3D print format
The different file formats for 3D printing・Cults
With the evolution of digital technology, 3D printing has become much more accessible today. Individuals and professionals can have their own equipment and make various printing models. All that is needed is to master the essential notions, particularly with regard to the adapted file formats. Indeed, depending on the field and for historical or practical reasons, certain file formats are preferred for 3D printing. We present here the most common formats for 3D printing, as well as their main characteristics.
STL is the acronym for "Stereolithography", one of the oldest 3D printing file formats. Developed in the late 1980s, this type of format is still widely used today. It describes the surface geometry of a 3D object without representing color, texture or other attributes. The STL format has the extension ".STL". These files are generated by a computer-aided design (CAD) program. To edit and repair your STL files, you can use software such as FreeCAD, Blender, MeshLab, MeshMixer, SketchUp, SculptGL and 3DSlash.
The STL file will simplify a 3D surface as a "tiling", a series of small triangles whose number will increase when it comes to representing and recreating curved surfaces as well as possible. When a large number of triangles must be used, the size of the file in STL format of a 3D model is quickly inflated.
The OBJ file format is also very popular in the 3D printing industry. Its extension is ".OBJ". It has the advantage of also encoding color and texture information, saved in a separate file with the extension ".MTL". The OBJ format files give the possibility to use non-triangular faces, with the adjacency of one face to the other. They can be opened with software such as Autodesk Maya 2013, Blender and MeshLab.
Developed in the 90's, 3DS is a file format that stores only the most basic information about geometry, appearance, scenes and animations. It allows to store properties such as color, material, texture, transmissivity, etc. With its ".3DS" extension, this 3D printing file format also has the advantage of being read by most of the existing software on the market such as 3dsMax, ABViewer, Blender, MeshLab, messiahStudio, Rain Swift 3D, SketchUp, TurboCAD, etc.
The SLDPRT file or its extension .SLDPRT is a 3D printing image format used by SolidWorks CAD software. It contains a 3D object or "part" that can be combined with other parts in a single ".SLDASM" assembly file. SLDPRT files are usually opened with SolidWorks software. However, they can be viewed using SolidWorks eDrawings Viewer, Autodesk Fusion 360, Adobe Acrobat 3D, Acrobat Pro 9 or later.
The SCAD format (.SCAD extension) is generated by OpenSCAD software, a free modeling program used for various 2D and 3D designs. The SCAD file can be used to design 3D objects with a specification of the object geometry and positioning information. It can only be opened with OpenSCAD.
The .BLEND format is the extension used by 3D animations and projects that have been developed with the 3D modeling tool Blender. This type of file has the capacity to contain multiple scenes as well as all the elements of a project such as objects, textures, 3D mesh and real-time interaction data, sounds, lighting data, animation keyframes, mapping layout and interface parameters. Note that only Blender software can handle this 3D file format.
Note that only Blender software can handle this 3D file format.
The 3MF file (.3MF extension) is used by various design programs to save 3D models for printing. This format includes the model, material and property data compressed with ZIP compression. 3MF files also provide storage for a print ticket, a thumbnail image and one or more digital signatures. They can be opened by programs such as Microsoft 3D Builder, Microsoft Paint 3D, Dassault Systemes SolidWorks, Dassault Systemes CATIA, McNeel Rhino, PTC Creo and Ultimaker Cura.
The file with the .GCODE extension contains the commands to define how a 3D printer should print. It stores instructions such as print speed, set temperature, and where the items to be printed should move. This 3D file format is created with cutting programs like Simplify3D and Slic3r. The reading can be done with Simplify3D, but also Blaze3D, GCode Viewer and NC Viewer.
The .SKP file is the format of the 3D model created by the SketchUp software. It takes into account wireframes, textures, shades and edge effects. This type of file is also used to store components that will be inserted into your document. Obviously, it can be opened by SketchUp, but also with programs such as IMSI TurboCAD Pro or Deluxe, Okino Computer Graphics PolyTrans, ACCA Edificius and Trimble 3D Warehouse.
It takes into account wireframes, textures, shades and edge effects. This type of file is also used to store components that will be inserted into your document. Obviously, it can be opened by SketchUp, but also with programs such as IMSI TurboCAD Pro or Deluxe, Okino Computer Graphics PolyTrans, ACCA Edificius and Trimble 3D Warehouse.
