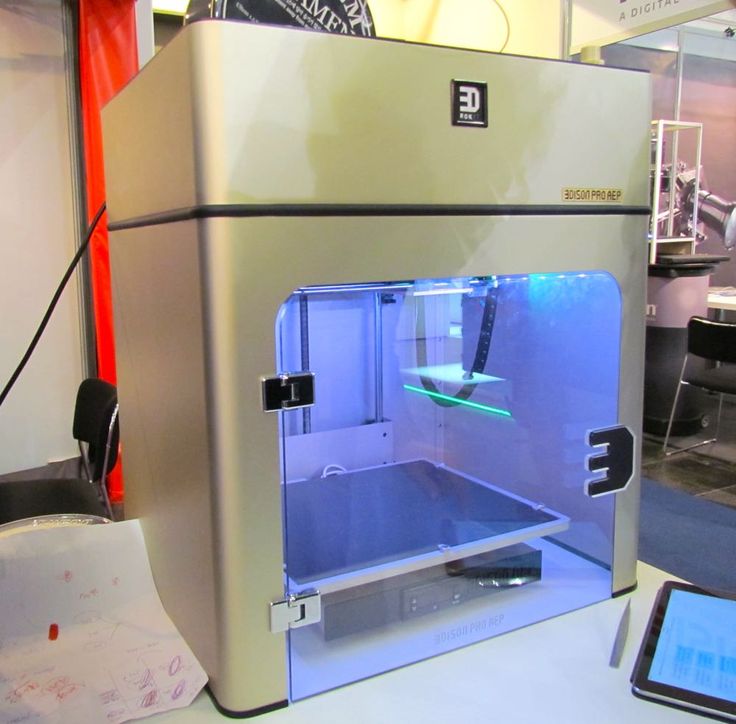
Wireless 3d printing
Learn How to Make Your Ender 3 Wireless & Other 3D Printers – 3D Printerly
3D printing by itself is pretty cool, but you know what’s even cooler? 3D printing wirelessly.
I think we all love some extra convenience, so why not add some when it comes to 3D printing? Some 3D printers come with wireless support built in, but the Ender 3 isn’t one of them, along with several other machines.
If you want to learn how to make your Ender 3 wireless and operate through Wi-Fi, you’ve come to the right place.
A combination of a Raspberry Pi and OctoPrint is the usual method to make an Ender 3 wireless. You can also use AstroBox for a more flexible Wi-Fi connection option since you can access your 3D printer from anywhere. A Wi-Fi SD card can only give you the ability to transfer files wirelessly.
There are upsides and downsides to each method, so keep reading to find out the steps to take and which choice is most common.
This article will detail how people get their Ender 3’s working wirelessly which makes their 3D printing journey that much better.
There are a few ways that Ender 3 users upgrade their machines to be able to print wirelessly. Some are really simple to do, while others take a little more of a walkthrough to get it right.
You also have differences in equipment and products to purchase to connect your Ender 3
- Wi-Fi SD card
- Raspberry Pi + OctoPrint
- Raspberry Pi + AstroBox
- Creality Wi-Fi Cloud Box
Wi-Fi SD Card
The first, but less used option is implementing a Wi-Fi SD card. All you need to do here is get yourself an adapter which inserts into your MicroSD slot into your Ender 3, then present a SD slot for the WiFi-SD card since they only come in the larger size.
You can get a pretty cheap one from Amazon, the LANMU Micro SD to SD Card Extension Cable Adapter is a great choice.
Once you’ve inserted the adapter and Wi-Fi SD card, you will be able to transfer your files wirelessly to your 3D printer, but there are limitations on this wireless strategy. You will still have to start off your prints manually and actually choose the print on your Ender 3.
You will still have to start off your prints manually and actually choose the print on your Ender 3.
It’s a fairly simple solution, but some people enjoy being able to send files straight to their 3D printer. This is also a much cheaper option than the other methods.
If you want more capabilities with your wireless 3D printing experience, I would choose the method below.
If you’ve never heard of a Raspberry Pi, welcome to a really cool gadget that has many technological possibilities. In basic terms, a Raspberry Pi is a mini computer that packs enough power to operate as its own device.
