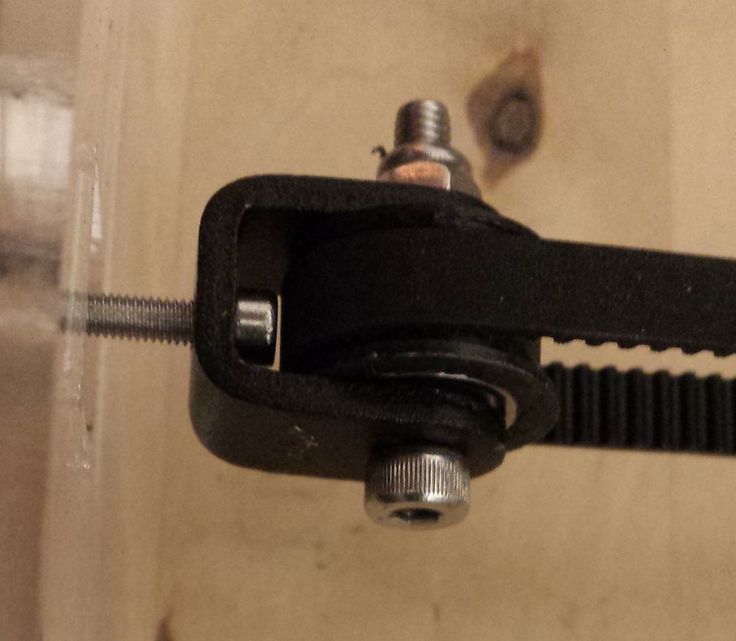
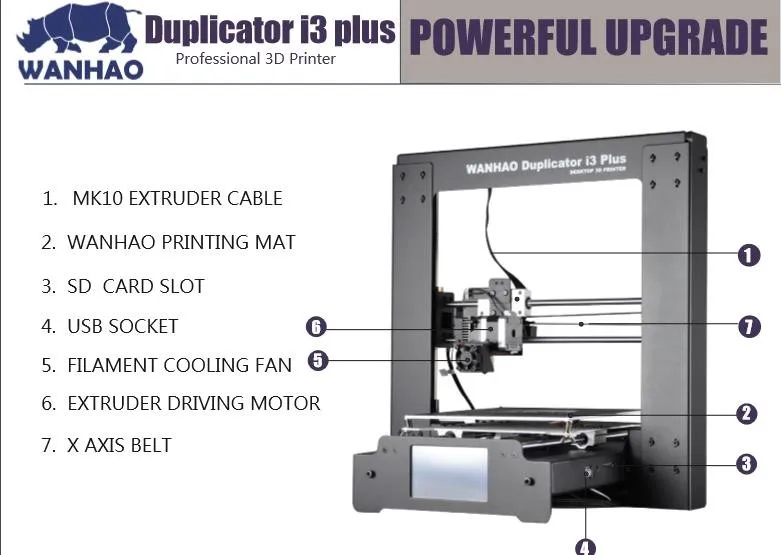
Zeropi 3d printer
3ders.org - ZeroPi, Arduino & Raspberry Pi compatible dev kit for 3D printers, surpasses Kickstarter goal
Oct 14, 2015 | By Benedict
The Kickstarter campaign for ZeroPi, an exciting new 3D printing gadget, has far surpassed its $5,000 target, reaching almost $30,000 with 24 days left to go. The ZeroPi, which customers can get their hands on for a mere $24 pledge, is an Arduino Zero Compatible development kit for robotic motion structure systems and 3D printers.
The ZeroPi has been designed to work with 3D printers, CNC mills, tracked mobile robots and more besides. The gadget has specially designed M4 holes, which enables its compatibility with Makeblock Aluminum mechanical parts. This allows designers to use the ZeroPi for a variation of open-source hardware or robotics projects. The ZeroPi has an MCU comprised of an Atmel SAMD21J18 and 32-bit ARM Cortex M0+, which is fully compatible with the official Arduino Zero, Raspberry Pi and other robot drive hardware.
