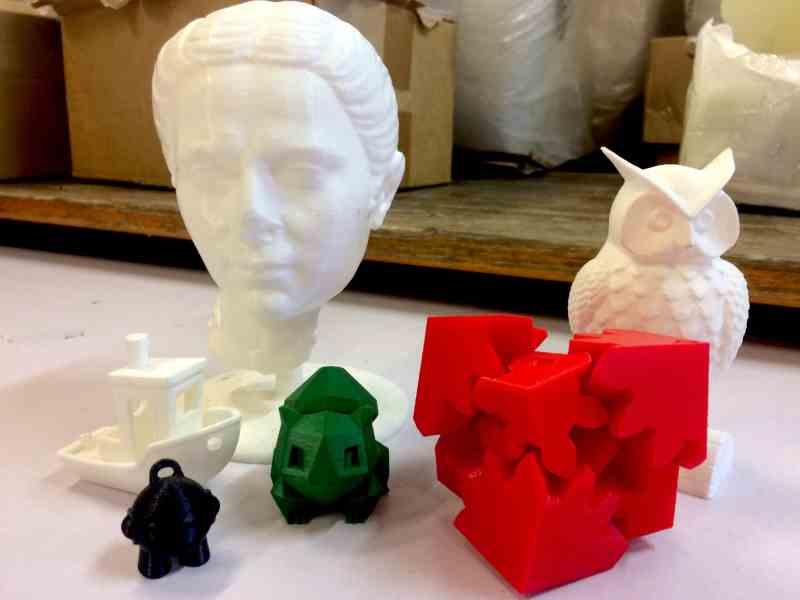
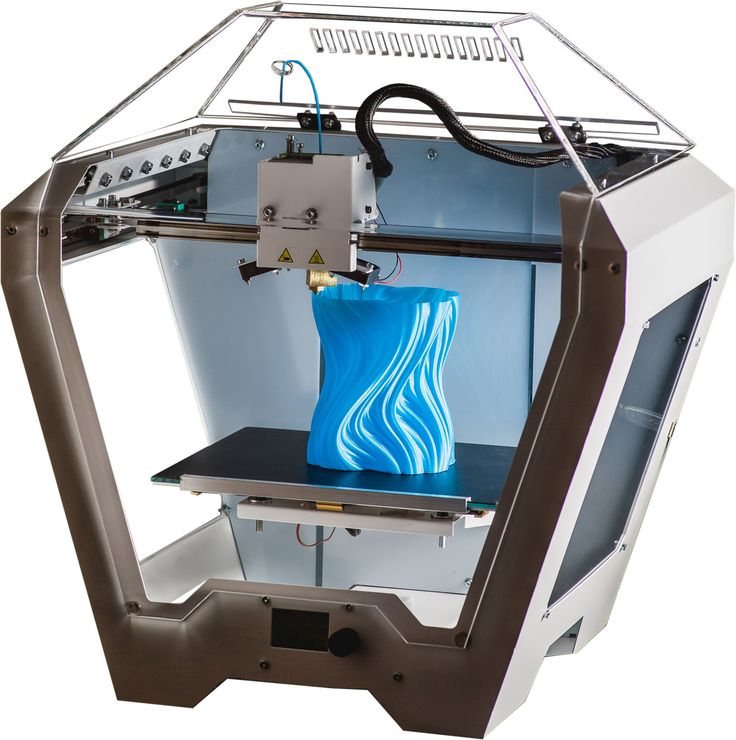
Who is using 3d printing
Five Industries Utilizing 3D Printing
Learn Blog
With a plethora of companies using professional 3D printers in their production processes, we want to identify industries that we believe can benefit most from additive manufacturing. By looking at these industries, it’s easy to understand how and why professional 3D printers are changing manufacturing as a whole.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry has some of the highest standards in part performance. Aerospace parts must withstand extreme temperatures and chemicals while being subjected to repeated loading, all while remaining as light as possible. Individual part failures often result in full system failures on aircraft carrying lives and cargo — so failure is simply not an option. Since part precision is critical for aircraft, aerospace engineers have taken to 3D printing inspection tooling to reduce costs for low-volume parts.
