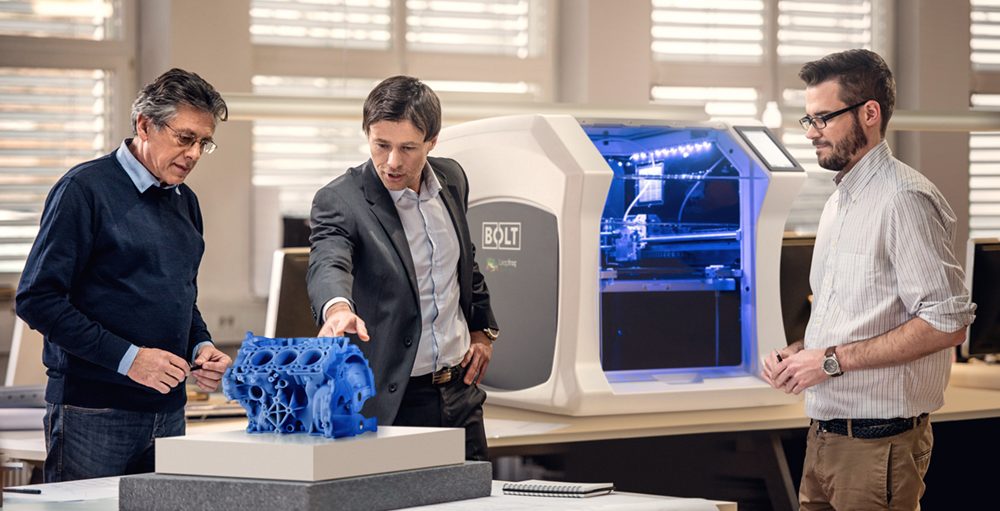
3D print engineering
Making it work: 3D printing and engineering
Adam Kohut12 December 2019
Applications
Engineering is about creating designs that work as efficiently as possible. Wasted time is wasted money, and to have a project stall because of an unforeseen design flaw or a delay in the supply chain can be as frustrating as it is costly. That’s why control is so valuable – control of your time, control of your costs, control of your entire process. And 3D printing is all about control.
Using 3D printing, engineers can create new prototypes – even those with complex internal structures and geometries – address problems, and find solutions, without ever leaving their working environments. The right 3D printer holds the potential to shrink development time from months to days, encourages collaboration between peers, and enables the creation of rapid prototypes and end-use parts – ensuring that projects are finished on deadline, within budget, and bring about desired results.
Design flexibility
When creating custom parts for small bore motorcycles, engineers at MNNTHBX (Man in the Box) know that the design and testing phases both have the capacity to be time-consuming and expensive, especially when using materials such as aluminum.
Using Ultimaker 3D printers, MNNTHBX is able to increase the flexibility of its designs and improve product test phases. It has also seen a marked increase in its return on investment, saving upwards of $1,000 per printed part.
A 3D print mounted on a part created by small-bore motorcycle parts manufacturer MNNTHBX
“Our printer basically paid for itself the first time we saw a product through prototyping. Being that we prototype roughly 15 products annually, the cost savings become apparent,” Greg Hatcher, Owner of MNNTHBX, said. “3D printing on Ultimaker mitigates risk and opens the door to creating working concepts on extremely low investment. Long gone are the days of spending thousands of dollars running multiple prototypes through traditional CNC machining methods. When we take a design to the machine shop, we know before we start that it’s a fully functional design meeting our standards.”
Proof of concept
It’s one thing to create a bold new design – it’s another entirely for that design to work as intended.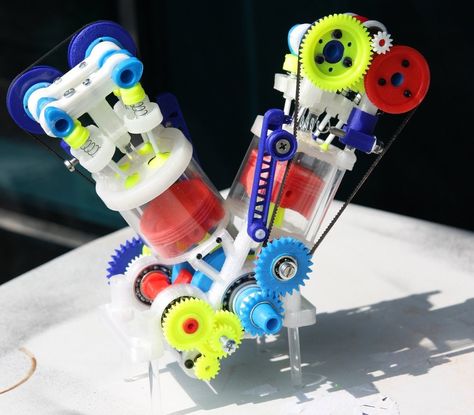 Sending those designs into space adds an additional level of complexity. Honeybee Robotics has contributed critical planetary analysis technology incorporated into three of NASA’s Mars mission, including planetary drills and sampling systems on the Curiosity rover.