FBX is a 3D printing file format popular in the film and video game industry. Developed by Kaydara and acquired by AutoDesk, it supports geometry and appearance properties such as color and texture, but also skeletal animations and morphs. AutoDesk will use an FBX file with the extension ".FBX" as the exchange format for its portfolio of software such as AutoCAD, Fusion 360, Maya, 3DS Max, etc.
A .RAR file is an archive that contains one or more compressed files. The compression ratio of this format is greater than the classic ZIP compression. It is used to compress files in order to reduce their size for easier transport and storage. You can extract files from a RAR archive with different decompression programs such as RARLAB WinRAR, Corel WinZip or B1 Free Archiver.
You can extract files from a RAR archive with different decompression programs such as RARLAB WinRAR, Corel WinZip or B1 Free Archiver.
Files with the .DWG extension are databases of 2D or 3D models created with AutoCAD. They consist of vector image information and metadata that describes the contents of the file. Many utilities are available to open this file format, including: Autodesk Auto CAD, Autodesk Inventor, Autodesk Design, Autodesk DWG, AutoDWG DWGSee, CADSoftTools ABViewer, Canvas X, Adobe Illustrator, Bricsys Bricscad, etc.
Used by 3D object editing programs such as Adobe Photoshop and Autodesk Maya, the .MTL format is used to store material parameters. This file is stored with another file in .OBJ format, and is used to describe how textures should be applied and the 3D coordinates to apply them to.
Previous
Next
4 common types of 3D printer file formats and when to use it
File formats are like the blueprints for printing three-dimensional objects. A 3D printer file is known to be the carrier of information from CAD model to 3D printer. It can encode a 3D model’s appearance, geometry, scene and animations. However, not all 3D printer file formats can carry all kinds of data.
A 3D printer file is known to be the carrier of information from CAD model to 3D printer. It can encode a 3D model’s appearance, geometry, scene and animations. However, not all 3D printer file formats can carry all kinds of data.
There are several 3D file formats that are used today. These are FBX, 3DS, COLLADA, IGES, STEP and many more. This blog post will introduce 4 3D printer file formats that are commonly used by engineers and designers and when to use it. These file formats are considered as “go-to” formats for 3D printing.
- STL
Nowadays, STL is known to be the most common file format in 3D printing. Ever since its invention in 1987, it has remained to be the de facto standard in the 3D printing industry.
STL (Standard Triangle Language/Standard Tessellation Language) is the first file format developed for 3D printing. Its corresponding file extension is .stl.
STL files save 3D models as surface of geometrical shapes and turn it into a triangular mesh. But, it cannot display information about the model’s colour or texture.
But, it cannot display information about the model’s colour or texture.
STL file format is used by some designers because of its flexibility and popularity. Almost any piece of software and hardware supports this file format. This means that you can use your favourite CAD programs, repair tools and slicers without any problems.
STL file format is also used when the 3D model requires a single type of colour. If you want to be able to download plenty of ready-to-use 3D models, then use STL file format.
- OBJ
OBJ (Wavefront OBJect) is a 3D printer file format that was originally used by graphics designers as a neutral interchange format for 3D graphics. It was first developed by Wavefront Technologies for its animation package. This file format has the extension .obj.
Unlike STL, OBJ can encode colour and texture information, it also supports both approximate and precise encoding of surface geometry. This means that it doesn’t restrict its surface mesh to triangular facets. The designer can also use polygons such as quadrilaterals. However, OBJ doesn’t support any kind of animation.
This means that it doesn’t restrict its surface mesh to triangular facets. The designer can also use polygons such as quadrilaterals. However, OBJ doesn’t support any kind of animation.
OBJ is often used when the 3D object requires more than one colour. It is also the choice of some developers because it offers a lot of flexibility on how it encodes the 3D model’s geometry.
Aside from that, with OBJ, the designer can use more advanced schemes such as free-form curves and free-form surfaces. These schemes can be used to encode curved geometry without losing any data.
This file format is also widely used in industries such as aerospace and automotive which are demanding when it comes to precision.