The team behind the ZeroPi are emphasising its 3D printing potential, calling it the “next generation mainboard for [the] 3D printer”. The developers have already successfully ported the Marlin and Repetier firmware to ZeroPi for use with I3 and Delta open-source 3D printers. These open-source 3D printers can now be directly controlled by the ZeroPi without the need for an expansion board. The ZeroPi team claim that their device is four times faster than the Mega2560, as well as being cheaper and smaller.
The aim behind the ZeroPi project is to increase usability and provide a cost-effective solution for makers working on a range of projects. “We want to create the opportunity for makers and professionals to use boards capable of printing high mesh objects and easy to use open source motherboard,” the team explain on their Kickstarter page. “Our ambition is to advance the entire community through an open-source motherboard with creativity and innovation. We hope ZeroPi can be useful to as many people and projects as possible.”
We hope ZeroPi can be useful to as many people and projects as possible.”
The ZeroPi Kickstarter campaign is already a massive success. Having set a target of $5,000, the project has already received close to $30,000 in pledges. The team are offering a range of incentives to potential backers: All 200 Early Bird ZeroPi devices have been snapped up, but there are still plenty of standard-price $24 (a steal!) ZeroPi devices available. More dedicated users can choose the pay $29 for the ZeroPi plus a Debugger which provides a full debug interface. For $48, backers can receive a ZeroPi plus 4 Stepper motor drivers, and there are further more expensive options for multiple devices and different motor combinations to suit a variety of robotics projects.
The ZeroPi team are able to ship their devices anywhere in the world, and customers can expect to receive their product by December 2015.
Posted in 3D Printer Accessories
Maybe you also like:
- T-Bone Cape motion control board launches on Indiegogo
- New extruder could lower costs of 3D printing cellular structures for drug testing
- New Ninja Printer Plate for consumer 3D printing
- mUVe3D releases improved Marlin firmware for all 3D printers
- Zecotek plans HD 3D display for 3D printers
- Add a smart LCD controller to your Robo3D printer
- Maker Kase: a handy cabinet for 3D printers
- Heated bed for ABS printing with the Printrbot Simple XL
- Next gen all metal 3D printer extruder from Micron
- Pico all-metal hotend 100% funded in 48 hours, B3 announces Stretch Goal
- Create it REAL announces first 3D printing Real Time Processor
- A larger and more powerful 3D printer extruder on Kickstarter
Tony wrote at 12/6/2016 4:31:44 PM:
Will this work with the rpi3 ?
Zero Pi - Etsy.
 de
deEtsy is no longer supporting older versions of your web browser in order to ensure that user data remains secure. Please update to the latest version.
Take full advantage of our site features by enabling JavaScript.
Find something memorable, join a community doing good.
(106 relevant results)
8 nuances worth paying attention to
Sooner or later, everyone will learn about 3D printing. And only a few lucky people, imbued with the opportunities that 3D printing opens up, catch themselves thinking that they want to purchase a 3D printer. The desire gradually develops into a serious decision and the search for the right option begins. And here the potential buyer is faced with the fact that he does not fully understand what to choose among the whole variety of 3D printers. We will try to answer this question in as much detail as possible. What to look for, and how to make a choice? We want to offer a small checklist of the nuances that you need to pay attention to when choosing a 3D printer. You need to decide for yourself for what tasks you will use this technique? What features should a 3D printer have to solve your problems? nine0003
And only a few lucky people, imbued with the opportunities that 3D printing opens up, catch themselves thinking that they want to purchase a 3D printer. The desire gradually develops into a serious decision and the search for the right option begins. And here the potential buyer is faced with the fact that he does not fully understand what to choose among the whole variety of 3D printers. We will try to answer this question in as much detail as possible. What to look for, and how to make a choice? We want to offer a small checklist of the nuances that you need to pay attention to when choosing a 3D printer. You need to decide for yourself for what tasks you will use this technique? What features should a 3D printer have to solve your problems? nine0003
Tip 1 : Decide on 3D printing technology
The first step is to decide on the technology of 3D printing. There are two main paths here. If you are faced with the task of manufacturing high-precision and miniature products, such as jewelry, then 3D printers using SLA or DLP technology are suitable for you. Such printers are specially designed for the manufacture of high-precision models. 3D printing in these printers occurs using a laser beam that illuminates the photopolymer resin. Hence the accuracy of the models. Prominent representatives of this segment: Form 2 3D printer or B9 3D printercreator If you are faced with a wider range of tasks, and functionality, part size, and low manufacturing cost are more important, then an FDM printer will suit you. 3D printing on this equipment involves layer-by-layer melting of plastic. If according to SLA printers everything is clear. The scope of their application is jewelry, dentistry, high-precision prototypes of small parts. Then we will dwell on FDM printers in more detail. There is a lot more variety of different options for implementing printers. nine0003