For 3D printing specifically, we can use this mini computer to expand our capabilities to 3D printer wirelessly, plus many other cool features along with that.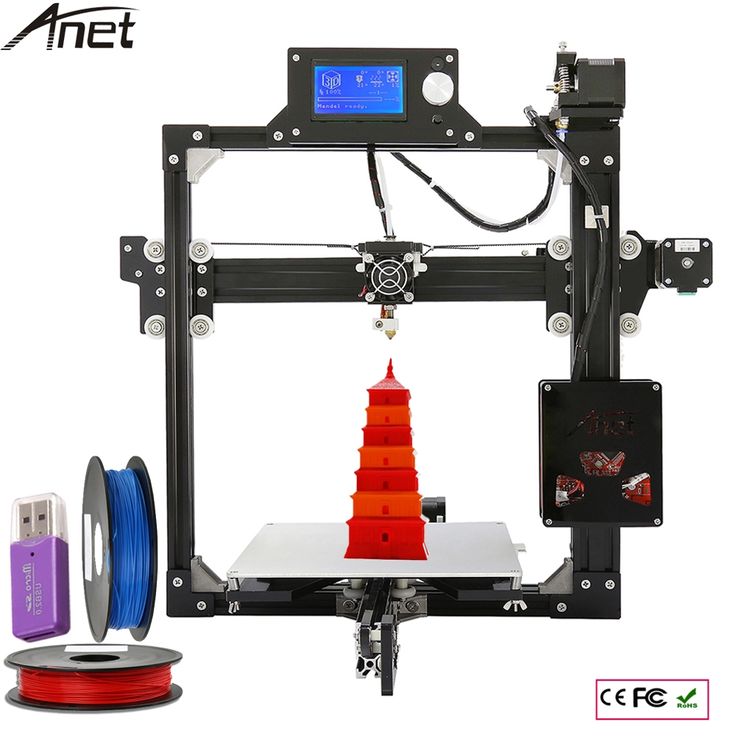
Now OctoPrint is a software that complements the Raspberry Pi enabling you to activate that Wi-Fi connection to connect to your 3D printer from anywhere. You can implement some basic commands and do even more with plugins.
There is a list of plugins on OctoPrint which give you many extra features, one example being the ‘Exclude Region’ plugin. This allows you to exclude a portion of your print area mid-print inside the G-Code tab.
This is perfect if you are printing multiple objects and one has a failure such as detatching from the bed or the support material fails, so you can exclude that part rather than stopping the print altogether.
Many people also connect cameras to their 3D printers using OctoPrint.
In this article, we take a look at how to set up OctoPrint for the Ender 3, a great candidate printer for remote operation.
The basic steps to follow are:
- Purchase a Raspberry Pi (with Wi-Fi embedded or add Wi-Fi dongle), Power Supply & SD Card
- Put OctoPi on your Raspberry Pi through an SD card
- Configure the Wi-Fi by going through your SD card
- Connect the Pi & SD card to your 3D printer using Putty & the IP address of the Pi
- Setup OctoPrint on your computer browser and you should be done
Here you will find a complete guided setup to connect your Ender 3 to the computer using OctoPrint. Below are the things that you will need.
Below are the things that you will need.
- Ender 3 3D Printer
- Raspberry Pi (CanaKit Raspberry Pi 3 B+ from Amazon) – includes power adapter,
- Power Adapter for Raspberry Pi
- Micro SD Card – 16GB should be enough
- Micro SD Card Reader (comes with Ender 3 already)
- Mini USB Cable for Ender 3 Printer
- Male Female USB Cable Adapter
The video below goes through the whole process which you can follow along with easily.
Connecting Pi to Wi-Fi
- Download the latest updated version of the OctoPi operating system (OctoPi image)
- Download & use Win32 Disk Imager to create the image on the SD card
- Plug in fresh SD card
- Once your OctoPi image is downloaded, ‘Extract All’ and ‘Write’ the image to the SD card
- Open the SD file Directory and look for the file titled “octopi-wpa-supplicant.
 txt”.
txt”.
In this file, there will be code as:
##WPA/WPA2 secured
#network={
#ssid=“type SSID here”
#psk=“type Password here”
#}
- At first, remove the ‘#’ symbol from the code lines to make them uncommented.
- It will become like this:
##WPA/WPA2 secured
network={
ssid=“type SSID here”
psk=“type Password here”
}
- Then put your SSID and set a password in the quotes.
- After adding the password, insert another code line as scan_ssid=1, just below the password code line (psk=“ ”).
- Set up your country name correctly.
- Save all changes.
Connecting the Computer to Pi
- Now connect it with your printer using the USB cable and power it on using a power adapter
- Insert the SD card into the Pi
- Open the command prompt and check the IP address of your Pi
- Insert it in the Putty application on your computer
- Login to the Pi using “pi” as the username and “raspberry” as the password
- Now open a web browser and type the Pi’s IP address in the search bar
- The Setup Wizard will be opened
- Set up your printer profile
- Set Origin at “Lower Left”
- Set Width (X) at 220
- Set Depth (Y) at 220
- Set Height (Z) at 250
- Click Next and Finish
Fix Pi Camera and Device on the Ender 3
- Fix the Pi camera on the 3D printer
- Insert one end of the ribbon cable in the camera and the other one in the Raspberry Pi ribbon cable slot
- Now fix the Raspberry Pi device on Ender 3
- Make sure that the ribbon cable is not tangled or stuck in anything
- Connect Pi with the Ender 3 power supply using a USB cable
- Installation is done
I’d go for the LABISTS Raspberry Pi Camera Module 1080P 5MP from Amazon. It’s a good quality, yet cheap option to get a nice visual on your 3D prints.
You can 3D print yourself OctoPrint camera mounts by checking out the Howchoo collection on Thingiverse.
A more premium, yet simple option to print wirelessly from your Ender 3 is by using AstroBox. With this device, you can control your machine from any location when they are both connected to the internet.
