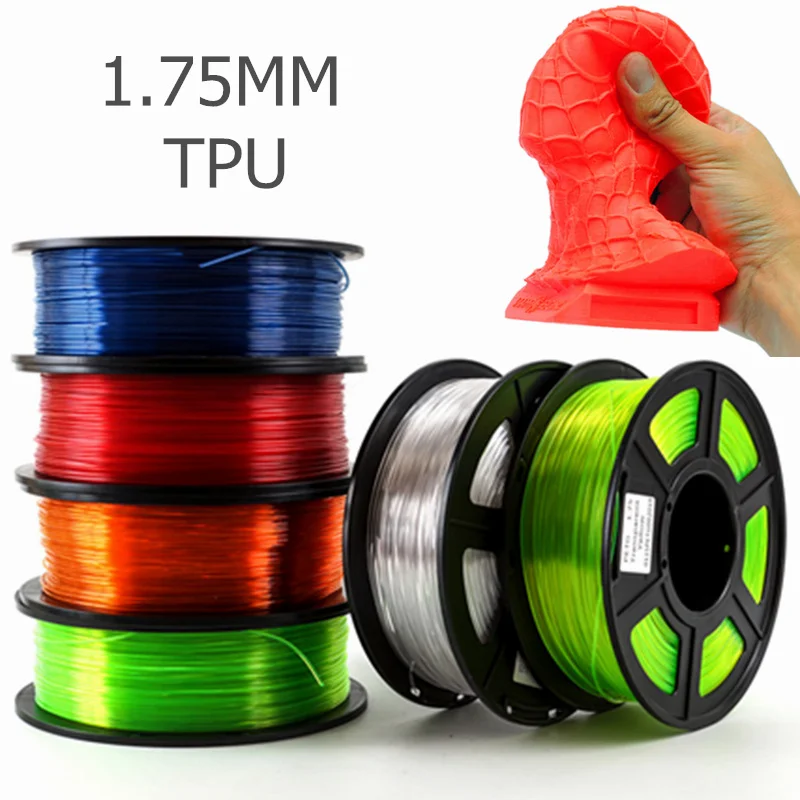
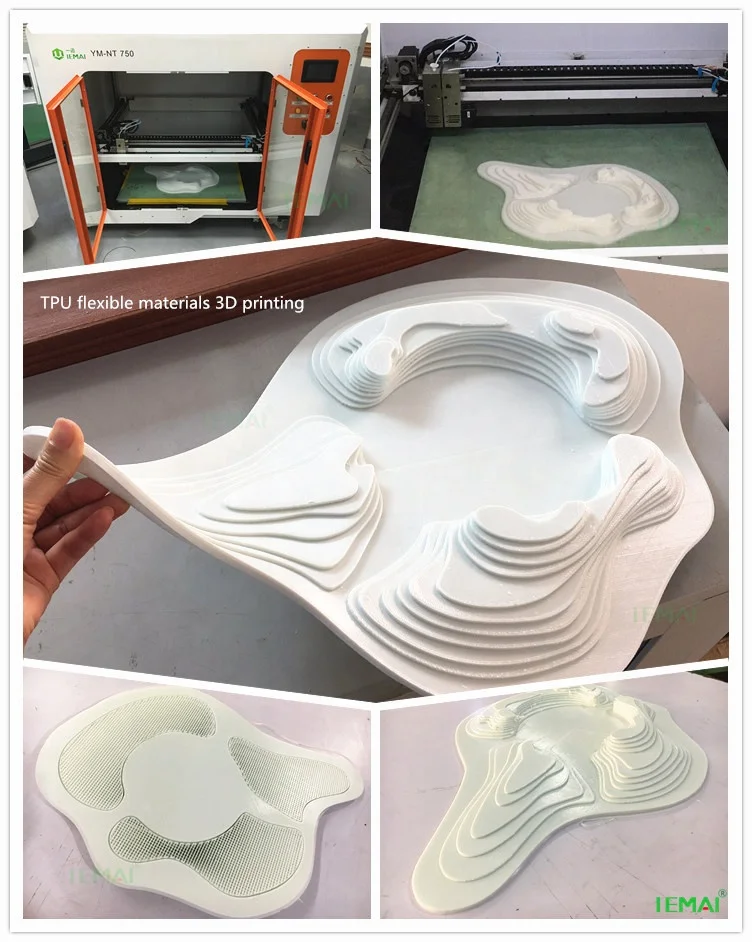
Tpu for 3d printing
3D Printing with TPU - NinjaTek
TPU filament is used to create flexible, durable 3D prints. You can stretch it and bend it, and it won’t break. NinjaTek® has been extruding TPU for over 50 years, bringing a level of expertise and knowledge unmatched by other companies.