Such printers are specially designed for the manufacture of high-precision models. 3D printing in these printers occurs using a laser beam that illuminates the photopolymer resin. Hence the accuracy of the models. Prominent representatives of this segment: Form 2 3D printer or B9 3D printercreator If you are faced with a wider range of tasks, and functionality, part size, and low manufacturing cost are more important, then an FDM printer will suit you. 3D printing on this equipment involves layer-by-layer melting of plastic. If according to SLA printers everything is clear. The scope of their application is jewelry, dentistry, high-precision prototypes of small parts. Then we will dwell on FDM printers in more detail. There is a lot more variety of different options for implementing printers. nine0003
Nuance 2: Evaluate your needs
Of course, you always want to get all the best and with maximum opportunities. Do you need all this to solve your current problems? What can be cited as an example? For example, the size of the working area of the FDM 3D printer. There are printers on the market with a large print area (1m x 1m x 1m), and with a very small one (100mm x 100mm x100mm). But for most tasks, a certain standard has already developed. This is the printable area within 200 x 200 x 200 mm. With slight fluctuations in size in one direction or another. Most 3D printers have exactly this size of the working area. This volume is enough to solve 95% of any tasks. But options are possible ... If you plan to manufacture small parts, then a smaller size will probably be enough for you. But if your work will be related to manufacturing, for example, a master model for casting, or large prototypes, then only then it makes sense to pay attention to a printer with a large print area. In other cases, the size of the print area larger than the standard is nothing more than a nice bonus. But as they say, you have to pay for everything. Therefore, most often it makes sense to focus on the “standard” print area. And even if the part you need to print is larger than the working area of your 3D printer, you can always cut it in a special editor, and then print 2 parts of the model and glue them together.
There are printers on the market with a large print area (1m x 1m x 1m), and with a very small one (100mm x 100mm x100mm). But for most tasks, a certain standard has already developed. This is the printable area within 200 x 200 x 200 mm. With slight fluctuations in size in one direction or another. Most 3D printers have exactly this size of the working area. This volume is enough to solve 95% of any tasks. But options are possible ... If you plan to manufacture small parts, then a smaller size will probably be enough for you. But if your work will be related to manufacturing, for example, a master model for casting, or large prototypes, then only then it makes sense to pay attention to a printer with a large print area. In other cases, the size of the print area larger than the standard is nothing more than a nice bonus. But as they say, you have to pay for everything. Therefore, most often it makes sense to focus on the “standard” print area. And even if the part you need to print is larger than the working area of your 3D printer, you can always cut it in a special editor, and then print 2 parts of the model and glue them together. nine0003
nine0003
Nuance 3 : Decide on the complexity of the products
You should decide for yourself how complex models you will print on a 3D printer. If you plan to manufacture complex prototypes, or complex art models, then you need a 3D printer that can print with two materials. This is necessary so that your printer can print supports from soluble material. If the models are not the most complex, then you can get by with one extruder and save the budget. A complex model is a model with a large number of elements suspended in the air, or a model whose elements have angles of more than 30 degrees. nine0003
Point 4: Decide on the list of materials to be used.
Another important point. You must immediately determine for yourself a list of possible materials with which you are going to print. This primarily applies to materials with a high degree of shrinkage, such as ABS and Nylon. In order to print with such materials, a heated table is clearly required in a 3D printer. And it is very desirable to have a closed case to provide a thermal circuit around the model. If you plan to print only with PLA plastic. You don't need a heated table. But still it is better that the printer has a heated table. Now the difference in the cost of printers with a heated table is practically the same as the cost without it. But you get a universal solution with which you can perform the full range of tasks facing a 3D printer. One more moment. Ability to print with flexible materials Quite a number of 3D printers face the problem of printing with flexible materials. Of course, printing with various Flexes and Rubbers is very interesting at first glance. But the use of these materials in life is not very common. Usually, for most people, this happens like this: A couple of models are printed, and the understanding comes that this is not a fast and rather complicated process. And this is where the acquaintance with flexible materials ends.