- AMF
AMF was introduced in 2011 as a replacement for STL file format and then was called “STL 2.0”. AMF was developed to address the shortcomings of STL format. Some issues that STL has includes bloated, error-prone, incapable of storing colour, material and texture information.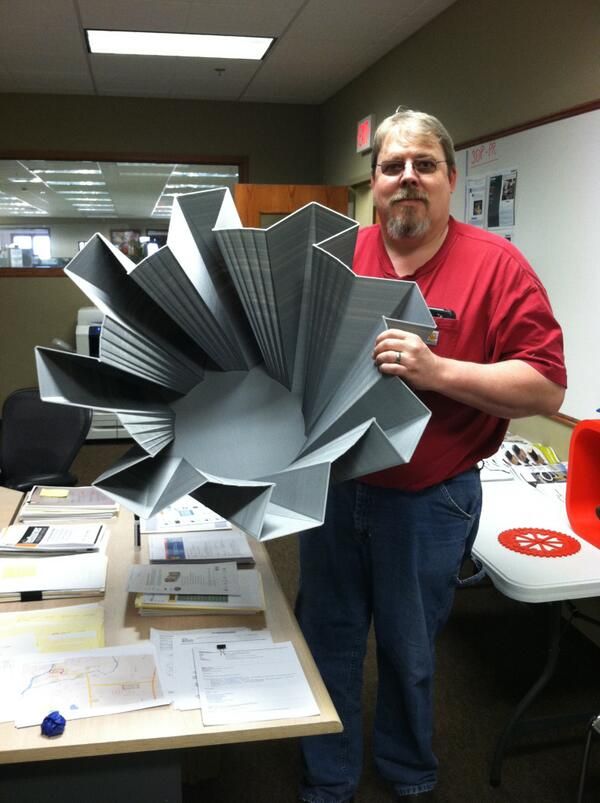
AMF is an XML-based format that has native support for geometry, lattices, scales, duplicates and orientation. Thus, it is a superior format for STL file.
Unfortunately, the 3D printing industry has been slightly slow to adopt this format in spite of its technical advantage.
When to use AMF?AFM 3D file format is used if a 3D model requires precision, multiple materials and multi-colours all at once. This format will ensure that the file will be easy to read, write and process.
Furthermore, aside from planar straight triangles, AMF allows curved triangles. In this way, you can easily describe a curved surface without the use of many facets.
- 3MF
As 3D printing industry advances, developers are trying to look for solutions to some of the notable problems with STL. Thus, Microsoft, along with other big companies such as Autodesk, 3D Systems, EOS, Stratasys, Ultimaker, etc.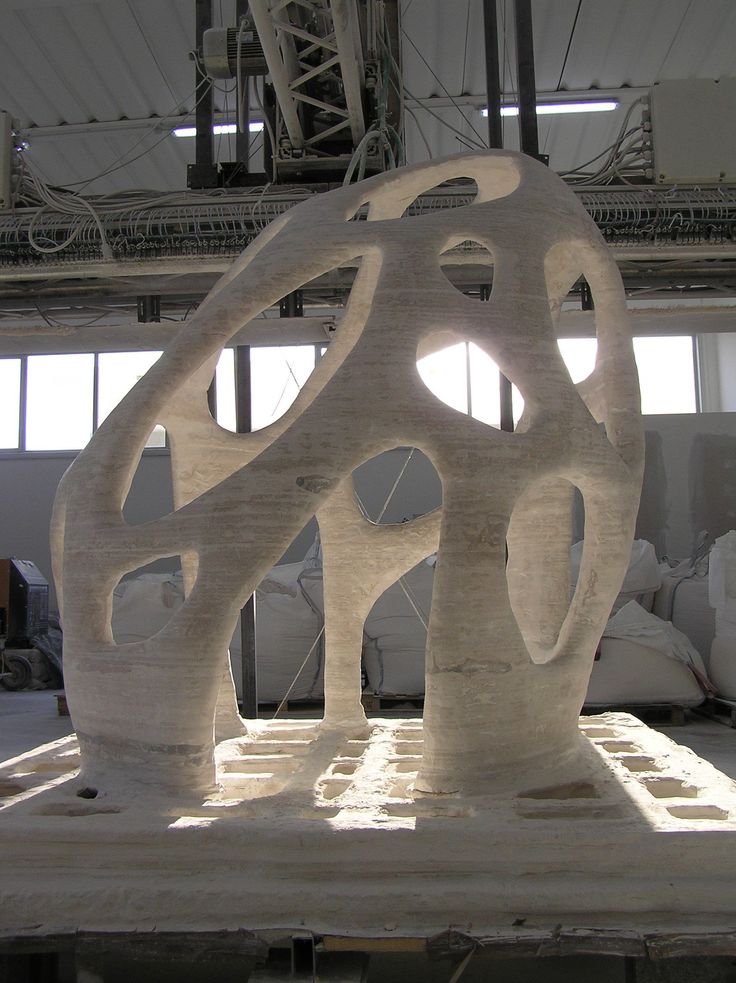 developed 3MF 3D printer file. It has the goal of creating a seamless and high-quality 3D printing experience for consumers and manufacturers.
