3D printer printers
The Best Cheap 3D Printers for 2022
While we'd hesitate to call 3D printing a mature technology, you might say it has reached its teenage years. Through their first decade-and-change, 3D printers have come down in price, grown easier to set up and operate, and become more reliable. And you may pay less than you expect: Many once-high-end features have migrated down to inexpensive models.
PC Labs has been reviewing 3D printers since 2013. Today, the state of 3D printing is strong, but that wasn’t always the case. For the first several years, it was often an adventure getting one of these printers up and running, let alone successfully through our testing regimen. Issues with filament-based—aka fused filament fabrication (FFF) or fused deposition modeling (FDM)—printers were abundant.
(Photo: Zlata Ivleva)
More About Our Picks
Original Prusa Mini
4.5 Outstanding
Best Overall Budget 3D Printer
Bottom Line:
It requires assembly and calibration care (plus shipping from the Czech Republic), but the Original Prusa Mini is a compact, open-frame 3D printer that consistently produces superb-quality output for a great price.
Pros
- Top-notch object quality
- Supports a variety of filament types
- Useful, professionally printed user guide
- Great support resources
- Versatile, user-friendly software
Cons
- First-layer calibration can be tricky
- Only includes starter packets of filament
- Requires monitoring if young children or pets are around
Read Our Original Prusa Mini Review
XYZprinting da Vinci Mini
4.0 Excellent
Best Budget 3D Printer for Schools, Community Centers
Bottom Line:
The XYZprinting da Vinci Mini is a consumer-oriented 3D printer that provides a winning combination of low price, ease of setup and use, solid print quality, and smooth, misprint-free operation.
Pros
- Very low price.
- Reasonably priced filament.
- Good print quality.
- No misprints in testing.
- Easy setup and operation.

- Quiet.
- Prints over a USB or Wi-Fi connection.
Cons
- Occasional problems in trying to launch prints.
- Removing printed objects from the print bed is sometimes tricky.
Read Our XYZprinting da Vinci Mini Review
Toybox 3D Printer
4.0 Excellent
Best Budget 3D Printer for Children
Bottom Line:
The Toybox 3D Printer works well as a model designed for children, offering reliable printing from a browser or mobile device and a few thousand toys to print, plus creative options to output drawings or photos. Just bear in mind the tiny build area.
Pros
- Reliable, misprint-free printing
- Easy setup
- One-touch operation
- Well-composed help resources
- Access to more than 2,000 printable toys and projects
- Lets you create your own printable designs
Cons
- Tiny build area
- Not ideal for importing 3D files created elsewhere
Read Our Toybox 3D Printer Review
Monoprice Mini Delta V2 3D Printer
4. 0 Excellent
0 Excellent
Best Budget 3D Printer for Beginners, Non-Techies
Bottom Line:
3D printing gurus will be intrigued by the Monoprice Mini Delta V2's use of the delta rather than Cartesian coordinate system, but beginners will just enjoy its low price, ease of use, and speedy printing.
Pros
- Sub-$200 price
- Quick, nearly misprint-free printing
- Easy setup and operation
- Sturdy steel-and-aluminum frame
- Supports multiple filament types
Cons
- Tiny build area
- So-so print quality
- Mere one-year warranty
Read Our Monoprice Mini Delta V2 3D Printer Review
Anycubic i3 Mega S
3.5 Good
Best Budget 3D Printer With an Open Design, Big Build Area
Bottom Line:
The Anycubic i3 Mega S, an inexpensive open-frame 3D printer, produced decent-quality prints in our testing. To get the most out of it, though, may require precise calibration.
Pros
- Modestly priced
- Large build area for an inexpensive printer
- Supports a variety of filament types
- Generally solid print quality
- Uses well-known Cura software
Cons
- Finicky print-platform alignment
- Supported coils of filament are small
- Poorly placed spool holder
Read Our Anycubic i3 Mega S Review
Anycubic Vyper
3.5 Good
Best Budget 3D Printer for the Biggest Build Area Possible
Bottom Line:
Anycubic's modestly priced Vyper whips up large 3D prints on its open-frame design, and provides automatic print-bed leveling. Just know that some minor assembly is required—and printed objects may require a bit of cleanup.
