What does a 3d scanner do
How Does a 3D Scanner Work?
Many digital engineering strategies that enable the future of product development, manufacturing, quality control, and production begin with 3D scanning. 3D scanners work with advanced technology and specialized software to create a tool that delivers game-changing results. For those still working with mechanical tools and traditional coordinate measuring machine (CMM) technology, 3D scanners work as an easy gateway to advanced manufacturing and engineering strategies. Keep reading below to understand more about how 3D scanners work and what the technology is capable of so you can begin accessing its benefits now.
Understanding How a 3D Scanner Works
A 3D scanner works by capturing data from a physical object's surface to describe its shape in an accurate, digital, three-dimensional format. Unlike measurement data from a CMM, high-quality 3D scan data is used for more than just inspection and dimensional analysis. The resulting measurement data enables faster, more accessible digital analysis and inspection in a visual, in-depth reporting method. 3D scanners also work to replicate parts in reverse engineering, assure fit, form, and function of components in remote locations, validate CAD models of 3D printed parts, and open the door to more digital strategies.
What are the Different Types of 3D Scanners?
There are many different types of 3D scanners available for various applications. Creating a digital model of any physical part requires a 3D scanner to collect accurate data to form its geometric identity, but not every type of 3D scanner works for every type of application. For example, if you are a DIY at-home hobbyist, you can make a simple 3D scanner with your mobile phone or make a 3D scanner with a Microsoft Kinect. However, while these 3D scanners work well for fun projects, they won't deliver manufacturing-grade accuracy and detailed requirements. Metrology-grade 3D scanning equipment is necessary for industrial use.
A laser 3D scanner is another type of 3D scanner that uses specialized software and a laser probe to project a laser line along the part's surface while sensor cameras continuously record the changing distance and shape of the laser line, resulting in a collection of XYZ coordinates.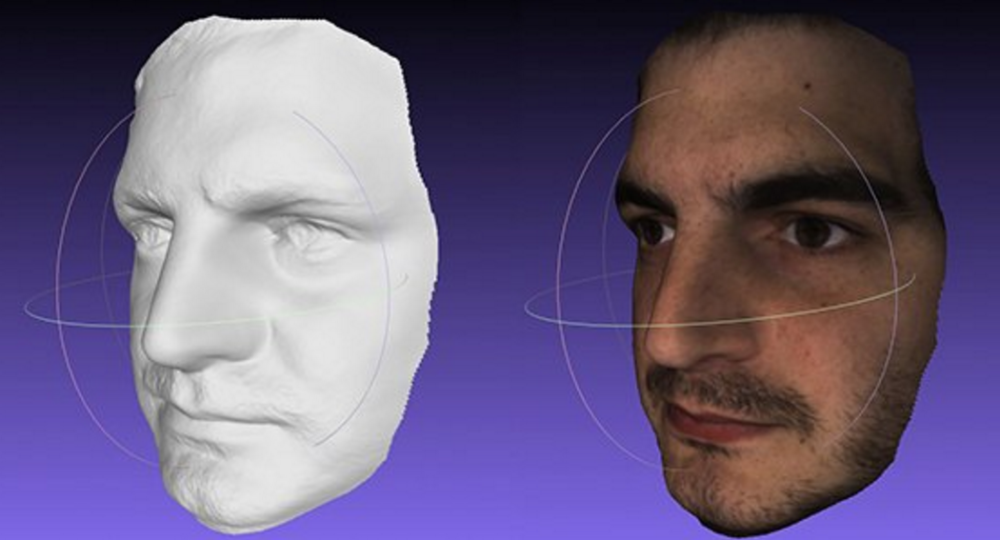 While these scanners are a quick way to collect data points from a physical object, other 3D scanners, such as structured light 3D scanners, can collect higher quality data. Structured light 3D scanners have established trust due to their high precision accuracy, which is why they're used widely throughout manufacturing.
While these scanners are a quick way to collect data points from a physical object, other 3D scanners, such as structured light 3D scanners, can collect higher quality data. Structured light 3D scanners have established trust due to their high precision accuracy, which is why they're used widely throughout manufacturing.
How Does a 3D Scanner Work with Structured Light?
A 3D scanner works with structured light using the principles of triangulation. The sensor projects a precise shifting fringe pattern across the part's surface, and two cameras capture the surface geometry based on the pattern distortion, calculating 3D coordinate measurements. The 3D scanner collects and processes millions of X-Y-Z data points into a "point cloud," creating a detailed digital twin of the object. Since the distance between the sensor, cameras, and angles is all known, the principle of triangulation is applied, producing accurate, reliable measurement results.