There is a Raspberry Pi 3 AstroBox Kit which you can get directly from the AstroBox website and it includes the following:
- Raspberry Pi 3B+
- Wi-Fi dongle
- Pre-flashed 16 GB microSD Card with AstroBox Software
- Power Supply for the Pi 3
- Case for the Pi 3
The AstroBox simply plugs into your 3D printer and enables Wi-Fi along with a connection with the cloud. You can easily manage your 3D printer with your phone, tablet or any other device which has connection to a local network.
Along with a standard USB camera, you can also monitor your prints, real-time from anywhere.
AstroBox Features:
- Remote monitoring of your prints
- Ability to slice designs on the cloud
- Wireless Management of your 3D Printer (No pesky cables!)
- No more SD cards to load STL files
- Simple, Clean, Intuitive Interface
- Mobile friendly and works on any web enabled device or using the AstroPrint Mobile App
- No need for a laptop/computer to be connected to your printer
- Automatic updates
AstroBox Touch
The AstroBox also has another product which extends the capabilities to be able to have a touchscreen interface. The video below showcases how it looks and how it works.
The video below showcases how it looks and how it works.
It does have some capabilities that you don’t get with OctoPrint. One user described how his kids could fully control and Ender 3 using just a Chromebook. The touch interface is really good and modern, compared to many touchscreen UI out there.
The last option that you might want to use to make your Ender 3 wireless is the Creality Wi-Fi Cloud Box, which helps to remove the SD card and cables, allowing you to control your 3D printer remotely from anywhere.
This product is fairly new at time of writing, and really has the chance to transform many 3D printer users’ experience with FDM printing. One of the early testers of the Creality Wi-Fi Box described their experience in this post.
You can also get the Aibecy Creality Wi-Fi Box which is the same thing but just sold by another seller on Amazon.
3D printing directly from your machine will soon be a task that is out-of-date as we develop the technology to easily 3D print wirelessly, with little setup.
The benefits of the Creality Wi-Fi Box are as follows:
- Simplicity of printing – connecting your 3D printer via the Creality Cloud app – online slicing and printing
- A cheap solution for wireless 3D printing
- You’re getting a powerful performance and very stable archive of software and hardware
- Professional-looking aesthetic in a black matte shell, with a signal light in the middle & eight symmetrical cooling holes at the front
- Very small device, yet large enough for great performance
In the package, it comes with:
- Creality Wi-Fi Box
- 1 Micro USB Cable
- 1 Product Manual
- 12-Month Warranty
- Great Customer Service
OctoPrint Raspberry Pi 4B & 4K Webcam Installation
For the highest quality 3D printing experience using a Raspberry Pi, you can use the Raspberry Pi 4B along with a 4K webcam. This will allow you to make some amazing videos of your 3D prints that you can share to your friends and family.
This will allow you to make some amazing videos of your 3D prints that you can share to your friends and family.
The video below by Michael at Teaching Tech goes through the process.
You can get yourself the Canakit Raspberry Pi 4B Kit from Amazon which gives you everything you need to get started without having to worry about the smaller parts. It also includes a premium clear Raspberry Pi case with an in-built fan mount.
A really good 4K webcam on Amazon is the Logitech BRIO Ultra HD Webcam. The video quality is definitely in the top-tier range for desktop cameras, an item that can really transform your visual displaying capabilities.
- It has a premium glass lens, 4K image sensor, high dynamic range (HDR), along with autofocus
- Looks great in many lights, and has a ring light to automatically adjust and contrast to compensate for the environment
- 4K streaming and recording with optical and infrared sensors
- HD 5X zoom
- Ready for your favorite video meeting apps such as Zoom and Facebook
You can really record some awesome 3D prints with the Logitech BRIO, so if you want to modernize your camera system, I’d definitely get it.
AstroPrint Vs OctoPrint for Wireless 3D Printing
AstroPrint is actually based on an earlier version of OctoPrint, being combined with new phone/tablet apps, along with a slicer that operates through a Cloud network. AstroPrint is a lot easier to setup compared to OctoPrint, but they do both run off a Raspberry Pi.
Practically speaking, AstroPrint is a software that carries fewer functions than OctoPrint, but has more emphasis on user-friendliness. You would want to go with AstroPrint if you just want basic wireless 3D printing capabilities without the extras.
If you think you’ll want to add more advanced features to your 3D printing, you probably should go for OctoPrint.
They have a larger community of contributors who are always developing new plugins and functions. It was built to thrive on customizations and unique features.
Duet 2 Wi-Fi
Duet 2 WiFi is an advanced and fully functional electronic controller specially used for 3D printers and CNC (Computer Numerical Control) devices.
It is the same as its old version Duet 2 Ethernet but the upgraded version is 32-bit and offers Wi-Fi connectivity to work wirelessly.
Pronterface
Pronterface is a host software that is used to control your 3D printer functionalities. It is built from the open-source software suite Printrun which is licensed under GNU.
It provides the user with a GUI (Graphical User Interface) access. Because of its GUI, the user can easily configure the printer and can print the STL files just connecting it with a USB cable.