Pros
- Relatively large build area
- Automatic bed leveling
- Simple assembly
Cons
- Short (one-year) warranty
- Includes only a small starter filament coil
- Using Cura software with the Vyper requires tweaking a couple of settings
- Test prints showed some "hairy" filament residue
Read Our Anycubic Vyper Review
Creality Ender-3 V2
3. 5 Good
5 Good
Best Budget 3D Printer for Tinkerers and DIY Types
Bottom Line:
Hands-on tweaking defines Creality's budget-price Ender-3 V2, an open-frame 3D printer that you build from a kit. It produces generally above-par prints, but its print bed can be tricky to keep leveled.
Pros
- Inexpensive
- Slightly above-average print quality
- Good-size build area for its price
- Supports several filament types
Cons
- Manual print-bed leveling can be tricky
- Setup instructions could be deeper, more legible
- Questionable quality control on some parts
Read Our Creality Ender-3 V2 Review
Flashforge Finder 3D Printer
3.5 Good
Best 3D Printer for the Very Tightest Budgets
Bottom Line:
The Flashforge Finder 3D Printer is moderately priced and offers good print quality, but it proved tricky to get up and running in our tests.
Pros
- Quiet.
- Good print quality.
- Connects via USB 2.0 cable, USB thumb drive, or Wi-Fi.
- Reasonably priced.
Cons
- Some objects pulled off the platform during testing.
- Poor documentation.
- Modest build volume.
- Limited to printing with polylactic acid filament (PLA).
Read Our Flashforge Finder 3D Printer Review
Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer
3.5 Good
Best Budget 3D Printer for Dabbling in Small Objects
Bottom Line:
The Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer is a compact, stylish 3D printer with above-par overall print quality, but, alas, a tiny build area for the money.
Pros
- Small, lightweight for a desktop 3D printer.
- Easy to set up and use.
- Supports PLA, PETG, and wood composite filaments.
- Multiple-color support.
- Wi-Fi camera monitors print jobs.

- Prints from USB drives, SD cards, or mobile devices.
Cons
- High price for its capabilities.
- Small build area.
- Too-brief warranty.
Read Our Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer Review
XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro
3.5 Good
Best Budget 3D Printer With Closed Design, Roomy Build Area
Bottom Line:
The XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro is a moderately priced closed-frame 3D printer with a large build volume and overall good performance, but a potentially balky filament-feeding system.
Pros
- Spacious build area
- Works with third-party filaments
- Self-leveling print bed
Cons
- Build plate is not heated
- Limited to PLA- and PETG-based filaments
- Guide tube is prone to detaching
Read Our XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro Review
Monoprice Voxel 3D Printer
3. 0 Average
0 Average
Best Budget 3D Printer for Cheap Filament
Bottom Line:
The Monoprice Voxel is an under-$400 3D printer that's easy to set up and use. It exhibits generally good print quality, but it was unable to print two of our test objects.
Pros
- Easy to set up and use.
- Budget price for printer and filament spools.
- Supports PLA, ABS, and several composite filament types.
- Versatile software.
- Prints over Ethernet or Wi-Fi, or from a USB thumb drive.
Cons
- Frequent misprints on certain test objects.
- Slightly balky touch screen.
Read Our Monoprice Voxel 3D Printer Review
Filament feeders had to be coaxed into delivering filament from the spool to the extruder. Print beds had to be manually aligned. The extruder or hot end had to be positioned just right to minimize the gap between the nozzle and the build plate (the flat surface on which the object is printed). Objects frequently stuck to the build plate, and required careful, sometimes unsuccessful, efforts to pry them off. These and other issues required painstaking effort to resolve, often combined with calls to tech support.
Objects frequently stuck to the build plate, and required careful, sometimes unsuccessful, efforts to pry them off. These and other issues required painstaking effort to resolve, often combined with calls to tech support.
Not so much anymore. While they can still be rebellious at times, 3D printers have grown up a lot, and achieving the 3D printer basics has gotten a lot less likely to end in a shouting match over small things.
What to Look for in a Cheap 3D Printer
The big difference is the change that has come to the cheaper models. Nowadays, many of those ornery 3D-printing issues have been resolved (most of the time, anyway), even for consumer and bargain-priced 3D printers. Automatic print-bed leveling is the norm, and you can usually remove 3D-printed objects from heated and/or flexible build plates with a minimum of coaxing. Most 3D printer manufacturers have either developed and refined their own software, or have adapted an open-source printing platform such as Cura(Opens in a new window).