developed 3MF 3D printer file. It has the goal of creating a seamless and high-quality 3D printing experience for consumers and manufacturers.
3MF features a geometry representation similar to STL but more compact than AMF 3D printer file format. However, 3MF is relatively new to the manufacturing industry. It still lacks more industry recognition.
When to use 3MF?3MF is often used by designers who want to avoid frustrations related to print failures, bad geometry, etc. 3MF file format can also handle 3D models that use different colours and materials. Thus, it can be used for complicated 3D printing projects.
3MF file format is trying to resolve all issues from other 3D printer file format and bring it together in a single file. Hence, it is considered as an ideal format for the future of 3D printing.
ConclusionThere are a lot of 3D file formats that are used by 3D printing designers today. But STL, OBJ, AMF, and 3MF are the most important among all of them. They have their own strengths and varies in their levels of compatibility with software and hardware.
They have their own strengths and varies in their levels of compatibility with software and hardware.
It is vital to understand and know the key differences between these 3D printer file formats. Your choice of 3d file format can greatly affect the production efficiency, 3D printing toolchain and the quality of 3D prints.
If you have more questions or want to learn more about 3D printing-related topics, cooperate with a 3D printing service provider in Sydney. Aside from that, they can offer services such as 3D design modelling, industrial 3D printing and many more.
Types of files for 3D modeling and 3D printing
3D models
- STL
- OBJ
- STEP
- Engineering software
- Art software
Almost everyone knows what types of files are used to save images: PNG, JPG, BMP, TIFF and others. But what about volume models? It would seem that we are adding a third dimension, but the file size is often smaller than even the image of the same model. In this article, we will tell you everything you need to know about files for storing models and even more: conversion methods, features of each type of file, and the file format for 3D printing.
But what about volume models? It would seem that we are adding a third dimension, but the file size is often smaller than even the image of the same model. In this article, we will tell you everything you need to know about files for storing models and even more: conversion methods, features of each type of file, and the file format for 3D printing.
3D model storage features
Unlike images, the voxel (voxel - volumetric pixel) storage method has not taken root in the world of 3D models. Only a few craftsmen use it when creating games or in scientific research. This is due to the history of the emergence of three-dimensional graphics: unlike the appearance of photography, three-dimensional graphics were originally created on a computer, and were used for animation. Voxels are much more difficult to animate, so they began to use the polygon storage method instead: the entire model consists of many polygons - triangles that have three points. It's like creating sculptures out of paper - by putting together a lot of flat pieces, you can get something voluminous and even smooth.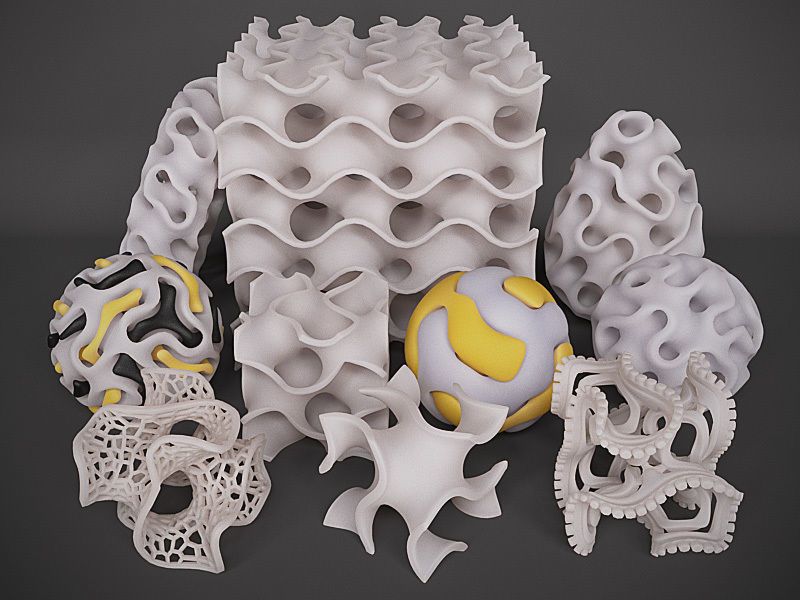
Dolphin Polygon Model
Although this method of saving as polygons cannot be called raster, these methods have much in common: the impossibility of increasing the quality, the direct relationship between the quality and file weight, ease of editing. This is the most practical format for saving and using models in 3D printing, but not the only one. Next, we will look at the most popular formats for storing 3D models.