Sending those designs into space adds an additional level of complexity. Honeybee Robotics has contributed critical planetary analysis technology incorporated into three of NASA’s Mars mission, including planetary drills and sampling systems on the Curiosity rover.
Honeybee Robotics’ projects demand complex, load-bearing metal parts that can survive harsh environments. Using 3D printing, engineers were able to quickly and cheaply test concepts and establish project parameters, rather than relying fully on methods of outsourced fabrication, which were slower and more costly.
A soil scooper partially created with 3D printing by Honeybee Robotics
“A lot of what we do is to build subsystems and then test their performance,” says Yoni Saltzman, Project Engineer, said. “How fast they are, things like that. So physically building key elements of the robot is what the printer allows us to do cheaply and quickly.”
End-use parts
At a Heineken brewery in Seville, Spain, Ultimaker printers are used to create parts in-house, which are then implemented on its bottling line, replacing metal parts that are heavy, and tend to knock bottles over.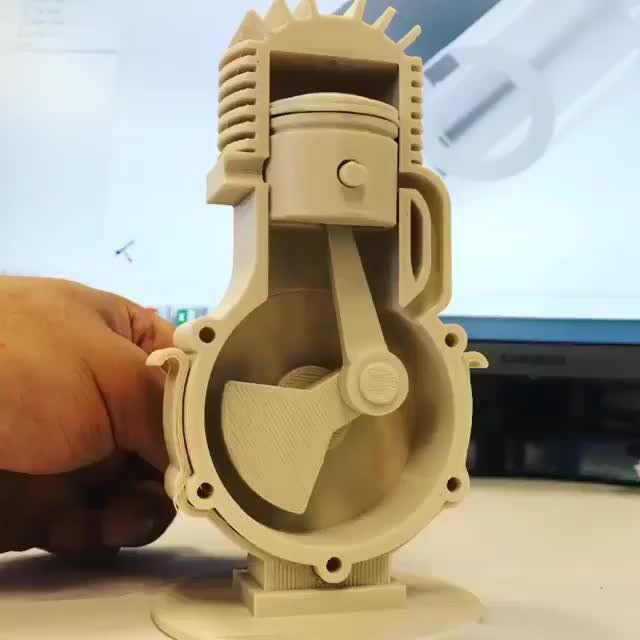 The redesigned 3D printed parts are lighter and cheaper alternatives, and now play active roles in Heineken’s manufacturing environment.
The redesigned 3D printed parts are lighter and cheaper alternatives, and now play active roles in Heineken’s manufacturing environment.
“3D printing has proven to be a technology that helps us, brings value to us, and enables our people to work more efficiently,” Juan Padilla, Packaging Manager at the plant, said.
Watch the videoLow-volume production
3D printing can also play a part in low-volume production of complex parts. IMI Precision Engineering is a world leader in motion and fluid control technologies. It needed a new additive manufacturing technique that would allow the creation of geometrically complex parts. By turning to 3D printing and the Ultimaker S5, the firm saved thousands of dollars in part creation – and nearly 2,000 hours per year in labor.
A finished complex print created by IMI Precision Engineering
“The Ultimaker S5 offered the best value, with the size and materials we needed to print all the parts,” Kathryn Jones, an IMI Graduate Engineer, said.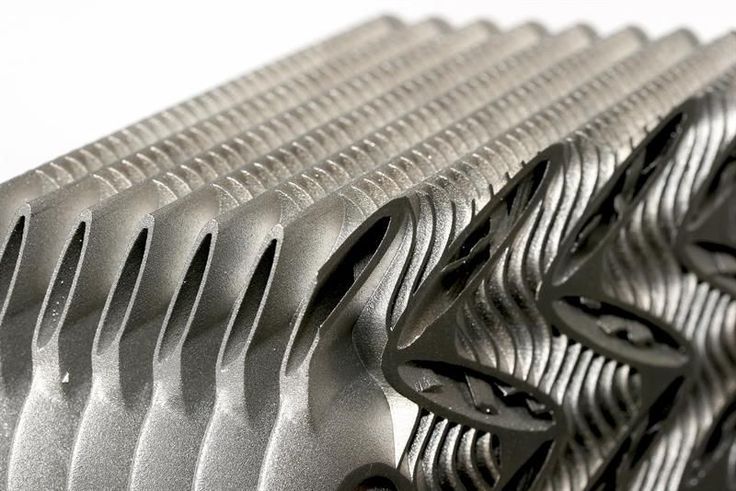 “It added new capability to another 3D printer that we had purchased last year, with lower costs for low volume parts and improved manufacturing efficiency.”