In the last few years, additive manufacturing has advanced rapidly, and advancements in the 3D printing industry have developed better solutions for aircraft manufacturers. Professional 3D printers can now print in high-performance thermoplastics reinforced with continuous fiber reinforcement (CFR) for additional strength, such as ULTEM™ 9085 Filament. Furthermore, professional 3D printers are now able to print larger parts at faster speeds, widening the scope of possible aerospace applications for the benefits of AM.
White Paper: Why Additive, Why Now?
How has 3D printing developed in recent years? Learn what today's AM platforms are capable of, and how they are solving new problems.
Automotive
The automotive industry has been charging ahead with additive manufacturing, with high-profile companies such as Audi using 3D printers. It’s not just the Audis of the world that are using 3D printers — everything from race car teams to sub manufacturers (OEMs) for each car manufacturer are utilizing 3D printers. Initially, the value of the 3D printing industry reaching automotive manufacturers focused on building the tooling and fixtures that aide the manufacturing process. The most common parts printed by automotive manufacturers are fixtures, cradles, and prototypes, which need to be stiff and strong, as well as durable.
However, professional 3D printers are now used to print high-strength, fiber-reinforced end use parts as well. Garry Rogers Motorsport, for example, uses a professional 3D printer to print numerous end-use parts such as steering wheels.
It’s also not unheard of for some to use professional 3D printers to fabricate replacement parts for centuries-old cars. This ensures there are enough pieces to service legacy cars as well as standard maintenance, repairment, and operations.
Manufacturing
From jigs and fixtures all the way to end-of-arm tooling, industrial 3D printers are completely turning the decades-old manufacturing industry on its head. Companies are able to create custom, low-volume tooling and fixtures at a fraction of the traditional price, giving designers and engineers more time to spend on revenue-generating parts. Due to 3D printing industry advances, mall manufacturers get the same advantages with a professional 3D printer as giant, global manufacturers, to improve and expedite processing while mitigating downtime. Companies are also able to have more creative freedom while saving on labor costs and time. Metal fabrication company Lean Machine, for instance, has approached 3D printing with a design for additive manufacturing (DFAM) approach, saving them upwards of $4000 per tool.
Metal fabrication company Lean Machine, for instance, has approached 3D printing with a design for additive manufacturing (DFAM) approach, saving them upwards of $4000 per tool.
Robotics
From customizability to reduced weight, these factors make successful robotics parts match well with 3D printing capabilities. Parts like grippers and sensor mounts are expensive to fabricate and need to be custom designed for different uses. Robotics engineers utilize 3D printers for end-of-arm tooling and end-use parts, from gripper fingers to entire robot components to reduce the weight of the overall product to ensure the tools can move faster and carry heavier items. Instead of paying large amounts of money for a non-customized design, 3D printing industry technologies allow robotics companies to design and fabricate light, complex parts such as end-of-arm tooling at a fraction of the cost. Haddington Dynamics, for example, is utilizing its four printers to create 3D printed robot arms for NASA and GoogleX for 58% less than traditional manufacturing.
Haddington Dynamics, for example, is utilizing its four printers to create 3D printed robot arms for NASA and GoogleX for 58% less than traditional manufacturing.
Education
As the 3D printing industry grows, educational institutes are rushing to make sure they stay on the cutting edge of the new technology for research and education purposes. From professors printing parts for educational tools to convey the lesson plan to PhD students utilizing the printers for research, 3D printers serve a variety of purposes in colleges. Colleges like Oklahoma State University and Purdue University in Indiana have taken a great interest in teaching their students about emerging additive manufacturing materials and technology.
Want to test the strength of our parts? Request a free sample part or sign up for a demo!
*The ULTEM™ and 9085 trademarks are used under license from SABIC, its affiliates or subsidiaries.