Universal 3D Model File Formats
In fact, there are as many different methods for storing 3D models as there are for storing photos and videos. But there are also universal formats that, although with some restrictions, can be opened in almost any program.
STL
Contrary to misconceptions, STL was not originally intended for artistic modeling. It was developed by the Albert Consulting Group and was intended for an early 3D printing method - stereolithography. Hence the name of the file - STereoLithography. After some time, the company openly published the format and since then it has gained immense popularity.
The STL format is widely used due to the simplicity of its structure: polygons (facets) and their normals. The former are needed to set the surface, and the latter to indicate where the outer side of the polygon is located. Therefore, this format can be considered the most universal.
Comparison of CAD model and STL model
Due to the fact that the model is defined using many triangles, it is impossible to accurately define curved surfaces, because this would require an infinite number of triangles, and therefore an infinite data store. But when used in 3D printing, this minus is not so important, since the accuracy specified using triangles is higher than the printing accuracy.
OBJ
This format is very similar to STL, but differs in the ability to apply textures, set the material and store other information. Therefore, OBJ can be called an extended version of STL and is mainly intended for artistic modeling programs such as Blender, Autodesk Maya, 3Ds Max, Meshlab and others.
Processing an OBJ model in Blender
STEP
Now we are moving on to the engineering side of 3D modeling, because STEP is the only format that can be opened in any engineering modeling program and freely edited with the tools built into the program. STEP was originally developed as a world standard format for storing products on a computer, and was intended for a complete development cycle of a part. That is why all serious engineering modeling and physical simulation programs can work with this format. A distinctive feature of STEP is its high accuracy: the model is created with tools that allow you to set curves using formulas. Therefore, the precision in this format is infinite: no matter how much you increase it, the curved line will remain a curve, and will not become a lot of straight lines.
Creating a model in CAD SolidWorks
To create models in STEP format, CAD (Computer-Aided Design) is used. Thanks to the ISO standard, all CAD programs can work in this format. But not all data is freely transferred from one program to another via STEP. For us, the most important thing is the transfer of model geometry, and simulations, material and other data that the STEP format does not store are of secondary importance.
Proprietary formats
This category includes file formats that can only be opened in one program - in which the files were created. They are intended only for storing projects, often they cannot be used in 3D printing. An exception is the Ultimaker Cura slicer, which has the ability to add plug-ins that allow you to open files of programs such as Inventor, Siemens NX, Solidworks and others directly from the slicer.
Engineering programs
As mentioned earlier, these programs are called CAD. Since this software is often intended for production, they also have a common file format (STEP). Some programs, often produced by one company, allow you to work in a common ecosystem. For example, in many of Autodesk's engineering software, format compatibility can be found: Fusion 360 can open a file created in Inventor. But with this method of opening, some information about the product will still be lost, for example, information about the physical simulations performed. Therefore, if the part is not developed to the end, you should not move it between different programs.
Since this software is often intended for production, they also have a common file format (STEP). Some programs, often produced by one company, allow you to work in a common ecosystem. For example, in many of Autodesk's engineering software, format compatibility can be found: Fusion 360 can open a file created in Inventor. But with this method of opening, some information about the product will still be lost, for example, information about the physical simulations performed. Therefore, if the part is not developed to the end, you should not move it between different programs.
Art programs
This category includes programs created for visualization: animation, special effects, creation of figures and models for video games. Unlike the previous case, chaos reigns in artistic modeling programs. Each program has its own format, and the general STL format limits the functionality of each program to the simplest tools. But this is enough to create models that will later be printed on a 3D printer, since only the geometry of the model is important.