In order to print with such materials, a heated table is clearly required in a 3D printer. And it is very desirable to have a closed case to provide a thermal circuit around the model. If you plan to print only with PLA plastic. You don't need a heated table. But still it is better that the printer has a heated table. Now the difference in the cost of printers with a heated table is practically the same as the cost without it. But you get a universal solution with which you can perform the full range of tasks facing a 3D printer. One more moment. Ability to print with flexible materials Quite a number of 3D printers face the problem of printing with flexible materials. Of course, printing with various Flexes and Rubbers is very interesting at first glance. But the use of these materials in life is not very common. Usually, for most people, this happens like this: A couple of models are printed, and the understanding comes that this is not a fast and rather complicated process. And this is where the acquaintance with flexible materials ends. Therefore, it makes sense to demand such an opportunity from the printer if printing with such materials is very necessary. nine0003
Therefore, it makes sense to demand such an opportunity from the printer if printing with such materials is very necessary. nine0003
Nuance 5: Construction and kinematics
Next, you need to pay attention to the design of the 3D printer. Even if you are not a great specialist in technology, you can immediately see that some printers have an open design. And others are closed. As they like to be called in the Russian-speaking community "cubes". What does the appearance say? Printers with an open design, usually have kinematics with a horizontally moving table (based on Prusa 3D printers). This kinematics has some inherent flaws. Such as, not the highest print speed and possible print quality problems associated with the complexity of the settings. First of all, this is the so-called wobble. Also, the lack of a closed case can cause print quality problems with high shrinkage plastics (ABS, Nylon). The main advantage of printers of this design is their price. It is usually lower. But as you know, you have to pay for everything. In this case, the worst performance. The so-called "cubes" today, is the main design, which is represented by leading manufacturers on the market. Such printers are built according to the lifting table scheme. And they lack most of the shortcomings that are inherent in printers from the previous group. “Cubes” usually have a closed body, which allows the highest quality printing with plastics with a high degree of shrinkage. Closed case printers are more rigid. This results in better quality printing. The kinematics of moving the print head is represented by various designs. They have their pros and cons. But most of them have advantages over moving table printer circuits. nine0003
The main advantage of printers of this design is their price. It is usually lower. But as you know, you have to pay for everything. In this case, the worst performance. The so-called "cubes" today, is the main design, which is represented by leading manufacturers on the market. Such printers are built according to the lifting table scheme. And they lack most of the shortcomings that are inherent in printers from the previous group. “Cubes” usually have a closed body, which allows the highest quality printing with plastics with a high degree of shrinkage. Closed case printers are more rigid. This results in better quality printing. The kinematics of moving the print head is represented by various designs. They have their pros and cons. But most of them have advantages over moving table printer circuits. nine0003
Nuance 6: Diameter and changeable nozzle
Most 3D printers on the market come with 0. 3-0.4mm nozzles. This is enough to solve the vast majority of tasks facing a 3D printer. Some of the printers have the ability to install a nozzle of a different diameter, others do not. As we wrote above, the need to print with nozzles with a diameter other than 0.3-0.4 mm arises very infrequently. This mainly concerns, or personal experiments, or some very specific tasks. If you do not plan to do this, then this opportunity is not so necessary. What do we mean by specific tasks? This is especially true for printing large items, where it is very important to reduce the printing time. This can be achieved by using large diameter nozzles. For example, with a diameter of 0.6-0.8 mm, or even a diameter of 1 mm. For printers with a large printable area, the ability to change nozzles is already a vital necessity. Therefore, here, as in the case of a heated table, the ability to change nozzles is a good bonus. It is not mandatory, but very useful if you do not have to pay extra for it. nine0003
3-0.4mm nozzles. This is enough to solve the vast majority of tasks facing a 3D printer. Some of the printers have the ability to install a nozzle of a different diameter, others do not. As we wrote above, the need to print with nozzles with a diameter other than 0.3-0.4 mm arises very infrequently. This mainly concerns, or personal experiments, or some very specific tasks. If you do not plan to do this, then this opportunity is not so necessary. What do we mean by specific tasks? This is especially true for printing large items, where it is very important to reduce the printing time. This can be achieved by using large diameter nozzles. For example, with a diameter of 0.6-0.8 mm, or even a diameter of 1 mm. For printers with a large printable area, the ability to change nozzles is already a vital necessity. Therefore, here, as in the case of a heated table, the ability to change nozzles is a good bonus. It is not mandatory, but very useful if you do not have to pay extra for it. nine0003