“It added new capability to another 3D printer that we had purchased last year, with lower costs for low volume parts and improved manufacturing efficiency.”
Ready to introduce 3D printing into your workflow?
Discover Ultimaker 3D printers
Engineering-Grade 3D Printers | MatterHackers
- Home
- Store
- 3D Printers
- Engineering-Grade 3D Printers
Exacting and accurate 3D printers that can 3D print with a variety of advanced materials to achieve their prototyping and production needs. These 3D printers are also capable of reaching temperatures of up to 400°C for robust material applications. For companies and businesses looking to get started in additive manufacturing and prototyping with 3D printing, while using advanced materials like PEI, PEEK, Polycarbonate, polypropylene and carbon-infused nylons like NylonX, these 3D printers are an excellent choice.
Engineering-Grade 3D Printers Collections
All Engineering-Grade 3D Printers 3D Printers
Engineering-Grade 3D Printers
Ultimaker
Professional, engineering-grade 3D printers for rapid digital manufacturing.
Intamsys 3D Printers
3D Printers capable of printing high-performance functional materials.
MakerBot
High-performance, reliable, tinker-free 3D Printers
Raise3D
All Raise3D products: 3D printers, nozzles, filament, parts, etc
BCN3D
Accurate & Reliable IDEX 3D Printers and branded filament and accessories
LulzBot 3D Printers
Open-Source, Robust 3D Printers
MakerGear 3D Printers
Precise, Compact 3D Printers
Guides & Articles
How to Succeed with Quantum Dichromatic PLA Filament
Follow this guide for tips and tricks on how to get the best results when 3D printing with Quantum Dichromatic PLA filament.
How To Succeed with LayerLock SLA Build Surfaces
Successfully achieve strong bed adhesion for Laser, DLP, and SLA resin prints using LayerLock SLA Resin 3D Printing Build Surfaces.
How To Build A Successful Makerspace
Find out the necessary components to create an effective space for your maker community.
How to Succeed When 3D Printing with Polypropylene
Successfully produce 3D printed parts out of polypropylene filament with these tips on achieving stronger bed adhesion and minimizing shrinkage.
Tech Breakdown and How to Succeed: Ionic Hybrid Support Material
Supporting engineering-grade filament has been difficult without a support material dedicated to higher temperature 3D printing. Ionic aims to solve that.
How To Succeed with OBC 3D Printing Filament
From Dow Chemical, OBC combines flexible and rigid into one unique material with properties of both.
How To Succeed with LayerLock Garolite Build Surfaces
Successfully achieve strong bed adhesion for NylonX, NylonG, and standard filaments using LayerLock Garolite Build Surfaces.
How to Succeed with LayerLock Powder Coated PEI Build Plates
Powder coated PEI steel sheets are a great alternative build surface for strong bed adhesion. Here's how you can succeed using this durable build plate.
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With Nylon
Learn how to 3D print Nylon like a pro. Nylon is a stronger and more durable alternative to PLA or ABS and easy to 3D print with using these Tips and Tricks.
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With ASA Filament
Follow this step-by-step guide to learn how to print with ASA, the perfect material for any outdoor projects.
What is 3D printing and how it can be used! Interesting!