What separates more expensive 3D printers from cheap ones ("cheap" defined as $500 or less, for the purposes of this article) is often a select group of features. These include the build volume, the type of frame, the varieties of supported filament, the software, and the connectivity mix. Let's run through those in turn.
What's the Right Build Volume for a 3D Printer?
A 3D printer’s build volume is the maximum dimensions (HWD) of a part that it can print. (We say “a part” because a 3D-printed object can consist of multiple parts that are printed, then glued or otherwise pieced together.) While the smallest build volume of any 3D printer we have tested is 3.9 by 3.9 by 4.9 inches, we consider any build volume smaller than 6 by 6 by 6 inches to be small, any between that and 10 by 10 by 10 inches as medium, and any printer with at least one build dimension of more than 10 inches as having a large build volume.
(Photo: Molly Flores)
As a general rule, inexpensive 3D printers have small build volumes, while more expensive ones have larger build volumes. This depends in part on the type of printer. Closed-frame 3D printers—and most semi-open models, which have a rigid top, base, and sides but are open in front and, often, back—tend to have small build volumes, while open-frame printers, lacking as rigid a physical structure, often have relatively large build volumes for the price. You'll want to weigh the build volume against the kinds of objects you will print.
This depends in part on the type of printer. Closed-frame 3D printers—and most semi-open models, which have a rigid top, base, and sides but are open in front and, often, back—tend to have small build volumes, while open-frame printers, lacking as rigid a physical structure, often have relatively large build volumes for the price. You'll want to weigh the build volume against the kinds of objects you will print.
Should I Get an Open-Frame or Closed-Frame 3D Printer?
Which brings us to the frame "form factor" question: open-frame versus closed-frame. Closed-frame 3D printers are boxlike devices, with a rigid base, walls (with a see-through door in front), and top. Among their advantages? They muffle the operating noise, as well as reduce the odor from melted filament (which is potentially an issue with ABS plastic), and they provide some protection for people or pets who might inadvertently touch the hot extruder. A downside: They tend to have smaller build volumes than open-frame 3D printers, which have fewer (often, no) walls to constrict them.
(Photo: Zlata Ivleva)
Low-cost 3D printers include both open-frame and closed-frame models, as well as a few stereolithography printers. If a relatively large build volume is a priority, you’re likely to get more bang for the buck with an open-frame model. Open-frames do have some clear downsides by definition: They tend to be noisy, emit odors when certain plastics are melted, and provide little protection for someone who might touch the hot extruder.
(Photo: Molly Flores)
Also, recognize some potential negatives of open frames, depending on the model. Some require assembly, being essentially kits, and most require more setup care than a closed-frame printer, plus more maintenance to keep them running smoothly. Still, these very traits should not deter—and may even appeal to—hobbyists and DIY folks.
What Should I Look for in 3D Printer Software and Connectivity?
Gone are the days when tinkerers had to cobble together several different programs to get a 3D printer to run. Manufacturers either include their own 3D printing program or modify an existing platform such as the open-source Cura.
Manufacturers either include their own 3D printing program or modify an existing platform such as the open-source Cura.
3D printing software performs three main functions: processing an object file (resizing, moving, rotating, and in some cases duplicating it), slicing it (into virtual layers, based on your chosen resolution), and printing it. These are almost universally combined into a seamless process. Some high-end printers have software that supports a wider range of settings you can tweak, but even the basic suites work at least reasonably well.
More likely to vary among the cheaper set is the array of connection options from model to model. Nearly all have a USB Type-A port to fit a thumb drive for printing from document files. Most also have a USB Type-B port for connecting directly to a computer, and some offer Wi-Fi, too (or as an alternative), while a handful let you connect via Ethernet to share the printer across a local network.
Some printers support storing 3D files on an SD or microSD card (which may also contain the printer’s system files). Most 3D printer manufacturers (even the discount ones) have a mobile app to launch and monitor print jobs, and a few provide access to cloud services from which you can print.
Most 3D printer manufacturers (even the discount ones) have a mobile app to launch and monitor print jobs, and a few provide access to cloud services from which you can print.
