3D printer object scanner
How to Choose the Best 3D Scanner to Use With Your 3D Printer
3D scanning has an important place at the beginning and end of 3D fabrication workflows. Engineers, product designers, and researchers use 3D scanners as a faster and more efficient way to start constructing digital models, whether by incorporating existing designs via reverse engineering, digitizing hand-sculpted clay designs, or referencing the exact shape of the human body.
After fabrication, 3D scanning can support quality control and help to verify the accuracy of a 3D printed part, or, after the part has been used, a scanner can reveal how it’s performed—a scan of a deformed part can show you where to reinforce the design in the next revision.
With such a wide range of product options from handheld 3D scanners to desktop 3D scanners, it can be difficult to choose the best 3D scanning system that’s right for your application and budget. In this post, we explore the most important factors to consider when purchasing a 3D scanner and showcase some of the key applications that are empowered by combining 3D scanning and 3D printing.
White Paper
3D scanning and 3D printing workflows can be applied to replication and restoration, reverse engineering, metrology, and more. Download our white paper to explore these applications and learn how to get started.
Download the White Paper
There are multiple scanning technologies currently on the market, all offering their own advantages and weaknesses.
Laser triangulation uses light projected onto the object to take up to millions of measurements (dots) per second. The light reflected from the dots back into the scanner’s sensor to help it capture the geometry of the object. These types of scanners are often the most accurate, and are great for highly detailed parts that have opaque surfaces.
Laser triangulation scanners do have limitations. For example, this technology is not used in most portable scanners because the laser dots need to project from a stable source, and the source has to be kept a close distance from the scanned object. Laser triangulation scanners don’t always work on transparent or shiny surfaces either. Typically, they require reflective markers to be applied onto the object, which need to be removed after use and can be an obstacle depending on the object being scanned.
Laser triangulation scanners don’t always work on transparent or shiny surfaces either. Typically, they require reflective markers to be applied onto the object, which need to be removed after use and can be an obstacle depending on the object being scanned.
Finally, the laser dots can be harmful to human eyes, so it is important to use extra safety precautions when scanning body parts with a laser triangulation system, or to check with your scanner manufacturer to make sure the device is eye-safe.
Structured light scanners (also known as white light scanners or blue light scanners) generally use a projector with two cameras at angles on either side. A pattern of light is projected and laid over the component being scanned, the cameras capture the ways in which the object deforms the light pattern, and then multiple images are integrated into a single 3D snapshot.
Structured light scanners are available in both stationary and portable format—the technology is the most commonly used process for handheld 3D scanners.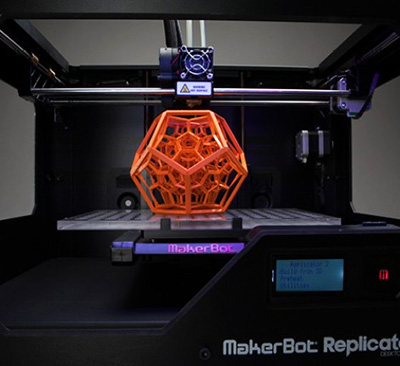 Structured light scanners are far more common in medical applications, since it is safe to use on both humans and animals and excels when an object is not perfectly still. Traditional white light scanners have been slower to scan than laser triangulation scanners.
Structured light scanners are far more common in medical applications, since it is safe to use on both humans and animals and excels when an object is not perfectly still. Traditional white light scanners have been slower to scan than laser triangulation scanners.
Structured light scanning is the most commonly used technology in handheld 3D scanners.
Depth-sensing cameras project a field of dots in infrared (IR) to sample a 3D scene. Depth-sensing cameras are simple to use and are the least expensive scanning option, but their accuracy and resolution are low, and fine details are sometimes lost. Large objects may be captured with depth-sensing cameras, but accuracy declines with increased distance from the subject and at steeper angles to the camera.
Photogrammetry means the act of deriving precise measurements from photographs. It involves taking a set of overlapping photos of an object, building, person, or environment, and converting them into a 3D model using a number of computer algorithms.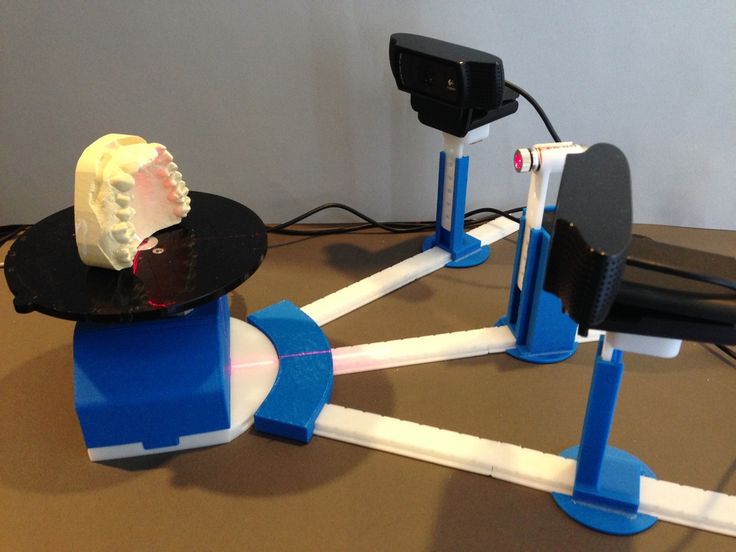 This is the most commonly used method when creating a 3D scan with a smartphone, since modern phone cameras are capable of capturing and combining a large numbers of photos. Photogrammetry should be considered the least expensive and least accurate method for creating 3D prints, and is not suitable for serious business applications.
This is the most commonly used method when creating a 3D scan with a smartphone, since modern phone cameras are capable of capturing and combining a large numbers of photos. Photogrammetry should be considered the least expensive and least accurate method for creating 3D prints, and is not suitable for serious business applications.
LiDAR (light detection and ranging) sensors can be found on some higher-end smartphones and tablets, such as the latest versions of the iPhone Pro and the iPad Pro. This has made the iPhone and iPad viable scanners for those with only occasional scanning needs, offering performance a step above devices that only have access to photogrammetry. Applications that generate 3D mesh files via your smartphone’s or tablet's camera should be seen as the floor for entry-level scanning; users should expect additional work in their CAD software to remove gaps in meshes and improve the 3D model for applications like sending it to a 3D printer. Smartphones use fewer light points when scanning objects, resulting in less detail than a true, stand-alone scanner. iPhones are good substitutes for scanners if you have significant CAD design ability or need to transfer basic models into a digital space.
iPhones are good substitutes for scanners if you have significant CAD design ability or need to transfer basic models into a digital space.
WEBINAR
Watch this webinar with Peel 3D to explore how to integrate 3D scanners into your 3D printing workflow to elevate your product development process.
Watch the Webinar Now
Scan accuracy varies considerably between scanner technologies, and higher accuracy generally comes at a higher cost. The required tolerances of your final part can be a helpful guide for determining your accuracy requirements for a 3D scanner.
| High Price, Highest Accuracy ($15,000 and more) | More Affordable, High Accuracy ($12,000 and under) | Low price, Low Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Zeiss T-Scan Hawk Scantech Simscan EviXscan Optima+ M Creaform HandyScan 307 Silver Series | peel 3d peel 1, peel 2 & peel 2-S FARO Freestyle 2 Polyga Compact S1 | iPhone Pro and iPad Pro Structure Sensor Matter and Form 3D Scanner V2 Revopoint POP |
With accuracy in the range of 0. 1 mm or better, laser and structured light scanners are a good fit for professional applications and alongside high-resolution 3D printers. Formlabs stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers (such as the Form 3+) produce parts at a similar accuracy, and with a similar printable area, to the scan volume of many desktop 3D scanners.