Demonstration from Markforged Application Engineer Ross Adams on 3D printing applications in the Aerospace industry.Customer Success Stories
NASA JPL's Team CoSTAR
NASA JPL's Team CoSTAR used their Markforged printers to print parts for field use in the DARPA Challenge
3D Printing for Education
All of the blogs and the information contained within those blogs are copyright by Markforged, Inc. and may not be copied, modified, or adopted in any way without our written permission. Our blogs may contain our service marks or trademarks, as well as of those our affiliates. Your use of our blogs does not constitute any right or license for you to use our service marks or trademarks without our prior permission. Markforged Information provided in our blogs should not be considered professional advice. We are under no obligation to update or revise blogs based on new information, subsequent events, or otherwise.
and may not be copied, modified, or adopted in any way without our written permission. Our blogs may contain our service marks or trademarks, as well as of those our affiliates. Your use of our blogs does not constitute any right or license for you to use our service marks or trademarks without our prior permission. Markforged Information provided in our blogs should not be considered professional advice. We are under no obligation to update or revise blogs based on new information, subsequent events, or otherwise.
Never miss an article
Subscribe to get new Markforged content in your inbox
required required requiredSubmit
6 Industries Being Transformed by 3D Printing
Time to read: 4 min
3D printing has grown from $4.4 billion in 2013 to an industry bringing in a projected $21 billion in 2021. This major growth is due to the growing number of applications of this technology across industries from printing food to building colonies on Mars. Other more practical applications for 3D printing include innovations in the healthcare, automotive, construction, and manufacturing sectors. Plastics, metals, ceramics, and even human cells are being used as material to print vital components of these industries — faster and at a lower cost. By starting with a 3D digital file (either downloading it from the internet or designing it with software), complex shapes can be uploaded to a computer and printed layer by layer into a tangible, usable object. 3D printing requires a 3D printer, the proper materials, and a 3D sketch. Individuals might even choose to contract 3D printing services if they do not have all the necessary parts for the job, or need help tooling a custom prototype or part as one stage of a bigger project. The future of 3D printing is still being realized, with professionals in several industries already making some groundbreaking strides — for this reason, some are calling the 3D printer the harbinger of the 4th industrial revolution.
This major growth is due to the growing number of applications of this technology across industries from printing food to building colonies on Mars. Other more practical applications for 3D printing include innovations in the healthcare, automotive, construction, and manufacturing sectors. Plastics, metals, ceramics, and even human cells are being used as material to print vital components of these industries — faster and at a lower cost. By starting with a 3D digital file (either downloading it from the internet or designing it with software), complex shapes can be uploaded to a computer and printed layer by layer into a tangible, usable object. 3D printing requires a 3D printer, the proper materials, and a 3D sketch. Individuals might even choose to contract 3D printing services if they do not have all the necessary parts for the job, or need help tooling a custom prototype or part as one stage of a bigger project. The future of 3D printing is still being realized, with professionals in several industries already making some groundbreaking strides — for this reason, some are calling the 3D printer the harbinger of the 4th industrial revolution.
Using human tissue and cells as material, healthcare professionals are now able to 3D print skin, body parts, and organs with cells that are compatible with a particular person’s anatomy — leaving less room for rejection. 3D printing is powering medical breakthroughs comprising the bioprinting, replication, and prosthetics fields. There are several medical advancements in which 3D printing is lending a hand. The technology has encouraged the anticipation of solving organ donation shortages, transforming heart surgery, and the creation of custom braces for chronic health problems such as scoliosis. Additionally, sterile surgical instruments can be made quickly while remaining inexpensive, and correcting deformity due to certain trauma and injury can be made possible and easier with 3D printing. In addition to being able to 3D print surgical instruments, the technology can also help improve the healthcare supply chain by making medical items more available, abundant, and obtainable at a lower cost.
Science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) have become increasingly popular, thanks in part to the fact that 3D printing is helping transform classrooms at every level, from K-12 to college. For instance, engineering students can now print out their prototypes, students studying architecture can make 3D models of their structures, and chemistry students can print 3D sculptures of molecules. Teachers of various subjects who have access to a 3D printer and materials can print out educational aids. 3D printing can supplement a curriculum, help increase problem-solving skills, and foster a deeper, more foundational knowledge of complex subjects.
AerospaceBoeing, Airbus, and even NASA are all taking advantage of 3D printing. The ability to quickly produce lightweight parts at a low cost is valuable to aerospace professionals. 3D printing parts for engines, satellite production, aircraft body parts and fixtures, and even taxi drones to facilitate takeoffs and landings are changing the aerospace manufacturing and production chains. These lightweight parts are affordable, but also help cut fuel costs.