While high-end 3D printers tend to have an abundance of connection choices, discount models vary widely in their choices. Some are generous and some are basic, so it pays to assess what a given model offers.
What Should I Look for in Filament Support?
Filament support tends to be a key area that separates the cheaper models from the higher-end ones. (See our guide to understanding 3D printing filaments for more particulars.) Inexpensive 3D printers tend to support a limited number of plastic filament types, some of them only PLA and/or ABS.
Recommended by Our Editors
3D Printing: What You Need to Know
3D Printer Filaments Explained
(Photo: Molly Flores)
PLA (polylactic acid) is a biodegradable, plant-based polymer, while ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is the same tough plastic that Legos are made from. Objects printed from ABS are durable and nontoxic, though the material can be tricky to work with. ABS can emit an acrid, unpleasant odor during printing, and the bottom corners of objects being printed with it have a tendency to curl upward a bit, especially if you are using a non-heated print bed. This can lead to unsightly prints, and/or prints prematurely pulling off the build plate, ruining them.
Objects printed from ABS are durable and nontoxic, though the material can be tricky to work with. ABS can emit an acrid, unpleasant odor during printing, and the bottom corners of objects being printed with it have a tendency to curl upward a bit, especially if you are using a non-heated print bed. This can lead to unsightly prints, and/or prints prematurely pulling off the build plate, ruining them.
Many entry-level and low-price 3D printers stick exclusively to PLA. If you want to experiment with a larger variety of filaments—which include water-soluble filament, wood- and metal-laced composites, and both tough and flexible varieties—you may have to pay more, although a few discount models support a wide range of materials.
Should I Consider a 3D Printing Pen Instead?
Although they aren’t printers per se, inexpensive 3D pens are close kin to 3D printers—using the same filament types and a similar extrusion system—and we include them in the 3D printing category. Rather than tracing out a programmed pattern, you use the 3D pen much like a normal pen, except that you draw with molten plastic. You can trace a pattern or draw freehand, and even draw in three dimensions as the plastic quickly solidifies and hardens once extruded.
You can trace a pattern or draw freehand, and even draw in three dimensions as the plastic quickly solidifies and hardens once extruded.
Most 3D pens cost less than $100, and some cost $50 or less. At a glance, 3D pens may appear to be toys, but some artists and craftspeople have taken to them, as it is possible to make quite complicated and beautiful objects with them. If your aim in 3D printing is something closer to freehand design and free expression than computer-centric, structured, and repeatable output, you might give one a try.
So, Which Cheap 3D Printer Should I Buy?
Buying a budget 3D printer needn’t mean a world of sacrifice. Plenty of capable and reliable models sell at less than $500, and while they may not be as feature-rich as their more expensive cousins, there's no sense in paying for things you don’t need.
Many casual 3D-printing experimenters will be fine with printing over a USB cable or from a thumb drive, and sticking to PLA may be the best choice for a starter 3D printer. If you focus just on the features you want, you may be pleasantly surprised at what you find. Here we feature the best under-$500 3D printers we have reviewed. Also check out our guide to our favorite 3D printers overall.
If you focus just on the features you want, you may be pleasantly surprised at what you find. Here we feature the best under-$500 3D printers we have reviewed. Also check out our guide to our favorite 3D printers overall.
3D Printers You'll Love in 2022
At MatterHackers, we have tested and approved the best 3D printers available for your specific need. What type of 3D printer should you buy? Whether you're looking for a reliable 3D printer for your business for rapid prototyping, or an educator looking to advance the way your students learn, MatterHackers can find the best 3D printer to fit your requirements. Our wide selection of the best 3D printers paired with our staff's expert-level knowledge ensures that your additive manufacturing experience will be a success the first time around. We want you to have the best 3D printing experience for your use-case - let us help you find the best 3D printer.
What is 3D Printing?3D printing, which is also known as additive manufacturing, is a process where physical, three-dimensional objects, parts, or models are made layer-by-layer from Computer-Aided Design, or CAD, and digital files.
There are two main types of 3D printing:
- Fused Deposition Molding (FDM)
- Stereolithography (SLA)
FDM 3D printing is also known as fused filament fabrication (FFF 3D printing), and it is the process where thermoplastic 3D printing filament is extruded through a heated nozzle that melts the plastic, allowing it to follow the path of your digital file layer-by-layer until your object is complete.
