3D parts printer
3D Printer Spare Parts and Upgrades
Shop by category.
Build Surfaces
Nozzles
Hot-Ends
Extruders
Fans
Heatbreaks
Mainboards
Heating Cartridges
Thermistors
PTFE Tubes
FEP Film
Stepper Motors
3D Printer Enclosures
Displays
Bearings
Others
Suitable for Specific Brands
Spare Parts & Upgrades: 872 products
Sort byRelevanceBestsellersCustomer ReviewsPrice, Low to HighPrice, High to LowNew arrivalsHighest Discount
-
E3D V6 Brass Nozzle - 1.75 mm 7 diameters- Smooth finish
- High performance
- Fine details
-
3DJAKE Threaded Inserts (50-piece set) 5 Model types- Special shape for a perfect hold
- Easy installation
- Insert for various plastic parts
-
BROZZL MK8 Brass Nozzle 5 diameters- Smooth finish
- Non-stick
- High precision
-
BuildTak PEI film 32 sizes- First-class production
- Easy to apply
- Ideal with the FlexPlate system
-
E3D Ball Bearings 5 Model types- With metal cover
- Many uses
-
BondTech CHT Coated Nozzle M6 x 1.75 mm 7 diameters- Nickel plated
- Higher melting capacity
- High hotend compatibility
-
Qidi Tech Extruder 6 Model types- Original spare part
- Available for different printers
-
Creality Magnetic Build Surface 12 Model types- An original spare part from Creality 3D
- Available for various 3D printers
-
BROZZL Brass Nozzles for the CR-10S Pro 4 diameters- Smooth finish
- Non-stick
- High precision
-
Creality Hotend 23 Model types- Original spare part
- From Creality
-
E3D V6 Nozzle X - 1.75 mm 7 diameters- Extremely hard
- Unique nano-coating
- Easy cleaning
-
Antclabs BLTouch Levelling Sensor- High precision
- Works with all surfaces
- Easy installation
-
BROZZL MK8 Nozzle - Copper Plated 4 diameters- Smooth finish
- Non-stick
- High precision
-
Capricorn XS Ultra Low Friction PTFE Bowden 4 Model types- Extremely low friction
- Ideal for flexible and brittle materials
- Different sizes available
-
Micro-Swiss Direct Drive Extruder for Creality CR-10 & Ender 3 2 Model types- Dual drive gear
- Easy filament loading
- For flexible filaments
-
BROZZL MK8 Nozzle - Hardened Steel 4 diameters- Smooth finish
- Non-stick
- High precision
-
Micro-Swiss All Metal Hotend Kit for CR-10- All metal
- Better heat dissipation
- No adjustments required
-
E3D Thermistor- Easy connection
- Cartridge style
- With extension cord
-
Creality Mainboard 23 Model types- An original spare part from Creality 3D
- Available for various 3D printers
-
BondTech Drivegear Kit 1.75 mm 2 Model types- CNC machined
- Made of hardened steel
-
E3D V6 Hardened Steel Nozzle - 1.75 mm 5 diameters- Strong abrasion resistance
- Especially for abrasive filaments
- Long service life
-
Capricorn TL Transparent PTFE Bowden 4 Model types- High quality
- Different sizes
- Perfect dimensions
-
Micro-Swiss Bowden Dual Gear Extruder- Reliable and firm filament grip
- More accurate extrusion movements
- CNC precision gears
-
Noctua NF-A4x10 Fan 2 Model types- Ultra-quiet
- Premium quality
- Excellent long-term stability
All prices incl. VAT.
VAT.
Shapeways: 3D Printing Service Online
3D Printing Service
Create and customize. Streamline and save. Break down design barriers and scale your business with Shapeways 3D printing services.
Why 3D Printing?
Reduce Assembly Time
Don’t waste time putting products together! Rely on 3D printing to make complex geometries that can be printed as one piece—or consolidated in one build.
Fast Turnaround
Working on a project for a customer that has to be just right? Get models back fast, and 3D print new iterations, if needed, for final feedback and production.
Reliable Quality
Proprietary processes, expert 3D printing operators, and inspections are our secrets to delivering exceptional, quality products every time.
Parts 3D Printed
3D Printing Technologies
Materials and Finishings
Countries Shipped
Customers Served
Cutting Edge Technologies
Manufacture high-quality products in over 90 of the best materials and finishes, from plastics to metals.