1 mm or better, laser and structured light scanners are a good fit for professional applications and alongside high-resolution 3D printers. Formlabs stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers (such as the Form 3+) produce parts at a similar accuracy, and with a similar printable area, to the scan volume of many desktop 3D scanners.
Besides the accuracy between measured points and their actual location, scanners also vary in terms of resolution, which is the distance between captured points at a given scan distance. This means that details on the scanned object that are smaller than the scanner’s resolution won’t be captured. For example, a highly accurate 3D scanner with a lower resolution might detect the general shape of jewelry on a statue, but not clearly show individual details on a ring or necklace. Depending on your project requirements, this may or may not be a dealbreaker.
An easy way to remember these metrics is: accuracy is the measurement error between the part and digital value. Resolution refers to the density of measurements.
Resolution refers to the density of measurements.
Accuracy can mean slightly different things depending on the manufacturer and 3D scanning technology. For example, the accuracy of handheld scanners depends on the distance to the subject and the quality of scan reconstruction, while desktop scanners have consistent accuracy within the constrained scan volume. If you are considering buying a 3D scanner for precise measurement, make sure to compare like to like.
In general, structured light scanning provides the best resolution and accuracy when compared to laser scanning. For some artistic use-cases for 3D scanning you may need a lot of detail, while overall accuracy is less important—especially if you don’t require your part to fit precisely with other parts in an assembly. In these cases, photogrammetry is an excellent low-cost option to explore.
Both depth-sensing cameras and photogrammetry are a good solution for scanning large objects in order to create 3D printed scale models and also offer enough accuracy for capturing the shape of the human body.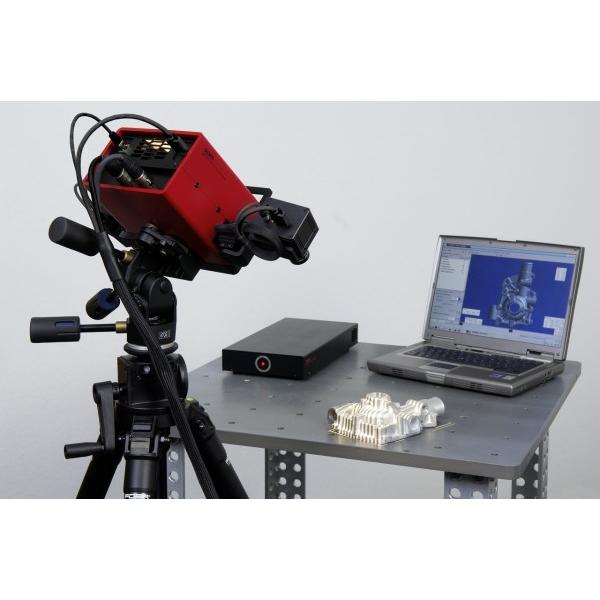
Several entry-level laser scanners are available using technology similar to higher-end systems. These scanners are a great way to start replicating small objects at 1:1 scale. As one would expect, the accuracy of entry-level laser 3D scanners is lower than a high-end scanner, but they can easily provide enough detail to replicate small decorative objects and figures where accuracy is not critical.
If you only have occasional 3D scanning needs, digitization services can scan your object, as well as perform CAD translation and accuracy inspection.
The area that a 3D scanner can capture varies significantly between scanners. Find a scanner that fits your size and resolution requirements without too much overhead, as cost typically increases with scan volume.
Handheld scanners can be manually moved around the object and have fewer size constraints than desktop models. Most inexpensive handheld scanners can capture objects from the size of a basketball to an entire room.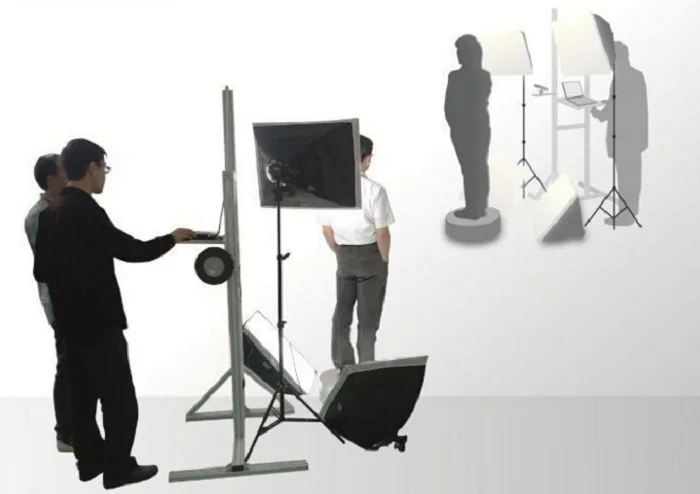 High-end handheld scanners have an even wider range, and fill the niche for all objects that require precise measurements, but cannot fit in a desktop scanner. Handheld scanners are also able to capture objects nearly instantaneously, which makes them well-suited for taking human measurements (where the subject is not perfectly still) for ergonomics and medical applications.
High-end handheld scanners have an even wider range, and fill the niche for all objects that require precise measurements, but cannot fit in a desktop scanner. Handheld scanners are also able to capture objects nearly instantaneously, which makes them well-suited for taking human measurements (where the subject is not perfectly still) for ergonomics and medical applications.
If the area of the model can’t be seen by the scanner, it will cause a gap in the model. You can automatically repair small missing sections with most scan software programs to create a 3D printable model. However, repaired holes are rarely accurate to the original object. For parts that demand close to perfect accuracy, auto-repair of gaps or holes will not be sufficient. Read our MeshMixer tutorial for advanced tips to edit and repair 3D files for 3D printing.
Many scanners use turntables to increase what the scanner can see. The sophistication of a scanner’s turntable affects how easily and completely the object is captured: some scanners have the ability to move the object around multiple axes, imaging the object from more angles.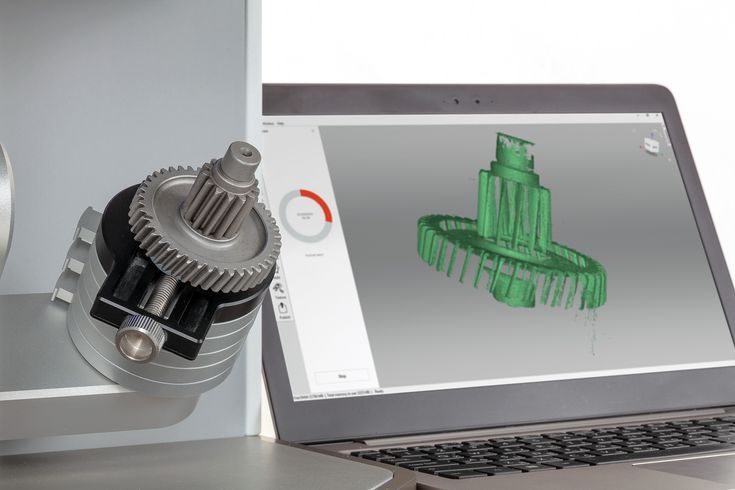 This feature is important when reverse engineering plastic parts with deep recesses and ribs, which are impossible to capture from a single angle.
This feature is important when reverse engineering plastic parts with deep recesses and ribs, which are impossible to capture from a single angle.
Scanners may rotate the object to capture occluded areas. Red regions are occluded and will be missing in the scan. Areas with deep relief are difficult for a single axis turntable to fully capture due to occlusion.