Does the Ender 3 Pro Come With Wi-Fi?
Unfortunately, the Ender 3 Pro doesn’t come with Wi-Fi, but we can enable a wireless connection by either using a Wi-Fi SD card, a Raspberry Pi & OctoPrint software combination, a Raspberry Pi & AstroBox combination, or by using the Creality Wi-Fi Cloud Box.
In order to keep prices down and let people make their own choices for upgrades, the Ender 3 Pro has kept functionality and extra features to a minimum, mainly focusing on the what you need to get some of the best printing quality right out the box.
10 Simple Ways To 3D Print Over Wi-Fi – Printing It 3D
Several brands like Ultimaker and MakerBot manufacture 3D printers equipped with LAN or Ethernet ports and Wi-Fi compatibility. However, your 3D printer may not have such features. Thus, you have to use a compatible intermediary device, adapter, or tool to 3D print over Wi-Fi.
Here are 10 simple ways to 3D print over Wi-Fi:
- Use remote access software.
- Consider using the AstroBox Touch.
- Opt for the AstroBox Gateway.
- Try using the Raspberry Pi and AstroPrint.
- Use the Raspberry Pi and OctoPrint.
- Use the AstroPrint Plugin for OctoPi.
- Try using Microsoft IoT Core.
- Consider the Creality Wi-Fi Box.
- Use Wi-Fi Modules.
- Consider using the Silex USB Device Server.
Technically, you need a reliable way to connect your 3D printer to the internet network so that you can access it over Wi-Fi, irrespective of your real-time location. This article offers 10 options for you to choose the simplest or most convenient and affordable solution to 3D print over Wi-Fi.
This article offers 10 options for you to choose the simplest or most convenient and affordable solution to 3D print over Wi-Fi.
1. Use Remote Access Software
Using a computer, laptop, or smartphone with a 3D printer through a USB cable can use remote access software to connect over Wi-Fi. Of course, the intermediary device must be on and connected to the internet. However, the device you use for remote access doesn’t have to be onsite or connected to the same network. Thus, you can 3D print from anywhere.
You may consider the Chrome Remote Desktop. Google’s solution works for all computers, laptops, and phones, irrespective of the operating system. You can use the network in your house and the Wi-Fi at any place you’re at a time to access the system connected to your 3D printer.
There’s no shortage of remote access software today. You can check out the likes of TeamViewer and FlexiHub. TeamViewer is a proprietary remote connectivity software, but it has a free version for non-commercial private use. You can always test such options to 3D print over Wi-Fi.
You can always test such options to 3D print over Wi-Fi.
However, what if a 3D printer has only an SD card slot, or you don’t want to keep a computer, laptop, or phone hooked all the time to access the system over Wi-Fi? Remote access software can work only when two or more systems are powered and online. Thus, you need alternatives.
2. Consider Using the AstroBox Touch
Raspberry Pi enthusiasts have been using the single-board computer to make various devices over the years, from video doorbells with two-way audio to DIY adapters for 3D printers so that they can be connected via Ethernet and Wi-Fi. Now, you can get similar solutions off the shelf.
AstroBox Touch is a plug-and-play tool that instantly transforms your 3D printer into a network device. Made by AstroPrint, AstroBox Touch is among the simplest ways to 3D print over Wi-Fi. Also, the solution is a complete interface for you to manage everything on your 3D printer.
The only significant demerit of AstroBox Touch is its price. At ~$200, the turnkey solution with USB and Ethernet ports, built-in Wi-Fi, SD card slot, standard power cable, and touch screen may not be readily affordable for everyone. However, its convenient use is undisputed.
At ~$200, the turnkey solution with USB and Ethernet ports, built-in Wi-Fi, SD card slot, standard power cable, and touch screen may not be readily affordable for everyone. However, its convenient use is undisputed.
3D printing is a complex process, and several things can go wrong every time you try a unique model with complicated design elements. The last thing you need is unpredictable hiccups or failed prints due to an unreliable solution enabling you to 3D print over Wi-Fi.
AstroBox Touch offers wireless 3D printing, remote monitoring, fleet management, data and file sync for all connected devices, and compatibility with desktop, phone, and web. Also, you get a cloud-based library for designs, files, codes, compiled analytics, online slicer, and more.
3. Opt for the AstroBox Gateway
AstroBox Gateway is the predecessor of AstroPrint’s Touch version. However, the touchscreen isn’t the only missing feature. The two models have different software, the Gateway has no access to the app store, and the setup is through hotspot only, whereas Touch has the screen.
More importantly, AstroBox Gateway isn’t a plug-and-play solution. You need to assemble it, and the device isn’t exactly for those looking for a turnkey gadget. Still, the significant difference in price of almost $100 between AstroBox Gateway and AstroBox Touch warrants a mention.
AstroBox Gateway enables you to 3D print over Wi-Fi. You can use web or browser-based access to monitor your prints remotely. Also, you get auto software updates, video streaming, camera compatibility, and multifaceted access through a desktop, mobile app, and web portal.