Gcode - format for 3D printing
Actually Gcode is more than just a file format. It is a separate programming language. But instead of executing commands by a computer, commands in this language are executed by a 3D printer. Initially, this language was developed for complex CNC machines, and a 3D printer is one of the simplest representatives of this type of device. Unlike previous formats, gcode can be easily edited manually, thereby giving commands to the printer directly, bypassing the computer. With this, you can create macros that make it easier to work with a 3D printer. You can read more about working with the gcode language and creating macros in an article on our website.
3D model file format conversion
If you have a need to move the model between programs for 3D modeling, then you should determine in which group the program is from where and where you want to move the model. If you are transferring it from one CAD program to another, then it is best to use the STEP format so as not to limit the number of tools for further modeling. In all other cases, the only option is the STL format, which some CAD systems can recognize and in which art programs can save the model. It should be taken into account that when transferring a model from an art program to CAD, each polygon is transferred as a separate surface, so working with STL files in engineering programs can cause difficulties both in processing and in simple viewing of the model. This is due to the principles of CAD: it performs the processing of each surface separately, and the more surfaces, the more calculations need to be performed for one operation.
In all other cases, the only option is the STL format, which some CAD systems can recognize and in which art programs can save the model. It should be taken into account that when transferring a model from an art program to CAD, each polygon is transferred as a separate surface, so working with STL files in engineering programs can cause difficulties both in processing and in simple viewing of the model. This is due to the principles of CAD: it performs the processing of each surface separately, and the more surfaces, the more calculations need to be performed for one operation.
Tip: if the quality of the model is not so important when transferring a model from an artistic modeling program to CAD, then it is better to reduce the number of polygons as much as possible. This reduces the load on the computer and increases the speed when processing the model in CAD.
#Useful
Expert in the field of additive and subtractive technologies, 3D equipment and CNC machines with over 10 years of experience.
Share
all materials
Do you have any questions?
Our specialists will help you with the choice of 3D equipment or accessories, consult on any questions.
Various file formats for 3D printing・Cults
With the development of digital technology, 3D printing has become much more accessible today. Individuals and professionals can have their own equipment and make various print models. All that is required is a good understanding of the basic concepts, especially in relation to the respective file formats. Indeed, depending on the field and for historical or practical reasons, certain file formats are preferred for 3D printing. Here are the most common 3D printing formats and their main characteristics.
STL is short for "Stereolithography", one of the oldest file formats for 3D printing. Developed in the late 1980s, this type of format is still widely used today. It describes the surface geometry of a 3D object without displaying color, texture, or other attributes. The STL format has the ".STL" extension. These files are generated by computer-aided design (CAD) software. Programs such as FreeCAD, Blender, MeshLab, MeshMixer, SketchUp, SculptGL, and 3DSlash can be used to edit and repair STL files.
The STL format has the ".STL" extension. These files are generated by computer-aided design (CAD) software. Programs such as FreeCAD, Blender, MeshLab, MeshMixer, SketchUp, SculptGL, and 3DSlash can be used to edit and repair STL files.
The STL file simplifies a 3D surface into a "tessellation", a series of small triangles that increase in number when it is necessary to represent and recreate curved surfaces as best as possible. When a large number of triangles need to be used, the size of the 3D model STL file increases rapidly.
The OBJ file format is also very popular in the 3D printing industry. Its extension is ".OBJ". It has the advantage that it also encodes color and texture information, which is stored in a separate file with a ".MTL" extension. OBJ files allow the use of non-triangular faces, with one face adjoining another. They can be opened with programs such as Autodesk Maya 2013, Blender and MeshLab .
Developed in the 1990s, 3DS is a file format that stores only the most basic information about geometry, appearance, scenes, and animation. It allows you to save properties such as color, material, texture, transmissivity, etc. With the ".3DS" extension, this 3D printing file format also has the advantage that it can be read by most programs on the market, such as 3dsMax, ABViewer, Blender, MeshLab, messiahStudio, Rain Swift 3D, SketchUp, TurboCAD etc.
It allows you to save properties such as color, material, texture, transmissivity, etc. With the ".3DS" extension, this 3D printing file format also has the advantage that it can be read by most programs on the market, such as 3dsMax, ABViewer, Blender, MeshLab, messiahStudio, Rain Swift 3D, SketchUp, TurboCAD etc.