Cost concerns are straightforward; how much you are willing to spend on a scanner will reflect your business’s budget and how often the scanner is going to be used. Higher cost scanners will be able to capture small objects and create highly-detailed meshes that don’t require significant touch-ups in CAD software. Handheld scanners are also often on the higher end of the price range, due to their portable nature. The low-cost scanning market offers a wide range of options, but you have to know what to look for.
Use this flowchart to determine what scanner you need based on accuracy, scan volume, and budget.
Download the high-resolution version of this infographic here.
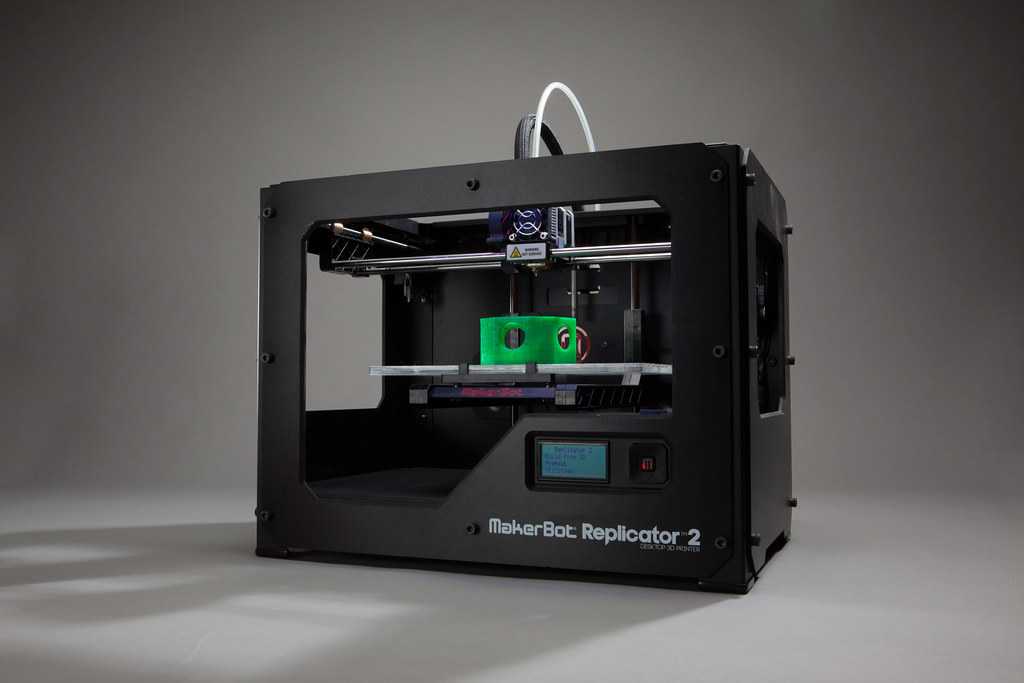
A 3D scanner expands the capabilities of a 3D printer, allowing you to replicate the shape of almost any object. Together, the two technologies create a powerful, digital workflow that can simplify and sophisticate processes in a range of industries.
The output from a 3D scanner is a mesh of triangles representing the surface of an object at a real-world scale. In some cases, the scan can be used directly to replicate objects without any CAD work. A hybrid workflow can also be powerful, where solid CAD models are combined with scanned 3D models. For example, customized ergonomics capture a physical imprint of a part of the human body, and integrate them with a mechanical design.
3D scanners are also valuable tools for measuring the accuracy of manufactured objects. Many factors affect 3D print accuracy, and metrology-grade 3D scanners provide a clear picture of how a material performs for demanding applications.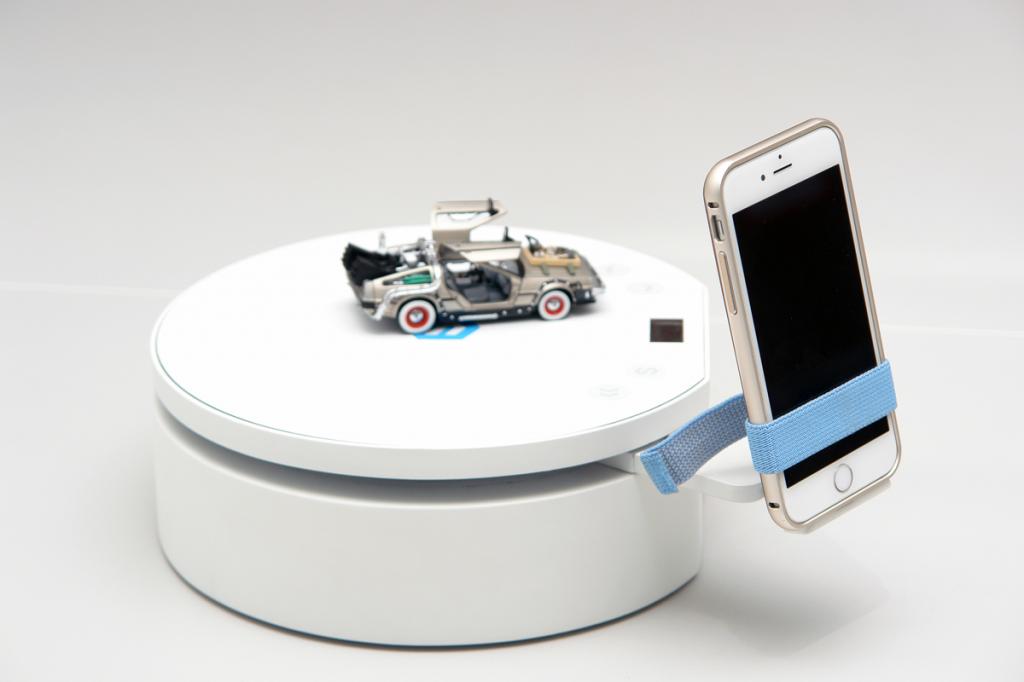
A variety of powerful workflows are enabled by combining a 3D printer and a 3D scanner:
- Reverse engineering to create replacement parts, products with custom ergonomics, and more.
- Replication and restoration of parts, especially in art and jewelry.
- Consumer audio for creating custom earpieces.
- Dental and medical applications, and how 3D scanning is enabling patient-specific workflows.
- Metrology to validate and measure the accuracy of manufactured objects.
Webinar
Watch this webinar for a detailed look at how to start using 3D scanning to improve part design and production when paired with reverse engineering CAD and 3D printing.
Watch the Webinar Now
3D scanners and 3D printers are essential parts of digital workflows across industries. Download our white paper or watch our webinar to get a detailed look into how to start using 3D scanning to improve part design and production and learn how to pair 3D printing and 3D scanning to empower a variety of workflows in engineering, product design, and more.
Learn more about the 3D printer side of the equation: get to know stereolithography (SLA) and selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing technologies and see Formlabs advanced 3D printing materials for yourself with a free sample 3D printed part.
Explore Formlabs 3D PrintersRequest a Free Sample Part
3D Scanner: What Are the Best Available Low-Cost Solutions ?
Published on July 16, 2021 by Carlota V.
3D scanning is often used in the additive manufacturing (AM) sector to design a 3D model more easily than via modeling software. It captures data that is then transformed into a 3D model which can then be 3D printed. 3D scanners are based on two main technologies – laser triangulation and structured light – which will allow to obtain more or less precise details depending on the chosen device. Several affordable solutions, compared to professional scanners which are much more expensive, are available today to allow many users to bring their projects to life: whether you are a maker, a teacher or an industry leader, on of these low cost 3D scanners is bound to suit your needs! Easy to handle and transport, we have chosen some 3D scanners under $8,000 (€7,000), sorted by increasing price.
