaccuracies
Another potential problem with 3D printing is directly related to the type of machine or process used, with some printers having lower tolerances, meaning that final parts may differ from the original design. This can be fixed in post processing, but it must be considered that this will further increase the time and cost of production.
8. Copyright Issues
As 3D printing is becoming more popular and accessible there is a greater possibility for people to create fake and counterfeit products and it will almost be impossible to tell the difference. This has evident issues around copyright as well as for quality control.
Get Further Advice On 3D Printing
Need help with determining whether 3D printing is the right process for you?
Contact our team of world-leading experts with over 20 years of experience in the additive manufacturing field.
Our technology experts help to ensure our customers apply the correct technology process depending on each individual or company requirements:
Related Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Other pages - Page not found
Ratings and awards Management Expert Council Licenses and accreditations Reviews and thanks Sustainability Management and ESG Cooperation Corporate venture fund
About company >
Accompanying the conclusion of the SPIC Anti-crisis consulting Tax consulting Audit of RAS / IFRS Financial consulting due diligence Investment consulting and valuation HR consulting Management consulting Legal consulting Accounting consulting Transition to FSB Intellectual Property Management Attracting investments
Services and practices ›
Oil and gas Construction and development Mining and exploration Medicine and pharmaceuticals Energy Transport and logistic Food industry and agriculture infrastructure construction mechanical engineering Metallurgy IT industry Retail Light industry Financial sector Science and innovation Management companies Telecommunications and communications Chemical industry Timber industry and woodworking Production
All industries ›
company's news Legislative news Expert Publications Analytical studies
Press Center ›
Jobs Team Internship Alumni
Career >
Send a message and our managers will contact you as soon as possible
We use cookies to improve the site and its user experience. By continuing to use the site, you consent to the use of cookies.
By continuing to use the site, you consent to the use of cookies.
Accept
Industrial 3D printers Total Z
FDM and SLS 3D printers, drying and post-processing equipment
About company
FDM 3D printers
Industrial 3D printers Total Z PRO series
450-PRO 950-PRO
Total Z High Performance LPRO Series 3D Printers
1000-PRO-LL
Total Z G3 Series Desktop 3D Printers
250-G3 250-G3 (2X) XL250-G3(2X)
Total Z G5 Series Desktop 3D Printers
G5
SLS 3D printers Total Z
SLS-250
Portal systems for 3D printing with granules
Total Z AnyForm FGF
Total Z machines for drying and post-processing
Total Z D5Vacuum drying chambers
Help prepare plastic for printing.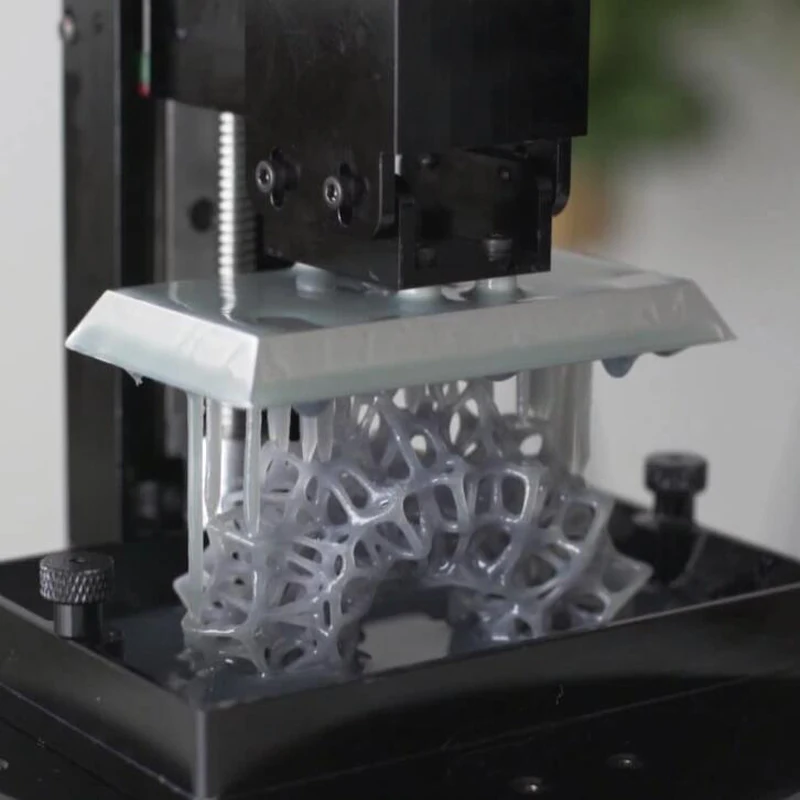 Remove moisture from hygroscopic materials. Reduce the risk of plastic "boiling", extruder breakage, deterioration of the surface quality of the product.
Remove moisture from hygroscopic materials. Reduce the risk of plastic "boiling", extruder breakage, deterioration of the surface quality of the product.
Watch →
Total Z MPC-310Acetone baths
Equipment for chemical post-processing of finished objects. Helps to achieve a glossy and smooth product surface.
Watch →
Total Z UB-450; 500; 650; 950; 1200;Ultrasonic baths
Machines for physical and chemical post-processing of models. Remove the supporting plastic from the surface of finished products. They clean the material in places inaccessible for manual processing.