HP Multi-Jet Fusion
- Nylon 12 with a smooth and finished surface
- Exhibits incredible strength, durability and stiffness
- Supports complex geometries and thin features Learn More
ExOne Binder Jetting
- Steel infused with Bronze
- Supports large parts
- Strong metal with an industrial look and feel Learn More
Our Services
Production Parts
Upload customized models for 3D printing service—ensuring durability and strength in materials that result in end-use products meant to last. Learn More
Rapid Prototyping
Take the guesswork out of product development with 3D printing services for high-performance models used in meetings, testing, and perfection of final parts. Learn More
Finishing
Whether designers prefer polishing, smoothing, dyeing–or a combination of finishing techniques–Shapeways 3D printing services can perfect those final touches with shine, gloss, and color. Learn More
Learn More
Professional Design Services
Bring your idea to life with 3D file design and optimization. Through our partnership with ZVerse, every customer has access to expert 3D Design solutions for any project need. Learn More
Rapid Prototyping
Our high quality printing enables you to assess factors such as ergonomics, usability, manufacturability, and material testing. Learn More
E-commerce Integrations
Launch your business through our marketplace by connecting to the Shapeways platform through our API, Shopify, or Etsy E-commerce Integrations. Learn More
Materials
Nylon 12 [Versatile Plastic]
Nylon 12 [Versatile Plastic] is a durable nylon plastic that can be used for a wide range of applications, both for prototyping and for end products. Printed using Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing services, when thin, it's flexible enough for hinges and springs and when thick, strong enough for structural components.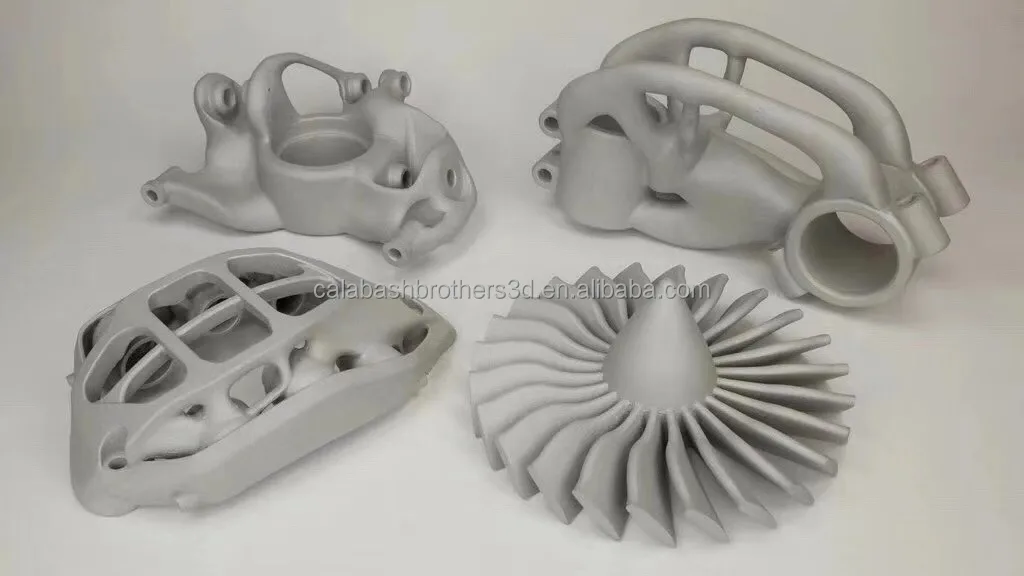 Learn More
Learn More
Accura 60
Accura 60 is a translucent and rigid acrylate-based plastic. Shapeways 3D prints this material using a large-format Stereolithography (SLA) printer capable of producing small to large parts with high resolution and detail as well as smooth surfaces with limited layer lines. Learn More
Stainless Steel 316L
Stainless Steel 316L is manufactured using ExOne’s ‘Triple Advanced Compaction Technology’ with Binder Jetting. Unlike our Steel that is infused with bronze, this material is a single alloy, composed of pure Stainless Steel. Learn More
Nylon 12
Nylon 12 (Versatile Plastic) is a durable nylon plastic that can be used for a wide range of applications, both for prototyping and for end products. Printed using Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), when thin, it's flexible enough for hinges and springs and when thick, strong enough for structural components. Learn More
Accura 60
Accura 60 is a translucent and rigid acrylate-based plastic. It is 3D printed using a large format stereolithography (SLA) printer capable of producing small to large parts with high resolution and detail as well as smooth surfaces with limited layer lines. Learn More
It is 3D printed using a large format stereolithography (SLA) printer capable of producing small to large parts with high resolution and detail as well as smooth surfaces with limited layer lines. Learn More
Stainless Steel 316L
Stainless Steel 316L is manufactured using ExOne’s "Triple Advanced Compaction Technology" with a binder jetting system. Unlike our Steel that is steel infused with bronze, this material is a single alloy, 100% Stainless steel 316L. Learn More
Testimonials
I like the ease of use in the Shapeways platform, being able to 3D print on-demand orders for the first time, and most of all–being able to scale my business. In the beginning years ago I basically had the change in my pocket and a credit line at my bank so I couldn’t order a ton of things, and you never know what’s going to sell.”