3D Scanner 2.0 from XYZprinting
Taiwanese manufacturer, XYZprinting, currently offers 5 scanners, though today we will focus on one of their more low-cost 3D scanners, the portable and high-resolution 3D Scanner 2.0. With a wider scanning range than its younger sibling the 1.0 A, the scanner can scan objects that are 5 x 5 x 5 ~ 100 x 100 x 200 cm using an Intel® RealSense™ Camera. The scan resolution is also superior to the 1.0A, between 0.2 and 1.5 mm with an operating range ranging from 25 to 60 cm. The manufacturer also provides XYZScan Handy, a scanning and post-editing software to edit your models after scanning. The product is lightweight measuring 41 x 157 x 61 mm with a weight of 238 g. It is available from €199.
Structure Sensor from Occipital
The Structure Sensor solution adds precise 3D vision to your mobile device, enabling 3D scanning among other features. The only equipment you will need for this 3D scanner to work is an iPad, then once you have downloaded the app Skanect Pro, it will work instantly.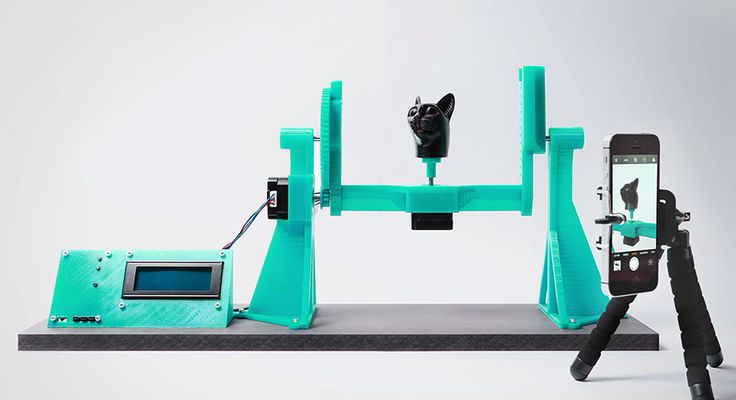
The new version of this device is smaller than the last, 109mm x 18mm x 24mm, and weighs about 65 g. It is recommended to use it on a 0.3 m to 5m scanning range. Some other features on this device include indoor mapping and virtual reality gaming! The Structure Sensor retails for $527.
POP 3D Scanner from Revopoint
The Revopoint POP is unique among 3D scanners as it has the distinction of being part of the highest crowdfunded campaign for a 3D scanner in Kickstarter, raising more than $2.28 million USD. It was developed by Revopoint, a company founded in 2014 by a group of young doctors and researchers from MIT, Kent University and other higher education institutions when they decided to focus on developing easy-to-use and cost-effective 3D scanners. It is safe to say that they certainly succeeded with their POP 3D scanner.
A binocular structured light 3D scanner that uses infrared as its light source, the Revopoint POP is a full-color scanner with an accuracy of up to 0. 3mm, texture scan and an 8Fps scanning speed. It has a number of interesting features, including the fact that it is easy to use outdoors because of it’s portable and can be powered by a power bank. With a cost of the scanner of only $549 in USA and about $599 in Europe, it is one of the most affordable options on our list, all while still being an effective, precise, high-resolution scanner. Not to mention, it can be used by a variety of users, as it supports four OS platforms – Windows, Android, Mac and iOS.
3mm, texture scan and an 8Fps scanning speed. It has a number of interesting features, including the fact that it is easy to use outdoors because of it’s portable and can be powered by a power bank. With a cost of the scanner of only $549 in USA and about $599 in Europe, it is one of the most affordable options on our list, all while still being an effective, precise, high-resolution scanner. Not to mention, it can be used by a variety of users, as it supports four OS platforms – Windows, Android, Mac and iOS.
Creality CR-Scan 01
Known for its affordable desktop 3D printers, manufacturer Creality has also developed a low-cost 3D scanner, the CR-Scan 01. Weighing only 1.91 kilos, this portable scanner is easy to handle and offers a scanning area of 536 x 378 mm. You will be able to scan your objects with an accuracy of up to 0.1 mm and export them in stl or obj format. Several scanning modes are offered, either manual or on a turntable. It is currently available from 589 €.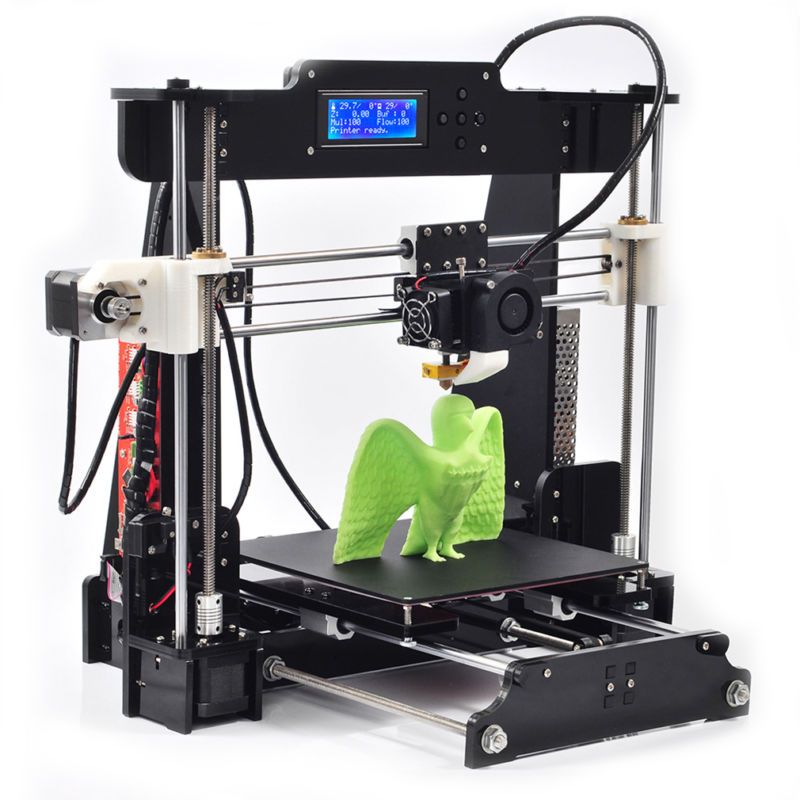
SOL 3D Scanner from Scan Dimension
This scanner was developed by Scan Dimension, based in Denmark, and is essentially a hybrid solution. It uses a combination of laser triangulation and white light technology to 3D scan real-life objects. The SOL 3D scanner can provide a resolution of up to 0.1 mm. The 3D scanning process is automated and you can choose between a near and far scanning mode.
The SOL 3D scanner also includes software to simplify your entire workflow. In a few steps you will be sending your 3D model to your 3D printer. This is a solution meant for makers, hobbyists, educators and entrepreneurs who may not have the most experience with 3D scanning devices but still want to achieve great results. The SOL 3D scanner retails for $699.
V2 from Matter & Form
The Matter and Form 3D Scanner V2 is a desktop 3D scanning solution manufactured by Matter & Form, a company founded in 2013. This company has made it its mission to develop and distribute affordable, high-resolution 3D scanners. With the V2, it has achieved that mission: the 3D scanner is available from $750 and is capable of producing high-quality scans with an accuracy of up to 0.1 mm. It weighs 1.71 kilograms (3.77 lbs) and has a height of 35.5 cm (13.5 in) and a width of 21 cm (8.25 in). The slim and foldable design allows the device to fit on small desks. The V2 allows scanning of objects with a maximum height of 25 cm (9.8 in) and a diameter of 18 cm (7.0 in). Windows and Mac scan files are supported, with multiple export options for 3D printing as well.