See 5 models →
Our capabilities
The equipment complies with Russian and international standards
Consumables for printers and equipment are always in stock
We participate in R&D, cooperate with research institutes
We work with defense enterprises and government customers
Operational warranty service
Departure and training on the territory of the customer
Implemented projects by industry
Aviation industry and special products
Supply of an industrial 3D printer for the project of the MS-21 passenger aircraft of Irkut Corporation.
Supply of high-temperature 3D equipment for the laboratory of additive technologies of VIAM.
Supply of a 3D printer for printing with experimental materials for the production of the Central Institute of Aviation Motors.
Shipbuilding
Selection of samples of engineering plastic for the project of printing body elements for a shipyard.
Auto industry
Supply of equipment for 3D prototyping to the plant of the AvtoVAZ group.
Rocket and space
Supply of the first production equipment for 3D printing to the Center for Additive Technologies of JSC RCC Progress.
Foundry
Fabrication of a matrix using FDM 3D printing for the production of piece metal parts that have been discontinued or to replace parts with a long delivery time.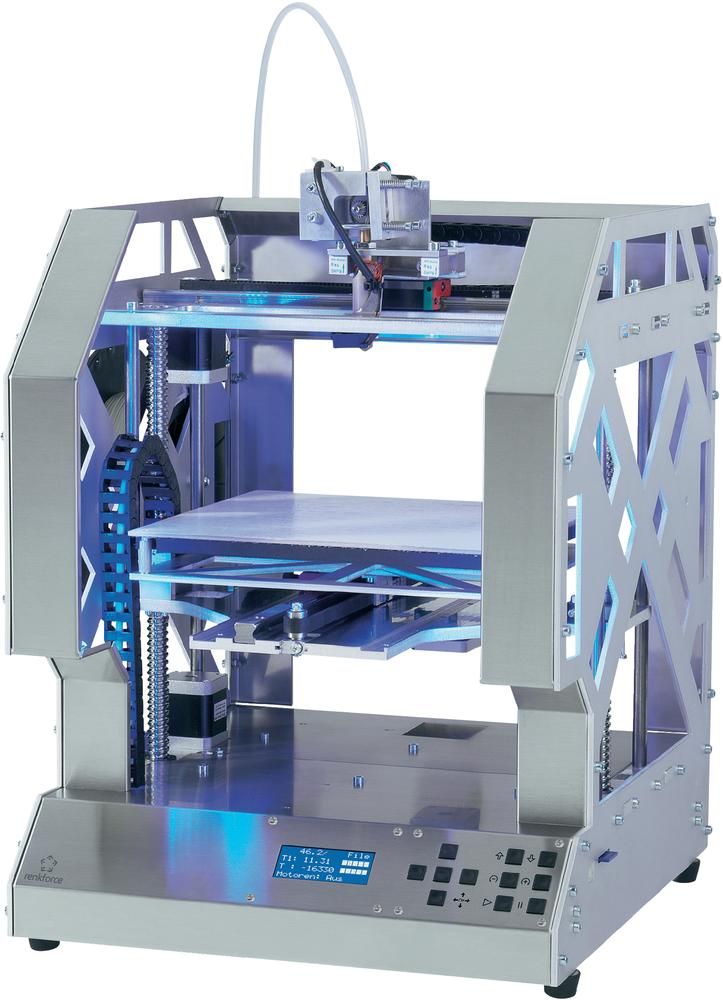
Education
Production of a desktop 3D printer for schoolchildren and students in collaboration with a team of developers of teaching materials for classrooms.
Electronics
Implementation of 3D equipment at the Simvol East Kazakhstan region.
Prototyping of lighting equipment for the Pyaterochka grocery store chain.
Agroprom
Complex equipping of the research agro-engineering center with equipment.
Aviation industry and special products
Supply of an industrial 3D printer for the project of the MS-21 passenger aircraft of Irkut Corporation.
Supply of high-temperature 3D equipment for the laboratory of additive technologies of VIAM.
Supply of a 3D printer for printing with experimental materials for the production of the Central Institute of Aviation Motors.
Shipbuilding
Selection of samples of engineering plastic for the project of printing body elements for a shipyard.
Auto industry
Supply of equipment for 3D prototyping to the plant of the AvtoVAZ group.
Rocket and space
Supply of the first production equipment for 3D printing to the Center for Additive Technologies of JSC RCC Progress.
Foundry
Fabrication of a matrix using FDM 3D printing for the production of piece metal parts that have been discontinued or to replace parts with a long delivery time.
Education
Production of desktop 3D printers for schoolchildren and students in collaboration with a team of developers of teaching materials for classrooms.
Electronics
Implementation of 3D equipment at the Simvol East Kazakhstan region.
Prototyping of lighting equipment for the Pyaterochka grocery store chain.
Agroprom
Complex equipping of the research agro-engineering center with equipment.
Services
3D printing
Casting
Reverse engineering
prototyping
Upcoming Events
New models of Total Z industrial 3D printing systems in Moscow at the Interplastica exhibition
Interplastica is a key event for the plastics and rubber market, which annually brings together experts from all over the world at one business platform.