This image depicts how structured light 3D scanners also work with the principle of triangulation. A light source sits between two cameras set angled towards each other, projecting a heterodyne "fringe" stripe-like pattern onto the physical object's surface. The stripes change in size and direction during data collection. The sensing cameras observe the contrast along the stripes' edge and assign those pixels X-Y-Z coordinates, quickly collecting precise, crisp scan data containing very little texturing. The software then transforms the data points into visible data that comprise an accurate, digital replica of the physical part.
A light source sits between two cameras set angled towards each other, projecting a heterodyne "fringe" stripe-like pattern onto the physical object's surface. The stripes change in size and direction during data collection. The sensing cameras observe the contrast along the stripes' edge and assign those pixels X-Y-Z coordinates, quickly collecting precise, crisp scan data containing very little texturing. The software then transforms the data points into visible data that comprise an accurate, digital replica of the physical part.
How Does a 3D Scanner Work with LED Technology?
Structured light 3D scanners traditionally used white light. Today, different light colors are available, but the most popular are blue light 3D scanners that use LED technology. Blue light helps capture data on shinier and darker colored surfaces and filters out the ambient light present inside labs or on the manufacturing shop floor. The result is a clean, clear, precise data set with low noise.
How Does a 3D Scanner Work for Quality 4.0?
The concept of Quality 4.0 incorporates advanced manufacturing technologies to propel quality processes into the future. Adopting 3D scanning lays the groundwork for these modernized dimensional inspection techniques while overcoming the shortcomings of traditional quality and manufacturing practices. For example, 3D scanners collect data that provides the ability to virtually deconstruct parts and pieces of an object without physically destructing anything. With this data, quality professionals also find problem areas, fix parts, validate and test objects before they're physically in production. The measurement data's high accuracy enables the fast and reliable creation of dimensional calculations such as CAD comparison, sectional analysis, GD&T, trend/SPC, and more.
How Does a 3D Scanner Work for Digital Twin Strategies?
3D scanners work as a tool to access digital twin concepts in Quality 4.0. The data captured with a 3D scanner becomes the physical object's digital twin; therefore, using an accurate 3D scanner matters. 3D scanners work for many digital twin applications, including digital assembly. In this method, engineers connect 3D scan data from multiple parts in remote locations for assembly within the software. The digital assembly process enables you to assess the fit of such components before physical parts are mass-produced and shipped.
The data captured with a 3D scanner becomes the physical object's digital twin; therefore, using an accurate 3D scanner matters. 3D scanners work for many digital twin applications, including digital assembly. In this method, engineers connect 3D scan data from multiple parts in remote locations for assembly within the software. The digital assembly process enables you to assess the fit of such components before physical parts are mass-produced and shipped.
3D scanners work for reverse engineering by using scan data from a physical object to create a 3D CAD model for product enhancements and archiving. Legacy parts are often described within two-dimensional drawings, not 3D CAD models. Accurate 3D scanners make it possible to reproduce legacy parts using precise three-dimensional data. The 3D scanner scans the part, and the resulting data becomes a reference to create a 3D CAD model that can be used to develop new molds, tooling, or new parts with the same dimensional characteristics as the original or engineering product enhancements. Good quality 3D scan data with a watertight mesh can also be used to 3D print a duplicate of the original and improves efficiency in the reverse engineering process.
Good quality 3D scan data with a watertight mesh can also be used to 3D print a duplicate of the original and improves efficiency in the reverse engineering process.
How Does a 3D Scanner Work for Adaptive machining?
Adaptive machining is a trending process popular with aerospace and power generation turbine engine components such as airfoils, blisks, molds, and dies. In adaptive machining, accurate structured light 3D scanners digitize a part's surface geometry and send the data back to process the updated machining tool paths, allowing for real-time adjustments without having to reposition in and out of the CNC machine. This process is used with new parts and parts that need repair to help reduce operating costs and lower cycle times while increasing accuracy.
Find Out if 3D Scanning is a Good Fit for Your Application
If you're ready to learn how 3D scanners will work for your specific application, contact a Capture 3D team member today. Our 3D scanners provide an accurate, reliable solution to the advanced metrology needs of industries with diverse applications everywhere. During an in-person or virtual demo, our team will show you how 3D scanning improves product design, streamlines production lines, improves quality control, and unlocks Quality 4.0 strategies that will elevate your industry to new possibilities.
During an in-person or virtual demo, our team will show you how 3D scanning improves product design, streamlines production lines, improves quality control, and unlocks Quality 4.0 strategies that will elevate your industry to new possibilities.
What is 3D Scanning? | Laser Design
First of all, let’s be clear that 3D laser scanning is not magical. True, the technologies that make it possible are very advanced and quite amazing. But behind the mirrors—found in the laser probe (without any smoke)—there is a lot of know-how and experience that makes the laser scanning experience seem so easy to Laser Design customers.
Read on or watch our video on What is 3D Scanning?