What is 3D printing
3D printing technology was patented in the 80s of the last century, but gained popularity relatively recently. New, promising techniques have been developed and the possibilities of 3D technologies have reached a completely new level. However, to this day, the technique is not known in all circles, and not everyone is aware of what 3D printing is. In today's article, we will try to explain in detail and in an accessible way what 3D printing is and where it is used. nine0005
However, to this day, the technique is not known in all circles, and not everyone is aware of what 3D printing is. In today's article, we will try to explain in detail and in an accessible way what 3D printing is and where it is used. nine0005
In short, 3D printing is a technique for manufacturing three-dimensional products based on digital models. Regardless of the specific technology, the essence of the process is the gradual layer-by-layer reproduction of objects.
This process uses a special device - a 3D printer, which prints certain types of materials. More details about it are written here. Other names for the technology are rapid prototyping or additive manufacturing. Often the phrase "additive technologies" is used in the meaning of "3D technologies". nine0005
3D printing steps
To make it clearer what 3D printing is, let's take a look at the playback process step by step. Below are the specific stages of 3D printing. How it works:
- 3D modeling of the required object is performed according to certain rules;
- The file with the digital model is loaded into the slicer program, which generates the control code for the 3D printer;
- Sets required 3D printing options;
- The code is written to a removable memory that connects to the 3D printer; nine0015
- 3D model reproduced.

Objects are reproduced gradually. According to the required shape, the selected material is applied layer by layer, forming the finished product. It is worth noting that the possibilities of 3D printing are almost limitless, that is, anything can be made. In some technologies, very thin overhanging elements are provided with supports, thanks to which they can be avoided from sagging.
Naturally, this is a very simplified description of the stages of 3D printing, but they give a very clear idea of the essence of the technique. nine0005
Other questions and answers about 3D printers and 3D printing:
- Basics What is 3D scanning?
- Basics What is a 3D model?
3D Printing Technologies
Different 3D printing technologies are used to reproduce different objects. They differ both in the consumables used, and in the speed and accuracy of printing. Here are the main 3D printing technologies:
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM) .
 One of the most common 3D printing technologies, used in most desktop 3D printers, and represents an ideal price / quality ratio. Printing occurs by layer-by-layer supply of a thread of molten plastic;
One of the most common 3D printing technologies, used in most desktop 3D printers, and represents an ideal price / quality ratio. Printing occurs by layer-by-layer supply of a thread of molten plastic; - Laser stereolithography (SLA) . The formation of the object occurs due to the layer-by-layer illumination of a liquid photopolymer resin by a laser, which hardens under the influence of radiation. One of the variations of this technology is DLP 3D printing. It uses a special projector instead of a laser. Both 3D printing methods are used to create objects with a high degree of detail. In the case of DLP printing, speed is also an added advantage; nine0015
- Selective laser sintering (SLS) . Reproduction is performed by layer-by-layer melting of a special powder under the action of laser radiation. This 3D printing method is widely used in the industry for the manufacture of durable metal elements
3D Printing Applications
As you may have guessed by now, 3D printing is extremely versatile. The second name of the technology - rapid prototyping - speaks for itself. In the manufacture of prototypes and models of models, 3D printing can be simply indispensable. It is also a very cost-effective solution for small-scale production. In the aerospace and automotive industries, 3D technologies are already being used with might and main due to the high profitability and speed of manufacturing components. Culinary professionals are working on the development of 3D food printers, and in medicine, 3D printing has become something of a technology of the future. With the help of 3D bioprinting, it is planned to produce bones, organs and living tissues, but for now, implants and full-fledged medicines are printed on 3D printers. Desktop 3D printers can be used for domestic purposes: for repairs, making various household items, and so on. And designers, fashion designers, sculptors and artists appreciate the possibilities of 3D printing and 3D modeling as an unusual way to realize their talent.