A noteworthy fact is AstroPrint’s transparency regarding compatibility. The brand has a list of 3D printers classified as compatible per manufacturers, community, and AstroPrint. Check the list here — it also mentions the 3D printer brands and models that are ‘not verified’ as compatible.
4. Try Using the Raspberry Pi and AstroPrint
You can use AstroPrint’s platform and resources to 3D print over Wi-Fi without buying an AstroBox Touch or Gateway, but you need a Raspberry Pi. This option is affordable if you have a Raspberry Pi already. Otherwise, a ready-made AstroBox Touch or Gateway is more practical.
This option is affordable if you have a Raspberry Pi already. Otherwise, a ready-made AstroBox Touch or Gateway is more practical.
AstroBox Touch needs a Raspberry Pi 3 or 4 and won’t work with any earlier version. Refer to this stepwise guide to build your own AstroBox Touch. You can use this DIY tutorial to build an AstroBox Gateway using the now-discontinued Raspberry Pi 2 or any subsequent generation.
While these DIY solutions may be simple for tech-savvy users, the processes aren’t always straightforward for those unfamiliar with Raspberry Pi, PCIe, soldering touchscreens onto the single-board computer, and circuitry related issues, among other common prerequisites.
5. Use the Raspberry Pi and OctoPrint
Like the DIY AstroBox Touch or Gateway using Raspberry Pi, you may also use the latter with OctoPrint or OctoPi. However, you’ll need an internet-enabled Raspberry Pi kit, including a memory card, cables for power, USB, and HDMI, an appropriate case, and preferably a fan.
You may buy the Wi-Fi dongle and other supplies separately if you have a Raspberry Pi. Else, you can consider something like the CanaKit Raspberry Pi 4 Kit (available on Amazon.com). This 128 GB storage & 4GB memory edition has most of the essentials you need for the project.
The other integral component is OctoPrint, available as the OctoPi image that you can download and set up. First, you must build your device, and then get the Raspberry Pi Imager and choose the specific purpose OS OctoPi to make your 3D printer Wi-Fi or internet-enabled.
Watch this YouTube video to use Raspberry Pi and OctoPrint to 3D print over Wi-Fi:
6. Use the AstroPrint Plugin for OctoPi
OctoPi or OctoPrint may or may not be convenient for everyone. The fascinating resources and unmatched control of OctoPrint can overwhelm beginners. In contrast, AstroPrint may be pretty straightforward. Fortunately, you don’t have to make such hard choices with Raspberry Pi.
The fascinating resources and unmatched control of OctoPrint can overwhelm beginners. In contrast, AstroPrint may be pretty straightforward. Fortunately, you don’t have to make such hard choices with Raspberry Pi.
There’s an AstroPrint plugin compatible with OctoPrint, thus your DIY Raspberry and OctoPi. You can check out and download the plugin here. Also, you may want to explore the significant differences between AstroPrint and OctoPrint if you’re unsure about choosing either or both.
7. Try Using Microsoft IoT Core
Microsoft IoT Core is a simple way to convert your 3D printer into a network device. Imagine the old school 2D printers connected via LAN, except for the fact that the modern version enables you to 3D print over Wi-Fi and remotely using a system running Windows 8.1 through 10.
However, you’ll still need an intermediary board, but that isn’t a problem because Microsoft IoT Core has been compatible with Raspberry for more than five years now. Thus, you can use Raspberry Pi with Windows 10 IoT Core and its Network 3D Printer app through LAN and Wi-Fi. Also, you can use the 3D Builder app on Windows devices to sync with your Microsoft account.
Also, you can use the 3D Builder app on Windows devices to sync with your Microsoft account.
This method works for Lulzbot, Makergear, Printrbot Play, Prusa i3 Mk2, CraftBot, Ultimaker 3D printers, and a few other brands & models. Also, check if your Windows version works with the Raspberry Pi you use. For example, you can’t use Windows 10 IoT Core on Raspberry Pi 4 yet.
8. Consider the Creality Wi-Fi Box
The Creality Wi-Fi Box is one of the most common recommendations you’ll find online, but it’s not a perfect solution. For starters, the Creality Wi-Fi Box (available on Amazon.com), sold by the Sovol 3D Store, is now the same package as the Creality Smart Kit (available on Amazon.com) of SainSmart. The Creality Wi-Fi Box is great because it’s lightweight and easy to carry.
Until recently, the Creality Smart Kit had a Wi-Fi Box and camera. Now, if you don’t want the camera, you have to consider the Entweg Original Creality Wi-Fi Box (available on Amazon.com). Apparently, the Entweg Wi-Fi Box doesn’t feature the Creality branding on the case. That apart, the box is easily one of the most affordable and simple ways to 3D print over Wi-Fi. However, there are concerns.
Apparently, the Entweg Wi-Fi Box doesn’t feature the Creality branding on the case. That apart, the box is easily one of the most affordable and simple ways to 3D print over Wi-Fi. However, there are concerns.
The Creality Wi-Fi Box is compatible with Android and iOS, so you can use your phone to feed a design, monitor the process. It also controls the print to an extent, but the interface won’t use the code you provide. The Creality Cloud app and slicer will process the file, and this takes time.