An SLDPRT file or its .SLDPRT extension is a 3D printing image format used by the SolidWorks CAD software. It contains a 3D object or "part" that can be combined with other parts into a single ".SLDASM" assembly file. SLDPRT files are usually opened with the SolidWorks program. However, they can be viewed using SolidWorks eDrawings Viewer, Autodesk Fusion 360, Adobe Acrobat 3D, Acrobat Pro 9 or later .
The SCAD format (.SCAD extension) is generated by OpenSCAD, a freeware modeling program used for various 2D and 3D projects. The SCAD file can be used to design 3D objects, specifying the object's geometry and positioning information. It can only be opened with OpenSCAD .
It can only be opened with OpenSCAD .
The .BLEND format is an extension used for 3D animation and projects designed with Blender's 3D modeling tool. This file type can contain multiple scenes as well as all project elements such as objects, textures, 3D meshes and real-time interaction data, sounds, lighting data, animation keyframes, display layouts, and interface settings. Please note that only Blender can work with this 3D file format.
The 3MF file (.3MF extension) is used by various design programs to save 3D models for printing. This format includes model, material, and property data compressed using ZIP compression. 3MF files also store a print ticket, a thumbnail image, and one or more digital signatures. They can be opened with programs such as Microsoft 3D Builder, Microsoft Paint 3D, Dassault Systemes SolidWorks, Dassault Systemes CATIA, McNeel Rhino, PTC Creo and Ultimaker Cura .
The .GCODE file contains commands that define how the 3D printer should print. It stores instructions such as print speed, set temperature, and where to move print items. This 3D file format is created with cutting software such as Simplify3D and Slic3r. Reading can be done with Simplify3D, as well as Blaze3D, GCode Viewer and NC Viewer.
It stores instructions such as print speed, set temperature, and where to move print items. This 3D file format is created with cutting software such as Simplify3D and Slic3r. Reading can be done with Simplify3D, as well as Blaze3D, GCode Viewer and NC Viewer.
A .SKP file is a 3D model format created by SketchUp. This takes into account wireframes, textures, shadows, and edge effects. This file type is also used to store components that will be inserted into the document. Of course it can be opened with SketchUp, but also with programs like IMSI TurboCAD Pro or Deluxe, Okino Computer Graphics PolyTrans, ACCA Edificius and Trimble 3D Warehouse .
FBX is a 3D printing file format popular in the film and video game industry. Developed by Kaydara and acquired by AutoDesk, it supports geometry and appearance properties such as color and texture, as well as skeletal animation and morphs. AutoDesk will use the ".FBX" FBX file as an interchange format for its software portfolio such as AutoCAD, Fusion 360, Maya, 3DS Max, etc.
Other file types are not exclusive to 3D but are regularly used in the field.
A .RAR file is an archive containing one or more compressed files. The compression ratio of this format is greater than that of the classic ZIP compression. It is used to compress files to reduce their size for easier transportation and storage. You can extract files from RAR archive using various unpacking programs such as RARLAB WinRAR, Corel WinZip or B1 Free Archiver .
.DWG files are databases of 2D or 3D models created in AutoCAD. They consist of information about the vector image and metadata that describes the contents of the file. There are many utilities available to open this file format, including: Autodesk Auto CAD, Autodesk Inventor, Autodesk Design, Autodesk DWG, AutoDWG DWGSee, CADSoftTools ABViewer, Canvas X, Adobe Illustrator, Bricsys Bricscad, etc.
Used in 3D editing programs such as Adobe Photoshop and Autodesk Maya, the .MTL format is used to store material settings. This file is stored along with another in .OBJ format and is used to describe how textures should be applied and the 3D coordinates they should be applied to.
This file is stored along with another in .OBJ format and is used to describe how textures should be applied and the 3D coordinates they should be applied to.
This page has been translated using machine translation. Suggest the best translation
Previous
ShareNext
Similar publications
Since their invention, 3D printers have proven that printing many objects is much more efficient than conventional manufacturing techniques. However, calibration is required for optimal performance when printing 3D parts. Many 3D printer owners find this procedure tedious and time-consuming. However, it is much easier than it seems if you know the right tips on how to do it. Cults3D presents the various steps you need to follow in order to successfully calibrate your printer.
Read more The plate is one of the most important parts of a 3D printer. For optimal printer performance, it must be properly cleaned after each print session.