SLA 3D printing is the process where liquid resins are cured or hardened layer-by-layer using a laser, LCD screen, or digital light projector. Once an SLA printed part is complete, it must be post-processed in UV light.
What is the Best 3D Printer?There are hundreds of 3D printers to choose from - which one is the best? Finding the best 3D printer entirely depends on what you want to make with your 3D printer, and of course, your budget. Do you want to 3D print big parts or small parts? Do you need to print strong, functional parts, or are you more interested in making models that won't need to be strong? Do your 3D printed parts need to be as clean and detailed as possible, or do you need them to just be functional with little detail? Every 3D printer has different characteristics that will determine which is the best 3D printer for you. If you need help deciding on which 3D printer is the best, contact [email protected] and we can help walk you through the hundreds of options available at MatterHackers.
If you need help deciding on which 3D printer is the best, contact [email protected] and we can help walk you through the hundreds of options available at MatterHackers.
A desktop 3D printer costs anywhere from $165 to $12,500. 3D Printing has become more accessible over the years as more options have become available in a wide price range.
Is 3D printing hard?No, 3D printing is easy to do! With the right tools and guidance from the experts at MatterHackers, you can learn to 3D print easily. Check out our article on the Top Ten Tips When Getting Started With 3D Printing and you'll be on your way to 3D printing like a pro in no time.
Is 3D printer filament expensive?No, 3D printer filament is not expensive. You can find base materials like PLA, ABS, and PETG for as low as $15.68 per 1kg spool, like our MH Build Series filament.
You can even print with real stainless steel metal on any desktop 3D printer for as low as $129 per 1kg spool, which in the world of metal manufacturing is an incredible rate that is much more efficient than traditional metal machining methods.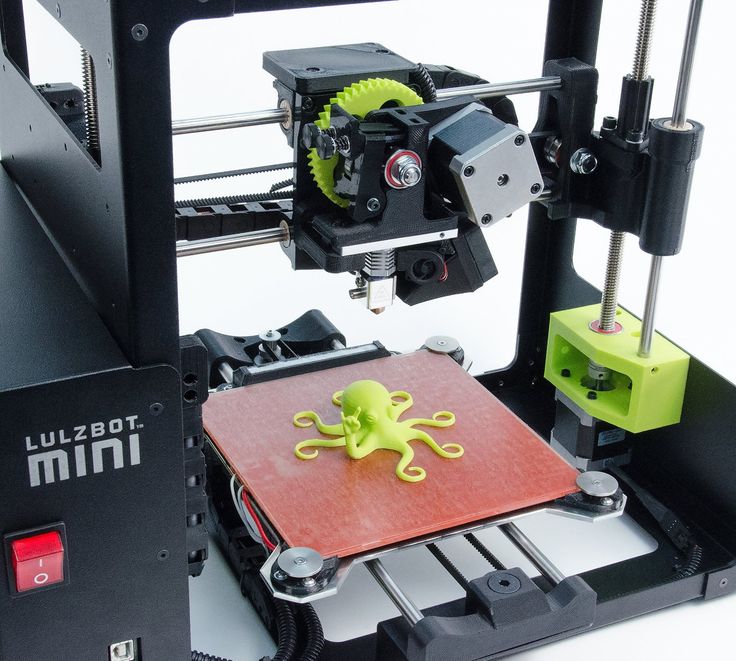
More advanced materials can be a little steeper in price based on the materials that they are made from, but all-in-all 3D printing is an incredibly cost-friendly way to create custom parts and products. You can browse all 3D printer filament here.
Is 3D Printer Resin Expensive?No, 3D printer resin is not expensive. You can find 3D Printer resin for as low as $15.97 per 500g bag, like our MH Build Series Resin.
Premium resins that are made for specific applications can be a little more expensive than average model resins. However, 3D printing is still a more affordable way to manufacture parts or create models when compared to traditional methods. You can browse all 3D printer resins here.
What Can a 3D Printer Make?You can make nearly anything with a 3D printer. Many industries use 3D printers for rapid prototyping, manufacturing functional end-use parts for products, or even custom jigs and fixtures. 3D printers can also be used in the home for creating fun items, things that break around the house, or even cookie cutters. With 3D printing, the sky is the limit!