What is TPU?
Uses & Applications
How to Print With TPU
Properties, Pros & Cons
FAQs About TPU
What is TPU 3D Printer Filament?
TPU, or Thermoplastic Polyurethane, is a flexible and durable 3D printing filament for beginners and pros alike. TPU has unique characteristics that make it elastic like rubber, yet durable like plastic.
TPU has qualities that other materials don’t have, such as vibration dampening, shock absorption and incredible elongation.
TPU Uses & Applications
TPU can be used in a number of industries across a variety of applications when you’re looking for high-performance materials. TPU’s shock absorption and vibration-dampening qualities make it the ideal material for prosthetics and orthotics (footwear inserts/insoles), as well as sporting goods and athletic equipment.
TPU’s soft, sleek feel lends itself well to the realistic texture needed for prosthetics. It’s even been used to make tracker-enabled turtle eggs to fool poachers.
Another advantage of TPU is its durability. It can take a beating. For example, when TPU is used to produce seals and gaskets, printed components hold up just as well as (if not better than) traditionally manufactured parts.
While durable, it’s also chemical resistant and non-marring. It can stretch around tools to protect them and other equipment from damage.
How to print with tpu
TPU can be somewhat tricky to print with because of its unique properties, but the prints you get have impressive quality and can withstand the test of time.
Temperature: TPU prints at moderate speeds and temperatures (225°C to 250°C).
Common issues: TPU has great elongation and stretchiness, but those properties can also cause some minor clogging and stringing. Check out our Troubleshooting Guide for common print issues and fixes.
Properties of TPU: Pros & Cons
Pros of TPU
- Flexible
- Stretchy like rubber
- Durable, shock- and impact-resistant
- Abrasion resistance
- Vibration dampening
- Huge variety of color and hardness options
Cons of TPU
- Can be a challenge to print for beginners due to its unique, high-performance properties
- Difficult to post-process because of its abrasion and chemical resistance
FAQs about TPU
Is TPU flexible?
Yes, TPU 3D printer filament is known for its flexibility, such as NinjaFlex® filament. There are some varieties of TPU filament with more rigid properties, like our Armadillo® filament. TPU is ideally suited for 3D printing applications where flexibility and durability are essential.
TPU is ideally suited for 3D printing applications where flexibility and durability are essential.
How soft is TPU filament?
TPU has a soft, smooth texture that lends itself to a number of applications. In addition to being soft, it has impact-resistant and elastic properties well suited for many industries, including healthcare and sports.
How fast can you print TPU?
TPU typically prints best at slower speeds. When combined with high heat, it will flow smoothly from the nozzle. If you’re looking for a quick-printing material that’s going to hold up with minimal issues, try our Cheetah® filament.
Which NinjaTek Filament Do You Need?
Compare hardness, elasticity, impact resistance and other properties of our 3D printer filaments.
Compare Products
Shop All Products
Related Resources
Shop Cheetah
Shop the fastest and easiest to print flexible filament on the market.
3D Printing by Industry
Fashion: Custom couture to cosplay costumes
Case Studies
Machinist designs protective covers for vise-grip pliers.
Raise3D: Reliable, Industrial Grade 3D Printer
Resilient and flexible rubber-like filament
TPU (Thermoplastic polyurethane) is a type of flexible and elastic 3D printing filament. Its rubber-like elasticity, resilience, and durability make it suitable for uses requiring impact-absorption and a soft-touch surface. Examples of TPU 3D printed parts include tubes, seals, bushings and vibration dampeners.
- Elastic and flexible
- Wear and tear resistance
- Durable and resilient
Compatibility: Premium PLA, Premium PVA
Raise3D Premium TPU-95A
Applications
- Seals, tubes
- Protective cases
- Shoes and insoles
- Bushings, gaskets
- End-use parts
Printing Guide
Recommended Print Settings
Nozzle temperature (°C)
210-230℃
Bed temperature (°C)
25-60℃
Layer height (mm)
0. 1-0.25 mm
1-0.25 mm
Printing speed (mm/s)
25-50 mm/s
Cooling fan
On
Drying temperature (°C)
70℃
Printing Notifications:
- Raft is not recommended for TPU.