Steven Jaworski
Owner | Voytek Medical
During the process, we used Shapeways capabilities to 3D print many prototypes. That meant we had the option to iterate very quickly, print objects, and test them to see if they were working correctly in terms of complexity, or too much complexity. ”
”
Yonatan Assouline
Manager & Co-Founder | Flamingo Works
Shapeways was really great when we worked together before, which led us to reach out again. It’s been so helpful to talk with them about what we could do in every aspect of 3D printing and finishing, and it saved us a lot of time in experimentation.”
Nathan Lachenmyer
Director of Technology | Sitara Systems
I like the ease of use in the Shapeways platform, being able to 3D print on-demand orders for the first time, and most of all–being able to scale my business. In the beginning years ago I basically had the change in my pocket and a credit line at my bank so I couldn’t order a ton of things, and you never know what’s going to sell.”
Steven Jaworski
Owner | Voytek Medical
During the process, we used Shapeways capabilities to 3D print many prototypes. That meant we had the option to iterate very quickly, print objects, and test them to see if they were working correctly in terms of complexity, or too much complexity. ”
”
Yonatan Assouline
Manager & Co-Founder | Flamingo Works
Shapeways was really great when we worked together before, which led us to reach out again. It’s been so helpful to talk with them about what we could do in every aspect of 3D printing and finishing, and it saved us a lot of time in experimentation.”
Nathan Lachenmyer
Director of Technology | Sitara Systems
Previous Next
Recent Articles
Trusted by Businesses Around the World
Steel 3D Printing - A Quick Guide / Sudo Null IT News
Any metal 3D printing technology can print with steel. This is the most popular material. But which steel grades and which technology is best for your application? Will printed steel parts really be as strong and durable as traditionally made parts? nine0003
Let's see how a 3D printed steel part is revolutionizing manufacturing and opening doors to new applications in aerospace, medical equipment, automotive, tool making, heavy industry, architecture and more. In addition, more affordable desktop printers are expanding the scope and scope of real steel 3D printed parts.
In addition, more affordable desktop printers are expanding the scope and scope of real steel 3D printed parts.
Strength of steel printed parts. nine0009 Cast steel part (left), 3D printed version (center). On the right, a fully 3D printed hinge requires no assembly. (Source: Desktop Metal)
The most common question when it comes to a 3D printed metal model is "Will it be as strong as a forged or cast part?" ?". The short answer is yes... and no.
3D printed steel parts can be just as strong, and sometimes even stronger, than those made in the traditional way. It depends on many factors such as: end use, type of steel, choice of 3D printing method, post-processing and shape of the part. Also, the comparison depends on which of the strength characteristics you focus on: tensile strength, static load strength, fatigue strength, etc. nine0003
Parts printed from steel are used in the aerospace industry, for the military, and also, for example, for the manufacture of a footbridge, shown below. Therefore, the strength of printed products is beyond doubt, but let's take a closer look.
Therefore, the strength of printed products is beyond doubt, but let's take a closer look.
A 3D printed or laser powder sintered (LPBF) steel part has a finer grain structure than cast metal products. This provides better tensile strength characteristics, but in other respects the cast parts are currently still stronger. Most often, LPBF 3D printing is used to replace cast components, but in some cases, 3D printed components can replace forged parts. nine0003
One study showed that, under certain conditions, stainless steel parts made using LPBF 3D printers were three times stronger than parts made from the same steel using the traditional method.