With the V2, it has achieved that mission: the 3D scanner is available from $750 and is capable of producing high-quality scans with an accuracy of up to 0.1 mm. It weighs 1.71 kilograms (3.77 lbs) and has a height of 35.5 cm (13.5 in) and a width of 21 cm (8.25 in). The slim and foldable design allows the device to fit on small desks. The V2 allows scanning of objects with a maximum height of 25 cm (9.8 in) and a diameter of 18 cm (7.0 in). Windows and Mac scan files are supported, with multiple export options for 3D printing as well.
RangeVision NEO
The NEO 3D scanner from the manufacturer RangeVision is an entry-level device with two 2-megapixel cameras, which works using Structured Light Scanning (SLS) technology. With an automatic scan mode, the scanner is suitable for all those who have little experience in digitizing objects. The SLS-3D scanner can capture objects from 30mm to 1200mm with a precision of 0.05mm, with 3D scans created using RangeVision software. Also included is a turntable and tripod, which make scanning easier for the user. According to the manufacturer, the NEO’s scans are suitable for reverse engineering, 3D modeling, historic preservation and, of course, 3D printing. The RangeVision NEO is available from around €2,190, making it one of the few low cost desktop 3D scanners available.
Also included is a turntable and tripod, which make scanning easier for the user. According to the manufacturer, the NEO’s scans are suitable for reverse engineering, 3D modeling, historic preservation and, of course, 3D printing. The RangeVision NEO is available from around €2,190, making it one of the few low cost desktop 3D scanners available.
Calibry, the low-cost 3D scanner, from Thor3D
Thor3D is a Russian manufacturer that is behind the Calibry portable 3D scanner. Based on structured light technology, it integrates a touch screen so that the user can follow the points it captures in real time. It offers accuracy down to 0.1 mm and is capable of scanning objects from 30 cm to 10 meters long. Black and glossy surfaces can be easily scanned and exported in stl, obj, ply or WRML formats. Finally, the Calibry is fast and convenient, capable of scanning up to 3 million points per second and weighing only 900 grams. It is available from 4,990 euros.
EINSCAN H from Shining 3D
The EinScan H is one of the most advanced versions of portable 3D scanners developed by the Chinese manufacturer Shining3D. Based on the hybrid structure light technology of LED and invisible infrared light, the EinScan H is able to perform human face scans more comfortably and without emitting strong light. It also incorporates a full-color camera and a large field of view for a truly impressive final quality of the models, ready for processing in just a few minutes. Its high resolution of 0.25 mm and data accuracy down to 0.05 mm make this a good choice in the market considering the price/performance ratio. In addition, it stands out for its light weight of almost 700g and intuitive user interface. The base price of this model is $5000 and you can get more information on the manufacturer’s website.
Eva Lite from Artec 3D
Artec 3D, based in Luxembourg, offers the Eva Lite as its cheapest option for 3D scanning. This professional scanner is specialized in the digitization of complex geometries, such as the human body, and is therefore increasingly used in the medical field. It works on the basis of structured light technology and, although it does not have the ability to capture colours and textures like most scanners of the brand, it has an accuracy of 0.5 mm.
This 3D scanner works with the software package Artec Studio. Artec Studio is a powerful tool for an optimized 3D scanning process. This software is able to perform, assemble and repair 3D scans. It is currently available at a price of $9,800. You can find more information HERE.
Any other low cost 3D printing scanners you think should be on this list? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages! And remember to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter, to get all the latest news in 3D printing send straight to your inbox! For more 3Dnatives articles about 3D scanners, click HERE.
technologies, methods and principles of operation of 3D scanners
Main / Blog / Useful / Principles of operation of a 3D scanner. Types of scanners, technologies and scanning methods
04/16/2021
Content
-
- What is 3D scan and for which it is used by
- How 3D scanner
- 3D scan technologies
- 3D scan methods
- Contact 3D scanners
- Non-contact 3D scanners
- Types of 3D scanners by usage
- Advantages and disadvantages of 3D scanners
- Things to consider when choosing a 3D scanner
- Applications
Currently, few people are not familiar with such a concept as 3D printing. Many companies are using modern 3D printers with might and main, recreating layouts of various shapes and sizes with their help. There are also those that recreate whole objects - not only small ones (for example, phone cases, souvenirs, sneakers), but also large ones (houses, engine parts, etc.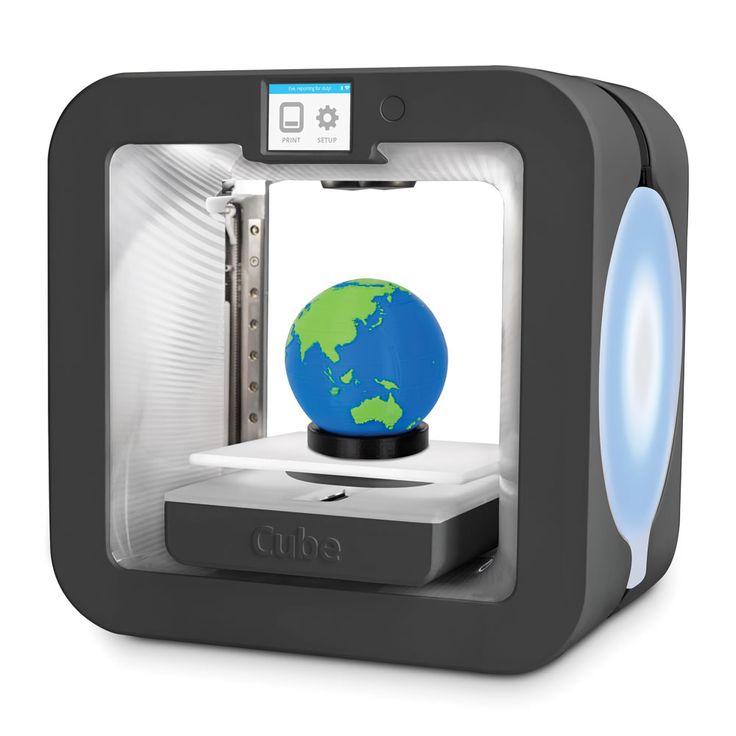 ). But all this would not be possible without 3D scanners. It is they who allow you to accurately copy almost anything - from huge buildings and structures to humans, animals, small objects and much more.
). But all this would not be possible without 3D scanners. It is they who allow you to accurately copy almost anything - from huge buildings and structures to humans, animals, small objects and much more.
What is 3D scanning and what is it used for
Three-dimensional scanning is a technology that appeared in the 60s of the 20th century. It was created in order to transfer the physical parameters of the object into a digital format in the form of a three-dimensional model. The need for this naturally arose when people around the world increasingly began to use computers both in everyday life and in production.
The first samples of 3D scanners were quite simple and did not have wide functionality. Gradually, they became more complex and improved, making it possible to achieve an ever clearer image of the object. This has become especially relevant with the advent of lasers.
3D scanners allow you to transfer object data into digital format
3D scanning has opened up new opportunities in various areas of human activity - from the automotive industry and the military industry to design, medicine and cinema.
How a 3D scanner works
A 3D scanner is a device that examines an object by digitizing it using sensors and using the information received to create a three-dimensional model. In fact, a 3D scanner creates a digital copy of a physical object of any configuration and complexity. In this, it fundamentally differs from its predecessors - conventional scanners that can only read information from documents and photos.
The scanning process itself can take place in different ways - depending on the type of 3D device and the technology used, as well as on what object you want to process with it - moving or static.
3D Scanning Technologies
There are 2 main types of 3D scanners - laser and optical. Their fundamental difference lies in how and with the help of what the “removal” of data takes place. Let's take a closer look at both.
Laser 3D scanning, as the name implies, uses a laser and can be carried out both at short and long distances from the object.