Nuance 7: Print thickness
It is important to understand that most models on a 3D printer are printed with a layer of 0. 1-0.2 mm. These are the optimal values that allow you to achieve quality and acceptable print speed. There are a certain number of printers that allow you to print with a layer of less than 0.05 mm, and get very high quality prints. But then there is the problem of a sharp increase in print time. And if such print quality is important to you, then it probably makes sense to turn your attention to 3D printers, which we talked about at the very beginning of the article. These are 3D printers using SLA or DLP technology. nine0003
1-0.2 mm. These are the optimal values that allow you to achieve quality and acceptable print speed. There are a certain number of printers that allow you to print with a layer of less than 0.05 mm, and get very high quality prints. But then there is the problem of a sharp increase in print time. And if such print quality is important to you, then it probably makes sense to turn your attention to 3D printers, which we talked about at the very beginning of the article. These are 3D printers using SLA or DLP technology. nine0003
Nuance 8: Extruder type
Today there are two main types of extruder. This is a direct extruder in which the bar feed motor is located in the printhead itself. And the so-called Bowden extruder, where the plastic feed motor is located on the body. And the plastic itself is fed to the extruder through a fluoroplastic tube. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each type of extruder? Bowden extruder, due to the lack of a motor on the print head, has less weight. And therefore, it has greater positioning accuracy, which affects the print quality. And a higher speed of movement, which, accordingly, has a positive effect on the speed of printing. But it has one drawback. It is usually difficult to print with flexible plastics on a Bowden extruder. Such as Rubber or Flex. All its positive features, this extruder reveals when using plastic with a diameter of 2.85-3.00 mm. But this type of plastic is less common than the now standard plastic with a diameter of 1.75 mm. And therefore, users of printers with such plastic are often deprived of the opportunity to use new types of materials. Which are primarily produced in the most common form factor of 1.75mm. The direct extruder usually doesn't have such big problems with flexible plastics. Easier to set up, but due to the greater mass of the print head, it is inferior to the Bowden extruder in terms of speed and positioning accuracy. What to prefer? This is the user's choice. We just wanted to talk about the pros and cons of these extruder types.
And therefore, it has greater positioning accuracy, which affects the print quality. And a higher speed of movement, which, accordingly, has a positive effect on the speed of printing. But it has one drawback. It is usually difficult to print with flexible plastics on a Bowden extruder. Such as Rubber or Flex. All its positive features, this extruder reveals when using plastic with a diameter of 2.85-3.00 mm. But this type of plastic is less common than the now standard plastic with a diameter of 1.75 mm. And therefore, users of printers with such plastic are often deprived of the opportunity to use new types of materials. Which are primarily produced in the most common form factor of 1.75mm. The direct extruder usually doesn't have such big problems with flexible plastics. Easier to set up, but due to the greater mass of the print head, it is inferior to the Bowden extruder in terms of speed and positioning accuracy. What to prefer? This is the user's choice. We just wanted to talk about the pros and cons of these extruder types. Of course, there are many more nuances when choosing a 3D printer. But we think that even our small list will force you to look and study some points that you may not have thought about more closely. And it will save you time and money when choosing a 3D printer. 3Dtool company has extensive experience in the 3D equipment market. We work with leading Russian and foreign manufacturers, offering high-quality equipment for a reasonable price. Our service center is staffed by highly qualified specialists who are able to solve any problem in the shortest possible time, and all offered 3D printers come with a 1-year warranty. nine0003
Of course, there are many more nuances when choosing a 3D printer. But we think that even our small list will force you to look and study some points that you may not have thought about more closely. And it will save you time and money when choosing a 3D printer. 3Dtool company has extensive experience in the 3D equipment market. We work with leading Russian and foreign manufacturers, offering high-quality equipment for a reasonable price. Our service center is staffed by highly qualified specialists who are able to solve any problem in the shortest possible time, and all offered 3D printers come with a 1-year warranty. nine0003
In our assortment you can always find 3D printers for your tasks:
1) Budget 3D printers
2) 3D printers for business
3) Large area 3D printers
4) SLA and DLP 3D printers
Do you have any questions?