With 3D printing, the sky is the limit!
3D printers in education
3D printing is one of the main educational trends of recent years. Schools and universities in Russia and around the world clearly understand that without the use of 3D printers today it is impossible to provide students with a truly comprehensive training.
- How 3D printers can help you learn
- For techies and creators
- Use cases
- Choosing a 3D printer
- How 3D printers can help you learn
- For techies and creators
- Use cases
- Choosing a 3D printer
Just a few years ago, 3D equipment was not well represented in domestic colleges and universities due to its high cost. But now the situation has changed. First, high-quality 3D printers at an affordable price began to appear on the market. In addition, the state actively supports innovative programs in educational institutions by allocating funds for the purchase of 3D printers and 3D scanners.
A few years ago, 3D equipment was not well represented in domestic colleges and universities due to its high cost. But now the situation has changed. First, high-quality 3D printers at an affordable price began to appear on the market. In addition, the state actively supports innovative programs in educational institutions by allocating funds for the purchase of 3D printers and 3D scanners.
How 3D Printers Help Education
Educational institutions around the world are using 3D printing. 3D printers improve the learning process, develop imaginative thinking among students, accustom future specialists to automated programming and design. 3D printing greatly increases the interest in the learning process, as it allows students to feel like a real innovator.
Having created a model on a computer, a student will be able to hold it in his hands in a few hours - this is a great motivation to create something new.
Students who use a 3D printer for educational purposes have the opportunity to learn from their own mistakes. On paper or a computer, it is difficult to notice the flaws of the model, and when creating a mock-up or test part, the student, having modeled it on a computer in a 3D program, holds it in his hands after a short period of time. If something does not work, then this is not a problem, you can try again.
On paper or a computer, it is difficult to notice the flaws of the model, and when creating a mock-up or test part, the student, having modeled it on a computer in a 3D program, holds it in his hands after a short period of time. If something does not work, then this is not a problem, you can try again.
For the educational institutions themselves, the installation of a 3D printer will not only raise the general prestige, but also train real specialists capable of performing real design tasks. At the same time, impressive costs for the purchase of the equipment itself and for its further use will not be required.
3D printers are great for all ages. 3D modeling devices will be of interest to younger students for general development, acquaintance with technology, for use in the game mode. High school students and students will appreciate the benefits of 3D printers from a practical point of view. With their help, it will be possible to implement author's projects, print practical tasks, develop creative abilities and skills.
How 3D printers help in education
3D printing is used by educational institutions around the world. 3D printers improve the learning process, develop imaginative thinking among students, accustom future specialists to automated programming and design. 3D printing greatly increases the interest in the learning process, as it allows students to feel like a real innovator.
Having created a model on a computer, a student will be able to hold it in his hands in a few hours - this is a great motivation to create something new.
Students who use a 3D printer for educational purposes have the opportunity to learn from their own mistakes. On paper or a computer, it is difficult to notice the flaws of the model, and when creating a mock-up or test part, the student, having modeled it on a computer in a 3D program, holds it in his hands after a short period of time. If something does not work, then this is not a problem, you can try again.
For the educational institutions themselves, the installation of a 3D printer will not only raise the general prestige, but also train real specialists capable of performing real design tasks. At the same time, impressive costs for the purchase of the equipment itself and for its further use will not be required.
3D printers are great for all ages. 3D modeling devices will be of interest to younger students for general development, acquaintance with technology, for use in the game mode. High school students and students will appreciate the benefits of 3D printers from a practical point of view. With their help, it will be possible to implement author's projects, print practical tasks, develop creative abilities and skills.
Technical and creative 3D printers
In technical universities 3D technologies are the most popular. Students can design objects, parts and layouts right in the classroom, make prototypes using a 3D printer, evaluate and test them. 3D printing, already included in the curriculum of many universities, enables students to bring their design ideas and ideas to life, thereby increasing their relevance in a high-tech manufacturing environment.
3D printing, already included in the curriculum of many universities, enables students to bring their design ideas and ideas to life, thereby increasing their relevance in a high-tech manufacturing environment.
3D printers that print plastic products are commonly used to teach engineering students. Such equipment allows to obtain durable prototypes and mechanisms that can withstand physical stress and be tested.