Laser scanner
For the most part, 3D laser scanners work on the principle of triangulation, when the camera finds a beam on the surface of an object and measures the distance to it, after which a cloud of points is created, each of which has its own coordinates in space, and a 3D model is built. Their "advantages" are affordable price and ease of use combined with high scanning accuracy. Of the "minuses" - there are restrictions on the remoteness and size of the object.
Another type of laser scanner works by measuring the response time of a beam from the surface of an object - the so-called laser range finder. They are widely used where it is necessary to create 3D models of various buildings and structures. It is not advisable to use them at short distances, since in such cases the response time is very short and the accuracy of the data is reduced. Otherwise, this type of scanner is characterized by high scanning speed and the ability to read all the details.
The disadvantage of laser scanners is the impossibility of their use on moving objects. Then optical 3D scanners come to the rescue, which shoot with one or more cameras from different angles an object illuminated by a special projector. Based on the received image, a three-dimensional image is built.
Optical scanner
A "contraindication" for the use of this technology are reflective and translucent surfaces - shiny, mirror or transparent. But when scanning a person, they are simply irreplaceable.
3D scanning methods
Any object can be digitized both by contact and non-contact methods. In the first case, active interaction with the subject is necessary, in the second, accordingly, no. Both of these methods have their advantages and disadvantages.
Contact 3D scanners
They have a mechanical probe with a special sensor that measures parameters and transmits the collected information to the device.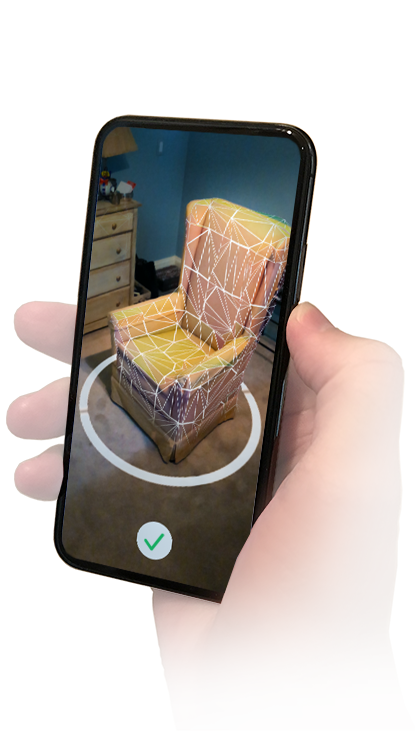 To do this, the object under study is placed on a special surface and fixed (if necessary). Such tight physical contact makes it possible to determine and then build a 3D image as accurately as possible, however, there is a small risk of damage to the prototype.
To do this, the object under study is placed on a special surface and fixed (if necessary). Such tight physical contact makes it possible to determine and then build a 3D image as accurately as possible, however, there is a small risk of damage to the prototype.
Non-contact 3D scanners
This category includes all devices capable of scanning at a distance. This is especially true for objects located in hard-to-reach places.
Non-contact 3D scanner
A stream of radiation (it can be ultrasound, light, X-rays or a laser) is directed to the object and reflected from it, it is recognized by the 3D scanner. They are similar in principle to a video camera and may require the use of additional devices for better lighting.
Non-contact 3D scanners come in 2 types:
-
Active - work with a laser beam or structured light directed at an object, which, when reflected, give information about the location of the object in the form of coordinates.

-
Passive - use time-of-flight rangefinders that read the time and distance that the laser beam travels to the object, and so - for each point in space, which ultimately allows you to accurately recreate its three-dimensional image.
Desktop 3D scanners are very popular and widespread, since they are mostly simple and safe to use, do not require any special technical skills and are quite cheap. The EinScan-SE 3D scanner is one such example. It can be used both at home and in the office. It has access to the API of many popular 3D printers, which makes it possible to immediately print the created three-dimensional model.
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Thor3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Shining 3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Shining 3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Range Vision |
Types of 3D scanners according to the principle of use
There is also a variety of species here.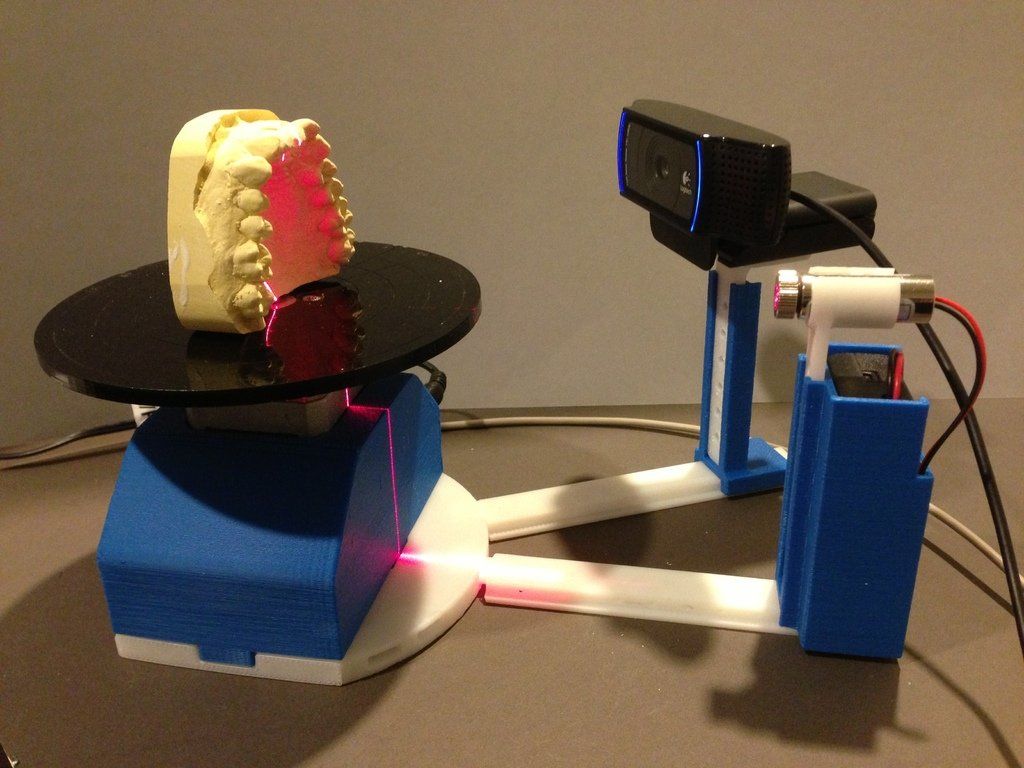 Let's highlight the main ones:
Let's highlight the main ones:
Manual: The are handy and simple models that are easy to use as they are quite compact and do not require special skills. True, their technical capabilities may be somewhat limited.
-
Portable: are mainly used for field work, they are convenient to take with you.
-
Desktop: have extended functionality and are used to create high-quality 3D models. Most often used in offices.
-
Stationary: are used, as a rule, in production, various enterprises, as they can scan a large number of objects of the same type at once. Mounted on special turntables.
Handheld 3D Scanner Calibry
Such a choice of products allows you to select the right model for a specific task. In some cases, scanners independently measure objects, in others - with the help of a person who sequentially moves the device until all the necessary information is collected.
Such options for hand-held 3D scanners as Calibry are in high demand among buyers. Despite the apparent simplicity of execution, it has a high resolution and scanning accuracy, due to which it is able to digitize objects with a length of 0.2 to 10 meters. Objects that have a non-standard surface - dark or shiny, with a large number of corners and small details will not become a problem either. Among other things, its undoubted advantage is its low weight, only 900 grams.
Advantages and disadvantages of 3D scanners
Surely, many of the potential buyers are wondering: do you really need a 3D scanner to invest a lot of money in it? What can this acquisition give and will such an investment be justified?