What is 3D Scanning?
3D Laser Scanning is a non-contact, non-destructive technology that digitally captures the shape of physical objects using a line of laser light. 3D laser scanners create “point clouds” of data from the surface of an object. In other words, 3D laser scanning is a way to capture a physical object’s exact size and shape into the computer world as a digital 3-dimensional representation.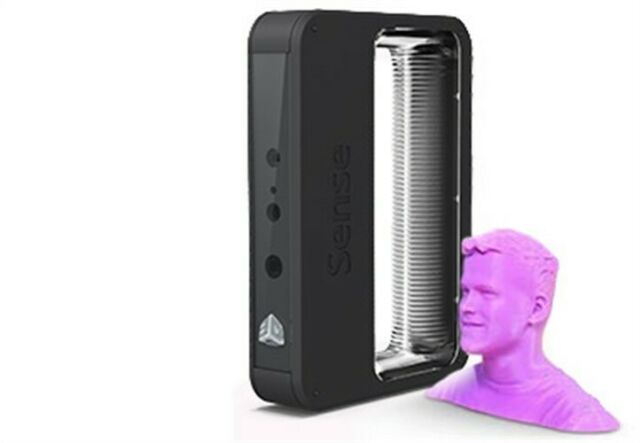
3D laser scanners measure fine details and capture free-form shapes to quickly generate highly accurate point clouds. 3D laser scanning is ideally suited to the measurement and inspection of contoured surfaces and complex geometries which require massive amounts of data for their accurate description and where doing this is impractical with the use of traditional measurement methods or a touch probe.
The 3D Scanning Process:
Data Acquisition via 3D Laser Scanning
3D Laser Scanning Process An object that is to be laser scanned is placed on the bed of the digitizer. Specialized software drives the laser probe above the surface of the object. The laser probe projects a line of laser light onto the surface while 2 sensor cameras continuously record the changing distance and shape of the laser line in three dimensions (XYZ) as it sweeps along the object.
Resulting Data
The shape of the object appears as millions of points called a “point cloud” on the computer monitor as the laser moves around capturing the entire surface shape of the object.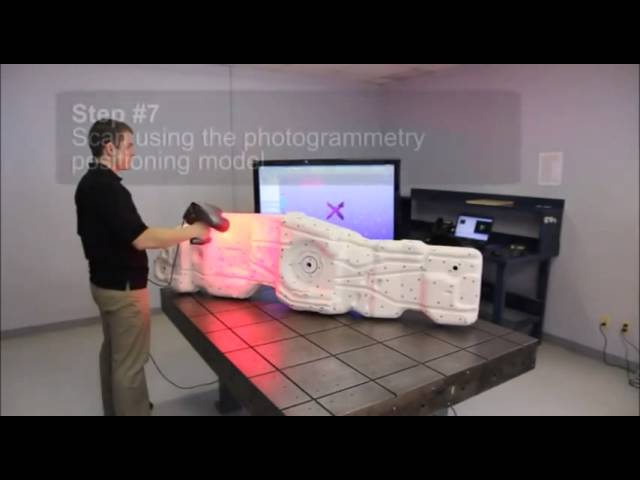 The process is very fast, gathering up to 750,000 points per second and very precise (to ±.0005″).
The process is very fast, gathering up to 750,000 points per second and very precise (to ±.0005″).
Modeling Choice Depends on Application
After the huge point cloud data files are created, they are registered and merged into one three-dimensional representation of the object and post-processed with various software packages suitable for a specific application.
Point Cloud Data for Inspection
If the data is to be used for inspection, the scanned object can be compared to the designer’s CAD nominal data. The result of this comparison process is delivered in the form of a “color map deviation report,” in PDF format, which pictorially describes the differences between the scan data and the CAD data.
CAD Model for Reverse Engineering
Laser scanning is the fastest, most accurate, and automated way to acquire 3D digital data for reverse engineering. Again, using specialized software, the point cloud data is used to create a 3D CAD model of the part’s geometry. The CAD model enables the precise reproduction of the scanned object, or the object can be modified in the CAD model to correct imperfections. Laser Design can provide a surface model or the more complex solid model, whichever results are needed for the application.
The CAD model enables the precise reproduction of the scanned object, or the object can be modified in the CAD model to correct imperfections. Laser Design can provide a surface model or the more complex solid model, whichever results are needed for the application.
Have additional questions? Check out our Glossary, sign-up for our eNewsletter, watch the 3D Laser Scanning Video or ask a question of your own!