- Optimize flowrate and printing speed for a better feeding and extrusion for soft filament.
- Dry TPU filament before printing.
For Raise3D Printer Users:
Choose the best 3D printer to start your printing journey with TPU. Find Pro3 Series, E2, Pro2 Series.
For ideaMaker Users:
Choose the right printing profile for TPU on ideaMaker IO and use it on ideaMaker. Download the latest version of ideaMaker.
Download the latest version of ideaMaker.
Success Stories
Raise3d Shows How to 3D Print Economical and Customized Orthotic InsolesRaise3D incorporates specialized FFF 3D printing into the production of orthotic insoles.
Learn more
A Guide to the Stages of 3D-Printed Production of Orthopedic InsolesLet’s take a closer look at the process of making insoles using 3D technologies, which can be divided into 4 stages.
Learn more
Raise3D’s Responds to Demand for Mask-Wearing ConnectorsBy using the E2 printer, the average daily production of mask-wearing connectors can reach 1500 units, and can be delivered on the very same day.
Learn more
3D Printing in Medicine: Customized Bolus and Shields For RadiotherapyWith the rapid advancement of flexible manufacturing in Biomedical fields, 3D printing is now widely implemented for medical purposes.
Learn more
3D-Printed Shoe Uppers: Efficient Small Batch Manufacturing and Improved PrototypingIn 2020, a few giants of the sneaker-manufacturing industry used Raise3D products to achieve more success.
Learn more
Flexible TPU plastic for printing on a 3D printer in Moscow: 1.75 mm, weight 1 kg
Learn more
Only high-quality products
Learn more
Subscribe to newsletter
Be the first to know about discounts!
TPU plastic Description Parameters
for printing and
for post-processing Physical
mechanical characteristics
Material: TPU - thermoplastic polyurethane
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a modern polymer material based on polyesters. The elasticity of printed products is the main property that determines the use of this plastic.
Press parameters:
Print temperature: 175-190 ° C
Table temperature: 50 ° C
Table cover: clean glass, glue BF-2, glue for 3D printing
speed speed prints: 15-20 mm/s.
Cooling: is recommended to be printed using efficient, annular airflow.
Density: 1.25 g/cm3
Features of TPU plastic and handling:
- Elasticity is the main property that determines the application.
- High resistance to deformation in both compression and tension.
- High strength, very soft. Shore hardness 75A
- No smell when printed.
- Excellent interlayer adhesion.
- The print speed is slow.
- Resistant to most solvents, fats, oils. Relative resistance to gasoline.
- Machining is very difficult due to the specific properties of the plastic.

- Wide operating temperature range.
- Bar accuracy ± 0.05 mm (reduced geometry tolerance).
- The FDM extruder head needs to be modified to eliminate gaps and cavities in the path of the bar from the feed gear to the hot zone of the print head. The use of bowden tube extruders is difficult due to the very low hardness of the material.
- Machining of TPU plastic products is difficult.
- Chemical treatment not applicable.
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a unique material, one of the most sought after polymeric materials. Operational and chemical properties have provided this material with a wide distribution in all industries with high requirements for the quality of materials.
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) combines wear resistance, lightness and elasticity, the ability to not change its color during its use. The material is resistant to low temperatures. rupture and aggressive environments, adheres well to the surface, restores shape when deformed, is able to perfectly resist punctures, has slip resistance.
TPU plastic is the first flexible, Flex-plastic in the line of plastics produced by the Moscow FDplast plant. Possessing excellent structural and technological properties, thermoplastic polyurethane is used in various industries, ranging from winding power cables, use in the development of the design of the bottom of shoes, the manufacture of protective accessories for electronic devices, and ending with a decorative overlay in the car interior.
Information on the properties of plastics and printing requirements can be found in the booklet "Flex for 3D printing FDplast".
Plastic storage
3D printing plastic must be stored in a dry place. Moisture and dampness greatly affect the filament, as a result, the plastic deteriorates, it becomes impossible to print from such plastic. There are no problems with the storage of plastic, it is practically not affected by the normal humidity of the ambient air. However, in order to obtain an ideal printing result, it is advisable to store the filament in a dry place, with silica gel.
3D Printing Tips
More >>
Download
Presentation. Plastic for 3D printing FDplast
Booklet. Plastic for 3D printing FDplast
Do you need a pipe? Call us and we will help you!
Send an order to the Plant's e-mail and our managers will contact you as soon as possible!