Call: +7 (495) 324-07-90 (Moscow) and 8 (800) 775-86-69 (toll-free in the Russian Federation) or write to the mail: sales@3dtool. ru and our employees will be happy to give you a detailed consultation on any topic of interest. nine0003
ru and our employees will be happy to give you a detailed consultation on any topic of interest. nine0003
How to choose nozzle size for 3D printer? Pros and cons
3DPrintStory 3D printing process How to choose nozzle size for 3D printer? Advantages and disadvantages
When choosing your 3D printer, the nozzle size of your 3D printer may have been the last thing on your mind. This is a detail that is often overlooked. But depending on what you need to print, the wrong nozzle diameter can get in the way. nine0003
In this article, we'll take a look at the different 3D printer nozzle sizes and why you should consider this assembly, what materials it's made of, understand the relationship between nozzle size and layer height, and how to measure the actual nozzle diameter.
How does nozzle size affect 3D printing?
Nozzle diameter affects the extrusion width of the 3D printer line. This affects some elements of your model. If you are 3D printing for business (make a lot of orders), you need to make sure your extruder is feeding the right amount of material. If too much material is fed, then more filament is used than is actually required for successful 3D printing. Well, a smaller number can simply lead to marriage. nine0003
Or maybe you're printing different designs, some of them very detailed and intricate, and some more practical (like a replacement doorknob) that just needs to be printed quickly and with maximum durability.
In any case, you will need the correct setting to save time, material and ensure the normal quality of the 3D model.
There is no easy answer to what is the best nozzle size for a 3D printer. You need to weigh what you want to achieve and what elements of the 3D model are most important to you. nine0003
nine0003
Depending on your 3D printer, the nozzle can be quite easily replaced (most of them are mounted on screws), and buying a package with different sizes will cost you a lot.
Most common 3D printer nozzle options
The most common standard nozzle size is the 0.4mm (or 0.35mm) nozzle used by most modern 3D printer manufacturers. The reason for this is that it is a rather large and yet versatile nozzle size. This means that you can print with exceptional detail in no time. nine0003
With the 0.4 mm 3D printing nozzle you can print up to a layer thickness of only 0.1 mm or up to 0.3 mm. The lower the layer height, the better the detail (on the Z axis) and the larger the layer height, the faster your 3D print will be, but with worse detail quality.
A common misconception is that if someone doesn't get good enough 3D print quality on their printer with a 0.4mm nozzle, they immediately think they need a smaller 3D print nozzle.
Another common smaller size is 0. 25 mm. Some 3D printers offer 0.2mm, 0.15mm, and Mass Portal is even experimenting with 0.1mm 3D printer nozzles. And the experiments are really interesting. Thanks to this miniature nozzle, they were able to print the clock mechanism with excellent detail. nine0003
25 mm. Some 3D printers offer 0.2mm, 0.15mm, and Mass Portal is even experimenting with 0.1mm 3D printer nozzles. And the experiments are really interesting. Thanks to this miniature nozzle, they were able to print the clock mechanism with excellent detail. nine0003
How is nozzle diameter related to 3D printer resolution?