90,000 technologies, methods and principles of 3D scanners04/16/2021
Content
-
- What is 3D scan and why it is used by
- How 3D scanner
- 3D scan technologies
- Methods 3D
- Contact 3D scanners
- Non-contact 3D scanners
- Types of 3D scanners according to the principle of use
- Advantages and disadvantages of 3D scanners
- Things to consider when choosing a 3D scanner
- Applications
Currently, few people are not familiar with such a concept as 3D printing. Many companies are using modern 3D printers with might and main, recreating layouts of various shapes and sizes with their help. There are also those that recreate whole objects - not only small ones (for example, phone cases, souvenirs, sneakers), but also large ones (houses, engine parts, etc.). But all this would not be possible without 3D scanners. It is they who allow you to accurately copy almost anything - from huge buildings and structures to humans, animals, small objects and much more.
Many companies are using modern 3D printers with might and main, recreating layouts of various shapes and sizes with their help. There are also those that recreate whole objects - not only small ones (for example, phone cases, souvenirs, sneakers), but also large ones (houses, engine parts, etc.). But all this would not be possible without 3D scanners. It is they who allow you to accurately copy almost anything - from huge buildings and structures to humans, animals, small objects and much more.
What is 3D scanning and what is it used for
Three-dimensional scanning is a technology that appeared in the 60s of the 20th century. It was created in order to transfer the physical parameters of the object into a digital format in the form of a three-dimensional model. The need for this naturally arose when people around the world increasingly began to use computers both in everyday life and in production.
The first samples of 3D scanners were quite simple and did not have wide functionality. Gradually, they became more complex and improved, making it possible to achieve an ever clearer image of the object. This has become especially relevant with the advent of lasers.
Gradually, they became more complex and improved, making it possible to achieve an ever clearer image of the object. This has become especially relevant with the advent of lasers.
3D scanners allow you to transfer object data into digital format
3D scanning has opened up new opportunities in various areas of human activity - from the automotive industry and the military industry to design, medicine and cinema.
How a 3D scanner works
A 3D scanner is a device that examines an object by digitizing it using sensors and using the information received to create a three-dimensional model. In fact, a 3D scanner creates a digital copy of a physical object of any configuration and complexity. In this, it fundamentally differs from its predecessors - conventional scanners that can only read information from documents and photos.
The scanning process itself can take place in different ways - depending on the type of 3D device and the technology used, as well as on what object you want to process with it - moving or static.
3D Scanning Technologies
There are 2 main types of 3D scanners - laser and optical. Their fundamental difference lies in how and with the help of what the “removal” of data takes place. Let's take a closer look at both.
3D laser scanning, as the name implies, uses a laser and can be carried out both at near and far distances from the object.
Laser Scanner
For the most part, 3D laser scanners work on the principle of triangulation, when the camera finds a beam on the surface of an object and measures the distance to it, after which a cloud of points is created, each of which has its own coordinates in space, and a 3D model is built. Their "advantages" are affordable price and ease of use combined with high scanning accuracy. Of the "minuses" - there are restrictions on the remoteness and size of the object.
Another type of laser scanner works by measuring the response time of a beam from the surface of an object - the so-called laser range finder. They are widely used where it is necessary to create 3D models of various buildings and structures. It is not advisable to use them at short distances, since in such cases the response time is very short and the accuracy of the data is reduced. Otherwise, this type of scanner is characterized by high scanning speed and the ability to read all the details.
They are widely used where it is necessary to create 3D models of various buildings and structures. It is not advisable to use them at short distances, since in such cases the response time is very short and the accuracy of the data is reduced. Otherwise, this type of scanner is characterized by high scanning speed and the ability to read all the details.
The disadvantage of laser scanners is the impossibility of their use on moving objects. Then optical 3D scanners come to the rescue, which shoot with one or more cameras from different angles an object illuminated by a special projector. Based on the received image, a three-dimensional image is built.
Optical scanner
A "contraindication" for the use of this technology are reflective and translucent surfaces - shiny, mirror or transparent. But when scanning a person, they are simply irreplaceable.
3D scanning methods
Any object can be digitized both by contact and non-contact methods. In the first case, active interaction with the subject is necessary, in the second, accordingly, no. Both of these methods have their advantages and disadvantages.
In the first case, active interaction with the subject is necessary, in the second, accordingly, no. Both of these methods have their advantages and disadvantages.
Contact 3D scanners
They have a mechanical probe with a special sensor that measures parameters and transmits the collected information to the device. To do this, the object under study is placed on a special surface and fixed (if necessary). Such tight physical contact makes it possible to determine and then build a 3D image as accurately as possible, however, there is a small risk of damage to the prototype.