3D scanning has become an integral part of any modern manufacturing process
In order to understand how much you need this equipment, we will list its advantages and disadvantages.
Benefits:
-
They make it possible to scan objects located at a remote distance and in places inaccessible to the presence.

-
They have the ability to "read" not only colors and images, but also to convey the texture of the surface.
-
Significantly speed up the process of "taking" data from any object, even a very complex one with a large number of planes.
-
A variety of models allows you to choose the most convenient version of the scanner, including manual or portable, which can be easily taken with you.
Weaknesses:
-
Some scanners are unable to recognize transparent or black and white objects. In this case, their preliminary preparation (treatment with a special composition) is required.
-
I do not always display complex objects correctly, with a large number of inserts and partitions.
-
To obtain a high-quality result, they require skills and abilities to work with certain computer programs for creating 3D models.
-
If the rules of operation are constantly violated, it may become necessary for expensive repairs to the equipment.

If you need high-precision and high-quality three-dimensional copies of objects, then you cannot do without a 3D scanner. It makes it possible to work in almost any conditions - indoors and outdoors, and with any objects by type and size. It is not surprising that now these devices are in great demand, which gives rise to the annual release of a large number of models, from which you can always choose the one that suits you in terms of quality and price.
Things to consider when choosing a 3D scanner
The computer equipment market offers a huge amount of all kinds of equipment, including devices for three-dimensional scanning. Navigating that variety is sometimes not at all easy: some buyers are only concerned about the cost, others are interested in the number of options (sometimes completely useless), but the most far-sighted look at the ratio of the first and second.
Choosing the right 3D scanner is a responsible matter
It is not always easy to take into account all the technical points that can significantly affect what result will be ultimately achieved.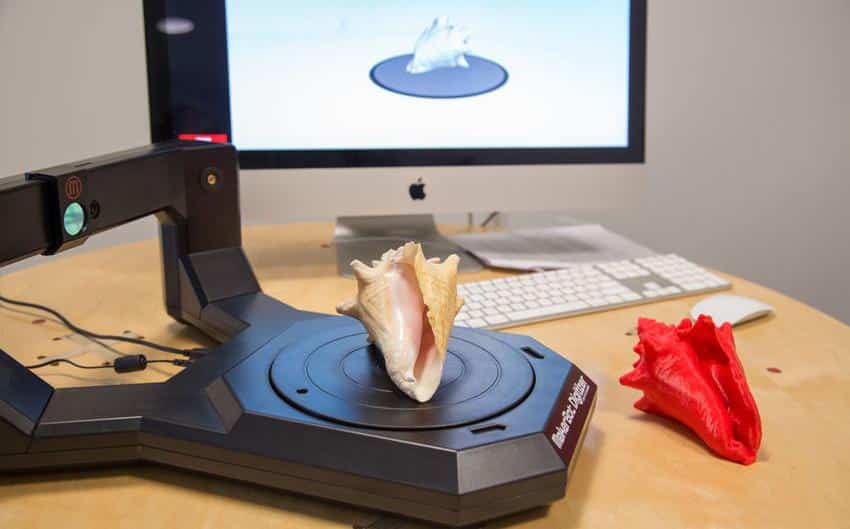 We will tell you what you should pay attention to if you are thinking about buying a 3D scanner.
We will tell you what you should pay attention to if you are thinking about buying a 3D scanner.
Be guided by the following parameters:
-
How high is the accuracy of the 3D scanner. This is one of the most important features. It needs to be targeted first.
-
Resolution also plays an important role. It follows from the first, since the accuracy of measurements and the quality of copying depend on the resolution.
-
In what range the device operates, how close / far it can be from the scanned object.
-
The scanning field is the parameters of that object, thing that it is able to process in 1 session.
-
Does the scanner capture various atypical types of surfaces with complex terrain - channels, partitions, holes, etc.).
-
Portability, mobility of the device - how easy it can be moved if desired, taken with you, its size.
-
The time it takes to prepare for work, as well as the duration of the digitization process itself.

-
The range of possibilities in terms of copying: are there any restrictions on shapes, textures, material, as well as operating conditions - temperature, light, etc.
Of course, the better the quality of the 3D scanner, the more expensive it is. However, you should focus primarily on the tasks that you face, and only then take into account everything else.
Applications
Three-dimensional scanners are in demand in many areas of human life. They are irreplaceable both in the industry, and for household needs. The range of their application is so wide that it is possible to list for a very long time. It's easier to say where they are not needed.
The most common areas of use are, of course, medicine, industry, architecture, construction, film industry and design.
For example, in dentistry, these devices allow you to create ultra-precise three-dimensional models of dentures. One type of such a scanner is Shining 3D's AutoScan DS-EX PRO, which does a great job with a variety of tasks while being quite affordable and reliable.
Medical 3D Scanner
In engineering, such technologies are also indispensable. Digital building prototypes are now much easier and faster to obtain than in the past, when it required multiple manual measurements and then entered into a database. Any physical object can now be recreated in three-dimensional form, moreover, in the shortest possible time and with a minimum error.
In cinemas, we can see with our own eyes "revived" fantastic characters, which were created using motion capture technology, which made them as realistic and impressive as possible. This would not have been possible without 3D scanners.
A few decades ago, it was even difficult to imagine all the things that we use all the time today. And in many ways this has become achievable thanks to three-dimensional digitization. This approach provides huge advantages in work (especially for technical specialists - engineers, designers, designers), however, in order to use them to the maximum, it is also necessary to understand computer programs for 3D scanning.
We will talk more about this topic in one of our next articles. And if you want to know more about it, stay tuned.
#Useful
Expert in the field of additive and subtractive technologies, 3D equipment and CNC machines with over 10 years of experience.
Share
all materials
Do you have any questions?
Our experts will help you with the choice of 3D equipment or accessories, consult on any questions.
3D scanning of objects - accuracy and quality of 3D models
3D scanning of objects
One of the components of 3D technologies is the 3D scanning technique, which allows you to quickly and easily obtain a digital model of the desired product. In short, 3D object scanning is the process of transforming the physical form of a real object into a digital form. This preserves the texture and even the color of the original sample. Thus, a 3D model of the required product can be obtained without any extra effort.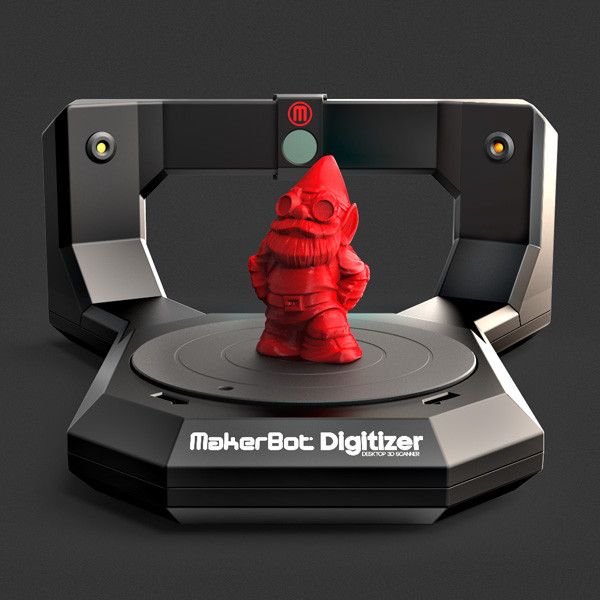 3D scanning of objects helps to prepare the necessary model for 3D printing and in some cases can play a decisive role in building a digital product.
3D scanning of objects helps to prepare the necessary model for 3D printing and in some cases can play a decisive role in building a digital product.