Theoretically, a smaller 3D printer nozzle can achieve greater precision. But for many 3D printers, especially cheaper or older models, a smaller extruder nozzle won't necessarily make a difference if your printer doesn't support the higher resolution you need. It's like putting low-profile, high-performance tires on an old classic car - it doesn't make it go faster, and it doesn't necessarily make it better cornering. nine0003
This is also similar to how the specifications of a 3D printer on paper (eg advertised resolution) do not always result in the best print quality of the finished product. Just as Ultimaker and Zortrax have very similar resolutions on paper, but in many actual tests, Zortrax produces better models than Ultimaker 2.
smaller nozzles as resolution across the board is getting better every day. nine0003
Let's look at the pros and cons of 3D printing with smaller nozzles. Some are less obvious than others. Next, we'll look at the larger, underpriced nozzles available. I hope after reading this article you will be able to answer the question: "What nozzle size should I print?".
You probably already guessed that the smaller the size of the nozzle in the extruder, the more detailed model you can get as a result of 3D printing. The thin nozzle is great for complex figures, or if you need to print very thin walls for aircraft skins, or high transparency models, etc. nine0003
The photo below shows the printed skin of a model aircraft, which was made with a standard 0.4 mm diameter nozzle. If the same skin is printed with a nozzle with a diameter of 0.2 mm, then the weight (and strength) would be halved.
It is worth noting that a 3D printer with a 0.2 mm nozzle feeds half as much material as a 0. 4 mm nozzle. And this actually leads to an increase in print time by the same two times. It should be noted that strength and detail are reciprocals of time. So to get high-quality 3D models using a thin nozzle and high resolution, you will have to be patient (2 times more than when printing with a standard 0.4 extruder :)). In some cases this is justified, in others it is a waste of time...
4 mm nozzle. And this actually leads to an increase in print time by the same two times. It should be noted that strength and detail are reciprocals of time. So to get high-quality 3D models using a thin nozzle and high resolution, you will have to be patient (2 times more than when printing with a standard 0.4 extruder :)). In some cases this is justified, in others it is a waste of time...
As a general rule, the smaller the nozzle size, the higher the chance of problems with the 3D printer. Especially if you are using cheap materials - they can work well with low models and thicker nozzles, but if you need detailed models that are printed using a thin nozzle, then you should also be puzzled by buying quality filaments for 3D printing.
Other factors are less obvious when 3D printing with a thin diameter nozzle - for example, protrusions can be a problem. This is because each layer has a smaller width for the next layer. Crossing bridges can also be difficult. nine0003
But there is good news too! Where overhangs form, the caliper material will be much easier to remove if printed with a thin nozzle. Due to the increased accuracy, your slicer can use a minimum amount of material between your model and supports, so they will break off more easily and have fewer damaged pads that need to be sanded.
Due to the increased accuracy, your slicer can use a minimum amount of material between your model and supports, so they will break off more easily and have fewer damaged pads that need to be sanded.
And finally, the most annoying thing about a thin nozzle is the ease with which it clogs. If you downsize to 0.2mm or even 0.1mm, you'll need a small particle to clog the hotend. You need to be very careful about the cleanliness of your 3D printing material and regularly clean the nozzle of your 3D printer. Otherwise, you will not end up with additional unnecessary problems. nine0003
It is also worth taking the time to understand the relationship between nozzle size and layer thickness. In short, the first parameter determines the horizontal detail (along the x and y axes), and the second adjusts the resolution along the vertical or z axis.
How to measure the nozzle size of a 3D printer?
Although the actual nozzle diameter should be engraved on the side of the nozzle, it is not always possible to read this value if it is already installed in the extruder or if you have been printing with it for some time. After all, there is the concept of wear and you may not be sure that the nozzle is the same size as before. nine0003
After all, there is the concept of wear and you may not be sure that the nozzle is the same size as before. nine0003
To determine what size your nozzle really is, very slowly extrude some material into the air (high speed may change shape or size) at the lowest setting you can feed material at (approximately 1 mm/s). Once cool, use a micrometer if you have one. They are generally more accurate than digital calipers. Keep in mind that the filament will probably expand after being extruded. Poor quality material or an extruder that is too hot (especially if you extrude at 1mm/s) will cause the material to expand more, resulting in inaccurate readings. nine0003
It is also useful to know the size to which your material expands after extrusion if you are working on getting a really nice and accurate model. So feel free to experiment with higher speeds that are a bit more like your actual 3D printing.
How is 3D printing layer height and nozzle diameter related?