In experiments comparing 3D printed steel parts to traditionally made steel parts, researchers create identical parts using two methods and compare their performance. However, head-to-head comparison of details is only part of the big picture. nine0003
nine0003
The main advantage of printing with steel is not only its strength, but also the unique ability to create internal channels and lattice fillings in parts, which is impossible using traditional manufacturing methods. Metal 3D printing makes it possible to produce parts faster than traditional production, since this method does not require the use of special equipment and tools, it allows you to create assemblies as a whole, eliminating the need for subsequent assembly and welding. Designing a printed part usually means that less metal is needed to make it, and therefore less weight, for the same strength. nine0003 MX3D Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) printed steel architectural support (Source: MX3D)
Steel 3D printing is also more stable and cost effective as it reduces waste. When using subtractive manufacturing methods, such as CNC machining, you make a part by cutting it out of a large one, with a lot of waste. With additive manufacturing, you only use the material you need to make the finished product. nine0003
nine0003
Steel 3D printing is not intended to replace traditional methods in all areas, but it may be a better choice for a wide range of applications. Particularly when the required parts are unique and designed for specific applications, such as rocket engines, racing cars or the oil and gas industry. 3D printing is the fastest and most flexible technology for mass production and prototype production. For military and industrial applications, steel 3D printing is a faster and more efficient way to create individual parts for vehicles and machines. Stainless steel 3D printing is rapidly finding applications in medicine to create unique surgical instruments and implants. nine0003
If you know what characteristics your final product should have (tensile strength, compressive strength, hardness, density, etc.), then all these parameters can be incorporated into the product at the production stage.
Types of steel for 3D printing
Metal powder is the most used metal material for 3D printing (Source: GKN Additive) There are thousands of different grades of steels and alloys with different mechanical properties, used in traditional manufacturing but in 3D printing there are only a few dozen of them, and some of them are unique, created specifically for this technology. Among the steel options, the following can be distinguished:
Among the steel options, the following can be distinguished:
-
Stainless steel (316L, 304L , 17-4PH, 15-5PH, 420, 254, Ph2, GP1, 630, 410).
-
Tool steel (D2, M2, h23, h21, MS1, 1.2709).
-
Low alloy steel (4140).
-
Structural alloyed (20MnCr5).
Recently, unique alloys have been developed specifically for 3D printing, designed to solve the problems that occur with classical production methods. nine0003
For example, 3D printer manufacturer Desktop Metal released a patented stainless steel in 2022 that the company says combines the tensile strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance of 13-8 PH stainless steel, combined with the hardness low alloy steel like 4140. The company says customers can go to market with this material and skip the galvanizing step to protect products from corrosion.
ExOne offers two special blends of steel and bronze that the company says allows 3D printed steel parts to achieve increased corrosion resistance while being easy to machine and polish. nine0003
nine0003
While most of the metal powders used in 3D printing are similar to those used for other manufacturing methods, their numbers are on the rise as more companies adopt the technology. Some metal powder manufacturers, such as GKN, also make custom powders for specific 3D printing applications.
How to print with steel
The strength, properties and applications of 3D printed steel products largely depend on which 3D printing technology you use. Some methods produce stronger parts, other methods provide better hardness or abrasion resistance, and some technologies are simply very fast. nine0003
Below are the main metal 3D printing methods, their properties and some of the most common application examples.
Fused Deposition Printing (FDM)
BCN3D's Epsilon printer extrudes metal filament from stainless steel (Source: BCN3D) as more printer manufacturers certify metallic filaments for use on their printers, such as Ultimaker, BCN3D, Makerbot, Raise3D. Raise3D has recently released a complete metal printing suite - Metalfuse (3D printer, debinding oven and sintering oven). This method is still much more popular for printing plastics, but with new plastic filaments filled with stainless steel powder, strong metal parts can be produced. nine0003
Raise3D has recently released a complete metal printing suite - Metalfuse (3D printer, debinding oven and sintering oven). This method is still much more popular for printing plastics, but with new plastic filaments filled with stainless steel powder, strong metal parts can be produced. nine0003 FDM media was once limited to thermoplastics. Companies like BASF Forward AM and The Virtual Foundry now offer metal filaments that can be used on almost any FDM printer as long as it has a hardened steel nozzle for abrasive media.