Non-contact 3D scanners
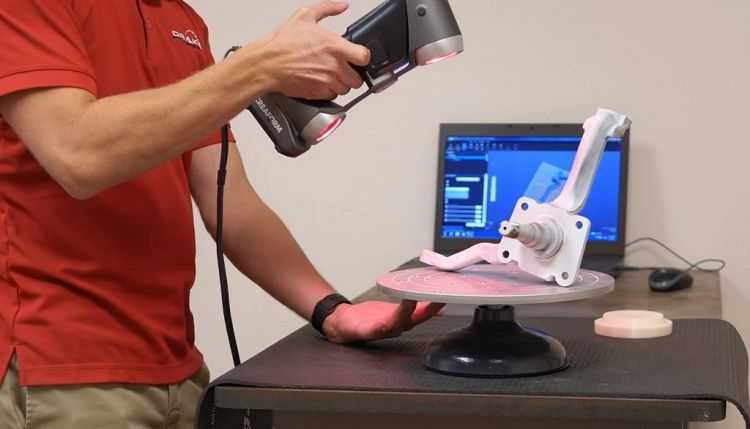
This category includes all devices capable of scanning at a distance. This is especially true for objects located in hard-to-reach places.
Non-contact 3D scanner
A stream of radiation (it can be ultrasound, light, X-rays or a laser) is directed to an object and reflected from it, it is recognized by a 3D scanner. They are similar in principle to a video camera and may require the use of additional devices for better illumination.
They are similar in principle to a video camera and may require the use of additional devices for better illumination.
Non-contact 3D scanners come in 2 types:
-
Active - work with the help of a laser beam or structured light directed at an object, which, when reflected, give information about the location of the object in the form of coordinates.
-
Passive - use time-of-flight rangefinders that read the time and distance that the laser beam travels to the object, and so - for each point in space, which ultimately allows you to accurately recreate its three-dimensional image.
Desktop 3D scanners are very popular and widespread, since they are mostly simple and safe to use, do not require any special technical skills and are quite cheap. The EinScan-SE 3D scanner is one such example. It can be used both at home and in the office. It has access to the API of many popular 3D printers, which makes it possible to immediately print the created three-dimensional model.
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Thor3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Shining 3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Shining 3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Range Vision |
Types of 3D scanners according to the principle of use
There is also a variety of species here. Let's highlight the main ones:
-
Manual: The are handy and simple models that are easy to use as they are quite compact and do not require special skills. True, their technical capabilities may be somewhat limited.
-
Portable: are mainly used for field work, they are convenient to take with you.
-
Desktop: have extended functionality and are used to create high-quality 3D models. Most often used in offices.
-
Stationary: are used, as a rule, in production, various enterprises, as they can scan a large number of objects of the same type at once. Mounted on special turntables.
Handheld 3D Scanner Calibry
Such a choice of products allows you to select the right model for a specific task. In some cases, scanners independently measure objects, in others - with the help of a person who sequentially moves the device until all the necessary information is collected.
Such options for hand-held 3D scanners as Calibry are in high demand among buyers. Despite the apparent simplicity of execution, it has a high resolution and scanning accuracy, due to which it is able to digitize objects with a length of 0.2 to 10 meters. Objects that have a non-standard surface - dark or shiny, with a large number of corners and small details will not become a problem either. Among other things, its undoubted advantage is its low weight, only 900 grams.
Among other things, its undoubted advantage is its low weight, only 900 grams.
Advantages and disadvantages of 3D scanners
Surely, many of the potential buyers are wondering: do you really need a 3D scanner to invest a lot of money in it? What can this acquisition give and will such an investment be justified?
3D scanning has become an integral part of any modern manufacturing process
In order to understand how much you need this equipment, we will list its advantages and disadvantages.
Benefits:
-
They make it possible to scan objects located at a remote distance and in places inaccessible to the presence.
-
They have the ability to "read" not only colors and images, but also to convey the texture of the surface.
-
Significantly speed up the process of "taking" data from any object, even a very complex one with a large number of planes.
-
A variety of models allows you to choose the most convenient version of the scanner, including manual or portable, which can be easily taken with you.
Weaknesses:
-
Some scanners are unable to recognize transparent or black and white objects. In this case, their preliminary preparation (treatment with a special composition) is required.
-
I do not always display complex objects correctly, with a large number of inserts and partitions.
-
To obtain a high-quality result, they require skills and abilities to work with certain computer programs for creating 3D models.
-
If the rules of operation are constantly violated, it may become necessary for expensive repairs to the equipment.
If you need high-precision and high-quality three-dimensional copies of objects, then you cannot do without a 3D scanner. It makes it possible to work in almost any conditions - indoors and outdoors, and with any objects by type and size. It is not surprising that now these devices are in great demand, which gives rise to the annual release of a large number of models, from which you can always choose the one that suits you in terms of quality and price.
It is not surprising that now these devices are in great demand, which gives rise to the annual release of a large number of models, from which you can always choose the one that suits you in terms of quality and price.