These lightweight parts are affordable, but also help cut fuel costs.
The successful car company Audi has been using 3D printing for quite some time now and has no plans of stopping. Similar to aerospace, the automotive industry is heavily interested in the ability to print lightweight parts — some of which may be complex and seldom-used — on-demand and at low cost. The automotive industry can use 3D printing for engine and body parts, chassis, and in the future may be able to 3D print whole cars much faster than current manufacturing times currently allow for — making them more fuel-efficient and reducing factory waste byproduct in the process.
ConstructionConstruction is using 3D printing to fabricate anything from tiny hardware to lightweight, durable tools to printing entire houses. 3D printing is making its way into the interior design industry to produce office chairs, desks, and tables. A private firm in China has claimed to have 3D printed 10 full-sized, detached single-story houses in 24 hours. It is not out of the realm of possibility to think that full cities can be 3D printed at record speed. 3D printing can be attractive to professionals in the construction industry because it cuts down labor time and cost, and minimizes inefficiencies. This is especially relevant since these professionals are looking to build complex, intricate structures in a shorter, more sustainable manner.
It is not out of the realm of possibility to think that full cities can be 3D printed at record speed. 3D printing can be attractive to professionals in the construction industry because it cuts down labor time and cost, and minimizes inefficiencies. This is especially relevant since these professionals are looking to build complex, intricate structures in a shorter, more sustainable manner.
Most of the industries above have taken advantage of 3D printing for manufacturing benefits. Traditional manufacturing processes that have been in place for generations are now being transformed — allowing goods to be produced at an extraordinary speed, using less and fewer materials, and reducing labor. 3D printing can be used alongside, or in place of, CNC machining to produce precise iterations of complex, custom manufactured parts, custom manufacturing parts. 3D printing and CNC machining will be used throughout manufacturing chains, cutting the cost for manufacturing mid to large units of products, or one-off prototypes. 3D printing during the manufacturing process can also cut down on waste, making for a more sustainable manufacturing process for any industry and reducing the carbon footprint for one of the most wasteful aspects of any industry.
3D printing during the manufacturing process can also cut down on waste, making for a more sustainable manufacturing process for any industry and reducing the carbon footprint for one of the most wasteful aspects of any industry.
Robotics, and especially industrial robots, are extremely complicated machines with delicate parts. 3D printing can be used to replace these parts in a quick, cost-effective way. Robotics, when used for 3D printers, can move in an incredible variety of angles, able to create complex shapes for custom and large-scale objects. It is not far off to think that sending robotics with 3D printers to Mars could lead to the building of other larger robotics to 3D print houses for a colony in space. The applications for 3D printing are fascinating and only recently becoming realized. It is not known fully how this will impact industries going forward in the future — however, the possibilities are seemingly limitless.
Thank you for subscribing!
90,000 sectors of the use of 3D printers industries of 3D printersSupplier of 3D equipment since 2010
9000 +7 495 646-15-338 800 333-12-823D-scanners 3d-printer-printer-software software
on company clients of clients and projects. 3D
3D
Contacts
Professional 3D printers are actively used in various areas of production, business, and research. We have collected for you the most common solutions for popular areas in which 3D printing is effectively used.
Education & Research
How 3D Printing Helps Students and Research Work
Learn More >
Education and Research
How 3D Printing Helps Student Work and Research Learn more
3 >
Mechanical engineering
A wide range of industrial production tasks to be solved
Learn more >>
Mechanical engineering
A wide range of industrial production tasks to be solved
Read more >>
Architecture
How 3D printing helps in quick and high-quality visualization
more >>
Architecture
How 3D-Propaging helps in fast and high-quality visualization
more >>
Literal production
Printing of moulds, stencils, burnt-out masters and casting samples in silicone
Learn more >>
Foundry
Printing of molds, waxes, die-casting masters and samples for silicone casting
Read more >>
Dentistry
All about direct printing templates for crowns, bridges, surgical templates, imaging models
Read more >>
Dentistry
All about Direct Printing Templates for Crowns, Bridges, Surgical Templates, Imaging Templates
More >>
Electronics Manufacturing
Production of concepts, cases, test samples, tooling, master models
More >>
Electronics manufacturing
Manufacturing of concepts, cases, test samples, tooling, master models
More >>
Jewelry Making
Fast and Accurate Wax Making
More >>
Jewelry Making
Fast and Accurate Wax Making
Read more >>
3D printing as a business
Prototyping center, figurine printing studio, gift making
Read more >>
3D printing as a business
Prototyping center, figurine printing studio, souvenir making Read more > >
2
2 > Advice on choosing a 3D printer
Call 8 800 333-12-82
Write to WhatsAppLeave a request for a call
Come to our demo room
Learn more I confirm the accuracy of the information I entered and agree to the processing of my personal data in accordance with the privacy policy and user agreement.