These materials are approximately 80% metal and 20% plastic. After printing, the post-processing process removes the plastic, resulting in 100% metal parts. nine0003
Due to the removal of the bonding plastic, FDM metal parts shrink during post-processing. The amount of shrinkage is constant and can be taken into account in CAD systems, which allows to obtain relatively accurate finished parts.
Forward AM's 316L Stainless Steel Ultrafuse filament produces finished parts with material properties that the company claims are comparable to injection molded metal parts. nine0003 (Source: BCN3D)
nine0003 (Source: BCN3D)
While 3D printing with metallic materials may not be suitable for demanding applications such as aerospace, the economics of producing simple metal components without critical loads on an affordable FDM printer can outweigh the impossibility of applying them in some areas.
Metal prototype parts and finished parts that will not be subjected to extreme stress are ideal uses for this technology. nine0003
Bound Metal Deposition (BMD)
Desktop Metal's Studio System 3D printer used bonded metal bars that were extruded layer by layer to form a metal part (Source: Desktop Metal) Similar to FDM, Metal mesh deposition method (BMD) or bonded powder extrusion (BPE) is a 3D printing process based on extrusion. This method uses bonded metal rods or bonded powdered metal filaments, which consist of a much higher percentage of metal powder than the filaments used in FDM. As with FDM, post-treatment to remove the binder and heat treatment in a final sintering oven are required.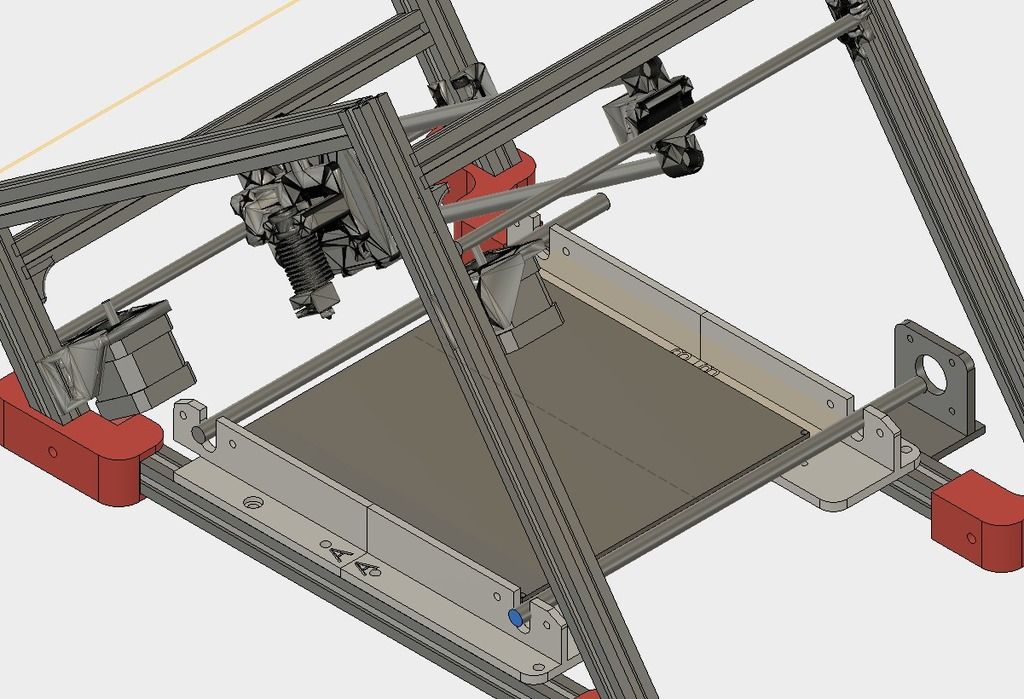 nine0003
nine0003
There are only a few 3D printers using this method such as Desktop Metal, Markforged and more recently 3DGence, but more companies are entering this market, so stay tuned. These printers are valued as a convenient solution for office 3D metal printing, they are more expensive than most FDM printers, but cheaper than the powder-based metal 3D printing technologies described below.