If you don’t intend to print your unique designs with customized codes, the Creality Wi-Fi Box should work fast and without glitches for most models in its library. Also, this box is compatible with every Creality 3D printer as long as you use a connected device running Android or iOS.
Some users have reported their disappointment about the camera’s resolution. However, if you want to have a visual feed for remote monitoring, the Wi-Fi box and camera kit may be worth considering. Besides, the cost isn’t even remotely close to what you may pay for a Raspberry Pi, an AstroBox Touch or Gateway, or other mainboards and essential components for a DIY rig.
Besides, the cost isn’t even remotely close to what you may pay for a Raspberry Pi, an AstroBox Touch or Gateway, or other mainboards and essential components for a DIY rig.
9. Use Wi-Fi Modules
Raspberry Pi, OctoPrint, AstroBox Touch, or Gateway, all such devices require a Wi-Fi module. Likewise, Microsoft IoT Core also needs a connected Raspberry Pi to have onboard Wi-Fi or an Ethernet connection for you to access the 3D printer using the internet and remotely.
However, not all Wi-Fi modules and adapters or sensors work as you may expect them to in real-world settings with actual 3D printers of different brands. Mainboards and Wi-Fi modules may not be simple for every user to work with, and the experiences can be starkly different.
Two relatively known 3D Wi-Fi modules are GeeeTech and BigTreeTech. GeeeTech’s 3D Wi-Fi Module works with the EasyPrint app. The entire setup is somewhat simple, and the interface has many features to access, initiate, control, and monitor a 3D print over Wi-Fi. Also, GeeeTech has a comprehensive manual to configure the module with your 3D printer and Wi-Fi.
Also, GeeeTech has a comprehensive manual to configure the module with your 3D printer and Wi-Fi.
Unfortunately, the 3D Wi-Fi Module’s theory isn’t exactly what users experience in practice. Besides, the module is unavailable online at the time of writing this guide. Still, you may want to watch the following YouTube video to check out how a GeeeTech 3D Wi-Fi Module could work, if it does:
The other option is the BigTreeTech Direct Wireless Module (available on Amazon.com). This Wi-Fi Sensor works with SKR Pro V1.1 and SKR Mini E3 mainboards or motherboards. Thus, if you want a Raspberry Pi alternative, you can use BigTreeTech’s SKR board and Wi-Fi Module.
This setup is essentially a substitute for Raspberry Pi with OctoPrint, AstroPrint, or Microsoft IoT Core. The Wi-Fi Module is reasonably priced, but it operates at 3.3 V, so it’s not compatible with any board that runs on 5 V, like Raspberry Pi. Also, BigTreeTech’s Wi-Fi sensor has a frequency range of 2.4 GHz – 2.5 GHz, not the 5 GHz that many Wi-Fi adapters are compatible with.
The Wi-Fi Module is reasonably priced, but it operates at 3.3 V, so it’s not compatible with any board that runs on 5 V, like Raspberry Pi. Also, BigTreeTech’s Wi-Fi sensor has a frequency range of 2.4 GHz – 2.5 GHz, not the 5 GHz that many Wi-Fi adapters are compatible with.
There are other incompatibility issues related to software and hardware. However, BigTreeTech has a bouquet of essential components that you may use if you wish to try such ways to 3D print over Wi-Fi. Here’s a YouTube video to give you an idea of how BigTreeTech components work:
10. Consider Using the Silex USB Device Server
The Silex DS-520AN USB Device Server (available on Amazon.com) is a relatively expensive way to 3D print over Wi-Fi. However, it’s as reliable and simple as the AstroBox, Microsoft IoT Core, and remote access software. As an added advantage, you can use Silex for various USB-enabled hardware.
However, it’s as reliable and simple as the AstroBox, Microsoft IoT Core, and remote access software. As an added advantage, you can use Silex for various USB-enabled hardware.
This USB server supports 802.11n Wi-Fi and Ethernet. You can set it up with 3D printers, flash drives, scanners, cameras, and other hardware. Silex has its Virtual Link software for Windows 7 through 10 and Server 2019, including many previous generations.
Also, you can connect a 3D printer to a chosen network with the AutoConnect feature and access it through multiple Windows devices. Furthermore, Silex USB Device Server works with Citrix, Hyper-V, and VMware, among other virtualization programs.
10 reasons to use OctoPrint for 3D printing
3DPrintStory Reviews 10 Reasons to Use OctoPrint for 3D Printing
Surely everyone had problems with 3D printing, which was left overnight in the hope of getting a finished 3D model in the morning. Or it was simply not possible to constantly monitor the 3D printing process in order to stop it in time. e in case of an error. It is this problem - the problem of monitoring 3D printing - that is solved with the help of the wonderful free and open source software OctoPrint.
Or it was simply not possible to constantly monitor the 3D printing process in order to stop it in time. e in case of an error. It is this problem - the problem of monitoring 3D printing - that is solved with the help of the wonderful free and open source software OctoPrint.