- +7 495 646-15-338 800 333-12-82
2010–2022, Globatek JSC. All rights reserved.
Privacy policy and personal data processingPrices on the site are for reference only. Not an offer.
10 industries that 3D printing is starting to change
3D printing has come a long way from printing small prototype buildings out of plastic. Today, 3D printing is fulfilling its potential in a range of industries, from aerospace to apparel and footwear.
This technology not only allows you to create items with incredible precision, but also saves money.
Today, there are many materials that allow you to make a wide variety of objects using 3D printing.
Below we describe the industries in which this technology is applied.
1. Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, everything must be made with high precision. Precision plays a very important role here in the execution of every space mission, and the industry itself is extremely important for the development of mankind.
3D printing has already begun to change the industry, it is used to replace many parts that have become too expensive to produce. In addition, the technology is used to test prototypes.
ULTEM 9085 is a thermoplastic commonly used in aircraft construction that can be melted down and used in 3D printing.
2. Architecture
3D printing technology helps save time on building construction.
With this technology, printing houses is as fast as printing documents.
And when creating a design, you can share it with other users by placing an object in the database.
3. Food
While 3D printing doesn't save lives, it could change the way we think about food.
Nevertheless, experts note that in the future humanity will face a shortage of food, it is already becoming increasingly difficult to feed the growing population of the planet.
However, science is looking for ways to grow meat and use alternative materials to produce food.
4. Product design
Technology allows you to design something on a computer, then print it in an hour, test it, find flaws, redesign, print a second prototype - and all this takes only half a day.
Previously, concepts were produced, but now 3D printing technology makes it possible to get closer to an almost identical representation of products in a very short amount of time.
5. Medicine
3D printing plays an important role in almost every aspect of medicine. When it comes to prototyping, technology allows you to create ready-made models that will cost less and take less time to create, and these will be ready-made models that are completely usable.
Clarity and precision allows you to print ultra-fine lines that allow you to create the smallest tools.
In addition, 3D printing technology allows you to recreate parts of the human body using various materials. Scientists are constantly working to create new materials and textures.
6. Dentistry
Making dental models is very useful, but it is not always possible to make them taking into account the individual characteristics of a person.
3D printing technology allows you to make exact copies of a patient's teeth to replace them, or crowns that can last longer.
Objet Digital is a dedicated 3D printer designed for use in the field of dentistry.
He uses materials that are very similar in structure to bone to print teeth.
7. Construction
In Dubai, 3D printing is an increasingly common way to construct buildings. Cazza, a 3D printed construction company, plans to build the world's first 3D printed skyscraper.
They created special machines that can build buildings from the bottom up.
Companies around the world have expressed interest in such machines.
In addition, this method of building construction leaves less debris. During construction, environmentally friendly materials can be used.
During construction, environmentally friendly materials can be used.
8. Agriculture
It may seem strange to use this technology in agriculture, but it is true. Many farms need specialized tools, which cost between $8,000 and $12,000 and can take months to complete.
PLA, or polylactic acid, is a material that is used for 3D printing and costs $0.25 per 1.5 cu. m. This can significantly save money and time for farmers who are looking to upgrade their machines.
9. Making clothes and shoes
So far, 3D printed clothes have not entered the mass market, but the idea of such clothes has been developed since 2013.
The idea is that in the future, customers can print clothes, which suits their individual sizes.
10. Organ printing
3D bioprinting is a new application that is developing at a rapid pace.
Scientists have made great progress in printing ribs, but they also believe that in the future it will be possible to print hearts, kidneys, livers and other organs.