In simple terms, this is the thickness of each line of extruded material that makes up each layer of your model. The thinner the layer height (or layer thickness), the finer the print detail in the Z-axis (the vertical dimension of your model), but the more layers will be required. Increases print time. nine0003
The thinner the layer height (or layer thickness), the finer the print detail in the Z-axis (the vertical dimension of your model), but the more layers will be required. Increases print time. nine0003
These characteristics are related, but not completely. For example, you can print using a thinner, thicker nozzle if vertical resolution is less important to you. Or you can use a thicker nozzle with a very small layer height. Although in this case, do not get too carried away. To maintain adequate pressure, your layer height should be at least 20% less than your nozzle width - and in most cases, for best 3D printing results, it should be around 50%. nine0003
How to determine the correct distance from the nozzle to the desktop of a 3D printer?
With the correct setting of the distance between the table and the nozzle, the base of the finished model should have an almost perfectly smooth, glassy surface. Many people assume that you need to use a stylus to properly set the distance between the nozzle and the 3D printer bed, but in fact, even that can be too thick. So it's worth thinking in the direction of the already proven table calibration with a piece of paper. You should use thin paper. For example, check paper is a great choice. Place the receipt paper under the nozzle and gradually lower the nozzle down until the receipt paper resists a little when you try to push it out. 3D printing at this height will give the bottom of the model a great look, and in the case of tall models, the print will definitely not go astray. nine0003
So it's worth thinking in the direction of the already proven table calibration with a piece of paper. You should use thin paper. For example, check paper is a great choice. Place the receipt paper under the nozzle and gradually lower the nozzle down until the receipt paper resists a little when you try to push it out. 3D printing at this height will give the bottom of the model a great look, and in the case of tall models, the print will definitely not go astray. nine0003
What is the maximum 3D print layer height compared to the nozzle size?
You don't necessarily need a layer height calculator on your 3D printer, but typically the maximum layer height is 50% of the nozzle width. In some cases, you can go higher (perhaps 75%), but in this case, you must be aware that you can sacrifice reliability.
It's best to experiment with your model's parameters if you understand the relationship between the 3D printer's nozzle size and the layer height you'll be using to print. So for a 0.4mm nozzle, you will need to print with a layer height of 0.2mm, or up to 0.3mm. Your minimum should be around 0.1mm. If less, then in fact you just increase the waiting time without much benefit (on the same 0.4 mm nozzle). nine0003
So for a 0.4mm nozzle, you will need to print with a layer height of 0.2mm, or up to 0.3mm. Your minimum should be around 0.1mm. If less, then in fact you just increase the waiting time without much benefit (on the same 0.4 mm nozzle). nine0003
In most cases, it is worth printing thinner layers with smaller nozzle diameters and generally thicker layers with thicker nozzles. Just note that if you are printing with a thicker nozzle diameter and very thin layer height, you will need to lower the extrusion settings in your slicer to prevent overfeeding.
It's also worth noting that no matter what the size, you should always make sure you always have a clean nozzle. One of the easiest ways to do this is to use a high quality cleaning floss. You only need to use a few grams of it each time you brush, but this will prevent carbon buildup over time. nine0003
So why should I use a 0.8mm nozzle or thicker?
Similar nozzle sizes were more common on older 3D printers but are making a comeback. It's all about using what you need and nothing more. For a large number of models, the 0.4mm headroom that your 3D printer probably comes with may be overkill in terms of detail.
It's all about using what you need and nothing more. For a large number of models, the 0.4mm headroom that your 3D printer probably comes with may be overkill in terms of detail.
If you're looking for strength and speed, but detail is less important, a 0.8mm or even 1.0mm nozzle is worth it. And don't forget that models printed with a 0.8mm nozzle can be very detailed, as a lot depends on your 3D printer as well. nine0003
The only slight disadvantage may be that you use more material, but with thicker part walls you can probably compensate with less infill.
There is no single optimal nozzle size for all models, you just need to take all factors into account and decide which nozzle size is best for you.
What nozzle size should I use for composite materials?
It is worth noting that composite materials (any particulate filament such as wood filler, copper filler, carbon fiber nylon or glass reinforced nylon) will cause extrusion problems when using a thinner nozzle.