OctoPrint is a Raspberry Pi-based 3D printer application that allows you to remotely control your 3D printer. Created by Gina Heusge in 2012, the software is constantly being improved with new versions and new features (via plugins) coming out regularly.
In this article, we highlight the top 10 reasons to use OctoPrint. Some of the problems in this list are solved with the help of additional plugins. By the end of this list, you'll probably want to try OctoPrint if you haven't already.
Wireless 3D printing
Many budget 3D printers do not provide the ability to control or monitor the 3D printer wirelessly. Models must either be downloaded to an SD card or transferred directly via cable. These connection options have their limitations. OctoPrint offers an excellent solution to this problem.
These connection options have their limitations. OctoPrint offers an excellent solution to this problem.
As we briefly mentioned earlier, OctoPrint provides software that is installed on the Raspberry Pi and then connected to the 3D printer. Thanks to the wireless capabilities provided by Raspberry Pi, you can control your 3D printer wirelessly via LAN.
OctoPrint allows you to remotely send G codes, control the temperature of the extruder and hot end, monitor the 3D printing process, and much more. Thanks to OctoPrint's wireless 3D printing capabilities, you can always control your 3D printer, even if you are not physically present.
3D printing from anywhere in the world
As you know, wireless 3D printing is convenient if you are at home and on the same network. But what if you left home and wanted to start printing and was finished when you got home? Or what if you want to keep an eye on the 3D printing process when you're not at home?
Plug-in OctoPrint Anywhere allows you to manage (start and stop) and control 3D printing from literally anywhere. This is a website that can be accessed from your computer or mobile device.
This is a website that can be accessed from your computer or mobile device.
This plugin has a lot of fans, but keep in mind that the OctoPrint developers recently announced that it will eventually be replaced by a more elaborate and updated plugin called Spaghetti Detective.
View G-code
Typically, OctoPrint users monitor the 3D printing process via a webcam connected to their Raspberry Pi. However, if you don't have a webcam or just want to check your 3D print in a different way, the G-code viewer is a great tool.
This underrated OctoPrint feature shows nozzle position and layer number in real time. You can also find the status of your 3D print in the window just below the renderer, which shows the current G-code commands being sent to the 3D printer.
Commands from the terminal
The ability to send commands from the terminal is a great feature for more advanced users. You can view the codes sent to the 3D printer in real time.
One of the most useful features is sending custom G-code commands to your 3D printer. Instead of relying on another program to communicate with your printer, such as Pronterface, you can directly send commands to the OctoPrint terminal.
This feature can be useful in a number of scenarios. If you need to calibrate your 3D printer, you can view the existing system presets in a terminal command. Some commands also allow you to enter and save new calibrated values. This is a very handy feature for those who like to tinker with their 3D printer at a deeper level.
Slow motion
You know that 3D printing is a long process, it can take hours to print one model. Setting up a time-lapse video allows you to view the entire 3D printing process, which lasts several hours, in a matter of seconds.
With OctoPrint and with a camera connected to your Raspberry Pi, you can capture excellent frame-by-frame 3D printing video by setting the frame rate and interval between shots. For true enthusiasts, there are also more advanced customization options.
For true enthusiasts, there are also more advanced customization options.
OctoPrint stores the timelapse locally on the Raspberry Pi and you can download it to your computer. Another useful feature of time-lapse video is the ability to determine the exact cause of a 3D print failure, or at least the point at which the failure occurred.
Octolapse is a plug-in that builds on the functionality of OctoPrint's Timelapse section to produce cleaner, crisper videos.
Slicing 3D Models in the Cloud
Cloud Slicing, as the name suggests, is a remote slicing feature that allows you to slice your 3D models without actually installing the slicing software on your computer. Model slicing is performed using a plugin installed on the Raspberry Pi.
Consider a scenario where your laptop is full of applications and you can't/don't want to install a new slicer. Or imagine not wanting a slicer for every computer you use. This is where the Cloud Slicing plugin fits in perfectly. This feature uses the Cura or Slic3r engine plugin.
This feature uses the Cura or Slic3r engine plugin.
Touch screen for user interface
Touch screen user interface has become the norm for many everyday devices. However, many 3D printers still lack this useful feature.
With the OctoPrint TouchUI plugin, you can add this feature and display the OctoPrint interface on the touch screen. This plugin will allow you to use OctoPrint without connecting a computer. The user interface on the touch screen is very similar to that in the browser, so the transition in terms of learning a new interface will not be difficult.
Installing a touch screen can seem like a tedious task, but there are plenty of tutorials and videos to help you through the process.
Open-source community
Individual developers have spent hours of their time improving 3D printing, including free and open source programs such as Marlin, Cura, and OctoPrint itself.
OctoPrint's popularity is largely due to open source and free access. All source code is available on the GitHub page. Thanks to this, many users and developers have shared their ideas and brought them to life. User-developed plugins greatly extend the functionality of OctoPrint.
All source code is available on the GitHub page. Thanks to this, many users and developers have shared their ideas and brought them to life. User-developed plugins greatly extend the functionality of OctoPrint.
Manage multiple 3D printers
As you can imagine, this function is useful if you are working with more than one 3D printer. You can connect multiple webcams to one Raspberry Pi.