What to consider when choosing a 3D scanner
The computer equipment market offers a huge amount of all kinds of equipment, including devices for three-dimensional scanning. Navigating that variety is sometimes not at all easy: some buyers are only concerned about the cost, others are interested in the number of options (sometimes completely useless), but the most far-sighted look at the ratio of the first and second.
Choosing the right 3D scanner is a big deal
It is not always easy to take into account all the technical points that can significantly affect what result will be ultimately achieved. We will tell you what you should pay attention to if you are thinking about buying a 3D scanner.
Focus on the following parameters:
-
How high is the accuracy of the 3D scanner.
 This is one of the most important features. It needs to be targeted first.
This is one of the most important features. It needs to be targeted first. -
Resolution also plays an important role. It follows from the first, since the accuracy of measurements and the quality of copying depend on the resolution.
-
In what range the device operates, how close / far it can be from the scanned object.
-
The scanning field is the parameters of that object, thing that it is able to process in 1 session.
-
Does the scanner capture various atypical types of surfaces with complex terrain - channels, partitions, holes, etc.).
-
Portability, mobility of the device - how easy it can be moved if desired, taken with you, its size.
-
The time it takes to prepare for work, as well as the duration of the digitization process itself.
-
The range of possibilities in terms of copying: are there any restrictions on shapes, textures, material, as well as operating conditions - temperature, light, etc.

Of course, the better the quality of the 3D scanner, the more expensive it is. However, you should focus primarily on the tasks that you face, and only then take into account everything else.
Applications
Three-dimensional scanners are in demand in many areas of human life. They are irreplaceable both in the industry, and for household needs. The range of their application is so wide that it is possible to list for a very long time. It's easier to say where they are not needed.
The most common areas of use are, of course, medicine, industry, architecture, construction, film industry and design.
For example, in dentistry, these devices allow you to create ultra-precise three-dimensional models of dentures. One type of such a scanner is Shining 3D's AutoScan DS-EX PRO, which does a great job with a variety of tasks while being quite affordable and reliable.
Medical 3D Scanner
In engineering, such technologies are also indispensable. Digital building prototypes are now much easier and faster to obtain than in the past, when it required multiple manual measurements and then entered into a database. Any physical object can now be recreated in three-dimensional form, moreover, in the shortest possible time and with a minimum error.
Digital building prototypes are now much easier and faster to obtain than in the past, when it required multiple manual measurements and then entered into a database. Any physical object can now be recreated in three-dimensional form, moreover, in the shortest possible time and with a minimum error.
In cinemas, we can see with our own eyes "revived" fantastic characters, which were created using motion capture technology, which made them as realistic and impressive as possible. This would not have been possible without 3D scanners.
A few decades ago, it was even difficult to imagine all the things that we use all the time today. And in many ways this has become achievable thanks to three-dimensional digitization. This approach provides huge advantages in work (especially for technical specialists - engineers, designers, designers), however, in order to use them to the maximum, it is also necessary to understand computer programs for 3D scanning.
We will talk more about this topic in one of our next articles. And if you want to know more about it, stay tuned.
And if you want to know more about it, stay tuned.
#Useful
Expert in the field of additive and subtractive technologies, 3D equipment and CNC machines with over 10 years of experience.
Share
all materials
How does a 3d scanner work? Device, principle and technologies of 3D scanning
3D Scanner is a stationary or small handheld device for scanning objects with complex spatial geometry. Simple scanners process images in a plane, while 3d scans physical volumetric objects, displaying information as a polygonal model or a cloud of points. Three-dimensional scanning devices are used in medicine (dentistry, plastic surgery, making prostheses, organ models, etc.), for creating computer games, in the film industry, design, architecture, engineering, for designing industrial parts, cars, for reconstructing objects in archeology. Scanners analyze and digitally recreate a three-dimensional model of an object, its shape and color with a high degree of detail, working in different conditions (with insufficient visibility, in the dark, with vibration), with any materials, provide the desired format of output information for software for work with her on the computer.
How does a 3D scanner work?
The principle of operation of the 3d scanner is the ability of the device to determine the distance to an object, convert the received data into a digital image (three-dimensional model), transfer it to a computer. The scanner determines the coordinates of points in space on the surface of the processed object, analyzes them, and forms a detailed digital model. Cameras, lasers, rangefinders, devices for illumination are involved in its work.
3D scanning technologies
- Contact (contacts with the object).
- Non-contact (without object contact). These are the most promising and new technologies that allow you to create models of objects simply by directing a laser beam, light, waves at them. The scanner is applied at a distance and is able to create a copy of a hard-to-reach object without physical contact with it.

Non-contact 3d scanners
The two most common scanning technologies are optical (passive and radiation) and active laser.