The second name of the technology - rapid prototyping - speaks for itself. In the manufacture of prototypes and models of models, 3D printing can be simply indispensable. It is also a very cost-effective solution for small-scale production. In the aerospace and automotive industries, 3D technologies are already being used with might and main due to the high profitability and speed of manufacturing components. Culinary professionals are working on the development of 3D food printers, and in medicine, 3D printing has become something of a technology of the future. With the help of 3D bioprinting, it is planned to produce bones, organs and living tissues, but for now, implants and full-fledged medicines are printed on 3D printers. Desktop 3D printers can be used for domestic purposes: for repairs, making various household items, and so on. And designers, fashion designers, sculptors and artists appreciate the possibilities of 3D printing and 3D modeling as an unusual way to realize their talent. nine0005
nine0005
Well, that was a brief description of what 3D printing is. We hope we were able to provide the necessary information in an accessible way. If you have additional questions that we have not covered, write to us by e-mail and we, if necessary, will add your questions! Best regards, 3DDevice team.
We also want to remind you about the possibility to order 3D printing, 3D scanning, 3D modeling services or purchase of related equipment and consumables with delivery throughout Ukraine in 3DDevice. If you have any questions, please contact us at one of the phone numbers listed here. We look forward to collaborating! nine0005
Return to the main page
3D printing on order in Nizhny Novgorod, cost of services
The cost of printing on a 3d printer allows you to use the service not only for commercial and state enterprises, but also for individuals - innovative production technologies have become widely available. Prototyping of 3d models is the reading of information from a computer program by special equipment and translation into a real object by successive building up layer by layer until the formation of a finished product. ProPlast-NN LLC carries out 3d printing to order - the price of is calculated individually depending on the size of the object, the number of ordered samples, the material from which they will be made and the method of prototyping.
ProPlast-NN LLC carries out 3d printing to order - the price of is calculated individually depending on the size of the object, the number of ordered samples, the material from which they will be made and the method of prototyping.
3d printing and prototyping - the latest technologies in practice
The combination of computer technology with production allows you to multiply the speed of production, reduce the cost of creating the necessary items. Volumetric printing is developing at a rapid pace, from the realm of fantasy, it has become a familiar production process, which can be carried out using various methods. Order 3d printing in Nizhny Novgorod for one model or batch of products, just call Pro Plast-NN LLC at the numbers listed on the site. The customer will receive a three-dimensional plastic part, made with a high degree of accuracy according to the drawings or based on a real analogue. Small-scale production of products by 3D printing and prototyping is possible.
Where created 3d models and prototypes are used
Prototyping on 3d printers allows you to quickly and at low cost get a sample of the desired part from a polymer material, made with a high degree of accuracy, without roughness or distortion. Depending on the technology used and the material from which the sample is made, the product acquires high-tech properties: ideal shape, strength, plasticity, temperature stability. Models have found application in many areas, so they make custom 3d printing companies of different specializations:
- medicine;
- automotive;
- serial industrial production: mechanical engineering, instrumentation, metallurgy;
- architecture - when creating models of buildings and complexes;
- designs;
- souvenir production.
How 3d prototyping is carried out
The basis for prototyping is a 3d image of an object, compiled by a computer program with three-dimensional modeling functions. nine0046 3d custom prototyping is performed with high accuracy of transferring an image into a physical object using one of several possible methods:
nine0046 3d custom prototyping is performed with high accuracy of transferring an image into a physical object using one of several possible methods:
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling). A moving molten polymer thread forms an object of complex geometric shape in layers, which can subsequently withstand high mechanical and thermal loads.
- SLS (Eng. Selective Laser Sintering). This is the sintering of a powder in a container under the targeted action of a laser beam. nine0015
- MJM (from the English. Multi Jet Modeling - modeling with many nozzles). Multi-nozzle 3d printer prototyping , applying molten material with multiple inkjet heads, based on the principle of a laser printer.