Update form
Contacts
Moscow plant FDplast
Office in Moscow
Building projects
how to print, characteristics and properties
TPU filament (REC Easy Flex) makes it possible to print flexible, elastic and durable parts from thermoplastic polyurethane.
Main Advantages and Disadvantages of TPU (REC Easy Flex)
Easy Flex (TPU) is the most flexible and wear resistant material in the REC flexible polymer range, highly resistant to oils, gasolines, alkalis and some acids, high wear resistance and excellent strength at bending and tensile deformations.
The material is frost-resistant, maintains fairly high temperatures when heated and practically does not age when exposed to ultraviolet radiation (dyes can degrade, but the physical and mechanical properties of the material itself are preserved), has good resistance to sea water, fats, is not affected by microbes or bacteria.
Excellent environmental resistance makes TPU an excellent choice for outdoor parts. Moreover, TPU has a low vulnerability to plastic deformation or "creep", that is, it retains its shape well under prolonged and repeated deformation, which makes it possible to use this polymer in the production of functional parts that work in bending, compression and tension.
In industry, thermoplastic polyurethane most often serves as an alternative to natural rubber and is used in the production of seals and sanitary gaskets, profiles and hoses, car tires and tyres, shock absorbers and dampers, various fasteners, connecting and decorative elements, shoe soles and orthopedic inlays, friction linings for hand tools, windings of power cables and components of electrical equipment, sports equipment and much more. 93
Mechanical REC Easy Flex:
- Izod impact strength: non-breakable
- Tensile strength along layers: 27.
 96 MPa
96 MPa - Tensile modulus along layers: 74 MPa
- Bending strength: 3.5 MPa
- Flexural modulus: 68 MPa
- Maximum bending load: 4.8 N
- Tensile strength across layers: N/A
- Cross-layer tensile modulus: N/A
- Maximum tensile strength: 662 N
- Compressive strength: 6 MPa
- Compressive modulus: 44 MPa
- Maximum compression load: 670 N
- Elongation: 617%
- Biodegradability: N/A
- Dielectric constant: n/a
- Tensile strength at 23°C: N/A
- Flexural strength 2.8 mm/min. 23°C: N/A
- Shore hardness (A scale): 95
- Oil and petrol resistance (maximum shape change in 24 hours): N/A
- Oxygen index, %O2 according to GOST 21793-76: n/a
- Mass fraction of ash according to GOST 15973: n/a
3D Printing Preparation Guidelines TPU (REC Easy Flex)
TPU is highly hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture well.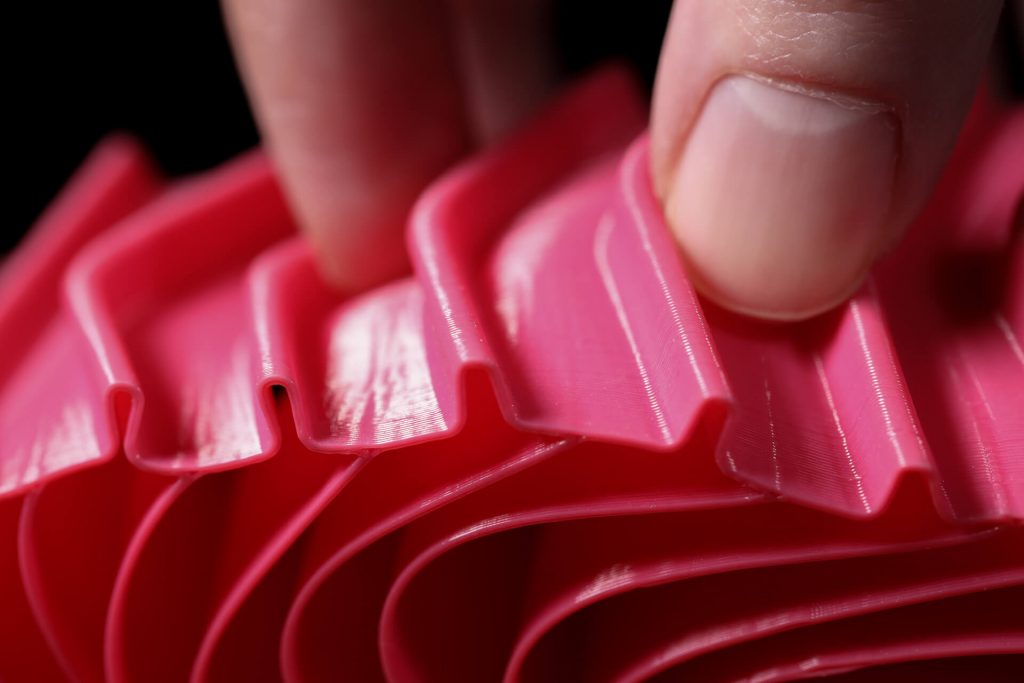 In case of problems with interlayer adhesion and the appearance of defects on the laid layers (irregularities, bubbles, delamination), the filament must be dried. With the correct 3D printing temperature and the use of dry material, the resulting products will exhibit very high tensile strength.