Active emission principle
Scanner emits structured, intermittent light, laser triangulation. A laser beam, a beam of light generated in a special way (diodes, lamp flashes), and waves are directed to the object under study. Based on the analysis of their reflection and position, a three-dimensional copy of the object is formed.
Passive radiation principle
Do not emit anything, analyze the light or infrared (thermal) radiation of an object. Work like a human eye;
Photometric non-contact passive 3d scanning technology
Scanners from this group are represented on the market by the XYZprinting model. These are quite compact simple models that have only basic 3D scanning functions.
Pluses: reasonable price and compactness.
Device
Passive 3d scanner device (on the example of the specified model): housing, one compact camera, USB cable for connecting to a computer and transferring the image of the scanned object to it. Scanner without stand, manual, made in the form of a stapler.
How it works
A light-sensitive camera captures light from an object, processes it, and forms a three-dimensional model, exporting it to a computer. The user can have two modes of operation: scanning a person or objects. To get started, you need to install the software on your computer, connect the device to it via a USB cable, select the operating mode, press the button on the scanner and, slowly swiping it in front of the object, scan.
How the technology works
The device uses passive scanning photometric technology without any radiation and projection onto the object.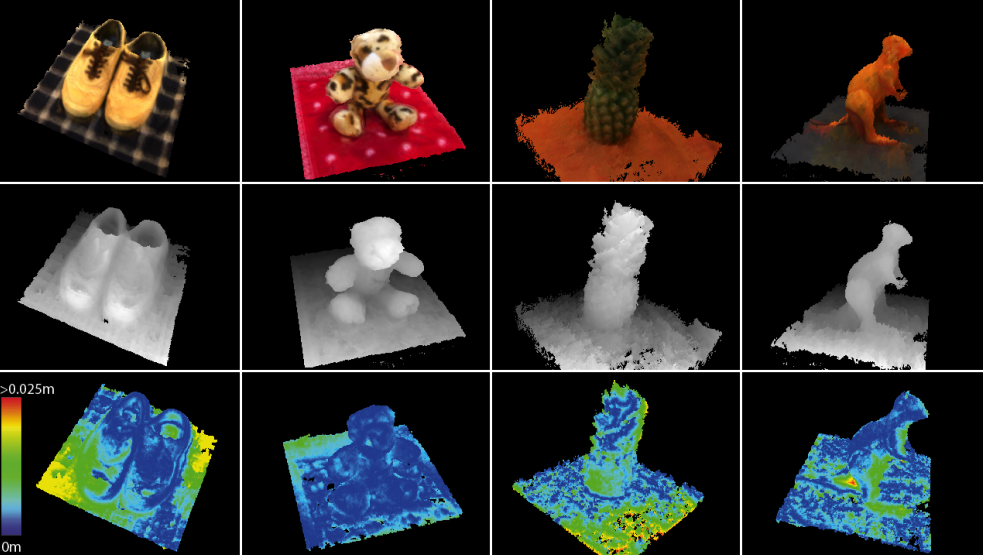 The work is carried out with a slightly improved simple optical camera that captures visible light. The disadvantage is that if the lighting is insufficient, the object needs to be additionally illuminated.
The work is carried out with a slightly improved simple optical camera that captures visible light. The disadvantage is that if the lighting is insufficient, the object needs to be additionally illuminated.
Scanning is performed using the so-called silhouette method. It reproduces the contours of an object based on a sequence of frames captured by a video camera swept around the object against a well-contrasted background.
Stereoscopic non-contact passive 3d scanning system
Models with non-contact passive scanning technology
This type of device is represented by 3D Systems Sense, 4D Dynamics Gotcha models.
Device and principle of operation of a 3d scanner based on a non-contact passive scanning system
Devices are equipped with two cameras and an infrared sensor. The 3D Systems Sense scanner is made in the form of a stapler, it is a compact handheld device, it can be used with a tripod, in Gotcha (with a tripod and a handle), it is included. The principle of operation is passive optical. In both cases, power and data transfer is carried out via a USB cable. The devices have standard modes: scanning a person and an object.
The principle of operation is passive optical. In both cases, power and data transfer is carried out via a USB cable. The devices have standard modes: scanning a person and an object.
Scan technology
The camera uses this technology to detect infrared (thermal) radiation and normal light reflected from an object. The systems are stereoscopic, that is, they use two cameras. The device compares frames, based on small comparisons of differences between them, determines the distance at each point of the image and recreates the object in digital form.
3d scanners with laser active scanning
This group of devices is represented by the following scanner models: 3D Systems iSense, DAVID Starter-Kit ver.2, MakerBot Digitizer.
Device
Devices have two lasers and a camera. It should be noted that the laser safety of gadgets corresponds to level I, which is completely safe for the eyes. The iSense scanner is designed to work only with the iOS operating system and with Apple iPad above 4 generations. It is made in a compact case, which is installed on a mobile gadget and connected to it with a USB cable, the battery lasts for 4 hours of its operation. It attaches like a webcam, scans and immediately displays the image on the iPad.