These printers use their own proprietary filament. Desktop Metal and Markforged offer four types of steel. nine0003
Ideal niches for this technology are metal prototype parts, where it is necessary to test the functionality of a part before mass production using traditional methods. Popular applications are molds, punching dies, nozzles, impellers, fasteners and heat exchangers.
For example, Shukla Medical uses Markforged's Metal X printer to print steel prototypes of its orthopedic implant removal tools. nine0003
Laser powder sintering.
Laser powder sintering technology uses one or more lasers to melt powdered metal into a desired shape layer by layer (Source: GE Additive) metal printing. This technology is used by 80% of all metal 3D printers on the market.
This technology is used by 80% of all metal 3D printers on the market. This method uses powerful lasers to selectively sinter metal powder layer by layer. nine0003
LPBF 3D printers are available in a wide range of sizes, prices and laser powers. These and other characteristics affect the properties of the finished part, print speed and other parameters of the finished products.
Steel and steel alloys are the most popular material for LPBF equipment and, unlike FDM and BMD, metal powders are commercially available as they are most commonly used in traditional production methods.
LPBF is a technology that maximizes the quality of a 3D printed part. Applications include aerospace components such as monolithic thrust chambers, rocket engine components and heat exchangers, molds, tools and other applications, as well as high wear parts and surgical instruments. nine0003
Binder Jetting
Binder 3D printing technology uses metal powder and a binder to form metal parts (Sorrce: ExOne) binder, and not with a laser. During post-processing, the binder is removed.
During post-processing, the binder is removed. Binder application stands out for its high printing speed compared to other 3D printing methods or traditional manufacturing, and metal parts made with this technology have material properties equivalent to those made by metal injection molding. nine0003
The number of manufacturers producing metal-bonded inkjet 3D printers is much smaller than that of LPBF machines. Leading manufacturers include ExOne, Desktop Metal, Digital Metal, GE Additive and HP.
Binder blasting is ideal for medium to high volume production of metal tools and spare parts.
In fact, HP claims that its Metal Jet 3D printer was designed specifically for mass production of 316L stainless steel products. HP has partnered with Parmatech to produce metal parts for the medical industry. Pennsylvania-based ExOne uses this technology to manufacture hard metal cutting tools and tool steels. nine0003
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
(Source: GE Additive) Electron Beam Melting (EBM) is another powder cladding technology.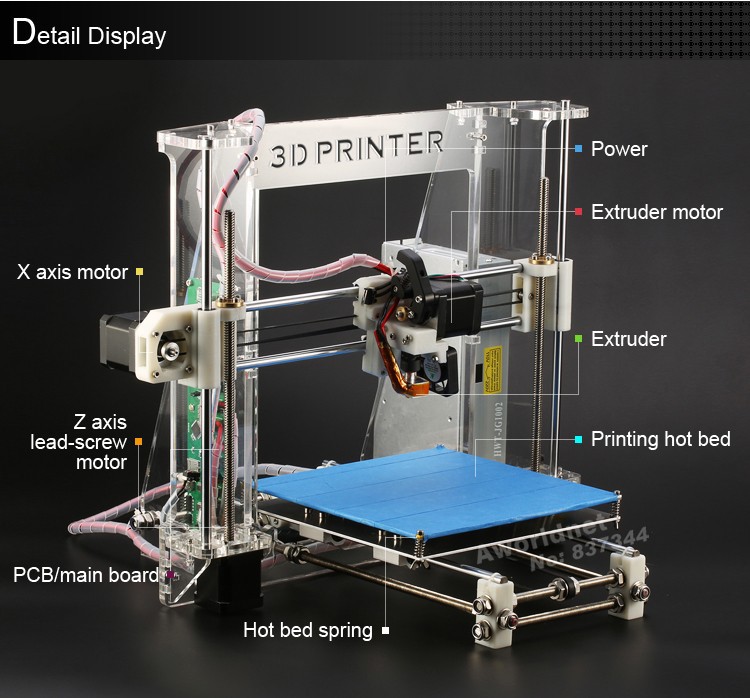 It works in a similar way to selective laser melting (SLM), but instead of using a laser as the energy source, it uses a much more powerful beam of charged particles.
It works in a similar way to selective laser melting (SLM), but instead of using a laser as the energy source, it uses a much more powerful beam of charged particles.