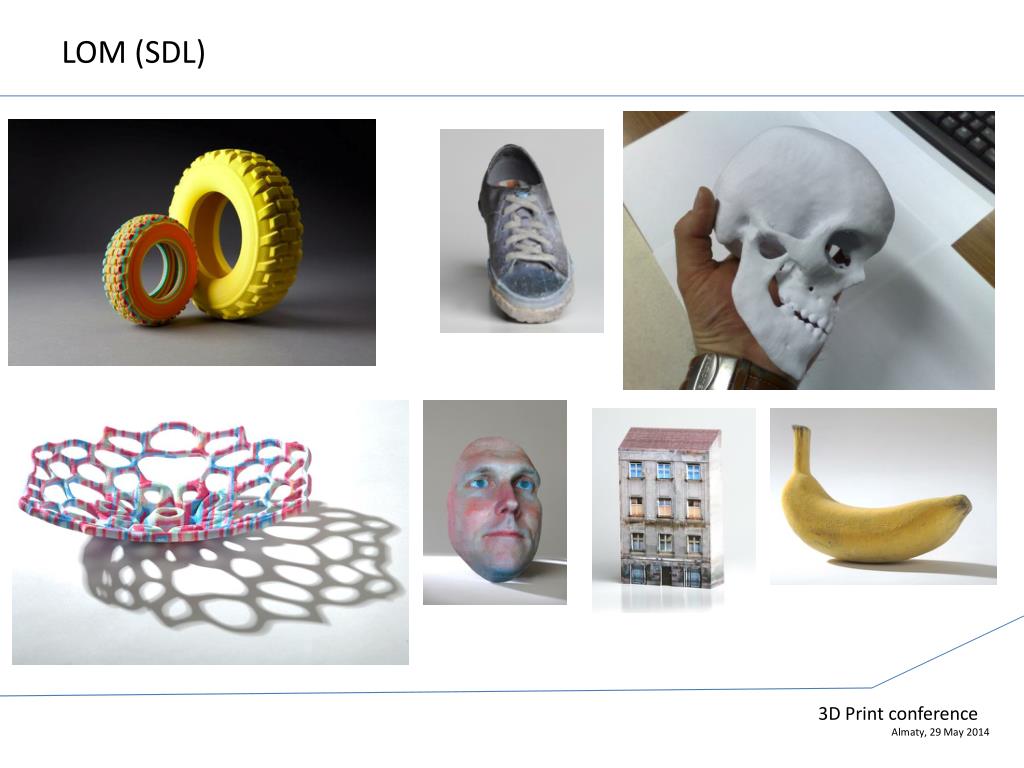
- LOM (from the English Laminated Object Manufacturing - the production of an object by lamination). Bonding layer by layer of thin films, as is done with lamination. After reaching the desired volume with a laser tool, an object of the desired shape is cut out of the mass.
 nine0015
nine0015 - SLM (from English Selective Laser Melting - selective laser melting). Selective fusion of metal with a targeted laser beam, resulting in a solid object.
- EBM (from the English Electron Beam Melting - electron beam melting). Creation of a product from a powder that is melted by a directed electron beam.
- STL (from English stereolithography - stereolithography). Purposeful formation of a solid object by a laser beam directed into a container with liquid polymer rubber. nine0015
Benefits of 3d printing and prototyping
What are the advantages and benefits for a customer who decides to order a 3D printing with a printer?
Before launching a new product into mass production, an enterprise can purchase a prototype, test it, make changes to avoid errors in the design development of the product, and reduce the cost of production.
If a private or public enterprise needs to produce a small batch of products, it is more profitable for him to apply for a small-scale prototyping service than to carry out design and engineering development and testing of prototypes, reconfigure production, use labor resources and equipment. nine0046 Printing on a 3D printer at affordable prices will save businesses a significant amount, reduce production costs.
nine0046 Printing on a 3D printer at affordable prices will save businesses a significant amount, reduce production costs.
The desired samples can be obtained in a short period, regardless of the degree of complexity of the object being created. Typically, the prototyping process lasts from one to ten days, depending on the specifics of the chosen manufacturing method. You can place an order for 3D printing at Pro Plast-NN LLC - we will answer your questions, calculate the cost, conclude an agreement and print products in a short time. nine0005
The cost of 3d printing with the printer is low, which allows customers to reduce their own costs for design development, testing and sample production. LLC "Pro Plast-NN" makes high-quality 3D printing - the price is calculated by managers individually, depending on the volume, complexity of the work, the chosen manufacturing method and the material from which the sample is printed.
The cost of prototyping and creating 3d models
Answer to question how much it costs to print on a 3d printer depends primarily on the number of ordered products, the material from which the product is made, the size of the object, and the technology of its manufacture.