In case of problems with interlayer adhesion and the appearance of defects on the laid layers (irregularities, bubbles, delamination), the filament must be dried. With the correct 3D printing temperature and the use of dry material, the resulting products will exhibit very high tensile strength.
When working with Easy Flex, it is recommended not to rush and limit the speed of the paving. The exact values depend on the equipment used, but the approximate print speed should be set in the region of 25 mm / s - it can be higher if the material feeds and sets well. Since TPU is elastic, the retract should be set to a higher value than when working with hard plastics - about 3 mm.
It is recommended to avoid Bowden filament feed (separate installation of feeder and head with connection through a long tube) in favor of direct extruders (solid feeder and hot end assemblies). Minimizing the distance between the feeder gears and the hotend inlet will help with problems caused by bar bending and compression under load, including winding filament around the gears. The pressure on the feed gears must be firm but not too strong to avoid deformation of the filament, which again can lead to interruptions in the supply of material.
The pressure on the feed gears must be firm but not too strong to avoid deformation of the filament, which again can lead to interruptions in the supply of material.
To increase adhesion to the work surface, it is recommended to use a stage heater and apply adhesive agents - varnishes or adhesives, such as The3D universal compound. The blowing of the laid material should not be too strong (no more than 20%) so that the layers have time to set well. As a general rule, airflow should only be used when 3D printing small models with short layer build times.
Printing on rafts is not recommended, as the material is almost not subject to heat shrinkage, and auxiliary structures will only complicate post-processing. Alternatively, before 3D printing the main model, a skirt can be built solely to check the stability of the melt supply.
Detailed information on the adhesive properties of REC Flex and other materials in multi-material 3D printing is available here.
Recommended settings for 3D printing with TPU (REC Easy Flex):
- Nozzle temperature: 215-235°C
- Table temperature: 30-60°C
- Airflow: 20%
- Recommended adhesives: The3D glue, blue tape
- Minimum nozzle diameter: 0.
 4 mm
4 mm
Storing TPU (REC Easy Flex)
As mentioned above, TPU is hygroscopic, so it is highly recommended to store unused filaments in sealed bags or containers with a sachet of silica gel inside.
If necessary, the filament can be dried using specialized equipment, a fruit dryer or an electric oven at 50°C for a minimum of four hours. Speeding up the process by raising the temperature is not recommended, as this may damage the material.
Before loading the material into the extruder, it is recommended to make sure that there is no dust on the filament that can form deposits in the hot end. If necessary, the filament can be cleaned directly during 3D printing by passing the filament through a simple foam filter (for example, such or such) on the way from the spool to the hot end.
For more information on storing and drying filaments of different materials, see the articles at the links below:
Filament storage
Plastic drying
Post-processing TPU (REC Easy Flex)
Like other flexible materials, thermoplastic polyurethane cannot be finely machined, such as sanded. The only practical option is cutting artifacts and supporting structures with cutting tools.
The only practical option is cutting artifacts and supporting structures with cutting tools.
In terms of chemical processing, the advantages of TPU also quickly turn into disadvantages: high chemical resistance does not allow smoothing surfaces with many commonly available solvents. Chemical processing will require dimethylformamide, tetrahydrofuran, ethyl acetate, cyclohexanone, or dimethylacetamide, with strict safety precautions in all cases.
Epoxy resins, cyanoacrylate (super glue) or polyurethane adhesives can be used for bonding, however, any adhesives can be a weak point in functional details, so it is recommended to print one-piece products immediately if possible.
When painting, be aware of the flexibility of the material and avoid hard primers and varnishes if the product will be subject to stress. Alternatively, liquid rubbers can be used to smooth surfaces and paint, if necessary with the addition of coloring pigments.
Safety TPU (REC Easy Flex)
Generally harmless under normal use, but not yet tested for safety in prolonged food contact.