3D printers for technical and creative professions
In technical universities 3D technologies are the most popular. Students can design objects, parts and layouts right in the classroom, make prototypes using a 3D printer, evaluate and test them. 3D printing, already included in the curriculum of many universities, enables students to bring their design ideas and ideas to life, thereby increasing their relevance in a high-tech manufacturing environment.
3D printers that print plastic products are commonly used to teach engineering students. Such equipment allows to obtain durable prototypes and mechanisms that can withstand physical stress and be tested.
Such equipment allows to obtain durable prototypes and mechanisms that can withstand physical stress and be tested.
Robotic Prosthetic Hand Design
Parts of a Miniature Aircraft Engine
Housing for a Test Model Aircraft
Robotic Prosthetic Hand Design
Parts of a Miniature Aircraft Engine
Aircraft test case
Creative specialties is another area where 3D printing is being used. Future architects and designers with the help of 3D printers can implement the most daring projects, experiment with materials and shapes. The ability to quickly visualize and physically implement their own projects allows students to master many aspects of their future profession much faster.
Full color 3D printers are the best choice for architecture and design students. Such equipment will allow your students to quickly get bright and visual visualizations of their projects.
Creative specialties is another area where 3D printing is actively used. Future architects and designers with the help of 3D printers can implement the most daring projects, experiment with materials and shapes. The ability to quickly visualize and physically implement their own projects allows students to master many aspects of their future profession much faster.
Future architects and designers with the help of 3D printers can implement the most daring projects, experiment with materials and shapes. The ability to quickly visualize and physically implement their own projects allows students to master many aspects of their future profession much faster.
Full color 3D printers are the best choice for architecture and design students. Such equipment will allow your students to quickly get bright and visual visualizations of their projects.
Student architectural layout
Design Chair
Design Development of shoes
Student architectural layout
Design Chair
Design development of shoes
Examples of use of 3D printers in education
9000 3D printers today are actively used in schools and schools and schools and universities throughout Russia. Their prototyping centers are open at Moscow State University, Moscow State Technical University. Bauman, MEPhI, Volga University and other universities. Here are some examples of the use of 3D printing by Western educational institutions:
Here are some examples of the use of 3D printing by Western educational institutions: SISSA International School for Special Studies significantly improves its design performance >>
Students around the world develop 3D modeling skills >>
Examples of using 3D printers in education
3D printers are now actively used in schools and universities throughout Russia. Their prototyping centers are open at Moscow State University, Moscow State Technical University. Bauman, MEPhI, Volga University and other universities. Here are some examples of the use of 3D printing by Western educational institutions:
SISSA International School for Advanced Studies significantly improves its design performance >>
Students around the world develop 3D modeling skills >>
3D printers for education
Stratasys F120
30127 30127
Total-Z AnyForm 450 PRO
3D Systems ProJet CJP 660 Pro
Stratasys F120
3DLAM Mini
Total-Z Anyform 450 Pro
3D Systems Projet CJP 660 Pro
10 advantages of 3D printer: Economy 9000
more recently, more recently for 3D to something completely new. The technology was underdeveloped, the hardware was too expensive for widespread use. But only a few years have passed, and the situation has changed radically. Not only did more and more 3D printers begin to appear in stores, but also some enthusiasts began to assemble this equipment themselves.
The technology was underdeveloped, the hardware was too expensive for widespread use. But only a few years have passed, and the situation has changed radically. Not only did more and more 3D printers begin to appear in stores, but also some enthusiasts began to assemble this equipment themselves.
1. Cost-Effective
While large scale projects with thousands of 3D printed parts are not cheap, they are still much more cost effective than other technologies. Many manufacturers use 3D printing for small runs or for prototyping. Plastic can also be used for injection molding, but casting small batches can require expensive equipment. But even in this case, manufacturers can produce cast 3D parts several times cheaper than using aluminum.
Prototype parts printed on Prusa i3 Bizon 3D printer, layer height 0.1mm, PLA material
Compared to traditional production methods, the entire process can take weeks or days, and most products are printed in hours.
 Some manufacturers have even begun to make parts to order, which has also allowed them to optimize their warehouse capacity and resource management scheme, making them more flexible. With this new approach, the manufacturer does not need to store every single part or component, they can simply be printed as needed and immediately put into action.