The recoater moves the powder onto the printing plate and an electron beam selectively melts each layer of powder. After each layer is printed, the plate is lowered and another one is applied on top of the previous layer. nine0003
EBM can be much faster than SLM, but SLM produces smoother and more accurate pieces. The electron beam is wider than the laser beam, so EBM cannot produce the same precise parts as SLM. Another difference is that the manufacturing process takes place in a vacuum chamber, which reduces the amount of impurities in the material that can lead to defects. That is why EBM is often chosen for printing components for the aerospace, automotive, defense, petrochemical and medical implant industries. nine0003
Titanium is the most popular metal for most EBM applications, however steel can be used.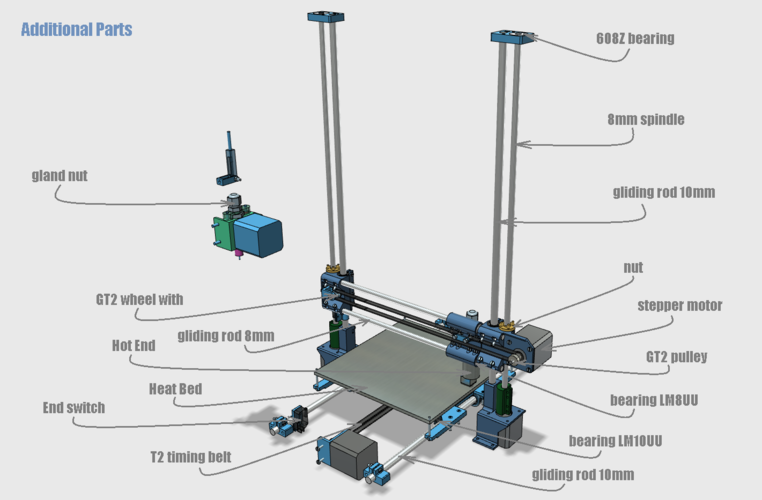
Cold Spray
(Source: Impact Innovations)Cold spray 3D printing is done by injecting metal powders through a jet nozzle into a supersonic stream of pressurized gases such as air, nitrogen or helium. The process is called "cold" because the metal particles do not melt, but hit the metal substrate and adhere to its surface during the so-called plastic deformation. nine0003
Cold spray printed products are not prone to porosity, thermal cracking and other defects associated with melt-based technologies. This method has several advantages over other production methods. The technology is used in the military and aerospace industries around the world. For example, the US Army uses cold spray to repair the mounts of a worn Bradley 25mm steel turret gun.
In the automotive industry, cold spray steel is used for crash repairs because the high strength steel substrates in cars can be susceptible to thermal repair methods such as welding. nine0003
Direct Energy Deposition (DED) and Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM)
WAAM Steel Parts from MX3D (Source: MX3D) Direct Energy Deposition (DED) uses welding powder or wire that enters through a nozzle and is fed into the power source to melt the metal. A melt region is created and applied to the substrate. DED is a new process, reminiscent of an old building technology known as "cladding", in which a coating is applied to a substrate, often for thermal insulation or weather resistance. DED is useful for fabricating large objects as a whole, as well as complex geometries that require extensive machining. DED can get such parts much closer to finished than traditional CNC machining. nine0003
A melt region is created and applied to the substrate. DED is a new process, reminiscent of an old building technology known as "cladding", in which a coating is applied to a substrate, often for thermal insulation or weather resistance. DED is useful for fabricating large objects as a whole, as well as complex geometries that require extensive machining. DED can get such parts much closer to finished than traditional CNC machining. nine0003
Because DED uses a coating process, it can be used to add complex geometries to existing steel parts, thus combining complexity with cost reduction. For example, the French company AddUp advertises a rocket nozzle that uses a preformed large 304 stainless steel hopper cone printed with an isogrid structure, usually made from a larger piece by traditional methods.