The video below provides instructions (in English) on how to install three printers on a Raspberry Pi:
Another option is to use OctoFarm, a free and open source service that allows you to control and monitor multiple 3D printers on a single Raspberry Pi. With it, you can monitor multiple 3D printers on the same screen, send files for 3D printing, and monitor the printing progress.
List of useful plugins for OctoPrint
In general, it is quite difficult to make the top 10 useful OctoPrint features, since the list is really huge. So below is a small selection of additional plugins that will help you simplify and secure the 3D printing process.
So below is a small selection of additional plugins that will help you simplify and secure the 3D printing process.
- Pushover: This plugin sends you push notifications when a print is completed or 3D print fails for some reason. A simple and very practical plugin.
- Heater timeout: It often happens that the 3D printer stays on and the extruder is still hot, which can cause a fire. This heater timeout plug-in disables hot end heating after a set amount of time. This will help you avoid potential fires and excessive electricity bills.
- Emergency stop: there is always the possibility that something might go wrong during 3D printing. This plugin adds a large red bar at the top of the OctoPrint user interface which, when clicked, will stop the 3D printer from working.
- Bed level visualizer: This plugin is great for those who have installed a bed level sensor on their 3D printer. This plugin allows you to view the table level measured by the sensor.
 In this way, you have a convenient graphical representation of your 3D printer's table, which will certainly help you with calibration.
In this way, you have a convenient graphical representation of your 3D printer's table, which will certainly help you with calibration. - Spaghetti detective: This is an extension of the Anywhere plugin that uses AI to detect 3D print fails. The plugin "knows" whether 3D printing takes the correct amount of time, and if not, notifies the user.
Perhaps that's all. This list is by no means complete, but it will surely be enough to open up new possibilities for you and optimize your 3D printing!
printing 3D model of the device and electronics control circuit with my own hands
After gaining access to a 3D printer, I decided to assemble a Qi charger with my own hands. In this tutorial, we will make a stylish wireless phone charger that is powerful enough to quickly charge modern smartphones and will respond to them by glowing LEDs.
Step 1: Model
The case was designed in Autodesk Fusion 360 and 3D printed. The top and bottom parts were printed in gray rubber, while the central part was unpainted.
Step 2: Printing
In order for the surface of the parts to be even, they were all printed at an angle. After printing was completed, all the supports were carefully detached. A little polishing brought the details to perfection. All the parts captured in the pictures above have just come out of the printer and have not yet been processed.
Important note: as you can see in the photo above, the wall of the lower part is broken. This did not happen when printing on a printer, it just could not withstand the load during assembly.
Step 3: Electronics
The most important part of our device is the wireless charger. I bought my PCB on eBay. There are three main characteristics when choosing a charging board:
- The charger must be Qi compatible. Qi technology is a near-universal standard that should charge almost all smartphones that support wireless charging.
- Three coils are much better than one. Most cheap chargers have only one coil that transmits electromagnetic energy to the phone.
 This greatly reduces the charging speed and also reduces the range of the charger
This greatly reduces the charging speed and also reduces the range of the charger - Charging indicator light. When the phone is charging from the coils, the indicator is on. In this project, we will introduce LED elements that will light up and go out while the phone is charging.
Charging circuits are rated for 5V, while the LED strips run on 12V. To use both together, I purchased a converter that steps down the 12V input to 5V. The body of the converter was larger than the specification stated, so I had to get rid of the body by covering the water sensitive areas with epoxy.
For the lighting effect I used a blue 12V diode strip. The width of the diode strip must be small enough to fit into the gap, the width of which is equal to the central part of the package printed in transparent rubber.
You will also need capacitors, transistors, resistors, relays, circuit boards or breadboards, and miscellaneous items.
Step 4: Relay/Transistor
My charging circuit contains two different types of backlight. When the phone is not charging, a current of 1.3V is applied to the red LEDs. When charging starts, the current rises to 3V, "lighting up" the blue diodes. This works great for me, as the transistors act as switches at similar current levels. To provide an audible alarm when the phone is charging, I also added a relay that makes a nice "click" when the current turns on or off. To control all the electronics, I created an unusual circuit that connected both circuits - a charging indication circuit and a 12V power supply.
When the phone is not charging, a current of 1.3V is applied to the red LEDs. When charging starts, the current rises to 3V, "lighting up" the blue diodes. This works great for me, as the transistors act as switches at similar current levels. To provide an audible alarm when the phone is charging, I also added a relay that makes a nice "click" when the current turns on or off. To control all the electronics, I created an unusual circuit that connected both circuits - a charging indication circuit and a 12V power supply.
Due to the fact that the current in the backlight circuit varies, I have the option of attaching a relay directly to the positive and negative terminals.
Step 5: LED Circuit
I don't have much circuit design experience so my circuit is not the best but it works well. Diode fading circuitry is very simple and is used to minimize the hardness of the on-to-off transition. When the voltage is applied, the brightness of the diodes quickly increases, and when the current is turned off, the diodes slowly go out and it looks very beautiful.