Some manufacturers have even begun to make parts to order, which has also allowed them to optimize their warehouse capacity and resource management scheme, making them more flexible. With this new approach, the manufacturer does not need to store every single part or component, they can simply be printed as needed and immediately put into action.
Miniature parts printed by Wanhao Duplicator 7 photopolymer 3D printer, layer height 0.5mm, photopolymer resin material
It not only affects the reputation of the company in its industry, insufficient technical control can lead to injury to employees and customers. Since 3D printing uses a completely different production method than most machine tool operations, the process has significantly fewer weaknesses and flaws overall.
Model printed on Picaso Designer X PRO 3D printer, 0.2 mm layer, ABS materials, HIPS
4. Less waste
The press is gaining more and more support in the form of supporters of the "green" movement. Because 3D printing produces significantly less waste than traditional processing, the technology is more environmentally friendly while reducing costs. 3D printing has even made its way into the textile industry, allowing clothing and prototypes to be printed.
Because 3D printing produces significantly less waste than traditional processing, the technology is more environmentally friendly while reducing costs. 3D printing has even made its way into the textile industry, allowing clothing and prototypes to be printed.
Hercules Strong 3D printed yacht steering parts. Details printed in 15 hours with a 0.5 mm nozzle and a layer height of 0.3 mm at a speed of 60 mm/s.
5. Greater customization
3D printed products are also highly customizable. Parts can be printed not only with light plastic, some next-generation models may also have a metal coating. As a result, objects are not only aesthetic, but also functional. In addition, they can acquire thermal and chemical resistance. The existing metallization method can also be used for plastic.
Functional parts printed on Hercules. Material ABS, nozzle diameter 0.5 mm, layer height 150 µm, filling 100%. The model consists of 3 parts: the body and 2 halves of the latch, after printing and processing, the parts were glued together with acetone.
The model consists of 3 parts: the body and 2 halves of the latch, after printing and processing, the parts were glued together with acetone.
6. Customer Accessibility
If some craftsmen set up small mechanical workshops, for example, in garages, then most of us cannot afford such a luxury. 3D printing allows you to bring a significant part of the manufacturing process directly into the home, made possible by the availability of user-grade 3D technology. While it turns out to be quite expensive for one-off projects, the price of 3D printers and consumables is dropping rapidly.
Technical wing caps in REC RUBBER or REC FLEX. The models are printed on a Prusa i3 Steel 3D printer.
7. High complexity
In most cases, when it comes to complex parts and elements, the manufacturing process imposes certain limitations. Techniques used in casting and finishing objects may not be subtle enough for sophisticated design details. 3D manufacturing processes make it possible to realize almost any design solution, regardless of its complexity, and in a reasonable time. This not only eliminates the extra assembly steps required by traditional methods, but also provides more freedom to create future-proof designs.
3D manufacturing processes make it possible to realize almost any design solution, regardless of its complexity, and in a reasonable time. This not only eliminates the extra assembly steps required by traditional methods, but also provides more freedom to create future-proof designs.
Zenit 3D printer print large parts from engine mockup
8. Less risk
While there are inherent risks associated with these new technologies, in terms of day-to-day business, 3D printing risks are significantly lower than with traditional manufacturing methods. Not only is 3D printing much cheaper when it comes to testing a new design or product, the printed prototypes themselves can stir up investor and customer interest and get them to decide whether to proceed with mass production of a product, whether it is worth the time and effort required.
Printing miniature model on Wanhao Duplicator i3 3D printer
9.
 Variety of materials
Variety of materials The materials used in today's 3D printers are much more diverse than most raw materials in traditional production methods. 3D printing also provides the ability to mix different substances, a luxury that is not always available with conventional methods. Although many 3D printer manufacturers offer their own, very limited set of sources, 3D printers can work not only with original materials, allowing you to simulate ceramics, metal, glass and more.
Wanhao D6 3D Printer PEGT, ABS-PC, PLA, SBS
The manufacturer not only needs to clearly understand what the customer wants, the manufacturer must also be able to explain what he himself can. Drawings, diagrams, diagrams are all good, of course, but there is nothing better than a real prototype that you can hold, look at and study. The fact that the materials are inexpensive, coupled with the short prototyping time on today's 3D printers, helps a lot during the prototyping phase, keeping all stakeholders connected.