A technology related to DED is wire-arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Instead of powder, WAAM uses a metal wire that is melted by an electric arc. The process is controlled by robotic arms.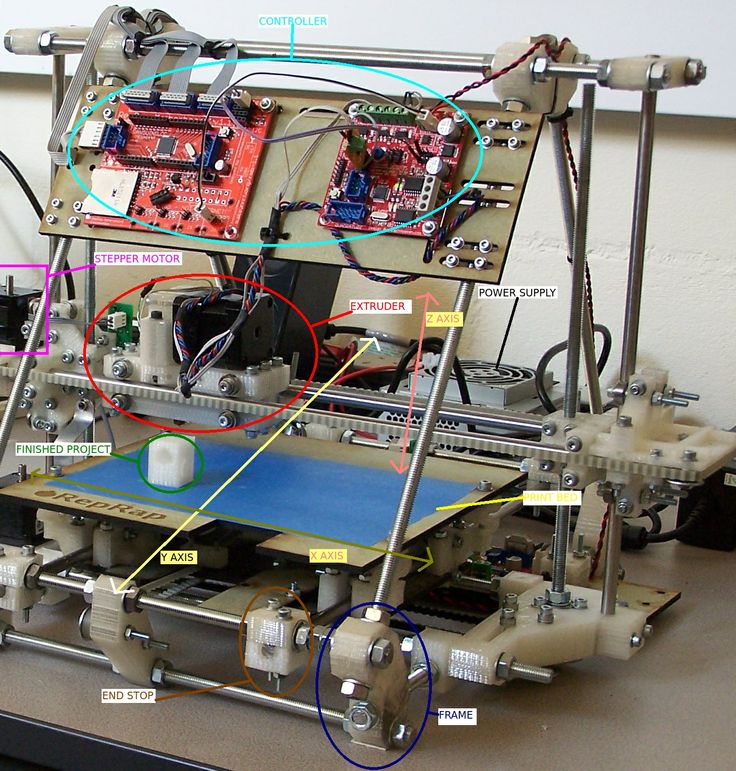 WAAM is also capable of producing large-sized metal parts, as demonstrated by the Dutch company MX3D and its nine thousand-pound 41-foot stainless steel bridge in Amsterdam, as well as an oil and gas equipment repair part, proving that parts can be made in the field. nine0003
WAAM is also capable of producing large-sized metal parts, as demonstrated by the Dutch company MX3D and its nine thousand-pound 41-foot stainless steel bridge in Amsterdam, as well as an oil and gas equipment repair part, proving that parts can be made in the field. nine0003
Micro 3D printing
Micro parts printed from steel (Source: 3D MicroPrint)Micro scale additive manufacturing, or micro 3D printing, can produce products with a resolution of a few microns (or less). There are three micro 3D printing methods to produce metal parts.
LMM (lithography-based metal fabrication) is a light-based technology that creates tiny parts from raw materials, including stainless steel, for applications such as surgical instruments and micro-mechanical parts. nine0003
Electrochemical deposition is the latest micrometal 3D printing process developed by the Swiss company Exaddon. In this process, the printing nozzle applies liquid with metal ions, creating details at the atomic level.
A third micrometal 3D printing method is microselective laser sintering, in which a layer of metal nanoparticle ink is applied to a substrate, then dried to produce a uniform layer of nanoparticles.
German researchers have successfully tested micro SLS printing of hollow microneedles using 316L stainless steel. nine0003 Metal parts from 3D Systems, Desktop Metal, MX3D and Materalise.
Techno Print 3D Company
This is our first review of the most popular and inexpensive 3D printers for 2020. The list will include the best-selling devices in two price ranges (up to 30 tr and up to 60 tr). Printers working with both plastic filament (FDM) and photopolymers (LCD/DLP) will be presented. This list will always be up to date, as it is periodically updated and supplemented. Read more→
The Chinese company Dazz3D announces the launch of the project on KickStarter and accepts pre-orders for Dazz3D Basic and Dazz3D Pro 3D printers. These revolutionary new devices are aimed at both the professional and amateur markets. Read more→
Read more→
We all know that precise calibration of the 3D printer desktop is the foundation and the key to successful printing on any FDM printer. In this article we will talk about the main and most popular ways to level the "bed". So, as mentioned above, 3D printing without desktop calibration is impossible. We face this process Read more→
It's hard to go through a day today without hearing about 3D printing technology, which is bursting into our lives at an incredible speed. More and more people around the world are becoming addicted to 3D printing technology as it becomes more accessible and cheaper every day. Now almost anyone can afford to buy a 3D printer, and with the help of Read more→
The FormLabs Form 2 and Ultimaker 3 are perhaps the most popular 3D printers today, capable of high quality printing with incredible surface detail. Moreover, these two devices use completely different technologies, and therefore, there are a lot of differences between them.