The key device in the process of 3D scanning is a 3D scanner - a device that reads the physical parameters of objects and creates a 3D model based on them.
3D scanning of objects can be useful in the design of any complex elements, 3D modeling of which manually is extremely laborious. In particular, 3D scanning is useful for modeling various fixtures, components, main and spare parts. Often it is used in the absence of drawings and other documentation for the product, as well as when it is necessary to convert figured surfaces into a digital form, including art forms and casts.
3D scanning process
The 3D scanning process generally resembles a human three-dimensional vision system. The process of obtaining data with a 3D scanner resembles the formation of a three-dimensional image seen in the human brain.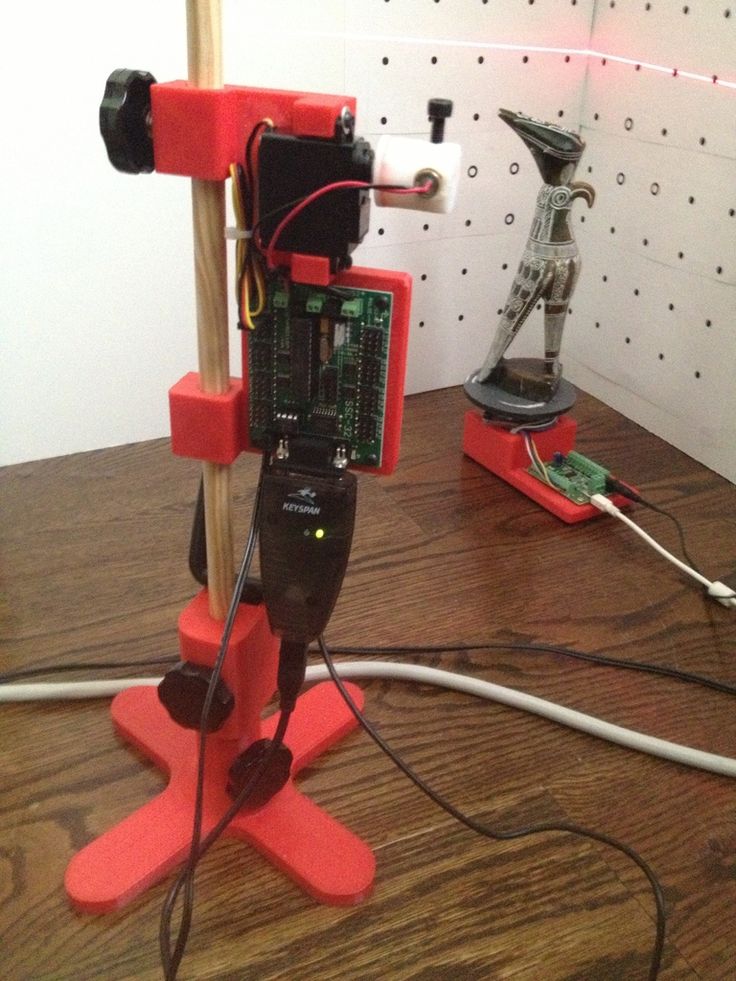 To do this, the 3D scanner compares two images that are offset from each other. The required accuracy of building a 3D model is achieved through the use of additional technological methods, for example, a periodic flash or laser illumination.
To do this, the 3D scanner compares two images that are offset from each other. The required accuracy of building a 3D model is achieved through the use of additional technological methods, for example, a periodic flash or laser illumination.
As for scanning accuracy, it depends both on the specific device and on the characteristics of the original product. It is possible to carry out 3D scanning of objects from 1 cm (with all the details), the maximum dimensions are not limited. To achieve the best detail, upon completion of the 3D scanning process, the 3D model is subjected to additional refinement by a specialist. Thus, thanks to 3D scanning of objects, digital models are almost flawless. Error for 3D scanning of objects with a surface area of 100 cm 2 is 1 mm and can be eliminated with subsequent refinement. 3D scanning of large objects can be implemented by batch processing of object photos from all sides.
Other questions and answers about 3D printers and 3D printing:
- Basics What is 3D printing?
- Basics What is a 3D model?
3D scanning methods
For a better understanding of the technology, it would not hurt to list the existing 3D scanning methods. There are two of them: contact and non-contact. The first one requires direct contact of the 3D scanner with the object. The non-contact method divides peripherals into two types:
There are two of them: contact and non-contact. The first one requires direct contact of the 3D scanner with the object. The non-contact method divides peripherals into two types:
- Active 3D scanners that emit a beam of directed waves onto an object and record their reflection. Possible types of radiation include x-rays, ultrasound, and light;
- Passive 3D scanners that capture ambient radiation reflected from an object, most often light.
All 3D scanning methods have their advantages and disadvantages, which affect the cost of 3D scanners, the speed and accuracy of scanning, as well as the range of objects available for scanning. When buying your own 3D scanner, it is recommended to study this issue in more detail, but it is better to get high-quality advice from professionals. The 3DDevice team is ready to help you with this and recommend the best 3D scanner model.
3D scanning and 3D printing
3D scanning and 3D printing complement each other, since the scanned 3D models are most often used for subsequent reproduction on a 3D printer.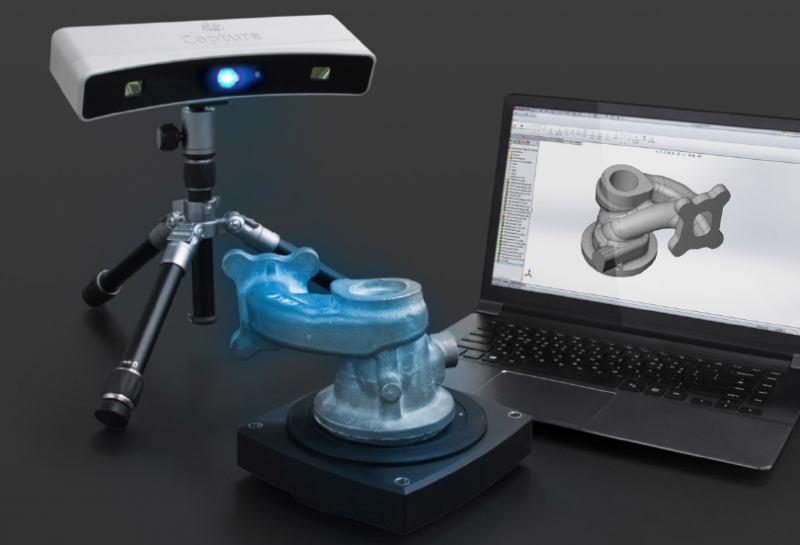 At the moment, 3D scanning is used for a variety of purposes and industries. Using a 3D scanner, 3D models of real people are created, which can then be reproduced through full-color 3D plaster printing. A more promising use of 3D scanning is in medicine, where it is used to create ultra-precise surgical models and implants. You can read more about our contribution to this branch of medicine here. Also interesting is the direction of using technology in the production of individual footwear and clothing.
At the moment, 3D scanning is used for a variety of purposes and industries. Using a 3D scanner, 3D models of real people are created, which can then be reproduced through full-color 3D plaster printing. A more promising use of 3D scanning is in medicine, where it is used to create ultra-precise surgical models and implants. You can read more about our contribution to this branch of medicine here. Also interesting is the direction of using technology in the production of individual footwear and clothing.
In general, the possibilities of using 3D scanning of objects are quite enough. We hope we were able to explain in detail the essence of the technique. If you have additional questions that we have not covered, write to us by e-mail and we, if necessary, will add your questions! Best regards, 3DDevice team.
Our company also separately provides a 3D scanning service for objects of any size. For all questions, please contact us in any way convenient for you. Contacts are listed here.