The iSense scanner is designed to work only with the iOS operating system and with Apple iPad above 4 generations. It is made in a compact case, which is installed on a mobile gadget and connected to it with a USB cable, the battery lasts for 4 hours of its operation. It attaches like a webcam, scans and immediately displays the image on the iPad.
Models
DAVID Starter-Kit ver.2 3D scanner device: webcams and laser sensors with automatic adjustment function. The device comes with a tripod and tripod.
Maker Bot Digitizer is slightly different in design from the previous model. The body of the scanner is made as a pedestal, one part of which is a rotating platform, the other is equipped with two lasers on the sides and a camera in the middle. They scan an object located on the site.
How technology works
Let's describe how a 3D scanner works. Laser scanning is based on the triangulation method. This is an active scan tool. It uses laser beams by projecting it onto an object. The laser processes the surface of the object, its points are fixed on its different parts. The camera captures the laser dots on it, the angle of displacement of the laser beam and transmits the data to a computer with the appropriate software, which forms the object in digital form.
This is an active scan tool. It uses laser beams by projecting it onto an object. The laser processes the surface of the object, its points are fixed on its different parts. The camera captures the laser dots on it, the angle of displacement of the laser beam and transmits the data to a computer with the appropriate software, which forms the object in digital form.
The scanning technology is called “triangulation”, because the triangle of the device's functional elements is involved in the work: the laser point on the object, its emitter, and the camera. In most cases, the dot is formed by a laser streak or spot passing over the surface of the object.
Structured light 3d scanning technology
Models that use structured or intermittent light technology in their work: DAVID SLS-2, RangeVision Smart, RangeVision Standard Plus, RangeVision Advanced, RangeVision Premium. A separate group includes manual Artec Spider, Artec Eva, Artec Eva Lite.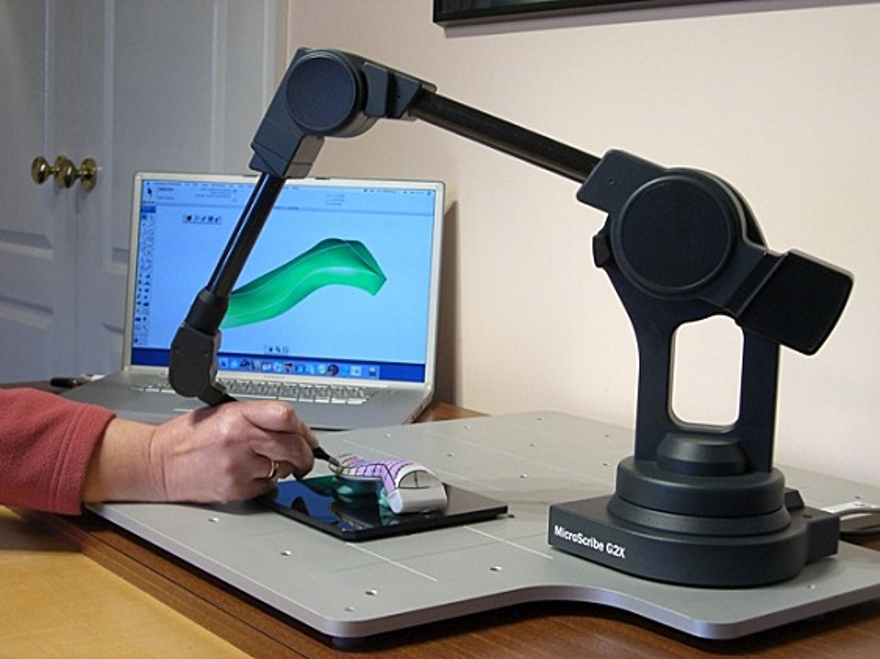
Device
The main functional elements of these devices are cameras and a light source that structures it in a special way and directs it to the scanned object. In the DAVID SLS-2 model, a video projector serves as a light source. These are mounted on a tripod with a tripod, which are included. This allows you to set up and calibrate instruments, install them in different positions and securely fix them, reducing vibration. Light sources in devices are halogen lamps, diodes, video projector.
Artec Spider, Artec Eva, Artec Eva Lite are made in a compact body with an iron-like handle. The handle has control buttons and outputs for interface and power cords. At the bottom there is also a hole for standard photo tripods and legs for fixing the device on the surface. 3d scanner device has the following. From the bottom it is equipped with a 3D camera (there are three of them in Artec Spider) with increased resolution, from the top of the device - a flash (projector) of structured illumination, a central color texture camera in the middle, along with light sources in the form of 6 or 12 diode bulbs.